INTEGRATED ASSESSMENT OF RISK LEVEL Title BY HAZARDS IN THE COASTAL ZONE OF V (CASES STUDY : CAM RANH-PHAN RI COA ZONE)
|
|
|
- Dale Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTEGRATED ASSESSMENT OF RISK LEVEL Title BY HAZARDS IN THE COASTAL ZONE OF V (CASES STUDY : CAM RANH-PHAN RI COA ZONE) Author(s) Mai, Trong Nhuan; Nguyen, Tai Tue; Tran, Dang Quy; Nguyen, Thi Hoang H Annual Report of FY 2006, The Core Citation between Japan Society for the Promo Vietnamese Academy of Science and T P.133-P.140 Issue 2007 Date Text Version publisher URL DOI Rights Osaka University
2 Osaka University
3 INTEGRATED ASSESSMENT OF RISK LEVEL CAUSED BY HAZARDS IN THE COASTAL ZONE OF VIETNAM (CASES STUDY: CAM RANH - PHAN RI COASTAL ZONE) Abstract Mai Trong Nhuan\ Nguyen Tai Tue\ Nguyen Thi Hong Hue\ Tran Dang Quy\ Nguyen Thi Hoang Dao Manh Tien 2 J University o/sciences, Hanoi National University 2jVIarine Geology Union nhuallll1t@vl1u.edu.vl1 The Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone is subjected to 10 kinds of hazards arranged in decreasing sequence of risk level: salinization, typhoon and flood, sedimentation causing channel changes, coastal erosion, sand drift, sea level rise, earthquake, environmental pollution by heavy metals, environmental pollution by organic compounds (PCBs) and land cracking. By studying and zoning the risk levels caused by hazards, the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone can be differentiated into 3 areas with different risk levels: low risk area (DI<I), moderate risk area (I<DI<I,7), high risk area (1,7<DI<3,4). To mitigate these hazards, besides engineering measures, non-engineering measures are also proposed, comprising: integrated assessment of hazard risk levels, hazard forecasting, hazard risk level zoning, vulnerability assessment. It is also proposed to prepare a master plan for integrated management of the coastal zone and a land-use master plan based on the results of hazard risk level zoning and vnlnerability assessment. 1. Introduction The coastal zone of Vietnam is rich in natural resources (mineral resources, wetland, positional resources, tourist resources... ), with high population density and concentration of many economic sectors. However, the coastal zone also has a great potential of hazards such as typhoon, flood, erosion, channel changing, sand drift earthquake, land cracking, environmental pollution... seriously threatening the sustainable development. Those hazards are interrelated with each other in their causes, influencing factors or mutual intensification. Therefore, to enhance the efficiency in preventing and controlling coastal zone hazards, their integrated study and assessment are required. This is a common approach worldwide in the field of research for hazard mitigation (Cutter et all, 1996, 2000; Kasperson, 2001,... ), but it is still relatively new in Vietnam (Mai Trong Nhuan et al., 2002, 2004). The Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone (Fig. 1) is rich in mineral resources, positional resources, wetland and diverse marine ecosystems... These are favorable natural conditions for the development of industry, aquaculture fishing, tourism, port operation and water way transport... However, the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone is also affected by many hazards such as: earthquake, land cracking, slumping, coastal erosion, sedimentation causing channel changes, sand drift, typhoon and flood, sea level rise and some geochemical hazards. These hazards, together with the low capability of the community to respond, prevent and control hazards cause ever increasing human and property losses, as well as degradation of the natural resources in the coastal zone... Therefore, it is necessary to carry out integrated assessment of hazard risk levels in Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone with the aim to identify priority areas for investment in prevention and mitigation of losses, sustainable use of the territory and territorial waters, protection of natural resources to serve the sustainable development In the mean time it is necessary to make advance toward regional and international integration in the field of disaster research and mitigation. This paper presents the results of the research in this direction in the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri costal zone
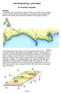
4 2, Some factors affecting the geohazards in the coastal zone Geologic formations The intrusive, sedimentary, volcano-sedimentary, terrigenous rocks and Quaternary sediments in the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone are divided into two main groups in terms of their resistance to hazards. Group of solid formations with high resistance to hazards 100' 32' los" 45' 109' 00' 109' 15' 109' 21' 12'1l0 1r;:;;:==::±=~--_'l""'---=--::~~412'1l0 11'45' ;;;-i±~-111'45' 11"30 i---...,--f-+--..,.----t--"----t----{11"30' 11'15' woo 1. GC{)logic conditions Hard rock, with high bearing ~capacity. moderate erosion resistance Unconsolidated sediments, moderate Cbeating capacity, low toxic content 2. Geodynamic processes [EUplifted area [E[ Subsided area I2!iFault: a) certain, b) Inferred 3. Oceanography C;:Winter current L::..Sununer current 11'16' 11'1l0' 10'55' L-.".- --'-...-'. -' Jl0' '00' Fig. 1 Geological, structural and oceanogl'aphic characteristics of Cam Rauh-Pilan Ri coastal zone The geologic formations of this group consist of sedimentary, volcano-sedimentary rocks aged Middle Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous and magmatic intrusions of Cu Mong (GblEem), Phan Rang (G P IE pr), Dinh Quan (GDilJ3dq), Deo Ca (GDilK2 de) and Ca Na (G/K2en) complexes. These magmatic complexes occur in Ba cape, Dinh mountain, Da Chong mountain, to the west of Cam Ranh bay, Cam Linh cape, Hon Chut, Quyt cape, Sop cape, Da Hang mountain... Parts of these solid geologic formations have created firm islands and coast line which are of high resistance to hazards (Fig. 1). Group of unconsolidated formations with low resistance to hazards The geologic formations of this group consist of unconsolidated Quaternary sediments occurring along the coast from Hon Ngoai - Hon Tai, Ca Tien, Hon Do - Ninh Chu, Dong Hai - Vinh Hao, Lagan cape to Phan Ri and around Binh Da, Binh Hung peninsulas. These formations form coast sections which are strongly affected by erosion hazards. Geologic structure and geodynamic conditions The Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone belongs to the 109'15' 109'21' margin ofindochina uplifted block and the East Sea subsided block with two main fault systems. The NE-SW trending fault system passes through the area of Phan Rang town, slightly dipping SE-wards and has undergone right strike-slip in Paleogene - Miocene. The NE- SW trending fault system dips SW and is a normal fault.... Step-down faulting activities are clearly expressed in the thickness of the marine sediments, the dissection, destruction of Pre-Cenozoic formations and indications of seismic activities. Hydrography In the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri offshore area there are two main sea-wave directions: W - SW in summer and E - NE in winter. The waves here are highest in the whole country (0.9 - l.im), in the rainstorm season waves can reach a height of 7-8m even 10m. The tide is of irregular diurnal regime, with the duration of rising tide longer than that of the falling tide. The tide amplitude during the high tide period reaches 1.5-2m and increases southward. The sea currents in the study area are of predominantly E - NE direction. They tend to run along the coast in N-S direction. Human activities The Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone is populated by many ethnic groups, mainly the Kinh people. The population is unevenly distributed, concentrated in plain, river mouth, coastal port areas, along roads and in towns and townships (Cam Ranh town, Phan Rang town, Ca Na town ship, Phan Ri Cua township... ). The main occupations include mining, tourist service, aquaculture and fishing, salt production, processing industry, etc. Human activities such as extraction of corrals to make souvenirs, extraction of sand from the sea beach, etc., intensifies some hazards such as erosion, slumping, flood, some geochemical hazards
5 3. Characteristics of geohazards Geodynamic hazards Earthquake: According to Nguyen Dinh Xuyen et ai., (1996) in the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone there is possibility of earthquakes of magnitude 8 with M = , focal depth of h = 15-20km along the 109 meridian fault. Earthquake of magnitude 7 with M = , h = 10-15km may occur in Ba river, Bato - Cung Son areas... Most of the remaining area is the earthquake transmission area with maximum intensity ofi max =6-7 (Fig. 3). Land cracking: Due to the impacts of the Nha Trang - Tanh Ninh and Mui Dinh - Vung Tau fault systems, in the Ca Na valley, which is an intramontane graben, about 1-3km. Wide block has been separated and subsided. This disturbed zone extends further to the north within the Phan Rang plain. At Dinh cape, a sublatitudinal fracture system also split the mountain, creating parallel or alternate joint systems. Coastal erosion: The coastal sections in the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone being eroded are not great in number, but the -;;-350, erosion evolves in a complicated manner and is concentrated in ""- some key areas. Ninh Thuan province has 11 coast section being erode, with a total length of 10 km, accounting for 2.6% of the total length of the coast. The coast of Phan Rang area is being most intensively eroded, usually reaching a rate of over 10 mlyear. The coast from the end of the Ninh Chu tourist area to Khanh Rai has been eroded over a length of 2,000 m and with a width of 500m. In , the sea invaded some residential houses in Ninh Chu village, forcing some households to resettle. The coast from Khanh Nhon to Khanh Tuong (Ninh Rai district) during the last 10 years has been = ~300-l c "' _ H.;;;":~'I---- eroded inland 10-15m, threatening the Dam Vua industrial Mnh HOi Alan Rang Mnh Aluac CamRanh Tuy Aloog park (Fig. 2). Fig. 2: Erosion areas in some localities of The coast to the Long Song river mouth, since 1965 to present Cam Ranh-Phan Ri coastalzone has invaded 200 m inland, in period it invaded 70 m inland. At present, the coast in this area is being strongly eroded with a rate of2-3 mlyear. In the Long Song river mouth area in the period the 1000 m long western bank has been eroded 250 m inland, the 1500 m long Eastern bank has been invaded by the sea 303 m inland. Sedimentation causing channel changes: In the Ca Na river mouth the sedimentation has made it impossible for the ships to access the Ca Na port during the ebb tide and they must wait for the rising tide to enter the port for mooring. Some other river mouths such as Dam Nai, Kinh Dinh, Phan Ri river mouths have been also affected by sedimentation, causing channel changes and difficulties for navigation.. Sand drift: Sand drift hazard is common in the areas from Khanh Nhon to Khanh Rai, from Ninh Chu to Tu Thien and from Ca Na to Phan Ri (Fig. 3). The material building up the shore in these areas are quartz sand with grain size from medium to fine, with low coherence, thus moves easily under the action of wind. Sand is accumulated by the wind into dunes with height up to 10m along the coast. These sand dunes are continuous formed and move inland. The moving velocity of these sand dunes is 2-4 mlyear. The sand dunes moves into population and cultivation areas, burying houses, rice fields, gardens, etc., causing adverse impacts on the lives of the local people. Typhoon andflood: From 1954 to 1990, 10 typhoons landed on the area from Cam Ranh to Binh Thuan, in average there was a typhoon in every three years. Although the typhoons landing on the area are not great in number, they cause strong winds of force 7-8 in the offshore area, drowning boats, ships, causing human and property losses to the fishing people. The typhoon on 17 December 1964 caused a historic flood on the Cai river - Phan Rang, some places were 2-4 m under water, the water level measured was 6.07m above sea level. In November 1979, the flood peak in Phan Rang was 4.6 m. On 19 December 1993, the typhoon No 11 caused a flood on the Cai river with water level of 4.75 m, exceeding the alarming level 3; the average flood rise was 10.6 cmlh
6 Hazards related with the global sea level rise: According to Nguyen Ngoc Thuy (1995), in the coastal zone of Vietnam, the average annual rate of sea level rise is 2mm/year. According to the calculations of scientists, in 100 years the sea water will rise by 1 m and its area of influence will include the low land areas with elevation below 10m. The area with direct impacts of the 1 m sea level rise in the study area will comprise most of the Binh Thuan and Ninh Thuan plains to the elevation of 10m. The group of geochemical hazards total concentration of pesticides in the sediments varies within ng/g, the common concentration is l ng/g. The area with highest concentration of pesticides in the sediments is to the east of Sop cape - at the entrance of Cam Ranh bay and in Phan Rang bay. 11"45' The total concentration of polychlobiphenyl (PCBs) in the sediments varies within ng/g, the most common one is l.47 ng/g. The highest PCB concentration characterizes the areas NE of Ca Tien cape, inside Cam Ranh bay, 11"30' and at the entrance of Cam Ranh bay. Although they have not reach the threshold level, pesticides and PCBs may cause harms to man by through bottom dwelling animals. Salinization: Salinization of surface water takes 11'15' place in all river mouths in the study area. In the rainy season, the salinization boundary is only 1-2 km away from the river mouth, but in the dry season the salinization boundary is pushed 5-7km inland, with relatively high TDS, 3-30g/1, 11'1)0' therefore water in many places cannot be used for agricultural production. The whole area of Phan 10"fi5'IO'-:-:e''''' 32 Rang - Thap Cham urban area is salinized, 75% of the area of Ninh Thuan and Binh Thuan plains are also salinized, especially the coastal areas such as Ca Na, Lien Huong, Phuoc The, Phan Ri '46' 12'1)0',--...:.::.c-=- 1. Dynamic hazards [l;;'earthqullke 1 Strong sand drift. with T = I year I:QWeaksanddrift, with T= 1 year [ "Strong slwnp, with T = 1 year ICModerate erosion with T= 10 years ~Low land area affected by sea level rise 00 C Moderate flood area OLow flood area [2Salinized area 2, Geochemical hazards ~Hg pollution in sediments ~As pollution in sediments C Sb pollution in sediments ~Mn pollution in water ~Hgpol1utionin water 109' 15' 109'21' 12'1)0' 11'46' 11"30' 11'15' 11'1)0' C-' '-46-' '0-0' '-1(;-' -'10~~~~' Fig. 3: Distribution of some hazards in the Cam Ranh-Phan ill costal zone Environmental pollution by heavy metals: The water environment in the area is being polluted by Cu and Zn in both bottom and surface layers. The areas with sea water in the surface layer being most strongly polluted by Cu include Noi island - Cam Linh cape, La Gan cape - Phan Ri, Sung Trau cape - Cau island and the area at the entrance of Cam Ranh bay with pollution intensity from moderate to high (pollution coefficient T tc = ; T tc = CxlCtc: where Cx is the content of an element in the environment; Ctc - is the maximum permissible limit in the Vietnam standard for the corresponding environment, Mai Trong Nhuan, 2001). The area with highest Zn pollution is Phan Rang and the area south of Cau island, with pollution coefficient up to 3.2. Besides, Zn pollution is also found at the entrance of Cam Ranh bay and the area from Sung Trau cape to Cau island with pollution coefficient T tc = The superficial sediments in the study area are being polluted by Cu and Hg with an intensity from low to high. The sediments which are most strongly polluted by Cu are those in the area at he entrance of Van Phong bay with pollution coefficient of l.65, less in the area of Phan Rang bay and some other areas (T tc = l.01 - l.65). Nearly all superficial sediments on the sea bed of Cam Ranh - Phan Ri area are being polluted by Hg, especially the sediments at the entrance of Cam Ranh bay, Da Vach cape and Phan Rang bay with highest pollution coefficient T tc = 4.6. To the south, the concentration of Hg in the sediments decreases but still causes pollution with T tc = Pollution by pesticides and polychlobipheny: The 101)"32' 100'
7 4. Hazard risk level zoning The previous researches on hazards only provided individual and qualitative information on possible impacts of one or some hazards within a certain area. These information are still not of sufficient scientific basis to propose measures for preventing and mitigation of hazards. Therefore, this paper will introduce the method of zoning risk level due to many hazards and consequently proposes measures for territory and territorial water planning which can help to avoid risks caused by hazards and meet the requirement for sustainable development The hazards risk level zoning is implemented in 5 stages as follows: Stage 1: Establishing a field survey network, with area 1km2 or 4 km 2, corresponding with the rectangular grid of the 1:50,000 or 1:100,000 scale maps. Stage 2: Identifying hazards on the survey network and giving them point values in terms of risk level based on various indicators (type, intensity, frequency etc.) for each kind of hazards according by the formula: G = (F+A)*M (1), where G is the total point value ofthe hazard; F is the frequency; A is the area affected; M is the intensity of the hazard. Stage 3: Identifying hazards and calculating the total point value of hazard risk level in each rectangular cell of the map, by the formula: DIi = SH/SHtb(2), where: DIi is the risk level for each cell,; SH is the total point value of risk level in the ith cell; SHtb is the total point value for risk level of the whole study area. Stage 4: Plotting the result of calculating the risk level on the cells of the map. Stage 5: Delineating areas with different hazard risk levels: ifdii < 1 the area is of the area is oflow risk; if 1 < DIi < l.7 the area is of moderate risk; if 1.7 < DIi < 3.4; the area is of high risk and ifdii > 3.4 the area is of very high risk. The Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone is affected by 10 kinds of geohazards, which include earthquake, land cracking, coastal erosion, sedimentation causing channel changes, sand drift" typhoon and flood, sea level rise, environmental pollution by metals, environmental pollution by organic compounds and salinization. Applying the formula (1) one can calculate the risk level for each kind of hazard and arrange the hazards in decreasing sequence of risk level (Table 1). Table 1: Hazard risk levels in the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone No Hazards F A M G Salinization Typhoon and flood Sedimentation causing channel changes Coastal erosion Sand drift Sea level rise Earthquake Environmental pollution by heavy metals Environmental pollution by organic compounds Land
8 As a results of calculating the point value of individual hazard and giving the point value on each rectangular cell of the 1: 50,000 scale map, the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone is divided into 3 areas with different risk levels (Fig. 4): Tlte low risk area (DI < 1): consisting of areas from Da Vach cape to Hon Do cape, from Dinh cape to Sung Trau cape and the area of La Gan cape. The shore is composed of solid bedrock which has high hazard resistance. The human activities are moderate. Geohazards have occurred locally with intensity from low to moderate. The water and superficial sediments are practically not polluted. Moderate risk area (1 < DI < 1,7): Consists of the coastal zone from the South of Cam Ranh township to Kenh Nam flood plain of Dinh river, Vinh Tuong, Ca Na to Ca Tha cape and the whole offshore area with 10-30m water depth. The coast is composed of unconsolidated sediments which are of low resistance to hazards. Human activities are mainly aquaculture and fishing together with ecological tourist service which is fairly developed. Hazards occur locally, with moderate intensity. The sea water is not polluted, the superficial sediments show indications of pollution. risk area (1,7 < DI < 3,4): Comprises the area at the entrance of Cam Ranh bay, Ninh Chu - Vinh Tuong bay, the area of Phan Ri Cua. The coast is composed of unconsolidated sediments. The los' 32' los'45' 109'00' 109'1(i' 100'21' 12'1)0', "'7 1 ""'; 1,...!..",...~--..,.:::,;.,.;.;...-..;;12'1)O 11"45' 11'30' 11'1)0' V!@'!!!.,,'uoal: Low risk Area 2: Moderate risk 3: High risk \~=r~!~~..,...,... :..;..;..--'...,_~_="""_"="'_='10'\'i5' los' 45' 100'15' 100' 21' Fig. 4: Hazard risk level zoning of Cam Ranh-Phan Ri coastal zone superficial sediments are mainly of fine fraction (sandy and clayey mud). Human activities include a military port, aquaculture ponds, cultural, educational, transport facilities, etc.. Dynamic hazards include many types such as sedimentation, erosion salinization in local to wide extent, with intensity from high to very high. Environmental pollution of water and sediments takes place with very high pollution coefficient. 5. Recommendation of measures for,.,vv"'.. ~'u To mitigate natural hazards in general and geohazards in particular, the two main directions should be follows: Applying engineering measures for mitigating hazards. Applying non-engineering measures for mitigating hazards, adapting to or avoiding hazards. In the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone in general, many engineering measures have been applied against hazards, such as construction of stone revetment against erosion and sedimentation in Ninh Chu - Khanh Hai, Khanh Nhon - Khanh Tuong, Tri Hai, Nhon Hai, Phuoc The, Hoa Phu, Long Song river mouth, Phan Ri river mouth... However, the hazard mitigation efficiency of these measures is very limited (Fig. 2), causing the waste of resources. Therefore it is recommended to apply more consistent measures for preventing and avoiding hazards by non-engineering measures. This group of measures need a long time, but it is of high economic efficiency and large capability to mitigate hazards for the coastal zone. Non engineering measures applied to Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone include: -138-
9 los' 31' 108" 45' 12'1)0' r-----, :.:.:,'7-;;;-",...,.~ LEGEND 1. Hazard forecast zoning 'a) Area with M"" 6, TS 500)" p2:0.1 insoy ~ b} Area with M"'5.TS 500 y, ~O.l in50y a) Area with M== 6, T5 200 y, ~O.l in 20y b) Area.. vith M= 5,T::= 200 y. p2.0.1 in 20y ilij Sedimentation causing channel changes ZJ Moderate coastal erosionwitht= 10yem 5J Stroogs\ump v.ith T= 10 years 11"45'!3l Low land affeded by global sea level rise DMod!ttteflooduea C Low flood area GSaliniztdsoilarea ~S211dyflyuea '2. Other symbols 11"30' 11'16' l1'ild' 10"55', Fig. 5 Schematic forecasting map of some hazards in Cam Ranh-Phan Ri coastal zone 6. Forecasting for preventing and avoiding Hazards were investigated and delineated based on the risk level of each kind of hazard and are shown on the schematic forecasting map of some hazards in Cam Ranh - Phan Ri area (Fig. 5). Master plans for rational use of the territory and territorial waters of localities of the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone must be based on the hazards risk level zoning map and coastal zone hazards forecasting map. In low risk areas it is possible to build permanent buildings requiring high safety level, which are the best place for evacuation and escape when hazards occur. Population areas, urban areas, schools, hospitals etc., may be established, but it is ]necessary to enhance the capability of preventing and controlling hazards. The area with moderate risk can be planned for construction of temporary, simple, compact facilities, aquaculture service stations, for maintaining aquaculture (along the coast and in cages) in parallel with the plantation of mangrove forests, and establishment of ecological tourist areas. If it is planned for construction of important facilities such as an urban area, chemical plant, residential area, etc. measures for strengthening the capability to resist hazards must be adopted. For high risk areas, it recommended not to invest in development of high density population areas and socio-economic facilities and use the territory for agricultural and aquaculture such as schools, hospitals, etc. but only exploit production. On the basis of the study and integrated assessment of hazards, it is necessary to compile a socio-natural system vulnerability map for the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone as the first stage in the process of integrated coastal zone management (ICZM) (lvfai Trang Nhuan et al.,) 7. Conclusion 1) The Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone has 10 kinds of hazards with decreasing risk level as follows: Salinization, typhoon and flood, sedimentation causing channel changes, coastal erosion, sand drift, sea level rise, earthquake, environmental pollution by heavy metals, environmental pollution by organic compounds, land cracking. 2) As a result of the integrated study and assessment of the hazards in the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri coastal zone, three areas with different risk levels have been differentiated in this coastal zone: low risk area, moderate risk area and high risk area. 3) Engineering measures for preventing and controlling hazards in Cam Ranh - Phan Ri costal zone are still not effective. Non-engineering measures such as working out hazard risk level zoning maps, hazard forecasting map, vulnerability map of the socio-natural system, which will serve as an important basis for integrated management of the coastal zone
10 References 1. Mai Trong Nhuan. Environmental geochemistry (2001). Hanoi National University Publishing House. 2. Mai Trong Nhuan, Dao Manh Tien et ai., (2002). Geohazard map of the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri shallow offshore area (0-30 m water depth). Archive of the Marine Geology Union. 3. Mai Trong Nhuan, Dao Manh Tien et al., (2002). Environmental geology map of the Cam Ranh - Phan Ri shallow offshore area (0-30 m water depth). Archive of the Marine Geology Union.. 4. Mai Trong Nhuan et ai., (2002). Vulnerability assessment of the socio-natural system of coastal zone (case study: Khanh Hoa province). Science Journal of the Hanoi National University No 3 : Mai Trong Nhuan, Dao Manh Tien et al., (2004). Environmental geology status map of the Phan Thiet - Ho Tram shallow offshore area (0-30 m water depth). Archive of the Marine Geology Union. 6. Cutter, SL, (1996). Vulnerability to Environmental Hazards. Progress in Human Geography 20: Cutter, SL. et ai., (2000). Revealing the Vulnerability of People and Places: A case study of Georgetown County, South Carolina. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 90(4), 2000: Kasperson, R, (2001). Vulnerability and Global Environmental Change. IHDP, V. 2/01: NOAA (1999). Community Vulnerability Assessment Tool CD - ROM. NOAA Coastal Services Center. 10. Toms, G. et ai., (1996). Viet Nam Coastal Zone Vulnerability Assessment. Viet Nam VA Project Final Report:
Vietnam Coastal Erosion - Cause and Challenges -
 Administration of Sea and Islands Center for Oceanography University of Transport and Communications, Hanoi Vietnam Vietnam Coastal Erosion - Cause and Challenges - Presenters: Pham Hoang KIEN Le Van CONG
Administration of Sea and Islands Center for Oceanography University of Transport and Communications, Hanoi Vietnam Vietnam Coastal Erosion - Cause and Challenges - Presenters: Pham Hoang KIEN Le Van CONG
EVALUATION OF THE VULNERABILITY OF TitleCOASTAL SOCIO-NATURAL SYSTEMS (EXAM FROM KHANH HOA COASTAL ZONE) Author(s) Nguyen, Thi Thuy Hang; Pham, Hung T
 EVALUATION OF THE VULNERABILITY OF TitleCOASTAL SOCIO-NATURAL SYSTEMS (EXAM FROM KHANH HOA COASTAL ZONE) Author(s) Mai, Trong Nhuan; Tran, Thanh Hai; Nguyen, Thi Thuy Hang; Pham, Hung T Annual Report of
EVALUATION OF THE VULNERABILITY OF TitleCOASTAL SOCIO-NATURAL SYSTEMS (EXAM FROM KHANH HOA COASTAL ZONE) Author(s) Mai, Trong Nhuan; Tran, Thanh Hai; Nguyen, Thi Thuy Hang; Pham, Hung T Annual Report of
Current Status of Vietnam Coastal Erosion and Major Measures for Mitigation
 Vietnam Administration of Sea and Islands Center for Oceanography University of Transport and Communications Current Status of Vietnam Coastal Erosion and Major Measures for Mitigation Case Study: Thanh
Vietnam Administration of Sea and Islands Center for Oceanography University of Transport and Communications Current Status of Vietnam Coastal Erosion and Major Measures for Mitigation Case Study: Thanh
2014 Summer training course for slope land disaster reduction Taipei, Taiwan, Aug
 MINISTRY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HYDROTECH RESEARCH INSTITUTE MINISTRY OF NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT VIETNAM INSTITUTE OF GEOSCIENCES AND MINERAL RESOURCES (VIGMR) 2014 Summer training course
MINISTRY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HYDROTECH RESEARCH INSTITUTE MINISTRY OF NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT VIETNAM INSTITUTE OF GEOSCIENCES AND MINERAL RESOURCES (VIGMR) 2014 Summer training course
Huong River. Serial No. : Viet Nam-8 Location: Thua Thien Hue Province, Viet Nam N 16 00' '
 Viet Nam 8 Huong River Map of River Table of Basic Data Name: Huong River Serial No. : Viet Nam-8 Location: Thua Thien Hue Province, Viet Nam N 16 00' - 14 40' E 107 07' - 107 50' 2 Area: 2,830 km Length
Viet Nam 8 Huong River Map of River Table of Basic Data Name: Huong River Serial No. : Viet Nam-8 Location: Thua Thien Hue Province, Viet Nam N 16 00' - 14 40' E 107 07' - 107 50' 2 Area: 2,830 km Length
SIMULATION OF A WORST CASE TSUNAMI SCENARIO FROM THE MANILA TRENCH TO VIETNAM
 SIMULATION OF A WORST CASE TSUNAMI SCENARIO FROM THE MANILA TRENCH TO VIETNAM Nguyen Hong Phuong, Vu Ha Phuong, Pham The Truyen Earthquake Information and Tsunami Warning Centre, VAST OUTLINE Earthquake
SIMULATION OF A WORST CASE TSUNAMI SCENARIO FROM THE MANILA TRENCH TO VIETNAM Nguyen Hong Phuong, Vu Ha Phuong, Pham The Truyen Earthquake Information and Tsunami Warning Centre, VAST OUTLINE Earthquake
THE MODEL OF SPATIAL ORGANIZATION OF COASTAL FISHERMEN VILLAGES IN THE SOUTH CENTRAL COAST OF VIETNAM
 i MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING MINISTRY OF CONSTRUCTION HANOI ARCHITECTURAL UNIVERSITY TRAN VAN HIEN THE MODEL OF SPATIAL ORGANIZATION OF COASTAL FISHERMEN VILLAGES IN THE SOUTH CENTRAL COAST OF
i MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING MINISTRY OF CONSTRUCTION HANOI ARCHITECTURAL UNIVERSITY TRAN VAN HIEN THE MODEL OF SPATIAL ORGANIZATION OF COASTAL FISHERMEN VILLAGES IN THE SOUTH CENTRAL COAST OF
Populations effected by flood top ten districts
 2050 - Populations effected by flood top ten districts 14 Extreme A2 Extreme A2 with dyke District Area (Ha) Population 2050 People affected Percent area affected People affected Percent area affected
2050 - Populations effected by flood top ten districts 14 Extreme A2 Extreme A2 with dyke District Area (Ha) Population 2050 People affected Percent area affected People affected Percent area affected
HEAVY RAIN OVER MID-CENTRAL REGION OF VIETNAM
 HEAVY RAIN OVER MID-CENTRAL REGION OF VIETNAM ----------------------------------------------------------------------- S.Eng. Dang Thi Mai; Dr. Nguyen Thi Tan Thanh National Hydro Meteorological Service
HEAVY RAIN OVER MID-CENTRAL REGION OF VIETNAM ----------------------------------------------------------------------- S.Eng. Dang Thi Mai; Dr. Nguyen Thi Tan Thanh National Hydro Meteorological Service
EROSION MECHANISM OF NGA BAY RIVERBANKS, HO CHI MINH CITY, VIETNAM
 EROSION MECHANISM OF NGA BAY RIVERBANKS, HO CHI MINH CITY, VIETNAM Abstract Bui Trong Vinh 1, Nguyen Hai Truong 1 1 Department of Geo-Environment, Faculty of Geology and Petroleum Engineering Ho Chi Minh
EROSION MECHANISM OF NGA BAY RIVERBANKS, HO CHI MINH CITY, VIETNAM Abstract Bui Trong Vinh 1, Nguyen Hai Truong 1 1 Department of Geo-Environment, Faculty of Geology and Petroleum Engineering Ho Chi Minh
VARIATION OF VERTICAL STRESS IN THE HANOI TROUGH
 VARIATION OF VERTICAL STRESS IN THE HANOI TROUGH Nguyen Van Huong, Phan Trong Trinh Institute of Geological Sciences, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology Cu Minh Hoang PetroVietnam Exploration Production
VARIATION OF VERTICAL STRESS IN THE HANOI TROUGH Nguyen Van Huong, Phan Trong Trinh Institute of Geological Sciences, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology Cu Minh Hoang PetroVietnam Exploration Production
Land subsidence due to groundwater withdrawal in Hanoi, Vietnam
 Land Subsidence (Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Land Subsidence, The Hague, October 1995). 1AHS Publ. no. 234, 1995. 55 Land subsidence due to groundwater withdrawal in Hanoi, Vietnam
Land Subsidence (Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Land Subsidence, The Hague, October 1995). 1AHS Publ. no. 234, 1995. 55 Land subsidence due to groundwater withdrawal in Hanoi, Vietnam
Investigation, assessment and warning zonation for landslides in the mountainous regions of Vietnam
 Investigation, assessment and warning zonation for landslides in the mountainous regions of Vietnam (State-Funded Landslide Project SFLP) Dr. Eng. Le Quoc Hung Add: 67 Chien Thang Street, Ha Dong District,
Investigation, assessment and warning zonation for landslides in the mountainous regions of Vietnam (State-Funded Landslide Project SFLP) Dr. Eng. Le Quoc Hung Add: 67 Chien Thang Street, Ha Dong District,
Flash flood disaster in Bayangol district, Ulaanbaatar
 Flash flood disaster in Bayangol district, Ulaanbaatar Advanced Training Workshop on Reservoir Sedimentation Management 10-16 October 2007. IRTCES, Beijing China Janchivdorj.L, Institute of Geoecology,MAS
Flash flood disaster in Bayangol district, Ulaanbaatar Advanced Training Workshop on Reservoir Sedimentation Management 10-16 October 2007. IRTCES, Beijing China Janchivdorj.L, Institute of Geoecology,MAS
Assessment of climate change impacts on salinity intrusion in Hong-Thai Binh and Dong Nai river basins
 VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 27 (2011) 54-61 Assessment of climate change impacts on salinity intrusion in Hong-Thai Binh and Dong Nai river basins Tran Hong Thai, Tran Thi Van* Vietnam Institute
VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 27 (2011) 54-61 Assessment of climate change impacts on salinity intrusion in Hong-Thai Binh and Dong Nai river basins Tran Hong Thai, Tran Thi Van* Vietnam Institute
Proposal for Research and Investment Activities in the Coast and Estuaries (A Case Study in the North Central Coast of Viet Nam)
 2017/SOM3/EPWG/019 Agenda Item: 7.2.3 Proposal for Research and Investment Activities in the Coast and Estuaries (A Case Study in the North Central Coast of Viet Nam) Purpose: Information Submitted by:
2017/SOM3/EPWG/019 Agenda Item: 7.2.3 Proposal for Research and Investment Activities in the Coast and Estuaries (A Case Study in the North Central Coast of Viet Nam) Purpose: Information Submitted by:
International Symposium on Natural Disaster Mitigation. Local vulnerability assessment of landslides and debris flows
 International Symposium on Natural Disaster Mitigation of landslides and debris flows Lessons learnt from Cam Pha town and Van Don district, Quang Ninh province, Vietnam Nguyen Quoc Phi Faculty of Environment
International Symposium on Natural Disaster Mitigation of landslides and debris flows Lessons learnt from Cam Pha town and Van Don district, Quang Ninh province, Vietnam Nguyen Quoc Phi Faculty of Environment
INTRODUCTION. Climate
 INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property.
 Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
Newsletter # 2. Pilot sites in Greece. December 2018
 A HarmonizEd framework to Mitigate coastal EroSion promoting ICZM protocol implementation Newsletter # 2 December 2018 View of a beach in Ammolofi ( Paggaio Municipality ) Pilot sites in Greece 1. Name
A HarmonizEd framework to Mitigate coastal EroSion promoting ICZM protocol implementation Newsletter # 2 December 2018 View of a beach in Ammolofi ( Paggaio Municipality ) Pilot sites in Greece 1. Name
HCMC CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACT AND ADAPTATION ADB/HCMC PPC. Director ICEM International Centre for Environmental Management
 HCMC CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACT AND ADAPTATION STUDY ADB/HCMC PPC Jeremy Carew-Reid Jeremy Carew-Reid Director ICEM International Centre for Environmental Management Adaptation planning capacity 2 Increasing
HCMC CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACT AND ADAPTATION STUDY ADB/HCMC PPC Jeremy Carew-Reid Jeremy Carew-Reid Director ICEM International Centre for Environmental Management Adaptation planning capacity 2 Increasing
D DAVID PUBLISHING. 1. Introduction. 2. Methodology. Truong Thanh Phi
 Journal of Geological Resource and Engineering 2 (2016) 81-88 doi:10.17265/2328-2193/2016.02.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Some Results of Quantitative Analysis of Fracture Orientation Distribution along the
Journal of Geological Resource and Engineering 2 (2016) 81-88 doi:10.17265/2328-2193/2016.02.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Some Results of Quantitative Analysis of Fracture Orientation Distribution along the
Result of Field Geological Survey and Ground Truth for the Analysis Date: 2007/7/5 Location (UTM) Elev Geological Unit Point No. NT-02 VSW Index 260,7
 Date: Point No. 2007/7/5 NT-01 Result of Field Geological Survey and Ground Truth for the Analysis Location (UTM) Topography of granite hill in flat land Lithology: Medium grained hornblende granite. Topography:
Date: Point No. 2007/7/5 NT-01 Result of Field Geological Survey and Ground Truth for the Analysis Location (UTM) Topography of granite hill in flat land Lithology: Medium grained hornblende granite. Topography:
Nguyen Ngoc Thach 1, *, Pham Xuan Canh 2 VNU University of Science, 334 Nguyen Trai, Hanoi, Vietnam
 VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 8 (01) 44-6 Risk assessment of flash muddy flood and inundation of western Tam Dao mountainous region, Vinh Phuc province, Vietnam by using intergrated concept of
VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 8 (01) 44-6 Risk assessment of flash muddy flood and inundation of western Tam Dao mountainous region, Vinh Phuc province, Vietnam by using intergrated concept of
D DAVID PUBLISHING. Analytical Results of Cam Ranh Tuy Phong Fault Characteristics and Its Relation to Mud Eruption in Nam Trung Bo Area, Viet Nam
 Journal of Geological Resource and Engineering 7 (2016) 335-344 doi:10.17265/2328-2193/2016.07.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Analytical Results of Cam Ranh Tuy Phong Fault Characteristics and Its Relation to
Journal of Geological Resource and Engineering 7 (2016) 335-344 doi:10.17265/2328-2193/2016.07.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Analytical Results of Cam Ranh Tuy Phong Fault Characteristics and Its Relation to
Disclaimer. This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries.
 Disclaimer This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries. The views expressed in the report do not necessarily reflect the views of the ADRC. The boundaries and
Disclaimer This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries. The views expressed in the report do not necessarily reflect the views of the ADRC. The boundaries and
BURGAS CASE STUDY: LAND-SEA INTERACTIONS. Dr. Margarita Stancheva
 BURGAS CASE STUDY: LAND-SEA INTERACTIONS Dr. Margarita Stancheva Name of presentation NEED FOR COHERENCE BETWEEN LAND AND SEA ACTIVITIES Name presenter Burgas is the fourth largest city in Bulgaria and
BURGAS CASE STUDY: LAND-SEA INTERACTIONS Dr. Margarita Stancheva Name of presentation NEED FOR COHERENCE BETWEEN LAND AND SEA ACTIVITIES Name presenter Burgas is the fourth largest city in Bulgaria and
Recent development of the National Hydro-Meteorological Service (NHMS) of Viet Nam for disaster risk reduction
 Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment National Hydro-Meteorological Service Recent development of the National Hydro-Meteorological Service (NHMS) of Viet Nam for disaster risk reduction Tran Van
Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment National Hydro-Meteorological Service Recent development of the National Hydro-Meteorological Service (NHMS) of Viet Nam for disaster risk reduction Tran Van
Development of Modeling System to Simulate Hydrodynamic and Environmental Quantities in the Hai Phong Estuary, Vietnam
 34 th IAHR World Congress - Balance and Uncertainty 6 June - 1 July 011, Brisbane, Australia 33 rd Hydrology & Water Resources Symposium 10 th Hydraulics Conference Development of Modeling System to Simulate
34 th IAHR World Congress - Balance and Uncertainty 6 June - 1 July 011, Brisbane, Australia 33 rd Hydrology & Water Resources Symposium 10 th Hydraulics Conference Development of Modeling System to Simulate
VULNERABILITY OF WATER SUPPLY TO NATURAL HAZARDS IN JAMAICA
 VULNERABILITY OF WATER SUPPLY TO NATURAL HAZARDS IN JAMAICA RAFI AHMAD rafi.ahmad@uwimona.edu.jm Unit for disaster studies, Department of Geography & Geology, The University of the West Indies, Mona Kingston
VULNERABILITY OF WATER SUPPLY TO NATURAL HAZARDS IN JAMAICA RAFI AHMAD rafi.ahmad@uwimona.edu.jm Unit for disaster studies, Department of Geography & Geology, The University of the West Indies, Mona Kingston
MINISTRY OF NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT
 MINISTRY OF NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT HÀ NỘI, 2016 CLIMATE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISE SCENARIOS FOR VIET NAM SPM Summary for policymakers Main authors: Tran Thuc, Nguyen Van Thang, Huynh Thi Lan
MINISTRY OF NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT HÀ NỘI, 2016 CLIMATE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISE SCENARIOS FOR VIET NAM SPM Summary for policymakers Main authors: Tran Thuc, Nguyen Van Thang, Huynh Thi Lan
CLIMATE CHANGE IN VIET NAM: Observed and Future Projection
 2017 ACTS Workshop on Extreme Weather Forecast and Water Resources Management CLIMATE CHANGE IN VIET NAM: Observed and Future Projection Mai Van KHIEM Viet Nam Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology and Climate
2017 ACTS Workshop on Extreme Weather Forecast and Water Resources Management CLIMATE CHANGE IN VIET NAM: Observed and Future Projection Mai Van KHIEM Viet Nam Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology and Climate
AN OVERVIEW OF RESEARCH AND POTENTIAL IN VIETNAM
 AN OVERVIEW OF RESEARCH AND INVESTIGATION OF GAS HYDRATE POTENTIAL IN VIETNAM Vu Truong Son 1, Do Tu Chung 1, Trinh Nguyen Tinh 1, Nguyen Bieu 2, Tran Van Tri 2, Nguyen Duc Thang 2, Tran Nghi 3 1. Marine
AN OVERVIEW OF RESEARCH AND INVESTIGATION OF GAS HYDRATE POTENTIAL IN VIETNAM Vu Truong Son 1, Do Tu Chung 1, Trinh Nguyen Tinh 1, Nguyen Bieu 2, Tran Van Tri 2, Nguyen Duc Thang 2, Tran Nghi 3 1. Marine
Monitoring Urban Space Expansion Using Remote Sensing Data in Ha Long City, Quang Ninh Province in Vietnam
 Monitoring Urban Space Expansion Using Remote Sensing Data in Ha Long City, Quang Ninh Province in Vietnam MY Vo Chi, LAN Pham Thi, SON Tong Si, Viet Key words: VSW index, urban expansion, supervised classification.
Monitoring Urban Space Expansion Using Remote Sensing Data in Ha Long City, Quang Ninh Province in Vietnam MY Vo Chi, LAN Pham Thi, SON Tong Si, Viet Key words: VSW index, urban expansion, supervised classification.
Prevention and remediation of rockslide at left portal of north tunnel of Da Nang Qu ang Ngai expressway in Quang Nam, Vietnam
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Prevention and remediation of rockslide at left portal of north tunnel of Da Nang Qu ang Ngai expressway in Quang Nam, Vietnam To
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Prevention and remediation of rockslide at left portal of north tunnel of Da Nang Qu ang Ngai expressway in Quang Nam, Vietnam To
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP. Possible Written Response Exam Questions
 Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
Heather Schlosser Army Corps of Engineers Coastal Studies Group August 28, 2008
 Got sand? Regional Sediment Management in Orange County Heather Schlosser Army Corps of Engineers Coastal Studies Group August 28, 2008 Regional Sediment Management Regional sediment management recognizes
Got sand? Regional Sediment Management in Orange County Heather Schlosser Army Corps of Engineers Coastal Studies Group August 28, 2008 Regional Sediment Management Regional sediment management recognizes
RISK OF TYPHOON AND STORM SURGES IN COASTAL AREAS OF VIETNAM
 RISK OF TYPHOON AND STORM SURGES IN COASTAL AREAS OF VIETNAM Hoang Duc Cuong, Nguyen Ba Thuy, Nguyen Van Huong, Du Duc Tien Vietnam National Center for Hydro-meteorological Forecasting (NCHMF) Hanoi, 26-27
RISK OF TYPHOON AND STORM SURGES IN COASTAL AREAS OF VIETNAM Hoang Duc Cuong, Nguyen Ba Thuy, Nguyen Van Huong, Du Duc Tien Vietnam National Center for Hydro-meteorological Forecasting (NCHMF) Hanoi, 26-27
Sri Lanka has a coastline of km excluding the shoreline of bays and inlets.
 Defining and Demarcating Coastal zones in Sri Lanka Procedure, Challenges and What needs to be done? Dr. Anil Premaratne Director General Coast Conservation Coast Conservation Department Sri Lanka 1 Sri
Defining and Demarcating Coastal zones in Sri Lanka Procedure, Challenges and What needs to be done? Dr. Anil Premaratne Director General Coast Conservation Coast Conservation Department Sri Lanka 1 Sri
Using Reanalysis SST Data for Establishing Extreme Drought and Rainfall Predicting Schemes in the Southern Central Vietnam
 Using Reanalysis SST Data for Establishing Extreme Drought and Rainfall Predicting Schemes in the Southern Central Vietnam Dr. Nguyen Duc Hau 1, Dr. Nguyen Thi Minh Phuong 2 National Center For Hydrometeorological
Using Reanalysis SST Data for Establishing Extreme Drought and Rainfall Predicting Schemes in the Southern Central Vietnam Dr. Nguyen Duc Hau 1, Dr. Nguyen Thi Minh Phuong 2 National Center For Hydrometeorological
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Wainui Beach Management Strategy (WBMS) Summary of Existing Documents. GNS Tsunami Reports
 Wainui Beach Management Strategy (WBMS) Summary of Existing Documents GNS Tsunami Reports a) Review of Tsunami Hazard and Risk in New Zealand ( National Risk Report ) b) Review of New Zealand s Preparedness
Wainui Beach Management Strategy (WBMS) Summary of Existing Documents GNS Tsunami Reports a) Review of Tsunami Hazard and Risk in New Zealand ( National Risk Report ) b) Review of New Zealand s Preparedness
Team 09 Nguyen chau lan (Vietnam) Dilum Wannigasekara (Sri lanka)
 Team 09 Nguyen chau lan (Vietnam) Dilum Wannigasekara (Sri lanka) contents Part I: Landslide in Vietnam Part II: Case study of Landslide in sri lanka Part I: Introduction of Landslide in hoa binh province
Team 09 Nguyen chau lan (Vietnam) Dilum Wannigasekara (Sri lanka) contents Part I: Landslide in Vietnam Part II: Case study of Landslide in sri lanka Part I: Introduction of Landslide in hoa binh province
Geologic Trips San Francisco and the Bay Area
 Excerpt from Geologic Trips San Francisco and the Bay Area by Ted Konigsmark ISBN 0-9661316-4-9 GeoPress All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced without written permission in writing,
Excerpt from Geologic Trips San Francisco and the Bay Area by Ted Konigsmark ISBN 0-9661316-4-9 GeoPress All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced without written permission in writing,
East Asia & Southeast Asia region
 Deltas at Risk Dynamics and vulnerability of river delta system East Asia & Southeast Asia region Yoshiki Saito Geological Survey of Japan Huanghe (Yellow River) Plateau Tibetan Himalayas Old Huanghe (500
Deltas at Risk Dynamics and vulnerability of river delta system East Asia & Southeast Asia region Yoshiki Saito Geological Survey of Japan Huanghe (Yellow River) Plateau Tibetan Himalayas Old Huanghe (500
Module 10: Resources and Virginia Geology Topic 4 Content: Virginia Geology Notes
 Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
 CLASSIFYING SMALL AREAS IN HANOI FO TitleLANSCAPE MANAGEMENT-BASED ON FACTOR CLUSTER ANALYSIS METHOD Author(s) Nguyen, Cao Huan; Nguyen, An Thinh; Sawaki, Masanori Annual Report of FY 2004, The Core Citation
CLASSIFYING SMALL AREAS IN HANOI FO TitleLANSCAPE MANAGEMENT-BASED ON FACTOR CLUSTER ANALYSIS METHOD Author(s) Nguyen, Cao Huan; Nguyen, An Thinh; Sawaki, Masanori Annual Report of FY 2004, The Core Citation
M14/3/GEOGR/SP2/ENG/TZ0/XX/Q GEOGRAPHY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2. Monday 19 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 20 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M14/3/GEOGR/SP2/ENG/TZ0/XX/Q 22145203 GEOGRAPHY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2 Monday 19 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 20 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do
M14/3/GEOGR/SP2/ENG/TZ0/XX/Q 22145203 GEOGRAPHY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2 Monday 19 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 20 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do
Directed Reading. Section: Types of Maps
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Types of Maps 1. What are some of the characteristics of an area shown on maps used by Earth scientists? a. types of animals, types of plants, types of minerals
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Types of Maps 1. What are some of the characteristics of an area shown on maps used by Earth scientists? a. types of animals, types of plants, types of minerals
Long-term sediment distribution calculation taking into account sea level rise and the development of Day estuary
 VNU Journal of Science, Natural Sciences and Technology 28, No. 3S (212) 57-62 Long-term sediment distribution calculation taking into account sea level rise and the development of Day estuary Nguyen Xuan
VNU Journal of Science, Natural Sciences and Technology 28, No. 3S (212) 57-62 Long-term sediment distribution calculation taking into account sea level rise and the development of Day estuary Nguyen Xuan
STATUS OF COASTAL EROSION OF VIETNAM AND PROPOSED MEASURES FOR PROTECTION
 STATUS OF COASTAL EROSION OF VIETNAM AND PROPOSED MEASURES FOR PROTECTION Assoc. Prof., Dr. Assoc. Prof., Dr. Prof., DSc. Eng. Ngo Ngoc Cat Pham Huy Tien Do Dinh Sam Nguyen Ngoc Binh The coastal zone of
STATUS OF COASTAL EROSION OF VIETNAM AND PROPOSED MEASURES FOR PROTECTION Assoc. Prof., Dr. Assoc. Prof., Dr. Prof., DSc. Eng. Ngo Ngoc Cat Pham Huy Tien Do Dinh Sam Nguyen Ngoc Binh The coastal zone of
KHI X L T SÔNG H NG VÀO SÔNG ÁY
 XÂY D NG B N NG P L T KHU V C H DU TÓM T T T KHI X L T SÔNG H NG VÀO SÔNG ÁY Lê Vi t S n 1 Bài báo này trình bày k t qu nghiên c u, ánh giá r i ro ng p l vùng h du sông áy khi x l t sông H ng vào sông
XÂY D NG B N NG P L T KHU V C H DU TÓM T T T KHI X L T SÔNG H NG VÀO SÔNG ÁY Lê Vi t S n 1 Bài báo này trình bày k t qu nghiên c u, ánh giá r i ro ng p l vùng h du sông áy khi x l t sông H ng vào sông
Hydraulic modelling for flood vulnerability assessment, case study in river basins in North Central Vietnam
 Hydraulic modelling for flood vulnerability assessment, case study in river basins in North Central Vietnam Tran Ngoc Anh 1*,2, Dang Dinh Kha 1,2, Dang Dinh Duc 2, Nguyen Thanh Son 1 1 Faculty of Hydrology
Hydraulic modelling for flood vulnerability assessment, case study in river basins in North Central Vietnam Tran Ngoc Anh 1*,2, Dang Dinh Kha 1,2, Dang Dinh Duc 2, Nguyen Thanh Son 1 1 Faculty of Hydrology
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis
 Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis By The British Geographer Situation Lyme Regis, with a population of 4400 is located in the centre of the Heritage Jurassic Coast in Dorset, South England. It is exposed to
Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis By The British Geographer Situation Lyme Regis, with a population of 4400 is located in the centre of the Heritage Jurassic Coast in Dorset, South England. It is exposed to
Physical Geography: Patterns, Processes, and Interactions, Grade 11, University/College Expectations
 Geographic Foundations: Space and Systems SSV.01 explain major theories of the origin and internal structure of the earth; Page 1 SSV.02 demonstrate an understanding of the principal features of the earth
Geographic Foundations: Space and Systems SSV.01 explain major theories of the origin and internal structure of the earth; Page 1 SSV.02 demonstrate an understanding of the principal features of the earth
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
ANALYSIS OF CHANGES IN THE RIVERBANKS OF MEKONG RIVER - VIETNAM BY USING MULTI-TEMPORAL REMOTE SENSING DATA
 ANALYSIS OF CHANGES IN THE RIVERBANKS OF MEKONG RIVER - VIETNAM BY USING MULTI-TEMPORAL REMOTE SENSING DATA Lam Dao Nguyen a, Nguyen Thanh Minh a, Pham Thi Mai Thy b, Hoang Phi Phung a and Hoang Van Huan
ANALYSIS OF CHANGES IN THE RIVERBANKS OF MEKONG RIVER - VIETNAM BY USING MULTI-TEMPORAL REMOTE SENSING DATA Lam Dao Nguyen a, Nguyen Thanh Minh a, Pham Thi Mai Thy b, Hoang Phi Phung a and Hoang Van Huan
CHAPTER V ECONOMIC EFFECTIVENESS OF THE GEOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION Based on Contract No. 01/2014/VLSK of Prospecting for gold at the scale of 1:25,000
 CHAPTER V ECONOMIC EFFECTIVENESS OF THE GEOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION Based on Contract No. 0/204/VLSK of Prospecting for gold at the scale of :25,000 over the 99. km 2 area in North, Northeast of Vang Tat,
CHAPTER V ECONOMIC EFFECTIVENESS OF THE GEOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION Based on Contract No. 0/204/VLSK of Prospecting for gold at the scale of :25,000 over the 99. km 2 area in North, Northeast of Vang Tat,
New GCSE Geography AQA
 Learning Checklist Half Term 1 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October 1.1.1 Tectonic Hazards Plate tectonics theory. Global distribution of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions and their
Learning Checklist Half Term 1 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October 1.1.1 Tectonic Hazards Plate tectonics theory. Global distribution of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions and their
Storms. 3. Storm types 4. Coastal Sectors 5. Sorm Location and Seasonality 6. Storm Severity 7. Storm Frequency and grouping 8. The design storm event
 1. Introduction Storms 2. The Impact of Storms on the coast 3. Storm types 4. Coastal Sectors 5. Sorm Location and Seasonality 6. Storm Severity 7. Storm Frequency and grouping 8. The design storm event
1. Introduction Storms 2. The Impact of Storms on the coast 3. Storm types 4. Coastal Sectors 5. Sorm Location and Seasonality 6. Storm Severity 7. Storm Frequency and grouping 8. The design storm event
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10
 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
What landforms make up Australia?!
 What landforms make up Australia? The tectonic forces of folding, faulting and volcanic activity have created many of Australia's major landforms. Other forces that work on the surface of Australia, and
What landforms make up Australia? The tectonic forces of folding, faulting and volcanic activity have created many of Australia's major landforms. Other forces that work on the surface of Australia, and
PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS. Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES. Faulting. Folding 9/6/2012. TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS GRADATIONAL TECTONIC
 TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the scientific study
TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the scientific study
The UN-GGIM: Europe core data initiative to encourage Geographic information supporting Sustainable Development Goals Dominique Laurent, France
 INSPIRE conference Strasbourg 6 September 2017 The UN-GGIM: Europe core data initiative to encourage Geographic information supporting Sustainable Development Goals Dominique Laurent, France Introduction
INSPIRE conference Strasbourg 6 September 2017 The UN-GGIM: Europe core data initiative to encourage Geographic information supporting Sustainable Development Goals Dominique Laurent, France Introduction
BURGAS CASE STUDY: LAND-SEA INTERACTIONS
 BURGAS CASE STUDY: LAND-SEA INTERACTIONS Dr. Margarita Stancheva IO-BAS, Bulgaria Name of presentation CROSS BORDER MARITIME SPATIAL PLANNING IN THE BLACK SEA ROMANIA AND BULGARIA (MARSPLAN BS) Project
BURGAS CASE STUDY: LAND-SEA INTERACTIONS Dr. Margarita Stancheva IO-BAS, Bulgaria Name of presentation CROSS BORDER MARITIME SPATIAL PLANNING IN THE BLACK SEA ROMANIA AND BULGARIA (MARSPLAN BS) Project
Optical Remote Sensing Method for Detecting Urban Green Space as Indicator Serving City Sustainable Development
 Proceedings Optical Remote Sensing Method for Detecting Urban Green Space as Indicator Serving City Sustainable Development Tran Thi Van *, Nguyen Dang Huyen Tran, Ha Duong Xuan Bao, Dinh Thi Thanh Phuong,
Proceedings Optical Remote Sensing Method for Detecting Urban Green Space as Indicator Serving City Sustainable Development Tran Thi Van *, Nguyen Dang Huyen Tran, Ha Duong Xuan Bao, Dinh Thi Thanh Phuong,
The Geology of Sebago Lake State Park
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Impacts of climate change on the flow in Hong-Thai Binh and Dong Nai river basins
 VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 27 (2011) 98-106 Impacts of climate change on the flow in Hong-Thai Binh and Dong Nai river basins Tran Hong Thai*, Tran Thuc Vietnam Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology
VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 27 (2011) 98-106 Impacts of climate change on the flow in Hong-Thai Binh and Dong Nai river basins Tran Hong Thai*, Tran Thuc Vietnam Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology
VNREDSat-1. Vietnam Natural Resources, Environment and Disaster monitoring Satellite. Lai Anh Khoi SPACE TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE
 VNREDSat-1 Vietnam Natural Resources, Environment and Disaster monitoring Satellite Lai Anh Khoi SPACE TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE JPTM2014 Yangon, Nov. 19-21, 2014 General information (1) Project Owner: Vietnam
VNREDSat-1 Vietnam Natural Resources, Environment and Disaster monitoring Satellite Lai Anh Khoi SPACE TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE JPTM2014 Yangon, Nov. 19-21, 2014 General information (1) Project Owner: Vietnam
A Roundup of Recent Debris Flow Events in Taiwan
 2015 International Workshop on Typhoon and Flood APEC Experience Sharing on Hazardous Weather Events and Risk Management A Roundup of Recent Debris Flow Events in Taiwan Hsiao-Yuan(Samuel) Yin Ph.D. sammya@mail.swcb.gov.tw
2015 International Workshop on Typhoon and Flood APEC Experience Sharing on Hazardous Weather Events and Risk Management A Roundup of Recent Debris Flow Events in Taiwan Hsiao-Yuan(Samuel) Yin Ph.D. sammya@mail.swcb.gov.tw
Holocene evolution of Dahab coastline Gulf of Aqaba, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt 1
 Holocene evolution of Dahab coastline Gulf of Aqaba, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt 1 Magdy Torab* 2 * Prof. of Geomorphology, Department of Geography, Damanhour University, Egypt 3 E-mail: magdytorab@hotmail.com.
Holocene evolution of Dahab coastline Gulf of Aqaba, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt 1 Magdy Torab* 2 * Prof. of Geomorphology, Department of Geography, Damanhour University, Egypt 3 E-mail: magdytorab@hotmail.com.
OVERVIEW OF GEOTHERMAL RESOURCE EVALUATION OF BANG LE THUY- QUANG BINH
 Proceedings of the 8th Asian Geothermal Symposium, December 9-10, 2008 OVERVIEW OF GEOTHERMAL RESOURCE EVALUATION OF BANG LE THUY- QUANG BINH Nguyen Tien Hung 1. Shigetaka Nakanishi 2, Shigeo Tezuka 3
Proceedings of the 8th Asian Geothermal Symposium, December 9-10, 2008 OVERVIEW OF GEOTHERMAL RESOURCE EVALUATION OF BANG LE THUY- QUANG BINH Nguyen Tien Hung 1. Shigetaka Nakanishi 2, Shigeo Tezuka 3
Margarita Stancheva Hristo Stanchev & Robert Young 2. MEDCOAST JUBILEE WORKSHOP May 2015, Iberotel Sarigerme Park, Dalaman, Turkey
 Margarita Stancheva Hristo Stanchev & Robert Young 2 INTRODUCTION: Bulgarian Black Sea coast INTRODUCTION: Increasing pressure on Bulgarian coastal zone In 2011, of the 7 364 570 people that lived in Bulgaria,
Margarita Stancheva Hristo Stanchev & Robert Young 2 INTRODUCTION: Bulgarian Black Sea coast INTRODUCTION: Increasing pressure on Bulgarian coastal zone In 2011, of the 7 364 570 people that lived in Bulgaria,
Moreton Bay and Key Geographic Concepts Worksheet
 Moreton Bay and Key Geographic Concepts Worksheet The Australian Curriculum: Geography draws on seven key geographic concepts: place scale space environment change interconnection sustainability They are
Moreton Bay and Key Geographic Concepts Worksheet The Australian Curriculum: Geography draws on seven key geographic concepts: place scale space environment change interconnection sustainability They are
Graduate School of Civil and Ecological Engineering, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
 Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture 10 (2016) 1297-1303 doi: 10.17265/1934-7359/2016.11.011 D DAVID PUBLISHING Ho-Shong Hou Graduate School of Civil and Ecological Engineering, I-Shou University,
Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture 10 (2016) 1297-1303 doi: 10.17265/1934-7359/2016.11.011 D DAVID PUBLISHING Ho-Shong Hou Graduate School of Civil and Ecological Engineering, I-Shou University,
WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE
 UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
Nguyen Hoang Khanh Linh, Le Ngoc Phuong Quy, Truong Do Minh Phuong and Nguyen Trac Ba An
 Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology A and B & Hue University Journal of Science 7 (2017) 48-59 doi: 10.17265/2161-6256/2017.10.007S D DAVID PUBLISHING Application of Remote Sensing and GIS Technology
Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology A and B & Hue University Journal of Science 7 (2017) 48-59 doi: 10.17265/2161-6256/2017.10.007S D DAVID PUBLISHING Application of Remote Sensing and GIS Technology
Opportunities to Improve Ecological Functions of Floodplains and Reduce Flood Risk along Major Rivers in the Puget Sound Basin
 Opportunities to Improve Ecological Functions of Floodplains and Reduce Flood Risk along Major Rivers in the Puget Sound Basin Christopher Konrad, US Geological Survey Tim Beechie, NOAA Fisheries Managing
Opportunities to Improve Ecological Functions of Floodplains and Reduce Flood Risk along Major Rivers in the Puget Sound Basin Christopher Konrad, US Geological Survey Tim Beechie, NOAA Fisheries Managing
Electrical Resistivity Survey for Delineating Seawater Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer
 Electrical Resistivity Survey for Delineating Seawater Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer Sung-Ho Song*, Gyu-Sang Lee*, Jin-Sung Kim*, Baekuk Seong*, Young-gyu Kim*, Myung-Ha Woo* and Namsik Park** Abstract
Electrical Resistivity Survey for Delineating Seawater Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer Sung-Ho Song*, Gyu-Sang Lee*, Jin-Sung Kim*, Baekuk Seong*, Young-gyu Kim*, Myung-Ha Woo* and Namsik Park** Abstract
E2993 v4. Background on Natural Disaster. Environmental Assessment (EA) Viet Nam Managing Natural Hazards Project (VN-Haz/WB5) ANNEX 4
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Environmental Assessment (EA) ANNEX 4 Background on Natural Disaster 1. This annex presents
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Environmental Assessment (EA) ANNEX 4 Background on Natural Disaster 1. This annex presents
TOWARDS CLIMATE-RESILIENT COASTAL MANAGEMENT: OPPORTUNITIES FOR IMPROVED ICZM IN BELIZE
 TOWARDS CLIMATE-RESILIENT COASTAL MANAGEMENT: OPPORTUNITIES FOR IMPROVED ICZM IN BELIZE CHANTALLE SAMUELS Coastal Zone Management Authority and Institute The Caribbean Community Climate Change Centre VULNERABILITY
TOWARDS CLIMATE-RESILIENT COASTAL MANAGEMENT: OPPORTUNITIES FOR IMPROVED ICZM IN BELIZE CHANTALLE SAMUELS Coastal Zone Management Authority and Institute The Caribbean Community Climate Change Centre VULNERABILITY
Scientific bases for defining the coastal zone of Quang Binh, Quang Tri, Thua Thien Hue provinces
 VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 26 (2010) 8-18 Scientific bases for defining the coastal zone of Quang Binh, Quang Tri, Thua Thien Hue provinces Nguyen Hieu*, Nguyen Cao Huan, Dang Van Bao Hanoi
VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 26 (2010) 8-18 Scientific bases for defining the coastal zone of Quang Binh, Quang Tri, Thua Thien Hue provinces Nguyen Hieu*, Nguyen Cao Huan, Dang Van Bao Hanoi
ME KONG RIVER COMMISSION FLASH FLOOD GUIDANCE SYSTEM (MRCFFGS)
 NATIONAL HYDRO-METEOROLOGICAL SERVICE IN VIETNAM NATIONAL CENTER FOR HYDRO-METEOROLOGICAL FORECASTING ME KONG RIVER COMMISSION FLASH FLOOD GUIDANCE SYSTEM (MRCFFGS) http://www.nchmf.gov.vn 29 Nov 1 Dec
NATIONAL HYDRO-METEOROLOGICAL SERVICE IN VIETNAM NATIONAL CENTER FOR HYDRO-METEOROLOGICAL FORECASTING ME KONG RIVER COMMISSION FLASH FLOOD GUIDANCE SYSTEM (MRCFFGS) http://www.nchmf.gov.vn 29 Nov 1 Dec
Procurement Plan. 3. Reference to (if any) Project Operational/Procurement Manual: January 28, 2016.
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized I. General Plan 1. Bank s approval Date of the procurement Plan September 28, 2015 2.
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized I. General Plan 1. Bank s approval Date of the procurement Plan September 28, 2015 2.
Word Cards. 2 map. 1 geographic representation. a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth. a visual representation of an area
 Name: Date: Hour: Word Cards 1 geographic representation a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth Example: A map is a representation of an actual location or place. 2 map a visual
Name: Date: Hour: Word Cards 1 geographic representation a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth Example: A map is a representation of an actual location or place. 2 map a visual
24.0 Mineral Extraction
 Chapter 24 - Mineral Extraction 24.0 Mineral Extraction 24.1 Introduction Apart from gravel, sand, rock, limestone and salt extraction in relatively small quantities mineral extraction is not a strong
Chapter 24 - Mineral Extraction 24.0 Mineral Extraction 24.1 Introduction Apart from gravel, sand, rock, limestone and salt extraction in relatively small quantities mineral extraction is not a strong
Mechanism of tsunami generation,propagation and runup -sharing experiences with Japanese
 Mechanism of tsunami generation,propagation and runup -sharing experiences with Japanese Mechanism of tsunami generation Predicting the propagation, runup and inundation of tsunamis Near and far-field
Mechanism of tsunami generation,propagation and runup -sharing experiences with Japanese Mechanism of tsunami generation Predicting the propagation, runup and inundation of tsunamis Near and far-field
Model development for web - atlas system applying in administration management
 VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 28 (2012) 29-36 Model development for web - atlas system applying in administration management Bui Ngoc Quy* Ha Noi University of Mining and Geology, Dong Ngac, Tu
VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 28 (2012) 29-36 Model development for web - atlas system applying in administration management Bui Ngoc Quy* Ha Noi University of Mining and Geology, Dong Ngac, Tu
Vulnerability of Bangladesh to Cyclones in a Changing Climate
 Vulnerability of Bangladesh to Cyclones in a Changing Climate Susmita Dasgupta Kiran Pandey Mainul Huq Zahirul Huq Khan M.M. Zahid Ahmed Nandan Mukherjee Malik Fida Khan 2010 Bangladesh: Tropical Cyclone
Vulnerability of Bangladesh to Cyclones in a Changing Climate Susmita Dasgupta Kiran Pandey Mainul Huq Zahirul Huq Khan M.M. Zahid Ahmed Nandan Mukherjee Malik Fida Khan 2010 Bangladesh: Tropical Cyclone
Application #: TEXT
 TOWN OF FORT MYERS BEACH 2008 PROPOSED COMPREHENSIVE PLAN AMENDMENTS Application #: 2008-13-TEXT Description: Modify the Coastal Management and Future Land Use Elements to reflect the state s new definition
TOWN OF FORT MYERS BEACH 2008 PROPOSED COMPREHENSIVE PLAN AMENDMENTS Application #: 2008-13-TEXT Description: Modify the Coastal Management and Future Land Use Elements to reflect the state s new definition
Coastal Processes 101 & The Regs. Greg Berman (Woods Hole Sea Grant & Cape Cod Cooperative Extension)
 Coastal Processes 101 & The Regs Greg Berman (Woods Hole Sea Grant & Cape Cod Cooperative Extension) March 26, 2019 Coastal Processes 101 & The Regs Outline: ~15 min talk Coastal Processes What is Erosion?
Coastal Processes 101 & The Regs Greg Berman (Woods Hole Sea Grant & Cape Cod Cooperative Extension) March 26, 2019 Coastal Processes 101 & The Regs Outline: ~15 min talk Coastal Processes What is Erosion?
Environmental and geomatics assessment of the Ha Thanh basin to hydrological hazards in central Vietnam
 282 Hydrology in a Changing World: Environmental and Human Dimensions Proceedings of FRIEND-Water 2014, Montpellier, France, October 2014 (IAHS Publ. 363, 2014). Environmental and geomatics assessment
282 Hydrology in a Changing World: Environmental and Human Dimensions Proceedings of FRIEND-Water 2014, Montpellier, France, October 2014 (IAHS Publ. 363, 2014). Environmental and geomatics assessment
STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY
 . CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY 26 CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY Kundalika is a major river in konkan region of Maharashtra. River originates in Western Ghats at an altitude of 820 m ASL
. CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY 26 CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY Kundalika is a major river in konkan region of Maharashtra. River originates in Western Ghats at an altitude of 820 m ASL
Threat to the Surface Water Resources
 4.10 WMA OVERVIEW The Breede Gouritz WMA comprises the Breede, Overberg, the Karoo and Klein Karoo and Outeniqua Coastal Area (Stilbaai to Plettenberg Bay) catchments. The WMA is located in south-western
4.10 WMA OVERVIEW The Breede Gouritz WMA comprises the Breede, Overberg, the Karoo and Klein Karoo and Outeniqua Coastal Area (Stilbaai to Plettenberg Bay) catchments. The WMA is located in south-western
Geol 117 Lecture 18 Beaches & Coastlines. I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition:
 I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
CHAPTER 6 CLIMATE AND CLIMATE - RELATED DISASTER PROFILE OF HA TINH
 CHAPTER 6 CLIMATE AND CLIMATE - RELATED DISASTER PROFILE OF HA TINH 6.1. Introduction This Chapter provides background climatic data for Ha Tinh, as a prelude to the climate change scenarios and vulnerability
CHAPTER 6 CLIMATE AND CLIMATE - RELATED DISASTER PROFILE OF HA TINH 6.1. Introduction This Chapter provides background climatic data for Ha Tinh, as a prelude to the climate change scenarios and vulnerability
Evacuation Alarm Using the Improved Magnitude Method to Damage Caused by Typhoon 9918
 ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Evacuation Alarm Using the Improved Magnitude Method to Damage Caused by Typhoon 9918 R. Hashimura
ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Evacuation Alarm Using the Improved Magnitude Method to Damage Caused by Typhoon 9918 R. Hashimura
Bishkek City Development Agency. Urban Planning Bishkek
 Bishkek City Development Agency Urban Planning Bishkek Bishkek City Development Agency Official name City budget Population Area GRP Import value Export value External trade turnover Foreign direct investments
Bishkek City Development Agency Urban Planning Bishkek Bishkek City Development Agency Official name City budget Population Area GRP Import value Export value External trade turnover Foreign direct investments
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
