MicroRNA mir-34 provides robustness to environmental stress response via
|
|
|
- Marjory Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MicroRNA mir-34 provides robustness to environmental stress respoe via the DAF-16 network in C. elega Meltem Isik 1,2, T. Keith Blackwell 2, and Eugene Berezikov 1,3 1 Hubrecht Ititute-KNAW and University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands; 2 Joslin Diabetes Center, Harvard Stem Cell Ititute, and Harvard Medical School Department of Genetics, Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America; 3 European Research Ititute for the Biology of Ageing, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands. Supplementary Figures and Tables: Supplementary Figure S1. Morphological defects in mir-34(gk437) dauers. Supplementary Figure S2. Effect of iulin respoe element (IRE), DAF-12, GA-repeat deletio on Pmir kb ::gfp expression in dauers. Supplementary Figure S3. Pmir kb ::gfp expression is regulated by DAF-16 in both adult and dauer stages. Supplementary Figure S4. Gene overlap analysis for up- and down-regulated genes for conditio tested in microarray analysis, class 1, class 2, dauer and non-dauer genes. Supplementary Figure S5. Both mir-34(gk437) and mir-34oe result in impaired stress respoe. Supplementary Figure S6. Model for daf-16/mir-34 feedback inhibition loop in regulating dauer morphogenesis and survival and environmental stress respoe. Supplementary Table S4. C. elega strai used in the study. Supplementary Table S5. Sequences of oligonucleotides used in the study.
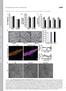
2 A N2 mir-34(gk437) rescue mir-34oe B Supplementary Figure S1. Morphological defects in mir-34(gk437) dauers. (A) Defects in alae formation. Alae positio are indicated by arrows. Alae are formed by single protruding ridges in wild-type animals, and it is split into several ridges in mir34(gk437) dauers. The defect is rescued in the rescue and overexpression strai. (B) Defects in body shapes due to bulges in hypodermis (indicated by arrows).
3 A sequence 1 sequence 2 B Pmir-34::gfp Pmir-34 seq1 ::gfp Pmir-34 seq2 ::gfp hypodermis whole dauer Supplementary Figure S2. Effect of iulin respoe element (IRE), DAF-12, GA-repeat deletio on Pmir kb ::gfp expression in dauers. (A) Location and sequence of tested deletio. (B) Hypodermal expression of Pmir kb ::gfp is diminished in dauers when sequence 1 (DAF-12 binding element and IRE) is deleted from mir-34 promoter. Both hypodermal and seam cell Pmir34::gfp expression in dauers is lost when GA-repeat elements are deleted from mir-34 promoter.
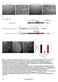
4 VNC & vulval precursor cells hypodermis DNC & tail hypodermis B daf-7(e1372); daf-16(mu86) daf-7(e1372) daf-2(e1370) N2 A fluorescence deity C D daf-16(mu86) daf-2(e1370) daf-2(e1370); daf-16(mu86) Merge DiI GFP DIC WT Supplementary Figure S3. Pmir-342.2kb::gfp expression is regulated by DAF-16 in both adult and dauer stages. (A) DAF-16 regulates mir-34 expression in dauers. (B) Pmir-342.2kb::gfp expression levels in excretory gland cells of (i) WT, (ii) daf-2(e1370), (iii) daf-2(e1370);daf-16(mu86), (iv) daf-16(mu86), (v) hif-1(ia4) and (vi) jnk-1(gk7) backgrounds (C) Quantification of fluorescence deity of Pmir-342.2kb::GFP in various genetic backgrounds, under heat stress and glucose supplementation. Data are expressed in arbitrary fluorescence units. Error bars represent SD. Statistical significance is calculated by two-tailed unpaired t test. P < 0.001, P < (D) DAF-16 is required for mir-34 expression in AWC amphid neuro of adults.
5 Supplementary Figure S4. Gene overlap analysis for up- and down-regulated genes for conditio tested in microarray analysis, class 1, class 2, dauer and non-dauer genes. GeneOverlap package was used to determine log2(odds) ratio values (green scale). Numbers represent P values for statistical significance of overlaps (Fisher s exact test).
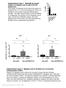
6 A i ii iii iv v vi vii N2_adult_20 o C vs N2_dauer_20 o C mir-34(-)_dauer_20 o C vs mir-34oe_dauer_20 o C N2_adult_20 o C vs N2_adult_25 o C mir-34(-)_adult_20 o C vs mir-34(-)_adult_25 o C mir-34oe_adult_20 o C vs mir-34oe_adult_25 o C mir-34(-)_adult_20 o C vs mir-34oe_adult_20 o C mir-34(-)_adult_25 o C vs mir-34oe_adult_25 o C B 100 Heat Stress Survival (%) N2 mir-34(gk437) mir-34oe rescue 10 C Survival (%) time (hr) Starvation * D % survival Hypoxic Stress N2 mir-34(gk437) mir-34 OE rescue 0 N2 mir-34(gk437) mir-34 OE rescue Supplementary Figure S5. Both mir-34(gk437) and mir-34oe result in impaired stress respoe. (A) Heatmap showing overlap between stress respoe genes induced by growth at high temperature and dauer formation and its correlation with mir-34 mutation and overexpression in dauer and adult stages. (B D) Survival under different stress conditio: heat stress (B), starvation (C) and hypoxic stress (D). Error bars represent SD. P < 0.01, P < 0.001, P < , unpaired two-tailed t test. All compariso are to WT.
7 Threshold Iulin-like signaling pathway iulin-like peptides TGF-β signaling pathway DAF-7 ligand DAF-2 receptor DAF-1 receptor DAF-16 PQM-1 mir-34 Dauer morphogenesis and survival Environmental stress respoe myc network (MDL-1, MXL-3) Supplementary Figure S6. Model for daf-16/mir-34 feedback inhibition loop in regulating dauer morphogenesis and survival and environmental stress respoe. Iulin signaling pathway and other pathways (i.e TGF-β signaling pathway) that directly and indirectly regulate DAF-16 nuclear localization, respectively, can modulate mir-34 levels. After mir-34 levels reach a threshold, DAF-16 levels drop down via targeting of daf-16 mrna by mir-34. A similar feedback inhibition loop may also be present between mir-34 and myc network. This crosstalk between mir-34, DAF-16 and myc network is necessary for regulation of dauer morphogenesis and survival and environmental stress respoe.
8 Supplementary Table S4. Strai used in this study. Strain name BER107 BER108 Genotype mir-34(gk437)x (outcrossed 9x from VC1051) daf-2(e1370)iii (outcrossed 4x from CB1370) BER109 daf-7(e1372)iii (outcrossed 4x from CB1372) BER110 daf-16(mu86)i (outcrossed 4x from CF1038 BER111 BER128 BER126 BER127 BER124 BER125 BER101 BER103 BER102 BER104 BER105 BER106 BER113 BER114 BER115 BER116 BER117 BER120 BER (+)] BER (+)] daf-16(mu86) I; muis61 (outcrossed 9x from CF1139) daf-16(mu86) I; muis61; mir-34(gk437) daf-2 (e1370)iii;mir-34(gk437) daf-7(e1372)iii; mir-34(gk437) unc-119(ed3)iii oxis[pmir kb ::mir-34; unc-119(+)] unc-119(ed3)iii oxis[pmir kb ::mir-34; unc-119(+)]; mir-34(gk437) unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb ::gfp; unc-119(+)] unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb ::gfp; unc-119(+)] unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb ::gfp; unc-119(+)] unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb :gfp; unc-119(+)] unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir-34 seq1 ::gfp; unc-119(+)] unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir-34 seq2 ::gfp; unc-119(+)] daf-1(e1487)iv; unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb ::gfp; unc-119(+)] daf-2 (e1370)iii; unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb ::gfp; unc-119(+)] daf-3(mgdf90)x; unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb ::gfp; unc-119(+)] daf-7(e1372)iii; unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb ::gfp; unc-119(+)] daf-9(e1406)x; unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb ::gfp; unc-119(+)] daf-16(mu86)i; unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb ::gfp; unc-119(+)] daf-2(e1370)iii; daf-16(mu86); unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb ::gfp; uncdaf-7(e1372)iii; daf-16(mu86); unc-119(ed3)iii Is[Pmir kb ::gfp; unc-
9 Supplementary Table S5. Primer sequences used in this study Cloning of mir-34 promoter Pmir kb -PstI-F gaactgcagccactggtttgcaaataattag Pmir kb -XbaI-R cgctctagacgttataagaataatagtcagtag Cloning of mir-34 gene mir-34-noti-f atagcggccgcccactggtttgcaaataattag mir-34-bamhi-r ataggatcctcaaagaagcgttttaaagaag mir-34 promoter truncatio Pmir-34-Not1-R atagcggccgccgttataagaataatagtcag Pmir kb -BsptI-F atacttaaggtttgagtttaaaaaaaaag Pmir kb -BsptI-F atacttaagagcgaagagggaggtaaggt Pmir kb -BsptI-F atacttaagttcttagtagtagaagaagaa mir-34 promoter deletio by Quickchange Pmir-34 Δseq2 -F GAAAAGGAGCgggaaacatagatagaggtaAAAGGGAGTAAGAGGACAGGAACAgggtga Pmir-34 Δseq2 -R tcaccctgttcctgtcctcttactcccttttacctctatctatgtttcccgctccttttc Pmir-34 Δseq1 -F ggacgacaagatagatcgaaaaggagcacaggaacagggtgagaaccccgcct Pmir-34 Δseq1 -R aggcggggttctcaccctgttcctgtgctccttttcgatctatcttgtcgtcc Identification of mir-34 mutation mir-34(gk437)-f1 gaagatactcaaactttgcttg mir-34(gk437)-r1 gaattcttgatcaatccattg mir-34(gk437)-f2 gcctcgttcgttcgctcttg mir-34(gk437)-r2 gaagcgttttaaagaagcgtcg
MIR-237 is Likely a Developmental Timing Gene that Regulates the L2-to-L3 Transition in C. Elegans
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Master's Theses (2009 -) Dissertations, Theses, and Professional Projects MIR-237 is Likely a Developmental Timing Gene that Regulates the L2-to-L3 Transition
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Master's Theses (2009 -) Dissertations, Theses, and Professional Projects MIR-237 is Likely a Developmental Timing Gene that Regulates the L2-to-L3 Transition
Upstream Elements Regulating mir-241 and mir-48 Abstract Introduction
 Upstream Elements Regulating mir-241 and mir-48 Hanna Vollbrecht, Tamar Resnick, and Ann Rougvie University of Minnesota: Twin Cities Undergraduate Research Scholarship 2012-2013 Abstract Caenorhabditis
Upstream Elements Regulating mir-241 and mir-48 Hanna Vollbrecht, Tamar Resnick, and Ann Rougvie University of Minnesota: Twin Cities Undergraduate Research Scholarship 2012-2013 Abstract Caenorhabditis
Dauer larva quiescence alters the circuitry of microrna pathways regulating cell fate progression in C. elegans
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 2177 Development 139, 2177-2186 (2012) doi:10.1242/dev.075986 2012. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Dauer larva quiescence alters the circuitry of microrna pathways regulating
RESEARCH ARTICLE 2177 Development 139, 2177-2186 (2012) doi:10.1242/dev.075986 2012. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Dauer larva quiescence alters the circuitry of microrna pathways regulating
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2717
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Dendrite length is not secondary to body length. Dendrite growth proceeds independently of the rate of body growth and decreases in rate in adults. n 20 on dendrite measurement, n
Supplementary Fig. 1. Dendrite length is not secondary to body length. Dendrite growth proceeds independently of the rate of body growth and decreases in rate in adults. n 20 on dendrite measurement, n
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion Rationale for using maternal ythdf2 -/- mutants as study subject To study the genetic basis of the embryonic developmental delay that we observed, we crossed fish with different
Supplementary Discussion Rationale for using maternal ythdf2 -/- mutants as study subject To study the genetic basis of the embryonic developmental delay that we observed, we crossed fish with different
Bi Lecture 8 Genetic Pathways and Genetic Screens
 Bi190-2013 Lecture 8 Genetic Pathways and Genetic Screens WT A 2X:2A her-1 tra-1 1X:2A her-1 tra-1 Female body Male body Female body Male body her-1(lf) B 2X:2A her-1(lf) tra-1 1X:2A her-1(lf) tra-1 Female
Bi190-2013 Lecture 8 Genetic Pathways and Genetic Screens WT A 2X:2A her-1 tra-1 1X:2A her-1 tra-1 Female body Male body Female body Male body her-1(lf) B 2X:2A her-1(lf) tra-1 1X:2A her-1(lf) tra-1 Female
Random Boolean Networks
 Random Boolean Networks Boolean network definition The first Boolean networks were proposed by Stuart A. Kauffman in 1969, as random models of genetic regulatory networks (Kauffman 1969, 1993). A Random
Random Boolean Networks Boolean network definition The first Boolean networks were proposed by Stuart A. Kauffman in 1969, as random models of genetic regulatory networks (Kauffman 1969, 1993). A Random
Adam J. Schindler, L. Ryan Baugh, David R. Sherwood* Abstract. Introduction
 Identification of Late Larval Stage Developmental Checkpoints in Caenorhabditis elegans Regulated by Insulin/IGF and Steroid Hormone Signaling Pathways Adam J. Schindler, L. Ryan Baugh, David R. Sherwood*
Identification of Late Larval Stage Developmental Checkpoints in Caenorhabditis elegans Regulated by Insulin/IGF and Steroid Hormone Signaling Pathways Adam J. Schindler, L. Ryan Baugh, David R. Sherwood*
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline. The pie-1 promoter and 3 utr were used to express yfp::gpr-1 in the germline. Expression levels from the yfp::gpr-1(cai 1.0)-expressing
Supplementary Figure 1 Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline. The pie-1 promoter and 3 utr were used to express yfp::gpr-1 in the germline. Expression levels from the yfp::gpr-1(cai 1.0)-expressing
microrna pseudo-targets
 microrna pseudo-targets Natalia Pinzón Restrepo Institut de Génétique Humaine (CNRS), Montpellier, France August, 2012 microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7 5 N NNNNNNNNNNNNNN NNNNNN 3 the seed
microrna pseudo-targets Natalia Pinzón Restrepo Institut de Génétique Humaine (CNRS), Montpellier, France August, 2012 microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7 5 N NNNNNNNNNNNNNN NNNNNN 3 the seed
robustness: revisting the significance of mirna-mediated regulation
 : revisting the significance of mirna-mediated regulation Hervé Seitz IGH (CNRS), Montpellier, France October 13, 2012 microrna target identification .. microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7
: revisting the significance of mirna-mediated regulation Hervé Seitz IGH (CNRS), Montpellier, France October 13, 2012 microrna target identification .. microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7
Follow this and additional works at:
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2014 The DAF-16 FOXO transcription factor regulates natc-1 to modulate stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans,
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2014 The DAF-16 FOXO transcription factor regulates natc-1 to modulate stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans,
The geneticist s questions. Deleting yeast genes. Functional genomics. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Functional genomics..is a field of molecular biology that attempts to make use of the vast wealth of data produced by genomic projects (such as genome sequencing projects)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Functional genomics..is a field of molecular biology that attempts to make use of the vast wealth of data produced by genomic projects (such as genome sequencing projects)
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3848
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
The C. elegans developmental timing protein LIN-42 regulates diapause in response to environmental cues
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 3501 Development 137, 3501-3511 (2010) doi:10.1242/dev.048850 2010. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd The C. elegans developmental timing protein LIN-42 regulates diapause in
RESEARCH ARTICLE 3501 Development 137, 3501-3511 (2010) doi:10.1242/dev.048850 2010. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd The C. elegans developmental timing protein LIN-42 regulates diapause in
University of Massachusetts Medical School Wan-Ju Liu University of Maryland
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Program in Systems Biology Publications and Presentations Program in Systems Biology 5-13-2014 Multiple transcription factors directly regulate
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Program in Systems Biology Publications and Presentations Program in Systems Biology 5-13-2014 Multiple transcription factors directly regulate
Wan-Ju Liu 1,2, John S Reece-Hoyes 3, Albertha JM Walhout 3 and David M Eisenmann 1*
 Liu et al. BMC Developmental Biology 2014, 14:17 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multiple transcription factors directly regulate Hox gene lin-39 expression in ventral hypodermal cells of the C. elegans embryo
Liu et al. BMC Developmental Biology 2014, 14:17 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multiple transcription factors directly regulate Hox gene lin-39 expression in ventral hypodermal cells of the C. elegans embryo
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review
 AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
Natural Variation, Development, and Adaptive Phenotypes in C. elegans
 Natural Variation, Development, and Adaptive Phenotypes in C. elegans Bradly Alicea http://publish.illinois.edu/bradly-alicea Fly/Worm Club, UIUC, April 22, 2015 with input from Nathan Schroeder, Rebecca
Natural Variation, Development, and Adaptive Phenotypes in C. elegans Bradly Alicea http://publish.illinois.edu/bradly-alicea Fly/Worm Club, UIUC, April 22, 2015 with input from Nathan Schroeder, Rebecca
Food perception without ingestion leads to metabolic changes and irreversible developmental arrest in C. elegans
 Kaplan et al. BMC Biology (2018) 16:112 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-018-0579-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Food perception without ingestion leads to metabolic changes and irreversible developmental
Kaplan et al. BMC Biology (2018) 16:112 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-018-0579-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Food perception without ingestion leads to metabolic changes and irreversible developmental
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1
 Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2662
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Genes required for axon pathfinding and extension in the C. elegans nerve ring
 Development 126, 3679-3692 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV8610 3679 Genes required for axon pathfinding and extension in the C. elegans nerve ring Jennifer A.
Development 126, 3679-3692 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV8610 3679 Genes required for axon pathfinding and extension in the C. elegans nerve ring Jennifer A.
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice Supplementary Figure 2.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Hes5. Hes Relative mrna levels
 A a Absolute mrna levels 6 5 4 3 2 1 hjag1 EP cdl1 EP Jag1 E2+1 b d m Hey1 c e EP Hey1 Dl1 E2+1 f h m Hey1 g i EP Hey1 1 a Hes5 Hes5 a Hes5 Hes5 B a b EP e 1.4 1.2 EP GFP GFP E2+1 c m Hey1 d Hey1 Relative
A a Absolute mrna levels 6 5 4 3 2 1 hjag1 EP cdl1 EP Jag1 E2+1 b d m Hey1 c e EP Hey1 Dl1 E2+1 f h m Hey1 g i EP Hey1 1 a Hes5 Hes5 a Hes5 Hes5 B a b EP e 1.4 1.2 EP GFP GFP E2+1 c m Hey1 d Hey1 Relative
downstream (0.8 kb) homologous sequences to the genomic locus of DIC. A DIC mutant strain (ro- 6
 A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
The β-catenin homolog BAR-1 and LET-60 Ras coordinately regulate the Hox gene lin-39 during Caenorhabditis elegans vulval development
 Development 125, 3667-3680 (1998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 DEV5223 3667 The β-catenin homolog BAR-1 and LET-60 Ras coordinately regulate the Hox gene lin-39 during
Development 125, 3667-3680 (1998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 DEV5223 3667 The β-catenin homolog BAR-1 and LET-60 Ras coordinately regulate the Hox gene lin-39 during
23-. Shoot and root development depend on ratio of IAA/CK
 Balance of Hormones regulate growth and development Environmental factors regulate hormone levels light- e.g. phototropism gravity- e.g. gravitropism temperature Mode of action of each hormone 1. Signal
Balance of Hormones regulate growth and development Environmental factors regulate hormone levels light- e.g. phototropism gravity- e.g. gravitropism temperature Mode of action of each hormone 1. Signal
Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization
 Cell Metabolism Supplemental Information Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization Prashant Mishra, Grigor Varuzhanyan,
Cell Metabolism Supplemental Information Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization Prashant Mishra, Grigor Varuzhanyan,
Written Exam 15 December Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no
 Technical University of Denmark Written Exam 15 December 2008 Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no. 27041 Aids allowed: Open book exam Provide your answers and calculations on separate
Technical University of Denmark Written Exam 15 December 2008 Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no. 27041 Aids allowed: Open book exam Provide your answers and calculations on separate
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, Gene Expression Regulation Mutations
 Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Measuring TF-DNA interactions
 Measuring TF-DNA interactions How is Biological Complexity Achieved? Mediated by Transcription Factors (TFs) 2 Regulation of Gene Expression by Transcription Factors TF trans-acting factors TF TF TF TF
Measuring TF-DNA interactions How is Biological Complexity Achieved? Mediated by Transcription Factors (TFs) 2 Regulation of Gene Expression by Transcription Factors TF trans-acting factors TF TF TF TF
Optimization of the heme biosynthesis pathway for the production of. 5-aminolevulinic acid in Escherichia coli
 Supplementary Information Optimization of the heme biosynthesis pathway for the production of 5-aminolevulinic acid in Escherichia coli Junli Zhang 1,2,3, Zhen Kang 1,2,3, Jian Chen 2,3 & Guocheng Du 2,4
Supplementary Information Optimization of the heme biosynthesis pathway for the production of 5-aminolevulinic acid in Escherichia coli Junli Zhang 1,2,3, Zhen Kang 1,2,3, Jian Chen 2,3 & Guocheng Du 2,4
The Timing of lin-4 RNA Accumulation Controls the Timing of Postembryonic Developmental Events in Caenorhabditis elegans
 Developmental Biology 210, 87 95 (1999) Article ID dbio.1999.9272, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on The Timing of lin-4 RNA Accumulation Controls the Timing of Postembryonic Developmental
Developmental Biology 210, 87 95 (1999) Article ID dbio.1999.9272, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on The Timing of lin-4 RNA Accumulation Controls the Timing of Postembryonic Developmental
Timing of the onset of a developmental cell death is controlled by transcriptional induction of the C. elegans ced-3 caspase-encoding gene
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 1357 Development 134, 1357-1368 (2007) doi:10.1242/dev.02818 Timing of the onset of a developmental cell death is controlled by transcriptional induction of the C. elegans ced-3 caspase-encoding
RESEARCH ARTICLE 1357 Development 134, 1357-1368 (2007) doi:10.1242/dev.02818 Timing of the onset of a developmental cell death is controlled by transcriptional induction of the C. elegans ced-3 caspase-encoding
ACCGGTTTCGAATTGACAATTAATCATCGGCTCGTATAATGGTACC TGAAATGAGCTGTTGACAATTAATCATCCGGCTCGTATAATGTGTGG AATTGTGAGCGGATAACAATTTCACAGGTACC
 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE S1. Promoter and riboswitch sequences used in this study. Predicted transcriptional start sites are bolded and underlined. Riboswitch sequences were obtained from Topp et al., Appl Environ
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE S1. Promoter and riboswitch sequences used in this study. Predicted transcriptional start sites are bolded and underlined. Riboswitch sequences were obtained from Topp et al., Appl Environ
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/5/e1602426/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In vivo mapping of tissue- and subcellular-specific proteomes in Caenorhabditis elegans The PDF file includes: Aaron
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/5/e1602426/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In vivo mapping of tissue- and subcellular-specific proteomes in Caenorhabditis elegans The PDF file includes: Aaron
Structure and Function Analysis of LIN-14, a Temporal Regulator of Postembryonic Developmental Events in Caenorhabditis elegans
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Mar. 2000, p. 2285 2295 Vol. 20, No. 6 0270-7306/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Structure and Function Analysis of LIN-14,
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Mar. 2000, p. 2285 2295 Vol. 20, No. 6 0270-7306/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Structure and Function Analysis of LIN-14,
Stochastic simulations
 Stochastic simulations Application to molecular networks Literature overview Noise in genetic networks Origins How to measure and distinguish between the two types of noise (intrinsic vs extrinsic)? What
Stochastic simulations Application to molecular networks Literature overview Noise in genetic networks Origins How to measure and distinguish between the two types of noise (intrinsic vs extrinsic)? What
Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering
 Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering by Valverde et. Al Published in Science 2004 Presented by Boyana Grigorova CBMG 688R Feb. 12, 2007 Circadian Rhythms: The Clock Within
Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering by Valverde et. Al Published in Science 2004 Presented by Boyana Grigorova CBMG 688R Feb. 12, 2007 Circadian Rhythms: The Clock Within
Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
 KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
A Novel zf-mynd Protein, CHB-3, Mediates Guanylyl Cyclase Localization to Sensory Cilia and Controls Body Size of Caenorhabditis elegans
 A Novel zf-mynd Protein, CHB-3, Mediates Guanylyl Cyclase Localization to Sensory Cilia and Controls Body Size of Caenorhabditis elegans Manabi Fujiwara 1 *, Takayuki Teramoto 1, Takeshi Ishihara 1, Yasumi
A Novel zf-mynd Protein, CHB-3, Mediates Guanylyl Cyclase Localization to Sensory Cilia and Controls Body Size of Caenorhabditis elegans Manabi Fujiwara 1 *, Takayuki Teramoto 1, Takeshi Ishihara 1, Yasumi
Caenorhabditis elegans by a member of TGF-β family
 Development 126, 1337-1347 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV6385 1337 Regulation of body length and male tail ray pattern formation of Caenorhabditis elegans by
Development 126, 1337-1347 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV6385 1337 Regulation of body length and male tail ray pattern formation of Caenorhabditis elegans by
Honors Biology Reading Guide Chapter 11
 Honors Biology Reading Guide Chapter 11 v Promoter a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA located near the start of a gene that is the binding site for RNA polymerase and the place where transcription begins
Honors Biology Reading Guide Chapter 11 v Promoter a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA located near the start of a gene that is the binding site for RNA polymerase and the place where transcription begins
Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Lectures 22-23 Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes From Mechanisms in Bacteria 123 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes
Eukaryotic Gene Expression Lectures 22-23 Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes From Mechanisms in Bacteria 123 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes
Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus:
 m Eukaryotic mrna processing Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus: Cap structure a modified guanine base is added to the 5 end. Poly-A tail
m Eukaryotic mrna processing Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus: Cap structure a modified guanine base is added to the 5 end. Poly-A tail
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The phenotypes of PI , BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
Multiple levels of regulation specify the polarity of an asymmetric cell division in C. elegans
 Development 127, 4587-4598 (2) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2 DEV4424 4587 Multiple levels of regulation specify the polarity of an asymmetric cell division in C. elegans
Development 127, 4587-4598 (2) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2 DEV4424 4587 Multiple levels of regulation specify the polarity of an asymmetric cell division in C. elegans
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
Heterochronic genes control the stage-specific initiation and expression of the dauer larva developmental program in Caenorhabditis elegans
 Heterochronic genes control the stage-specific initiation and expression of the dauer larva developmental program in Caenorhabditis elegans Zhongchi Liu and Victor Ambros Department of Cellular and Developmental
Heterochronic genes control the stage-specific initiation and expression of the dauer larva developmental program in Caenorhabditis elegans Zhongchi Liu and Victor Ambros Department of Cellular and Developmental
Multistability in the lactose utilization network of Escherichia coli
 Multistability in the lactose utilization network of Escherichia coli Lauren Nakonechny, Katherine Smith, Michael Volk, Robert Wallace Mentor: J. Ruby Abrams Agenda Motivation Intro to multistability Purpose
Multistability in the lactose utilization network of Escherichia coli Lauren Nakonechny, Katherine Smith, Michael Volk, Robert Wallace Mentor: J. Ruby Abrams Agenda Motivation Intro to multistability Purpose
Types of biological networks. I. Intra-cellurar networks
 Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Computer Simulation and Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Biophysics
 Victor Bloomfield Computer Simulation and Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Biophysics An Introduction Using R Springer Contents Part I The Basics of R 1 Calculating with R 3 1.1 Installing R 3 1.1.1
Victor Bloomfield Computer Simulation and Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Biophysics An Introduction Using R Springer Contents Part I The Basics of R 1 Calculating with R 3 1.1 Installing R 3 1.1.1
lon-1 Regulates Caenorhabditis elegans Body Size Downstream of the dbl-1 TGF Signaling Pathway
 Developmental Biology 246, 418 428 (2002) doi:10.1006/dbio.2002.0662 lon-1 Regulates Caenorhabditis elegans Body Size Downstream of the dbl-1 TGF Signaling Pathway Lisa L. Maduzia, Tina L. Gumienny, Cole
Developmental Biology 246, 418 428 (2002) doi:10.1006/dbio.2002.0662 lon-1 Regulates Caenorhabditis elegans Body Size Downstream of the dbl-1 TGF Signaling Pathway Lisa L. Maduzia, Tina L. Gumienny, Cole
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. JAK/STAT in early wing development (a-f) Wing primordia of second instar larvae of the indicated genotypes labeled to visualize expression of upd mrna
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. JAK/STAT in early wing development (a-f) Wing primordia of second instar larvae of the indicated genotypes labeled to visualize expression of upd mrna
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/345/ra91/dc1 Supplementary Materials for TGF-β induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition proceeds through stepwise activation of multiple feedback loops Jingyu
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/345/ra91/dc1 Supplementary Materials for TGF-β induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition proceeds through stepwise activation of multiple feedback loops Jingyu
Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday
 Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday 1. What is the Central Dogma? 2. How does prokaryotic DNA compare to eukaryotic DNA? 3. How is DNA
Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday 1. What is the Central Dogma? 2. How does prokaryotic DNA compare to eukaryotic DNA? 3. How is DNA
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J INTEGRINS I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. and M. Spector, Ph.D. Regulator
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J INTEGRINS I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. and M. Spector, Ph.D. Regulator
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its
 Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
mab-3 is a direct tra-1 target gene regulating diverse aspects of C. elegans
 Development 127, 4469-4480 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV9741 4469 mab-3 is a direct tra-1 target gene regulating diverse aspects of C. elegans male sexual development
Development 127, 4469-4480 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV9741 4469 mab-3 is a direct tra-1 target gene regulating diverse aspects of C. elegans male sexual development
Supporting information for
 Supporting information for Rewiring multi-domain protein switches: transforming a fluorescent Zn 2+ -sensor into a light-responsive Zn 2+ binding protein Stijn J.A. Aper and Maarten Merkx Laboratory of
Supporting information for Rewiring multi-domain protein switches: transforming a fluorescent Zn 2+ -sensor into a light-responsive Zn 2+ binding protein Stijn J.A. Aper and Maarten Merkx Laboratory of
Chapter 4 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays.
 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
Andres Bendesky 1, Jason Pitts 1, Matthew V. Rockman 2, William C. Chen 3, Man-Wah Tan 3, Leonid Kruglyak 4, Cornelia I. Bargmann 1 * Abstract
 Long-Range Regulatory Polymorphisms Affecting a GABA Receptor Constitute a Quantitative Trait Locus (QTL) for Social Behavior in Caenorhabditis elegans Andres Bendesky 1, Jason Pitts 1, Matthew V. Rockman
Long-Range Regulatory Polymorphisms Affecting a GABA Receptor Constitute a Quantitative Trait Locus (QTL) for Social Behavior in Caenorhabditis elegans Andres Bendesky 1, Jason Pitts 1, Matthew V. Rockman
m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 m6 m7 m8 wt m m m m m m m m8 - + wt +
 otherwise, you couldn't grow them!) You perform pairwise infections with each of your mutant bacteriophage strains and get the following results: (+) = pair of phages lysed host cells, (-) = pair of phages
otherwise, you couldn't grow them!) You perform pairwise infections with each of your mutant bacteriophage strains and get the following results: (+) = pair of phages lysed host cells, (-) = pair of phages
Supplemental Data. Yamamoto et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc WT + HCO 3. slac1-4/δnc #5 + HCO 3 WT + ABA. slac1-4/δnc #5 + ABA
 I (pa) I (pa) A WT + HCO 3 B 2 V (mv) 15 1 5 5 2 slac14/δnc #5 + HCO 3 4 6 WT (n = 6) 8 WT + HCO 3 (n = 7) slac14/δnc #5 (n = 6) slac14/δnc #5 + HCO 3 (n = 1) C WT + ABA D 2 V (mv) 15 1 5 5 2 slac14/δnc
I (pa) I (pa) A WT + HCO 3 B 2 V (mv) 15 1 5 5 2 slac14/δnc #5 + HCO 3 4 6 WT (n = 6) 8 WT + HCO 3 (n = 7) slac14/δnc #5 (n = 6) slac14/δnc #5 + HCO 3 (n = 1) C WT + ABA D 2 V (mv) 15 1 5 5 2 slac14/δnc
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mediates anoxia response and. Department of Biological Sciences, University of North Texas, Denton, TX, 76203
 Genetics: Published Articles Ahead of Print, published on September 15, 2006 as 10.1534/genetics.106.061390 Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mediates anoxia response and survival in Caenorhabditis
Genetics: Published Articles Ahead of Print, published on September 15, 2006 as 10.1534/genetics.106.061390 Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mediates anoxia response and survival in Caenorhabditis
Chemosensory Neurons Function in Parallel to Mediate a Pheromone Response in C. elegans
 Neuron, Vol. 17, 719 728, October, 1996, Copyright 1996 by Cell Press Chemosensory Neurons Function in Parallel to Mediate a Pheromone Response in C. elegans Wendy S. Schackwitz, Takao Inoue, in the environment
Neuron, Vol. 17, 719 728, October, 1996, Copyright 1996 by Cell Press Chemosensory Neurons Function in Parallel to Mediate a Pheromone Response in C. elegans Wendy S. Schackwitz, Takao Inoue, in the environment
Abl Kinase Inhibits the Engulfment of Apoptotic [corrected] Cells in Caenorhabditis elegans
![Abl Kinase Inhibits the Engulfment of Apoptotic [corrected] Cells in Caenorhabditis elegans Abl Kinase Inhibits the Engulfment of Apoptotic [corrected] Cells in Caenorhabditis elegans](/thumbs/74/71020578.jpg) Abl Kinase Inhibits the Engulfment of Apoptotic [corrected] Cells in Caenorhabditis elegans The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Abl Kinase Inhibits the Engulfment of Apoptotic [corrected] Cells in Caenorhabditis elegans The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
with%dr.%van%buskirk%%%
 with%dr.%van%buskirk%%% How$to$do$well?$ Before$class:$read$the$corresponding$chapter$ Come$to$class$ready$to$par9cipate$in$Top$Hat$ Don t$miss$an$exam!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!$ But$I m$not$good$with$science
with%dr.%van%buskirk%%% How$to$do$well?$ Before$class:$read$the$corresponding$chapter$ Come$to$class$ready$to$par9cipate$in$Top$Hat$ Don t$miss$an$exam!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!$ But$I m$not$good$with$science
TNFα 18hr. Control. CHX 18hr. TNFα+ CHX 18hr. TNFα: 18 18hr (KDa) PARP. Cleaved. Cleaved. Cleaved. Caspase3. Pellino3 shrna. Control shrna.
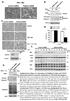 Survival ( %) a. TNFα 18hr b. Control sirna Pellino3 sirna TNFα: 18 18hr c. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna Caspase3 Actin Control d. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna *** 100 80 60 CHX 18hr 40 TNFα+ CHX 18hr
Survival ( %) a. TNFα 18hr b. Control sirna Pellino3 sirna TNFα: 18 18hr c. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna Caspase3 Actin Control d. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna *** 100 80 60 CHX 18hr 40 TNFα+ CHX 18hr
Lesson Overview. Gene Regulation and Expression. Lesson Overview Gene Regulation and Expression
 13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression THINK ABOUT IT Think of a library filled with how-to books. Would you ever need to use all of those books at the same time? Of course not. Now picture a tiny bacterium
13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression THINK ABOUT IT Think of a library filled with how-to books. Would you ever need to use all of those books at the same time? Of course not. Now picture a tiny bacterium
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Table S1. Aspergillus nidulans strains used in this study Strain Genotype Derivation
 Supplemental Material De Souza et al., 211 Table S1. Aspergillus nidulans strains used in this study Strain Genotype Derivation CDS295 pyrg89; pyroa4; pyrg Af ::son promotor::gfp-son nup98/nup96 ; chaa1
Supplemental Material De Souza et al., 211 Table S1. Aspergillus nidulans strains used in this study Strain Genotype Derivation CDS295 pyrg89; pyroa4; pyrg Af ::son promotor::gfp-son nup98/nup96 ; chaa1
FGF signaling functions in the hypodermis to regulate fluid balance in C. elegans
 Research article 2595 FGF signaling functions in the hypodermis to regulate fluid balance in C. elegans Peng Huang and Michael J. Stern* Yale University School of Medicine, Department of Genetics, I-354
Research article 2595 FGF signaling functions in the hypodermis to regulate fluid balance in C. elegans Peng Huang and Michael J. Stern* Yale University School of Medicine, Department of Genetics, I-354
Current Biology, Volume 18. David J. Reiner, Michael Ailion, James H. Thomas, and Barbara J. Meyer
 Supplemental Data C. elegans Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Ortholog SCD-2 Controls Dauer Formation by Modulating TGF-β Signaling David J. Reiner, Michael Ailion, James H. Thomas, and Barbara J. Meyer Supplemental
Supplemental Data C. elegans Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Ortholog SCD-2 Controls Dauer Formation by Modulating TGF-β Signaling David J. Reiner, Michael Ailion, James H. Thomas, and Barbara J. Meyer Supplemental
Haploid & diploid recombination and their evolutionary impact
 Haploid & diploid recombination and their evolutionary impact W. Garrett Mitchener College of Charleston Mathematics Department MitchenerG@cofc.edu http://mitchenerg.people.cofc.edu Introduction The basis
Haploid & diploid recombination and their evolutionary impact W. Garrett Mitchener College of Charleston Mathematics Department MitchenerG@cofc.edu http://mitchenerg.people.cofc.edu Introduction The basis
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression
 Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
Biological Roles of Cytokinins
 Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
FUNDAMENTALS of SYSTEMS BIOLOGY From Synthetic Circuits to Whole-cell Models
 FUNDAMENTALS of SYSTEMS BIOLOGY From Synthetic Circuits to Whole-cell Models Markus W. Covert Stanford University 0 CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York Contents /... Preface, xi
FUNDAMENTALS of SYSTEMS BIOLOGY From Synthetic Circuits to Whole-cell Models Markus W. Covert Stanford University 0 CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York Contents /... Preface, xi
The C. elegans SMOC-1 protein acts cell non-autonomously to promote bone. Melisa S. DeGroot, Herong Shi, Alice Eastman, Alexandra N.
 Genetics: Early Online, published on December 5, 2018 as 10.1534/genetics.118.301805 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 The C. elegans SMOC-1 protein acts cell non-autonomously to promote bone morphogenetic protein
Genetics: Early Online, published on December 5, 2018 as 10.1534/genetics.118.301805 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 The C. elegans SMOC-1 protein acts cell non-autonomously to promote bone morphogenetic protein
Germline stem cell differentiation entails regional control of cell fate. regulator GLD-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans
 Genetics: Early Online, published on January 12, 216 as 1.1534/genetics.115.185678 Germline stem cell differentiation entails regional control of cell fate regulator GLD-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans John
Genetics: Early Online, published on January 12, 216 as 1.1534/genetics.115.185678 Germline stem cell differentiation entails regional control of cell fate regulator GLD-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans John
A Synthetic Oscillatory Network of Transcriptional Regulators
 A Synthetic Oscillatory Network of Transcriptional Regulators Michael Elowitz & Stanislas Leibler Nature, 2000 Presented by Khaled A. Rahman Background Genetic Networks Gene X Operator Operator Gene Y
A Synthetic Oscillatory Network of Transcriptional Regulators Michael Elowitz & Stanislas Leibler Nature, 2000 Presented by Khaled A. Rahman Background Genetic Networks Gene X Operator Operator Gene Y
The DAF-7 TGF- signaling pathway regulates chemosensory receptor gene expression in C. elegans
 The DAF-7 TGF- signaling pathway regulates chemosensory receptor gene expression in C. elegans Katherine M. Nolan, 1,2 Trina R. Sarafi-Reinach, 1,2 Jennifer G. Horne, 1 Adam M. Saffer, 1 and Piali Sengupta
The DAF-7 TGF- signaling pathway regulates chemosensory receptor gene expression in C. elegans Katherine M. Nolan, 1,2 Trina R. Sarafi-Reinach, 1,2 Jennifer G. Horne, 1 Adam M. Saffer, 1 and Piali Sengupta
AP Biology. Free-Response Questions
 2018 AP Biology Free-Response Questions College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
2018 AP Biology Free-Response Questions College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
16 CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION
 16 CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION Chapter Outline 16.1 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION IN PROKARYOTES The operon is the unit of transcription in prokaryotes The lac operon for lactose metabolism is transcribed
16 CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION Chapter Outline 16.1 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION IN PROKARYOTES The operon is the unit of transcription in prokaryotes The lac operon for lactose metabolism is transcribed
Midterm 1. Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77
 Midterm 1 Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77 NAME: TA (circle one) Jody Westbrook or Jessica Piel Section (circle one) Tue Wed Thur MCB 141 First Midterm Feb. 21, 2008 Only answer 4 of these 5 problems.
Midterm 1 Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77 NAME: TA (circle one) Jody Westbrook or Jessica Piel Section (circle one) Tue Wed Thur MCB 141 First Midterm Feb. 21, 2008 Only answer 4 of these 5 problems.
The Caenorhabditis elegans APC-related gene apr-1 is required for epithelial cell migration and Hox gene expression
 The Caenorhabditis elegans APC-related gene apr-1 is required for epithelial cell migration and Hox gene expression Erika Fröhli Hoier, 1 William A. Mohler, 2 Stuart K. Kim, 3 and Alex Hajnal 1,4 1 Division
The Caenorhabditis elegans APC-related gene apr-1 is required for epithelial cell migration and Hox gene expression Erika Fröhli Hoier, 1 William A. Mohler, 2 Stuart K. Kim, 3 and Alex Hajnal 1,4 1 Division
JMJ14-HA. Col. Col. jmj14-1. jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA. Methylene Blue. Methylene Blue
 Fig. S1 JMJ14 JMJ14 JMJ14ΔFYR Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14-HA Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA Fig. S1. The expression level of JMJ14 and truncated JMJ14 with FYR (FYRN + FYRC) domain deletion
Fig. S1 JMJ14 JMJ14 JMJ14ΔFYR Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14-HA Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA Fig. S1. The expression level of JMJ14 and truncated JMJ14 with FYR (FYRN + FYRC) domain deletion
daf-31 Encodes the Catalytic Subunit of N Alpha- Acetyltransferase that Regulates Caenorhabditis elegans Development, Metabolism and Adult Lifespan
 daf-31 Encodes the Catalytic Subunit of N Alpha- Acetyltransferase that Regulates Caenorhabditis elegans Development, Metabolism and Adult Lifespan Di Chen 1. *, Jiuli Zhang 2., Justin Minnerly 2, Tiffany
daf-31 Encodes the Catalytic Subunit of N Alpha- Acetyltransferase that Regulates Caenorhabditis elegans Development, Metabolism and Adult Lifespan Di Chen 1. *, Jiuli Zhang 2., Justin Minnerly 2, Tiffany
Computational Genomics. Reconstructing dynamic regulatory networks in multiple species
 02-710 Computational Genomics Reconstructing dynamic regulatory networks in multiple species Methods for reconstructing networks in cells CRH1 SLT2 SLR3 YPS3 YPS1 Amit et al Science 2009 Pe er et al Recomb
02-710 Computational Genomics Reconstructing dynamic regulatory networks in multiple species Methods for reconstructing networks in cells CRH1 SLT2 SLR3 YPS3 YPS1 Amit et al Science 2009 Pe er et al Recomb
Transport of glucose across epithelial cells: a. Gluc/Na cotransport; b. Gluc transporter Alberts
 Figure 7 a. Secondary transporters make up the largest subfamily of transport proteins. TAGI 2000. Nature 408, 796 1. Na+- or H+-coupled cotransporters - Secondary active transport 2/7-02 Energy released
Figure 7 a. Secondary transporters make up the largest subfamily of transport proteins. TAGI 2000. Nature 408, 796 1. Na+- or H+-coupled cotransporters - Secondary active transport 2/7-02 Energy released
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
