Nomenclature what s in a name? Read Payne 2016
|
|
|
- Annabella Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 xx Nomenclature what s in a name? Read Payne 2016
2 xx Nomenclature Cypripedium reginae Cypripedium hirsutum what s in a name? Cypripedium spectabile showy lady s-slipper queen lady s-slipper
3 Nomenclature - Using Names Two of the goals for Systematics: 1. Identify and name species 2. Classify or place the species in groups Plantae Magnoliophyta Liliopsida Asparagales Orchidaceae Cypripedium Cypripedium acaule Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Hierarchical classification Cypripedium acaule Stemless lady slipper
4 Nomenclature - Using Names Latin is a language as dead as dead can be. First it killed the Romans, and now its killing me! (previous Botany student)
5 Common Names Advantages? descriptive, colorful easy to remember only names for most people Disadvantages? one species = many common names Moccasin flower Pink lady s slipper Stemless lady s slipper
6 Common Names 15 names in English 44 in French 81 in Dutch 105 in German 245 common names but only 1 Latin name Nymphaea alba L. European white waterlily
7 Common Names Advantages? descriptive, colorful easy to remember only names for most people Disadvantages? one species = many common names one common name = 2+ species e.g., fireweed Chamerion evening primrose family Erectites aster family
8 Common Names Advantages? descriptive, colorful easy to remember only names for most people Disadvantages? one species = many common names one common name = 2+ species e.g., loosestrife Lythrum loosestrife family Lysimachia primrose family
9 Common Names Advantages? descriptive, colorful easy to remember only names for most people Disadvantages? one species = many common names one name = 2+ species names can be confusing Sweet fern (not a fern!)
10 Common Names Advantages? descriptive, colorful easy to remember only names for most people Disadvantages? one species = many common names one name = 2+ species names can be confusing Pineapple (not a conifer or apple!)
11 Common Names Advantages? descriptive, colorful easy to remember only names for most people Disadvantages? one species = many common names one name = 2+ species names can be confusing Welcome-home-husband-nomatter-how-drunk-ye-be (also called Hen & chicks)
12 Common Names Advantages? descriptive, colorful easy to remember only names for most people Disadvantages? one species = many common names one name = 2+ species names can be confusing most plants have no common name? Buxbaum s sedge Carex buxbaumii
13 Scientific Names Necessary all species need names uniform system of naming to avoid confusion Carex buxbaumii Wahlenb.
14 Scientific Names Necessary all species need names uniform system of naming to avoid confusion facilitates information - retrieval Arabidopsis thaliana
15 Scientific Names Necessary all species need names uniform system of naming to avoid confusion facilitates information - retrieval International Code of Nomenclature for fungi, algae, and plants (ICN) adopted 2011 Melbourne
16 Scientific Names Descriptive! (at least some times) May-apple Podophyllum peltatum - umbrella foot leaf
17 Scientific Names Scientific names - why binomials? New Yorker Matthew Pace Serratula Botany 2015 foliis Ph.D. grad lanceolato oblongis serratis pendulis The species of Serratula with leaves oblong to lanceolate shaped, serrate edged, and drooping Carolus Linnaeus on a field trip - using polynomials describing the New York ironweed
18 Scientific Names Scientific names - why binomials? Serratula foliis lanceolato oblongis serratis pendulis The species of Serratula with leaves oblong to lanceolate shaped, serrate edged, and drooping Carolus Linnaeus on a field trip - using polynomials describing the New York ironweed
19 Scientific names - why binomials? Scientific Names binomial polynomial trivial name
20 Scientific names - why binomials? Scientific Names binomial polynomial Which would you rather learn? Serratula foliis lanceolato oblongis serratis pendulis or Serratula noveboracensis
21 Scientific Names The species name Species name = binomial (2 names): Serratula noveboracensis Genus name: Serratula capitalized italicized or underlined plural = genera Specific epithet or trivial name: noveboracensis not capitalized italicized or underlined Latin ending agrees in gender with genus name Serratula noveboracensis L.
22 The scientific name Scientific Names Scientific name = species name + authority: Serratula noveboracensis L. Species name: Serratula noveboracensis Serratula noveboracensis L. Authority: Linnaeus (abbreviated L. ) - the name of the person or persons who provided this binomial for this species
23 Synonyms - duplicate names Scientific Names French botanist Andre Michaux transfers New York ironweed to genus Vernonia Vernonia noveboracensis (L.) Michx. Serratula tinctoria L. Serratula noveboracensis L. Vernonia noveboracensis (L.) Michx. Authority = Michaux (came up with this binomial) Parenthetical authority = Linnaeus (first used the specific epithet for this species)
24 Because of synonomy - proliferation of scientific names - the type method is used to track names and lessen confusion Every species name must be linked to an herbarium specimen and deposited in an herbarium Holotype: the particular specimen designated by the author, which automatically fixes the application of the name ----type: other specimens to replace holotype when lost or unknown (e.g., syntype, neotype, lectotype, paratype) Type Method
25 Type Method The Berlin Herbarium 3 rd largest herbarium in the world lost over 20,000 holotypes in May 1944 due to Allied bombing Holotype: the particular specimen designated by the author, which automatically fixes the application of the name ----type: other specimens to replace holotype when lost or unknown
26 Melody and Kelsey think they collected a new species of Cannabis Type Method
27 Type Method Required steps in authoring a name for a putative new species of Cannabis: Find binomial not already taken Specific epithets occupied in Cannabis Cannabis americana Cannabis chinensis Cannabis erratica Cannabis foetens Cannabis generalis Cannabis gigantea Cannabis indica Cannabis intersita Cannabis kafiristanica Cannabis lupulus Cannabis macrosperma Cannabis ruderalis Cannabis sativa
28 Type Method Required steps in authoring a name for a putative new species of Cannabis: Find binomial not already taken Name after someone important? C. obamaei X X C. sytsmae Cannabis trumpii
29 Type Method Required steps in authoring a name for a putative new species of Cannabis: Find binomial not already taken Cannabis trumpii Sain & Huisman Make a type specimen & deposit in Wisconsin State Herbarium Sain & Huisman 3162 (WIS) Latin or English description of new species Publish in journal or visible paper product seen in libraries OR now electronically! = VALID species name, but not necessarily good or ACCEPTED species name!
30 Type Method Required steps in authoring a name for a putative new species of Cannabis: / Published = Accepted Specific epithets occupied in Cannabis Cannabis americana Cannabis chinensis Cannabis erratica Cannabis foetens Cannabis generalis Cannabis gigantea Cannabis indica Cannabis intersita Cannabis kafiristanica Cannabis lupulus Cannabis macrosperma Cannabis ruderalis Cannabis sativa only accepted Cannabis trumpii?
31 Type Method The type method means that there is a type specimen for every named species Canada goldenrod Solidago canadensis L. has a type specimen in the Linnean collection in London
32 Type Method The type method continues up the hierarchical system of classification! Canada goldenrod Solidago canadensis L. is the first named species of the genus Solidago the Linnean type specimen for the species is also the type specimen for the genus Solidago
33 Type Method Solidago belongs to family Asteraceae, typified by the genus Aster This herbarium specimen of Aster amellus also typifies the order Asterales and the subclass Asteridae Italian aster Aster amellus L. - type specimen from Linnaeus collection in London Aster amellus - type species of the genus Aster AND family Asteraceae
34 Aster renaming... and here the story gets messy! What if Aster is not natural? then only Aster amellus and relatives remain in genus Aster Italian aster Aster amellus L. - type specimen from Linnaeus collection in London
35 Aster renaming North American asters related to other North American genera Aster novae-angliae New England aster Italian aster related to other genera in Eurasia Aster amellus - aster
36 Aster renaming Erigeron - daisy fleabane Heterotheca - golden aster Grindelia - gumweed Solidago - goldenrod Aster amellus - aster Euthamia - grassleaved goldenrod
37 Aster renaming Aster novae-angliae L. (New England aster) = Symphyotrichum novaeangliae (L.) Nesom Confusion can be an issue with ICN rules of synonymy and ranks
38 Phylocode lessens confusion? Alternative nomenclatural code enacted in Paris, 2004 Rankless, only phylogenetic lineages or clades named above species level Therefore, no genus, family & therefore no binomial necessary More on this later... Kevin DeQueiroz & Phil Cantino 2 architects of the Phylocode
39 Rules of Botanical Nomenclature 1. Names based on nomenclatural types Species Genus Family etc.
40 Magnolia virginiana L. A special species from SE United States represents the type specimen for the phylum Magnoliophyta or flowering plants... as well as other groups in the hierarchy (Magnoliopsida, Magnoliidae, Magnoliales, Magnoliaceae, Magnolia) Type Method In this classification system, what species is the type for flowering plants?
41 Rules of Botanical Nomenclature Family names based on type genus: Magnoliaceae for Magnolia 8 families are allowed to keep old names not based on type method: Asteraceae Poaceae Brassicaceae Apiaceae Fabaceae Lamiaceae Clusiaceae Arecaceae Compositae Gramineae Cruciferae Umbelliferae Leguminosae Labiatae Guttiferae Palmae
42 Rules of Botanical Nomenclature 2. Only one accepted name for a taxonomic group: Vernonia noveboracensis (L.) Michx. Others are synonyms: Serratula noveboracensis L. Serratula noveboracensis L. Vernonia noveboracensis (L.) Michx.
43 Rules of Botanical Nomenclature 3. Names must be treated as Latin, but a lot of latitude! Allium Muilla by Sereno Watson
44 Rules of Botanical Nomenclature 4. Nomenclature based on rule of priority 1st published binomial for a species in a genus is the accepted name (starting point: Species Plantarum 1753)
45 Rules of Botanical Nomenclature 4. Nomenclature based on rule of priority 1st published binomial for a species in a genus is the accepted name (starting point: Species Plantarum 1753) Penstemon brachyanthus Bauhin 1688 Penstemon formosus Linnaeus 1753 Penstemon micranthus Nutt Penstemon procerus Gray 1835 Penstemon tolmiei Cronquist 1958
46 Rules of Botanical Nomenclature 5. Botanical nomenclature independent from zoological nomenclature Cecropia
47 Rules of Botanical Nomenclature 5. Botanical nomenclature independent from zoological nomenclature Pieris
48 Rules of Botanical Nomenclature 5. Botanical nomenclature independent from zoological nomenclature Anisoptera Anisoptera
49 Rules of Botanical Nomenclature 5. Botanical nomenclature independent from zoological nomenclature Anisoptera Mallotus
50 Rules of Botanical Nomenclature 5. Botanical nomenclature independent from zoological nomenclature Heliconia & Heliconius
What is this tree? Naming things. wapu'niaka'kwosêt
 What is this tree? Naming things wapu'niaka'kwosêt What is this tree? Naming things Wafer-ash Stinking-ash Hop-tree Ptelea trifoliata Rutaceae citrus family 1. Inventory earth s biota: Worldwide: 1.6 million
What is this tree? Naming things wapu'niaka'kwosêt What is this tree? Naming things Wafer-ash Stinking-ash Hop-tree Ptelea trifoliata Rutaceae citrus family 1. Inventory earth s biota: Worldwide: 1.6 million
Print Names and Classification
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 6-30-2006 Print Names and Classification Larry A. Sagers Utah State University Follow this and additional
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 6-30-2006 Print Names and Classification Larry A. Sagers Utah State University Follow this and additional
10/5/2016. Topic 03 The Code. I. Introduction. A. The International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (ICN) 1.
 Topic 03 The Code A. The International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (ICN) 1. What 1 A. The International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (ICN) 1. What 2. Main Goal
Topic 03 The Code A. The International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (ICN) 1. What 1 A. The International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (ICN) 1. What 2. Main Goal
APG for Dummies. BGEN Annual Conference Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh November 2010
 APG for Dummies BGEN Annual Conference Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh November 2010 A FEW DEFINITIONS: Angiosperms = the flowering plants Phylogenetics = the study of evolutionary relationships within
APG for Dummies BGEN Annual Conference Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh November 2010 A FEW DEFINITIONS: Angiosperms = the flowering plants Phylogenetics = the study of evolutionary relationships within
SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT
 SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY B1: Naming and classification of organisms Biology of Plants - Raven et al. 2005 pp. 219-237 INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY Taxonomy Naming Describing Classifying
SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY B1: Naming and classification of organisms Biology of Plants - Raven et al. 2005 pp. 219-237 INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY Taxonomy Naming Describing Classifying
The Classification of Plants and Other Organisms. Chapter 18
 The Classification of Plants and Other Organisms Chapter 18 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1 Define taxonomy Explain why the assignment of a scientific name to each species is important for biologists KEY TERMS TAXONOMY
The Classification of Plants and Other Organisms Chapter 18 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1 Define taxonomy Explain why the assignment of a scientific name to each species is important for biologists KEY TERMS TAXONOMY
Plant Systematics. What is Systematics? or Why Study Systematics? Botany 400. What is Systematics or Why Study Systematics?
 Plant Systematics Botany 400 http://botany.wisc.edu/courses/botany_400/ What is Systematics? or Why Kenneth J. Sytsma Melody Sain Kelsey Huisman Botany Department University of Wisconsin Pick up course
Plant Systematics Botany 400 http://botany.wisc.edu/courses/botany_400/ What is Systematics? or Why Kenneth J. Sytsma Melody Sain Kelsey Huisman Botany Department University of Wisconsin Pick up course
Plant Names and Classification
 Plant Names and Classification Science of Taxonomy Identification (necessary!!) Classification (order out of chaos!) Nomenclature (why not use common names?) Reasons NOT to use common names Theophrastus
Plant Names and Classification Science of Taxonomy Identification (necessary!!) Classification (order out of chaos!) Nomenclature (why not use common names?) Reasons NOT to use common names Theophrastus
Introduction to Biological Classification & Naming
 Introduction to Biological Classification & Naming A. Taxonomy 1. What is it? A. Taxonomy 1. What is it? Science of naming and classifying groups of organisms A. Taxonomy 1. What is it? Science of naming
Introduction to Biological Classification & Naming A. Taxonomy 1. What is it? A. Taxonomy 1. What is it? Science of naming and classifying groups of organisms A. Taxonomy 1. What is it? Science of naming
Biology Classification Unit 11. CLASSIFICATION: process of dividing organisms into groups with similar characteristics
 Biology Classification Unit 11 11:1 Classification and Taxonomy CLASSIFICATION: process of dividing organisms into groups with similar characteristics TAXONOMY: the science of classifying living things
Biology Classification Unit 11 11:1 Classification and Taxonomy CLASSIFICATION: process of dividing organisms into groups with similar characteristics TAXONOMY: the science of classifying living things
Biologists use a system of classification to organize information about the diversity of living things.
 Section 1: Biologists use a system of classification to organize information about the diversity of living things. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are
Section 1: Biologists use a system of classification to organize information about the diversity of living things. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are
The practice of naming and classifying organisms is called taxonomy.
 Chapter 18 Key Idea: Biologists use taxonomic systems to organize their knowledge of organisms. These systems attempt to provide consistent ways to name and categorize organisms. The practice of naming
Chapter 18 Key Idea: Biologists use taxonomic systems to organize their knowledge of organisms. These systems attempt to provide consistent ways to name and categorize organisms. The practice of naming
Taxonomy and Biodiversity
 Chapter 25/26 Taxonomy and Biodiversity Evolutionary biology The major goal of evolutionary biology is to reconstruct the history of life on earth Process: a- natural selection b- mechanisms that change
Chapter 25/26 Taxonomy and Biodiversity Evolutionary biology The major goal of evolutionary biology is to reconstruct the history of life on earth Process: a- natural selection b- mechanisms that change
Learning Outcome B1 13/10/2012. Student Achievement Indicators. Taxonomy: Scientific Classification. Student Achievement Indicators
 Classification of Living Organisms Learning Outcome B1 Learning Outcome B1 Apply the Kingdom System of classification to study the diversity of organisms. Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
Classification of Living Organisms Learning Outcome B1 Learning Outcome B1 Apply the Kingdom System of classification to study the diversity of organisms. Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
The name of a species consisted of a generic name (noun) followed by 1 or more Latin modifiers.
 Chapter 17 Naming and Organizing Plants and Microbes Botanical Nomenclature Nomenclature- the giving and using of names Historically, there have been two independent kinds of botanical nomenclature. 1)
Chapter 17 Naming and Organizing Plants and Microbes Botanical Nomenclature Nomenclature- the giving and using of names Historically, there have been two independent kinds of botanical nomenclature. 1)
The Living World. AIIMS,CBSE,AIPMT, AFMC,Bio.Tech & PMT, Contact : , Mail at :- by AKB
 The Living World Very Short Answer Questions 1. What does ICBN stand for? A: International Code for Botanical Nomenclature. 2. What is flora? A: It is a publication containing actual account of habitat,
The Living World Very Short Answer Questions 1. What does ICBN stand for? A: International Code for Botanical Nomenclature. 2. What is flora? A: It is a publication containing actual account of habitat,
Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food.
 Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food. Heterotrophs must get energy by eating autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food. Heterotrophs must get energy by eating autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
1. Most important plant families
 1. Alexey Shipunov Minot State University July 16, 2013 Outline Important details of plant construction 1 Important details of plant construction 2 3 Outline Important details of plant construction 1 Important
1. Alexey Shipunov Minot State University July 16, 2013 Outline Important details of plant construction 1 Important details of plant construction 2 3 Outline Important details of plant construction 1 Important
Classification of Organisms
 Classification of Organisms Main Idea *****Chapter 14***** Students should be able to: * Understand why a classification system is important * Understand that there are a variety of ways to classify organisms
Classification of Organisms Main Idea *****Chapter 14***** Students should be able to: * Understand why a classification system is important * Understand that there are a variety of ways to classify organisms
Dendrology FOR 320 Spring Semester 2013
 Dendrology FOR 320 Spring Semester 2013 Week 1; Wednesday Introductions - Instructor, TAs, Peer TAs Announcements: Handouts - Syllabus - go over this with class - Web Site -http://webpages.uidaho.edu/dtank/dendrology/dendrology_2013.html
Dendrology FOR 320 Spring Semester 2013 Week 1; Wednesday Introductions - Instructor, TAs, Peer TAs Announcements: Handouts - Syllabus - go over this with class - Web Site -http://webpages.uidaho.edu/dtank/dendrology/dendrology_2013.html
Zoology. Classification
 Zoology Zoology involves studying all aspects of organisms belonging to the animal kingdom taxonomy, animal physiology, comparative anatomy, and ecology. Our study of Zoology will be focused on the different
Zoology Zoology involves studying all aspects of organisms belonging to the animal kingdom taxonomy, animal physiology, comparative anatomy, and ecology. Our study of Zoology will be focused on the different
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
 CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS 1. Taxonomy The branch of biology that deals with the classification of living organisms About 1.8 million species of plants and animals have been identified. Some scientists
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS 1. Taxonomy The branch of biology that deals with the classification of living organisms About 1.8 million species of plants and animals have been identified. Some scientists
Biol 317: Plant Classification & Identification Summer 2012
 Biol 317: Plant Classification & Identification Summer 2012 Instructor: Ryan Miller Office: 408 Hitchcock Office hours: TTH 10-11am or by appointment Email: rjarekm@uw.edu Course website: http://courses.washington.edu/bot113/summer/
Biol 317: Plant Classification & Identification Summer 2012 Instructor: Ryan Miller Office: 408 Hitchcock Office hours: TTH 10-11am or by appointment Email: rjarekm@uw.edu Course website: http://courses.washington.edu/bot113/summer/
Regional Flora- Introduction to Plant Taxonomy. Plant taxonomy. Taxonomists use information about: -structure. -chemical composition.
 Regional Flora- Introduction to Plant Taxonomy Plant taxonomy Palynology Paleobotany Molecular Biology Morphology Anatomy Biochemistry Genetics Taxonomy Physiology Evolution Ecology Population Biology
Regional Flora- Introduction to Plant Taxonomy Plant taxonomy Palynology Paleobotany Molecular Biology Morphology Anatomy Biochemistry Genetics Taxonomy Physiology Evolution Ecology Population Biology
Where do species names come from?
 Where do species names come from? What is a binomial name? What does it mean? Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species Author, date A B C D species D Genus A B C Family 1 Conus geographus Linnaeus,
Where do species names come from? What is a binomial name? What does it mean? Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species Author, date A B C D species D Genus A B C Family 1 Conus geographus Linnaeus,
Chapter 17. Organizing Life's Diversity
 Chapter 17 Organizing Life's Diversity Key Concepts: Chapter 17 1. List the six kingdoms. 2. Our current system of classification was originally based on structures; scientists now base classification
Chapter 17 Organizing Life's Diversity Key Concepts: Chapter 17 1. List the six kingdoms. 2. Our current system of classification was originally based on structures; scientists now base classification
The Tree of Life. Phylogeny
 The Tree of Life Phylogeny Phylogenetics Phylogenetic trees illustrate the evolutionary relationships among groups of organisms, or among a family of related nucleic acid or protein sequences Each branch
The Tree of Life Phylogeny Phylogenetics Phylogenetic trees illustrate the evolutionary relationships among groups of organisms, or among a family of related nucleic acid or protein sequences Each branch
Botany 4 Herbalist. Part 2 Using the Key. How to Use the Keys
 Botany 4 Herbalist Part 2 Using the Key How to Use the Keys As can be seen in the reading, even though plant identification and classification can be very useful for a herbalist, many of the reforming
Botany 4 Herbalist Part 2 Using the Key How to Use the Keys As can be seen in the reading, even though plant identification and classification can be very useful for a herbalist, many of the reforming
Finding Order in Diversity
 Lesson Overview 18.1 Scientists have been trying to identify, name, and find order in the diversity of life for a long time. The first scientific system for naming and grouping organisms was set up long
Lesson Overview 18.1 Scientists have been trying to identify, name, and find order in the diversity of life for a long time. The first scientific system for naming and grouping organisms was set up long
Classification & Taxonomy
 Classification: classifying organisms into groups Taxonomy: naming organisms and groups of organisms These two generally go hand in hand, but keep in mind that you can put things into groups without naming
Classification: classifying organisms into groups Taxonomy: naming organisms and groups of organisms These two generally go hand in hand, but keep in mind that you can put things into groups without naming
Finding Order in Diversity
 Finding Order in Diversity Videos Scishow Taxonomy: https://youtu.be/f38bmgpcz_i Bozeman Taxonomy: https://youtu.be/tyl_8gv7rie Terms to Know 1. Radiometric Dating 12. Miller and Urey s 2. Geologic Time
Finding Order in Diversity Videos Scishow Taxonomy: https://youtu.be/f38bmgpcz_i Bozeman Taxonomy: https://youtu.be/tyl_8gv7rie Terms to Know 1. Radiometric Dating 12. Miller and Urey s 2. Geologic Time
Organizing Life on Earth
 Organizing Life on Earth Inquire: Organizing Life on Earth Overview Scientists continually obtain new information that helps to understand the evolutionary history of life on Earth. Each group of organisms
Organizing Life on Earth Inquire: Organizing Life on Earth Overview Scientists continually obtain new information that helps to understand the evolutionary history of life on Earth. Each group of organisms
Classification. copyright cmassengale
 Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are 13 billion known species of organisms This is only 5% of all organisms that ever lived!!!!! New organisms are still being found and identified 2 What is
Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are 13 billion known species of organisms This is only 5% of all organisms that ever lived!!!!! New organisms are still being found and identified 2 What is
First things first: What IS classification and WHY do we do it (or DO we)? How are living things classified? Classification Systems
 How are living things classified? Objective: Describe the system used today to classify organisms (including the seven levels of classification as well as scientific names) First things first: What IS
How are living things classified? Objective: Describe the system used today to classify organisms (including the seven levels of classification as well as scientific names) First things first: What IS
Unit Two: Biodiversity. Chapter 4
 Unit Two: Biodiversity Chapter 4 A. Classifying Living Things (Ch.4 - page 100) Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving ( changing ): new evidence is discovered laws and theories are tested and possibly
Unit Two: Biodiversity Chapter 4 A. Classifying Living Things (Ch.4 - page 100) Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving ( changing ): new evidence is discovered laws and theories are tested and possibly
Biogeography. Lecture 11
 Biogeography. Lecture 11 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University February 19, 2016 Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 11 February 19, 2016 1 / 14 Outline Taxonomy Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture
Biogeography. Lecture 11 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University February 19, 2016 Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 11 February 19, 2016 1 / 14 Outline Taxonomy Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture
Why do we classify things? Supermarket aisles Libraries Classes Teams/sports Members of a family Roads Cities Money
 Classification 1 2 I. Diversity of Life A) 13 billion known species of organisms B) This is only 5% of all organisms that ever lived!!!!! C) New organisms are still being found and identified Why do we
Classification 1 2 I. Diversity of Life A) 13 billion known species of organisms B) This is only 5% of all organisms that ever lived!!!!! C) New organisms are still being found and identified Why do we
9.3 Classification. Lesson Objectives. Vocabulary. Introduction. Linnaean Classification
 9.3 Classification Lesson Objectives Outline the Linnaean classification, and define binomial nomenclature. Describe phylogenetic classification, and explain how it differs from Linnaean classification.
9.3 Classification Lesson Objectives Outline the Linnaean classification, and define binomial nomenclature. Describe phylogenetic classification, and explain how it differs from Linnaean classification.
Master Gardeners. Plant Nomenclature. Developed by Steve Dubik. 1
 Master Gardeners Plant Nomenclature Developed by Steve Dubik sdubik@umd.edu Steve.dubik@montgomerycollege.edu 1 Plant classification Carl von Linne (a.k.a., Carlolus Linnaeus) (1707-1778) Binomial system
Master Gardeners Plant Nomenclature Developed by Steve Dubik sdubik@umd.edu Steve.dubik@montgomerycollege.edu 1 Plant classification Carl von Linne (a.k.a., Carlolus Linnaeus) (1707-1778) Binomial system
Biol 117/317; Summer Quarter
 Biol 117/317; Summer Quarter Instructor: Yaowu Yuan Office: 408 Hitchcock Office hour: by appointment Email: colreeze@u.washington.edu Course website: http://courses.washington.edu/bot113/summer/2008 Pat
Biol 117/317; Summer Quarter Instructor: Yaowu Yuan Office: 408 Hitchcock Office hour: by appointment Email: colreeze@u.washington.edu Course website: http://courses.washington.edu/bot113/summer/2008 Pat
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity Slide 2 of 26
 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity 2 of 26 Natural selection and other processes have led to a staggering diversity of organisms. Biologists have identified and named about 1.5 million species so far. They
18-1 Finding Order in Diversity 2 of 26 Natural selection and other processes have led to a staggering diversity of organisms. Biologists have identified and named about 1.5 million species so far. They
Carolus Linnaeus System for Classifying Organisms. Unit 3 Lesson 2
 Carolus Linnaeus System for Classifying Organisms Unit 3 Lesson 2 Students will be able to: Conclude some of the classification benefits and importance. Define what is meant by species. Describe the binomial
Carolus Linnaeus System for Classifying Organisms Unit 3 Lesson 2 Students will be able to: Conclude some of the classification benefits and importance. Define what is meant by species. Describe the binomial
Dendrology FOR 320 Spring Semester 2014
 Dendrology FOR 320 Spring Semester 2014 Week 1; Wednesday Introductions - Instructor, TAs, Peer TAs Announcements: Handouts - Syllabus - go over this with class - Web Site -http://webpages.uidaho.edu/dtank/dendrology/dendrology_2014.html
Dendrology FOR 320 Spring Semester 2014 Week 1; Wednesday Introductions - Instructor, TAs, Peer TAs Announcements: Handouts - Syllabus - go over this with class - Web Site -http://webpages.uidaho.edu/dtank/dendrology/dendrology_2014.html
8/23/2014. Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Taxonomy. Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms. It has two main purposes: to identify organisms to represent relationships among organisms
 Taxonomy Taxonomy Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms. It has two main purposes: to identify organisms to represent relationships among organisms Binomial Nomenclature Our present biological
Taxonomy Taxonomy Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms. It has two main purposes: to identify organisms to represent relationships among organisms Binomial Nomenclature Our present biological
Chapter 17A. Table of Contents. Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification. Section 2 How Biologists Classify Organisms
 Classification of Organisms Table of Contents Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification
Classification of Organisms Table of Contents Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification
Station 1. Explain how scientists use each item below to determine the evolutionary relationships among organisms. 1. Structural similarities:
 Station 1 Explain how scientists use each item below to determine the evolutionary relationships among organisms. 1. Structural similarities: 2. Breeding behavior: 3. Geographical distribution: 4. Chromosome
Station 1 Explain how scientists use each item below to determine the evolutionary relationships among organisms. 1. Structural similarities: 2. Breeding behavior: 3. Geographical distribution: 4. Chromosome
Classification of Living Things
 Classification of Living Things What is classification? Classification: putting things into orderly groups based on similar characteristics. Ways we classify things Supermarket aisles Libraries Classes
Classification of Living Things What is classification? Classification: putting things into orderly groups based on similar characteristics. Ways we classify things Supermarket aisles Libraries Classes
EMu: Taxonomy Document Version 1
 KE EMu Documentation EMu: Taxonomy Document Version 1 KE EMu Version 3.2 Copyright 1997-2006 KE Software Pty Ltd This work is copyright and may not be reproduced except in accordance with the provisions
KE EMu Documentation EMu: Taxonomy Document Version 1 KE EMu Version 3.2 Copyright 1997-2006 KE Software Pty Ltd This work is copyright and may not be reproduced except in accordance with the provisions
Diatom nomenclatural rules and best practices
 Diatom nomenclatural rules and best practices Jana Veselá, Chelsea R. Smith & Marina G. Potapova Diatom Herbarium Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University 1900 Benjamin Franklin Parkway, Philadelphia,
Diatom nomenclatural rules and best practices Jana Veselá, Chelsea R. Smith & Marina G. Potapova Diatom Herbarium Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University 1900 Benjamin Franklin Parkway, Philadelphia,
What is taxonomy? Taxonomy is the grouping and naming of organisms. Biologists who study this are called taxonomists
 Taxonomy What is taxonomy? Taxonomy is the grouping and naming of organisms Biologists who study this are called taxonomists How did it start? People wanted to organize their world so they began grouping,
Taxonomy What is taxonomy? Taxonomy is the grouping and naming of organisms Biologists who study this are called taxonomists How did it start? People wanted to organize their world so they began grouping,
CLASSIFICATION. Why Classify? 2/18/2013. History of Taxonomy Biodiversity: variety of organisms at all levels from populations to ecosystems.
 Why Classify? Classification has been around ever since people paid attention to organisms. CLASSIFICATION One primeval system was based on harmful and non-harmful organisms. Life is easier when we organize
Why Classify? Classification has been around ever since people paid attention to organisms. CLASSIFICATION One primeval system was based on harmful and non-harmful organisms. Life is easier when we organize
ANY TAXONOMIC ENTITY WITHIN RANK
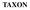 TAXON TAXONOMIC TAXON AP ANY TAXONOMIC ENTITY WITHIN RANK TAXONOMIC TAXON RANK VS TAXON APPLIED RANK VS TAXON D APPLIED PROKARYOTES PROKARYOTES PHYLOGENTIC TREE FIRST CELL EUKARYOTES DOMAIN RANK 3 PROKARYOTES
TAXON TAXONOMIC TAXON AP ANY TAXONOMIC ENTITY WITHIN RANK TAXONOMIC TAXON RANK VS TAXON APPLIED RANK VS TAXON D APPLIED PROKARYOTES PROKARYOTES PHYLOGENTIC TREE FIRST CELL EUKARYOTES DOMAIN RANK 3 PROKARYOTES
Classification Systems. Classification is just a fancy word for organization. So this chapter is equivalent to Biology cleaning its room!
 Classification Systems Classification is just a fancy word for organization. So this chapter is equivalent to Biology cleaning its room! A Vast Science Biology, the study of life, is no simple science.
Classification Systems Classification is just a fancy word for organization. So this chapter is equivalent to Biology cleaning its room! A Vast Science Biology, the study of life, is no simple science.
Classification. Species of Organisms. What is Classification?
 Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are known species of organisms This is organisms that ever lived!!!!! are still being found and identified 2 What is Classification? is the arrangement of organisms
Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are known species of organisms This is organisms that ever lived!!!!! are still being found and identified 2 What is Classification? is the arrangement of organisms
Botanical Nomenclature
 Botanical Nomenclature International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN) until 2010 International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants from 2011 1 Naming Plants Phrase name: a plant name
Botanical Nomenclature International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN) until 2010 International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants from 2011 1 Naming Plants Phrase name: a plant name
Finding Order in Diversity
 Finding Order in Diversity Key Questions What are the goals of binomial nomenclature and systematics? How did Linnaeus group species into larger taxa? Vocabulary binomial nomenclature genus systematics
Finding Order in Diversity Key Questions What are the goals of binomial nomenclature and systematics? How did Linnaeus group species into larger taxa? Vocabulary binomial nomenclature genus systematics
TAXONOMY. The Science of Classifying Organisms. Chapter 18
 TAXONOMY The Science of Classifying Organisms Chapter 18 Why do we need to classify? Imagine a store..how do you know where to find the milk or the cereal? Are they in the same aisle? How is the store
TAXONOMY The Science of Classifying Organisms Chapter 18 Why do we need to classify? Imagine a store..how do you know where to find the milk or the cereal? Are they in the same aisle? How is the store
Cladograms. A diagram that shows evolutionary relationships
 Cladograms A diagram that shows evolutionary relationships TAXONOMY The Science of Classifying Organisms Why do we need to classify? Imagine a store..how do you know where to find the milk or the cereal?
Cladograms A diagram that shows evolutionary relationships TAXONOMY The Science of Classifying Organisms Why do we need to classify? Imagine a store..how do you know where to find the milk or the cereal?
The Language of Horticulture
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 6-30-2002 The Language of Horticulture Larry A. Sagers Utah State University Follow this and additional
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 6-30-2002 The Language of Horticulture Larry A. Sagers Utah State University Follow this and additional
Class XI Chapter 1 The Living World Biology
 Question 1: Why are living organisms classified? A large variety of plants, animals, and microbes are found on earth. All these living organisms differ in size, shape, colour, habitat, and many other characteristics.
Question 1: Why are living organisms classified? A large variety of plants, animals, and microbes are found on earth. All these living organisms differ in size, shape, colour, habitat, and many other characteristics.
CHAPTER 10 Taxonomy and Phylogeny of Animals
 CHAPTER 10 Taxonomy and Phylogeny of Animals 10-1 10-2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Linnaeus and Taxonomy More than 1.5 million species of
CHAPTER 10 Taxonomy and Phylogeny of Animals 10-1 10-2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Linnaeus and Taxonomy More than 1.5 million species of
 Question 1: Why are living organisms classified? A large variety of plants, animals, and microbes are found on earth. All these living organisms differ in size, shape, colour, habitat, and many other characteristics.
Question 1: Why are living organisms classified? A large variety of plants, animals, and microbes are found on earth. All these living organisms differ in size, shape, colour, habitat, and many other characteristics.
Organizing Life s Diversity Section 17.1 Classification
 Organizing Life s Diversity Section 17.1 Classification Scan Section 1 of your book. Write three questions that come to mind from reading the headings and the illustration captions. 1. 2. 3. Review species
Organizing Life s Diversity Section 17.1 Classification Scan Section 1 of your book. Write three questions that come to mind from reading the headings and the illustration captions. 1. 2. 3. Review species
CLASS XI BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 1: LIVING WORLD
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 1: LIVING WORLD Biology is the science of life forms and non-living processes. The living world comprises an amazing diversity of living organisms. In order to facilitate
CLASS XI BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 1: LIVING WORLD Biology is the science of life forms and non-living processes. The living world comprises an amazing diversity of living organisms. In order to facilitate
TAXONOMY. The Science of Classifying Organisms
 TAXONOMY The Science of Classifying Organisms Why do we need to classify? Imagine a store..how do you know where to find the milk or the cereal? Are they in the same aisle? How is the store organized?
TAXONOMY The Science of Classifying Organisms Why do we need to classify? Imagine a store..how do you know where to find the milk or the cereal? Are they in the same aisle? How is the store organized?
How are living things classified?
 Classification Systems How are living things classified?! Learning Goals 12, 13, 14, 15 & 16 on your rubric! TAXONOMY: The study of classification, or how living things are grouped! Aristotle classified
Classification Systems How are living things classified?! Learning Goals 12, 13, 14, 15 & 16 on your rubric! TAXONOMY: The study of classification, or how living things are grouped! Aristotle classified
Classification of Living Things Ch.11 Notes
 Classification of Living Things Ch.11 Notes Why do we classify things?! Supermarket aisles! Libraries! Classes! Teams/sports! Members of a family! Roads! Cities! Money What is classification?! Classification:
Classification of Living Things Ch.11 Notes Why do we classify things?! Supermarket aisles! Libraries! Classes! Teams/sports! Members of a family! Roads! Cities! Money What is classification?! Classification:
Need for systematics. Applications of systematics. Linnaeus plus Darwin. Approaches in systematics. Principles of cladistics
 Topics Need for systematics Applications of systematics Linnaeus plus Darwin Approaches in systematics Principles of cladistics Systematics pp. 474-475. Systematics - Study of diversity and evolutionary
Topics Need for systematics Applications of systematics Linnaeus plus Darwin Approaches in systematics Principles of cladistics Systematics pp. 474-475. Systematics - Study of diversity and evolutionary
Using Trees for Classifications. Introduction
 Using Trees for Classifications The Phylogenetic Cibele Caio Principles and Practice of Phylogenetic Systematics, Spring 2009 Introduction The impusle to characterize and classify species Ancient Aristoteles
Using Trees for Classifications The Phylogenetic Cibele Caio Principles and Practice of Phylogenetic Systematics, Spring 2009 Introduction The impusle to characterize and classify species Ancient Aristoteles
Horticulture in Florida
 Horticulture in Florida Science, Mathematics, and Language Arts Brief Description: Students will determine the different characteristics used for grouping and naming plants with common and scientific names.
Horticulture in Florida Science, Mathematics, and Language Arts Brief Description: Students will determine the different characteristics used for grouping and naming plants with common and scientific names.
TAXONOMY. The Science of Classifying Organisms
 TAXONOMY The Science of Classifying Organisms Why do we need to classify? Imagine a store..how do you know where to find the milk or the cereal? Are they in the same aisle? How is the store organized?
TAXONOMY The Science of Classifying Organisms Why do we need to classify? Imagine a store..how do you know where to find the milk or the cereal? Are they in the same aisle? How is the store organized?
Higher National Unit specification. General information for centres. Plant Classification and Systematics. Unit code: F1MR 35
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Plant Classification and Systematics Unit code: F1MR 35 Unit purpose: An appreciation of the diversity of plants is a fundamental
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Plant Classification and Systematics Unit code: F1MR 35 Unit purpose: An appreciation of the diversity of plants is a fundamental
Taxonomy Lab: An exercise in taxonomy, evolution, and classification, Interdisciplinary... Introduction. Background. The Role of Taxonomy
 Page 1 of 5 Introduction We use this lab in Patterns and Processes, Evolution of Past & Present Ecosystems, and Tropical Marine Ecology. This exercise illustrates the creativity involved in taxonomy and
Page 1 of 5 Introduction We use this lab in Patterns and Processes, Evolution of Past & Present Ecosystems, and Tropical Marine Ecology. This exercise illustrates the creativity involved in taxonomy and
Background: Why Is Taxonomy Important?
 Background: Why Is Taxonomy Important? Taxonomy is the system of classifying, or organizing, living organisms into a system based on their similarities and differences. Imagine you are a scientist who
Background: Why Is Taxonomy Important? Taxonomy is the system of classifying, or organizing, living organisms into a system based on their similarities and differences. Imagine you are a scientist who
The Road to the Six Kingdoms
 Bio 2201 Unit 2 The Road to the Six Kingdoms A 2011study estimated there are about 8.6 million species on earth. Only 1.8 million species have been identified and named. *Chromista is a sub-kingdom group
Bio 2201 Unit 2 The Road to the Six Kingdoms A 2011study estimated there are about 8.6 million species on earth. Only 1.8 million species have been identified and named. *Chromista is a sub-kingdom group
BIOL 325 Plant Systematics Sample Topics & Questions for Exam 1 This document and questions are the copyright of CRHardy, 2016 onwards.
 BIOL 325 Plant Systematics Name: Sample Topics & Questions for Exam 1 This document and questions are the copyright of CRHardy, 2016 onwards. Topic 01 Introduction, Sample Topics & Questions: 1. What major
BIOL 325 Plant Systematics Name: Sample Topics & Questions for Exam 1 This document and questions are the copyright of CRHardy, 2016 onwards. Topic 01 Introduction, Sample Topics & Questions: 1. What major
Chapter 26. Phylogeny and the Tree of Life. Lecture Presentations by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Lecture Presentations by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Investigating the Tree of Life Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a species or group of
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Lecture Presentations by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Investigating the Tree of Life Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a species or group of
Concept Modern Taxonomy reflects evolutionary history.
 Concept 15.4 Modern Taxonomy reflects evolutionary history. What is Taxonomy: identification, naming, and classification of species. Common Names: can cause confusion - May refer to several species (ex.
Concept 15.4 Modern Taxonomy reflects evolutionary history. What is Taxonomy: identification, naming, and classification of species. Common Names: can cause confusion - May refer to several species (ex.
Classifying and Exploring Life
 Classifying and Exploring Life Classifying Organisms Key Concepts What methods are used to classify living things into groups? Why does every species have a scientific name? What do you think? Read the
Classifying and Exploring Life Classifying Organisms Key Concepts What methods are used to classify living things into groups? Why does every species have a scientific name? What do you think? Read the
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this lesson:
 Unit C: Classification of Agricultural Crops Lesson 1: Classifying and Naming Plants Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Unit C: Classification of Agricultural Crops Lesson 1: Classifying and Naming Plants Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
NAME: DATE: PER: CLASSIFICATION OF LIFE Powerpoint Notes
 NAME: DATE: PER: CLASSIFICATION OF LIFE Powerpoint Notes 1. Species of Organisms a) There are known species of organisms b) This is only of all organisms that ever lived. c) are still being found and identified.
NAME: DATE: PER: CLASSIFICATION OF LIFE Powerpoint Notes 1. Species of Organisms a) There are known species of organisms b) This is only of all organisms that ever lived. c) are still being found and identified.
The Tree of Life. Chapter 17
 The Tree of Life Chapter 17 1 17.1 Taxonomy The science of naming and classifying organisms 2000 years ago Aristotle Grouped plants and animals Based on structural similarities Greeks and Romans included
The Tree of Life Chapter 17 1 17.1 Taxonomy The science of naming and classifying organisms 2000 years ago Aristotle Grouped plants and animals Based on structural similarities Greeks and Romans included
The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time.
 Evolution The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time. Divergent evolution is the accumulation of differences between groups which can lead to the formation of new species.
Evolution The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time. Divergent evolution is the accumulation of differences between groups which can lead to the formation of new species.
Classifying Marine Mammals
 Name: Period: Date: Part I 1. Our current system of classification divides living things into a hierarchy, starting with the most general and becoming more specific. In the space below, list the seven
Name: Period: Date: Part I 1. Our current system of classification divides living things into a hierarchy, starting with the most general and becoming more specific. In the space below, list the seven
PHYLOGENY & THE TREE OF LIFE
 PHYLOGENY & THE TREE OF LIFE PREFACE In this powerpoint we learn how biologists distinguish and categorize the millions of species on earth. Early we looked at the process of evolution here we look at
PHYLOGENY & THE TREE OF LIFE PREFACE In this powerpoint we learn how biologists distinguish and categorize the millions of species on earth. Early we looked at the process of evolution here we look at
CHAPTER-1 THE LIVING WORLD MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 1 CHAPTER-1 THE LIVING WORLD MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. As we go from species to kingdom in a taxonomic hierarchy, the number of common characteristics a. Will decrease b. Will increase c. Remain same
1 CHAPTER-1 THE LIVING WORLD MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. As we go from species to kingdom in a taxonomic hierarchy, the number of common characteristics a. Will decrease b. Will increase c. Remain same
Kingdom: What s missing? List the organisms now missing from the above list..
 Life Science 7 Chapter 9-1 p 222-227 Classification: Sorting It All Out Objectives Explain why and how organisms are classified. List the eight levels of classification. Explain scientific names. Describe
Life Science 7 Chapter 9-1 p 222-227 Classification: Sorting It All Out Objectives Explain why and how organisms are classified. List the eight levels of classification. Explain scientific names. Describe
Objectives. Classification. Activity. Scientists classify millions of species
 Objectives Classification Notes 8.1 Summarize classification Describe the evidence used to classify organisms. List the seven levels of classification. Describe and list the six kingdoms of living organisms
Objectives Classification Notes 8.1 Summarize classification Describe the evidence used to classify organisms. List the seven levels of classification. Describe and list the six kingdoms of living organisms
Classification. 18a. Lab Exercise. Contents. Introduction. Objectives. 18a
 Lab Exercise Classification Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Classification of Organisms 4 Activity.2 Phylogenetic Analysis 5 Resutls Section 7 Objectives - To create a classification of
Lab Exercise Classification Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Classification of Organisms 4 Activity.2 Phylogenetic Analysis 5 Resutls Section 7 Objectives - To create a classification of
Page # 1. 1, , , ,000, ,000, % 2. 20% 3. 50% 4. 75% 5. ~ 99%
 Our best estimate is that Earth has about how many species? Earthʼs Tree of Life 1. 1,000 2. 10,000 3. 100,000 4. 1,000,000 5. 10,000,000 Biologists have named about what percentage of the species on Earth?
Our best estimate is that Earth has about how many species? Earthʼs Tree of Life 1. 1,000 2. 10,000 3. 100,000 4. 1,000,000 5. 10,000,000 Biologists have named about what percentage of the species on Earth?
Biology 2.1 Taxonomy: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum. ICan2Ed.com
 Biology 2.1 Taxonomy: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum ICan2Ed.com Taxonomy is the scientific field that catalogs, describes, and names living organisms. The way to divide living organisms into groups based on
Biology 2.1 Taxonomy: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum ICan2Ed.com Taxonomy is the scientific field that catalogs, describes, and names living organisms. The way to divide living organisms into groups based on
Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms
 Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms Why do we need it? problems with different languages common names can be confusing examples: woodchuck, groundhog crayfish,
Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms Why do we need it? problems with different languages common names can be confusing examples: woodchuck, groundhog crayfish,
6 Kingdoms 1.Eubacteria 2.Archaebacteria 3.Protista 4.Fungi 5.Plantae 6.Animalia "Dear King Phillip Came Over From Greece Saturday"
 Unit 7 Classification & Plants What you Need to Know: Classification: Classification, Taxonomy, Binomial Nomenclature + Scientific Names, Kingdoms, Cladograms, Kingdoms and Domains // Characteristics of
Unit 7 Classification & Plants What you Need to Know: Classification: Classification, Taxonomy, Binomial Nomenclature + Scientific Names, Kingdoms, Cladograms, Kingdoms and Domains // Characteristics of
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this lesson:
 Unit A: Understanding Horticulture Lesson 4: Classifying Ornamental Plants Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Describe
Unit A: Understanding Horticulture Lesson 4: Classifying Ornamental Plants Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Describe
Classification. Sorting It All Out. section 1. Chapter 9
 Classification Chapter 9 Sorting It All Out section 1 1 Why Classify? Classification Is the division of organisms into groups or classes based on common characteristics For thousands of years, humans have
Classification Chapter 9 Sorting It All Out section 1 1 Why Classify? Classification Is the division of organisms into groups or classes based on common characteristics For thousands of years, humans have
THE SCIENCE OF PHYTOSYSTEMATICS
 THE SCIENCE OF PHYTOSYSTEMATICS Phytosystematics is a science within Botany, including traditional taxonomy, the description, identification, nomenclature and classification of plants. Its subject is the
THE SCIENCE OF PHYTOSYSTEMATICS Phytosystematics is a science within Botany, including traditional taxonomy, the description, identification, nomenclature and classification of plants. Its subject is the
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Biologists estimate that there are about 5 to 100 million species of organisms living on Earth today. Evidence from morphological, biochemical, and gene sequence
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Biologists estimate that there are about 5 to 100 million species of organisms living on Earth today. Evidence from morphological, biochemical, and gene sequence
The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time.
 Evolution The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time. Divergent evolution Goldfields and Ahinahina (silversword) a highly evolved member of the composite family. Evolution
Evolution The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time. Divergent evolution Goldfields and Ahinahina (silversword) a highly evolved member of the composite family. Evolution
(i) Growth (ii) Reproduction (iii) Metabolism (iv) Ability to sense the surrounding and respond to the stimuli
 1 LESSON THE LIVING WORLD Introduction The term living, can be defined by certain distinctive characteristics exhibited by the living organisms. Growth, reproduction, ability to sense environment and mount
1 LESSON THE LIVING WORLD Introduction The term living, can be defined by certain distinctive characteristics exhibited by the living organisms. Growth, reproduction, ability to sense environment and mount
