Goals. Structural Analysis of the EGR Family of Transcription Factors: Templates for Predicting Protein DNA Interactions
|
|
|
- Gregory Patrick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Structural Analysis of the EGR Family of Transcription Factors: Templates for Predicting Protein DNA Interactions Jamie Duke 1,2 and Carlos Camacho 3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Department of Computational Biology, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA Department of Biological Sciences, Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, NY Department of Computational Biology, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA Goals Investigate the diversity of the EGR family of proteins Carry out homology modeling between resolved structures and known human EGR proteins Test the structures with protein DNA docking algorithms to determine the specific protein DNA interactions 1
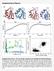
2 Background Information Zinc Fingers Nucleic Acid binding domain Classic C2H2 conformation coordinating a zinc ion Conserved Pattern: x-c-x(1-5)-c-x(12)-h-x(3-6)-h Conserved aromatic ring 24 residue β β α motif Multiple domains used to recognize specific DNA sequences Most commonly studied family is EGR family with 2 3 zinc finger domains Also known as Zif268, Nerve Growth Factor Induced Protein, and Krox proteins Referenced from Pfam Acc. No: PF00096 ( Zinc Finger Binding Each Finger recognizes 3 nucleotides Recognition occurs in the α-helix of the finger Recognition is overlapped by the 3 domains DNA binding site can be changed with mutation to the protein 5 1AAY 1G2D Finger 3 Finger 2 Finger R T E TR T Q H G QR T R N E QR N N G C GT TA GT GA GA CA GA T G N N N C G C A A T C A C T C T G T C T A C N Paillard et al. Fig 1A and 1B 3 2
3 zf-c2h2 Family Diversity Currently, there are 32,874 identified zinc fingers of the type zf-c2h2 (Pfam 17.0) There are 5264 proteins with identified zinc fingers, which are represented in 235 different architectures Distribution: Eukaryota: 5233 proteins Vertebrata: 3435 proteins Amphibians: 218 protiens Humans: 1390 proteins Mice: 1085 Fungi: 395 proteins Viruses: 19 proteins Archea: 12 proteins zf-c2h2 MSA Snapshot of the multiple sequence alignment for the domain (* conserved residue) EGR1_HUMAN/ FACD...ICG...RKFARS...DERKRHTKI...H ZFP60_MOUSE/ FECK...ECG...KAFHFS...SQLNNHKTS...H ACE2_YEAST/ YSCDF.PGCT...KAFVRN...HDLIRHKIS...H SUHW_DROAN/ YACK...ICG...KDFTRS...YHLKRHQKYS.SC ZNF76_HUMAN/ YTCPE.PHCG...RGFTSA...TNYKNHVRI...H TTKB_DROME/ YPCP...FCF...KEFTRK...DNMTAHVKI..IH XFIN_XENLA/ YKCG...LCE...RSFVEK...SALSRHQRV...H Q17793_CAEEL/ YQCQ...LCK...KSISRHGQYANLLNHLSR...H TF3A_BUFAM/ YPCRKDSTCP...FVGKTW...SDYMKHAAE..LH ZN592_HUMAN/ YTCG...YCTEDSPSFPRP...SLLESHISL..MH * * * * 3
4 zf-c2h2 Family Diversity There are 42 structures of zf-c2h2 proteins in the Protein Data Bank 11 structures were applicable to our interests Of the 42 structures: 20 were from x-ray crystallography 22 were developed through NMR At least 15 were duplicate structures We only considered structures that were developed through x-ray crystallography and had either 2 or 3 zinc fingers, as they would belong to the EGR family Homology Modeling We chose two proteins with known structures to perform homology modeling, 1G2D and 1AAY Allows us to compare the predicted structure against the known structure to determine the accuracy of the prediction A Zif268 variant (1G2D) was selected for the target of the homology modeling, with the template being Zif268 (1AAY) The 1G2D recognizes the DNA Sequence: 5 GCTATAAAA 3 The sequences are 83% similar, with 81% sequence identity 1AAY MERPYACPVESCDRRFSRSDELTRHIRIHTGQKPFQCRICMRNFS MERPYACPVESCDRRFS+ L HIRIHTGQKPFQCRICMRNFS 1G2D MERPYACPVESCDRRFSQKTNLDTHIRIHTGQKPFQCRICMRNFS 1AAY RSDHLTTHIRTHTGEKPFACDICGRKFARSDERKRHTKIHLRQKD + L HIRTHTGEKPFACDICGRKFA R RHTKIHLRQKD 1G2D QHTGLNQHIRTHTGEKPFACDICGRKFATLHTRDRHTKIHLRQKD 4
5 Homology Modeling We were concerned with positions -1, 3 and 6 in the α-helix The Consensus Server, developed in part by Dr. Camacho, was used to perform the homology modeling ( Since threading algorithms are used in the Consensus method, the side chains of amino acids can only be predicted to the extent of the corresponding amino acid from the template. Serine Lysine the method can only place Cα and Cβ atoms, leaving four carbon atoms positions undeterminable. CHARMM was used to complete the side chains Side Chain Relaxation via Molecular Dynamic Simulations We chose to relax the side chains for each domain independently to find the most favorable state Simulations were run using a constrained backbone to conserve the structure that was predicted in the previous step Run-time totaled of 4.2 ns for each domain 200 ps for system equilibration, Each time step was 2 fs This simulation did not take into account ions and without the DNA present We were particularly interested in the states of the three residues involved in DNA recognition 5
6 RMSD Analysis and Clustering RMSD analysis was performed between the results of the MD simulations and the crystal structure Cα atoms were aligned to produce a minimized RMSD calculation The RMSD was calculated for symmetric structures where applicable (i.e. arginine residues) to further minimize the RMSD A neighbor clustering algorithm was also applied to analyze the snapshots produced from the MD simulation Performed on a single side chain Calculated for all pairs of snapshots Clustering took place within a 1.0 Å threshold Clusters were ranked based upon the number of snapshots that were included. RMSD vs Time for Position 3 in Helix RMSD (Å) Time (ns) 6
7 RMSD vs. Time for Residue 6 in Helix 3 RMSD (Å) Time (ns) 7
8 Results Through RMSD and cluster analysis, we have determined that most of the residues reach an equilibrium point that is highly similar to the crystal structure. Cluster analysis revealed that the cluster with the most amount of neighbors is generally highly similar to the crystal structure. There are a few residues that are seen in the simulation that seem to fluctuate between two states, as can be seen in Figure 3. We believe that this fluctuation may be correlated to the mechanism by which the protein recognizes the DNA. 8
9 Other Models This method was also run in two other situations: Modeling Zif268 (1AAY) using the Zif268 variant (1G2D) as a template Modeling Designed Zinc Finger (1MEY) using Zif268 as the template Shares 49% identity with 1AAY Shares 47% identity with 1G2D Preliminary results and analysis show similar findings to 1G2D modeled after 1AAY Conclusions and Future Applications Through this method we are able to effectively determine a homology model of zinc finger proteins, more specifically zinc finger proteins in the EGR family. The modeled side chains are found to be in a state that is similar to the crystal structure, even when in an unbound state, which is particularly important for the key residues involved in DNA recognition. Since the modeled domains are in a desirable conformation, it is possible to perform docking experiments with homology modeled zinc fingers, which is currently being done using an DNA-protein docking algorithm developed in the lab. Future applications include modeling EGR proteins with an undetermined structure to see if the model is able to recognize the proper DNA sequence. 9
10 Acknowledgements Dr. Carlos J. Camacho, Advisor Christoph Champ BBSI Department of Computational Biology, University of Pittsburgh NIH NSF References J.C. Prasad, S.R. Comeau, S. Vajda, and C.J. Camacho. Consensus alignment for reliable framework prediction in homology modeling. Bioinformatics : Paillard G., Deremble C., Lavery R. Looking into DNA Recognition: Zinc Finger Binding Specificity. Nucleic Acids Research : A. Bateman, L. Coin, R. Durbin, R.D. Finn, V. Hollich, S. Griffiths-Jones, A. Khanna, M. Marshall, S. Moxon, E.L.L. Sonnhammer, D.J. Studholme, C. Yeats, S.R. Eddy. The Pfam Protein Families Database. Nucleic Acids Research: Database Issue : D138- D
Structural analysis of the EGR family of transcription factors: Templates for predicitng protein - DNA internations
 Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Collections 8-15-2006 Structural analysis of the EGR family of transcription factors: Templates for predicitng protein - DNA
Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Collections 8-15-2006 Structural analysis of the EGR family of transcription factors: Templates for predicitng protein - DNA
SI Materials and Methods
 SI Materials and Methods Gibbs Sampling with Informative Priors. Full description of the PhyloGibbs algorithm, including comprehensive tests on synthetic and yeast data sets, can be found in Siddharthan
SI Materials and Methods Gibbs Sampling with Informative Priors. Full description of the PhyloGibbs algorithm, including comprehensive tests on synthetic and yeast data sets, can be found in Siddharthan
Bioengineering & Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Dept. Computational Biology, University of Pittsburgh, PGH, PA
 Pharmacophore Model Development for the Identification of Novel Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors Edwin Kamau Dept Chem & Biochem Kennesa State Uni ersit Kennesa GA 30144 Dept. Chem. & Biochem. Kennesaw
Pharmacophore Model Development for the Identification of Novel Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors Edwin Kamau Dept Chem & Biochem Kennesa State Uni ersit Kennesa GA 30144 Dept. Chem. & Biochem. Kennesaw
Truncated Profile Hidden Markov Models
 Boise State University ScholarWorks Electrical and Computer Engineering Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 11-1-2005 Truncated Profile Hidden Markov
Boise State University ScholarWorks Electrical and Computer Engineering Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 11-1-2005 Truncated Profile Hidden Markov
Protein Structure Prediction II Lecturer: Serafim Batzoglou Scribe: Samy Hamdouche
 Protein Structure Prediction II Lecturer: Serafim Batzoglou Scribe: Samy Hamdouche The molecular structure of a protein can be broken down hierarchically. The primary structure of a protein is simply its
Protein Structure Prediction II Lecturer: Serafim Batzoglou Scribe: Samy Hamdouche The molecular structure of a protein can be broken down hierarchically. The primary structure of a protein is simply its
Modelling of Possible Binding Modes of Caffeic Acid Derivatives to JAK3 Kinase
 John von Neumann Institute for Computing Modelling of Possible Binding Modes of Caffeic Acid Derivatives to JAK3 Kinase J. Kuska, P. Setny, B. Lesyng published in From Computational Biophysics to Systems
John von Neumann Institute for Computing Modelling of Possible Binding Modes of Caffeic Acid Derivatives to JAK3 Kinase J. Kuska, P. Setny, B. Lesyng published in From Computational Biophysics to Systems
Molecular Modeling. Prediction of Protein 3D Structure from Sequence. Vimalkumar Velayudhan. May 21, 2007
 Molecular Modeling Prediction of Protein 3D Structure from Sequence Vimalkumar Velayudhan Jain Institute of Vocational and Advanced Studies May 21, 2007 Vimalkumar Velayudhan Molecular Modeling 1/23 Outline
Molecular Modeling Prediction of Protein 3D Structure from Sequence Vimalkumar Velayudhan Jain Institute of Vocational and Advanced Studies May 21, 2007 Vimalkumar Velayudhan Molecular Modeling 1/23 Outline
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling. Chapter 4 Part I
 Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Computational Modeling of Protein Kinase A and Comparison with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Data
 Computational Modeling of Protein Kinase A and Comparison with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Data ABSTRACT Keyword Lei Shi 1 Advisor: Gianluigi Veglia 1,2 Department of Chemistry 1, & Biochemistry, Molecular
Computational Modeling of Protein Kinase A and Comparison with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Data ABSTRACT Keyword Lei Shi 1 Advisor: Gianluigi Veglia 1,2 Department of Chemistry 1, & Biochemistry, Molecular
Sequence Based Bioinformatics
 Structural and Functional Analysis of Inosine Monophosphate Dehydrogenase using Sequence-Based Bioinformatics Barry Sexton 1,2 and Troy Wymore 3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Department
Structural and Functional Analysis of Inosine Monophosphate Dehydrogenase using Sequence-Based Bioinformatics Barry Sexton 1,2 and Troy Wymore 3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Department
Structure to Function. Molecular Bioinformatics, X3, 2006
 Structure to Function Molecular Bioinformatics, X3, 2006 Structural GeNOMICS Structural Genomics project aims at determination of 3D structures of all proteins: - organize known proteins into families
Structure to Function Molecular Bioinformatics, X3, 2006 Structural GeNOMICS Structural Genomics project aims at determination of 3D structures of all proteins: - organize known proteins into families
Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics II. Hidden Markov Model for Biological Sequences
 Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics II. Hidden Markov Model for Biological Sequences Jianlin Cheng, PhD Department of Computer Science University of Missouri 2008 Free for Academic
Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics II. Hidden Markov Model for Biological Sequences Jianlin Cheng, PhD Department of Computer Science University of Missouri 2008 Free for Academic
Supplementary Figures:
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1: The two strings converge to two qualitatively different pathways. A) Models of active (red) and inactive (blue) states used as end points for the string calculations
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1: The two strings converge to two qualitatively different pathways. A) Models of active (red) and inactive (blue) states used as end points for the string calculations
Protein Dynamics. The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron.
 Protein Dynamics The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron. Below is myoglobin hydrated with 350 water molecules. Only a small
Protein Dynamics The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron. Below is myoglobin hydrated with 350 water molecules. Only a small
Week 10: Homology Modelling (II) - HHpred
 Week 10: Homology Modelling (II) - HHpred Course: Tools for Structural Biology Fabian Glaser BKU - Technion 1 2 Identify and align related structures by sequence methods is not an easy task All comparative
Week 10: Homology Modelling (II) - HHpred Course: Tools for Structural Biology Fabian Glaser BKU - Technion 1 2 Identify and align related structures by sequence methods is not an easy task All comparative
Cooperativity and Specificity of Cys 2 His 2 Zinc Finger Protein-DNA Interactions: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study
 7662 J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 7662 7671 Cooperativity and Specificity of Cys 2 His 2 Zinc Finger Protein-DNA Interactions: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study Juyong Lee, Jin-Soo Kim, and Chaok Seok*
7662 J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 7662 7671 Cooperativity and Specificity of Cys 2 His 2 Zinc Finger Protein-DNA Interactions: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study Juyong Lee, Jin-Soo Kim, and Chaok Seok*
Introduction to" Protein Structure
 Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS II. Spring 2018
 STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS II Spring 2018 Syllabus Course Number - Classification: Chemistry 5412 Class Schedule: Monday 5:30-7:50 PM, SERC Room 456 (4 th floor) Instructors: Ronald Levy, SERC 718 (ronlevy@temple.edu)
STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS II Spring 2018 Syllabus Course Number - Classification: Chemistry 5412 Class Schedule: Monday 5:30-7:50 PM, SERC Room 456 (4 th floor) Instructors: Ronald Levy, SERC 718 (ronlevy@temple.edu)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Fall 2017 Databases and Protein Structure Representation October 2, 2017 Molecular Biology as Information Science > 12, 000 genomes sequenced, mostly bacterial (2013) > 5x10 6 unique sequences available
Fall 2017 Databases and Protein Structure Representation October 2, 2017 Molecular Biology as Information Science > 12, 000 genomes sequenced, mostly bacterial (2013) > 5x10 6 unique sequences available
Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings. 10/7/2003 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 7 1
 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 10/7/2003 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 7 1 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 10/7/2003 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 7 2 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings
Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 10/7/2003 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 7 1 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 10/7/2003 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 7 2 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings
A conserved P-loop anchor limits the structural dynamics that mediate. nucleotide dissociation in EF-Tu.
 Supplemental Material for A conserved P-loop anchor limits the structural dynamics that mediate nucleotide dissociation in EF-Tu. Evan Mercier 1,2, Dylan Girodat 1, and Hans-Joachim Wieden 1 * 1 Alberta
Supplemental Material for A conserved P-loop anchor limits the structural dynamics that mediate nucleotide dissociation in EF-Tu. Evan Mercier 1,2, Dylan Girodat 1, and Hans-Joachim Wieden 1 * 1 Alberta
Why Proteins Fold? (Parts of this presentation are based on work of Ashok Kolaskar) CS490B: Introduction to Bioinformatics Mar.
 Why Proteins Fold? (Parts of this presentation are based on work of Ashok Kolaskar) CS490B: Introduction to Bioinformatics Mar. 25, 2002 Molecular Dynamics: Introduction At physiological conditions, the
Why Proteins Fold? (Parts of this presentation are based on work of Ashok Kolaskar) CS490B: Introduction to Bioinformatics Mar. 25, 2002 Molecular Dynamics: Introduction At physiological conditions, the
Homology Modeling. Roberto Lins EPFL - summer semester 2005
 Homology Modeling Roberto Lins EPFL - summer semester 2005 Disclaimer: course material is mainly taken from: P.E. Bourne & H Weissig, Structural Bioinformatics; C.A. Orengo, D.T. Jones & J.M. Thornton,
Homology Modeling Roberto Lins EPFL - summer semester 2005 Disclaimer: course material is mainly taken from: P.E. Bourne & H Weissig, Structural Bioinformatics; C.A. Orengo, D.T. Jones & J.M. Thornton,
Chemical Shift Restraints Tools and Methods. Andrea Cavalli
 Chemical Shift Restraints Tools and Methods Andrea Cavalli Overview Methods Overview Methods Details Overview Methods Details Results/Discussion Overview Methods Methods Cheshire base solid-state Methods
Chemical Shift Restraints Tools and Methods Andrea Cavalli Overview Methods Overview Methods Details Overview Methods Details Results/Discussion Overview Methods Methods Cheshire base solid-state Methods
CAP 5510 Lecture 3 Protein Structures
 CAP 5510 Lecture 3 Protein Structures Su-Shing Chen Bioinformatics CISE 8/19/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1 Protein Conformation 8/19/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 2 Protein Conformational Structures Hydrophobicity
CAP 5510 Lecture 3 Protein Structures Su-Shing Chen Bioinformatics CISE 8/19/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1 Protein Conformation 8/19/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 2 Protein Conformational Structures Hydrophobicity
Francisco Melo, Damien Devos, Eric Depiereux and Ernest Feytmans
 From: ISMB-97 Proceedings. Copyright 1997, AAAI (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved. ANOLEA: A www Server to Assess Protein Structures Francisco Melo, Damien Devos, Eric Depiereux and Ernest Feytmans Facultés
From: ISMB-97 Proceedings. Copyright 1997, AAAI (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved. ANOLEA: A www Server to Assess Protein Structures Francisco Melo, Damien Devos, Eric Depiereux and Ernest Feytmans Facultés
Prediction and refinement of NMR structures from sparse experimental data
 Prediction and refinement of NMR structures from sparse experimental data Jeff Skolnick Director Center for the Study of Systems Biology School of Biology Georgia Institute of Technology Overview of talk
Prediction and refinement of NMR structures from sparse experimental data Jeff Skolnick Director Center for the Study of Systems Biology School of Biology Georgia Institute of Technology Overview of talk
Life Science Webinar Series
 Life Science Webinar Series Elegant protein- protein docking in Discovery Studio Francisco Hernandez-Guzman, Ph.D. November 20, 2007 Sr. Solutions Scientist fhernandez@accelrys.com Agenda In silico protein-protein
Life Science Webinar Series Elegant protein- protein docking in Discovery Studio Francisco Hernandez-Guzman, Ph.D. November 20, 2007 Sr. Solutions Scientist fhernandez@accelrys.com Agenda In silico protein-protein
Procheck output. Bond angles (Procheck) Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics.
 Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu ----------------------------------------------------------------- Bond
Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu ----------------------------------------------------------------- Bond
Basics of protein structure
 Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
CSCE555 Bioinformatics. Protein Function Annotation
 CSCE555 Bioinformatics Protein Function Annotation Why we need to do function annotation? Fig from: Network-based prediction of protein function. Molecular Systems Biology 3:88. 2007 What s function? The
CSCE555 Bioinformatics Protein Function Annotation Why we need to do function annotation? Fig from: Network-based prediction of protein function. Molecular Systems Biology 3:88. 2007 What s function? The
Protein Structure Prediction, Engineering & Design CHEM 430
 Protein Structure Prediction, Engineering & Design CHEM 430 Eero Saarinen The free energy surface of a protein Protein Structure Prediction & Design Full Protein Structure from Sequence - High Alignment
Protein Structure Prediction, Engineering & Design CHEM 430 Eero Saarinen The free energy surface of a protein Protein Structure Prediction & Design Full Protein Structure from Sequence - High Alignment
Structure Investigation of Fam20C, a Golgi Casein Kinase
 Structure Investigation of Fam20C, a Golgi Casein Kinase Sharon Grubner National Taiwan University, Dr. Jung-Hsin Lin University of California San Diego, Dr. Rommie Amaro Abstract This research project
Structure Investigation of Fam20C, a Golgi Casein Kinase Sharon Grubner National Taiwan University, Dr. Jung-Hsin Lin University of California San Diego, Dr. Rommie Amaro Abstract This research project
Docking. GBCB 5874: Problem Solving in GBCB
 Docking Benzamidine Docking to Trypsin Relationship to Drug Design Ligand-based design QSAR Pharmacophore modeling Can be done without 3-D structure of protein Receptor/Structure-based design Molecular
Docking Benzamidine Docking to Trypsin Relationship to Drug Design Ligand-based design QSAR Pharmacophore modeling Can be done without 3-D structure of protein Receptor/Structure-based design Molecular
Syllabus of BIOINF 528 (2017 Fall, Bioinformatics Program)
 Syllabus of BIOINF 528 (2017 Fall, Bioinformatics Program) Course Name: Structural Bioinformatics Course Description: Instructor: This course introduces fundamental concepts and methods for structural
Syllabus of BIOINF 528 (2017 Fall, Bioinformatics Program) Course Name: Structural Bioinformatics Course Description: Instructor: This course introduces fundamental concepts and methods for structural
We used the PSI-BLAST program (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/) to search the
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS - in silico protein analysis We used the PSI-BLAST program (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/) to search the Protein Data Bank (PDB, http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/) and the NCBI non-redundant
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS - in silico protein analysis We used the PSI-BLAST program (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/) to search the Protein Data Bank (PDB, http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/) and the NCBI non-redundant
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information The Predicted Ensemble of Low-Energy Conformations of Human Somatostatin Receptor Subtype 5 and the Binding of Antagonists Sijia S. Dong, [a] Ravinder Abrol, [a, b] and William A.
Supporting Information The Predicted Ensemble of Low-Energy Conformations of Human Somatostatin Receptor Subtype 5 and the Binding of Antagonists Sijia S. Dong, [a] Ravinder Abrol, [a, b] and William A.
Giri Narasimhan. CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics. ECS 254; Phone: x3748
 CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics Giri Narasimhan ECS 254; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinfs07.html 2/15/07 CAP5510 1 EM Algorithm Goal: Find θ, Z that maximize Pr
CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics Giri Narasimhan ECS 254; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinfs07.html 2/15/07 CAP5510 1 EM Algorithm Goal: Find θ, Z that maximize Pr
Protein Bioinformatics. Rickard Sandberg Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology Karolinska Institutet sandberg.cmb.ki.
 Protein Bioinformatics Rickard Sandberg Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology Karolinska Institutet rickard.sandberg@ki.se sandberg.cmb.ki.se Outline Protein features motifs patterns profiles signals 2 Protein
Protein Bioinformatics Rickard Sandberg Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology Karolinska Institutet rickard.sandberg@ki.se sandberg.cmb.ki.se Outline Protein features motifs patterns profiles signals 2 Protein
Monte Carlo Simulations of Protein Folding using Lattice Models
 Monte Carlo Simulations of Protein Folding using Lattice Models Ryan Cheng 1,2 and Kenneth Jordan 1,3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Department of Computational Biology, University
Monte Carlo Simulations of Protein Folding using Lattice Models Ryan Cheng 1,2 and Kenneth Jordan 1,3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Department of Computational Biology, University
Computational Molecular Biology
 2013, Vol.3, No.1, 1-5 http://cmb.sophiapublisher.com Research Report Open Access Structural Analysis of the Mode of Interactions of SoxB Protein with SoxYZ Complex from Allochromatium vinosum in the Global
2013, Vol.3, No.1, 1-5 http://cmb.sophiapublisher.com Research Report Open Access Structural Analysis of the Mode of Interactions of SoxB Protein with SoxYZ Complex from Allochromatium vinosum in the Global
Signaling Proteins: Mechanical Force Generation by G-proteins G
 Signaling Proteins: Mechanical Force Generation by G-proteins G Ioan Kosztin Beckman Institute University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Collaborators: Robijn Bruinsma (Leiden & UCLA) Paul O Lague (UCLA)
Signaling Proteins: Mechanical Force Generation by G-proteins G Ioan Kosztin Beckman Institute University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Collaborators: Robijn Bruinsma (Leiden & UCLA) Paul O Lague (UCLA)
STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS I. Fall 2015
 STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS I Fall 2015 Info Course Number - Classification: Biology 5411 Class Schedule: Monday 5:30-7:50 PM, SERC Room 456 (4 th floor) Instructors: Vincenzo Carnevale - SERC, Room 704C;
STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS I Fall 2015 Info Course Number - Classification: Biology 5411 Class Schedule: Monday 5:30-7:50 PM, SERC Room 456 (4 th floor) Instructors: Vincenzo Carnevale - SERC, Room 704C;
β1 Structure Prediction and Validation
 13 Chapter 2 β1 Structure Prediction and Validation 2.1 Overview Over several years, GPCR prediction methods in the Goddard lab have evolved to keep pace with the changing field of GPCR structure. Despite
13 Chapter 2 β1 Structure Prediction and Validation 2.1 Overview Over several years, GPCR prediction methods in the Goddard lab have evolved to keep pace with the changing field of GPCR structure. Despite
Protein Structure Analysis with Sequential Monte Carlo Method. Jinfeng Zhang Computational Biology Lab Department of Statistics Harvard University
 Protein Structure Analysis with Sequential Monte Carlo Method Jinfeng Zhang Computational Biology Lab Department of Statistics Harvard University Introduction Structure Function & Interaction Protein structure
Protein Structure Analysis with Sequential Monte Carlo Method Jinfeng Zhang Computational Biology Lab Department of Statistics Harvard University Introduction Structure Function & Interaction Protein structure
A profile-based protein sequence alignment algorithm for a domain clustering database
 A profile-based protein sequence alignment algorithm for a domain clustering database Lin Xu,2 Fa Zhang and Zhiyong Liu 3, Key Laboratory of Computer System and architecture, the Institute of Computing
A profile-based protein sequence alignment algorithm for a domain clustering database Lin Xu,2 Fa Zhang and Zhiyong Liu 3, Key Laboratory of Computer System and architecture, the Institute of Computing
Absolute Entropy of a 2D Lattice Model for a Denatured Protein
 Absolute Entropy of a 2D Lattice Model for a Denatured Protein Jason Funt 1,4 and Hagai Meirovitch 2,3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute 2 Center for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics,
Absolute Entropy of a 2D Lattice Model for a Denatured Protein Jason Funt 1,4 and Hagai Meirovitch 2,3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute 2 Center for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics,
Supporting Information How does Darunavir prevent HIV-1 protease dimerization?
 Supporting Information How does Darunavir prevent HIV- protease dimerization? Danzhi Huang and Amedeo Caflisch a Department of Biochemistry University of Zürich, Winterthurerstrasse 9 CH-7 Zürich, Switzerland
Supporting Information How does Darunavir prevent HIV- protease dimerization? Danzhi Huang and Amedeo Caflisch a Department of Biochemistry University of Zürich, Winterthurerstrasse 9 CH-7 Zürich, Switzerland
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems
 Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Presenter: She Zhang
 Presenter: She Zhang Introduction Dr. David Baker Introduction Why design proteins de novo? It is not clear how non-covalent interactions favor one specific native structure over many other non-native
Presenter: She Zhang Introduction Dr. David Baker Introduction Why design proteins de novo? It is not clear how non-covalent interactions favor one specific native structure over many other non-native
Objectives. Comparison and Analysis of Heat Shock Proteins in Organisms of the Kingdom Viridiplantae. Emily Germain 1,2 Mentor Dr.
 Comparison and Analysis of Heat Shock Proteins in Organisms of the Kingdom Viridiplantae Emily Germain 1,2 Mentor Dr. Hugh Nicholas 3 1 Bioengineering & Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Department of Computational
Comparison and Analysis of Heat Shock Proteins in Organisms of the Kingdom Viridiplantae Emily Germain 1,2 Mentor Dr. Hugh Nicholas 3 1 Bioengineering & Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Department of Computational
Theory and Applications of Residual Dipolar Couplings in Biomolecular NMR
 Theory and Applications of Residual Dipolar Couplings in Biomolecular NMR Residual Dipolar Couplings (RDC s) Relatively new technique ~ 1996 Nico Tjandra, Ad Bax- NIH, Jim Prestegard, UGA Combination of
Theory and Applications of Residual Dipolar Couplings in Biomolecular NMR Residual Dipolar Couplings (RDC s) Relatively new technique ~ 1996 Nico Tjandra, Ad Bax- NIH, Jim Prestegard, UGA Combination of
Bioinformatics. Macromolecular structure
 Bioinformatics Macromolecular structure Contents Determination of protein structure Structure databases Secondary structure elements (SSE) Tertiary structure Structure analysis Structure alignment Domain
Bioinformatics Macromolecular structure Contents Determination of protein structure Structure databases Secondary structure elements (SSE) Tertiary structure Structure analysis Structure alignment Domain
Molecular modeling. A fragment sequence of 24 residues encompassing the region of interest of WT-
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Molecular dynamics Molecular modeling. A fragment sequence of 24 residues encompassing the region of interest of WT- KISS1R, i.e. the last intracellular domain (Figure S1a), has been
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Molecular dynamics Molecular modeling. A fragment sequence of 24 residues encompassing the region of interest of WT- KISS1R, i.e. the last intracellular domain (Figure S1a), has been
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Homology modeling of the XylS N-terminal domain Identification of template The analysis was based on XylS from Pseudomonas putida (SwissProt (Boeckmann et al. 2003) sequence entry
Supplementary Methods Homology modeling of the XylS N-terminal domain Identification of template The analysis was based on XylS from Pseudomonas putida (SwissProt (Boeckmann et al. 2003) sequence entry
Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently become
 Homology Modeling and Docking of Melatonin Receptors Andrew Kohlway, UMBC Jeffry D. Madura, Duquesne University 6/18/04 INTRODUCTION Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently
Homology Modeling and Docking of Melatonin Receptors Andrew Kohlway, UMBC Jeffry D. Madura, Duquesne University 6/18/04 INTRODUCTION Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently
Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor
 Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor Presented by Stephanie Lee Research Mentor: Dr. Rob Coalson Glycine Alpha 1 Receptor (GlyRa1) Member of the superfamily
Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor Presented by Stephanie Lee Research Mentor: Dr. Rob Coalson Glycine Alpha 1 Receptor (GlyRa1) Member of the superfamily
Better Bond Angles in the Protein Data Bank
 Better Bond Angles in the Protein Data Bank C.J. Robinson and D.B. Skillicorn School of Computing Queen s University {robinson,skill}@cs.queensu.ca Abstract The Protein Data Bank (PDB) contains, at least
Better Bond Angles in the Protein Data Bank C.J. Robinson and D.B. Skillicorn School of Computing Queen s University {robinson,skill}@cs.queensu.ca Abstract The Protein Data Bank (PDB) contains, at least
Gürol M. Süel, Steve W. Lockless, Mark A. Wall, and Rama Ra
 Gürol M. Süel, Steve W. Lockless, Mark A. Wall, and Rama Ranganathan, Evolutionarily conserved networks of residues mediate allosteric communication in proteins, Nature Structural Biology, vol. 10, no.
Gürol M. Süel, Steve W. Lockless, Mark A. Wall, and Rama Ranganathan, Evolutionarily conserved networks of residues mediate allosteric communication in proteins, Nature Structural Biology, vol. 10, no.
Tools for Cryo-EM Map Fitting. Paul Emsley MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
 Tools for Cryo-EM Map Fitting Paul Emsley MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology April 2017 Cryo-EM model-building typically need to move more atoms that one does for crystallography the maps are lower resolution
Tools for Cryo-EM Map Fitting Paul Emsley MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology April 2017 Cryo-EM model-building typically need to move more atoms that one does for crystallography the maps are lower resolution
Can a continuum solvent model reproduce the free energy landscape of a β-hairpin folding in water?
 Can a continuum solvent model reproduce the free energy landscape of a β-hairpin folding in water? Ruhong Zhou 1 and Bruce J. Berne 2 1 IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center; and 2 Department of Chemistry,
Can a continuum solvent model reproduce the free energy landscape of a β-hairpin folding in water? Ruhong Zhou 1 and Bruce J. Berne 2 1 IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center; and 2 Department of Chemistry,
COMP 598 Advanced Computational Biology Methods & Research. Introduction. Jérôme Waldispühl School of Computer Science McGill University
 COMP 598 Advanced Computational Biology Methods & Research Introduction Jérôme Waldispühl School of Computer Science McGill University General informations (1) Office hours: by appointment Office: TR3018
COMP 598 Advanced Computational Biology Methods & Research Introduction Jérôme Waldispühl School of Computer Science McGill University General informations (1) Office hours: by appointment Office: TR3018
Modeling for 3D structure prediction
 Modeling for 3D structure prediction What is a predicted structure? A structure that is constructed using as the sole source of information data obtained from computer based data-mining. However, mixing
Modeling for 3D structure prediction What is a predicted structure? A structure that is constructed using as the sole source of information data obtained from computer based data-mining. However, mixing
Chapter 5. Proteomics and the analysis of protein sequence Ⅱ
 Proteomics Chapter 5. Proteomics and the analysis of protein sequence Ⅱ 1 Pairwise similarity searching (1) Figure 5.5: manual alignment One of the amino acids in the top sequence has no equivalent and
Proteomics Chapter 5. Proteomics and the analysis of protein sequence Ⅱ 1 Pairwise similarity searching (1) Figure 5.5: manual alignment One of the amino acids in the top sequence has no equivalent and
Rex-Family Repressor/NADH Complex
 Kasey Royer Michelle Lukosi Rex-Family Repressor/NADH Complex Part A The biological sensing protein that we selected is the Rex-family repressor/nadh complex. We chose this sensor because it is a calcium
Kasey Royer Michelle Lukosi Rex-Family Repressor/NADH Complex Part A The biological sensing protein that we selected is the Rex-family repressor/nadh complex. We chose this sensor because it is a calcium
Overview & Applications. T. Lezon Hands-on Workshop in Computational Biophysics Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center 04 June, 2015
 Overview & Applications T. Lezon Hands-on Workshop in Computational Biophysics Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center 4 June, 215 Simulations still take time Bakan et al. Bioinformatics 211. Coarse-grained Elastic
Overview & Applications T. Lezon Hands-on Workshop in Computational Biophysics Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center 4 June, 215 Simulations still take time Bakan et al. Bioinformatics 211. Coarse-grained Elastic
Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Biomedical Informatics II. Hidden Markov Model for Biological Sequences
 Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Biomedical Informatics II. Hidden Markov Model for Biological Sequences Jianlin Cheng, PhD William and Nancy Thompson Missouri Distinguished Professor Department
Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Biomedical Informatics II. Hidden Markov Model for Biological Sequences Jianlin Cheng, PhD William and Nancy Thompson Missouri Distinguished Professor Department
A bioinformatics approach to the structural and functional analysis of the glycogen phosphorylase protein family
 A bioinformatics approach to the structural and functional analysis of the glycogen phosphorylase protein family Jieming Shen 1,2 and Hugh B. Nicholas, Jr. 3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer
A bioinformatics approach to the structural and functional analysis of the glycogen phosphorylase protein family Jieming Shen 1,2 and Hugh B. Nicholas, Jr. 3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer
Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics IV. Neural Network & Deep Learning Applications in Bioinformatics
 Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics IV. Neural Network & Deep Learning Applications in Bioinformatics Jianlin Cheng, PhD Department of Computer Science University of Missouri, Columbia
Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics IV. Neural Network & Deep Learning Applications in Bioinformatics Jianlin Cheng, PhD Department of Computer Science University of Missouri, Columbia
Protein Structure Determination
 Protein Structure Determination Given a protein sequence, determine its 3D structure 1 MIKLGIVMDP IANINIKKDS SFAMLLEAQR RGYELHYMEM GDLYLINGEA 51 RAHTRTLNVK QNYEEWFSFV GEQDLPLADL DVILMRKDPP FDTEFIYATY 101
Protein Structure Determination Given a protein sequence, determine its 3D structure 1 MIKLGIVMDP IANINIKKDS SFAMLLEAQR RGYELHYMEM GDLYLINGEA 51 RAHTRTLNVK QNYEEWFSFV GEQDLPLADL DVILMRKDPP FDTEFIYATY 101
Focus on PNA Flexibility and RNA Binding using Molecular Dynamics and Metadynamics
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Focus on PNA Flexibility and RNA Binding using Molecular Dynamics and Metadynamics Massimiliano Donato Verona 1, Vincenzo Verdolino 2,3,*, Ferruccio Palazzesi 2,3, and Roberto
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Focus on PNA Flexibility and RNA Binding using Molecular Dynamics and Metadynamics Massimiliano Donato Verona 1, Vincenzo Verdolino 2,3,*, Ferruccio Palazzesi 2,3, and Roberto
GC and CELPP: Workflows and Insights
 GC and CELPP: Workflows and Insights Xianjin Xu, Zhiwei Ma, Rui Duan, Xiaoqin Zou Dalton Cardiovascular Research Center, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Department of Biochemistry, & Informatics Institute
GC and CELPP: Workflows and Insights Xianjin Xu, Zhiwei Ma, Rui Duan, Xiaoqin Zou Dalton Cardiovascular Research Center, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Department of Biochemistry, & Informatics Institute
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Supplementary material and methods:
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Supplementary material and methods: - Computational
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Supplementary material and methods: - Computational
CMPS 6630: Introduction to Computational Biology and Bioinformatics. Tertiary Structure Prediction
 CMPS 6630: Introduction to Computational Biology and Bioinformatics Tertiary Structure Prediction Tertiary Structure Prediction Why Should Tertiary Structure Prediction Be Possible? Molecules obey the
CMPS 6630: Introduction to Computational Biology and Bioinformatics Tertiary Structure Prediction Tertiary Structure Prediction Why Should Tertiary Structure Prediction Be Possible? Molecules obey the
Introduction to Computational Structural Biology
 Introduction to Computational Structural Biology Part I 1. Introduction The disciplinary character of Computational Structural Biology The mathematical background required and the topics covered Bibliography
Introduction to Computational Structural Biology Part I 1. Introduction The disciplinary character of Computational Structural Biology The mathematical background required and the topics covered Bibliography
Protein Secondary Structure Prediction
 Protein Secondary Structure Prediction Doug Brutlag & Scott C. Schmidler Overview Goals and problem definition Existing approaches Classic methods Recent successful approaches Evaluating prediction algorithms
Protein Secondary Structure Prediction Doug Brutlag & Scott C. Schmidler Overview Goals and problem definition Existing approaches Classic methods Recent successful approaches Evaluating prediction algorithms
MBLG lecture 5. The EGG! Visualising Molecules. Dr. Dale Hancock Lab 715
 MBLG lecture 5 Dr. Dale Hancock D.Hancock@mmb.usyd.edu.au Lab 715 The EGG! Visualising Molecules In molecular biology and biochemistry it is better to view molecules as killer pythons rather than smarties.
MBLG lecture 5 Dr. Dale Hancock D.Hancock@mmb.usyd.edu.au Lab 715 The EGG! Visualising Molecules In molecular biology and biochemistry it is better to view molecules as killer pythons rather than smarties.
Bioengineering 215. An Introduction to Molecular Dynamics for Biomolecules
 Bioengineering 215 An Introduction to Molecular Dynamics for Biomolecules David Parker May 18, 2007 ntroduction A principal tool to study biological molecules is molecular dynamics simulations (MD). MD
Bioengineering 215 An Introduction to Molecular Dynamics for Biomolecules David Parker May 18, 2007 ntroduction A principal tool to study biological molecules is molecular dynamics simulations (MD). MD
Protein Structure Prediction
 Protein Structure Prediction Michael Feig MMTSB/CTBP 2006 Summer Workshop From Sequence to Structure SEALGDTIVKNA Ab initio Structure Prediction Protocol Amino Acid Sequence Conformational Sampling to
Protein Structure Prediction Michael Feig MMTSB/CTBP 2006 Summer Workshop From Sequence to Structure SEALGDTIVKNA Ab initio Structure Prediction Protocol Amino Acid Sequence Conformational Sampling to
Protein Structures: Experiments and Modeling. Patrice Koehl
 Protein Structures: Experiments and Modeling Patrice Koehl Structural Bioinformatics: Proteins Proteins: Sources of Structure Information Proteins: Homology Modeling Proteins: Ab initio prediction Proteins:
Protein Structures: Experiments and Modeling Patrice Koehl Structural Bioinformatics: Proteins Proteins: Sources of Structure Information Proteins: Homology Modeling Proteins: Ab initio prediction Proteins:
Examples of Protein Modeling. Protein Modeling. Primary Structure. Protein Structure Description. Protein Sequence Sources. Importing Sequences to MOE
 Examples of Protein Modeling Protein Modeling Visualization Examination of an experimental structure to gain insight about a research question Dynamics To examine the dynamics of protein structures To
Examples of Protein Modeling Protein Modeling Visualization Examination of an experimental structure to gain insight about a research question Dynamics To examine the dynamics of protein structures To
Protein Structures. Sequences of amino acid residues 20 different amino acids. Quaternary. Primary. Tertiary. Secondary. 10/8/2002 Lecture 12 1
 Protein Structures Sequences of amino acid residues 20 different amino acids Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary 10/8/2002 Lecture 12 1 Angles φ and ψ in the polypeptide chain 10/8/2002 Lecture 12 2
Protein Structures Sequences of amino acid residues 20 different amino acids Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary 10/8/2002 Lecture 12 1 Angles φ and ψ in the polypeptide chain 10/8/2002 Lecture 12 2
Molecular Modeling lecture 2
 Molecular Modeling 2018 -- lecture 2 Topics 1. Secondary structure 3. Sequence similarity and homology 2. Secondary structure prediction 4. Where do protein structures come from? X-ray crystallography
Molecular Modeling 2018 -- lecture 2 Topics 1. Secondary structure 3. Sequence similarity and homology 2. Secondary structure prediction 4. Where do protein structures come from? X-ray crystallography
Can protein model accuracy be. identified? NO! CBS, BioCentrum, Morten Nielsen, DTU
 Can protein model accuracy be identified? Morten Nielsen, CBS, BioCentrum, DTU NO! Identification of Protein-model accuracy Why is it important? What is accuracy RMSD, fraction correct, Protein model correctness/quality
Can protein model accuracy be identified? Morten Nielsen, CBS, BioCentrum, DTU NO! Identification of Protein-model accuracy Why is it important? What is accuracy RMSD, fraction correct, Protein model correctness/quality
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/309/5742/1868/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Toward High-Resolution de Novo Structure Prediction for Small Proteins Philip Bradley, Kira M. S. Misura, David Baker*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/309/5742/1868/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Toward High-Resolution de Novo Structure Prediction for Small Proteins Philip Bradley, Kira M. S. Misura, David Baker*
Protein Structure Prediction
 Page 1 Protein Structure Prediction Russ B. Altman BMI 214 CS 274 Protein Folding is different from structure prediction --Folding is concerned with the process of taking the 3D shape, usually based on
Page 1 Protein Structure Prediction Russ B. Altman BMI 214 CS 274 Protein Folding is different from structure prediction --Folding is concerned with the process of taking the 3D shape, usually based on
Tu 1,*, , Sweden
 Supplementary Material Computational studiess of the binding profile of phosphoinositide PtdIns(,4,5)P with the pleckstrin homology domain d of an oomycetee cellulose synthase Guanglin Kuang 1, Vincent
Supplementary Material Computational studiess of the binding profile of phosphoinositide PtdIns(,4,5)P with the pleckstrin homology domain d of an oomycetee cellulose synthase Guanglin Kuang 1, Vincent
Protein Structure: Data Bases and Classification Ingo Ruczinski
 Protein Structure: Data Bases and Classification Ingo Ruczinski Department of Biostatistics, Johns Hopkins University Reference Bourne and Weissig Structural Bioinformatics Wiley, 2003 More References
Protein Structure: Data Bases and Classification Ingo Ruczinski Department of Biostatistics, Johns Hopkins University Reference Bourne and Weissig Structural Bioinformatics Wiley, 2003 More References
Optimization and Frustration:
 Optimization and Frustration: The Dynamical Lattice Model of Proteins Sigismund Kobe and Frank Dressel Institut für Theoretische Physik, Technische Universität Dresden, D 01062 Dresden, Germany (http://www.physik.tu-dresden.de/~fdressel/dlm-main.html)
Optimization and Frustration: The Dynamical Lattice Model of Proteins Sigismund Kobe and Frank Dressel Institut für Theoretische Physik, Technische Universität Dresden, D 01062 Dresden, Germany (http://www.physik.tu-dresden.de/~fdressel/dlm-main.html)
Accurate prediction for atomic-level protein design and its application in diversifying the near-optimal sequence space
 Accurate prediction for atomic-level protein design and its application in diversifying the near-optimal sequence space Pablo Gainza CPS 296: Topics in Computational Structural Biology Department of Computer
Accurate prediction for atomic-level protein design and its application in diversifying the near-optimal sequence space Pablo Gainza CPS 296: Topics in Computational Structural Biology Department of Computer
Detection of Protein Binding Sites II
 Detection of Protein Binding Sites II Goal: Given a protein structure, predict where a ligand might bind Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University CS597A, Fall 2007 1hld Geometric, chemical, evolutionary
Detection of Protein Binding Sites II Goal: Given a protein structure, predict where a ligand might bind Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University CS597A, Fall 2007 1hld Geometric, chemical, evolutionary
Bayesian Inference of Protein and Domain Interactions Using The Sum-Product Algorithm
 Bayesian Inference of Protein and Domain Interactions Using The Sum-Product Algorithm Marcin Sikora, Faruck Morcos, Daniel J. Costello, Jr., and Jesús A. Izaguirre Department of Electrical Engineering,
Bayesian Inference of Protein and Domain Interactions Using The Sum-Product Algorithm Marcin Sikora, Faruck Morcos, Daniel J. Costello, Jr., and Jesús A. Izaguirre Department of Electrical Engineering,
Homology Modeling (Comparative Structure Modeling) GBCB 5874: Problem Solving in GBCB
 Homology Modeling (Comparative Structure Modeling) Aims of Structural Genomics High-throughput 3D structure determination and analysis To determine or predict the 3D structures of all the proteins encoded
Homology Modeling (Comparative Structure Modeling) Aims of Structural Genomics High-throughput 3D structure determination and analysis To determine or predict the 3D structures of all the proteins encoded
Protein Structure Prediction
 Protein Structure Prediction Michael Feig MMTSB/CTBP 2009 Summer Workshop From Sequence to Structure SEALGDTIVKNA Folding with All-Atom Models AAQAAAAQAAAAQAA All-atom MD in general not succesful for real
Protein Structure Prediction Michael Feig MMTSB/CTBP 2009 Summer Workshop From Sequence to Structure SEALGDTIVKNA Folding with All-Atom Models AAQAAAAQAAAAQAA All-atom MD in general not succesful for real
CMPS 3110: Bioinformatics. Tertiary Structure Prediction
 CMPS 3110: Bioinformatics Tertiary Structure Prediction Tertiary Structure Prediction Why Should Tertiary Structure Prediction Be Possible? Molecules obey the laws of physics! Conformation space is finite
CMPS 3110: Bioinformatics Tertiary Structure Prediction Tertiary Structure Prediction Why Should Tertiary Structure Prediction Be Possible? Molecules obey the laws of physics! Conformation space is finite
Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings. Bioinformatics (Lec 12)
 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 2/17/05 1 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 2/17/05 2 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 2/17/05 3 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings
Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 2/17/05 1 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 2/17/05 2 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 2/17/05 3 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings
Protein structure prediction. CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 10 and 12, 2017 Ron Dror
 Protein structure prediction CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 10 and 12, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Why predict protein structure? Can we use (pure) physics-based methods? Knowledge-based methods Two major
Protein structure prediction CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 10 and 12, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Why predict protein structure? Can we use (pure) physics-based methods? Knowledge-based methods Two major
Medical Research, Medicinal Chemistry, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium.
 Supporting Information Towards peptide vaccines against Zika virus: Immunoinformatics combined with molecular dynamics simulations to predict antigenic epitopes of Zika viral proteins Muhammad Usman Mirza
Supporting Information Towards peptide vaccines against Zika virus: Immunoinformatics combined with molecular dynamics simulations to predict antigenic epitopes of Zika viral proteins Muhammad Usman Mirza
Analysis and Prediction of Protein Structure (I)
 Analysis and Prediction of Protein Structure (I) Jianlin Cheng, PhD School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Central Florida 2006 Free for academic use. Copyright @ Jianlin Cheng
Analysis and Prediction of Protein Structure (I) Jianlin Cheng, PhD School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Central Florida 2006 Free for academic use. Copyright @ Jianlin Cheng
