Questions. through a moist outer covering. But tetrapods
|
|
|
- Cornelia Banks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
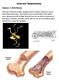
1 Questions. 1. Plants transitioned from freshwater to land in the Ordovician; vertebrates, in the Devonian. List and compare the adaptations with regard to gas exchange and support that enabled each group to make the switch. Air and Gas Exchange. In both plants and animals water loss is prevented by a water-impermeable outer covering waxy cuticle in plants; integument, in reptiles. In plants, this necessitated the evolution of stomata through which air could be exchanged with the environment. In tetrapods, exchange with the environment is via the mouth and throat, which, of course, existed in their lobefin ancestors. Likewise in plants, gas exchange occurs in the leaves; in tetrapods, in the lungs. In short, the ways in which plants and tetrapods exchange air and gases are quite different. There is, however, an interesting parallel. Contemporary amphibians respire in part, or principally, through the skin, which is moist and highly vascularized. This condition was achieved via the loss of scales, which their lobefin ancestors most certainly possessed. Early tetrapods (and living frogs and salamanders) were thus similar to nontracheophytes with gas exchange proceeding principally through a moist outer covering. But tetrapods
2 also had lungs and circulatory systems. When they evolved a water-impermeable integument, lung and circulatory capacity expanded. Had lungs and circulatory systems not existed pretransition, tetrapods might conceivably have evolved an insect-like anatomy in which air enters through spiracles and is delivered to the tissues via a branching network of trachea. Of course, tetrapod ancestors did have lungs, and these became larger and more highly vascularized. Additionally, by the time one gets to birds and mammals the circulation Insect respiratory system. of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is kept separate. Other structures (secondary palette, diaphragms, air sacs, etc.) also evolved to further augment fresh air acquisition. Support. In plants, support is provided by lignified xylem, which doubles as part of the plant circulatory 2
3 system. In tetrapods, support is provided by the skeleton, which was progressively strengthened and specialized (limbs) as they transitioned from water to land. 2. List and compare the adaptations regarding reproduction that enabled vertebrates and plants to transition from freshwater to land. In tetrapods, the amniotic egg and internal fertilization ended reproductive dependence on water. In plants, the corresponding adaptations are pollen and seeds. Two interesting differences between tetrapods and plants involve embryos. In plants, embryonic development in a womb comes early on; in animals, quite late, i.e., in mammals. Second, the embryos of seed plants manifest arrested development. No corresponding tetrapod resting stage that I can think of. 3
4 3. Compare dispersal in plants and animals. Animals, at least the motile ones, can move around themselves. In such cases, it is the young of the year that typically disperse. Especially in sedentary marine forms, there is often a free-swimming or planktonic larval form that gets distributed by the currents. Spores and seeds are the plant equivalents, being dispersed by wind, water and animals. Seed plants can also move their genotypes around via pollen, which can be wind- or animal-dispersed. There is really no animal equivalent, the picture of the giant clam in your text notwithstanding. 4
5 4. Physical constraints inability to transport water to a height of greater than about 120 m limit the maximum height of trees. Why should trees be tall in the first place? Why don t they allocate some of the energy that goes into trunk tissue to making more leaves? The short answer is competition. Absent overtopping, plants should be hemispheres of photosynthetic tissue, with a minimum of resources allocated for support. But if your neighbor overtops you, photosynthetic activity drops. So many plants invest in stems and tree trunks, which is why there are forests. Of course, not all plants pursue this Cecropia, a fast growing, shade-intolerant tropical tree, is typically found along roadsides and in openings in the forest. strategy. Some have evolved to make do in low-light intensity environments. Others (weeds) live in habitats where intermittent disturbance creates gaps in the forest, in environments subject to continuing disturbance that prevents the forest from ever growing up or in environments where a lack of resources such as water prevents canopy formation. 5
6 5. What are phytoliths? In what kinds of plants are they found? How do they help the plant defend against herbivores? Phytoliths are tiny accumulations of silica, (SiO2), within or between plant cells. They are widely distributed and form when dissolved silica absorbed by the roots is distributed to other parts of the plant where it precipitates to form small concretions. In some cases, phytoliths are species-specific and can be used to infer the composition of communities long gone, for example, at archaeological sites and in fossiliferous deposits. Phytoliths can occur within or between cells. Shown here are intercellular phytoliths from gourds (Piperno et al Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 99: Silica is an abrasive, and phytolyths can serve to deter, or at least wear down the teeth of, herbivores. Though not restricted to grasses, phytolyths are characteristic of the group, and played a role in the evolution of high crowned cheek teeth in grazers such as horses, antelope and deer. 6
7 Phytolyths recovered from12,000 year old ground sloth remains enable paleontologists to deduce what these animals ate. 7
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport
 Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
Adjustments to Life in Air
 1 Adjustments to Life in Air Plants and Animals no buoyancy, need skeletal support desiccation physical-chemical environmental extremes (temperature, humidity, salinity) no nutrients in air reproductive
1 Adjustments to Life in Air Plants and Animals no buoyancy, need skeletal support desiccation physical-chemical environmental extremes (temperature, humidity, salinity) no nutrients in air reproductive
Organization of Plant Tissue. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Organization of Plant Tissue Plant Systems Shoot System The Leaf The Stem The Flower Root System The Shoot System Has two main functions: to conduct photosynthesis and to produce flowers for sexual reproduction
Organization of Plant Tissue Plant Systems Shoot System The Leaf The Stem The Flower Root System The Shoot System Has two main functions: to conduct photosynthesis and to produce flowers for sexual reproduction
Internal Adaptations
 Station 1: Bird Bones Internal Adaptations The bones of birds have hollow openings inside. Therefore, bird bones are less dense than human bones. These hollow spaces cause the bird to have lighter mass,
Station 1: Bird Bones Internal Adaptations The bones of birds have hollow openings inside. Therefore, bird bones are less dense than human bones. These hollow spaces cause the bird to have lighter mass,
Diversity in Living Organism
 Diversity in Living Organism Why do we classify organisms? Answer:- There are millions of species on this earth. For anybody, it is impossible to study about each of them in his lifetime. Classification
Diversity in Living Organism Why do we classify organisms? Answer:- There are millions of species on this earth. For anybody, it is impossible to study about each of them in his lifetime. Classification
What is a Plant? Plant Life Cycle. What did they evolve from? Original Habitat 1/15/2018. Plant Life Cycle Alternation of Generations
 What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL Annual Exam 2017 BIOLOGY
 ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL Annual Exam 2017 BIOLOGY NAME: FORM: TIME: 2 Hours Section A: Section A answer ALL questions. This section carries 50 marks. Section B: Section B answer BOTH questions. This
ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL Annual Exam 2017 BIOLOGY NAME: FORM: TIME: 2 Hours Section A: Section A answer ALL questions. This section carries 50 marks. Section B: Section B answer BOTH questions. This
Comparing Plants & Animals
 Section 6.1 Comparing Plants & Animals p. 164-168 Major Similarities: They are both multi-cellular, eukaryotes. Their sizes both range from microscopic to very large. Major Differences: How they obtain
Section 6.1 Comparing Plants & Animals p. 164-168 Major Similarities: They are both multi-cellular, eukaryotes. Their sizes both range from microscopic to very large. Major Differences: How they obtain
Kingdom Plantae. Biology : A Brief Survey of Plants. Jun 22 7:09 PM
 Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Root cross-section (Ranunculus)
 Plant Lab Review Root cross-section (Ranunculus) Epidermis Cortex Vascular Cylinder Phloem Endodermis Xylem Ranunculus Root Cross section Give three functions of the root Anchor plant Absorb water and
Plant Lab Review Root cross-section (Ranunculus) Epidermis Cortex Vascular Cylinder Phloem Endodermis Xylem Ranunculus Root Cross section Give three functions of the root Anchor plant Absorb water and
1 Plant Characteristics!
 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Plant Characteristics! CHAPTER 1 Plant Characteristics! Identify common traits of plants. What are Plants? Plants are multicellular eukaryotic organisms with cell wallscellulosechloroplasts
www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Plant Characteristics! CHAPTER 1 Plant Characteristics! Identify common traits of plants. What are Plants? Plants are multicellular eukaryotic organisms with cell wallscellulosechloroplasts
22 3 Seedless Vascular Plants Slide 1 of 33
 22 3 Seedless Vascular Plants 1 of 33 Evolution of Vascular Tissue Plants have vascular tissue, which is specialized to conduct water and nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem carries water from the roots
22 3 Seedless Vascular Plants 1 of 33 Evolution of Vascular Tissue Plants have vascular tissue, which is specialized to conduct water and nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem carries water from the roots
A. camouflage B. hibernation C. migration D. communication. 8. Beetles, grasshoppers, bees, and ants are all.
 1. A flounder is a type of fish. The flounder can change its color to match the surroundings. If a shark approaches, the flounder lays still, blending into the sandy ocean bottom. This is known as. 2 Which
1. A flounder is a type of fish. The flounder can change its color to match the surroundings. If a shark approaches, the flounder lays still, blending into the sandy ocean bottom. This is known as. 2 Which
The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants.
 INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants. Plants are abundant in almost every environment that
INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants. Plants are abundant in almost every environment that
Biologists have used many approaches to estimating the evolutionary history of organisms and using that history to construct classifications.
 Phylogenetic Inference Biologists have used many approaches to estimating the evolutionary history of organisms and using that history to construct classifications. Willi Hennig developed d the techniques
Phylogenetic Inference Biologists have used many approaches to estimating the evolutionary history of organisms and using that history to construct classifications. Willi Hennig developed d the techniques
Unit 2B- The Plants. Plants can be classified according to the presence or absence of vascular tissue.
 Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
Kingdom Plantae. A Brief Survey of Plants
 Kingdom Plantae A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as follows: 1. Common cellular
Kingdom Plantae A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as follows: 1. Common cellular
Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles
 Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles Section 1: Introduction to Plants Cuticle: a waxy or fatty and watertight layer on the external wall of epidermal cells Spore: a reproductive cell or multicellular
Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles Section 1: Introduction to Plants Cuticle: a waxy or fatty and watertight layer on the external wall of epidermal cells Spore: a reproductive cell or multicellular
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline)
 Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Chapter 7: Diversity in Living Organisms Science
 Chapter 7: Diversity in Living Organisms Science In Text Questions Page No: 80 1. Why do we classify organisms? : There are millions of organisms on this earth. So, it is harder to study them one by one.
Chapter 7: Diversity in Living Organisms Science In Text Questions Page No: 80 1. Why do we classify organisms? : There are millions of organisms on this earth. So, it is harder to study them one by one.
Biology Slide 1 of 28
 Biology 1 of 28 2 of 28 22-4 Seed Plants Seed plants are the most dominant group of photosynthetic organisms on land. 3 of 28 22-4 Seed Plants Seed plants are divided into two groups: Gymnosperms bear
Biology 1 of 28 2 of 28 22-4 Seed Plants Seed plants are the most dominant group of photosynthetic organisms on land. 3 of 28 22-4 Seed Plants Seed plants are divided into two groups: Gymnosperms bear
Structures of Seed Plants
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Name: Grade 5 ( ) Date:
 SCIENCE REVISION ANSWER KEY. QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: 1. Mollusks 2. Vertebrates 3. Invertebrates 4. Arthropods 5. Archaebacterial
SCIENCE REVISION ANSWER KEY. QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: 1. Mollusks 2. Vertebrates 3. Invertebrates 4. Arthropods 5. Archaebacterial
Key Plant Unit Test Multiple Choice
 Plant Unit Test Multiple Choice For questions 1 25, circle the letter of the best answer from the choices provided. (2 pts each) For questions 1 3, refer to the diagram of the plant cell below: A B C D
Plant Unit Test Multiple Choice For questions 1 25, circle the letter of the best answer from the choices provided. (2 pts each) For questions 1 3, refer to the diagram of the plant cell below: A B C D
COMMON ENTRANCE EXAMINATION AT 13+ SCIENCE LEVEL 2 BIOLOGY MARK SCHEME. Specimen Paper. (for first examination in Autumn 2017)
 COMMON ENTRANCE EXAMINATION AT 3+ SCIENCE LEVEL 2 BIOLOGY MARK SCHEME Specimen Paper (for first examination in Autumn 207) This is a suggested, not a prescriptive, mark scheme. 2835SM29 Independent Schools
COMMON ENTRANCE EXAMINATION AT 3+ SCIENCE LEVEL 2 BIOLOGY MARK SCHEME Specimen Paper (for first examination in Autumn 207) This is a suggested, not a prescriptive, mark scheme. 2835SM29 Independent Schools
Life Science. Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like. animals and humans. Like all living. things they need key things to live;
 6.6.3 Life Science Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like animals and humans. Like all living things they need key things to live; water, sunlight, oxygen and food. Plants are different
6.6.3 Life Science Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like animals and humans. Like all living things they need key things to live; water, sunlight, oxygen and food. Plants are different
SCIENCE REVISION BOOKLET MID SEMESTER
 SCIENCE REVISION BOOKLET MID SEMESTER 1-2018 NAME: GRADE: 5 ( ) DATE: 1 QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: Air sacs, arthropods, Cytoplasm,
SCIENCE REVISION BOOKLET MID SEMESTER 1-2018 NAME: GRADE: 5 ( ) DATE: 1 QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: Air sacs, arthropods, Cytoplasm,
Classification of organisms. The grouping of objects or information based on similarities Taxonomy: branch of biology that classifies organisms
 Bell Work: Think about your CD, video game, DVD or book collection at home. How would you separate this collection into different groups? What would the groups be? Try to come up with 4 or 5. Classification
Bell Work: Think about your CD, video game, DVD or book collection at home. How would you separate this collection into different groups? What would the groups be? Try to come up with 4 or 5. Classification
Are these organisms. animals or not?
 1 2 3 4 5 Are these organisms 6 7 8 animals or not? 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Typical Animal Characteristics Eukaryotic Multicellular Ability to move Reproduce Obtain food (heterotrophic)
1 2 3 4 5 Are these organisms 6 7 8 animals or not? 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Typical Animal Characteristics Eukaryotic Multicellular Ability to move Reproduce Obtain food (heterotrophic)
What Is an Animal? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. About 98 percent of all animals are invertebrates. The Kingdom Animalia
 What Is an Animal? What characteristics do all animals have? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. Scientists estimate that there are between 1 and 2 million species of animals! Some, like whales
What Is an Animal? What characteristics do all animals have? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. Scientists estimate that there are between 1 and 2 million species of animals! Some, like whales
Manitoba Curriculum Framework of Outcomes Grades K-3
 Grades K-3 Reference Specific Learning Outcomes Wetlands Rainforest It is expected that students will: 100-4 observe and identify similarities and differences in the needs of living Organisms, Migration,
Grades K-3 Reference Specific Learning Outcomes Wetlands Rainforest It is expected that students will: 100-4 observe and identify similarities and differences in the needs of living Organisms, Migration,
Roots, Shoots & Leaves
 Name Test Date Hour Plant Structure & Function #2 - Notebook Roots, Shoots & Leaves LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the functions of roots I can explain the nitrogen fixing process and why it is needed.
Name Test Date Hour Plant Structure & Function #2 - Notebook Roots, Shoots & Leaves LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the functions of roots I can explain the nitrogen fixing process and why it is needed.
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Date: 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Date: 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and
Diversity in Living Organisms
 Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years ago. The
Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years ago. The
Class IX Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms Science
 Question 1: Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years
Question 1: Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years
What Shapes an Ecosystem? Section 4-2 pgs 90-97
 What Shapes an Ecosystem? Section 4-2 pgs 90-97 What Shapes an Ecosystem? If you ask an ecologist where a particular organism lives, that person might say the organism lives on a Caribbean coral reef,
What Shapes an Ecosystem? Section 4-2 pgs 90-97 What Shapes an Ecosystem? If you ask an ecologist where a particular organism lives, that person might say the organism lives on a Caribbean coral reef,
Botany: Part I Overview of Plants & Plant Structure
 Botany: Part I Overview of Plants & Plant Structure Plant evolution Plant Evolution Chlorophytes Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Chlorophytes are a green
Botany: Part I Overview of Plants & Plant Structure Plant evolution Plant Evolution Chlorophytes Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Chlorophytes are a green
1. What makes plants different than animals?
 1. What makes plants different than animals? tiger lily tiger 1. Plants are producers, which means they make their own food (through photosynthesis). 2. While plants can move certain structures, they cannot
1. What makes plants different than animals? tiger lily tiger 1. Plants are producers, which means they make their own food (through photosynthesis). 2. While plants can move certain structures, they cannot
Chapter What is a Plant? Biology. Slide 1 of 33. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Chapter 22.1 Biology What is a Plant? 1 of 33 Objectives 1. Describe the basic characteristics of life. 2. Describe what plants need to survive. 3. Describe the life cycle of plants. 4. Describe how the
Chapter 22.1 Biology What is a Plant? 1 of 33 Objectives 1. Describe the basic characteristics of life. 2. Describe what plants need to survive. 3. Describe the life cycle of plants. 4. Describe how the
PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts)
 PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts) 1. SEEDS--Without this part of the seed, the embryo has no food to grow before photosynthesis. a. seed coat b. embryo c. leaves d. cotyledon e. tap root 2. SEEDS--Which
PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts) 1. SEEDS--Without this part of the seed, the embryo has no food to grow before photosynthesis. a. seed coat b. embryo c. leaves d. cotyledon e. tap root 2. SEEDS--Which
Name: Date: Period: Forms a spore producing structure called an ascus Morals Truffles Yeast
 Name: Date: Period: Fungi and Plant Unit Review Worksheet Part I (KEY) Directions: Treat this like an assessment and answer as much as you can without ANY help. See how much you actually know by highlighting/starring
Name: Date: Period: Fungi and Plant Unit Review Worksheet Part I (KEY) Directions: Treat this like an assessment and answer as much as you can without ANY help. See how much you actually know by highlighting/starring
4/30/2014. The lives of modern plants and fungi are intertwined We depend on plants and indirectly, fungi for much of our food.
 and the Colonization of Land The lives of modern plants and fungi are intertwined We depend on plants and indirectly, fungi for much of our food. Plants are often harmed by fungi. On the other hand, nearly
and the Colonization of Land The lives of modern plants and fungi are intertwined We depend on plants and indirectly, fungi for much of our food. Plants are often harmed by fungi. On the other hand, nearly
Some History: In the life cycle of the kelp Laminaria. One way to separate algae from protozoa is that. Rocks of Cambrian Age (ca.
 One way to separate algae from protozoa is that a. Protozoa are photosynthetic, while algae are not. b. Algae are photosynthetic, while protozoa are not. c. Protozoa are prokaryotic, while algae are eukaryotic.
One way to separate algae from protozoa is that a. Protozoa are photosynthetic, while algae are not. b. Algae are photosynthetic, while protozoa are not. c. Protozoa are prokaryotic, while algae are eukaryotic.
5.5 Organisms (Living Systems)
 Science Trivia 5 th grade Updated 2012 5.5 Organisms (Living Systems) 1 The brain or center of a cell that controls its activities - 2 3 What is the liquid in a cell that contains chemicals needed to keep
Science Trivia 5 th grade Updated 2012 5.5 Organisms (Living Systems) 1 The brain or center of a cell that controls its activities - 2 3 What is the liquid in a cell that contains chemicals needed to keep
Evolution Common Assessment 1
 Evolution Common Assessment 1 1. The field of biology that includes the study of the origin of new species through time is known as 5. A. biochemistry B. evolution C. ecology D. embryology 2. Evidence
Evolution Common Assessment 1 1. The field of biology that includes the study of the origin of new species through time is known as 5. A. biochemistry B. evolution C. ecology D. embryology 2. Evidence
The move from water to land. The move from water to land. Chapter 16- Evolution of Plants. Green algae are the ancestors to all plants
 Chapter 16- Evolution of Plants From Protists to Plants Moving right along! Green algae are the ancestors to all plants Who, ME? Wow I feel so important! Charophyceans 475 million years ago, shallow seas
Chapter 16- Evolution of Plants From Protists to Plants Moving right along! Green algae are the ancestors to all plants Who, ME? Wow I feel so important! Charophyceans 475 million years ago, shallow seas
Plant Structure Size General Observations
 Kingdom Plantae Plant Structure Size General Observations Diversity Within the Plant Kingdom Pine Trees What is a plant? Multicellular Eukaryotes Perform Photosynthesis (base of all terrestrial food chains)
Kingdom Plantae Plant Structure Size General Observations Diversity Within the Plant Kingdom Pine Trees What is a plant? Multicellular Eukaryotes Perform Photosynthesis (base of all terrestrial food chains)
1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Environmental Studies
 Grade 5 pcangel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Environmental Studies Index No:- I. Underline the correct answer. 1. Deserts are. a. dry places with so much of water
Grade 5 pcangel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Environmental Studies Index No:- I. Underline the correct answer. 1. Deserts are. a. dry places with so much of water
Name Date Block. Plant Structures
 Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
Diversity of Organisms and Classification
 Diversity of Organisms and Classification Essential Vocabulary DNA Prokaryotic: : a cell that lacks a nucleus. Eukaryotic: : a cell that has a nucleus and other complex structures Feeding Autotrophic:
Diversity of Organisms and Classification Essential Vocabulary DNA Prokaryotic: : a cell that lacks a nucleus. Eukaryotic: : a cell that has a nucleus and other complex structures Feeding Autotrophic:
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Natural Science. WRITERS Belén Garrido Alan Martin. SCIENCE CONSULTANT Cristina Quincy. ILLUSTRATIONS Jordi Baeza Javier Hernández
 3 Natural Science Natural Science 3 Learning Lab is a collective work, conceived, designed and created by the Primary Education department at Santillana, under the supervision of Teresa Grence. WRITERS
3 Natural Science Natural Science 3 Learning Lab is a collective work, conceived, designed and created by the Primary Education department at Santillana, under the supervision of Teresa Grence. WRITERS
History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale
 History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale Agenda or Summary Layout The Geological Time-Scale 1 2 3 The Geological Time-Scale The Beginning of Life Cambrian Explosion The Geological Time-Scale
History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale Agenda or Summary Layout The Geological Time-Scale 1 2 3 The Geological Time-Scale The Beginning of Life Cambrian Explosion The Geological Time-Scale
Ecological Succession
 Ecological Succession Primary succession will ALWAYS be on areas where there is NO SOIL a) bare rock from a retreating glacier, b) newly cooled lava; c) abandoned lot with an impervious surface (parking
Ecological Succession Primary succession will ALWAYS be on areas where there is NO SOIL a) bare rock from a retreating glacier, b) newly cooled lava; c) abandoned lot with an impervious surface (parking
Behavioral and Structural Adaptations PPT Guided Notes
 A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES SAMPLE. Biology. Secondary Science 7B. Years 7 9. Written by Valerie Marett. CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 542
 AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES Biology Secondary Science 7B Years 7 9 Written by Valerie Marett CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 542 Science for Secondary Students 7B Biology Contents Living and Non-Living
AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES Biology Secondary Science 7B Years 7 9 Written by Valerie Marett CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 542 Science for Secondary Students 7B Biology Contents Living and Non-Living
Chapter 15. Plant Evolution and Classification Worksheets. (Opening image copyright Jonathan Lingel, Used under license from Shutterstock.com.
 Chapter 15 Plant Evolution and Classification Worksheets (Opening image copyright Jonathan Lingel, 2010. Used under license from Shutterstock.com.) Lesson 15.1: Introduction to the Plant Kingdom Lesson
Chapter 15 Plant Evolution and Classification Worksheets (Opening image copyright Jonathan Lingel, 2010. Used under license from Shutterstock.com.) Lesson 15.1: Introduction to the Plant Kingdom Lesson
Chapter 32 Intro to Animals. Image from:
 Chapter 32 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Animals Invertebrates (animals without a backbone) Porifera Cnidaria Worms Mollusks Echinoderms Arthropods Animals
Chapter 32 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Animals Invertebrates (animals without a backbone) Porifera Cnidaria Worms Mollusks Echinoderms Arthropods Animals
BIO10 Plant Lecture Notes ch. 17. Plant Kingdom
 Plant Kingdom Characteristics of the Plant Kingdom; eukaryotic, multicellular, sexually reproducing organisms autotroph feed themselves by photosynthesis Facts about members of this kingdom the dominant
Plant Kingdom Characteristics of the Plant Kingdom; eukaryotic, multicellular, sexually reproducing organisms autotroph feed themselves by photosynthesis Facts about members of this kingdom the dominant
The Theory of Evolution
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 13 DIRECTED READING The Theory of Evolution Section 13-1: The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Darwin Proposed a Mechanism for Evolution Mark each statement below T if it
Name Date Class CHAPTER 13 DIRECTED READING The Theory of Evolution Section 13-1: The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Darwin Proposed a Mechanism for Evolution Mark each statement below T if it
Seed Plants. Gymnosperms & Angiosperms
 Seed Plants Gymnosperms & Angiosperms 1 Quick Defs Vascular = xylem and phloem Xylem = Brings water/nutrients from roots to the plant. Phloem = Brings sugars down from the leaves 2 Evolution Of Land Plants
Seed Plants Gymnosperms & Angiosperms 1 Quick Defs Vascular = xylem and phloem Xylem = Brings water/nutrients from roots to the plant. Phloem = Brings sugars down from the leaves 2 Evolution Of Land Plants
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28
 Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
NOTES: CH 35 - Plant Structure & Growth
 NOTES: CH 35 - Plant Structure & Growth In their evolutionary journey, plants adapted to the problems of a terrestrial existence as they moved from water to land ANGIOSPERMS (flowering plants) -most diverse
NOTES: CH 35 - Plant Structure & Growth In their evolutionary journey, plants adapted to the problems of a terrestrial existence as they moved from water to land ANGIOSPERMS (flowering plants) -most diverse
Biology 162 LAB EXAM 2, PM version Thursday 24 April 2003 page 1
 Biology 162 LAB EXAM 2, PM version Thursday 24 April 2003 page 1 Question Set 1: Animal EVOLUTIONARY BIODIVERSITY (a). We have mentioned several times in class that the concepts of Developed and Evolved
Biology 162 LAB EXAM 2, PM version Thursday 24 April 2003 page 1 Question Set 1: Animal EVOLUTIONARY BIODIVERSITY (a). We have mentioned several times in class that the concepts of Developed and Evolved
Early-bird Special The following terms refer to alternation of generation:
 Early-bird Special The following terms refer to alternation of generation: Homosporous ( one type of spore. a single type of spore produces a single type of gametophyte which produces both male and female
Early-bird Special The following terms refer to alternation of generation: Homosporous ( one type of spore. a single type of spore produces a single type of gametophyte which produces both male and female
What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics. I. Characteristics of Animals. Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen
 What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. Characteristics of Animals A. All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, have ways of moving to reproduce, obtain
What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. Characteristics of Animals A. All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, have ways of moving to reproduce, obtain
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Name 5 reasons why we think plants are A OK 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. Plant Cells: Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. They develop from multicellular
Introduction to Plants Name 5 reasons why we think plants are A OK 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. Plant Cells: Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. They develop from multicellular
Biology. Chapter 21. Plant Evolution. Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr. Cengage Learning 2015
 Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 21 Plant Evolution 21.1 How Did Plants Adapt To Life on Land? Plants evolved from green algae, and underwent an adaptive radiation on land
Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 21 Plant Evolution 21.1 How Did Plants Adapt To Life on Land? Plants evolved from green algae, and underwent an adaptive radiation on land
Nerve cells have many branches that help them send signals throughout the body.
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
All About Plants. What are plants?
 All About Plants What are plants? Plants are living things that are made up of cells. They need air, water, soil, and sunlight to live. They cannot move from place to place, but their leaves move to catch
All About Plants What are plants? Plants are living things that are made up of cells. They need air, water, soil, and sunlight to live. They cannot move from place to place, but their leaves move to catch
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta
 Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
The Vascular Plant Body
 The Vascular Plant Body Like animals, plants are made up of specialized cells that are organized into tissues, which are themselves organized into systems of organs. The various parts of plants are adapted
The Vascular Plant Body Like animals, plants are made up of specialized cells that are organized into tissues, which are themselves organized into systems of organs. The various parts of plants are adapted
Plants Notes. Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light
 Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
Kingdom: Plantae. Domain Archaea. Domain Eukarya. Domain Bacteria. Common ancestor
 Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Cells, Tissues, and Systems
 Cells, Tissues, and Systems In multicellular organisms, cells specialize to carry out various functions. Many cells performing the same task make up tissues. A number of tissues grouped together to perform
Cells, Tissues, and Systems In multicellular organisms, cells specialize to carry out various functions. Many cells performing the same task make up tissues. A number of tissues grouped together to perform
Chapter 29: Plant Tissues
 Chapter 29: Plant Tissues Shoots and Roots Shoots (Leaves and Stem) Produce food by photosynthesis Carry out reproductive functions Roots Anchor the plant Penetrate the soil and absorb water and dissolved
Chapter 29: Plant Tissues Shoots and Roots Shoots (Leaves and Stem) Produce food by photosynthesis Carry out reproductive functions Roots Anchor the plant Penetrate the soil and absorb water and dissolved
Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups. Mrs. Hilliard
 Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups Mrs. Hilliard Communication in Science Choose one of the three topics to write a detailed procedure for. 1. How to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. 2. How to brush your
Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups Mrs. Hilliard Communication in Science Choose one of the three topics to write a detailed procedure for. 1. How to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. 2. How to brush your
The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves.
 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. 1 of 34 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Roots: absorb
23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. 1 of 34 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Roots: absorb
Assignment 5 Phylogeny Due July 4
 Assignment 5 Phylogeny Due July 4 1. Multiple-choice (1 point) The number of species that have been described is about but scientists estimate that there are at least species. 500,000 known, at least 1
Assignment 5 Phylogeny Due July 4 1. Multiple-choice (1 point) The number of species that have been described is about but scientists estimate that there are at least species. 500,000 known, at least 1
Being a Biologist. Summary Sheets. Gleniffer High School
 Being a Biologist Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 DNA I have extracted DNA and understand its function. I can express an informed view of the risks and benefits of DNA profiling. SCN 3-14b Chromosomes
Being a Biologist Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 DNA I have extracted DNA and understand its function. I can express an informed view of the risks and benefits of DNA profiling. SCN 3-14b Chromosomes
23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Slide 1 of 34
 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants 1 of 34 Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. These organs perform functions such as the transport of nutrients,
23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants 1 of 34 Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. These organs perform functions such as the transport of nutrients,
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6
 Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land
 Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Name Period Concept 29.1 Land plants evolved from green algae 1. Plants colonized land about
Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Name Period Concept 29.1 Land plants evolved from green algae 1. Plants colonized land about
Honors Biology Ecology Concept List
 1. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. a. mutualism and commensalism b. parasitism and predation c. species richness and species diversity d. primary succession and secondary
1. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. a. mutualism and commensalism b. parasitism and predation c. species richness and species diversity d. primary succession and secondary
Spring th Grade
 Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate Tubes for Transport Warm Up 1 Tubes for Transport Nonvascular plants are simple plants that lack vascular tissue, which easily transports
Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate Tubes for Transport Warm Up 1 Tubes for Transport Nonvascular plants are simple plants that lack vascular tissue, which easily transports
Directed Reading A. Section: Structures of Seed Plants. is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. is called ROOTS. size.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants 1. Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals through a plant is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. 2. Vascular
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants 1. Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals through a plant is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. 2. Vascular
1 Looking at Fossils. What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils tell us about the history of life on earth?
 CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 1 Looking at Fossils California Science Standards 7.3.c, 7.4.c, 7.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 1 Looking at Fossils California Science Standards 7.3.c, 7.4.c, 7.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
The City School North Nazimabad Boys Campus
 The City School North Nazimabad Boys Campus 1 st COMPREHENSIVE WORKSHEET SEPTEMBER 2015 SCIENCE CLASS 7 Teacher Name: Ms.Seema Adil Class: 7 Date:5 th November 2016 Name: Section: Date: CHAPTER: CLASSIFYING
The City School North Nazimabad Boys Campus 1 st COMPREHENSIVE WORKSHEET SEPTEMBER 2015 SCIENCE CLASS 7 Teacher Name: Ms.Seema Adil Class: 7 Date:5 th November 2016 Name: Section: Date: CHAPTER: CLASSIFYING
Discuss: March 15, Plants part 2.notebook NITROGEN CYCLE. Animated Nitrogen Cycle. Jan 3 5:33 PM. Jan 3 8:20 PM. Carbon Cycle BrainPOP
 Plant Kingdom Review What cycles are needed for plant life? - Carbon-Oxygen Cycle (including Photosynthesis) - Nitrogen Cycle - Water Cycle Let's take a look at the first two... Jan 3 5:33 PM Jan 3 8:20
Plant Kingdom Review What cycles are needed for plant life? - Carbon-Oxygen Cycle (including Photosynthesis) - Nitrogen Cycle - Water Cycle Let's take a look at the first two... Jan 3 5:33 PM Jan 3 8:20
copyright cmassengale Kingdoms and Classification
 1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
Fossils ACTIVITY I: FOSSILIZATION. Activity 1 is for K 2 nd. Activities I and II are for 3 rd 5 th
 Fossils Activity 1 is for K 2 nd. Activities I and II are for 3 rd 5 th OVERVIEW How does a living thing become a fossil? The mysterious processes by which evidence of past life is preserved are explored
Fossils Activity 1 is for K 2 nd. Activities I and II are for 3 rd 5 th OVERVIEW How does a living thing become a fossil? The mysterious processes by which evidence of past life is preserved are explored
Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls
 1 Plant Characteristics: Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls chloroplast vacuole Golgi body Cell wall nucleus mitochondria Cell membrane 2
1 Plant Characteristics: Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls chloroplast vacuole Golgi body Cell wall nucleus mitochondria Cell membrane 2
Station 1 Fossil Record
 The very first horses evolved on the North American continent over 55 million years ago. The horse fossil record is very rich in transitional species. This is a series of skulls and front leg fossils of
The very first horses evolved on the North American continent over 55 million years ago. The horse fossil record is very rich in transitional species. This is a series of skulls and front leg fossils of
8/25/ Opening Questions: Name the ist. Chapter 9 Biodiversity 2: Fungi and Plants Module Hyperlinks. Match the subject with the scientist:
 Chapter 9 Biodiversity 2: Fungi and Plants Module Hyperlinks 9.1. Fungi 9.2. Fungi structure and reproduction 9.3. Plant adaptations 9.4. Plant bodies consist of roots, stems, and leaves. 9.5. Plant bodies
Chapter 9 Biodiversity 2: Fungi and Plants Module Hyperlinks 9.1. Fungi 9.2. Fungi structure and reproduction 9.3. Plant adaptations 9.4. Plant bodies consist of roots, stems, and leaves. 9.5. Plant bodies
(b) The foods synthesized by the plants are stored as. (c) In photosynthesis solar energy is captured by the pigment called.
 WORKSHEET -1 CHAPTER- HOW DO PLANTS LIVE SUBJECT-BIOLOGY GRADE:7 LEVEL 1 1. Fill in the blanks: (a) Green plants are called since they synthesize their own food. (b) The foods synthesized by the plants
WORKSHEET -1 CHAPTER- HOW DO PLANTS LIVE SUBJECT-BIOLOGY GRADE:7 LEVEL 1 1. Fill in the blanks: (a) Green plants are called since they synthesize their own food. (b) The foods synthesized by the plants
GRADE 6: Life science 3. UNIT 6L.3 6 hours. Classification. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 6: Life science 3 Classification UNIT 6L.3 6 hours About this unit This unit is the third of five units on life science for Grade 6. The unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
GRADE 6: Life science 3 Classification UNIT 6L.3 6 hours About this unit This unit is the third of five units on life science for Grade 6. The unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
Where Do Bat Wings Come From?
 Where o at Wings ome From? 1 ats are the only mammals that have evolved the power of flight. They can avoid obstacles and slip through tight spaces. Many species are nocturnal and use echolocation to guide
Where o at Wings ome From? 1 ats are the only mammals that have evolved the power of flight. They can avoid obstacles and slip through tight spaces. Many species are nocturnal and use echolocation to guide
