Frontiers in CardioVascular Biology
|
|
|
- Blaise Newton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Frontiers in CardioVascular Biology Young Investigator Award Mitofusin 2 controls calcium transmission between the SR and mitochondria and regulates the bioenergetic feedback response in cardiac myocytes Maxie Meiser Klinik für Innere Medizin III Universitätsklinikum des Saarlandes Homburg, Germany Conflict of Interest: none
2 Physiology: Excitation-contraction coupling and mitochondrial energetics Na + I Na Na + Mito Oxidative Phosphorylation NCX Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR) SERCA SERCA T-tubulus I Ca ATP ADP RyR2 Cytosol Myofilaments
3 ph Intermembrane Space Inner Mitochondrial Membrane Mitochondrial Matrix I H + Q III c IV V II H + H + H + Ψ m -180 mv e - NADH NAD + ATP ADP Krebs Cycle + FADH 2 FAD + MCU Cytosol
4 Privileged communication between SR and mitochondria K d ( ) µm Kohlhaas & Maack, Circulation 2010;122:
5 Physical tethers between SR and mitochondria 3D-electron tomography in mouse hearts jsr Hayashi et al., J Cell Sci 2009;122: Mito removed Tether jsr
6 Mitofusins 1 and 2 Redundant roles in mitochondrial fusion Outer mitochondrial membrane Mfn2 Mfn1 Mfn2 Mfn2 Mfn1 Mfn1
7 Mitofusins 1 and 2 Redundant roles in mitochondrial fusion Mfn2 Mfn1 Mfn2 Mfn2 Mfn1 Mfn1
8 Mitofusins 1 and 2 Redundant roles in mitochondrial fusion Mfn2 Mfn1 Mfn2 Mfn2 Mfn1 Mfn1
9 Mitofusin 2: Tethers ER to mitochondria in fibroblasts Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum De Brito & Scorrano; Nature 2008;456:
10 Mitofusin 2 Possible linker protein between SR and mitochondria in cardiac myocytes? Mfn2 MCU Mfn1 MCU Mfn2 RyR RyR RyR Mfn2 Mfn2 Mfn2 Sarcoplasmic reticulum
11 Mitofusin 2 Possible linker protein between SR and mitochondria in cardiac myocytes? Mfn2 MCU Mfn1 MCU RyR RyR RyR Mfn2 Mfn2 Mfn2 Mfn2 Mfn1-KO
12 Mitofusin 2 Possible linker protein between SR and mitochondria in cardiac myocytes? Mfn2 MCU Mfn1 RyR RyR RyR MCU Mfn2 Mfn2 Mfn2 Mfn2 Mfn1-KO
13 Mfn2 deficiency impairs the spatial association of mitochondria to the SR WT
14 Experimental Protocol Wild Type (WT) Mfn1-KO Isolated cardiac myocytes Electrical Field Stimulation Isoproterenol (30 nm) 0.5 Hz 5 Hz 0.5 Hz Sarcomere Shortening
15 ph H + H + H + H + I Q III c IV V II NADH/NAD + FADH 2 /FAD Autofluorescence e - NADH Krebs Cycle NAD + + FADH 2 FAD + Rhod-2 ATP ADP MCU Indo-1
16 Unchanged cytosolic and mitochondrial signaling in Mfn1-KO myocytes [ ] c (F 405/485 ) [ ] c Mfn1-KO WT Time (s) [ ] m (F/F 0 ) [ ] m Mfn1-KO WT Time (s) Mfn1-KO mitoch. matrix (Rhod-2) [ ] m (F/F 0 ) 3.0 Mfn1-KO WT [ ] c (F 405/485 ) Diastolic [ ] m (F/F 0 ) Hz 0.5 Hz 0.5 Hz 0 Isoproterenol 30 nm WT Mfn1-KO Time (s) cytosol MCU IMM* (Indo-1)
17 Unchanged bioenergetic feedback response in Mfn1-KO myocytes Isoproterenol 5 Hz 0.5 Hz 0.5 Hz Mfn1-KO NADH (%) WT Mfn1-/- I Q II III 60 FAD + (%) e - NADH NAD + NADH / FAD Krebs Cycle + FADH 2 FAD Time (s)
18 Unchanged sarcomere shortening in Mfn2 KO myocytes Intact cardiac myocytes 5 Hz 0.5 Hz 0.5 Hz Isoproterenol 30 nm Sarcomere shortening Cytosolic [ ] FS (%) Hz 0.5 Hz 0.5 Hz Isoproterenol 30 nm WT Time (s) [ ] c (F 405/485 ) [ ] c (F 405/485 ) * sys. dias Time (s) *p<0.05 vs. WT
19 Decreased mitochondrial accumulation in myocytes [ ] c (F 405/485 ) [ ] c WT Time (s) [ ] m (F/F 0 ) [ ] m WT Time (s) mitoch. matrix (Rhod-2) MCU IMM* [ ] m (F/F 0 ) 2.0 WT [ ] c (F 405/485 ) cytosol (Indo-1)
20 Decreased mitochondrial accumulation in myocytes 5 Hz 0.5 Hz 0.5 Hz Isoproterenol 30 nm Diastolic [ ] m (F/F 0 ) inset WT mitoch. matrix (Rhod-2) Time (s) MCU IMM* Min 0-3 F/F Hz Iso * WT cytosol (Indo-1) sec *p<0.05
21 Impaired bioenergetic feedback response in myocytes NADH / FAD + FAD + (%) NADH (%) Hz 0.5 Hz 0.5 Hz ** ** ** Isoproterenol WT Mfn2-/ Time (s) e - NADH I Krebs Cycle Q II NAD + + III FADH 2 FAD +
22 Impaired bioenergetic feedback response in myocytes NADH / FAD + FAD + (%) NADH (%) Hz 0.5 Hz 0.5 Hz ** ** ** Isoproterenol WT Mfn2-/ Time (s) [ ] m (F/F 0 ) e - NADH I 0.5 Hz Iso Krebs Cycle Q II NAD + + # III WT sec Mfn2-/- FADH 2 FAD +
23 ph Intermembrane Space FCCP H + I H + H + H + Q III c IV V H + Inner Mitochondrial Membrane II Oligomycin Mitochondrial Matrix H + e - NADH NAD + ATP ADP Krebs Cycle + λ exc =540 nm λ em =605 nm TMRM MCU Ψ m -180 mv Cytosol
24 Unchanged mitochondrial membrane potential ( Ψ m ) in myocytes Ψ m (F/F 0 ) FCCP & Oligomycin WT Ψ m (A.U.) 1.8 WT Time (s) 0.0 Basal FCCP +Oligom.
25 Deletion of Mfn2, but not Mfn1, induces dilated cardiomyopathy Mfn1-KO
26 Conclusions Mfn2, but not Mfn1 tethers mitochondria to the SR in cardiac myocytes is a molecular determinant of a mitochondrial microdomain in cardiac myocytes important for energy supply and demand matching Defects in SR-mitochondria transmission may play a causal role for the development of heart failure.
27 Acknowledgments Maack lab Financial Support DFG - KFO 196 DFG - SFB 894 HOMFOR Washington University, St. Louis, USA Gerald Dorn Yun Chen Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, USA Gyorgy Csordas
28
29 Specific localization of rhod-2 and indo-1 in mitochondria and cytosol, respectively [ ] c (F 405/485 ) [ ] m (F/F 0 ) Isoproterenol systolic 5 Hz systolic diastolic diastolic Con Ru360 Ru360 Con * * [ ] c (F 405/485 ) [ ] m (F/F 0 ) Patch-clamped cardiac myocytes Ru360 Con Con Ru360 Ru360 mitoch. matrix cytosol MCU Rhod-2 IMM* Indo Time (s) Time (s) *IMM= inner mitochondrial membrane
30 Postnatal deletion of Mfn1 or Mfn2 Mfn1-KO
A Model Based Analysis of Steady-State versus Dynamic Elements in the Relationship between Calcium and Force
 A Model Based Analysis of Steady-State versus Dynamic Elements in the Relationship between Calcium and Force Casey L. Overby, Sanjeev G. Shroff BACKGROUND Cardiac contraction and calcium. Intracellular
A Model Based Analysis of Steady-State versus Dynamic Elements in the Relationship between Calcium and Force Casey L. Overby, Sanjeev G. Shroff BACKGROUND Cardiac contraction and calcium. Intracellular
Cellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport Chain
 Cellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport Chain 2006-2007 Cellular respiration What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP 2006-2007 ATP accounting so far Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb s cycle 2 ATP
Cellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport Chain 2006-2007 Cellular respiration What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP 2006-2007 ATP accounting so far Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb s cycle 2 ATP
Modeling. EC-Coupling and Contraction
 Bioeng 6460 Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity Modeling of EC-Coupling and Contraction Frank B. Sachse fs@cvrti.utah.edu Overview Quiz Excitation-Contraction Coupling Anatomy Cross Bridge Binding Coupling
Bioeng 6460 Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity Modeling of EC-Coupling and Contraction Frank B. Sachse fs@cvrti.utah.edu Overview Quiz Excitation-Contraction Coupling Anatomy Cross Bridge Binding Coupling
5/31/2013. Mechanical-Energetic Coupling in Airway Smooth Muscle. Evolution of Academic Medical Centers
 Mechanical-Energetic Coupling Mayo Clinic One of the World s Largest Medical Centers Gary C. Sieck, Ph.D. Department of Physiology & Biomedical Engineering Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Physiology &
Mechanical-Energetic Coupling Mayo Clinic One of the World s Largest Medical Centers Gary C. Sieck, Ph.D. Department of Physiology & Biomedical Engineering Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Physiology &
Cellular Electrophysiology and Biophysics
 BIOEN 6003 Cellular Electrophysiology and Biophysics Modeling of Force Development in Myocytes II Frank B. Sachse, University of Utah Overview Experimental Studies Sliding Filament Theory Group work Excitation-Contraction
BIOEN 6003 Cellular Electrophysiology and Biophysics Modeling of Force Development in Myocytes II Frank B. Sachse, University of Utah Overview Experimental Studies Sliding Filament Theory Group work Excitation-Contraction
Introduction to Physiology IV - Calcium Dynamics
 Introduction to Physiology IV - Calcium Dynamics J. P. Keener Mathematics Department Introduction to Physiology IV - Calcium Dynamics p.1/26 Introduction Previous lectures emphasized the role of sodium
Introduction to Physiology IV - Calcium Dynamics J. P. Keener Mathematics Department Introduction to Physiology IV - Calcium Dynamics p.1/26 Introduction Previous lectures emphasized the role of sodium
Mitochondrial dynamics in ischemia and reperfusion
 Mitochondrial dynamics in ischemia and reperfusion Derek J Hausenloy Reader in Cardiovascular Medicine, British Heart Foundation Senior Clinical Research Fellow, The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute, University
Mitochondrial dynamics in ischemia and reperfusion Derek J Hausenloy Reader in Cardiovascular Medicine, British Heart Foundation Senior Clinical Research Fellow, The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute, University
ETC/CHEMIOSIS. By: Leslie, Kelsey, Morgan
 ETC/CHEMIOSIS By: Leslie, Kelsey, Morgan WHY THIS IS IMPORTANT House Clip SO3E7 The Son of a Coma Guy- Time: 32:00 Patient was visiting his father who was in a vegetative state for 10 years, and his only
ETC/CHEMIOSIS By: Leslie, Kelsey, Morgan WHY THIS IS IMPORTANT House Clip SO3E7 The Son of a Coma Guy- Time: 32:00 Patient was visiting his father who was in a vegetative state for 10 years, and his only
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Overview 10 reactions u convert () to pyruvate (3C) u produces: 4 & NADH u consumes: u net: & NADH C-C-C-C-C-C fructose-1,6bp P-C-C-C-C-C-C-P DHAP P-C-C-C G3P C-C-C-P H P i P i pyruvate C-C-C 4 4 NAD +
Overview 10 reactions u convert () to pyruvate (3C) u produces: 4 & NADH u consumes: u net: & NADH C-C-C-C-C-C fructose-1,6bp P-C-C-C-C-C-C-P DHAP P-C-C-C G3P C-C-C-P H P i P i pyruvate C-C-C 4 4 NAD +
Mitochondrial Biogenesis is the process by which new mitochondria are formed in the cell.
 Mitochondrial Biogenesis is the process by which new mitochondria are formed in the cell. Purpose of Mitochondria: The mitochondria are organelles within the cell that are responsible for the biochemical
Mitochondrial Biogenesis is the process by which new mitochondria are formed in the cell. Purpose of Mitochondria: The mitochondria are organelles within the cell that are responsible for the biochemical
Cellular respiration ATP. Cellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport Chain. AP Biology. The point is to make ATP! What s the point?
 ellular respiration ellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport hain What s the point? The point is to make! accounting so far Glycolysis 2 Kreb s cycle 2 Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to
ellular respiration ellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport hain What s the point? The point is to make! accounting so far Glycolysis 2 Kreb s cycle 2 Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to
Lecture 10. Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis. Oxidative. Photo-Phosphorylation
 Lecture 10 Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation Photo-Phosphorylation Model of the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Glycerol-3-P Shuttle Outer Mitochondrial Membrane G3P DHAP
Lecture 10 Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation Photo-Phosphorylation Model of the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Glycerol-3-P Shuttle Outer Mitochondrial Membrane G3P DHAP
Homework - I. Hand draw the structure of an eukaryotic cell with all organelles clearly drawn and describe the function of each organelle.
 Homework - I Hand draw the structure of an eukaryotic cell with all organelles clearly drawn and describe the function of each organelle. Please get a book and read the chapter related to cell structure!!!
Homework - I Hand draw the structure of an eukaryotic cell with all organelles clearly drawn and describe the function of each organelle. Please get a book and read the chapter related to cell structure!!!
ATP. Division Ave. High School AP Biology. Cellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport Chain. Cellular respiration. The point is to make ATP!
 ellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport hain 2006-2007 ellular respiration What s the point? The point is to make! 2006-2007 1 accounting so far Glycolysis 2 Kreb s cycle 2 Life takes a lot of
ellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport hain 2006-2007 ellular respiration What s the point? The point is to make! 2006-2007 1 accounting so far Glycolysis 2 Kreb s cycle 2 Life takes a lot of
Chem Lecture 9 Pumps and Channels Part 1
 Chem 45 - Lecture 9 Pumps and Channels Part 1 Question of the Day: What two factors about a molecule influence the change in its free energy as it moves across a membrane? Membrane proteins function as
Chem 45 - Lecture 9 Pumps and Channels Part 1 Question of the Day: What two factors about a molecule influence the change in its free energy as it moves across a membrane? Membrane proteins function as
Basic mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis and antiarrhythmia
 EHRA EDUCATIONAL REVIEW AND PREPARATORY COURSE ON INVASIVE CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EUROPEAN HEART HOUSE, February 2011 Basic mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis and antiarrhythmia Antonio Zaza Università
EHRA EDUCATIONAL REVIEW AND PREPARATORY COURSE ON INVASIVE CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EUROPEAN HEART HOUSE, February 2011 Basic mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis and antiarrhythmia Antonio Zaza Università
Photosynthesis and cellular respirations
 The Introduction of Biology Defining of life Basic chemistry, the chemistry of organic molecules Classification of living things History of cells and Cells structures and functions Photosynthesis and cellular
The Introduction of Biology Defining of life Basic chemistry, the chemistry of organic molecules Classification of living things History of cells and Cells structures and functions Photosynthesis and cellular
Sarcoplasmic reticulum is an intermediary of mitochondrial and myofibrillar growth at the intercalated disc
 J Muscle Res Cell Motil (2016) 37:55 69 DOI 10.1007/s10974-016-9444-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sarcoplasmic reticulum is an intermediary of mitochondrial and myofibrillar growth at the intercalated disc Pauline
J Muscle Res Cell Motil (2016) 37:55 69 DOI 10.1007/s10974-016-9444-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sarcoplasmic reticulum is an intermediary of mitochondrial and myofibrillar growth at the intercalated disc Pauline
All organisms require a constant expenditure of energy to maintain the living state - "LIFE".
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION All organisms require a constant expenditure of energy to maintain the living state - "LIFE". Where does the energy come from and how is it made available for life? With rare exception,
CELLULAR RESPIRATION All organisms require a constant expenditure of energy to maintain the living state - "LIFE". Where does the energy come from and how is it made available for life? With rare exception,
Supplemental material
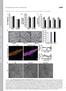 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics
 MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics MUDr. Jan Pláteník, PhD. Ústav lékařské biochemie 1.LF UK Helpful comments of Prof. MUDr. Jiří Kraml, DrSc., are acknowledged. 1 Respiratory chain and
MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics MUDr. Jan Pláteník, PhD. Ústav lékařské biochemie 1.LF UK Helpful comments of Prof. MUDr. Jiří Kraml, DrSc., are acknowledged. 1 Respiratory chain and
Change to Office Hours this Friday and next Monday. Tomorrow (Abel): 8:30 10:30 am. Monday (Katrina): Cancelled (05/04)
 Change to Office Hours this Friday and next Monday Tomorrow (Abel): 8:30 10:30 am Monday (Katrina): Cancelled (05/04) Lecture 10 Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation Photo-Phosphorylation
Change to Office Hours this Friday and next Monday Tomorrow (Abel): 8:30 10:30 am Monday (Katrina): Cancelled (05/04) Lecture 10 Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation Photo-Phosphorylation
Electron Transport Chain (Respiratory Chain) - exercise - Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Electron Transport Chain (Respiratory Chain) - exercise - Vladimíra Kvasnicová Respiratory chain (RCH) a) is found in all cells b) is located in a mitochondrion c) includes enzymes integrated in the inner
Electron Transport Chain (Respiratory Chain) - exercise - Vladimíra Kvasnicová Respiratory chain (RCH) a) is found in all cells b) is located in a mitochondrion c) includes enzymes integrated in the inner
Life Depends on Photosynthesis
 Photosynthesis Life Depends on Photosynthesis Most energy Comes from the Sun Life Depends on Photosynthesis Most energy Comes from the Sun Life Depends on Photosynthesis Most energy Comes from the Sun
Photosynthesis Life Depends on Photosynthesis Most energy Comes from the Sun Life Depends on Photosynthesis Most energy Comes from the Sun Life Depends on Photosynthesis Most energy Comes from the Sun
PHYSIOLOGY CHAPTER 9 MUSCLE TISSUE Fall 2016
 PHYSIOLOGY CHAPTER 9 MUSCLE TISSUE Fall 2016 2 Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Overview of Muscle Tissue types of muscle: are all prefixes for muscle Contractility all muscles cells can Smooth & skeletal
PHYSIOLOGY CHAPTER 9 MUSCLE TISSUE Fall 2016 2 Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Overview of Muscle Tissue types of muscle: are all prefixes for muscle Contractility all muscles cells can Smooth & skeletal
Lecture 13, 05 October 2004 Chapter 10, Muscle. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.
 Lecture 13, 05 October 2004 Chapter 10, Muscle Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2004 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Nate Swenson Vertebrate Physiology 437 18 1. Muscle A. Sarcomere
Lecture 13, 05 October 2004 Chapter 10, Muscle Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2004 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Nate Swenson Vertebrate Physiology 437 18 1. Muscle A. Sarcomere
Cellular Respiration. The mechanism of creating cellular energy. Thursday, 11 October, 12
 Cellular Respiration The mechanism of creating cellular energy What do we know?? What do we know?? Grade 5 - Food --> Energy What do we know?? Grade 5 - Food --> Energy Grade 10 - glu. + O2 --> CO2 + H20
Cellular Respiration The mechanism of creating cellular energy What do we know?? What do we know?? Grade 5 - Food --> Energy What do we know?? Grade 5 - Food --> Energy Grade 10 - glu. + O2 --> CO2 + H20
20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
 20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20.1 What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Metabolism? Electron transport - Role of oxygen in metabolism as final acceptor of electrons - In inner
20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20.1 What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Metabolism? Electron transport - Role of oxygen in metabolism as final acceptor of electrons - In inner
Edexcel (B) Biology A-level
 Edexcel (B) Biology A-level Topic 5: Energy for Biological Processes Notes Aerobic Respiration Aerobic respiration as splitting of the respiratory substrate, to release carbon dioxide as a waste product
Edexcel (B) Biology A-level Topic 5: Energy for Biological Processes Notes Aerobic Respiration Aerobic respiration as splitting of the respiratory substrate, to release carbon dioxide as a waste product
Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization
 Cell Metabolism Supplemental Information Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization Prashant Mishra, Grigor Varuzhanyan,
Cell Metabolism Supplemental Information Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization Prashant Mishra, Grigor Varuzhanyan,
Lecture 7 Cell Biolog y ٢٢٢ ١
 Lecture 7 ١ Mitochondria ٢ Mitochondria Mitochondria are the energy factories of the cells. The energy currency for the work that animals must do is the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Lecture 7 ١ Mitochondria ٢ Mitochondria Mitochondria are the energy factories of the cells. The energy currency for the work that animals must do is the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Bio102 Problems Photosynthesis
 Bio102 Problems Photosynthesis 1. Why is it advantageous for chloroplasts to have a very large (in surface area) thylakoid membrane contained within the inner membrane? A. This limits the amount of stroma
Bio102 Problems Photosynthesis 1. Why is it advantageous for chloroplasts to have a very large (in surface area) thylakoid membrane contained within the inner membrane? A. This limits the amount of stroma
Cardiolipin Remodeling by ALCAT1 Regulates Dilated Cardiomyopathy Through Oxidative Stress and Mitophagy. Yuguang (Roger) Shi
 Cardiolipin Remodeling by ALCAT1 Regulates Dilated Cardiomyopathy Through xidative Stress and Mitophagy Yuguang (Roger) Shi yus11@psu.eud Cardiolipin Biosynthetic and Remodeling Pathways Phosphatidic Acid
Cardiolipin Remodeling by ALCAT1 Regulates Dilated Cardiomyopathy Through xidative Stress and Mitophagy Yuguang (Roger) Shi yus11@psu.eud Cardiolipin Biosynthetic and Remodeling Pathways Phosphatidic Acid
Computational Modeling of the Cardiovascular and Neuronal System
 BIOEN 6900 Computational Modeling of the Cardiovascular and Neuronal System Modeling of Force Development in Myocytes Overview Recapitulation Modeling of Conduction Modeling of Force in Skeletal Muscle
BIOEN 6900 Computational Modeling of the Cardiovascular and Neuronal System Modeling of Force Development in Myocytes Overview Recapitulation Modeling of Conduction Modeling of Force in Skeletal Muscle
Dynamical Systems for Biology - Excitability
 Dynamical Systems for Biology - Excitability J. P. Keener Mathematics Department Dynamical Systems for Biology p.1/25 Examples of Excitable Media B-Z reagent CICR (Calcium Induced Calcium Release) Nerve
Dynamical Systems for Biology - Excitability J. P. Keener Mathematics Department Dynamical Systems for Biology p.1/25 Examples of Excitable Media B-Z reagent CICR (Calcium Induced Calcium Release) Nerve
(Be sure to clearly state the principles addressed in your discussion.)
 CELL QUESTION 1992: AP BIOLOGY A laboratory assistant prepared solutions of 0.8 M, 0.6 M, 0.4 M, and 0.2 M sucrose, but forgot to label them. After realizing the error, the assistant randomly labeled the
CELL QUESTION 1992: AP BIOLOGY A laboratory assistant prepared solutions of 0.8 M, 0.6 M, 0.4 M, and 0.2 M sucrose, but forgot to label them. After realizing the error, the assistant randomly labeled the
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.6 (2017) pp 2001 2019 2001 Rapid frequency-dependent changes in free mitochondrial calcium concentration in rat cardiac myocytes RobC.I.Wüst 1, Michiel Helmes 1,2,JodyL.Martin 3, Thomas J.
J Physiol 595.6 (2017) pp 2001 2019 2001 Rapid frequency-dependent changes in free mitochondrial calcium concentration in rat cardiac myocytes RobC.I.Wüst 1, Michiel Helmes 1,2,JodyL.Martin 3, Thomas J.
GR QUIZ WITH ANS KEY Cellular Processes. Part I: Multiple Choice. 1. In leaf cell, the synthesis of ATP occurs in which of the following?
 GR QUIZ WITH ANS KEY Cellular Processes Part I: Multiple Choice 1. In leaf cell, the synthesis of ATP occurs in which of the following? I. Ribosomes II. Mitochondria III. Chloroplasts A. I only B. II only
GR QUIZ WITH ANS KEY Cellular Processes Part I: Multiple Choice 1. In leaf cell, the synthesis of ATP occurs in which of the following? I. Ribosomes II. Mitochondria III. Chloroplasts A. I only B. II only
2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of October
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ 2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of 19-23 October Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which
Name: Class: _ Date: _ 2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of 19-23 October Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which
According to the diagram, which of the following is NOT true?
 Instructions: Review Chapter 44 on muscular-skeletal systems and locomotion, and then complete the following Blackboard activity. This activity will introduce topics that will be covered in the next few
Instructions: Review Chapter 44 on muscular-skeletal systems and locomotion, and then complete the following Blackboard activity. This activity will introduce topics that will be covered in the next few
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Development of a mitochondriotropic antioxidant based on caffeic acid: proof of concept on cellular and mitochondrial oxidative stress models José Teixeira a,b, Fernando Cagide a,
Supporting Information Development of a mitochondriotropic antioxidant based on caffeic acid: proof of concept on cellular and mitochondrial oxidative stress models José Teixeira a,b, Fernando Cagide a,
09/30/2017. Kyu-Sun Lee, Ph.D. Metabolism & Neurophysiology Research Group Hazard Monitoring BNT Res Center
 09/30/2017 Kyu-Sun Lee, Ph.D. Metabolism & Neurophysiology Research Group Hazard Monitoring BNT Res Center Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs
09/30/2017 Kyu-Sun Lee, Ph.D. Metabolism & Neurophysiology Research Group Hazard Monitoring BNT Res Center Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs
BIOLOGY 479 INTEGRATED PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY Dept. of Biological & Allied Health Sciences BLOOMSBURG UNIVERSITY of PENNSYLVANIA.
 BIOLOGY 479 INTEGRATED PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY Dept. of Biological & Allied Health Sciences BLOOMSBURG UNIVERSITY of PENNSYLVANIA LAB REPORT: Investigating Aerobic Respiration Michael Tekin Lab section:
BIOLOGY 479 INTEGRATED PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY Dept. of Biological & Allied Health Sciences BLOOMSBURG UNIVERSITY of PENNSYLVANIA LAB REPORT: Investigating Aerobic Respiration Michael Tekin Lab section:
UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM I. Functions of Muscular System A. Produces Movement Internal vs. External «locomotion & manipulation «circulate blood & maintain blood pressure «move fluids, food, baby B. Maintaining
UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM I. Functions of Muscular System A. Produces Movement Internal vs. External «locomotion & manipulation «circulate blood & maintain blood pressure «move fluids, food, baby B. Maintaining
Biology September 2015 Exam One FORM G KEY
 Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM G KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM G KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Biology September 2015 Exam One FORM W KEY
 Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
TISSUE. A) Types. (i)
 MUSCLES & MUSCLE TISSUE I. OVERVIEW - Muscle ( little mouse ) - tissue designed to cause movementt thru contraction ( shortening ). A) Types - There are some SIMILARITIES between muscle types: (i) All
MUSCLES & MUSCLE TISSUE I. OVERVIEW - Muscle ( little mouse ) - tissue designed to cause movementt thru contraction ( shortening ). A) Types - There are some SIMILARITIES between muscle types: (i) All
Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 Chapter 10 Chemotrophic Energy Metabolism: Aerobic Respiration Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Figure 10-1 Figure 10-6 Conversion of pyruvate The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl
Chapter 10 Chemotrophic Energy Metabolism: Aerobic Respiration Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Figure 10-1 Figure 10-6 Conversion of pyruvate The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl
Muscle tissue. Types. Functions. Cardiac, Smooth, and Skeletal
 Types Cardiac, Smooth, and Skeletal Functions movements posture and body position Support soft tissues Guard openings body temperature nutrient reserves Muscle tissue Special Characteristics of Muscle
Types Cardiac, Smooth, and Skeletal Functions movements posture and body position Support soft tissues Guard openings body temperature nutrient reserves Muscle tissue Special Characteristics of Muscle
TCA Cycle. Voet Biochemistry 3e John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 TCA Cycle Voet Biochemistry 3e Voet Biochemistry 3e The Electron Transport System (ETS) and Oxidative Phosphorylation (OxPhos) We have seen that glycolysis, the linking step, and TCA generate a large number
TCA Cycle Voet Biochemistry 3e Voet Biochemistry 3e The Electron Transport System (ETS) and Oxidative Phosphorylation (OxPhos) We have seen that glycolysis, the linking step, and TCA generate a large number
MITOCHONDRIAL LAB. We are alive because we make a lot of ATP and ATP makes (nonspontaneous) chemical reactions take place
 MITOCHONDRIAL LAB We are alive because we make a lot of ATP and ATP makes (nonspontaneous) chemical reactions take place We make about 95% of our ATP in the mitochondria We will isolate mitochondria, and
MITOCHONDRIAL LAB We are alive because we make a lot of ATP and ATP makes (nonspontaneous) chemical reactions take place We make about 95% of our ATP in the mitochondria We will isolate mitochondria, and
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005
 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
AP Biology Cellular Respiration
 AP Biology Cellular Respiration The bonds between H and C represents a shared pair of electrons These are high-energy electrons This represents chemical potential energy Hydro-carbons posses a lot of chemical
AP Biology Cellular Respiration The bonds between H and C represents a shared pair of electrons These are high-energy electrons This represents chemical potential energy Hydro-carbons posses a lot of chemical
2.A.2- Capture and Storage of Free Energy
 2.A.2- Capture and Storage of Free Energy Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce, and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. EU 2.A- Growth, reproduction
2.A.2- Capture and Storage of Free Energy Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce, and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. EU 2.A- Growth, reproduction
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Practice Test Name
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which H+ has just passed through the
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which H+ has just passed through the
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways
 Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
Chapter 2 Basic Cardiac Electrophysiology: Excitable Membranes
 Chapter Basic Cardiac Electrophysiology: Excitable Membranes Deborah A. Jaye, Yong-Fu Xiao, and Daniel C. Sigg Abstract Cardiomyocytes are excitable cells that have the ability to contract after excitation;
Chapter Basic Cardiac Electrophysiology: Excitable Membranes Deborah A. Jaye, Yong-Fu Xiao, and Daniel C. Sigg Abstract Cardiomyocytes are excitable cells that have the ability to contract after excitation;
M i t o c h o n d r i a
 M i t o c h o n d r i a Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Mitochondria Function: generation of metabolic energy in eukaryotic cells Generation of ATP from the breakdown of
M i t o c h o n d r i a Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Mitochondria Function: generation of metabolic energy in eukaryotic cells Generation of ATP from the breakdown of
Dominika Malińska. Laboratory of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes, Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, Polish Academy of Sciences
 2007 2013 m. Žmogiškųjų išteklių plėtros veiksmų programos 3 prioriteto Tyrėjų gebėjimų stiprinimas VP1-3.1-ŠMM-05-K priemonės MTTP tematinių tinklų, asociacijų veiklos stiprinimas projektas Lietuvos Biochemikų
2007 2013 m. Žmogiškųjų išteklių plėtros veiksmų programos 3 prioriteto Tyrėjų gebėjimų stiprinimas VP1-3.1-ŠMM-05-K priemonės MTTP tematinių tinklų, asociacijų veiklos stiprinimas projektas Lietuvos Biochemikų
Energy & Life: Cellular Respiration PART I: HARVESTING CHEMICAL ENERGY
 Energy & Life: Cellular Respiration PART I: HARVESTING CHEMICAL ENERGY Energy u Energy is not created or destroyed, it is transformed, changed. u E= ability to do work u Living things depend on energy
Energy & Life: Cellular Respiration PART I: HARVESTING CHEMICAL ENERGY Energy u Energy is not created or destroyed, it is transformed, changed. u E= ability to do work u Living things depend on energy
Chapter 4: Energy From the sun to you in two easy steps
 Chapter 4: Energy From the sun to you in two easy steps Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Understand and be able to explain the following: How energy flows from
Chapter 4: Energy From the sun to you in two easy steps Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Understand and be able to explain the following: How energy flows from
Forms of stored energy in cells
 Forms of stored energy in cells Electrochemical gradients Covalent bonds (ATP) Reducing power (NADH) During photosynthesis, respiration and glycolysis these forms of energy are converted from one to another
Forms of stored energy in cells Electrochemical gradients Covalent bonds (ATP) Reducing power (NADH) During photosynthesis, respiration and glycolysis these forms of energy are converted from one to another
of catabolic processes, like glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, as hydride ions (H ). This free energy is used to regenerate ATP in the matrix.
 Biochemistry I Oxidative Phosphorylation I. MITOCHONDRIA Mitochondria are cellular organelles which have two bilayer membranes, and two compartments defined by those membranes. Mitochondria are completely
Biochemistry I Oxidative Phosphorylation I. MITOCHONDRIA Mitochondria are cellular organelles which have two bilayer membranes, and two compartments defined by those membranes. Mitochondria are completely
Modeling. EC-Coupling and Contraction
 Bioeng 6460 Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity Modeling of EC-Coupling and Contraction Frank B. Sachse fs@cvrti.utah.edu Overview Recapitulation Group Work Excitation-Contraction Coupling Hill s Muscle
Bioeng 6460 Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity Modeling of EC-Coupling and Contraction Frank B. Sachse fs@cvrti.utah.edu Overview Recapitulation Group Work Excitation-Contraction Coupling Hill s Muscle
CP Biology Unit 5 Cell Energy Study Guide. Electron Carriers Electron Transport Chain Fermentation Glycolysis Krebs cycle Light-Dependent Reactions
 Name: KEY CP Biology Unit 5 Cell Energy Study Guide Vocabulary to know: ATP ADP Aerobic Anaerobic ATP Synthases Cellular Respiration Chlorophyll Chloroplast Electron Carriers Electron Transport Chain Fermentation
Name: KEY CP Biology Unit 5 Cell Energy Study Guide Vocabulary to know: ATP ADP Aerobic Anaerobic ATP Synthases Cellular Respiration Chlorophyll Chloroplast Electron Carriers Electron Transport Chain Fermentation
1. How is a partially charged battery like ADP?
 Name The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions. Complete the chart by writing a strategy to help you remember the meaning of each term. One has been done for you. Term Definition
Name The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions. Complete the chart by writing a strategy to help you remember the meaning of each term. One has been done for you. Term Definition
State state describe
 Warm-Up State the products of the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis, state which product has chemical energy, and describe how that product is made. KREBS ETC FADH 2 Glucose Pyruvate H 2 O NADH
Warm-Up State the products of the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis, state which product has chemical energy, and describe how that product is made. KREBS ETC FADH 2 Glucose Pyruvate H 2 O NADH
Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module : 15 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator Content Reviewer Content Writer Dr.S.K.Khare,Professor IIT Delhi. Dr. Ramesh Kothari,Professor UGC-CAS Department
Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module : 15 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator Content Reviewer Content Writer Dr.S.K.Khare,Professor IIT Delhi. Dr. Ramesh Kothari,Professor UGC-CAS Department
Giving you the energy you need!
 Giving you the energy you need! Use your dominant hand Open and close the pin (with your thumb and forefinger) as many times as you can for 20 seconds while holding the other fingers straight out! Repeat
Giving you the energy you need! Use your dominant hand Open and close the pin (with your thumb and forefinger) as many times as you can for 20 seconds while holding the other fingers straight out! Repeat
Energy Transformation. Metabolism = total chemical reactions in cells.
 Energy Transformation Metabolism = total chemical reactions in cells. metabole = change Metabolism is concerned with managing the material and energy resources of the cell -Catabolism -Anabolism -Catabolism
Energy Transformation Metabolism = total chemical reactions in cells. metabole = change Metabolism is concerned with managing the material and energy resources of the cell -Catabolism -Anabolism -Catabolism
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush
 number 8 Done by Ali Yaghi Corrected by Mamoon Mohamad Alqtamin Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush 0 P a g e Oxidative phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation has 3 major aspects: 1. It involves flow of electrons
number 8 Done by Ali Yaghi Corrected by Mamoon Mohamad Alqtamin Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush 0 P a g e Oxidative phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation has 3 major aspects: 1. It involves flow of electrons
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 7: Vital Harvest: Deriving Energy From Food
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 7: Vital Harvest: Deriving Energy From Food Deriving Energy from Food: What is the best carbohydrate source (for energy) in our food? Glucose! Where is the energy stored in glucose?
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 7: Vital Harvest: Deriving Energy From Food Deriving Energy from Food: What is the best carbohydrate source (for energy) in our food? Glucose! Where is the energy stored in glucose?
RESPIRATION AND FERMENTATION: AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC OXIDATION OF ORGANIC MOLECULES. Bio 107 Week 6
 RESPIRATION AND FERMENTATION: AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC OXIDATION OF ORGANIC MOLECULES Bio 107 Week 6 Procedure 7.2 Label test tubes well, including group name 1) Add solutions listed to small test tubes 2)
RESPIRATION AND FERMENTATION: AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC OXIDATION OF ORGANIC MOLECULES Bio 107 Week 6 Procedure 7.2 Label test tubes well, including group name 1) Add solutions listed to small test tubes 2)
Mitochondria Mitochondria were first seen by kollicker in 1850 in muscles and called them sarcosomes. Flemming (1882) described these organelles as
 Mitochondria Mitochondria were first seen by kollicker in 1850 in muscles and called them sarcosomes. Flemming (1882) described these organelles as filia Altmann (1890) observed these structures and named
Mitochondria Mitochondria were first seen by kollicker in 1850 in muscles and called them sarcosomes. Flemming (1882) described these organelles as filia Altmann (1890) observed these structures and named
A Dynamic Model of Excitation-Contraction Coupling during Acidosis in Cardiac Ventricular Myocytes
 3074 Biophysical Journal Volume 90 May 2006 3074 3090 A Dynamic Model of Excitation-Contraction Coupling during Acidosis in Cardiac Ventricular Myocytes Edmund J. Crampin and Nicolas P. Smith Bioengineering
3074 Biophysical Journal Volume 90 May 2006 3074 3090 A Dynamic Model of Excitation-Contraction Coupling during Acidosis in Cardiac Ventricular Myocytes Edmund J. Crampin and Nicolas P. Smith Bioengineering
REVIEW 3: METABOLISM UNIT RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Period Date REVIEW 3: METABOLISM UNIT RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Energy production through chemiosmosis a. pumping of H+
Period Date REVIEW 3: METABOLISM UNIT RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Energy production through chemiosmosis a. pumping of H+
Energy Converion: Mitochondria and Chloroplasts. Pınar Tulay, Ph.D.
 Energy Converion: Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Pınar Tulay, Ph.D. pintulay@gmail.com Energy Conversion Prokaryotes use plasma membrane to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) used in the cell function
Energy Converion: Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Pınar Tulay, Ph.D. pintulay@gmail.com Energy Conversion Prokaryotes use plasma membrane to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) used in the cell function
Membrane Physiology. Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Oct-18 1
 Membrane Physiology Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 22-10-2018 29-Oct-18 1 Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular fluids. 29-Oct-18 2 Transport through the cell membrane occurs by one of two basic processes:
Membrane Physiology Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 22-10-2018 29-Oct-18 1 Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular fluids. 29-Oct-18 2 Transport through the cell membrane occurs by one of two basic processes:
Biology A: Chapter 5 Annotating Notes
 Name: Pd: Biology A: Chapter 5 Annotating Notes -As you read your textbook, please fill out these notes. -Read each paragraph state the big/main idea on the left side. - On the right side you should take
Name: Pd: Biology A: Chapter 5 Annotating Notes -As you read your textbook, please fill out these notes. -Read each paragraph state the big/main idea on the left side. - On the right side you should take
Cell Respiration: Energy for Plant Metabolism
 Cell Respiration: Energy for Plant Metabolism Glucose is the originating molecule for respiration Production and consumption of ATP Coupled reactions: Endergonic reactions are coupled to exergonic ones
Cell Respiration: Energy for Plant Metabolism Glucose is the originating molecule for respiration Production and consumption of ATP Coupled reactions: Endergonic reactions are coupled to exergonic ones
What are mitochondria?
 What are mitochondria? What are mitochondria? An intracellular organelle. There are 100 to 1000s of mitochondria/cell. Most mitochondria come from the mother. Mitochondria have their own DNA Mitochondria
What are mitochondria? What are mitochondria? An intracellular organelle. There are 100 to 1000s of mitochondria/cell. Most mitochondria come from the mother. Mitochondria have their own DNA Mitochondria
Membrane Protein Pumps
 Membrane Protein Pumps Learning objectives You should be able to understand & discuss: Active transport-na + /K + ATPase ABC transporters Metabolite transport by lactose permease 1. Ion pumps: ATP-driven
Membrane Protein Pumps Learning objectives You should be able to understand & discuss: Active transport-na + /K + ATPase ABC transporters Metabolite transport by lactose permease 1. Ion pumps: ATP-driven
Illuminating Photosynthesis
 Name: Block: Date: Student #: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Internet Activity Illuminating Photosynthesis Go to lps.org and enter the jump code P4BR into the search box in the upper right corner.
Name: Block: Date: Student #: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Internet Activity Illuminating Photosynthesis Go to lps.org and enter the jump code P4BR into the search box in the upper right corner.
AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name
 AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the image below. 7. Base your answer to the following question on Which of the following choices correctly
AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the image below. 7. Base your answer to the following question on Which of the following choices correctly
Cellular Energy. The cell will store energy in molecules like sugars and ATP
 Cellular Energy Cellular Energy The cell will store energy in molecules like sugars and ATP Most cells have small stores of ATP that only last a few seconds, but cannot store energy there long-term. Cells
Cellular Energy Cellular Energy The cell will store energy in molecules like sugars and ATP Most cells have small stores of ATP that only last a few seconds, but cannot store energy there long-term. Cells
Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts)
 1 Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Describe the overall action of the Krebs cycle in generating ATP, NADH and FADH 2 from acetyl-coa 2: Understand the generation
1 Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Describe the overall action of the Krebs cycle in generating ATP, NADH and FADH 2 from acetyl-coa 2: Understand the generation
Modeling 3-D Calcium Waves from Stochastic Calcium sparks in a Sarcomere Using COMSOL
 Modeling 3-D Calcium Waves from Stochastic Calcium sparks in a Sarcomere Using COMSOL Zana Coulibaly 1, Leighton T. Izu 2 and Bradford E. Peercy 1 1 University of Maryland, Baltimore County 2 University
Modeling 3-D Calcium Waves from Stochastic Calcium sparks in a Sarcomere Using COMSOL Zana Coulibaly 1, Leighton T. Izu 2 and Bradford E. Peercy 1 1 University of Maryland, Baltimore County 2 University
Metabolism Review. A. Top 10
 A. Top 10 Metabolism Review 1. Energy production through chemiosmosis a. pumping of H+ ions onto one side of a membrane through protein pumps in an Electron Transport Chain (ETC) b. flow of H+ ions across
A. Top 10 Metabolism Review 1. Energy production through chemiosmosis a. pumping of H+ ions onto one side of a membrane through protein pumps in an Electron Transport Chain (ETC) b. flow of H+ ions across
AP Biology Big Idea 2 Unit Study Guide
 Name: Period: AP Biology Big Idea 2 Unit Study Guide This study guide highlights concepts and terms covered in the evolution unit. While this study guide is meant to be inclusive, any term or concept covered
Name: Period: AP Biology Big Idea 2 Unit Study Guide This study guide highlights concepts and terms covered in the evolution unit. While this study guide is meant to be inclusive, any term or concept covered
Cell Energetics. How plants make food and everyone makes energy!
 Cell Energetics How plants make food and everyone makes energy! Carbon Cycle Where did the mitochondria and chloroplast come from? Endosymbiotic Theory Endosymbiotic theory = a theory that some of the
Cell Energetics How plants make food and everyone makes energy! Carbon Cycle Where did the mitochondria and chloroplast come from? Endosymbiotic Theory Endosymbiotic theory = a theory that some of the
Computer Science Department Technical Report. University of California. Los Angeles, CA
 Computer Science Department Technical Report University of California Los Angeles, CA 995-1596 COMPUTER SIMULATION OF THE JAFRI-WINSLOW ACTION POTENTIAL MODEL Sergey Y. Chernyavskiy November 1998 Boris
Computer Science Department Technical Report University of California Los Angeles, CA 995-1596 COMPUTER SIMULATION OF THE JAFRI-WINSLOW ACTION POTENTIAL MODEL Sergey Y. Chernyavskiy November 1998 Boris
Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance
 Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance 1590 Jansen 1650 Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1665 Robert Hooke 1831 Matthias Schleiden 1831 Theodore Schwann 1855 Rudolf Virchow
Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance 1590 Jansen 1650 Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1665 Robert Hooke 1831 Matthias Schleiden 1831 Theodore Schwann 1855 Rudolf Virchow
Our patient for the day...
 Muscles Ch.12 Our patient for the day... Name: Eddy Age: Newborn Whole-body muscle contractions No relaxation Severe difficulty breathing due to inadequate relaxation of breathing muscles Diagnosed with
Muscles Ch.12 Our patient for the day... Name: Eddy Age: Newborn Whole-body muscle contractions No relaxation Severe difficulty breathing due to inadequate relaxation of breathing muscles Diagnosed with
Sequential forward and reverse transport of the Na + Ca 2+ exchanger generates Ca 2+ oscillations within mitochondria
 DOI: 1.138/s41467-17-2638-2 OPEN Sequential forward and reverse transport of the Na + Ca 2+ exchanger generates Ca 2+ oscillations within mitochondria Krishna Samanta 1, Gary R. Mirams 2 & Anant B. Parekh
DOI: 1.138/s41467-17-2638-2 OPEN Sequential forward and reverse transport of the Na + Ca 2+ exchanger generates Ca 2+ oscillations within mitochondria Krishna Samanta 1, Gary R. Mirams 2 & Anant B. Parekh
The Mitochondrion. Definition Structure, ultrastructure Functions
 The Mitochondrion Definition Structure, ultrastructure Functions Organelle definition Etymology of the name Carl Benda (1903): (mitos) thread; (khondrion) granule. Light microscopy identification First
The Mitochondrion Definition Structure, ultrastructure Functions Organelle definition Etymology of the name Carl Benda (1903): (mitos) thread; (khondrion) granule. Light microscopy identification First
Be sure to understand:
 Learning Targets & Focus Questions for Unit 6: Bioenergetics Chapter 8: Thermodynamics Chapter 9: Cell Resp Focus Q Ch. 10: Photosynthesis Chapter 8 (141-150) 1. I can explain how living systems adhere
Learning Targets & Focus Questions for Unit 6: Bioenergetics Chapter 8: Thermodynamics Chapter 9: Cell Resp Focus Q Ch. 10: Photosynthesis Chapter 8 (141-150) 1. I can explain how living systems adhere
AHL Topic 8 IB Biology Miss Werba
 CELL RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS AHL Topic 8 IB Biology Miss Werba TOPIC 8 CELL RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS 8.1 CELL RESPIRATION 1. STATE that oxidation involves the loss of electrons from an element,
CELL RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS AHL Topic 8 IB Biology Miss Werba TOPIC 8 CELL RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS 8.1 CELL RESPIRATION 1. STATE that oxidation involves the loss of electrons from an element,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Cell viability rate 0.8 0.6 0 0.05 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.7 1 Exposure duration (s) Supplementary Figure 1. Femtosecond laser could disrupt and turn off GFP without photons at 473 nm and keep cells alive.
Cell viability rate 0.8 0.6 0 0.05 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.7 1 Exposure duration (s) Supplementary Figure 1. Femtosecond laser could disrupt and turn off GFP without photons at 473 nm and keep cells alive.
Most cells are exquisitely responsive to calcium (Ca 2+ ) (1)
 Coupled Ca 2+ /H + transport by cytoplasmic buffers regulates local Ca 2+ and H + ion signaling Pawel Swietach a, Jae-Boum Youm a,b, Noriko Saegusa c, Chae-Hun Leem d, Kenneth W. Spitzer c, and Richard
Coupled Ca 2+ /H + transport by cytoplasmic buffers regulates local Ca 2+ and H + ion signaling Pawel Swietach a, Jae-Boum Youm a,b, Noriko Saegusa c, Chae-Hun Leem d, Kenneth W. Spitzer c, and Richard
Effect of enzyme deficiencies on oxidative phosphorylation: from isolated mitochondria to intact tissues. Theoretical studies.
 Effect of enzyme deficiencies on oxidative phosphorylation: from isolated mitochondria to intact tissues. Theoretical studies. Bernard Korzeniewski Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Jagiellonian
Effect of enzyme deficiencies on oxidative phosphorylation: from isolated mitochondria to intact tissues. Theoretical studies. Bernard Korzeniewski Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Jagiellonian
