Focus on PNA Flexibility and RNA Binding using Molecular Dynamics and Metadynamics
|
|
|
- Elijah Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Focus on PNA Flexibility and RNA Binding using Molecular Dynamics and Metadynamics Massimiliano Donato Verona 1, Vincenzo Verdolino 2,3,*, Ferruccio Palazzesi 2,3, and Roberto Corradini 1,4,* 1 Dipartimento di Chimica, University of Parma, Italy, 43124,Italy 2 Department of Chemistry and Applied Biosciences, ETH Zurich, c/o Universita` della Swizzera Italiana Campus, 6900 Lugano, Switzerland 3 Facolta` di Informatica, Instituto di Scienze Computazionali, Universita` della Svizzera Italiana, 6900 Lugano, Switzerland 4 National Institute for Biostructures and Biosystems (INBB)-Viale delle Medaglie d Oro, 305, Roma, Italy *Vincenzo Verdolino , vincenzo.verdolino@phys.chem.ethz.ch *Roberto Corradini , roberto.corradini@unipr.it CONTENTS SI1 sspna flexibility pp. 2 SI1a RMSD trend of sspna during 200 ns long MD simulation SI1b: FES local minima convergence SI2 γ-sspna flexibility 4 SI2a RMSD trend of modified γ-sspna during 200 ns long MD simulation SI2b: FES local minima convergence SI2c: sspna and γ-sspna structural analysis SI3 Re-annealing simulations on sspna 8 SI3c H-bonding Fraction SI4 MD equilibrated PNA:RNA structure from data bank 10 SI5 MD equilibrated γ-modified PNA:RNA structure 11 SI6 - Force field validations 11 SI7 - Stacking Variable 15 1
2 SI1 sspna flexibility SI1a RMSD trend of sspna during 200 ns long MD simulation In Fig. SI1a we report the Root Mean Square Deviation of sspna during 200 ns long MD simulation in order to investigate possible conformational transition with respect the initial helical one. Fig. SI1a: RMSD plot along with the MD time for the unmodified sspna. The initial structure characterized by helical symmetry lasts for 20 ns and turns into a multitude of locally stable conformations till the end of the simulation. 2
3 SI1b: FES local minima convergence In Fig. SI1b we report the local convergence analysis between the two minima A and B described in the main text. (Figure 2a) PDB Structures extracted from A and B available online Fig. SI1b: Energy difference between A and B minima converged after 150 ns 3
4 SI2 γ-sspna flexibility SI2a RMSD trend of modified γ-sspna during 200 ns long MD simulation In Fig. SI2a we report the Root Mean Square Deviation of modified γ-sspna during 200 ns long MD simulation in order to investigate possible conformational transition with respect the initial helical one. Fig. SI2a: RMSD plot along with the MD time for the modified γ-sspna. In this case the initial helical conformation is retained longer compared to sspna (55 ns instead of 20). The conformational displacement is smoother for the gamma modified and the RMSD fluctuation afterward considerably tighter denoting a higher degree of constraining and pre-organization. 4
5 SI2b: FES local minima convergence In Fig. SI2b we report the local convergence analysis between four minima C-F as described in the main text. (Figure 2b) The convergence criteria is more flexible than the one employed in SI1b but, due to the large configurational space explored and the larger number of local minima characterizing the FES we can consider qualitatively acceptable these results. In particular we show the recrossing between states (top left), the head to tail (H-T) collective variable behaviour (top right), the sequential stacking recrossing (bottom left) and lastly the local free energy convergence between these four states along 400 ns. We recognize the difficulties in quantitatively converging the FES mainly due to the exploration of the stacking collective variable. However, these results show that WT- MDMT simulations extensively explored the entire conformational space visiting, in several different events, the principal structure clusters (C-F). PDB Structures extracted from C-F and representative videos (files beginning.mov Supplementary Video S1: Beginning configuration of γ-sspna of WT-MDMT, and close.mov Supplementary Video S2: Close configuration of γ-sspna during WT-MDMT available online) of WT-MDMT trajectory available online. Fig. SI2b: Recrossing and energy differences between most important C-F local minima 5
6 Supplementary Video S1: Beginning configuration of γ-sspna of WT-MDMT Supplementary Video S2: Close configuration of γ-sspna during WT-MDMT SI2c: sspna and γ-sspna structural analysis The torsion angles H-N-C-H γ adjacent to the inter-residue amide bond on structures A-F reported in figure 2 (main text) have been monitored according to the following scheme SI2c, and comparing the corresponding torsion angle formed by the pro-r hydrogen in the corresponding monomer in the achiral sspna. H γ pro-r Scheme SI2c: Torsion angles considered for evaluation of conformation of structures A-F in Fig.2 In Fig. SI2c we report the histogram (weighted for the bias) of the distance between the sequential α-amino acidic hydrogens (red arrows in figure) calculated for the sspna (red curve) and γ-sspna (green curve). The two series of histograms are based on the WT- MDMT free energies reported in the main text. (Figure 2a and b respectively) As expected for a preorganized single strand the average distances (d1-d5) calculated for γ-sspna are significantly shorter than those in sspna. Most notably, the histogram resulting from the unmodified PNA shows an appreciable broadening at shorter and longer distances. On the contrary, the statistical distribution calculated for the γ-sspna is always very narrow. The unique exception is represented by the extremity d5 where the two systems behave similarly. 6
7 Fig. SI2c: Structural histogram analysis of the H--H distance of two sequential amino acids (d1-d5) for sspna (red) and γ-sspna (green) 7
8 SI3 Re-annealing simulations on sspna The PNA:RNA system considered in this study present the following sequences: N -GAACTC-C 3 -CTTGAG-5 In figure SI3a we report the base pairing recorded in 200 ns long MD simulations for all 5 different re-annealing. Fig. SI3a: Number of base paired as function of time for simulations 1-5 systems (structures reported in figure 4 of the main text). In figure SI3b we present the base pairing as a function of time for simulations 2-4 (structures reported in figure 4 of the main text) focusing on selected bases as described in picture. Pairing in central bases resulted determinant for inducing higher level of duplex re-annealing. 8
9 Fig. SI3b: Number of coupled bases as function of time for 2 (top left), 3 (top right) and (bottom left) systems (structures reported in figure 4 of the main text). In red is represented AT couple base pairing, in green CG one and in blue the total pairing of the duplex. SI3c H-bonding Fraction The complete disruption of the helical structure is achieved when the inter-molecular base pairing becomes ineffective. In order to track this phenomenon with our simulations we calculate the h-bonding parameter using the coordination function collective-variable as implemented in PLUMED2. For each base, this quantity ranges from 0 to 1 depending on the effective h-bonding interaction. Considering the whole PNA:RNA structure, the total pairing ranges from 0 (completely disrupted) to 6 (optimal pairing). The ratio between the recorded and the theoretical h-bonding at a given time frame defines the h-bonding fraction. Of particular interest is the h-bonding fraction calculated just before the duplex disruption as reported in the main article. We tested a wide range of time frames for calculating the h-bonding fraction just before the duplex disruption. In a sufficiently narrow time range (~10 ns before disruption) the h-bonding fraction is independent on this choice. We selected for the results reported in the main text 0.5 ns as the best time frame for h- bonding fraction calculation. 9
10 SI4 MD equilibrated PNA:RNA structure from data bank In Fig. SI4 we represent the minimized and thermally equilibrated structure of the unmodified PNA:RNA described in the article. This structure is used as the starting point for the MD and WT-MDMT simulations. Fig. SI4: Thermally equilibrated structure of PNA:RNA duplex (176D), taken from Protein Data Bank and successively used for our simulations. 10
11 SI5 MD equilibrated γ-modified PNA:RNA structure In Fig. SI5 we represent the minimized and thermally equilibrated structure of the modified PNA:RNA described in the article. This structure is used as the starting point for the MD and WT-MDMT simulations. Fig. SI5: Structure of γ-modified PNA:RNA. The duplex was generated from system 176D retrieved from Protein Data Bank, by manual insertion of serine side chain in gamma (C5) position, and subsequently thermally equilibrated. SI6 - Force field validations As a starting model for assessment of the force field for PNA duplexes, we have chosen the 176D 1 NMR structure (reported in the Protein Data Bank database), which is one of the few PNA:RNA duplex structures reported in literature at the time of this study (crystal structure of PNA:RNA duplex was resolved for the first time at the end of December 2015). 2 The sequences of PNA and RNA are respectively H-GAACTC-O - and 5 -GAGTTC- 3. This duplex was modified by removal of phosphate group bound to 5 residue of RNA, because the chosen force field (ff99sb) recognizes the RNA strand only without that group. In the literature there are no consolidated force fields for PNA, and thus one of our aims was to improve their availability similarly to other biological cases as proteins or nucleic acids that are nowadays widely accepted. In order to test the parameters chosen 3 we 11
12 performed a 200 ns long Molecular Dynamics simulation on the PNA:RNA duplex described above, using the protocol described in the Methods section. The duplex conformation was stable for all the simulation length with no significant structural modification. This can be inferred by examining the root mean square deviation (RMSD) that is less than 2.5 Å (Fig. SI6a). Fig. SI6a: RMSD plot of simulated PNA:RNA duplex as function of time. To better test the force field we checked the characteristic torsion angles of PNA obtained in the MD simulation, compared with those reported in literature. 4 The results are in good agreement with the experimental ones (Fig. SI6b). 12
13 Fig. SI6b: left, characteristic PNA angles; right, comparison between simulated angles and those reported in the literature. 4 Next, we considered the MD simulation of γ-modified PNA with the force field developed. Also in this case we needed the force field was validated before using it for further investigations on PNA properties. Therefore, we performed a 50 ns long simulation on a duplex obtained by manual insertion of serine side chain in γ position of each monomer of the PNA:RNA duplex 176D used in the previous simulation. This calculation was done with a shorter simulation time because this system was expected to be even more stable than the unmodified one, according to the general properties of γ-modified PNA. Indeed, also in this simulation the duplex resulted perfectly paired for the entire simulation, as proven by the low RMSD (Fig. SI6c). 13
14 Fig. SI6c: RMSD plot of simulated γ PNA:RNA duplex as function of time. Moreover, characteristic PNA angles were found also in this case to be compatible with those reported in literature (Fig. SI6d). Fig. SI6d: left, PNA bearing serine side chain in gamma position and its characteristic PNA angles; right, comparison between simulated angles and those reported in literature. 4,5 14
15 SI7 - Stacking Variable In order to better discriminate stacking stabilized conformations, we decided to use a local order parameter previously developed for describing crystal nucleation. 6 For each base, we defined a vector lying in the plane of the rings. This CV takes into account the distance, the angle and the coordination number between these vectors. Coordination number represents the number of vectors close within a defined cutoff. This parameter is important when studying nucleation since it determines the presence of an aggregate. The PNA considered in our study is 6 mer long and the maximum theoretical coordination number for each vector is then 5. However, our purpose is not to define an aggregate, but to discriminate stacking interactions. Therefore, for each couple of bases, we defined variables in order to have the coordination function ρ i (equation 1.2) always set to one, thus ruling out association. Distances and angles between these vectors are extremely important in stacking description: when two bases are stacked their distance should be defined in a given cutoff range and the angles should assume discrete values. An appropriate definition of this combination allows determining whether two or more bases are stacked (SI7 A) or fully (SI7 B C) and partially unstacked (SI7 D). SI7: Schematic examples of stacking, not stacking and partial stacking arrangements. In blue are represented vectors used to describe local order parameter. A) Two bases are stacked; B) two bases are too distant for stacking interaction; C) two bases are close, but not stacked. In this case distance is favorable, but not the angle; D) Distance between bases is optimal, but angle not completely thus leading to partial stacking. Going into the details, local order parameter is defined as the product of two sigmoidal and one single gaussian function: f ij = 1 1!e a r ij!r cut (1.1) ρ i = 1 1!e!b n i!n cut (Error! No text of specified style in document..1) 15
16 θ ij = k e! (θ ij!θ k ) 2 2 max /2σ k k!1 (1.2) where r ij are the distances between the above discussed vectors, r cut is cutoff distance for the stacking interaction, n i is coordination number, n cut is cutoff for coordination number, ϑ ij is the angle between the vectors, ϑ k is a favorable angle for stacking and σ k is the width of the gaussian applied on that angle. Lastly, a and b are exponential factors, determining how steep are the sigmoids. These functions essentially monitor respectively the distance between bases (equation 1.1), the coordination number (equation 1.2) and angle between bases (equation 1.3). As discussed above, the coordination parameters were set to obtain a value of ρ i = 1 (n cut = 1). The distance function f ij was set to have a value of 1 for distance within a range from 5.0 to 6.5 Å, depending on the couple of bases i and j considered. Above the cutoff distance, the f ij value rapidly decreases to 0. The angle function θ ij is a sum of functions, one for each characteristic angle chosen. For each angle ϑ k a Gaussian function that exhibits maximum value of 1 for ϑ k, is defined. In order to have stacking, bases should present opportune values of distances and angles. Based on MD simulation data, the coefficients (r cut, ϑ k, σ k, a) were tuned in order to maximize f ij and θ ij when bases are stacked. The functions here described are referred to a single couple of vectors, but in our system we have several possible couples and also multiple bases coupled at the same time. Description of every single couple is not meaningful alone, so to describe entirely the system we used a linear combination of these local order parameters, defined for couples of bases, and we considered this combination a measure of total stacking (Stk). SI - Bibliography 1. Brown, S. C., Thomson, S. A., Veal, J. M. & Davis, D. G. NMR solution structure of a peptide nucleic acid complexed with RNA. Science 265, (1994). 2. Kiliszek, A., Banaszak, K., Dauter, Z. & Rypniewski, W. The first crystal structures of RNA-PNA duplexes and a PNA-PNA duplex containing mismatches-toward antisense therapy against TREDs. Nucleic Acids Res (2015). doi: /nar/gkv REDDB Server. at < 4. Topham, C. M. & Smith, J. C. The influence of helix morphology on co-operative polyamide backbone conformational flexibility in peptide nucleic acid complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 292, (1999). 5. He, W. et al. The structure of a gamma-modified peptide nucleic acid duplex. Mol. Biosyst. 6, (2010). 6. Giberti, F., Salvalaglio, M., Mazzotti, M. & Parrinello, M. Insight into the nucleation of urea crystals from the melt. Chem. Eng. Sci. 121, (2015). 16
Structural and mechanistic insight into the substrate. binding from the conformational dynamics in apo. and substrate-bound DapE enzyme
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 215 Structural and mechanistic insight into the substrate binding from the conformational
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 215 Structural and mechanistic insight into the substrate binding from the conformational
Comparing crystal structure of M.HhaI with and without DNA1, 2 (PDBID:1hmy and PDBID:2hmy),
 Supporting Information 1. Constructing the starting structure Comparing crystal structure of M.HhaI with and without DNA1, 2 (PDBID:1hmy and PDBID:2hmy), we find that: the RMSD of overall structure and
Supporting Information 1. Constructing the starting structure Comparing crystal structure of M.HhaI with and without DNA1, 2 (PDBID:1hmy and PDBID:2hmy), we find that: the RMSD of overall structure and
Protein Structure. W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES
 Protein Structure W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the structure and characteristic properties of typical proteins. 2. List and describe the four levels of structure found in proteins. 3. Relate
Protein Structure W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the structure and characteristic properties of typical proteins. 2. List and describe the four levels of structure found in proteins. 3. Relate
T H E J O U R N A L O F G E N E R A L P H Y S I O L O G Y. jgp
 S u p p l e m e n ta l m at e r i a l jgp Lee et al., http://www.jgp.org/cgi/content/full/jgp.201411219/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F G E N E R A L P H Y S I O L O G Y S u p p l e m e n ta l D I S C U S
S u p p l e m e n ta l m at e r i a l jgp Lee et al., http://www.jgp.org/cgi/content/full/jgp.201411219/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F G E N E R A L P H Y S I O L O G Y S u p p l e m e n ta l D I S C U S
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling. Chapter 4 Part I
 Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Protein Dynamics. The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron.
 Protein Dynamics The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron. Below is myoglobin hydrated with 350 water molecules. Only a small
Protein Dynamics The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron. Below is myoglobin hydrated with 350 water molecules. Only a small
Protein Folding Prof. Eugene Shakhnovich
 Protein Folding Eugene Shakhnovich Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology Harvard University 1 Proteins are folded on various scales As of now we know hundreds of thousands of sequences (Swissprot)
Protein Folding Eugene Shakhnovich Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology Harvard University 1 Proteins are folded on various scales As of now we know hundreds of thousands of sequences (Swissprot)
Supplementary Figures:
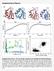 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1: The two strings converge to two qualitatively different pathways. A) Models of active (red) and inactive (blue) states used as end points for the string calculations
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1: The two strings converge to two qualitatively different pathways. A) Models of active (red) and inactive (blue) states used as end points for the string calculations
Secondary Structure. Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2. Structure and Function of Proteins. Further Reading. Φ, Ψ angles alone determine protein structure
 Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and peptides at aqueous graphene interfaces: Electronic Supplementary
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and
Goals. Structural Analysis of the EGR Family of Transcription Factors: Templates for Predicting Protein DNA Interactions
 Structural Analysis of the EGR Family of Transcription Factors: Templates for Predicting Protein DNA Interactions Jamie Duke 1,2 and Carlos Camacho 3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute,
Structural Analysis of the EGR Family of Transcription Factors: Templates for Predicting Protein DNA Interactions Jamie Duke 1,2 and Carlos Camacho 3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute,
Principles of Physical Biochemistry
 Principles of Physical Biochemistry Kensal E. van Hold e W. Curtis Johnso n P. Shing Ho Preface x i PART 1 MACROMOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS 1 1 Biological Macromolecules 2 1.1 General Principles
Principles of Physical Biochemistry Kensal E. van Hold e W. Curtis Johnso n P. Shing Ho Preface x i PART 1 MACROMOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS 1 1 Biological Macromolecules 2 1.1 General Principles
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2720 1 2 3 Tuning underwater adhesion with cation-π interactions Matthew A. Gebbie, Wei Wei, Alex M. Schrader,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2720 1 2 3 Tuning underwater adhesion with cation-π interactions Matthew A. Gebbie, Wei Wei, Alex M. Schrader,
Polypeptide Folding Using Monte Carlo Sampling, Concerted Rotation, and Continuum Solvation
 Polypeptide Folding Using Monte Carlo Sampling, Concerted Rotation, and Continuum Solvation Jakob P. Ulmschneider and William L. Jorgensen J.A.C.S. 2004, 126, 1849-1857 Presented by Laura L. Thomas and
Polypeptide Folding Using Monte Carlo Sampling, Concerted Rotation, and Continuum Solvation Jakob P. Ulmschneider and William L. Jorgensen J.A.C.S. 2004, 126, 1849-1857 Presented by Laura L. Thomas and
Enhanced sampling of transition states
 Enhanced sampling of transition states arxiv:1812.09032v1 [physics.chem-ph] 21 Dec 2018 Jayashrita Debnath,, Michele Invernizzi,, and Michele Parrinello,,, Department of Chemistry and Applied Biosciences,
Enhanced sampling of transition states arxiv:1812.09032v1 [physics.chem-ph] 21 Dec 2018 Jayashrita Debnath,, Michele Invernizzi,, and Michele Parrinello,,, Department of Chemistry and Applied Biosciences,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/309/5742/1868/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Toward High-Resolution de Novo Structure Prediction for Small Proteins Philip Bradley, Kira M. S. Misura, David Baker*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/309/5742/1868/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Toward High-Resolution de Novo Structure Prediction for Small Proteins Philip Bradley, Kira M. S. Misura, David Baker*
Time-dependence of key H-bond/electrostatic interaction distances in the sirna5-hago2 complexes... Page S14
 Supporting Information Probing the Binding Interactions between Chemically Modified sirnas and Human Argonaute 2 Using Microsecond Molecular Dynamics Simulations S. Harikrishna* and P. I. Pradeepkumar*
Supporting Information Probing the Binding Interactions between Chemically Modified sirnas and Human Argonaute 2 Using Microsecond Molecular Dynamics Simulations S. Harikrishna* and P. I. Pradeepkumar*
DNA Structure. Voet & Voet: Chapter 29 Pages Slide 1
 DNA Structure Voet & Voet: Chapter 29 Pages 1107-1122 Slide 1 Review The four DNA bases and their atom names The four common -D-ribose conformations All B-DNA ribose adopt the C2' endo conformation All
DNA Structure Voet & Voet: Chapter 29 Pages 1107-1122 Slide 1 Review The four DNA bases and their atom names The four common -D-ribose conformations All B-DNA ribose adopt the C2' endo conformation All
Introduction to" Protein Structure
 Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Exploring the Free Energy Surface of Short Peptides by Using Metadynamics
 John von Neumann Institute for Computing Exploring the Free Energy Surface of Short Peptides by Using Metadynamics C. Camilloni, A. De Simone published in From Computational Biophysics to Systems Biology
John von Neumann Institute for Computing Exploring the Free Energy Surface of Short Peptides by Using Metadynamics C. Camilloni, A. De Simone published in From Computational Biophysics to Systems Biology
Molecular Modeling lecture 2
 Molecular Modeling 2018 -- lecture 2 Topics 1. Secondary structure 3. Sequence similarity and homology 2. Secondary structure prediction 4. Where do protein structures come from? X-ray crystallography
Molecular Modeling 2018 -- lecture 2 Topics 1. Secondary structure 3. Sequence similarity and homology 2. Secondary structure prediction 4. Where do protein structures come from? X-ray crystallography
Tu 1,*, , Sweden
 Supplementary Material Computational studiess of the binding profile of phosphoinositide PtdIns(,4,5)P with the pleckstrin homology domain d of an oomycetee cellulose synthase Guanglin Kuang 1, Vincent
Supplementary Material Computational studiess of the binding profile of phosphoinositide PtdIns(,4,5)P with the pleckstrin homology domain d of an oomycetee cellulose synthase Guanglin Kuang 1, Vincent
Figure 1. Molecules geometries of 5021 and Each neutral group in CHARMM topology was grouped in dash circle.
 Project I Chemistry 8021, Spring 2005/2/23 This document was turned in by a student as a homework paper. 1. Methods First, the cartesian coordinates of 5021 and 8021 molecules (Fig. 1) are generated, in
Project I Chemistry 8021, Spring 2005/2/23 This document was turned in by a student as a homework paper. 1. Methods First, the cartesian coordinates of 5021 and 8021 molecules (Fig. 1) are generated, in
Preparing a PDB File
 Figure 1: Schematic view of the ligand-binding domain from the vitamin D receptor (PDB file 1IE9). The crystallographic waters are shown as small spheres and the bound ligand is shown as a CPK model. HO
Figure 1: Schematic view of the ligand-binding domain from the vitamin D receptor (PDB file 1IE9). The crystallographic waters are shown as small spheres and the bound ligand is shown as a CPK model. HO
Packing of Secondary Structures
 7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
Molecular Modeling Lecture 7. Homology modeling insertions/deletions manual realignment
 Molecular Modeling 2018-- Lecture 7 Homology modeling insertions/deletions manual realignment Homology modeling also called comparative modeling Sequences that have similar sequence have similar structure.
Molecular Modeling 2018-- Lecture 7 Homology modeling insertions/deletions manual realignment Homology modeling also called comparative modeling Sequences that have similar sequence have similar structure.
NMR, X-ray Diffraction, Protein Structure, and RasMol
 NMR, X-ray Diffraction, Protein Structure, and RasMol Introduction So far we have been mostly concerned with the proteins themselves. The techniques (NMR or X-ray diffraction) used to determine a structure
NMR, X-ray Diffraction, Protein Structure, and RasMol Introduction So far we have been mostly concerned with the proteins themselves. The techniques (NMR or X-ray diffraction) used to determine a structure
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Resonance assignment and NMR spectra for hairpin and duplex A 6 constructs. (a) 2D HSQC spectra of hairpin construct (hp-a 6 -RNA) with labeled assignments. (b) 2D HSQC or SOFAST-HMQC
Supplementary Figure 1 Resonance assignment and NMR spectra for hairpin and duplex A 6 constructs. (a) 2D HSQC spectra of hairpin construct (hp-a 6 -RNA) with labeled assignments. (b) 2D HSQC or SOFAST-HMQC
Theory and Applications of Residual Dipolar Couplings in Biomolecular NMR
 Theory and Applications of Residual Dipolar Couplings in Biomolecular NMR Residual Dipolar Couplings (RDC s) Relatively new technique ~ 1996 Nico Tjandra, Ad Bax- NIH, Jim Prestegard, UGA Combination of
Theory and Applications of Residual Dipolar Couplings in Biomolecular NMR Residual Dipolar Couplings (RDC s) Relatively new technique ~ 1996 Nico Tjandra, Ad Bax- NIH, Jim Prestegard, UGA Combination of
Characterization of the free-energy landscapes of proteins by NMR-guided metadynamics
 Characterization of the free-energy landscapes of proteins by NMR-guided metadynamics B Results and Discussion BIOPHYSICS ND COMPUTTIONL BIOLOGY SI Text Inset B χ χ Inset SI Text Inset C Folding of GB3
Characterization of the free-energy landscapes of proteins by NMR-guided metadynamics B Results and Discussion BIOPHYSICS ND COMPUTTIONL BIOLOGY SI Text Inset B χ χ Inset SI Text Inset C Folding of GB3
Lipid Regulated Intramolecular Conformational Dynamics of SNARE-Protein Ykt6
 Supplementary Information for: Lipid Regulated Intramolecular Conformational Dynamics of SNARE-Protein Ykt6 Yawei Dai 1, 2, Markus Seeger 3, Jingwei Weng 4, Song Song 1, 2, Wenning Wang 4, Yan-Wen 1, 2,
Supplementary Information for: Lipid Regulated Intramolecular Conformational Dynamics of SNARE-Protein Ykt6 Yawei Dai 1, 2, Markus Seeger 3, Jingwei Weng 4, Song Song 1, 2, Wenning Wang 4, Yan-Wen 1, 2,
MARTINI simulation details
 S1 Appendix MARTINI simulation details MARTINI simulation initialization and equilibration In this section, we describe the initialization of simulations from Main Text section Residue-based coarsegrained
S1 Appendix MARTINI simulation details MARTINI simulation initialization and equilibration In this section, we describe the initialization of simulations from Main Text section Residue-based coarsegrained
Exploring the Changes in the Structure of α-helical Peptides Adsorbed onto Carbon and Boron Nitride based Nanomaterials
 Exploring the Changes in the Structure of α-helical Peptides Adsorbed onto Carbon and Boron Nitride based Nanomaterials Dr. V. Subramanian Chemical Laboratory, IPC Division CSIR-Central Leather Research
Exploring the Changes in the Structure of α-helical Peptides Adsorbed onto Carbon and Boron Nitride based Nanomaterials Dr. V. Subramanian Chemical Laboratory, IPC Division CSIR-Central Leather Research
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Systematic Coarse-Grained Modeling of Complexation between Small Interfering RNA and Polycations Zonghui Wei 1 and Erik Luijten 1,2,3,4,a) 1 Graduate Program in Applied Physics, Northwestern
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Systematic Coarse-Grained Modeling of Complexation between Small Interfering RNA and Polycations Zonghui Wei 1 and Erik Luijten 1,2,3,4,a) 1 Graduate Program in Applied Physics, Northwestern
PROTEIN STRUCTURE AMINO ACIDS H R. Zwitterion (dipolar ion) CO 2 H. PEPTIDES Formal reactions showing formation of peptide bond by dehydration:
 PTEI STUTUE ydrolysis of proteins with aqueous acid or base yields a mixture of free amino acids. Each type of protein yields a characteristic mixture of the ~ 20 amino acids. AMI AIDS Zwitterion (dipolar
PTEI STUTUE ydrolysis of proteins with aqueous acid or base yields a mixture of free amino acids. Each type of protein yields a characteristic mixture of the ~ 20 amino acids. AMI AIDS Zwitterion (dipolar
Supporting Information How does Darunavir prevent HIV-1 protease dimerization?
 Supporting Information How does Darunavir prevent HIV- protease dimerization? Danzhi Huang and Amedeo Caflisch a Department of Biochemistry University of Zürich, Winterthurerstrasse 9 CH-7 Zürich, Switzerland
Supporting Information How does Darunavir prevent HIV- protease dimerization? Danzhi Huang and Amedeo Caflisch a Department of Biochemistry University of Zürich, Winterthurerstrasse 9 CH-7 Zürich, Switzerland
Structural Insights from Molecular Dynamics. Simulations of Tryptophan 7-Halogenase and
 Supporting Information Structural Insights from Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Tryptophan 7-Halogenase and Tryptophan 5-halogenase Jon Ainsley 1, Adrian J. Mulholland 2, Gary W. Black 1, Olivier Sparagano
Supporting Information Structural Insights from Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Tryptophan 7-Halogenase and Tryptophan 5-halogenase Jon Ainsley 1, Adrian J. Mulholland 2, Gary W. Black 1, Olivier Sparagano
Analysis of the simulation
 Analysis of the simulation Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař January 7, 2014 Thermodynamic properties time averages of thermodynamic quantites correspond to ensemble averages (ergodic theorem) some quantities
Analysis of the simulation Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař January 7, 2014 Thermodynamic properties time averages of thermodynamic quantites correspond to ensemble averages (ergodic theorem) some quantities
User Guide for LeDock
 User Guide for LeDock Hongtao Zhao, PhD Email: htzhao@lephar.com Website: www.lephar.com Copyright 2017 Hongtao Zhao. All rights reserved. Introduction LeDock is flexible small-molecule docking software,
User Guide for LeDock Hongtao Zhao, PhD Email: htzhao@lephar.com Website: www.lephar.com Copyright 2017 Hongtao Zhao. All rights reserved. Introduction LeDock is flexible small-molecule docking software,
SANDRO BOTTARO, PAVEL BANÁŠ, JIŘÍ ŠPONER, AND GIOVANNI BUSSI
 FREE ENERGY LANDSCAPE OF GAGA AND UUCG RNA TETRALOOPS. SANDRO BOTTARO, PAVEL BANÁŠ, JIŘÍ ŠPONER, AND GIOVANNI BUSSI Contents 1. Supplementary Text 1 2 Sample PLUMED input file. 2. Supplementary Figure
FREE ENERGY LANDSCAPE OF GAGA AND UUCG RNA TETRALOOPS. SANDRO BOTTARO, PAVEL BANÁŠ, JIŘÍ ŠPONER, AND GIOVANNI BUSSI Contents 1. Supplementary Text 1 2 Sample PLUMED input file. 2. Supplementary Figure
Bulk behaviour. Alanine. FIG. 1. Chemical structure of the RKLPDA peptide. Numbers on the left mark alpha carbons.
 Bulk behaviour To characterise the conformational behaviour of the peptide, first we looked at the statistics of alpha carbons and the torsion angles. Then they were correlated with positions of positively
Bulk behaviour To characterise the conformational behaviour of the peptide, first we looked at the statistics of alpha carbons and the torsion angles. Then they were correlated with positions of positively
Design of a Novel Globular Protein Fold with Atomic-Level Accuracy
 Design of a Novel Globular Protein Fold with Atomic-Level Accuracy Brian Kuhlman, Gautam Dantas, Gregory C. Ireton, Gabriele Varani, Barry L. Stoddard, David Baker Presented by Kate Stafford 4 May 05 Protein
Design of a Novel Globular Protein Fold with Atomic-Level Accuracy Brian Kuhlman, Gautam Dantas, Gregory C. Ireton, Gabriele Varani, Barry L. Stoddard, David Baker Presented by Kate Stafford 4 May 05 Protein
Current address: Department of Chemistry, Hong Kong Baptist University, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong,
 Hydrolysis of Cisplatin - A Metadynamics Study Supporting Information Justin Kai-Chi Lau a and Bernd Ensing* b Department of Chemistry and Applied Bioscience, ETH Zurich, USI Campus, Computational Science,
Hydrolysis of Cisplatin - A Metadynamics Study Supporting Information Justin Kai-Chi Lau a and Bernd Ensing* b Department of Chemistry and Applied Bioscience, ETH Zurich, USI Campus, Computational Science,
Protein structures and comparisons ndrew Torda Bioinformatik, Mai 2008
 Protein structures and comparisons ndrew Torda 67.937 Bioinformatik, Mai 2008 Ultimate aim how to find out the most about a protein what you can get from sequence and structure information On the way..
Protein structures and comparisons ndrew Torda 67.937 Bioinformatik, Mai 2008 Ultimate aim how to find out the most about a protein what you can get from sequence and structure information On the way..
Molecular Modelling. part of Bioinformatik von RNA- und Proteinstrukturen. Sonja Prohaska. Leipzig, SS Computational EvoDevo University Leipzig
 part of Bioinformatik von RNA- und Proteinstrukturen Computational EvoDevo University Leipzig Leipzig, SS 2011 Protein Structure levels or organization Primary structure: sequence of amino acids (from
part of Bioinformatik von RNA- und Proteinstrukturen Computational EvoDevo University Leipzig Leipzig, SS 2011 Protein Structure levels or organization Primary structure: sequence of amino acids (from
Controlling fluctuations
 Controlling fluctuations Michele Parrinello Department of Chemistry and Applied Biosciences ETH Zurich and ICS, Università della Svizzera Italiana, Lugano, Switzerland Today s menu Introduction Fluctuations
Controlling fluctuations Michele Parrinello Department of Chemistry and Applied Biosciences ETH Zurich and ICS, Università della Svizzera Italiana, Lugano, Switzerland Today s menu Introduction Fluctuations
Alpha-helical Topology and Tertiary Structure Prediction of Globular Proteins Scott R. McAllister Christodoulos A. Floudas Princeton University
 Alpha-helical Topology and Tertiary Structure Prediction of Globular Proteins Scott R. McAllister Christodoulos A. Floudas Princeton University Department of Chemical Engineering Program of Applied and
Alpha-helical Topology and Tertiary Structure Prediction of Globular Proteins Scott R. McAllister Christodoulos A. Floudas Princeton University Department of Chemical Engineering Program of Applied and
Biomolecules: lecture 10
 Biomolecules: lecture 10 - understanding in detail how protein 3D structures form - realize that protein molecules are not static wire models but instead dynamic, where in principle every atom moves (yet
Biomolecules: lecture 10 - understanding in detail how protein 3D structures form - realize that protein molecules are not static wire models but instead dynamic, where in principle every atom moves (yet
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Protein sequence alignment of Vibrionaceae with either a 40-residue insertion or a 44-residue insertion. Identical residues are indicated by red background.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Protein sequence alignment of Vibrionaceae with either a 40-residue insertion or a 44-residue insertion. Identical residues are indicated by red background.
Hyeyoung Shin a, Tod A. Pascal ab, William A. Goddard III abc*, and Hyungjun Kim a* Korea
 The Scaled Effective Solvent Method for Predicting the Equilibrium Ensemble of Structures with Analysis of Thermodynamic Properties of Amorphous Polyethylene Glycol-Water Mixtures Hyeyoung Shin a, Tod
The Scaled Effective Solvent Method for Predicting the Equilibrium Ensemble of Structures with Analysis of Thermodynamic Properties of Amorphous Polyethylene Glycol-Water Mixtures Hyeyoung Shin a, Tod
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Secondary structure of CAP (in the camp 2 -bound state) 10. α-helices are shown as cylinders and β- strands as arrows. Labeling of secondary structure is indicated. CDB, DBD and the hinge are
Figure S1. Secondary structure of CAP (in the camp 2 -bound state) 10. α-helices are shown as cylinders and β- strands as arrows. Labeling of secondary structure is indicated. CDB, DBD and the hinge are
Why Proteins Fold? (Parts of this presentation are based on work of Ashok Kolaskar) CS490B: Introduction to Bioinformatics Mar.
 Why Proteins Fold? (Parts of this presentation are based on work of Ashok Kolaskar) CS490B: Introduction to Bioinformatics Mar. 25, 2002 Molecular Dynamics: Introduction At physiological conditions, the
Why Proteins Fold? (Parts of this presentation are based on work of Ashok Kolaskar) CS490B: Introduction to Bioinformatics Mar. 25, 2002 Molecular Dynamics: Introduction At physiological conditions, the
Contents. xiii. Preface v
 Contents Preface Chapter 1 Biological Macromolecules 1.1 General PrincipIes 1.1.1 Macrornolecules 1.2 1.1.2 Configuration and Conformation Molecular lnteractions in Macromolecular Structures 1.2.1 Weak
Contents Preface Chapter 1 Biological Macromolecules 1.1 General PrincipIes 1.1.1 Macrornolecules 1.2 1.1.2 Configuration and Conformation Molecular lnteractions in Macromolecular Structures 1.2.1 Weak
Ranjit P. Bahadur Assistant Professor Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India. 1 st November, 2013
 Hydration of protein-rna recognition sites Ranjit P. Bahadur Assistant Professor Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India 1 st November, 2013 Central Dogma of life DNA
Hydration of protein-rna recognition sites Ranjit P. Bahadur Assistant Professor Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India 1 st November, 2013 Central Dogma of life DNA
Destruction of Amyloid Fibrils by Graphene through Penetration and Extraction of Peptides
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Destruction of Amyloid Fibrils by Graphene through Penetration and Extraction of Peptides Zaixing
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Destruction of Amyloid Fibrils by Graphene through Penetration and Extraction of Peptides Zaixing
CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 2 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 1 April 2004
 CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 2 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 1 April 2004 Lecture #2: 1 April 2004 Topics: Kinematics : Concepts and Results Kinematics of Ligands and
CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 2 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 1 April 2004 Lecture #2: 1 April 2004 Topics: Kinematics : Concepts and Results Kinematics of Ligands and
A.D.J. van Dijk "Modelling of biomolecular complexes by data-driven docking"
 Chapter 3. Various strategies of using Residual Dipolar Couplings in NMRdriven protein docking: application to Lys48-linked di-ubiquitin and validation against 15 N-relaxation data. Aalt D.J. van Dijk,
Chapter 3. Various strategies of using Residual Dipolar Couplings in NMRdriven protein docking: application to Lys48-linked di-ubiquitin and validation against 15 N-relaxation data. Aalt D.J. van Dijk,
Conformational Geometry of Peptides and Proteins:
 Conformational Geometry of Peptides and Proteins: Before discussing secondary structure, it is important to appreciate the conformational plasticity of proteins. Each residue in a polypeptide has three
Conformational Geometry of Peptides and Proteins: Before discussing secondary structure, it is important to appreciate the conformational plasticity of proteins. Each residue in a polypeptide has three
April, The energy functions include:
 REDUX A collection of Python scripts for torsion angle Monte Carlo protein molecular simulations and analysis The program is based on unified residue peptide model and is designed for more efficient exploration
REDUX A collection of Python scripts for torsion angle Monte Carlo protein molecular simulations and analysis The program is based on unified residue peptide model and is designed for more efficient exploration
Supplementary Information. The Solution Structural Ensembles of RNA Kink-turn Motifs and Their Protein Complexes
 Supplementary Information The Solution Structural Ensembles of RNA Kink-turn Motifs and Their Protein Complexes Xuesong Shi, a Lin Huang, b David M. J. Lilley, b Pehr B. Harbury a,c and Daniel Herschlag
Supplementary Information The Solution Structural Ensembles of RNA Kink-turn Motifs and Their Protein Complexes Xuesong Shi, a Lin Huang, b David M. J. Lilley, b Pehr B. Harbury a,c and Daniel Herschlag
Computer simulations of protein folding with a small number of distance restraints
 Vol. 49 No. 3/2002 683 692 QUARTERLY Computer simulations of protein folding with a small number of distance restraints Andrzej Sikorski 1, Andrzej Kolinski 1,2 and Jeffrey Skolnick 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Vol. 49 No. 3/2002 683 692 QUARTERLY Computer simulations of protein folding with a small number of distance restraints Andrzej Sikorski 1, Andrzej Kolinski 1,2 and Jeffrey Skolnick 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Presenter: She Zhang
 Presenter: She Zhang Introduction Dr. David Baker Introduction Why design proteins de novo? It is not clear how non-covalent interactions favor one specific native structure over many other non-native
Presenter: She Zhang Introduction Dr. David Baker Introduction Why design proteins de novo? It is not clear how non-covalent interactions favor one specific native structure over many other non-native
PDBe TUTORIAL. PDBePISA (Protein Interfaces, Surfaces and Assemblies)
 PDBe TUTORIAL PDBePISA (Protein Interfaces, Surfaces and Assemblies) http://pdbe.org/pisa/ This tutorial introduces the PDBePISA (PISA for short) service, which is a webbased interactive tool offered by
PDBe TUTORIAL PDBePISA (Protein Interfaces, Surfaces and Assemblies) http://pdbe.org/pisa/ This tutorial introduces the PDBePISA (PISA for short) service, which is a webbased interactive tool offered by
Supplemental Information for: Characterizing the Membrane-Bound State of Cytochrome P450 3A4: Structure, Depth of Insertion and Orientation
 Supplemental Information for: Characterizing the Membrane-Bound State of Cytochrome P450 3A4: Structure, Depth of Insertion and Orientation Javier L. Baylon, Ivan L. Lenov, Stephen G. Sligar and Emad Tajkhorshid
Supplemental Information for: Characterizing the Membrane-Bound State of Cytochrome P450 3A4: Structure, Depth of Insertion and Orientation Javier L. Baylon, Ivan L. Lenov, Stephen G. Sligar and Emad Tajkhorshid
Electro-Mechanical Conductance Modulation of a Nanopore Using a Removable Gate
 Electro-Mechanical Conductance Modulation of a Nanopore Using a Removable Gate Shidi Zhao a, Laura Restrepo-Pérez b, Misha Soskine c, Giovanni Maglia c, Chirlmin Joo b, Cees Dekker b and Aleksei Aksimentiev
Electro-Mechanical Conductance Modulation of a Nanopore Using a Removable Gate Shidi Zhao a, Laura Restrepo-Pérez b, Misha Soskine c, Giovanni Maglia c, Chirlmin Joo b, Cees Dekker b and Aleksei Aksimentiev
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015,
 Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
Biology Chemistry & Physics of Biomolecules. Examination #1. Proteins Module. September 29, Answer Key
 Biology 5357 Chemistry & Physics of Biomolecules Examination #1 Proteins Module September 29, 2017 Answer Key Question 1 (A) (5 points) Structure (b) is more common, as it contains the shorter connection
Biology 5357 Chemistry & Physics of Biomolecules Examination #1 Proteins Module September 29, 2017 Answer Key Question 1 (A) (5 points) Structure (b) is more common, as it contains the shorter connection
Fluorinated Peptide Nucleic Acids with Fluoroacetyl sidechain bearing 5- (F/CF 3 )-Uracil: Synthesis and Cell Uptake Studies. Supporting Information
 Fluorinated Peptide Nucleic Acids with Fluoroacetyl sidechain bearing 5- (F/CF 3 )-Uracil: Synthesis and Cell Uptake Studies Satheesh Ellipilli, Sandeep Palvai and Krishna N Ganesh* Chemical Biology Unit,
Fluorinated Peptide Nucleic Acids with Fluoroacetyl sidechain bearing 5- (F/CF 3 )-Uracil: Synthesis and Cell Uptake Studies Satheesh Ellipilli, Sandeep Palvai and Krishna N Ganesh* Chemical Biology Unit,
Useful background reading
 Overview of lecture * General comment on peptide bond * Discussion of backbone dihedral angles * Discussion of Ramachandran plots * Description of helix types. * Description of structures * NMR patterns
Overview of lecture * General comment on peptide bond * Discussion of backbone dihedral angles * Discussion of Ramachandran plots * Description of helix types. * Description of structures * NMR patterns
Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached
 Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached to HpUreI. Urea hydrolysis products 2NH 3 and 1CO 2
Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached to HpUreI. Urea hydrolysis products 2NH 3 and 1CO 2
Chapter 6 Cyclic urea - a new central unit in bent-core compounds
 82 Chapter 6 Cyclic urea - a new central unit in bent-core compounds A new class of five-ring bent-core molecules with a cyclic urea group as a central unit was synthesized [94]. A significant difference
82 Chapter 6 Cyclic urea - a new central unit in bent-core compounds A new class of five-ring bent-core molecules with a cyclic urea group as a central unit was synthesized [94]. A significant difference
Don t forget to bring your MD tutorial. Potential Energy (hyper)surface
 Don t forget to bring your MD tutorial Lab session starts at 1pm You will have to finish an MD/SMD exercise on α-conotoxin in oxidized and reduced forms Potential Energy (hyper)surface What is Force? Energy
Don t forget to bring your MD tutorial Lab session starts at 1pm You will have to finish an MD/SMD exercise on α-conotoxin in oxidized and reduced forms Potential Energy (hyper)surface What is Force? Energy
Peptides And Proteins
 Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptides And Proteins from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction B. omenclature And Conventions by amide bonds. on the left, right. 2 -terminal C-terminal triglycine
Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptides And Proteins from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction B. omenclature And Conventions by amide bonds. on the left, right. 2 -terminal C-terminal triglycine
Bioengineering 215. An Introduction to Molecular Dynamics for Biomolecules
 Bioengineering 215 An Introduction to Molecular Dynamics for Biomolecules David Parker May 18, 2007 ntroduction A principal tool to study biological molecules is molecular dynamics simulations (MD). MD
Bioengineering 215 An Introduction to Molecular Dynamics for Biomolecules David Parker May 18, 2007 ntroduction A principal tool to study biological molecules is molecular dynamics simulations (MD). MD
Introduction to Polymer Physics
 Introduction to Polymer Physics Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium February-May, 2016 Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium Introduction to Polymer Physics February-May, 2016 1 / 28 Polymers in Chemistry and
Introduction to Polymer Physics Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium February-May, 2016 Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium Introduction to Polymer Physics February-May, 2016 1 / 28 Polymers in Chemistry and
Introduction to Computational Structural Biology
 Introduction to Computational Structural Biology Part I 1. Introduction The disciplinary character of Computational Structural Biology The mathematical background required and the topics covered Bibliography
Introduction to Computational Structural Biology Part I 1. Introduction The disciplinary character of Computational Structural Biology The mathematical background required and the topics covered Bibliography
Examples of Protein Modeling. Protein Modeling. Primary Structure. Protein Structure Description. Protein Sequence Sources. Importing Sequences to MOE
 Examples of Protein Modeling Protein Modeling Visualization Examination of an experimental structure to gain insight about a research question Dynamics To examine the dynamics of protein structures To
Examples of Protein Modeling Protein Modeling Visualization Examination of an experimental structure to gain insight about a research question Dynamics To examine the dynamics of protein structures To
Structure Investigation of Fam20C, a Golgi Casein Kinase
 Structure Investigation of Fam20C, a Golgi Casein Kinase Sharon Grubner National Taiwan University, Dr. Jung-Hsin Lin University of California San Diego, Dr. Rommie Amaro Abstract This research project
Structure Investigation of Fam20C, a Golgi Casein Kinase Sharon Grubner National Taiwan University, Dr. Jung-Hsin Lin University of California San Diego, Dr. Rommie Amaro Abstract This research project
Fondamenti di Chimica Farmaceutica. Computer Chemistry in Drug Research: Introduction
 Fondamenti di Chimica Farmaceutica Computer Chemistry in Drug Research: Introduction Introduction Introduction Introduction Computer Chemistry in Drug Design Drug Discovery: Target identification Lead
Fondamenti di Chimica Farmaceutica Computer Chemistry in Drug Research: Introduction Introduction Introduction Introduction Computer Chemistry in Drug Design Drug Discovery: Target identification Lead
Secondary and sidechain structures
 Lecture 2 Secondary and sidechain structures James Chou BCMP201 Spring 2008 Images from Petsko & Ringe, Protein Structure and Function. Branden & Tooze, Introduction to Protein Structure. Richardson, J.
Lecture 2 Secondary and sidechain structures James Chou BCMP201 Spring 2008 Images from Petsko & Ringe, Protein Structure and Function. Branden & Tooze, Introduction to Protein Structure. Richardson, J.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Supplementary material and methods:
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Supplementary material and methods: - Computational
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Supplementary material and methods: - Computational
Free Radical-Initiated Unfolding of Peptide Secondary Structure Elements
 Free Radical-Initiated Unfolding of Peptide Secondary Structure Elements Thesis of the Ph.D. Dissertation by Michael C. Owen, M.Sc. Department of Chemical Informatics Faculty of Education University of
Free Radical-Initiated Unfolding of Peptide Secondary Structure Elements Thesis of the Ph.D. Dissertation by Michael C. Owen, M.Sc. Department of Chemical Informatics Faculty of Education University of
Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants. GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants Sense primer (5 to 3 ) Anti-sense primer (5 to 3 ) GAL1 mutants GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants Sense primer (5 to 3 ) Anti-sense primer (5 to 3 ) GAL1 mutants GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
Dihedral Angles. Homayoun Valafar. Department of Computer Science and Engineering, USC 02/03/10 CSCE 769
 Dihedral Angles Homayoun Valafar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, USC The precise definition of a dihedral or torsion angle can be found in spatial geometry Angle between to planes Dihedral
Dihedral Angles Homayoun Valafar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, USC The precise definition of a dihedral or torsion angle can be found in spatial geometry Angle between to planes Dihedral
Procheck output. Bond angles (Procheck) Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics.
 Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu ----------------------------------------------------------------- Bond
Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu ----------------------------------------------------------------- Bond
Simulating Folding of Helical Proteins with Coarse Grained Models
 366 Progress of Theoretical Physics Supplement No. 138, 2000 Simulating Folding of Helical Proteins with Coarse Grained Models Shoji Takada Department of Chemistry, Kobe University, Kobe 657-8501, Japan
366 Progress of Theoretical Physics Supplement No. 138, 2000 Simulating Folding of Helical Proteins with Coarse Grained Models Shoji Takada Department of Chemistry, Kobe University, Kobe 657-8501, Japan
Molecular dynamics simulations of anti-aggregation effect of ibuprofen. Wenling E. Chang, Takako Takeda, E. Prabhu Raman, and Dmitri Klimov
 Biophysical Journal, Volume 98 Supporting Material Molecular dynamics simulations of anti-aggregation effect of ibuprofen Wenling E. Chang, Takako Takeda, E. Prabhu Raman, and Dmitri Klimov Supplemental
Biophysical Journal, Volume 98 Supporting Material Molecular dynamics simulations of anti-aggregation effect of ibuprofen Wenling E. Chang, Takako Takeda, E. Prabhu Raman, and Dmitri Klimov Supplemental
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information doi: 10.1038/nchem.247 Amyloid!-Protein Oligomerization and the Importance of Tetramers and Dodecamers in the Aetiology of Alzheimer s Disease Summer L. Bernstein, Nicholas F.
Supplementary information doi: 10.1038/nchem.247 Amyloid!-Protein Oligomerization and the Importance of Tetramers and Dodecamers in the Aetiology of Alzheimer s Disease Summer L. Bernstein, Nicholas F.
Routine access to millisecond timescale events with accelerated molecular dynamics
 Routine access to millisecond timescale events with accelerated molecular dynamics Levi C.T. Pierce, Romelia Salomon-Ferrer, Cesar Augusto F. de Oliveira #, J. Andrew McCammon #, Ross C. Walker * SUPPORTING
Routine access to millisecond timescale events with accelerated molecular dynamics Levi C.T. Pierce, Romelia Salomon-Ferrer, Cesar Augusto F. de Oliveira #, J. Andrew McCammon #, Ross C. Walker * SUPPORTING
Introduction The gramicidin A (ga) channel forms by head-to-head association of two monomers at their amino termini, one from each bilayer leaflet. Th
 Abstract When conductive, gramicidin monomers are linked by six hydrogen bonds. To understand the details of dissociation and how the channel transits from a state with 6H bonds to ones with 4H bonds or
Abstract When conductive, gramicidin monomers are linked by six hydrogen bonds. To understand the details of dissociation and how the channel transits from a state with 6H bonds to ones with 4H bonds or
2: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE BODY
 1 2: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE BODY Although most students of human physiology have had at least some chemistry, this chapter serves very well as a review and as a glossary of chemical terms. In particular,
1 2: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE BODY Although most students of human physiology have had at least some chemistry, this chapter serves very well as a review and as a glossary of chemical terms. In particular,
Protein Structure Determination from Pseudocontact Shifts Using ROSETTA
 Supporting Information Protein Structure Determination from Pseudocontact Shifts Using ROSETTA Christophe Schmitz, Robert Vernon, Gottfried Otting, David Baker and Thomas Huber Table S0. Biological Magnetic
Supporting Information Protein Structure Determination from Pseudocontact Shifts Using ROSETTA Christophe Schmitz, Robert Vernon, Gottfried Otting, David Baker and Thomas Huber Table S0. Biological Magnetic
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL FOR
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL FOR THE LIPID-BINDING DOMAIN OF WILD TYPE AND MUTANT ALPHA- SYNUCLEIN: COMPACTNESS AND INTERCONVERSION BETWEEN THE BROKEN- AND EXTENDED-HELIX FORMS. Elka R. Georgieva 1, Trudy F.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL FOR THE LIPID-BINDING DOMAIN OF WILD TYPE AND MUTANT ALPHA- SYNUCLEIN: COMPACTNESS AND INTERCONVERSION BETWEEN THE BROKEN- AND EXTENDED-HELIX FORMS. Elka R. Georgieva 1, Trudy F.
NMR of Nucleic Acids. K.V.R. Chary Workshop on NMR and it s applications in Biological Systems November 26, 2009
 MR of ucleic Acids K.V.R. Chary chary@tifr.res.in Workshop on MR and it s applications in Biological Systems TIFR ovember 26, 2009 ucleic Acids are Polymers of ucleotides Each nucleotide consists of a
MR of ucleic Acids K.V.R. Chary chary@tifr.res.in Workshop on MR and it s applications in Biological Systems TIFR ovember 26, 2009 ucleic Acids are Polymers of ucleotides Each nucleotide consists of a
Physiochemical Properties of Residues
 Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
PHYSICS OF SOLID POLYMERS
 PYSIS OF SOLID POLYMERS Professor Goran Ungar WU E, Department of hemical and Biological Engineering Recommended texts: G. Strobl, The Physics of Polymers, Springer 996 (emphasis on physics) U. Gedde,
PYSIS OF SOLID POLYMERS Professor Goran Ungar WU E, Department of hemical and Biological Engineering Recommended texts: G. Strobl, The Physics of Polymers, Springer 996 (emphasis on physics) U. Gedde,
Conformational sampling of macrocycles in solution and in the solid state
 Conformational sampling of macrocycles in solution and in the solid state Paul Hawkins, Ph.D. Head of Scientific Solutions Stanislaw Wlodek, Ph.D. Senior Scientific Developer 6/6/2018 https://berkonomics.com/?p=2437
Conformational sampling of macrocycles in solution and in the solid state Paul Hawkins, Ph.D. Head of Scientific Solutions Stanislaw Wlodek, Ph.D. Senior Scientific Developer 6/6/2018 https://berkonomics.com/?p=2437
Multi-Scale Hierarchical Structure Prediction of Helical Transmembrane Proteins
 Multi-Scale Hierarchical Structure Prediction of Helical Transmembrane Proteins Zhong Chen Dept. of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602 Email: zc@csbl.bmb.uga.edu
Multi-Scale Hierarchical Structure Prediction of Helical Transmembrane Proteins Zhong Chen Dept. of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602 Email: zc@csbl.bmb.uga.edu
Details of Protein Structure
 Details of Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Anne Mølgaard, Kemisk Institut, Københavns Universitet Learning Objectives
Details of Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Anne Mølgaard, Kemisk Institut, Københavns Universitet Learning Objectives
