Cells. Teacher Materials
|
|
|
- Chastity Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Teacher Preparation Teacher Materials Before you begin this unit, photocopy and distribute the following to students: Word Web (page 15) Unit Vocabulary (page 16) Vocabulary Crossword Puzzle* (page 17) Student Briefs (pages 18 23) Unit Assessments (pages 24 34) * You may wish to decrease the difficulty of the crossword puzzle by providing students with a list of words as a reference. Key Unit Concepts are the smallest units of life. are microscopic. perform life functions, like producing food and taking in oxygen. are made up of many parts, including a cell membrane and a nucleus. The nucleus controls the cell. Chromosomes carry instructions for the cells. Chromosomes are located in the nucleus. Chromosomes are made up of the chemical molecule DNA. A person receives 23 chromosomes from each of his or her parents. Genes are located in the DNA. Genes determine our personal traits. Heredity means the passing of genes to subsequent generations. have different shapes according to the type of function they perform. Tissue is made of a single type of cell. Organs are made from multiple types of tissue. Organ systems are two or more organs working in tandem to perform a function. Discussion Topics Name some organs systems in the human body. What jobs do these systems perform? Discuss what makes people different from each other. Where do these differences come from? See Generic Strategies and Activities on pages 8 and 9 for additional strategies useful to presenting this unit. Teacher Created Resources, Inc. 13 #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science
2 Brief #1: The Parts of Activities Conduct an Interview: Interview family members to determine what familial traits all of you have in common. Make a list of what these traits are. Find Inherited Traits: There are many traits that people have that are inherited from their parents. Some of these traits are dimples, the ability to roll the tongue, attached or unattached earlobes, being right- or left-thumbed, or having the second toe on the foot being longer than the big toe. Have students examine themselves and classmates for some of these inherited traits. Be a Tour Guide: Pretend you are a cell tour guide. Take visitors on a walk through a human cell. Explain the different parts. Tell what jobs these various parts do. Make a Chart: Human beings have 46 chromosomes. But not all living things have the same number of chromosomes. Find out the number of chromosomes in the following animals and make a chart that shows this data: fruit fly, dog, cat, goldfish, horse, cow. Key Words: inherited traits, chromosomes in animals Brief #2: How Work Make an Informational Poster: The cells that form tissue in the human body come in many shapes. Research the shape of some human cells blood cells, muscle cells, nerve cells, bone cells, etc. Then create an informational poster that includes illustrations of the cells and text that describes how their shape helps them to get a job done. Write an Organ Monologue: Select one organ in the human body and write a monologue from the point of view of that organ. Make sure to include information about location, shape and size, and specific job. Key Words: types of human cells, shapes of human cells, organs of human body Brief #3: Organ Systems Research and Report: Select one of the following organ systems to research: respiratory system, digestive system, nervous system, skeletal system, or muscular system. Create a report that tells what the organs are in the system and how they work together. Includes illustrations, graphs, charts, or any other materials that you think will help provide information about the system. Key Words: systems of the human body Internet Resources a great site from the Nemours Foundation, designed especially for children of all ages; includes relevant information in the form of games, recipes, and articles #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science 14 Teacher Created Resources, Inc
3 Student Introduction: Word Web Name: Date: Directions: Use this word web to help you brainstorm the characteristics of cells. What do cells do? What are the different parts of cell? Teacher Created Resources, Inc. 15 #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science
4 Vocabulary 1. cell membrane the protective covering of a cell 2. cells the smallest units of life 3. chromosomes where the cell instructions are located 4. DNA a double-helix-shaped chemical molecule that contains genes and is located in the chromosomes 5. double helix the shape of DNA molecules; a shape like that of a twister ladder 6. genes the part of DNA that determines what our personal traits will be 7. microscopic something that can t be seen without using a microscope 8. neurons nerve cells 9. nucleus the control center of a cell 10. organ groups of different types of tissue working together to do a job 11. organ system two or more organs working together to perform a specific job or function 12. round cells cells that have a round shape, like red blood cells 13. tissue group of the same kinds of cells working together to do a job #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science 16 Teacher Created Resources, Inc
5 Vocabulary Crossword Puzzle Name: Date: Directions: Complete the crossword puzzle. All of the words are vocabulary from Unit # Across 4. shape of red blood cells 5. nerve cell 9. trait providers 10. group of same cells 11. location of cell instructions Down 1. can t be seen with the naked eye 2. two or more organs 3. double-helix molecule 6. cell covering 7. smallest unit of life 8. cell s control center Teacher Created Resources, Inc. 17 #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science
6 Focus have different parts that perform specific functions. Brief #1: The Parts of All living things on our planet are made up of cells. It doesn t matter whether the living thing is big or small, swims or flies, or is a plant or an animal. are the smallest units of life. They are the building blocks of life on Earth. are microscopic. If something is microscopic, that means that you can t see it without using a microscope. There are some animals on the Earth that are made up of only a single cell. But there are others, like elephants and people, that contain trillions and trillions of cells. The Life of a Cell Even though cells are tiny, they have the same basic needs as larger organisms. For example, cells need to take in oxygen and produce food. They also need to remove waste products from their systems. respond to changes in their environment, just as people do. do all of these things so they can grow and divide, which is how new cells are made. Parts Your body is made up of many different parts, and these parts all have different jobs to do. For example, your heart and lungs keep oxygen-rich blood circulating through your body. Your muscles enable you to move around. are also made up of smaller parts. These smaller parts help cells to do many of the same things that your body does. All cells have a cell membrane. The cell membrane is kind of like the skin of the cell. It protects the inner parts of the cell. The cell membrane allows things like oxygen and water to enter the cells. But it also allows waste materials, like carbon dioxide, to leave the cell. Vocabulary 1. cells 2. microscopic 3. cell membrane 4. nucleus 5. chromosomes also have mitochondria and vacuoles. Mitochondria combine oxygen and food to produce energy, while vacuoles store and break down materials. Inside every cell there is a nucleus. The cell nucleus is very important. The nucleus is the control center of the cell. Inside each nucleus there are chromosomes. Chromosomes hold the instructions for each cell. In other words, it is the chromosomes that tell each cell what their job is and how to do it. #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science 18 Teacher Created Resources, Inc
7 Brief #1: The Parts of (cont.) Parts (cont.) Chromosomes are made up of a chemical molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid. The abbreviation for this chemical molecule is DNA. DNA has a specific shape. This shape is called a double helix, which look a bit like a twisted ladder. Every cell nucleus has 46 chromosomes. Every person inherits half, or 23, of his/her chromosomes from his/her mother and the other half from his/her father. Part of the DNA in the chromosomes is made up of genes. Each gene carries one piece of information. It is our genes that determine how tall we become, the color of our eyes Vocabulary and hair, and other traits that make us who we are. All of the 6. DNA cells in a particular human body 7. double helix have copies of the same genes. Each person is made up of about 8. gene 50,000 different genes. double-helix-shaped DNA molecule mitochondrion nucleus Parts of an Animal Cell chromosome vacuole cell membrane Teacher Created Resources, Inc. 19 #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science
8 Brief #1: The Parts of (cont.) Learning Toolbox sung to the tune of Old MacDonald Old MacDonald s made of cells, DN-DN-A, And in his cells are chromosomes, DN-DN-A. 23 from Mom, 23 from Dad, 23 and 23, that makes 46, Old MacDonald s made of cells, DN-DN-A. Old MacDonald s chromosomes are made of DNA, And in that DNA you ll find fifty thousand genes. With a gene gene here, and a gene gene there, Here a gene, there a gene, fifty thousand gene genes, Old MacDonald s chromosomes are made of DNA. Your parents pass their genes to you, and then you pass them on, Heredity s the name of when the genes get passed along. With a trait trait here, and a trait trait there, Here a trait, there a trait, everywhere a trait trait, Everybody s made of cells, DN-DN-A. #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science 20 Teacher Created Resources, Inc
9 Focus Different types of cells perform specialized jobs in the human body. Brief #2: How Work The human body is made up of trillions and trillions of cells. But all of these cells are not the same. Your body is full of all different types of cells. There are muscle cells, bone cells, and cells that make up your hair and nails. These cells have different shapes that help them to do their job. All of these different types of cells work together to make the human body function. Some Cell Types Neurons are the cells that make up the nervous system. Neurons relay information from the brain to the body, and vice versa. For example, let s say that you wanted to reach your hand up to catch a ball. The neurons in your brain would very rapidly carry this message from your brain down through the muscles in your arm so you could raise it up in the air and catch the ball. Vocabulary Now let s say that you accidentally touched the handle of a very hot pot. Ouch! In this case, the neurons in your hand send an almost-instant message to your brain that tells you to let go of the handle! The special shape of the neuron helps it to do its job of sending and receiving information. The Neuron 1. neurons 2. round cells dendrites cell body axon Round cells are shaped just like their name. Red blood cells are round cells. The job of a red blood cell is to carry oxygen through the body. The specific shape of a red blood cell helps it to do its job. If you look carefully at the illustration to the right, you will see that red blood cells are smooth and have indentations in their middles. Those little indentations create more surface area. That means the cell can carry more oxygen. Their smoothness allows these cells to glide easily through the blood vessels. Teacher Created Resources, Inc. 21 #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science
10 Tissue Brief #2: How Work (cont.) Most cells are so small that they can t be seen without the help of a microscope. But if enough cells join together, they can become visible. This is how tissue is formed in the body. Tissue is a large group of the same kinds of cells that have joined together to do a job. can create all sorts of different types of tissue. Nerve cells, or neurons, join together to make nerve tissue. Muscle cells join together to make muscle tissue, and skin cells join together to make skin tissue. In fact, when you look at your skin, what you are really seeing are trillions and trillions of flat skin cells that are connected together like the fibers in a blanket. Organs Vocabulary 3. tissue 4. organ You know that your body isn t made up of just tissue. You are full of different types of organs that do special jobs. Your heart and lungs are organs that pump blood and oxygen throughout your body. Your brain is an organ that is located inside of your skull. Organs are made up of different types of tissue that work together to do a job that helps your body function. Fast Facts 1. Skin is the largest organ in your body. 2. Skin is made up of layers and layers of cells. 3. Skin protects other organs and helps keep germs and bacteria out. 4. You shed about 40,000 dead skin cells every minute. 5. The eyelid has the thinnest skin on the body. #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science 22 Teacher Created Resources, Inc
11 Brief #3: Organ Systems Focus The human body has several major organ systems. Inside of your body there are organs made of tissues, and these tissues are made of cells. But the organs in your body do not usually work separately from each other. Most of the organs in your body work together to get a job done. Think of the different parts of a bicycle. The wheels, gears, pedals, and chain all work together to make the bicycle move. An organ system is two or more organs that work together to help your body perform an important function or job. Some Organ Systems The skeletal system is one major organ system in the human body. This system is made up of 206 bones. The bones of the human body provide a frame for the muscles. They protect internal organs and make it possible for us to move around. Of course, your bones couldn t move around at all unless they were covered and connected by muscles. The muscles of the body form another major organ system. The human body has 640 muscles. And yet another organ system runs through your muscles, helping then to work. That is your nervous system. Vocabulary 1. organ system skull humerus vertebra sternum rib deltoid pectoralis biceps pelvis radius ulna femur abdominal quadriceps tibia fibula Teacher Created Resources, Inc. 23 #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science
12 Sentence-Completion Assessment Name: Date: Directions: Read each statement. Fill in the word or words that best complete the sentence. 1. A is the smallest unit of life. 2. In order to live, cells must take in and make. 3. The cell protects the inner parts of the cell. 4. The cell membrane is kind of like the of the cell. 5. The acts like the brain of the cell. 6. The chromosomes are located in the. 7. The tell each cell what to do and how to do it. 8. The number of chromosomes each person has is. 9. DNA is a molecule. 10. You inherit your chromosomes from your. GO #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science 28 Teacher Created Resources, Inc
13 Sentence-Completion Assessment (cont.) 11. DNA is located in the. 12. The carry information about our traits. 13. The number of genes that people have is about. 14. have different shapes to help them do specific. 15. A nerve cell is also called a. 16. The shape of a red blood cell is. 17. A group of the same cells working together is called. 18. The shape of a skin cell is. 19. When different groups of tissue work together, are formed. 20. An is two or more organs working together to do a specific job. Teacher Created Resources, Inc. 29 #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science
14 Unit #1 Crossword Puzzle (page 17) Across 4. round 5. neuron 9. genes 10. tissue 11. chromosomes Down 1. microscopic 2. organ system 3. DNA 6. membrane 7. cell 8. nucleus 5 N 10 T E U 1 M I C R O I S S C O P I 11 C O U N E 2 O 4 R G A N S Y S T E H R O M 3 D O U N O 8 N U C L E U S A D 9 G 6 M M B R A N O M E 7 C E N E Multiple-Choice (pages 24 27) 1. A 2. B 3. D 4. C 5. C 6. C 7. A 8. B 9. C 10. A 11. B 12. D 13. D 14. B 15. C 16. B S L L S 17. C 18. B 19. A 20. D Answer Key Sentence-Completion (pages 28 29) 1. cell 2. oxygen, food 3. membrane 4. skin 5. nucleus 6. nucleus 7. chromosomes chemical 10. parents 11 chromosomes 12. genes , jobs 15. neuron 16. round 17. tissue 18. flat 19. organs 20. organ system True-False (pages 30 31) 1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. T 6. F 7. T 8. F 9. T 10. F 11. T 12. T 13. F 14. T 15. F 16. F 17. F 18. F 19. T 20. F Matching (pages 32 33) 1. K 2. V 3. A 4. H 5. W 6. F 7. C 8. U 9. T 10. S 11. R 12. Q 13. J 14. G 15. P 16. B 17. D 18. O 19. N 20. I Graphic (page 34) Check graphics for accuracy and understanding. Use the diagram on page 19 as a guide. Unit #2 Crossword Puzzle (page 41) Across 4. trachea 6. larynx 9. arteries #2925 Differentiated Lessons: Science 216 Teacher Created Resources, Inc
VOCABULARY. Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System
 CELLS VOCABULARY Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System THE IMPORTANCE OF CELLS Cells are the smallest unit of life in all living things They are organized structures
CELLS VOCABULARY Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System THE IMPORTANCE OF CELLS Cells are the smallest unit of life in all living things They are organized structures
HUMAN BODY THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS REM 653 A TEACHING RESOURCE FROM...
 THE HUMAN BODY SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS A TEACHING RESOURCE FROM... REM 653 AUTHOR Melba Callender 1987, 2001 Copyright by Remedia Publications, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. The
THE HUMAN BODY SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS A TEACHING RESOURCE FROM... REM 653 AUTHOR Melba Callender 1987, 2001 Copyright by Remedia Publications, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. The
Living Things. perform a specific job in the body. Skin and lining of organs. Blood, bones, cartilage, fat. Brain and nerves
 Living Things Structure & Function BIG IDEA : All living things are made of cells A. Unicellular Organisms 1. Made of only one cell. 2. Examples paramecia, amoebas, bacteria B. Multicellular Organisms
Living Things Structure & Function BIG IDEA : All living things are made of cells A. Unicellular Organisms 1. Made of only one cell. 2. Examples paramecia, amoebas, bacteria B. Multicellular Organisms
Cells The Units of Life
 Before You Read Before you read the chapter, respond to these statements. Write an A if you agree with the statement. Write a D if you disagree with the statement. Before You Read Bacteria are the smallest
Before You Read Before you read the chapter, respond to these statements. Write an A if you agree with the statement. Write a D if you disagree with the statement. Before You Read Bacteria are the smallest
Cells. Teacher Materials
 Teacher Preperation Teacher Materials Before you begin this unit, photocopy and distribute the following to students: Student Introduction (page 15) Unit Vocabulary (page 16) Student Briefs (pages 17 22)
Teacher Preperation Teacher Materials Before you begin this unit, photocopy and distribute the following to students: Student Introduction (page 15) Unit Vocabulary (page 16) Student Briefs (pages 17 22)
Unit 2: Cells. Students will understand that the organs in an organism are made of cells that have structures & perform specific life functions
 Unit 2: Cells Students will understand that the organs in an organism are made of cells that have structures & perform specific life functions Vocabulary Cell Chloroplast Tissue Cell wall Organ Lysosome
Unit 2: Cells Students will understand that the organs in an organism are made of cells that have structures & perform specific life functions Vocabulary Cell Chloroplast Tissue Cell wall Organ Lysosome
SOME PAST KNOWLEDGE. Lesson 1
 OBJECTIVE: INTRODUCE BIOLOGY AND REVIEW SOME PAST KNOWLEDGE. Lesson 1 ON THE WHITEBOARDS! Brainstorm about what you remember about cells What you know about them (choose a colour) What you sort of remember
OBJECTIVE: INTRODUCE BIOLOGY AND REVIEW SOME PAST KNOWLEDGE. Lesson 1 ON THE WHITEBOARDS! Brainstorm about what you remember about cells What you know about them (choose a colour) What you sort of remember
How to use this book. How the book is organised. Answering questions. Learning and using the terminology. Developing skills
 How to use this book Welcome to the beginning of your Human and Social Biology course! We hope that you really enjoy your course, and that this book will help you to understand your work, and to do well
How to use this book Welcome to the beginning of your Human and Social Biology course! We hope that you really enjoy your course, and that this book will help you to understand your work, and to do well
STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure
 STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure Big Idea 14: Organization and Development of Living Organisms SC.6.L.14.1 Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms
STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure Big Idea 14: Organization and Development of Living Organisms SC.6.L.14.1 Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms
The Cells That Make Us By ReadWorks
 The Cells That Make Us By ReadWorks Mom, I m hurt, said Mike. What happened? asked Mike s mom. I stumbled and fell while playing football at the playground today. I scraped my knee, said Mike. You poor
The Cells That Make Us By ReadWorks Mom, I m hurt, said Mike. What happened? asked Mike s mom. I stumbled and fell while playing football at the playground today. I scraped my knee, said Mike. You poor
Cell Structure: Organelles. Unit Seventh Grade
 Cell Structure: Organelles Unit 3 --- Seventh Grade Cells are everywhere. Even though most cells cannot be seen with the naked eye, they make up every living thing. Your body contains trillions of cells.
Cell Structure: Organelles Unit 3 --- Seventh Grade Cells are everywhere. Even though most cells cannot be seen with the naked eye, they make up every living thing. Your body contains trillions of cells.
3 The Organization of Living Things
 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment
 Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
Nerve cells have many branches that help them send signals throughout the body.
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
WHAT S ON THE INSIDE An Introduction to Plant and Animal Cells
 W 531 WHAT S ON THE INSIDE An Introduction to Plant and Animal Cells Tonya Bain, UT Extension Agent, Crockett County Jennifer Richards, Curriculum Specialist, Tennessee 4-H Youth Development Tennessee
W 531 WHAT S ON THE INSIDE An Introduction to Plant and Animal Cells Tonya Bain, UT Extension Agent, Crockett County Jennifer Richards, Curriculum Specialist, Tennessee 4-H Youth Development Tennessee
Day 1 Let's Explore! *Recording Chart on Next Slide
 Day 1 Let's Explore! *Recording Chart on Next Slide *Copy in Science notebook. Which Hits First Objects Hypothesis Results BB vs G BB vs W BB vs PP BB vs T G vs W G vs PP G vs T W vs PP W vs T PP vs T
Day 1 Let's Explore! *Recording Chart on Next Slide *Copy in Science notebook. Which Hits First Objects Hypothesis Results BB vs G BB vs W BB vs PP BB vs T G vs W G vs PP G vs T W vs PP W vs T PP vs T
Specialized Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems. Chap 2, p. 67 Chap 9, p. 295 Chap 14, p
 Specialized Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems Chap 2, p. 67 Chap 9, p. 295 Chap 14, p. 468-471 2. I. Cell (Review) basic unit of structure and function in a living thing. They carry out the processes
Specialized Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems Chap 2, p. 67 Chap 9, p. 295 Chap 14, p. 468-471 2. I. Cell (Review) basic unit of structure and function in a living thing. They carry out the processes
You learned that Schleiden and Schwann discovered that all living
 42 A Closer Look R E A D I N G You learned that Schleiden and Schwann discovered that all living organisms are made up of one or more cells. This includes plants, animals, and many microbes. The microbes
42 A Closer Look R E A D I N G You learned that Schleiden and Schwann discovered that all living organisms are made up of one or more cells. This includes plants, animals, and many microbes. The microbes
Plant Cells and Animal Cells!
 SCIENCE ALLIANCE Christina examines Plant Cells and Animal Cells! by Carole Marsh 2008 Carole Marsh Permission is hereby granted to the individual purchaser or classroom teacher to reproduce materials
SCIENCE ALLIANCE Christina examines Plant Cells and Animal Cells! by Carole Marsh 2008 Carole Marsh Permission is hereby granted to the individual purchaser or classroom teacher to reproduce materials
Review. Watch the following video How Stuff Works - Cells video
 Types of Cells Review Watch the following video How Stuff Works - Cells video Multi-cellular Organisms Living things can be as simple as single-celled organisms such as a Paramecium or an Amoeba that lives
Types of Cells Review Watch the following video How Stuff Works - Cells video Multi-cellular Organisms Living things can be as simple as single-celled organisms such as a Paramecium or an Amoeba that lives
Unit 6L.1: Cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A collection of specialized cells makes tissues.
 Unit 6L.1: Living things are made of Specialized cells Tissues and Organs Cell Division By the end of this unit you will know: All living organisms are made of cells. A collection of specialized cells
Unit 6L.1: Living things are made of Specialized cells Tissues and Organs Cell Division By the end of this unit you will know: All living organisms are made of cells. A collection of specialized cells
Skeletal 2 - joints. Puzzle 1 bones
 Puzzle 1 bones Listed below are the names of some of the bones that make up your skeletal system. But the names have been encrypted using a secret code. Can you decipher this code to find out what they
Puzzle 1 bones Listed below are the names of some of the bones that make up your skeletal system. But the names have been encrypted using a secret code. Can you decipher this code to find out what they
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. cell organ cell membrane prokaryote organelles eukaryote cell wall
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. cell organ cell membrane prokaryote organelles eukaryote cell wall
Module 6 Note Taking Guide. Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life
 Module 6 Note Taking Guide Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life Lesson Page: Organization of Living Things The smallest level of organization for living things. Example: Oxygen, Hydrogen - A group of atoms
Module 6 Note Taking Guide Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life Lesson Page: Organization of Living Things The smallest level of organization for living things. Example: Oxygen, Hydrogen - A group of atoms
Station 1 Cell Structure and Function
 Station 1 Cell Structure and Function 1. What is the full name of the organelle that is abbreviated ER? Endoplasmic reticulum 2. What is the function of the ER? To turn DNA (blueprints) into protein (machines
Station 1 Cell Structure and Function 1. What is the full name of the organelle that is abbreviated ER? Endoplasmic reticulum 2. What is the function of the ER? To turn DNA (blueprints) into protein (machines
ZEBRAFISH CROSSWORD PUZZLE (LEVEL 1)
 ZEBRAFISH CROSSWORD PUZZLE (LEVEL 1) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 The organ that pumps blood through the body 6 An organ in the fish that takes oxygen from the water 7 Structures in the lung that take oxygen from
ZEBRAFISH CROSSWORD PUZZLE (LEVEL 1) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 The organ that pumps blood through the body 6 An organ in the fish that takes oxygen from the water 7 Structures in the lung that take oxygen from
CLASSIFICATION AND VARIATION
 1 Living organisms Living things are made of tiny units called cells. Cells help living organisms to carry out one or more of the following life processes. Draw lines to match each process to its definition.
1 Living organisms Living things are made of tiny units called cells. Cells help living organisms to carry out one or more of the following life processes. Draw lines to match each process to its definition.
Abraham Darby Academy KS3 Biology Cells, tissue, organs
 Abraham Darby Academy KS3 Biology Cells, tissue, organs Knowledge series Study Booklet 2017 Key terms Adaptation: A feature of an organism's body which helps it to survive. Bacteria: Single-celled micro-organisms.
Abraham Darby Academy KS3 Biology Cells, tissue, organs Knowledge series Study Booklet 2017 Key terms Adaptation: A feature of an organism's body which helps it to survive. Bacteria: Single-celled micro-organisms.
How do we define what it means to be alive?
 How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life-7 Characteristics of Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional
How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life-7 Characteristics of Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional
You learned that Schleiden and Schwann discovered that all living
 42 A Closer Look r e a d i n g You learned that Schleiden and Schwann discovered that all living organisms are made up of one or more cells. This includes plants, animals, and many microbes. The microbes
42 A Closer Look r e a d i n g You learned that Schleiden and Schwann discovered that all living organisms are made up of one or more cells. This includes plants, animals, and many microbes. The microbes
3.2. Eukaryotic Cells and Cell Organelles. Teacher Notes and Answers. section
 section 3.2 Eukaryotic Cells and Cell Organelles Teacher Notes and Answers SECTION 2 Instant Replay 1. Answers will vary. An example answer is a shapeless bag. 2. store and protect the DNA 3. mitochondria
section 3.2 Eukaryotic Cells and Cell Organelles Teacher Notes and Answers SECTION 2 Instant Replay 1. Answers will vary. An example answer is a shapeless bag. 2. store and protect the DNA 3. mitochondria
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms. Section 2: Inside Cells
 Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 2: 42 Essential Question: Are all cells the same? - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Organelle Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 2: 42 Essential Question: Are all cells the same? - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Organelle Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast
Introduction. Cells under the Light Microscope. Activity 1
 Introduction If you look at a thin slice taken from any plant or animal under a microscope, you can see it is made up of small boxes called cells. Most cells are too small to see with the naked eye, so
Introduction If you look at a thin slice taken from any plant or animal under a microscope, you can see it is made up of small boxes called cells. Most cells are too small to see with the naked eye, so
tissues are made of cells that work together, organs are )
 Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Genetic Changes Lesson 2 CW
 Guiding Question What theory serves as the basis of what we believe about how evolutionary changes occur? 7 th GRADE SCIENCE Genetic Changes Lesson 2 CW # Name: Date: Homeroom: I can Activator At the beginning
Guiding Question What theory serves as the basis of what we believe about how evolutionary changes occur? 7 th GRADE SCIENCE Genetic Changes Lesson 2 CW # Name: Date: Homeroom: I can Activator At the beginning
THE CELL THEORY (R+R+R+E+G+N+T+S) 3).
 CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
How do we define what it means to be alive?
 How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional definition: must
How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional definition: must
Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true.
 Unit 4 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. A stimulus is anything that threatens the
Unit 4 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. A stimulus is anything that threatens the
Is it possible to see atoms?
 Is it possible to see atoms? No How do we know about them? Through experiments What is the relationship between atoms and molecules? Atoms make up molecules Diagram the particles in each of the states
Is it possible to see atoms? No How do we know about them? Through experiments What is the relationship between atoms and molecules? Atoms make up molecules Diagram the particles in each of the states
Molecular and cellular biology is about studying cell structure and function
 Chapter 1 Exploring the World of the Cell In This Chapter Discovering the microscopic world Getting matter and energy Reading the genetic code Molecular and cellular biology is about studying cell structure
Chapter 1 Exploring the World of the Cell In This Chapter Discovering the microscopic world Getting matter and energy Reading the genetic code Molecular and cellular biology is about studying cell structure
Cells. Part 1: Characteristics of Living Things
 Cells Part 1: Characteristics of Living Things Introduction Living or Non-living? How do you know? What characteristics does it have that makes you think that way? Living? What makes something living?
Cells Part 1: Characteristics of Living Things Introduction Living or Non-living? How do you know? What characteristics does it have that makes you think that way? Living? What makes something living?
Cells Key Words. Task. Key words. Write a definition for each of the key words listed below. Microscope. Plant cell. Animal Cell.
 KS3 Science Cells Cells Key Words Task Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words Microscope Plant cell Animal Cell Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cell wall Chloroplasts Mitochondria
KS3 Science Cells Cells Key Words Task Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words Microscope Plant cell Animal Cell Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cell wall Chloroplasts Mitochondria
Chapter 1 Lesson 1 page 26
 Chapter 1 Lesson 1 page 26 1. organism- any living thing that can carry out its life on its own 2. unicellular-one-celled organism 3. multicellular- many-celled organism Chapter 1 Lesson 1 Cells Vocab
Chapter 1 Lesson 1 page 26 1. organism- any living thing that can carry out its life on its own 2. unicellular-one-celled organism 3. multicellular- many-celled organism Chapter 1 Lesson 1 Cells Vocab
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING VOCABULARY 1. Academic Vocabulary Which of the following words is the closest in meaning to the word structure? a. evidence c. duty b. shape d. location Complete each
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING VOCABULARY 1. Academic Vocabulary Which of the following words is the closest in meaning to the word structure? a. evidence c. duty b. shape d. location Complete each
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION. Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
Studying Life. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 1.3 Studying Life
 Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
Name: Period: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: _ Date: _ Cell Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The invention of the microscope made it possible for people to discover a.
Name: Period: _ Date: _ Cell Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The invention of the microscope made it possible for people to discover a.
 http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization MADE UP OF CELLS REPRO- DUCE 5 CHARACH- TERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO CHANGES GROW AND DEVELOP USE ENERGY cells the basic units of structure and function of all living
Levels of Organization MADE UP OF CELLS REPRO- DUCE 5 CHARACH- TERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO CHANGES GROW AND DEVELOP USE ENERGY cells the basic units of structure and function of all living
Mid-Unit 1 Study Guide
 Mid- Study Guide Lessons 1, 3, & 4 1.1 Essential Questions: What are living things made of? What term describes the smallest unit that can perform all of the functions necessary for life? Eukaryotic cells
Mid- Study Guide Lessons 1, 3, & 4 1.1 Essential Questions: What are living things made of? What term describes the smallest unit that can perform all of the functions necessary for life? Eukaryotic cells
GRADE 7 SCIENCE Post-Assessment
 ORANGE PUBLIC SCHOOLS OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION OFFICE OF SCIENCE GRADE 7 SCIENCE Post-Assessment Answer Key and Scoring Guide School Year 2013-2014 SGO Post-Assessment Grade 7 KEY 44 pts total
ORANGE PUBLIC SCHOOLS OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION OFFICE OF SCIENCE GRADE 7 SCIENCE Post-Assessment Answer Key and Scoring Guide School Year 2013-2014 SGO Post-Assessment Grade 7 KEY 44 pts total
Biology Test Review Science 8
 Biology Test Review Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems 304-7 Explain structural and functional relationships between and among cells, tissues, organs and systems in the human
Biology Test Review Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems 304-7 Explain structural and functional relationships between and among cells, tissues, organs and systems in the human
adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG)
 FOSS Living Systems Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG) algae a large plantlike group of water organisms
FOSS Living Systems Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG) algae a large plantlike group of water organisms
1. The picture below shows a paramecium. 2. Anya is observing an organism in the laboratory. The table below shows her observations.
 Name: Period: Date: Life Science MCAS Review Packet Directions: Answer each of the following questions under the standards. The question may be multiple choice or open response, if needed please use a
Name: Period: Date: Life Science MCAS Review Packet Directions: Answer each of the following questions under the standards. The question may be multiple choice or open response, if needed please use a
CELL Readings BCMS 1/1/2018
 CELL Readings BCMS 1/1/2018 3.1 Cell Biology Learning Objectives Explain how cells are observed. Define the three main parts of the cell theory. Explain the levels of organization in an organism. Introduction
CELL Readings BCMS 1/1/2018 3.1 Cell Biology Learning Objectives Explain how cells are observed. Define the three main parts of the cell theory. Explain the levels of organization in an organism. Introduction
Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms Worksheet
 Name Date Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms Worksheet Instructions for VIVED Science 1. Open the Plant Cell Structures and Animal (Human) Cell Structures sessions and follow the instructions. 2.
Name Date Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms Worksheet Instructions for VIVED Science 1. Open the Plant Cell Structures and Animal (Human) Cell Structures sessions and follow the instructions. 2.
CS8.1 Grade 8 Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems (grade 8)
 CS8.1 Grade 8 Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems (grade 8) Overview: Students will analyze the characteristics of cells, and compare structural and functional characteristics of plant and animal Students
CS8.1 Grade 8 Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems (grade 8) Overview: Students will analyze the characteristics of cells, and compare structural and functional characteristics of plant and animal Students
CELL THEORY & FUNCTION
 UNIT 1- THE CELL CELL THEORY & FUNCTION A Word From Bill Record your observations about the picture to the right. What do you think you are you looking at? Describe the structure with as much detail
UNIT 1- THE CELL CELL THEORY & FUNCTION A Word From Bill Record your observations about the picture to the right. What do you think you are you looking at? Describe the structure with as much detail
BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function
 BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function The cell is the smallest unit of life. Each living cell has a nucleus which functions to control the actions of the rest of the cell. Upon successful
BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function The cell is the smallest unit of life. Each living cell has a nucleus which functions to control the actions of the rest of the cell. Upon successful
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Student Exploration: Cell Types
 3. Names: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are you supposed to be learning in this activity? 2. Why do you think learning this
3. Names: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are you supposed to be learning in this activity? 2. Why do you think learning this
SNC2D BIOLOGY 4/1/2013. TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Animal & Plant Tissues (P.42-45) Animal Tissues. Animal Tissues
 SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Animal & Plant Tissues (P.42-45) Animal Tissues As you already know, groups of cells that work together to perform a task are called tissues. For example, muscle
SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Animal & Plant Tissues (P.42-45) Animal Tissues As you already know, groups of cells that work together to perform a task are called tissues. For example, muscle
Forces and Motion Study Guide
 Position: the location of an object Forces and Motion Study Guide Reference Point: any object that is not moving and can be used to describe the position of another object Distance: the length of a line
Position: the location of an object Forces and Motion Study Guide Reference Point: any object that is not moving and can be used to describe the position of another object Distance: the length of a line
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell. Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components.
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
Student Exploration: Cell Types
 Name: Period: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
Name: Period: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart
 CELLS, CELLS, CELLS A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart Cells Defined as the basic unit of living things. Cell Theory All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic units of structure
CELLS, CELLS, CELLS A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart Cells Defined as the basic unit of living things. Cell Theory All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic units of structure
Reading Selection: How do species change over time?
 Reading Selection: How do species change over time? 1. Who first studied how species change over time? Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) and Charles Darwin (1809-1882) both had ideas about how life on
Reading Selection: How do species change over time? 1. Who first studied how species change over time? Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) and Charles Darwin (1809-1882) both had ideas about how life on
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
How do species change over time?
 Who first studied how species change over time? How do species change over time? Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) and Charles Darwin (1809-1882) both had ideas about how life on earth changed over time.
Who first studied how species change over time? How do species change over time? Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) and Charles Darwin (1809-1882) both had ideas about how life on earth changed over time.
Unit 4: Cells. Biology 309/310. Name: Review Guide
 Unit 4: Cells Review Guide LEARNING TARGETS Place a checkmark next to the learning targets you feel confident on. Then go back and focus on the learning targets that are not checked. Identify the parts
Unit 4: Cells Review Guide LEARNING TARGETS Place a checkmark next to the learning targets you feel confident on. Then go back and focus on the learning targets that are not checked. Identify the parts
Cells: The Basic Unit Of Life
 Chapter 2 Cells: The Basic Unit Of Life A Joke Why did the chicken cross the playground? To get to the other slide!! 1 Can you name the world s largest cell???? It s the yolk of the ostrich egg. It s the
Chapter 2 Cells: The Basic Unit Of Life A Joke Why did the chicken cross the playground? To get to the other slide!! 1 Can you name the world s largest cell???? It s the yolk of the ostrich egg. It s the
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes
 Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Chapter 4 Cells: The Basic Units of Life The Big Idea All organisms are composed of one or more cells.
 Chapter 4 Cells: The Basic Units of Life The Big Idea All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Section 1 The Characteristics of Cells Key Concept Cells function similarly in all living organisms.
Chapter 4 Cells: The Basic Units of Life The Big Idea All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Section 1 The Characteristics of Cells Key Concept Cells function similarly in all living organisms.
What in the Cell is Going On?
 What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology
 Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Midterm Study Guide Major Concepts
 Midterm Study Guide Name 7 th Grade PSI Major Concepts 1. What is an atom? 2. What is a molecule? 3. What is an element? 4. What is a compound? 5. What are physical properties? Describe a few examples.
Midterm Study Guide Name 7 th Grade PSI Major Concepts 1. What is an atom? 2. What is a molecule? 3. What is an element? 4. What is a compound? 5. What are physical properties? Describe a few examples.
Unit 5: Living beings
 Unit 5: Living beings 1. Characteristics of living beings 2. Composition of living beings 3. The cell 4. The vital functions 5. Levels of organisation Think and answer? a. What living beings can you see
Unit 5: Living beings 1. Characteristics of living beings 2. Composition of living beings 3. The cell 4. The vital functions 5. Levels of organisation Think and answer? a. What living beings can you see
Cells and Genetics. Life Science. Cell parts. Cell parts cont. Cell processes. Cell Division 5/4/2015
 Cells and Genetics Life Science SOL Review Hooke was 1 st person to observe cells Cells Basic Unit of structure and function of life Prokaryote: bacteria/no nucleus Eukaryote: membrane structures; everything
Cells and Genetics Life Science SOL Review Hooke was 1 st person to observe cells Cells Basic Unit of structure and function of life Prokaryote: bacteria/no nucleus Eukaryote: membrane structures; everything
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics section 1 Meiosis Before You Read Think about the traits that make people unique. Some people are tall, while others are short. People can have brown, blue, or green
10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics section 1 Meiosis Before You Read Think about the traits that make people unique. Some people are tall, while others are short. People can have brown, blue, or green
Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card Do First in Handout
 Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card Do First in Handout Do First: Answer in your DFAD Answer the questions are in your Guided Notes, no DFAD this week. You have 4 mins. Thursday, February 15 th is
Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card Do First in Handout Do First: Answer in your DFAD Answer the questions are in your Guided Notes, no DFAD this week. You have 4 mins. Thursday, February 15 th is
Student Exploration: Cell Types
 3. Name: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
3. Name: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
7 th Grade PSI. Slide 1 / 116. Slide 2 / 116. Slide 3 / 116. Structure and Function & Information Processing. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 116 Slide 2 / 116 7 th Grade PSI Structure and Function & Information Processing 2015-11-07 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 116 Click on the topic to go to that section Cells: the Fundamental
Slide 1 / 116 Slide 2 / 116 7 th Grade PSI Structure and Function & Information Processing 2015-11-07 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 116 Click on the topic to go to that section Cells: the Fundamental
Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr
 Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr Learning Target: B.1.a Analyze the similarities and differences
Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr Learning Target: B.1.a Analyze the similarities and differences
Cells, Tissues and Organs
 Lesson One Aims By the end of this lesson you should be able to: recognise these cell structures as seen with a light microscope and with an electron microscope: nucleus, chromosomes, cell membrane, mitochondria,
Lesson One Aims By the end of this lesson you should be able to: recognise these cell structures as seen with a light microscope and with an electron microscope: nucleus, chromosomes, cell membrane, mitochondria,
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Mitochondria. Nickname: Batteries. bean shaped. Structure: Function: provides energy for the cell (powerhouse of the cell)
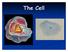 The Cell #1 Mitochondria Mitochondria Nickname: Batteries Structure: bean shaped Function: provides energy for the cell (powerhouse of the cell) Mitochondria #2 Nucleus Nucleus Nickname: Structure: Function:
The Cell #1 Mitochondria Mitochondria Nickname: Batteries Structure: bean shaped Function: provides energy for the cell (powerhouse of the cell) Mitochondria #2 Nucleus Nucleus Nickname: Structure: Function:
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1
 Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 How does a child inherit one copy of each gene from each parent? Compare what you already know with this flowchart. 1. Fill in each blank
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 How does a child inherit one copy of each gene from each parent? Compare what you already know with this flowchart. 1. Fill in each blank
From a Cell to an Organism
 From a Cell to an Organism Levels of Organization Life s Organization All matter is made of atoms. Atoms combine and form molecules. Molecules make up cells. A large animal, such as a Komodo dragon, is
From a Cell to an Organism Levels of Organization Life s Organization All matter is made of atoms. Atoms combine and form molecules. Molecules make up cells. A large animal, such as a Komodo dragon, is
What Is an Animal? Animal Characteristics
 1 What You Will Learn Animals are multicellular organisms. Animals have specialized cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Animals have seven basic characteristics. Why It Matters The characteristics
1 What You Will Learn Animals are multicellular organisms. Animals have specialized cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Animals have seven basic characteristics. Why It Matters The characteristics
Downloaded from
 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH FINAL TERM -2012 SCIENCE WORKSHEET CLASS V LESSON 3- THE MOON I. FILL IN THE BLANKS 1. The eclipse of the sun is called eclipse. 2. was the first Indian to go into the
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH FINAL TERM -2012 SCIENCE WORKSHEET CLASS V LESSON 3- THE MOON I. FILL IN THE BLANKS 1. The eclipse of the sun is called eclipse. 2. was the first Indian to go into the
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
Structure and Function of Plant and Animal Cells
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 8 Structure and Function of Plant and Animal Cells WORKBOOK Name: 8.1 A Closer Look pp. 158-164 Read pp. 158-159 Before the invention of microscope technology,
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 8 Structure and Function of Plant and Animal Cells WORKBOOK Name: 8.1 A Closer Look pp. 158-164 Read pp. 158-159 Before the invention of microscope technology,
Ms. Stacey-Ann Joseph HSB TEST 1
 SECTION A: LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT Circle the most appropriate answer for each question. 1. Which are not organisms? A. Bacteria B. Cars C. Trees D. Wolves 2. Which is defined by the power
SECTION A: LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT Circle the most appropriate answer for each question. 1. Which are not organisms? A. Bacteria B. Cars C. Trees D. Wolves 2. Which is defined by the power
1 st Semester Vocabulary
 1 st Semester Vocabulary 1. Qualitative Observation Observation that involves descriptions and characteristics. Example: Color and appearance The cat looks scared. The cat has green eyes. The cat has long
1 st Semester Vocabulary 1. Qualitative Observation Observation that involves descriptions and characteristics. Example: Color and appearance The cat looks scared. The cat has green eyes. The cat has long
Read It! Read It! The jellylike fluid inside the cell is called the. Plant cells and animal cells. have many of the same.
 Read It! Read It! 1. The smallest part of a living thing that carries out actions to keep the thing alive is a. 2. The jellylike fluid inside the cell is called the. Read It! Plant cells and animal cells
Read It! Read It! 1. The smallest part of a living thing that carries out actions to keep the thing alive is a. 2. The jellylike fluid inside the cell is called the. Read It! Plant cells and animal cells
2.1 CELL STRUCTURE. The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life.
 2.1.1 Microscopy The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life. A general introduction to the microscope. The light microscope All cells are microscopic which
2.1.1 Microscopy The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life. A general introduction to the microscope. The light microscope All cells are microscopic which
Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 18: From Cell To Organism
 Name Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 18: From Cell To Organism Date Objective: Students will be able to compare organisms unique cells and cellular organization. Essential Questions: 1.
Name Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 18: From Cell To Organism Date Objective: Students will be able to compare organisms unique cells and cellular organization. Essential Questions: 1.
Student Exploration: Cell Types
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
