Chapter 12: Intracellular sorting
|
|
|
- Constance George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 12: Intracellular sorting
2 Principles of intracellular sorting
3 Principles of intracellular sorting Cells have many distinct compartments (What are they? What do they do?) Specific mechanisms are required for transport of proteins in and out of each compartment.
4 Principles of intracellular sorting Proteins move between compartment in 2 different ways: 1) as proteins, via pores or translocases may be folded or unfolded 2) within vesicles requiring packaging and membrane fusion
5 Principles of intracellular sorting All (well, almost all) proteins begin in the cytosol 2 classes of import: 1) Post-translational import: Proteins are fully translated then sent to the correct location 2) Co-translational import: Proteins are simultaneously translated and imported.
6 Principles of intracellular sorting In the absence of specific signals, proteins remain in the cytosol Specific signal sequences (=targeting sequences) on the protein direct them to correct place The signal sequences are often (not always) cleaved by signal peptidases
7 Principles of intracellular sorting
8 Nuclear transport What is the nature of the barrier between the cytosol and the inside of the nucleus (i.e., the nuclear matrix)? What macromolecules need to get in and out of the nucleus?
9 Nuclear transport Access to the nucleus is via a nuclear pore complex Channel allows: -free diffusion of small particles -active transport of larger proteins
10 Nuclear transport
11
12 Nuclear transport: the proteins Proteins that need to be transported through nuclear pores have nuclear localization signals (NLS) NLS are short stretches of amino acids (e.g. KKKRK) found almost anywhere in the polypeptide (Why anywhere?) NLS can be specific for export (NES) or import (NIS) Some proteins have both NIS and NES
13 Nuclear transport: the receptors Proteins that transport cargo through nuclear pores are called nuclear transport receptors These proteins bind: -NLS of the cargo proteins -inner lining of nuclear pores A large gene family encodes Nuclear Import Receptors and Nuclear Export Receptors
14
15
16 Step 1: Translation and recognition Once a nuclear protein is made within the cytosol, it gets folded The NIS often extends from the protein as a loop, exposed on the surface The loop is recognized by a Nuclear Import Receptor
17 Step 2: Import The receptor binds to FG-repeats (ie PHE-GLY residues) on proteins that line the nuclear pore Receptor, with its cargo, walks along the FG-repeats to enter the nucleus Once inside, the protein is released The receptor protein is sent back out of the nucleus
18 Mitochondria and chloroplasts What is the nature of the barrier between the cytosol and the inside of the mitochondria/ chloroplast? How many compartments are there in these organelles? What macromolecules need to get in and out of these organelles?
19
20 Mitochondria and chloroplasts In contrast to the nucleus, mitochondria have: Extra membrane compartments Many membrane proteins Highly impermeable membranes Proteins are fully synthesized in the cytosol Targeted to mitochondria via N-terminal signal sequence Transported into mitochondria
21 Step 1. Targeting proteins to mitochondria Proteins are fully synthesized in the cytosol, but kept unfolded by chaperones (Hsp70 members) Mitochondrial proteins have an N-terminal signal sequence that is recognized by transport machinery on the mitochondrial outer membrane TOM (Transport across Outer Membrane) complexes include receptors and translocation channels
22
23 Step 2 Crossing the mitochondrial membranes Outer and inner mitochondrial membranes join at contact sites, where TOM complex interacts with TIM complex Unfolded proteins are threaded through the channels of TOM and TIM, and released into the mitochondrial matrix Signal sequence often cleaved
24 Step 3 Other mitochondrial locations Many proteins have 2 nd signals that result in transport to other mitochondrial locations (e.g. inner mitochondrial membrane, inter-membrane space)
25
26 Energy requirements ATP hydrolysis: needed for action of cytosolic chaperones and mitochondrial chaperones (both hsp70 members) Electrochemical gradient: protein import into mitochondria also requires a membrane potential
27 Endoplasmic Reticulum What is the nature of the barrier between the cytosol and the inside of the ER (the ER lumen)? What macromolecules need to get in and out of the ER?
28
29
30 Endoplasmic Reticulum Proteins destined for the ER are partially translated in the cytosol on free ribosomes Once the N-terminal signal peptide is made, it is recognized by a complex of RNA and protein (signal recognition particle or SRP) Once the SRP binds the nascent polypeptide, the complex associates with a specific receptor on the ER (SRP receptor)
31 Endoplasmic Reticulum Translation continues, and polypeptide is fed into the ER as it is synthesized (co-translational import) Signal sequence is usually cleaved by signal peptidase Another Hsp70 member, BiP lives in the ER lumen and helps pull proteins through the channel, and prevents premature folding
32 Endoplasmic Reticulum It is at this point that pathways diverge to give rise to: -ER lumen proteins (soluble) -ER membrane proteins that: -orient N-terminus in or out of the lumen -cross once or multiple times
33 ER lumen proteins
34 Single pass transmembrane proteins Some proteins cross the ER membrane once These have stop transfer sequences at specific sites on the proteins, typically a stretch of amino acids that give rise to a hydrophobic a-helix These sequences can cause the protein to be oriented N-terminal in or out
35 Single pass transmembrane proteins
36 Single pass transmembrane proteins
37 Single pass transmembrane proteins
38 Multi-pass transmembrane proteins
Protein Sorting. By: Jarod, Tyler, and Tu
 Protein Sorting By: Jarod, Tyler, and Tu Definition Organizing of proteins Organelles Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus/Vesicles How do they know where to go? Amino Acid Sequence
Protein Sorting By: Jarod, Tyler, and Tu Definition Organizing of proteins Organelles Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus/Vesicles How do they know where to go? Amino Acid Sequence
Tuesday 9/6/2018 Mike Mueckler
 Tuesday 9/6/2018 Mike Mueckler mmueckler@wustl.edu Intracellular Targeting of Nascent Polypeptides Mitochondria are the Sites of Oxidative ATP Production Sugars Triglycerides Figure 14-10 Molecular Biology
Tuesday 9/6/2018 Mike Mueckler mmueckler@wustl.edu Intracellular Targeting of Nascent Polypeptides Mitochondria are the Sites of Oxidative ATP Production Sugars Triglycerides Figure 14-10 Molecular Biology
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
Importance of Protein sorting. A clue from plastid development
 Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Cell functions depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Examples: A. Energy production
Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Cell functions depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Examples: A. Energy production
Scale in the biological world
 Scale in the biological world 2 A cell seen by TEM 3 4 From living cells to atoms 5 Compartmentalisation in the cell: internal membranes and the cytosol 6 The Origin of mitochondria: The endosymbion hypothesis
Scale in the biological world 2 A cell seen by TEM 3 4 From living cells to atoms 5 Compartmentalisation in the cell: internal membranes and the cytosol 6 The Origin of mitochondria: The endosymbion hypothesis
Cellular Transport. 1. Transport to and across the membrane 1a. Transport of small molecules and ions 1b. Transport of proteins
 Transport Processes Cellular Transport 1. Transport to and across the membrane 1a. Transport of small molecules and ions 1b. Transport of proteins 2. Vesicular transport 3. Transport through the nuclear
Transport Processes Cellular Transport 1. Transport to and across the membrane 1a. Transport of small molecules and ions 1b. Transport of proteins 2. Vesicular transport 3. Transport through the nuclear
Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I
 01.26.11 Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I Intracellular transport and compartments 1. Protein sorting: How proteins get to their appropriate destinations within the cell 2. Vesicular
01.26.11 Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I Intracellular transport and compartments 1. Protein sorting: How proteins get to their appropriate destinations within the cell 2. Vesicular
Transport between cytosol and nucleus
 of 60 3 Gated trans Lectures 9-15 MBLG 2071 The n GATED TRANSPORT transport between cytoplasm and nucleus (bidirectional) controlled by the nuclear pore complex active transport for macro molecules e.g.
of 60 3 Gated trans Lectures 9-15 MBLG 2071 The n GATED TRANSPORT transport between cytoplasm and nucleus (bidirectional) controlled by the nuclear pore complex active transport for macro molecules e.g.
7.06 Problem Set
 7.06 Problem Set 5 -- 2006 1. In the first half of the course, we encountered many examples of proteins that entered the nucleus in response to the activation of a cell-signaling pathway. One example of
7.06 Problem Set 5 -- 2006 1. In the first half of the course, we encountered many examples of proteins that entered the nucleus in response to the activation of a cell-signaling pathway. One example of
Protein Sorting, Intracellular Trafficking, and Vesicular Transport
 Protein Sorting, Intracellular Trafficking, and Vesicular Transport Noemi Polgar, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy, Biochemistry and Physiology Email: polgar@hawaii.edu Phone: 692-1422 Outline Part 1- Trafficking
Protein Sorting, Intracellular Trafficking, and Vesicular Transport Noemi Polgar, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy, Biochemistry and Physiology Email: polgar@hawaii.edu Phone: 692-1422 Outline Part 1- Trafficking
M i t o c h o n d r i a
 M i t o c h o n d r i a Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Mitochondria Function: generation of metabolic energy in eukaryotic cells Generation of ATP from the breakdown of
M i t o c h o n d r i a Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Mitochondria Function: generation of metabolic energy in eukaryotic cells Generation of ATP from the breakdown of
Scale in the biological world
 Scale in the biological world From living cells to atoms A cell seen by TEM Compartmentalisation in the cell: internal membranes and the cytosol The cytosol: more than just H2O RNAs Proteins Ribosomes
Scale in the biological world From living cells to atoms A cell seen by TEM Compartmentalisation in the cell: internal membranes and the cytosol The cytosol: more than just H2O RNAs Proteins Ribosomes
Lecture 4. Protein Translocation & Nucleocytoplasmic Transport
 Lecture 4 Protein Translocation & Nucleocytoplasmic Transport Chapter 12 MBoC (5th Edition) Alberts et al. Reference paper: Tran and Wente, Cell 125, 1041-1053, 2006 2/8/2012 1 Page 713 Molecular Biology
Lecture 4 Protein Translocation & Nucleocytoplasmic Transport Chapter 12 MBoC (5th Edition) Alberts et al. Reference paper: Tran and Wente, Cell 125, 1041-1053, 2006 2/8/2012 1 Page 713 Molecular Biology
The Discovery of Cells
 The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
CHAPTER 3. Cell Structure and Genetic Control. Chapter 3 Outline
 CHAPTER 3 Cell Structure and Genetic Control Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell Nucleus and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
CHAPTER 3 Cell Structure and Genetic Control Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell Nucleus and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures u specialized functions cilia
Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures u specialized functions cilia
Lecture 7 Cell Biolog y ٢٢٢ ١
 Lecture 7 ١ Mitochondria ٢ Mitochondria Mitochondria are the energy factories of the cells. The energy currency for the work that animals must do is the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Lecture 7 ١ Mitochondria ٢ Mitochondria Mitochondria are the energy factories of the cells. The energy currency for the work that animals must do is the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Translocation through the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Institute of Biochemistry Benoît Kornmann
 Translocation through the endoplasmic reticulum membrane Institute of Biochemistry Benoît Kornmann Endomembrane system Protein sorting Permeable to proteins but not to ions IgG tetramer (16 nm) Fully hydrated
Translocation through the endoplasmic reticulum membrane Institute of Biochemistry Benoît Kornmann Endomembrane system Protein sorting Permeable to proteins but not to ions IgG tetramer (16 nm) Fully hydrated
Name: TF: Section Time: LS1a ICE 5. Practice ICE Version B
 Name: TF: Section Time: LS1a ICE 5 Practice ICE Version B 1. (8 points) In addition to ion channels, certain small molecules can modulate membrane potential. a. (4 points) DNP ( 2,4-dinitrophenol ), as
Name: TF: Section Time: LS1a ICE 5 Practice ICE Version B 1. (8 points) In addition to ion channels, certain small molecules can modulate membrane potential. a. (4 points) DNP ( 2,4-dinitrophenol ), as
Turns sunlight, water & carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) into sugar & oxygen through photosynthesis
 CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 KEY
 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 KEY May 2, 2006 This is an OPEN BOOK exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes BUT NOT computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 KEY May 2, 2006 This is an OPEN BOOK exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes BUT NOT computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
Cell Organelles. Wednesday, October 22, 14
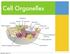 Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Reconstructing Mitochondrial Evolution?? Morphological Diversity. Mitochondrial Diversity??? What is your definition of a mitochondrion??
 Reconstructing Mitochondrial Evolution?? What is your definition of a mitochondrion?? Morphological Diversity Mitochondria as we all know them: Suprarenal gland Liver cell Plasma cell Adrenal cortex Mitochondrial
Reconstructing Mitochondrial Evolution?? What is your definition of a mitochondrion?? Morphological Diversity Mitochondria as we all know them: Suprarenal gland Liver cell Plasma cell Adrenal cortex Mitochondrial
Structure of mitochondria
 Structure of mitochondria Subcompartments of mitochondria Outer membrane (OM) Inner membrane (IM) Matrix Intermembrane space (IMS) Cristae membrane Inner boundary membrane Cristae compartment Molecular
Structure of mitochondria Subcompartments of mitochondria Outer membrane (OM) Inner membrane (IM) Matrix Intermembrane space (IMS) Cristae membrane Inner boundary membrane Cristae compartment Molecular
Chapter 16-part II. Translocation into chloroplast occurs via a similar strategy to the one used by mitochondira
 Chapter 16-part II Translocation into chloroplast occurs via a similar strategy to the one used by mitochondira Both occur post-translationally Both use two translocation complexes, one at each membrane
Chapter 16-part II Translocation into chloroplast occurs via a similar strategy to the one used by mitochondira Both occur post-translationally Both use two translocation complexes, one at each membrane
Common ground for protein translocation: access control for mitochondria and chloroplasts
 Common ground for protein translocation: access control for mitochondria and chloroplasts Enrico Schleiff*and Thomas Becker Abstract Mitochondria and chloroplasts import the vast majority of their proteins
Common ground for protein translocation: access control for mitochondria and chloroplasts Enrico Schleiff*and Thomas Becker Abstract Mitochondria and chloroplasts import the vast majority of their proteins
Overview of Cells. Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory
 Overview of Cells Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory Prokaryotic Cells Archaea Bacteria Come in many different shapes and sizes.5 µm 2 µm, up to 60 µm long Have large
Overview of Cells Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory Prokaryotic Cells Archaea Bacteria Come in many different shapes and sizes.5 µm 2 µm, up to 60 µm long Have large
!"#$%&'%()*%+*,,%-&,./*%01%02%/*/3452*%3&.26%&4752*,,*1%%
 !"#$%&'%()*%+*,,%-&,./*%01%02%/*/3452*%3&.26%&4752*,,*1%% !"#$%&'(")*++*%,*'-&'./%/,*#01#%-2)#3&)/% 4'(")*++*% % %5"0)%-2)#3&) %%% %67'2#72'*%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%4'(")0/./% % 8$+&'&,+"/7 % %,$&7&/9)7$*/0/%%%%%%%%%%
!"#$%&'%()*%+*,,%-&,./*%01%02%/*/3452*%3&.26%&4752*,,*1%% !"#$%&'(")*++*%,*'-&'./%/,*#01#%-2)#3&)/% 4'(")*++*% % %5"0)%-2)#3&) %%% %67'2#72'*%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%4'(")0/./% % 8$+&'&,+"/7 % %,$&7&/9)7$*/0/%%%%%%%%%%
Chapter 1. DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d
 Chapter 1 1. Matching Questions DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d 2. Matching Questions : Unbranched polymer that, when folded into its three-dimensional shape,
Chapter 1 1. Matching Questions DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d 2. Matching Questions : Unbranched polymer that, when folded into its three-dimensional shape,
Biological Process Term Enrichment
 Biological Process Term Enrichment cellular protein localization cellular macromolecule localization intracellular protein transport intracellular transport generation of precursor metabolites and energy
Biological Process Term Enrichment cellular protein localization cellular macromolecule localization intracellular protein transport intracellular transport generation of precursor metabolites and energy
and their organelles
 and their organelles Discovery Video: Cells REVIEW!!!! The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest
and their organelles Discovery Video: Cells REVIEW!!!! The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest
Cell Organelles Tutorial
 1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma. Reading: BCP Chapter 2
 Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Functional Unit of the Nervous System The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron. Neurons are cells specialized
Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Functional Unit of the Nervous System The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron. Neurons are cells specialized
Reading Assignments. A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides. Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
3.1 Cell Theory. KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life.
 3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. Many scientists contributed to
3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. Many scientists contributed to
Yeast ORFan Gene Project: Module 5 Guide
 Cellular Localization Data (Part 1) The tools described below will help you predict where your gene s product is most likely to be found in the cell, based on its sequence patterns. Each tool adds an additional
Cellular Localization Data (Part 1) The tools described below will help you predict where your gene s product is most likely to be found in the cell, based on its sequence patterns. Each tool adds an additional
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
2011 The Simple Homeschool Simple Days Unit Studies Cells
 1 We have a full line of high school biology units and courses at CurrClick and as online courses! Subscribe to our interactive unit study classroom and make science fun and exciting! 2 A cell is a small
1 We have a full line of high school biology units and courses at CurrClick and as online courses! Subscribe to our interactive unit study classroom and make science fun and exciting! 2 A cell is a small
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005
 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
Class Work 31. Describe the function of the Golgi apparatus? 32. How do proteins travel from the E.R. to the Golgi apparatus? 33. After proteins are m
 Eukaryotes Class Work 1. What does the word eukaryote mean? 2. What is the one major difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes? 3. List the different kingdoms of the eukaryote domain in the order in
Eukaryotes Class Work 1. What does the word eukaryote mean? 2. What is the one major difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes? 3. List the different kingdoms of the eukaryote domain in the order in
Chapter 31 Completing the Protein Life Cycle: Folding, Processing, and Degradation
 Chapter 31 Completing the Protein Life Cycle: Folding, Processing, and Degradation The newly produced proteins are not yet functional. They needs to undergo folding, processing, and modification to become
Chapter 31 Completing the Protein Life Cycle: Folding, Processing, and Degradation The newly produced proteins are not yet functional. They needs to undergo folding, processing, and modification to become
Tutorial 4 Protein Biochemistry 2 Genes to proteins: Protein synthesis, transport, targeting, and degradation
 IPAM Cells and Materials: At the Interface between Mathematics, Biology and Engineering Tutorial 4 Protein Biochemistry 2 Genes to proteins: Protein synthesis, transport, targeting, and degradation Dr.
IPAM Cells and Materials: At the Interface between Mathematics, Biology and Engineering Tutorial 4 Protein Biochemistry 2 Genes to proteins: Protein synthesis, transport, targeting, and degradation Dr.
Function and Illustration. Nucleus. Nucleolus. Cell membrane. Cell wall. Capsule. Mitochondrion
 Intro to Organelles Name: Block: Organelles are small structures inside cells. They are often covered in membranes. Each organelle has a job to do in the cell. Their name means little organ. Just like
Intro to Organelles Name: Block: Organelles are small structures inside cells. They are often covered in membranes. Each organelle has a job to do in the cell. Their name means little organ. Just like
REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Name AP Biology REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
Name AP Biology REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression
 Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
GENES AND CHROMOSOMES III. Lecture 5. Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S. Azam BIOL 266/
 GENES AND CHROMOSOMES III Lecture 5 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University CELL NUCLEUS AND THE CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION OPERONS Introduction All cells in a multi-cellular
GENES AND CHROMOSOMES III Lecture 5 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University CELL NUCLEUS AND THE CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION OPERONS Introduction All cells in a multi-cellular
The Cell. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 2 The Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
C h a p t e r 2 The Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology?
 Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life. B. Prokaryotic Cells. D. Organelles that Process Information. E. Organelles that Process Energy
 The Organization of Cells A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Lecture Series 4 The Organization of Cells B. Prokaryotic Cells C. Eukaryotic Cells D. Organelles that Process Information E. Organelles that
The Organization of Cells A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Lecture Series 4 The Organization of Cells B. Prokaryotic Cells C. Eukaryotic Cells D. Organelles that Process Information E. Organelles that
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005
 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
The Cell. What is a cell?
 The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
122-Biology Guide-5thPass 12/06/14. Topic 1 An overview of the topic
 Topic 1 http://bioichiban.blogspot.com Cellular Functions 1.1 The eukaryotic cell* An overview of the topic Key idea 1: Cell Organelles Key idea 2: Plasma Membrane Key idea 3: Transport Across Membrane
Topic 1 http://bioichiban.blogspot.com Cellular Functions 1.1 The eukaryotic cell* An overview of the topic Key idea 1: Cell Organelles Key idea 2: Plasma Membrane Key idea 3: Transport Across Membrane
Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year (1st Semester)
 Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year 2015-2016 (1st Semester) Day Date Topic Page No. Tuesday 20 September 2016 Cell and Cell Organelles CMB 47-53 Wednesday 21 September 2016 Biological Membranes CMB
Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year 2015-2016 (1st Semester) Day Date Topic Page No. Tuesday 20 September 2016 Cell and Cell Organelles CMB 47-53 Wednesday 21 September 2016 Biological Membranes CMB
Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function
 Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location ALL CELLS DNA Common in Animals Uncommon in Plants Lysosome
 CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
FREEMAN MEDIA INTEGRATION GUIDE Chapter 7: Inside the Cell
 FREEMAN MEDIA INTEGRATION GUIDE Chapter 7: Inside the Cell All media is on the Instructors Resource CD/DVD JPEG Resources Figures, Photos, and Tables PowerPoint Resources Chapter Outline with Figures Lecture
FREEMAN MEDIA INTEGRATION GUIDE Chapter 7: Inside the Cell All media is on the Instructors Resource CD/DVD JPEG Resources Figures, Photos, and Tables PowerPoint Resources Chapter Outline with Figures Lecture
The Cell Notes 1 of 11
 The Cell The basic unit of structure and function in living things The smallest units in living things The smallest units in living things that show the characteristics of life Organisms can be made of
The Cell The basic unit of structure and function in living things The smallest units in living things The smallest units in living things that show the characteristics of life Organisms can be made of
What is the central dogma of biology?
 Bellringer What is the central dogma of biology? A. RNA DNA Protein B. DNA Protein Gene C. DNA Gene RNA D. DNA RNA Protein Review of DNA processes Replication (7.1) Transcription(7.2) Translation(7.3)
Bellringer What is the central dogma of biology? A. RNA DNA Protein B. DNA Protein Gene C. DNA Gene RNA D. DNA RNA Protein Review of DNA processes Replication (7.1) Transcription(7.2) Translation(7.3)
Protein translocation across membranes
 Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1513 (2001) 1^24 www.bba-direct.com Review Protein translocation across membranes Fernando A. Agarraberes 1, J. Fred Dice * Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology,
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1513 (2001) 1^24 www.bba-direct.com Review Protein translocation across membranes Fernando A. Agarraberes 1, J. Fred Dice * Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology,
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 1 of 49 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic
1 of 49 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic
PROTEIN IMPORT INTO MITOCHONDRIA
 Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997. 66:863 917 Copyright c 1997 by Annual Reviews Inc. All rights reserved PROTEIN IMPORT INTO MITOCHONDRIA Walter Neupert Institut für Physiologische Chemie der Universität München,
Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997. 66:863 917 Copyright c 1997 by Annual Reviews Inc. All rights reserved PROTEIN IMPORT INTO MITOCHONDRIA Walter Neupert Institut für Physiologische Chemie der Universität München,
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.2 Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions 1. Which two domains consist of prokaryotic cells? 2. A major difference between
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.2 Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions 1. Which two domains consist of prokaryotic cells? 2. A major difference between
Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (55 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (55
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (55
1. Cell Theory Organelle containing the genetic information of the cell.
 GLOSSARY MATCHING GAME The words and definitions are all mixed up. Cut out each word and definition and glue the correct matches into your workbook. Word Definition 1. Cell Theory Organelle containing
GLOSSARY MATCHING GAME The words and definitions are all mixed up. Cut out each word and definition and glue the correct matches into your workbook. Word Definition 1. Cell Theory Organelle containing
Cell Organelles. a review of structure and function
 Cell Organelles a review of structure and function TEKS and Student Expectations (SE s) B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized
Cell Organelles a review of structure and function TEKS and Student Expectations (SE s) B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized
Chapter 7.2. Cell Structure
 Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE ORGANIZATION OF LIFE CELL THEORY TIMELINE
 CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE 1. composed of cells either uni/multi 2. reproduce sexual and/or asexual 3. contain DNA in cells 4. grow and develop 5. use material/energy in metabolic reactions 6. respond to
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE 1. composed of cells either uni/multi 2. reproduce sexual and/or asexual 3. contain DNA in cells 4. grow and develop 5. use material/energy in metabolic reactions 6. respond to
8/25/ Opening Questions: Are all living things made of cells? What are at least five things you know about cells?
 Chapter 3 The Cell: Module Hyperlinks 3.1 Cells are the fundamental units of life 3.2 Plant vs. animal cells 3.3 Membranes: structure 3.4 Membranes: function 3.5 The nucleus 3.6 Organelles in protein production
Chapter 3 The Cell: Module Hyperlinks 3.1 Cells are the fundamental units of life 3.2 Plant vs. animal cells 3.3 Membranes: structure 3.4 Membranes: function 3.5 The nucleus 3.6 Organelles in protein production
O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part II) Eukaryotic Cell Structure and Function
 O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part II) Eukaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cells These cells have membrane-bound structures called organelles. Cell processes occur in these organelles.
O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part II) Eukaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cells These cells have membrane-bound structures called organelles. Cell processes occur in these organelles.
BCMB Chapters 39 & 40 Translation (protein synthesis)
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 39 & 40 Translation (protein synthesis) Translation Genetic code trna Amino acyl trna Ribosomes Initiation Elongation Termination How is the nucleotide code translated into a protein
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 39 & 40 Translation (protein synthesis) Translation Genetic code trna Amino acyl trna Ribosomes Initiation Elongation Termination How is the nucleotide code translated into a protein
BCMB Chapters 39 & 40 Translation (protein synthesis)
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 39 & 40 Translation (protein synthesis) Translation Genetic code trna Amino acyl trna Ribosomes Initiation Elongation Termination How is the nucleotide code translated into a protein
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 39 & 40 Translation (protein synthesis) Translation Genetic code trna Amino acyl trna Ribosomes Initiation Elongation Termination How is the nucleotide code translated into a protein
Membrane Protein Channels
 Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
NO!!!!! BCMB Chapters 39 & 40 Translation (protein synthesis) BCMB Chapters 39 & 40 Translation (protein synthesis)
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 39 & 40 Translation How is the nucleotide code translated into a protein code? translation DNA RNA protein transcription 5 UCA 3 NH 2 Ser COO -????? Adapter Molecule Hypothesis (Crick,
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 39 & 40 Translation How is the nucleotide code translated into a protein code? translation DNA RNA protein transcription 5 UCA 3 NH 2 Ser COO -????? Adapter Molecule Hypothesis (Crick,
02/02/ Living things are organized. Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures. Learning Outcome B1
 Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
THE CELL 3/15/15 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I THE CELLULAR BASIS OF LIFE
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Lecture: M 6-9:30 Randall Visitor Center Lab: W 6-9:30 Swatek Anatomy Center, Centennial Complex Required Text: Marieb 9 th edition Dr. Trevor Lohman DPT (949) 246-5357 tlohman@llu.edu
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Lecture: M 6-9:30 Randall Visitor Center Lab: W 6-9:30 Swatek Anatomy Center, Centennial Complex Required Text: Marieb 9 th edition Dr. Trevor Lohman DPT (949) 246-5357 tlohman@llu.edu
Student Learning Outcomes: Nucleus distinguishes Eukaryotes from Prokaryotes
 9 The Nucleus Student Learning Outcomes: Nucleus distinguishes Eukaryotes from Prokaryotes Explain general structures of Nuclear Envelope, Nuclear Lamina, Nuclear Pore Complex Explain movement of proteins
9 The Nucleus Student Learning Outcomes: Nucleus distinguishes Eukaryotes from Prokaryotes Explain general structures of Nuclear Envelope, Nuclear Lamina, Nuclear Pore Complex Explain movement of proteins
Components of a functional cell. Boundary-membrane Cytoplasm: Cytosol (soluble components) & particulates DNA-information Ribosomes-protein synthesis
 Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
3.2 Cell Organelles. KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities.
 KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
Energy Converion: Mitochondria and Chloroplasts. Pınar Tulay, Ph.D.
 Energy Converion: Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Pınar Tulay, Ph.D. pintulay@gmail.com Energy Conversion Prokaryotes use plasma membrane to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) used in the cell function
Energy Converion: Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Pınar Tulay, Ph.D. pintulay@gmail.com Energy Conversion Prokaryotes use plasma membrane to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) used in the cell function
What Kind Of Molecules Carry Protein Assembly Instructions From The Nucleus To The Cytoplasm
 What Kind Of Molecules Carry Protein Assembly Instructions From The Nucleus To The Cytoplasm What kind of reaction produces large molecules by linking small molecules? molecules carry protein assembly
What Kind Of Molecules Carry Protein Assembly Instructions From The Nucleus To The Cytoplasm What kind of reaction produces large molecules by linking small molecules? molecules carry protein assembly
2. small / 70s ribosomes box; (2) Feature also present ( ) or absent ( ) in chloroplasts
 1(a)(i) 1. circular DNA box ; 2. small / 70s ribosomes box; (2) 1(a)(ii) Features present in mitochondria Surrounded by a double membrane Feature also present () or absent () in chloroplasts Crista present
1(a)(i) 1. circular DNA box ; 2. small / 70s ribosomes box; (2) 1(a)(ii) Features present in mitochondria Surrounded by a double membrane Feature also present () or absent () in chloroplasts Crista present
Molecular Biology - Translation of RNA to make Protein *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49485 1 Molecular Biology - Translation of RNA to make Protein * Jerey Mahr Based on Translation by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m49485 1 Molecular Biology - Translation of RNA to make Protein * Jerey Mahr Based on Translation by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
Biology 1 Notebook. Review Answers Pages 17 -?
 Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
Cell (Learning Objectives)
 Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance
 Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance 1590 Jansen 1650 Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1665 Robert Hooke 1831 Matthias Schleiden 1831 Theodore Schwann 1855 Rudolf Virchow
Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance 1590 Jansen 1650 Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1665 Robert Hooke 1831 Matthias Schleiden 1831 Theodore Schwann 1855 Rudolf Virchow
Module A Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport. Mr. Mitcheltree
 Module A Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Mr. Mitcheltree Surface area to Volume Ratio in Plants Surface area to Volume Ratio in us There are a number of necessary conditions that allow effective gaseous
Module A Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Mr. Mitcheltree Surface area to Volume Ratio in Plants Surface area to Volume Ratio in us There are a number of necessary conditions that allow effective gaseous
It s a Small World After All
 It s a Small World After All Engage: Cities, factories, even your own home is a network of dependent and independent parts that make the whole function properly. Think of another network that has subunits
It s a Small World After All Engage: Cities, factories, even your own home is a network of dependent and independent parts that make the whole function properly. Think of another network that has subunits
Chapter 4. Table of Contents. Section 1 The History of Cell Biology. Section 2 Introduction to Cells. Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features
 Cell Structure and Function Table of Contents Section 1 The History of Cell Biology Section 2 Introduction to Cells Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features Section 4 Unique Features of Plant Cells Section
Cell Structure and Function Table of Contents Section 1 The History of Cell Biology Section 2 Introduction to Cells Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features Section 4 Unique Features of Plant Cells Section
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 7, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 7, 2006
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 9 - TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
!! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called
 The Cell Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of
The Cell Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of
Life of the Cell. Learning Objectives
 Life of the Cell Society on a micro-scale 1 Learning Objectives 1. What are the characteristics that distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Which type of cell is believed to be older (more primitive)?
Life of the Cell Society on a micro-scale 1 Learning Objectives 1. What are the characteristics that distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Which type of cell is believed to be older (more primitive)?
Biology: Life on Earth
 Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells
 Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments Read Chapter 15 Endomembrane System Read Chapter 17 Cytoskeleton A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: All cells come from preexisting
Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments Read Chapter 15 Endomembrane System Read Chapter 17 Cytoskeleton A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: All cells come from preexisting
Reading Assignments. A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life. Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells
 Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments Read Chapter 15 Endomembrane System Read Chapter 17 Cytoskeleton A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: All cells come from preexisting
Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments Read Chapter 15 Endomembrane System Read Chapter 17 Cytoskeleton A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: All cells come from preexisting
Cellular Biology. Cells: theory, types, form & function, evolution
 Cellular Biology Cells: theory, types, form & function, evolution The Cell Theory Problems with the Cell Theory? The cell theory has three components: 1. all living organisms are made up of one or more
Cellular Biology Cells: theory, types, form & function, evolution The Cell Theory Problems with the Cell Theory? The cell theory has three components: 1. all living organisms are made up of one or more
Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (60 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (60
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (60
Mitochondria Mitochondria were first seen by kollicker in 1850 in muscles and called them sarcosomes. Flemming (1882) described these organelles as
 Mitochondria Mitochondria were first seen by kollicker in 1850 in muscles and called them sarcosomes. Flemming (1882) described these organelles as filia Altmann (1890) observed these structures and named
Mitochondria Mitochondria were first seen by kollicker in 1850 in muscles and called them sarcosomes. Flemming (1882) described these organelles as filia Altmann (1890) observed these structures and named
