Mitochondrial Quality Control
|
|
|
- Ronald McCormick
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mitochondrial Quality Control Oleh Khalimonchuk, Ph.D. Graduate Course 2214/BIOC 998 Stockholm, May 16, 2017
2 Respiration (ATP generation) Cofactors & key metabolites synthesis Ion homeostasis Lipid homeostasis ROS production/signaling Regulation of apoptosis Yeast Human Mitochondria are semi-autonomous organelles involved in a variety of vital cellular processes Sustaining normal mitochondrial function is critical as mitochondria are not produced de novo microcopyu.com
3 Composed of 1,000-1,500 proteins, majority of which are synthesized in the cytosol and imported into the organelle A small fraction of proteins (8-13) originates from the organelle s own genome The inner membrane is extremely protein-rich and is one of the major sites of essential mitochondrial functions Bohovych et al., Antiox. Redox Signal. (2015)
4 What can go wrong in a mitochondrion? Extensive ROS production by mitochondrial respiratory iiichain (MRC) can damage proteins and mtdna which iiiare in the close proximity to the MRC Improperly assembled redox cofactors can act as proiiioxidants (inherent ability to generate ROS via Fenton iiireactions ) Mismatches in subunits stoichiometry may lead to iiiaccumulation of unassembled/misfolded proteins Khalimonchuk et al., J. Biol. Chem. (2007); Khalimonchuk et al., J. Biol. Chem. (2012); Bohovych et al., Antioxid. Redox Signal. (2015)
5 Mitochondrial dysfunction - the road to ruin Nuclear DNA mutations mtdna mutations Misfolded proteins ROS MRC dysfunction Impaired mitochondrial dynamics Ca 2+ overload Impaired cellular energetics Cellular damage/death Cancers: Gliomas Lymphomas Neurological: Leigh syndrome Leukodystrophy Optic nerve atrophy Ataxias Neurodegenerative: Parkinsonism ALS Cardiovascular: Cardiomyopathies Peripheral artery disease and Aging Levytskyy et al., J. Neuroimmune Pharm. (2016) Vafai and Mootha, Nature (2012)
6 We re doomed!!! or are we?
7 Biogenesis Dynamics: fission/fusion Mitophagy Respiration (ATP generation) Cofactor synthesis Ion homeostasis Lipid homeostasis ROS production/signaling Regulation of apoptosis ROS scavenging Protein quality control repair/refolding/degradation DNA repair Multiple mechanisms are involved in sustaining of normal mitochondrial function Adapted from Figge et al., Bioessays (2013)
8 Mitochondrial quality control (MQC) Two levels of MQC: 1). Organellar 2). Molecular (aka intramitochondrial) Molecular and organellar MQC are interdependent and functionally intertwined Rugarli & Langer, EMBO J. (2012)
9 Organellar MQC fusion Mitochondrial content mixing via fusion helps to dilute the damage Fusion No fusion Youle & van der Bliek, Science (2012) Tsushima et al. (submitted)
10 Organellar MQC fusion OM fusion IM fusion OM and IM fusion are coordinated but physically separate events Charcot-Marie-Tooth Syndrome Dominant Optic Atrophy Detmer & Chan, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. (2007); Ishihara et al., Antioxid. Redox Signal. (2013); Wai & Langer, Trends Endocrin. Metab. (2016) Ubiquitination Phosphoylation SUMOylation Thiol oxidation
11 Organellar MQC fusion SIMH = Stress-induced mitochondrial hyperfusion SIMH relies on thiol oxidation of the conserved cysteine residues in Mfn1/2 Anand et al., BBA (2013); Wai & Langer, Trends Endocrin. Metab. (2016)
12 Organellar MQC fission Neurodegeneration Myocardial Infarction ER Mito Dnm1/Drp1 rings Otera & Mihara, J. Biochem. (2011); Hoppins & Nunnari, Science (2013); Wai & Langer, Trends Endocrin. Metab. (2016)
13 Organellar MQC - mitophagy Parkinsonism Youle & van der Bliek, Science (2012); Escobar-Henriques & Langer EMBO Rep. (2014) Damaged mitochondria can be segregated through fission and eliminated by mitophagy
14 Organellar MQC mitochondria-derived vesicles Anand et al., BBA (2013); Soubannier et al., PLoS One (2013); Bohovych et al., Antioxid. Redox Signal. (2015) Mitochondria-derived vesicles recently identified non-mitophagy clearance mechanism
15 Organellar/Molecular MQC UPS delivers Several other factors appear to work in parallel or concomitantly with PINK1/Parkin system (MITOL, MULAN, Mdm30, Vms1, DJ-1, etc.) MITOL, MULAN and Mdm30 are ubiquitin ligases involved mitochondria-associated degradation (MAD) Paget s disease ALS Anand et al., BBA (2013)
16 Organellar/Molecular MQC playing tag with mitochondria Vms1 is an auxiliary factor that tags damaged mitochondria and helps to recruit UPS machinery Heo et al., Mol. Cell (2010); Iryna Bohovych (unpublished) When neither hyperfusion, nor mitophagy can help cells undergo apoptosis
17 Molecular MQC - Proteases Hi there Removal of misfolded, damaged or non-assembled polypeptides Central roles in: mitochondrial biogenesis mitochondrial dynamics mitochondrial signaling lipid homeostasis apoptosis Bohovych et al., Antioxid. Redox Signal. (2015)
18 Molecular MQC - Proteases Two major classes of IMQC proteases: 1). ATP-dependent (AAA+ proteases) 2). ATP-independent Sauer & Baker, Annu. Rev. Biochem (2011); Levytskyy et al., J. Neuroimmune Pharm. (2016)
19 Molecular MQC - Proteases Parkinsonism HFD-induced obesity Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Dilated cardiomyopathy Mental Retardation CORDAS syndrome Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Spinocerebellar Ataxia type 28 Spastic Ataxia-Neuropathy Syndrome Parkinsonism Genetic interactions indicate tight functional coupling between MQC proteases Bohovych et al., J. Biol. Chem (2014)
20 Molecular MQC in the matrix Matrix MQC involves both soluble and mitochondrial inner membrane anchored proteases Removal of processed mitochondrial targeting signal peptides is yet another critical aspect of the matrix MQC Levytskyy et al., J. Neuroimmune Pharm. (2016) Alzheimer s disease
21 Molecular MQC in the IM and IMS Proteolytic processing Regulatory proteolysis Proteolytic removal of damaged proteins Adapted from Anand et al., BBA (2013)
22 Where molecular and organellar MQC intersect Stress-triggered cleavage of L- OPA1 by activated OMA1 protease stimulates fission and leads to metabolic re-tuning Control -DY ROS Heat stress Hypoxia (?) Oma1 MO Quiros et al., EMBO J. (2012); Bohovych et al., Sci. Rep. (2015); Wai & Langer, Trends Endocrin. Metab. (2016)
23 Where molecular and organellar MQC intersect PINK1 accumulation is a consequence of its attenuated turnover by PARL protease Anand et al., BBA (2013)
24 Mitochondrion to nucleus communication Retrograde responses Various signals are produced by mitochondria to communicate their functional states AMPK ROS, Ca 2+, ATP/ADP, NAD + /NADH Ac-CoA/Citrate Succinate/Fumarate (ATP/ADP) LON, m-aaa and likely Oma1 proteases participate in modulation of mitochondrial ROS and Ca 2+ levels TORC1 NRF2L MAPK Sirtuins HIF1a HIF1a (ROS) (NAD + /NADH; Ac-CoA) (Succinate/Fumarate)
25 Mitochondrion to nucleus communication - Metabolites Certain mitochondrial metabolites can be transported outside of the organelle and impinge on several signaling pathways or elicit epigenetic modifications Bohovych & Khalimonchuk, Front. Cell Dev. Biol. (2016)
26 Mitochondrion to nucleus communication - UPRmt Upon stress, AFTS-1/ATF5 localizes to the nucleus and initiates UPRmt-like response No stress Stress Phsp-6::GFP Ed Germany (unpublished) Bohovych & Khalimonchuk, Front. Cell Dev. Biol. (2016)
27 Mitochondrion to nucleus stress communication - ROS Destabilization of the respiratory supercomplexes in Oma1-deficient cells impinges on TORC1-Rim15-Msn2/4 signaling axis Bohovych & Khalimonchuk, Front. Cell Dev. Biol. (2016) Bohovych et al., Mol. Cell. Biol. (2016)
28 Take home messages Sustaining normal mitochondrial function is critical for cellular welfare Several aspects of mitochondrial function may turn into disaster routes and need to be tightly controlled by mitochondrial quality control mechanisms Mitochondrial quality control is a multi-faceted and hierarchal set of interdependent mechanisms at both molecular and organellar levels Mitochondrial proteases play key roles in the majority of MQC mechanisms Mitochondria effectively communicate with nucleus and other organelles via several mechanisms which involve MQC proteases Under certain conditions, transient mitochondria-derived ROS can be amplified and act as hormetic-like signals interfering with key cellular signaling pathways
Mitochondrial Quality Control
 Mitochondrial Quality Control Oleh Khalimonchuk, Ph.D. Graduate Course 2214/BIOC 998 Lincoln, June 14, 2016 Respiration (ATP generation) Cofactors & key metabolites synthesis Ion homeostasis Lipid homeostasis
Mitochondrial Quality Control Oleh Khalimonchuk, Ph.D. Graduate Course 2214/BIOC 998 Lincoln, June 14, 2016 Respiration (ATP generation) Cofactors & key metabolites synthesis Ion homeostasis Lipid homeostasis
Mitochondrial Quality Control
 Mitochondrial Quality Control You are here Oleh Khalimonchuk, Ph.D. Graduate Course 2214/BIOC 938 Charleston, May 20, 2015 biology4kids.com Cryo-electron microscopy Fluorescent microscopy Yeast Human Semi-autonomous,
Mitochondrial Quality Control You are here Oleh Khalimonchuk, Ph.D. Graduate Course 2214/BIOC 938 Charleston, May 20, 2015 biology4kids.com Cryo-electron microscopy Fluorescent microscopy Yeast Human Semi-autonomous,
M i t o c h o n d r i a
 M i t o c h o n d r i a Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Mitochondria Function: generation of metabolic energy in eukaryotic cells Generation of ATP from the breakdown of
M i t o c h o n d r i a Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Mitochondria Function: generation of metabolic energy in eukaryotic cells Generation of ATP from the breakdown of
What are mitochondria?
 What are mitochondria? What are mitochondria? An intracellular organelle. There are 100 to 1000s of mitochondria/cell. Most mitochondria come from the mother. Mitochondria have their own DNA Mitochondria
What are mitochondria? What are mitochondria? An intracellular organelle. There are 100 to 1000s of mitochondria/cell. Most mitochondria come from the mother. Mitochondria have their own DNA Mitochondria
Mitochondria associate with the cytoskeleton. Figure 14-5 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
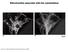 Mitochondria associate with the cytoskeleton Figure 14-5 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Special arrangements of mitochondria Figure 14-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science
Mitochondria associate with the cytoskeleton Figure 14-5 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Special arrangements of mitochondria Figure 14-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science
Scale in the biological world
 Scale in the biological world 2 A cell seen by TEM 3 4 From living cells to atoms 5 Compartmentalisation in the cell: internal membranes and the cytosol 6 The Origin of mitochondria: The endosymbion hypothesis
Scale in the biological world 2 A cell seen by TEM 3 4 From living cells to atoms 5 Compartmentalisation in the cell: internal membranes and the cytosol 6 The Origin of mitochondria: The endosymbion hypothesis
Lecture 7 Cell Biolog y ٢٢٢ ١
 Lecture 7 ١ Mitochondria ٢ Mitochondria Mitochondria are the energy factories of the cells. The energy currency for the work that animals must do is the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Lecture 7 ١ Mitochondria ٢ Mitochondria Mitochondria are the energy factories of the cells. The energy currency for the work that animals must do is the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Structure of mitochondria
 Structure of mitochondria Subcompartments of mitochondria Outer membrane (OM) Inner membrane (IM) Matrix Intermembrane space (IMS) Cristae membrane Inner boundary membrane Cristae compartment Molecular
Structure of mitochondria Subcompartments of mitochondria Outer membrane (OM) Inner membrane (IM) Matrix Intermembrane space (IMS) Cristae membrane Inner boundary membrane Cristae compartment Molecular
09/30/2017. Kyu-Sun Lee, Ph.D. Metabolism & Neurophysiology Research Group Hazard Monitoring BNT Res Center
 09/30/2017 Kyu-Sun Lee, Ph.D. Metabolism & Neurophysiology Research Group Hazard Monitoring BNT Res Center Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs
09/30/2017 Kyu-Sun Lee, Ph.D. Metabolism & Neurophysiology Research Group Hazard Monitoring BNT Res Center Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs
Biological Process Term Enrichment
 Biological Process Term Enrichment cellular protein localization cellular macromolecule localization intracellular protein transport intracellular transport generation of precursor metabolites and energy
Biological Process Term Enrichment cellular protein localization cellular macromolecule localization intracellular protein transport intracellular transport generation of precursor metabolites and energy
Yeast Genome-wide Screens to Ascertain the Genetic Landscape for Barth Syndrome. Christopher R. McMaster, PhD Dalhousie University
 Yeast Genome-wide Screens to Ascertain the Genetic Landscape for Barth Syndrome Christopher R. McMaster, PhD Dalhousie University Using Systematic Genetics to Identify Modifies Genes that Affect Fitness
Yeast Genome-wide Screens to Ascertain the Genetic Landscape for Barth Syndrome Christopher R. McMaster, PhD Dalhousie University Using Systematic Genetics to Identify Modifies Genes that Affect Fitness
Mitochondria are double-membrane
 Mitochondrial Fission, Fusion, and Stress Richard J. Youle 1 * and Alexander M. van der Bliek 2 * Mitochondrial fission and fusion play critical roles in maintaining functional mitochondria when cells
Mitochondrial Fission, Fusion, and Stress Richard J. Youle 1 * and Alexander M. van der Bliek 2 * Mitochondrial fission and fusion play critical roles in maintaining functional mitochondria when cells
The Mitochondrion. Renáta Schipp
 The Mitochondrion Renáta Schipp Origin Endosymbiothic theory the Mitochondria (and Chloroplastids) were originally free-living cells they lived in an endosymbiosis with a hostcell organellfree anaerobe
The Mitochondrion Renáta Schipp Origin Endosymbiothic theory the Mitochondria (and Chloroplastids) were originally free-living cells they lived in an endosymbiosis with a hostcell organellfree anaerobe
The Protein Import Machinery of Mitochondria A Regulatory Hub in Metabolism, Stress, and Disease
 The Protein Import Machinery of Mitochondria A Regulatory Hub in Metabolism, Stress, and Disease Angelika B. Harbauer, 1,2,3,4 René P. Zahedi, 5 Albert Sickmann, 5,6 Nikolaus Pfanner, 1,4, * and Chris
The Protein Import Machinery of Mitochondria A Regulatory Hub in Metabolism, Stress, and Disease Angelika B. Harbauer, 1,2,3,4 René P. Zahedi, 5 Albert Sickmann, 5,6 Nikolaus Pfanner, 1,4, * and Chris
Review Article The Emerging Role of Proteolysis in Mitochondrial Quality Control and the Etiology of Parkinson s Disease
 son s Disease Volume 2012, Article ID 382175, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2012/382175 Review Article The Emerging Role of Proteolysis in Mitochondrial Quality Control and the Etiology of son s Disease Riya Shanbhag,
son s Disease Volume 2012, Article ID 382175, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2012/382175 Review Article The Emerging Role of Proteolysis in Mitochondrial Quality Control and the Etiology of son s Disease Riya Shanbhag,
MITOCHONDRIAL BIOGENESIS AND REDOX REGULATION
 MITOCHONDRIAL BIOGENESIS AND REDOX Claude A. Piantadosi, MD Professor of Medicine and Pathology Duke University Medical Center Durham, N.C. USA Objectives Provide an overview of the physiological and pathological
MITOCHONDRIAL BIOGENESIS AND REDOX Claude A. Piantadosi, MD Professor of Medicine and Pathology Duke University Medical Center Durham, N.C. USA Objectives Provide an overview of the physiological and pathological
Scale in the biological world
 Scale in the biological world From living cells to atoms A cell seen by TEM Compartmentalisation in the cell: internal membranes and the cytosol The cytosol: more than just H2O RNAs Proteins Ribosomes
Scale in the biological world From living cells to atoms A cell seen by TEM Compartmentalisation in the cell: internal membranes and the cytosol The cytosol: more than just H2O RNAs Proteins Ribosomes
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
Signal Transduction. Dr. Chaidir, Apt
 Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division
 Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
GO ID GO term Number of members GO: translation 225 GO: nucleosome 50 GO: calcium ion binding 76 GO: structural
 GO ID GO term Number of members GO:0006412 translation 225 GO:0000786 nucleosome 50 GO:0005509 calcium ion binding 76 GO:0003735 structural constituent of ribosome 170 GO:0019861 flagellum 23 GO:0005840
GO ID GO term Number of members GO:0006412 translation 225 GO:0000786 nucleosome 50 GO:0005509 calcium ion binding 76 GO:0003735 structural constituent of ribosome 170 GO:0019861 flagellum 23 GO:0005840
Mitochondria Mitochondria were first seen by kollicker in 1850 in muscles and called them sarcosomes. Flemming (1882) described these organelles as
 Mitochondria Mitochondria were first seen by kollicker in 1850 in muscles and called them sarcosomes. Flemming (1882) described these organelles as filia Altmann (1890) observed these structures and named
Mitochondria Mitochondria were first seen by kollicker in 1850 in muscles and called them sarcosomes. Flemming (1882) described these organelles as filia Altmann (1890) observed these structures and named
Mitochondrial dynamics in ischemia and reperfusion
 Mitochondrial dynamics in ischemia and reperfusion Derek J Hausenloy Reader in Cardiovascular Medicine, British Heart Foundation Senior Clinical Research Fellow, The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute, University
Mitochondrial dynamics in ischemia and reperfusion Derek J Hausenloy Reader in Cardiovascular Medicine, British Heart Foundation Senior Clinical Research Fellow, The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute, University
Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 Chapter 10 Chemotrophic Energy Metabolism: Aerobic Respiration Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Figure 10-1 Figure 10-6 Conversion of pyruvate The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl
Chapter 10 Chemotrophic Energy Metabolism: Aerobic Respiration Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Figure 10-1 Figure 10-6 Conversion of pyruvate The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl
16 The Cell Cycle. Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization
 The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
Life Sciences 1a: Section 3B. The cell division cycle Objectives Understand the challenges to producing genetically identical daughter cells
 Life Sciences 1a: Section 3B. The cell division cycle Objectives Understand the challenges to producing genetically identical daughter cells Understand how a simple biochemical oscillator can drive the
Life Sciences 1a: Section 3B. The cell division cycle Objectives Understand the challenges to producing genetically identical daughter cells Understand how a simple biochemical oscillator can drive the
Importance of Protein sorting. A clue from plastid development
 Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Cell functions depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Examples: A. Energy production
Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Cell functions depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Examples: A. Energy production
Reconstructing Mitochondrial Evolution?? Morphological Diversity. Mitochondrial Diversity??? What is your definition of a mitochondrion??
 Reconstructing Mitochondrial Evolution?? What is your definition of a mitochondrion?? Morphological Diversity Mitochondria as we all know them: Suprarenal gland Liver cell Plasma cell Adrenal cortex Mitochondrial
Reconstructing Mitochondrial Evolution?? What is your definition of a mitochondrion?? Morphological Diversity Mitochondria as we all know them: Suprarenal gland Liver cell Plasma cell Adrenal cortex Mitochondrial
Fusion and Fission: Interlinked Processes Critical for Mitochondrial Health
 I R E V I E W S E Review in Advance first posted online on August 29, 2012. (Changes may still occur before final publication online and in print.) N C A D V A N Fusion and Fission: Interlinked Processes
I R E V I E W S E Review in Advance first posted online on August 29, 2012. (Changes may still occur before final publication online and in print.) N C A D V A N Fusion and Fission: Interlinked Processes
Mitochondrial phosphoproteome
 Mitochondrial phosphoproteome Claire Lemaire UMR8221, CNRS, CEA, Université Paris-Sud CEA Saclay/ ibitec-s/sb2sm/lpm Mai 2014 1 Importance of the regulation by phosphorylation A large proportion of the
Mitochondrial phosphoproteome Claire Lemaire UMR8221, CNRS, CEA, Université Paris-Sud CEA Saclay/ ibitec-s/sb2sm/lpm Mai 2014 1 Importance of the regulation by phosphorylation A large proportion of the
The ubiquitin-proteasome-system
 Repository of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin (Germany) http://edoc.mdc-berlin.de/13359/ The ubiquitin-proteasome-system Sommer, Thomas; Wolf, Dieter H. NOTICE: this is the
Repository of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin (Germany) http://edoc.mdc-berlin.de/13359/ The ubiquitin-proteasome-system Sommer, Thomas; Wolf, Dieter H. NOTICE: this is the
Endurance, Energy, Healthy Aging
 Endurance, Energy, Healthy Aging NR is being extensively researched in major universities and hospitals Effects of NR on metabolism are nothing short of astonishing. Researcher from Weill Cornell Medical
Endurance, Energy, Healthy Aging NR is being extensively researched in major universities and hospitals Effects of NR on metabolism are nothing short of astonishing. Researcher from Weill Cornell Medical
Cell Organelles. a review of structure and function
 Cell Organelles a review of structure and function TEKS and Student Expectations (SE s) B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized
Cell Organelles a review of structure and function TEKS and Student Expectations (SE s) B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized
Mitochondrial Biogenesis is the process by which new mitochondria are formed in the cell.
 Mitochondrial Biogenesis is the process by which new mitochondria are formed in the cell. Purpose of Mitochondria: The mitochondria are organelles within the cell that are responsible for the biochemical
Mitochondrial Biogenesis is the process by which new mitochondria are formed in the cell. Purpose of Mitochondria: The mitochondria are organelles within the cell that are responsible for the biochemical
Tuesday 9/6/2018 Mike Mueckler
 Tuesday 9/6/2018 Mike Mueckler mmueckler@wustl.edu Intracellular Targeting of Nascent Polypeptides Mitochondria are the Sites of Oxidative ATP Production Sugars Triglycerides Figure 14-10 Molecular Biology
Tuesday 9/6/2018 Mike Mueckler mmueckler@wustl.edu Intracellular Targeting of Nascent Polypeptides Mitochondria are the Sites of Oxidative ATP Production Sugars Triglycerides Figure 14-10 Molecular Biology
Energy Converion: Mitochondria and Chloroplasts. Pınar Tulay, Ph.D.
 Energy Converion: Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Pınar Tulay, Ph.D. pintulay@gmail.com Energy Conversion Prokaryotes use plasma membrane to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) used in the cell function
Energy Converion: Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Pınar Tulay, Ph.D. pintulay@gmail.com Energy Conversion Prokaryotes use plasma membrane to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) used in the cell function
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION AND DYSFUNCTION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION AND DYSFUNCTION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 mitochondrial function and dysfunction mitochondrial function and dysfunction pdf mitochondrial function and
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION AND DYSFUNCTION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 mitochondrial function and dysfunction mitochondrial function and dysfunction pdf mitochondrial function and
4) Please cite Dagda et al J Biol Chem 284: , for any publications or presentations resulting from use or modification of the macro.
 Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Way to impose membrane curvature
 Way to impose membrane curvature Sar1 reticulons? clathrin and other vesicle coats dynamin BAR domains McMahon, 2005 The ER is continuous with the nuclear envelope and contains tubules and sheets Gia Voeltz
Way to impose membrane curvature Sar1 reticulons? clathrin and other vesicle coats dynamin BAR domains McMahon, 2005 The ER is continuous with the nuclear envelope and contains tubules and sheets Gia Voeltz
Components of a functional cell. Boundary-membrane Cytoplasm: Cytosol (soluble components) & particulates DNA-information Ribosomes-protein synthesis
 Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways
 Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
Mitochondrie et muscle lisse. Vladimir Veksler
 Mitochondrie et muscle lisse Vladimir Veksler Main mitochonrial functions Energy production ATP consumption rate in smooth and striated muscle smooth muscle striated (cardiac) muscle at rest 30 µmol/min/g
Mitochondrie et muscle lisse Vladimir Veksler Main mitochonrial functions Energy production ATP consumption rate in smooth and striated muscle smooth muscle striated (cardiac) muscle at rest 30 µmol/min/g
Mitochondrial protein quality control in health and disease
 BJP British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/bph.12430 www.brjpharmacol.org Themed Issue: Mitochondrial Pharmacology: Energy, Injury & Beyond REVIEW Mitochondrial protein quality control in health and
BJP British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/bph.12430 www.brjpharmacol.org Themed Issue: Mitochondrial Pharmacology: Energy, Injury & Beyond REVIEW Mitochondrial protein quality control in health and
Chapter 02 Cell Physiology
 Human Physiology From Cells to Systems 9th Edition Sherwood TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/human-physiology-cells-systems-9th-editionsherwood-test-bank/ Human Physiology
Human Physiology From Cells to Systems 9th Edition Sherwood TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/human-physiology-cells-systems-9th-editionsherwood-test-bank/ Human Physiology
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things copyright cmassengale 2 What is life? Alive? Alive? What is life? Thus life defies a one sentence answer/definition Instead, life is recognized
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things copyright cmassengale 2 What is life? Alive? Alive? What is life? Thus life defies a one sentence answer/definition Instead, life is recognized
Rhomboids and proteolysis in the Dicty mitochondrion
 Rhomboids and proteolysis in the Dicty mitochondrion DR ELINOR THOMPSON UNIVERSITY OF GREENWICH Rhomboids Membrane located proteases Unusual Ubiquitous across evolution One in prokaryotes: multigene families
Rhomboids and proteolysis in the Dicty mitochondrion DR ELINOR THOMPSON UNIVERSITY OF GREENWICH Rhomboids Membrane located proteases Unusual Ubiquitous across evolution One in prokaryotes: multigene families
Functions and dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics
 Functions and dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics Scott A. Detmer and David C. Chan Abstract Recent findings have sparked renewed appreciation for the remarkably dynamic nature of mitochondria. These
Functions and dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics Scott A. Detmer and David C. Chan Abstract Recent findings have sparked renewed appreciation for the remarkably dynamic nature of mitochondria. These
Class IX: Biology Chapter 5: The fundamental unit of life. Chapter Notes. 1) In 1665, Robert Hooke first discovered and named the cells.
 Class IX: Biology Chapter 5: The fundamental unit of life. Key learnings: Chapter Notes 1) In 1665, Robert Hooke first discovered and named the cells. 2) Cell is the structural and functional unit of all
Class IX: Biology Chapter 5: The fundamental unit of life. Key learnings: Chapter Notes 1) In 1665, Robert Hooke first discovered and named the cells. 2) Cell is the structural and functional unit of all
Mitochondrial Biogenesis: Is an Old Dog Still Teaching Us New Tricks? Meeting on the Assembly of the Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Biological Sciences Faculty Research and Publications Biological Sciences, Department of 1-1-2008 Mitochondrial Biogenesis: Is an Old Dog Still Teaching Us
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Biological Sciences Faculty Research and Publications Biological Sciences, Department of 1-1-2008 Mitochondrial Biogenesis: Is an Old Dog Still Teaching Us
2011 The Simple Homeschool Simple Days Unit Studies Cells
 1 We have a full line of high school biology units and courses at CurrClick and as online courses! Subscribe to our interactive unit study classroom and make science fun and exciting! 2 A cell is a small
1 We have a full line of high school biology units and courses at CurrClick and as online courses! Subscribe to our interactive unit study classroom and make science fun and exciting! 2 A cell is a small
Drosophila Apoptosis and the Regulation of the Caspase Cascade
 Drosophila Apoptosis and the Regulation of the Caspase Cascade Kate Stafford March 18, 2005 Abstract The caspase cascade in Drosophila is controlled primarily by DIAP1 (Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis),
Drosophila Apoptosis and the Regulation of the Caspase Cascade Kate Stafford March 18, 2005 Abstract The caspase cascade in Drosophila is controlled primarily by DIAP1 (Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis),
Chapter Cells and the Flow of Energy A. Forms of Energy 1. Energy is capacity to do work; cells continually use energy to develop, grow,
 Chapter 6 6.1 Cells and the Flow of Energy A. Forms of Energy 1. Energy is capacity to do work; cells continually use energy to develop, grow, repair, reproduce, etc. 2. Kinetic energy is energy of motion;
Chapter 6 6.1 Cells and the Flow of Energy A. Forms of Energy 1. Energy is capacity to do work; cells continually use energy to develop, grow, repair, reproduce, etc. 2. Kinetic energy is energy of motion;
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Chapter 12: Intracellular sorting
 Chapter 12: Intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Cells have many distinct compartments (What are they? What do they do?) Specific mechanisms are
Chapter 12: Intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Cells have many distinct compartments (What are they? What do they do?) Specific mechanisms are
Energy and Cellular Metabolism
 1 Chapter 4 About This Chapter Energy and Cellular Metabolism 2 Energy in biological systems Chemical reactions Enzymes Metabolism Figure 4.1 Energy transfer in the environment Table 4.1 Properties of
1 Chapter 4 About This Chapter Energy and Cellular Metabolism 2 Energy in biological systems Chemical reactions Enzymes Metabolism Figure 4.1 Energy transfer in the environment Table 4.1 Properties of
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 30, Please print your name:
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 30, 2014 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 30, 2014 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Cell (Learning Objectives)
 Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
Structural biology of mitochondria. Werner Kühlbrandt Max Planck Institute of Biophysics Frankfurt, Germany
 Structural biology of mitochondria Werner Kühlbrandt Max Planck Institute of Biophysics Frankfurt, Germany The mitochondrion Powerhouse of the eukaryotic cell Produces almost all ATP to drive cellular
Structural biology of mitochondria Werner Kühlbrandt Max Planck Institute of Biophysics Frankfurt, Germany The mitochondrion Powerhouse of the eukaryotic cell Produces almost all ATP to drive cellular
Mitochondrial DNA Prof. Immo E. Scheffler
 Mitochondrial DNA Molecular Genetics Human Mitochondrial Diseases Immo E. Scheffler Professor of Biology University of California, San Diego 1 Mitochondria 2 cristae 3 1 Fig 12. Mitochondria of a heart
Mitochondrial DNA Molecular Genetics Human Mitochondrial Diseases Immo E. Scheffler Professor of Biology University of California, San Diego 1 Mitochondria 2 cristae 3 1 Fig 12. Mitochondria of a heart
122-Biology Guide-5thPass 12/06/14. Topic 1 An overview of the topic
 Topic 1 http://bioichiban.blogspot.com Cellular Functions 1.1 The eukaryotic cell* An overview of the topic Key idea 1: Cell Organelles Key idea 2: Plasma Membrane Key idea 3: Transport Across Membrane
Topic 1 http://bioichiban.blogspot.com Cellular Functions 1.1 The eukaryotic cell* An overview of the topic Key idea 1: Cell Organelles Key idea 2: Plasma Membrane Key idea 3: Transport Across Membrane
CHAPTER 3. Cell Structure and Genetic Control. Chapter 3 Outline
 CHAPTER 3 Cell Structure and Genetic Control Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell Nucleus and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
CHAPTER 3 Cell Structure and Genetic Control Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell Nucleus and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of October
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ 2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of 19-23 October Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which
Name: Class: _ Date: _ 2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of 19-23 October Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which
Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma. Reading: BCP Chapter 2
 Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Functional Unit of the Nervous System The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron. Neurons are cells specialized
Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Functional Unit of the Nervous System The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron. Neurons are cells specialized
Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life
 Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life Review Introduction Main contents Group discussions Unless otherwise noted, pictures are taken from wikipedia.org Review 1 Organic
Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life Review Introduction Main contents Group discussions Unless otherwise noted, pictures are taken from wikipedia.org Review 1 Organic
Principles of Cellular Biology
 Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
UNIT 1: WELLNESS & HOMEOSTASIS. Biology notes 1 Mr.Yeung
 UNIT 1: WELLNESS & HOMEOSTASIS Biology notes 1 Mr.Yeung WHAT IS UNIT 1 ABOUT? Wellness & Homeostasis 0. Wellness (Reading labels/homeostasis/ serving size) 1. Cell Biology (Ch.3) Cell organelles Cell types
UNIT 1: WELLNESS & HOMEOSTASIS Biology notes 1 Mr.Yeung WHAT IS UNIT 1 ABOUT? Wellness & Homeostasis 0. Wellness (Reading labels/homeostasis/ serving size) 1. Cell Biology (Ch.3) Cell organelles Cell types
An overview of the recent knowledge about mitochondrial fusion and fission and related neurodegenerative diseases
 Acta Medica 2016; 5: 71 78 acta medica REVIEW ARTICLE An overview of the recent knowledge about mitochondrial fusion and fission and related neurodegenerative diseases Evrim AKSU 1, [BSc.], Burcu BALCI-HAYTA
Acta Medica 2016; 5: 71 78 acta medica REVIEW ARTICLE An overview of the recent knowledge about mitochondrial fusion and fission and related neurodegenerative diseases Evrim AKSU 1, [BSc.], Burcu BALCI-HAYTA
7 Characteristics of Life
 7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
Supplemental Information. The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51. Requires ADP as a Cofactor
 Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
Introduction to molecular biology. Mitesh Shrestha
 Introduction to molecular biology Mitesh Shrestha Molecular biology: definition Molecular biology is the study of molecular underpinnings of the process of replication, transcription and translation of
Introduction to molecular biology Mitesh Shrestha Molecular biology: definition Molecular biology is the study of molecular underpinnings of the process of replication, transcription and translation of
Cardiolipin Remodeling by ALCAT1 Regulates Dilated Cardiomyopathy Through Oxidative Stress and Mitophagy. Yuguang (Roger) Shi
 Cardiolipin Remodeling by ALCAT1 Regulates Dilated Cardiomyopathy Through xidative Stress and Mitophagy Yuguang (Roger) Shi yus11@psu.eud Cardiolipin Biosynthetic and Remodeling Pathways Phosphatidic Acid
Cardiolipin Remodeling by ALCAT1 Regulates Dilated Cardiomyopathy Through xidative Stress and Mitophagy Yuguang (Roger) Shi yus11@psu.eud Cardiolipin Biosynthetic and Remodeling Pathways Phosphatidic Acid
Dynamic survey of mitochondria by ubiquitin
 Review Ubiquitylation: mechanism and functions Review series Dynamic survey of mitochondria by ubiquitin Mafalda Escobar-Henriques 1,* & Thomas Langer 1,2 Abstract Ubiquitin is a post-translational modifier
Review Ubiquitylation: mechanism and functions Review series Dynamic survey of mitochondria by ubiquitin Mafalda Escobar-Henriques 1,* & Thomas Langer 1,2 Abstract Ubiquitin is a post-translational modifier
Frontiers in CardioVascular Biology
 Frontiers in CardioVascular Biology Young Investigator Award Mitofusin 2 controls calcium transmission between the SR and mitochondria and regulates the bioenergetic feedback response in cardiac myocytes
Frontiers in CardioVascular Biology Young Investigator Award Mitofusin 2 controls calcium transmission between the SR and mitochondria and regulates the bioenergetic feedback response in cardiac myocytes
Membrane depolarization activates the mitochondrial protease OMA1 by stimulating self-cleavage
 Scientific Report Membrane depolarization activates the mitochondrial protease OMA1 by stimulating self-cleavage Kuan Zhang, Huihui Li & Zhiyin Song* Abstract Mitochondrial inner membrane fusion depends
Scientific Report Membrane depolarization activates the mitochondrial protease OMA1 by stimulating self-cleavage Kuan Zhang, Huihui Li & Zhiyin Song* Abstract Mitochondrial inner membrane fusion depends
Tour of the Cell 2. AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell 2 2007-2008 Cells gotta work to live! What jobs do cells have to do? make proteins proteins control every cell function make energy for daily life for growth make more cells growth repair
Tour of the Cell 2 2007-2008 Cells gotta work to live! What jobs do cells have to do? make proteins proteins control every cell function make energy for daily life for growth make more cells growth repair
ATP. Division Ave. High School AP Biology. Tour of the Cell 2. Cells gotta work to live! Making Energy. What jobs do cells have to do?
 Tour of the Cell 2 Cells gotta work to live! What jobs do cells have to do? u make proteins proteins control every cell function u make energy for daily life for growth u make more cells growth repair
Tour of the Cell 2 Cells gotta work to live! What jobs do cells have to do? u make proteins proteins control every cell function u make energy for daily life for growth u make more cells growth repair
Unit 1: Metabolic Processes
 1 Unit 1: Metabolic Processes 1. Describe the structure and function of the macromolecules necessary for the normal metabolic functions of all living things, and the role of enzymes in maintaining normal
1 Unit 1: Metabolic Processes 1. Describe the structure and function of the macromolecules necessary for the normal metabolic functions of all living things, and the role of enzymes in maintaining normal
Quiz answers. Allele. BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 17: The Quiz (and back to Eukaryotic DNA)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 17: The Quiz (and back to Eukaryotic DNA) http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Quiz answers Kinase: An enzyme
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 17: The Quiz (and back to Eukaryotic DNA) http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Quiz answers Kinase: An enzyme
Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy
 6 Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy Energy is stored in chemical bonds and can be released and transformed by metabolic pathways. Chemical energy available to do work is termed free energy
6 Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy Energy is stored in chemical bonds and can be released and transformed by metabolic pathways. Chemical energy available to do work is termed free energy
Types of biological networks. I. Intra-cellurar networks
 Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA
 Section A. Multiple choice questions 1. Which of the following is not a polymer? a. glucose b. starch 2. Polypeptides are assembled from: a. hexoses b. glycerol c. cellulose d. DNA c. nucleotides d. amino
Section A. Multiple choice questions 1. Which of the following is not a polymer? a. glucose b. starch 2. Polypeptides are assembled from: a. hexoses b. glycerol c. cellulose d. DNA c. nucleotides d. amino
All organisms require a constant expenditure of energy to maintain the living state - "LIFE".
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION All organisms require a constant expenditure of energy to maintain the living state - "LIFE". Where does the energy come from and how is it made available for life? With rare exception,
CELLULAR RESPIRATION All organisms require a constant expenditure of energy to maintain the living state - "LIFE". Where does the energy come from and how is it made available for life? With rare exception,
Effect of enzyme deficiencies on oxidative phosphorylation: from isolated mitochondria to intact tissues. Theoretical studies.
 Effect of enzyme deficiencies on oxidative phosphorylation: from isolated mitochondria to intact tissues. Theoretical studies. Bernard Korzeniewski Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Jagiellonian
Effect of enzyme deficiencies on oxidative phosphorylation: from isolated mitochondria to intact tissues. Theoretical studies. Bernard Korzeniewski Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Jagiellonian
The Discovery of Cells
 The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
Review. From ATP to PTP and Back: A Dual Function for the Mitochondrial ATP Synthase Gerald Dorn, Editor
 Review This Review is part of a thematic series on Mitochondria, which includes the following articles: Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species at the Heart of the Matter: New Therapeutic Approaches for
Review This Review is part of a thematic series on Mitochondria, which includes the following articles: Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species at the Heart of the Matter: New Therapeutic Approaches for
ATP ATP. The Jobs of Cells. Making Energy. Making Energy. Cells need power! ATP ATP 10/5/2015. Cells have 3 main jobs
 The Jobs of Cells 2007-2008 Making Energy Cells have 3 main jobs make energy need energy for all activities need to clean up waste produced while making energy make proteins proteins do all the work in
The Jobs of Cells 2007-2008 Making Energy Cells have 3 main jobs make energy need energy for all activities need to clean up waste produced while making energy make proteins proteins do all the work in
Microscope History Robert Hooke
 1 Microscope History Robert Hooke First described cells in 1665. He viewed thin slices of cork and compared the boxy partitions he observed to the cells (small rooms) in a monastery. (1635 1702) 2 Microscope
1 Microscope History Robert Hooke First described cells in 1665. He viewed thin slices of cork and compared the boxy partitions he observed to the cells (small rooms) in a monastery. (1635 1702) 2 Microscope
Cell Division and Reproduction
 Cell Division and Reproduction What do you think this picture shows? If you guessed that it s a picture of two cells, you are right. In fact, the picture shows human cancer cells, and they are nearing
Cell Division and Reproduction What do you think this picture shows? If you guessed that it s a picture of two cells, you are right. In fact, the picture shows human cancer cells, and they are nearing
Cells. A. The iodine diffused into the bag. B. The starch was changed to sugar.
 Name: Date: 1. A student filled a bag of dialysis tubing with a milky-white starch solution and placed the bag in a beaker of iodine-water as shown in the diagram. An hour later, the student observed that
Name: Date: 1. A student filled a bag of dialysis tubing with a milky-white starch solution and placed the bag in a beaker of iodine-water as shown in the diagram. An hour later, the student observed that
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material JCB Hoppins et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201107053/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Internal agreement of MITO-MAP data and consistency
Supplemental material JCB Hoppins et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201107053/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Internal agreement of MITO-MAP data and consistency
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures u specialized functions cilia
Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures u specialized functions cilia
S1 Gene ontology (GO) analysis of the network alignment results
 1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
 Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Biochemistry: A Review and Introduction
 Biochemistry: A Review and Introduction CHAPTER 1 Chem 40/ Chem 35/ Fundamentals of 1 Outline: I. Essence of Biochemistry II. Essential Elements for Living Systems III. Classes of Organic Compounds IV.
Biochemistry: A Review and Introduction CHAPTER 1 Chem 40/ Chem 35/ Fundamentals of 1 Outline: I. Essence of Biochemistry II. Essential Elements for Living Systems III. Classes of Organic Compounds IV.
!"#$%&'%()*%+*,,%-&,./*%01%02%/*/3452*%3&.26%&4752*,,*1%%
 !"#$%&'%()*%+*,,%-&,./*%01%02%/*/3452*%3&.26%&4752*,,*1%% !"#$%&'(")*++*%,*'-&'./%/,*#01#%-2)#3&)/% 4'(")*++*% % %5"0)%-2)#3&) %%% %67'2#72'*%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%4'(")0/./% % 8$+&'&,+"/7 % %,$&7&/9)7$*/0/%%%%%%%%%%
!"#$%&'%()*%+*,,%-&,./*%01%02%/*/3452*%3&.26%&4752*,,*1%% !"#$%&'(")*++*%,*'-&'./%/,*#01#%-2)#3&)/% 4'(")*++*% % %5"0)%-2)#3&) %%% %67'2#72'*%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%4'(")0/./% % 8$+&'&,+"/7 % %,$&7&/9)7$*/0/%%%%%%%%%%
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
Cellular respiration. How do living things stay alive? Cellular Respiration Burning. Photosynthesis. Cellular Respiration
 How do living things stay alive? Cellular Respiration Burning Happens in ALL living things inside cells and has the main goal of producing ATP the fuel of life It does not matter whether the organisms
How do living things stay alive? Cellular Respiration Burning Happens in ALL living things inside cells and has the main goal of producing ATP the fuel of life It does not matter whether the organisms
Chapter 02 Levels of organization of the human body
 Chapter 02 Levels of organization of the human body Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following lists the levels of organization of the human body in the correct order? A. chemical level, organelle
Chapter 02 Levels of organization of the human body Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following lists the levels of organization of the human body in the correct order? A. chemical level, organelle
THYLAKOID GRANUM / GRANA
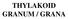 THYLAKOID GRANUM / GRANA THYLAKOID GRANUM + STACKED THYLAKOID VESICLES THYLAKOID GRANUM THYLAKOID GRANUM + STACKED THYLAKOID VESICLES --- SITE: LIGHT RXT THYLAKOID GRANUM THYLAKOID GRANUM G STACKED THYLAKOID
THYLAKOID GRANUM / GRANA THYLAKOID GRANUM + STACKED THYLAKOID VESICLES THYLAKOID GRANUM THYLAKOID GRANUM + STACKED THYLAKOID VESICLES --- SITE: LIGHT RXT THYLAKOID GRANUM THYLAKOID GRANUM G STACKED THYLAKOID
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell. Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components.
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
