(a) v 1. v a. v i. v s. (b)
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Stevens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Outlin RETIMING Struturl optimiztion mthods. Gionni D Mihli Stnford Unirsity Rtiming. { Modling. { Rtiming for minimum dly. { Rtiming for minimum r. Synhronous Logi Ntwork Synhronous Logi Ntwork Synhronous logi ntwork: { Vrils. { Booln qutions. i d s { Synhronous dly nnottion. () Synhronous ntwork grph: { Vrtis $ qutions $ I/O, gts. { Edgs $ dpndnis $ nts. i 2 () d s { Wights $ synh. dlys $ rgistrs.
2 (n) (n) (n) d (n) (n) (n) s (n) = i (n) i (n;) = i (n;) i (n;2) = (n) (n) = (n) + d (n;) = d (n) (n;) + d (n) (n) = (n) = (n;) Synhronous Logi Ciruit Modling Stt-sd modl: { Trnsition digrms or tls. { Expliit notion of stt. { Impliit notion of r nd dly. = i i@ = i@ i@2 = d = + d@ = + d = s Struturl modl: { Synhronous logi ntwork. { Impliit notion of stt. { Expliit notion of r nd dly. Approhs to synhronous logi optimiztion Optimiz omintionl logi only. Optimiz rgistr position only: { Rtiming. Optimiz orll iruit: { Priphrl rtiming. { Synhronous trnsformtions: Algri. Sprt rgistrs from omintionl logi Optimiz omintionl logi y trnsformtions: { Modify qutions. { Modify grph strutur. Connt rgistrs k into th ntwork: { Good huristi. { Limitd y th prtitioning strtgy. Booln.
3 Rtiming Mo rgistr position. Do not modify omintionl logi. d x d x Prsr ntwork strutur: { Modify wights. () x x () { Do not modify grph strutur. () (d) Assumptions Rtiming Vrtx dly is onstnt: Glol optimiztion thniqu [Lisrson]. { No fnout dly dpndny. Chngs rgistr positions: { ts r: hngs rgistr ount. { ts yl-tim: hngs pth dlys twn rgistr pirs. Grph topology is inrint: { No logi trnsformtions. Synhronous implmnttion: { Cyls h positi wights. { Edgs h non-ngti wights. Soll in polynomil tim. Considr topologil pths: { No fls pth nlysis.
4 Rtiming Rtiming of rtx: f { Intgr. { Rgistrs mod from output to input. Rtiming of ntwork: { Vtor of rtx rtiming. f A fmily of quilnt ntworks r spid y: { Th originl ntwork. { A rtiming tor. Dnitions: Dnitions nd proprtis { w( i j ) { wight of dg ( i j ). { ( i ::: j ) { pth from i to j. { d( i ::: j ){ pth dly from i to j. 2 u r= r = RETIMING of n EDGE PATH 2 u w(u,) = w(u,) = 2 til 2 hd Proprtis: { Rtiming of n dg ( i j ): w ij = w ij + r j ; r i. w(pth) = 2 CYCLE 2 { Rtiming of pth ( i ::: j ): til w(yl) = hd w( i ::: j ) = w( i ::: j ) + r j ; r i : { Cyl wights r inrint.
5 Lgl rtiming Rnd nlysis Clok priod. Lst rgistr pth: Rtiming tor suh tht: { No dg wight is ngti: w ij = w ij + r j ; r i 8i j. { Eh pth ( i ::: j ) with d( i ::: j ) > hs t lst on rgistr: w( i ::: j ) = w( i ::: j ) + r j ; r i 8i j. Ft: { Originl grph hs no yls with wight ) nw grph hs no yls with wight. { W ( i j ) = min w( i ::: j ). { Or ll pths twn i nd j. Critil dly: { D( i j ) = mx d( i ::: j ) { Or ll th pths from i to j with wight W ( i j ). Thr xists rtx pir i j whos D( i j ) ounds th yl-tim. Minimum yl-tim rtiming prolm f Find minimum lu of th lok priod suh tht thr xist rtiming tor whr: { r i ; r j w ij 8( i j ) 2 E { r i ; r j W ( i j ) ; 8 i j jd( i j ) >. Vrtis:. Pths: ( ) nd ( ). W ( ) = 2 nd D( ) = 6. Solution: { Gin lu of : sol linr onstrints. mthods: Bllmn-Ford or drit. MILP. Rlxtion.
6 Minimum yl-tim rtiming lgorithm Comput ll-pir W ( i j ) nd D( i j ). { Wrshll-Floyd lgorithm ( O(V ) ). f Sort th lmnts of D in drsing ordr. Binry srh for in D( i j ) suh tht: { Thr xist lgl rtiming. { Bllmn-Ford lgorithm ( O(V ) ). Rmrks: { Rsult is glol optimum. { Orll omplxity is O(V logv ). Constrints (rst typ): { r ; r or quilntly r r ; { r ; r or quilntly r r ; { = Sort lmnts of D: f { ( ). 2 Slt: = 9: { PASS. Slt: = : { PASS. Slt: < : { FAIL. Constrints (sond typ): { r ; r 2 ; or quilntly r r ; { r ; r f ; or quilntly r f r + { r f ; r g ; or quilntly r g r f + { r g ; r f 2 ; or quilntly r f r g ; { r g ; r ; or quilntly r r g ; 2
7 = f Rlxtion-sd lgorithm Rtionl Look for pths with xssi dly. f Mk thm shortr y pulling losr th trminl rgistr. Solutions: { ;[222] T (LP from ). { Som othr pths my om too long. { Thos pths whos til hs n mod. Us n itrti pproh. { ;[222] T (Equilnt solution). Rlxtion-sd lgorithm = Dn rtx dt rdy tim: { Totl dly from rgistr oundry. () f f (2) Itrti pproh: f f { Find rtis with dt rdy tim >. () (2) { Rtim ths rtis y. f f Proprtis: () (2) { Finds lgl rtiming in t most jv j itrtions, if on xists.
8 Dt-rdy tims: { t = t = t = t d = t = t f = t g = 24 t h = 24. Rtim: ft f t g t h g y. Dt-rdy tims: { t = t = t = t d = t = t f = t g = 4 t h = 4. Rtim: { ft t g t h g y. Dt-rdy tims: { t = t = t = t d = t = t f = t g = t h =, { TIMING FEASIBLE NETWORK! Minimum r rtiming prolm Find rtiming tor tht minimizs th numr of rgistrs. Simpl r modling: { Ery pos.-wightd dg! rgistr. { Totl rgistr r ost quls totl of wights. Rgistr shring modl: { Ery st of positily-wightd dgs with ommon til! shift-rgistr. { Rgistr r ost quls mximum of wights on outgoing dgs. Minimum r rtiming simpl modl () Rgistr rition t rtx : { r (indgr() ; outdgr()). () Totl r rition: { P r (indgr() ; outdgr()). () Ar minimiztion prolm: { min X 2V r (indgr() ; outdgr()). { s.t. r i ; r j w( i j ) for ry ( i j ).
9 min Minimum r rtiming undr yl tim onstrint { X r (indgr() ; outdgr()). s.t. 2V { r i ; r j w( i j ) for ry ( i j ). { r i ; r j W ( i j ) ; 8 i j jd( i j ) >. Minimum r rtiming lgorithm Linr progrm. Trnsform into mthing prolm: { Edmonds-Krp lgorithm. { Polynomil tim. Rmrk: { Rgistr shring modl n trnsformd into th simpl modl. { Sm solution lgorithms. Summry of rtiming Squntil optimiztion thniqu for: { Cyl tim or rgistr r. Applil to: { Synhronous logi modls. { Arhitturl dt-pth modls: Rsours with dlys. Ext lgorithm in polynomil tim. Prolms: { Dly modling. { Ntwork grnulrity.
a b v a v b v c v = a d + bd +c d +ae r = p + a 0 s = r + b 0 4 ac + ad + bc + bd + e 5 = a + b = q 0 c + qc 0 + qc (a) s v (b)
 Outlin MULTIPLE-LEVEL LOGIC OPTIMIZATION Gionni D Mihli Stnfor Unirsit Rprsnttions. Tonom of optimition mthos: { Gols: r/l. { Algorithms: lgri/booln. { Rul-s mthos. Empls of trnsformtions. Booln n lgri
Outlin MULTIPLE-LEVEL LOGIC OPTIMIZATION Gionni D Mihli Stnfor Unirsit Rprsnttions. Tonom of optimition mthos: { Gols: r/l. { Algorithms: lgri/booln. { Rul-s mthos. Empls of trnsformtions. Booln n lgri
COMP108 Algorithmic Foundations
 Grdy mthods Prudn Wong http://www.s.liv..uk/~pwong/thing/omp108/01617 Coin Chng Prolm Suppos w hv 3 typs of oins 10p 0p 50p Minimum numr of oins to mk 0.8, 1.0, 1.? Grdy mthod Lrning outoms Undrstnd wht
Grdy mthods Prudn Wong http://www.s.liv..uk/~pwong/thing/omp108/01617 Coin Chng Prolm Suppos w hv 3 typs of oins 10p 0p 50p Minimum numr of oins to mk 0.8, 1.0, 1.? Grdy mthod Lrning outoms Undrstnd wht
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Example: Change-Making Problem
 CSC 801- Dsign n Anlysis of Algorithms Ltur 11 Gry Thniqu Exmpl: Chng-Mking Prolm Givn unlimit mounts of oins of nomintions 1 > > m, giv hng for mount n with th lst numr of oins Exmpl: 1 = 25, 2 =10, =
CSC 801- Dsign n Anlysis of Algorithms Ltur 11 Gry Thniqu Exmpl: Chng-Mking Prolm Givn unlimit mounts of oins of nomintions 1 > > m, giv hng for mount n with th lst numr of oins Exmpl: 1 = 25, 2 =10, =
Paths. Connectivity. Euler and Hamilton Paths. Planar graphs.
 Pths.. Eulr n Hmilton Pths.. Pth D. A pth rom s to t is squn o gs {x 0, x 1 }, {x 1, x 2 },... {x n 1, x n }, whr x 0 = s, n x n = t. D. Th lngth o pth is th numr o gs in it. {, } {, } {, } {, } {, } {,
Pths.. Eulr n Hmilton Pths.. Pth D. A pth rom s to t is squn o gs {x 0, x 1 }, {x 1, x 2 },... {x n 1, x n }, whr x 0 = s, n x n = t. D. Th lngth o pth is th numr o gs in it. {, } {, } {, } {, } {, } {,
b. How many ternary words of length 23 with eight 0 s, nine 1 s and six 2 s?
 MATH 3012 Finl Exm, My 4, 2006, WTT Stunt Nm n ID Numr 1. All our prts o this prolm r onrn with trnry strings o lngth n, i.., wors o lngth n with lttrs rom th lpht {0, 1, 2}.. How mny trnry wors o lngth
MATH 3012 Finl Exm, My 4, 2006, WTT Stunt Nm n ID Numr 1. All our prts o this prolm r onrn with trnry strings o lngth n, i.., wors o lngth n with lttrs rom th lpht {0, 1, 2}.. How mny trnry wors o lngth
12. Traffic engineering
 lt2.ppt S-38. Introution to Tltrffi Thory Spring 200 2 Topology Pths A tlommunition ntwork onsists of nos n links Lt N not th st of nos in with n Lt J not th st of nos in with j N = {,,,,} J = {,2,3,,2}
lt2.ppt S-38. Introution to Tltrffi Thory Spring 200 2 Topology Pths A tlommunition ntwork onsists of nos n links Lt N not th st of nos in with n Lt J not th st of nos in with j N = {,,,,} J = {,2,3,,2}
12/3/12. Outline. Part 10. Graphs. Circuits. Euler paths/circuits. Euler s bridge problem (Bridges of Konigsberg Problem)
 12/3/12 Outlin Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Algorithms n Dt Struturs Introution Trminology Implmnting Grphs Grph Trvrsls Topologil Sorting Shortst Pths Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Ciruits 1 Ciruits Cyl 2 Eulr
12/3/12 Outlin Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Algorithms n Dt Struturs Introution Trminology Implmnting Grphs Grph Trvrsls Topologil Sorting Shortst Pths Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Ciruits 1 Ciruits Cyl 2 Eulr
Outline. Circuits. Euler paths/circuits 4/25/12. Part 10. Graphs. Euler s bridge problem (Bridges of Konigsberg Problem)
 4/25/12 Outlin Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Algorithms n Dt Struturs Introution Trminology Implmnting Grphs Grph Trvrsls Topologil Sorting Shortst Pths Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Ciruits 1 2 Eulr s rig prolm
4/25/12 Outlin Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Algorithms n Dt Struturs Introution Trminology Implmnting Grphs Grph Trvrsls Topologil Sorting Shortst Pths Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Ciruits 1 2 Eulr s rig prolm
5/9/13. Part 10. Graphs. Outline. Circuits. Introduction Terminology Implementing Graphs
 Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Algorithms n Dt Struturs 1 Introution Trminology Implmnting Grphs Outlin Grph Trvrsls Topologil Sorting Shortst Pths Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Ciruits 2 Ciruits Cyl A spil yl
Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Algorithms n Dt Struturs 1 Introution Trminology Implmnting Grphs Outlin Grph Trvrsls Topologil Sorting Shortst Pths Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Ciruits 2 Ciruits Cyl A spil yl
Algorithmic and NP-Completeness Aspects of a Total Lict Domination Number of a Graph
 Intrntionl J.Mth. Comin. Vol.1(2014), 80-86 Algorithmi n NP-Compltnss Aspts of Totl Lit Domintion Numr of Grph Girish.V.R. (PES Institut of Thnology(South Cmpus), Bnglor, Krntk Stt, Ini) P.Ush (Dprtmnt
Intrntionl J.Mth. Comin. Vol.1(2014), 80-86 Algorithmi n NP-Compltnss Aspts of Totl Lit Domintion Numr of Grph Girish.V.R. (PES Institut of Thnology(South Cmpus), Bnglor, Krntk Stt, Ini) P.Ush (Dprtmnt
Math 61 : Discrete Structures Final Exam Instructor: Ciprian Manolescu. You have 180 minutes.
 Nm: UCA ID Numr: Stion lttr: th 61 : Disrt Struturs Finl Exm Instrutor: Ciprin nolsu You hv 180 minuts. No ooks, nots or lultors r llow. Do not us your own srth ppr. 1. (2 points h) Tru/Fls: Cirl th right
Nm: UCA ID Numr: Stion lttr: th 61 : Disrt Struturs Finl Exm Instrutor: Ciprin nolsu You hv 180 minuts. No ooks, nots or lultors r llow. Do not us your own srth ppr. 1. (2 points h) Tru/Fls: Cirl th right
V={A,B,C,D,E} E={ (A,D),(A,E),(B,D), (B,E),(C,D),(C,E)}
 Introution Computr Sin & Enginring 423/823 Dsign n Anlysis of Algorithms Ltur 03 Elmntry Grph Algorithms (Chptr 22) Stphn Sott (Apt from Vinohnrn N. Vriym) I Grphs r strt t typs tht r pplil to numrous
Introution Computr Sin & Enginring 423/823 Dsign n Anlysis of Algorithms Ltur 03 Elmntry Grph Algorithms (Chptr 22) Stphn Sott (Apt from Vinohnrn N. Vriym) I Grphs r strt t typs tht r pplil to numrous
CSE 373: More on graphs; DFS and BFS. Michael Lee Wednesday, Feb 14, 2018
 CSE 373: Mor on grphs; DFS n BFS Mihl L Wnsy, F 14, 2018 1 Wrmup Wrmup: Disuss with your nighor: Rmin your nighor: wht is simpl grph? Suppos w hv simpl, irt grph with x nos. Wht is th mximum numr of gs
CSE 373: Mor on grphs; DFS n BFS Mihl L Wnsy, F 14, 2018 1 Wrmup Wrmup: Disuss with your nighor: Rmin your nighor: wht is simpl grph? Suppos w hv simpl, irt grph with x nos. Wht is th mximum numr of gs
Outline. 1 Introduction. 2 Min-Cost Spanning Trees. 4 Example
 Outlin Computr Sin 33 Computtion o Minimum-Cost Spnnin Trs Prim's Alorithm Introution Mik Joson Dprtmnt o Computr Sin Univrsity o Clry Ltur #33 3 Alorithm Gnrl Constrution Mik Joson (Univrsity o Clry)
Outlin Computr Sin 33 Computtion o Minimum-Cost Spnnin Trs Prim's Alorithm Introution Mik Joson Dprtmnt o Computr Sin Univrsity o Clry Ltur #33 3 Alorithm Gnrl Constrution Mik Joson (Univrsity o Clry)
ECE 407 Computer Aided Design for Electronic Systems. Circuit Modeling and Basic Graph Concepts/Algorithms. Instructor: Maria K. Michael.
 0 Computr i Dsign or Eltroni Systms Ciruit Moling n si Grph Conptslgorithms Instrutor: Mri K. Mihl MKM - Ovrviw hviorl vs. Struturl mols Extrnl vs. Intrnl rprsnttions Funtionl moling t Logi lvl Struturl
0 Computr i Dsign or Eltroni Systms Ciruit Moling n si Grph Conptslgorithms Instrutor: Mri K. Mihl MKM - Ovrviw hviorl vs. Struturl mols Extrnl vs. Intrnl rprsnttions Funtionl moling t Logi lvl Struturl
Graph Isomorphism. Graphs - II. Cayley s Formula. Planar Graphs. Outline. Is K 5 planar? The number of labeled trees on n nodes is n n-2
 Grt Thortil Is In Computr Sin Vitor Amhik CS 15-251 Ltur 9 Grphs - II Crngi Mllon Univrsity Grph Isomorphism finition. Two simpl grphs G n H r isomorphi G H if thr is vrtx ijtion V H ->V G tht prsrvs jny
Grt Thortil Is In Computr Sin Vitor Amhik CS 15-251 Ltur 9 Grphs - II Crngi Mllon Univrsity Grph Isomorphism finition. Two simpl grphs G n H r isomorphi G H if thr is vrtx ijtion V H ->V G tht prsrvs jny
Module graph.py. 1 Introduction. 2 Graph basics. 3 Module graph.py. 3.1 Objects. CS 231 Naomi Nishimura
 Moul grph.py CS 231 Nomi Nishimur 1 Introution Just lik th Python list n th Python itionry provi wys of storing, ssing, n moifying t, grph n viw s wy of storing, ssing, n moifying t. Bus Python os not
Moul grph.py CS 231 Nomi Nishimur 1 Introution Just lik th Python list n th Python itionry provi wys of storing, ssing, n moifying t, grph n viw s wy of storing, ssing, n moifying t. Bus Python os not
V={A,B,C,D,E} E={ (A,D),(A,E),(B,D), (B,E),(C,D),(C,E)}
 s s of s Computr Sin & Enginring 423/823 Dsign n Anlysis of Ltur 03 (Chptr 22) Stphn Sott (Apt from Vinohnrn N. Vriym) s of s s r strt t typs tht r pplil to numrous prolms Cn ptur ntitis, rltionships twn
s s of s Computr Sin & Enginring 423/823 Dsign n Anlysis of Ltur 03 (Chptr 22) Stphn Sott (Apt from Vinohnrn N. Vriym) s of s s r strt t typs tht r pplil to numrous prolms Cn ptur ntitis, rltionships twn
Graphs. CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University. Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari
 Grphs CSC 1300 Disrt Struturs Villnov Univrsity Grphs Grphs r isrt struturs onsis?ng of vr?s n gs tht onnt ths vr?s. Grphs n us to mol: omputr systms/ntworks mthm?l rl?ons logi iruit lyout jos/prosss f
Grphs CSC 1300 Disrt Struturs Villnov Univrsity Grphs Grphs r isrt struturs onsis?ng of vr?s n gs tht onnt ths vr?s. Grphs n us to mol: omputr systms/ntworks mthm?l rl?ons logi iruit lyout jos/prosss f
Graphs. Graphs. Graphs: Basic Terminology. Directed Graphs. Dr Papalaskari 1
 CSC 00 Disrt Struturs : Introuon to Grph Thory Grphs Grphs CSC 00 Disrt Struturs Villnov Univrsity Grphs r isrt struturs onsisng o vrs n gs tht onnt ths vrs. Grphs n us to mol: omputr systms/ntworks mthml
CSC 00 Disrt Struturs : Introuon to Grph Thory Grphs Grphs CSC 00 Disrt Struturs Villnov Univrsity Grphs r isrt struturs onsisng o vrs n gs tht onnt ths vrs. Grphs n us to mol: omputr systms/ntworks mthml
CS200: Graphs. Graphs. Directed Graphs. Graphs/Networks Around Us. What can this represent? Sometimes we want to represent directionality:
 CS2: Grphs Prihr Ch. 4 Rosn Ch. Grphs A olltion of nos n gs Wht n this rprsnt? n A omputr ntwork n Astrtion of mp n Soil ntwork CS2 - Hsh Tls 2 Dirt Grphs Grphs/Ntworks Aroun Us A olltion of nos n irt
CS2: Grphs Prihr Ch. 4 Rosn Ch. Grphs A olltion of nos n gs Wht n this rprsnt? n A omputr ntwork n Astrtion of mp n Soil ntwork CS2 - Hsh Tls 2 Dirt Grphs Grphs/Ntworks Aroun Us A olltion of nos n irt
Weighted graphs -- reminder. Data Structures LECTURE 15. Shortest paths algorithms. Example: weighted graph. Two basic properties of shortest paths
 Dt Strutur LECTURE Shortt pth lgorithm Proprti of hortt pth Bllmn-For lgorithm Dijktr lgorithm Chptr in th txtook (pp ). Wight grph -- rminr A wight grph i grph in whih g hv wight (ot) w(v i, v j ) >.
Dt Strutur LECTURE Shortt pth lgorithm Proprti of hortt pth Bllmn-For lgorithm Dijktr lgorithm Chptr in th txtook (pp ). Wight grph -- rminr A wight grph i grph in whih g hv wight (ot) w(v i, v j ) >.
Announcements. Not graphs. These are Graphs. Applications of Graphs. Graph Definitions. Graphs & Graph Algorithms. A6 released today: Risk
 Grphs & Grph Algorithms Ltur CS Spring 6 Announmnts A6 rls toy: Risk Strt signing with your prtnr sp Prlim usy Not grphs hs r Grphs K 5 K, =...not th kin w mn, nywy Applitions o Grphs Communition ntworks
Grphs & Grph Algorithms Ltur CS Spring 6 Announmnts A6 rls toy: Risk Strt signing with your prtnr sp Prlim usy Not grphs hs r Grphs K 5 K, =...not th kin w mn, nywy Applitions o Grphs Communition ntworks
CS61B Lecture #33. Administrivia: Autograder will run this evening. Today s Readings: Graph Structures: DSIJ, Chapter 12
 Aministrivi: CS61B Ltur #33 Autogrr will run this vning. Toy s Rings: Grph Struturs: DSIJ, Chptr 12 Lst moifi: W Nov 8 00:39:28 2017 CS61B: Ltur #33 1 Why Grphs? For xprssing non-hirrhilly rlt itms Exmpls:
Aministrivi: CS61B Ltur #33 Autogrr will run this vning. Toy s Rings: Grph Struturs: DSIJ, Chptr 12 Lst moifi: W Nov 8 00:39:28 2017 CS61B: Ltur #33 1 Why Grphs? For xprssing non-hirrhilly rlt itms Exmpls:
Similarity Search. The Binary Branch Distance. Nikolaus Augsten.
 Similrity Srh Th Binry Brnh Distn Nikolus Augstn nikolus.ugstn@sg..t Dpt. of Computr Sins Univrsity of Slzurg http://rsrh.uni-slzurg.t Vrsion Jnury 11, 2017 Wintrsmstr 2016/2017 Augstn (Univ. Slzurg) Similrity
Similrity Srh Th Binry Brnh Distn Nikolus Augstn nikolus.ugstn@sg..t Dpt. of Computr Sins Univrsity of Slzurg http://rsrh.uni-slzurg.t Vrsion Jnury 11, 2017 Wintrsmstr 2016/2017 Augstn (Univ. Slzurg) Similrity
0.1. Exercise 1: the distances between four points in a graph
 Mth 707 Spring 2017 (Drij Grinrg): mitrm 3 pg 1 Mth 707 Spring 2017 (Drij Grinrg): mitrm 3 u: W, 3 My 2017, in lss or y mil (grinr@umn.u) or lss S th wsit or rlvnt mtril. Rsults provn in th nots, or in
Mth 707 Spring 2017 (Drij Grinrg): mitrm 3 pg 1 Mth 707 Spring 2017 (Drij Grinrg): mitrm 3 u: W, 3 My 2017, in lss or y mil (grinr@umn.u) or lss S th wsit or rlvnt mtril. Rsults provn in th nots, or in
An undirected graph G = (V, E) V a set of vertices E a set of unordered edges (v,w) where v, w in V
 Unirt Grphs An unirt grph G = (V, E) V st o vrtis E st o unorr gs (v,w) whr v, w in V USE: to mol symmtri rltionships twn ntitis vrtis v n w r jnt i thr is n g (v,w) [or (w,v)] th g (v,w) is inint upon
Unirt Grphs An unirt grph G = (V, E) V st o vrtis E st o unorr gs (v,w) whr v, w in V USE: to mol symmtri rltionships twn ntitis vrtis v n w r jnt i thr is n g (v,w) [or (w,v)] th g (v,w) is inint upon
Planar Upward Drawings
 C.S. 252 Pro. Rorto Tmssi Computtionl Gomtry Sm. II, 1992 1993 Dt: My 3, 1993 Sri: Shmsi Moussvi Plnr Upwr Drwings 1 Thorm: G is yli i n only i it hs upwr rwing. Proo: 1. An upwr rwing is yli. Follow th
C.S. 252 Pro. Rorto Tmssi Computtionl Gomtry Sm. II, 1992 1993 Dt: My 3, 1993 Sri: Shmsi Moussvi Plnr Upwr Drwings 1 Thorm: G is yli i n only i it hs upwr rwing. Proo: 1. An upwr rwing is yli. Follow th
CSE 373. Graphs 1: Concepts, Depth/Breadth-First Search reading: Weiss Ch. 9. slides created by Marty Stepp
 CSE 373 Grphs 1: Conpts, Dpth/Brth-First Srh ring: Wiss Ch. 9 slis rt y Mrty Stpp http://www.s.wshington.u/373/ Univrsity o Wshington, ll rights rsrv. 1 Wht is grph? 56 Tokyo Sttl Soul 128 16 30 181 140
CSE 373 Grphs 1: Conpts, Dpth/Brth-First Srh ring: Wiss Ch. 9 slis rt y Mrty Stpp http://www.s.wshington.u/373/ Univrsity o Wshington, ll rights rsrv. 1 Wht is grph? 56 Tokyo Sttl Soul 128 16 30 181 140
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Problm A town hs st of houss nd st of rods A rod conncts nd only houss A rod conncting houss u nd v hs rpir cost w(u, v) Gol: Rpir nough (nd no mor) rods such tht:
Minimum Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Problm A town hs st of houss nd st of rods A rod conncts nd only houss A rod conncting houss u nd v hs rpir cost w(u, v) Gol: Rpir nough (nd no mor) rods such tht:
Cycles and Simple Cycles. Paths and Simple Paths. Trees. Problem: There is No Completely Standard Terminology!
 Outlin Computr Sin 331, Spnnin, n Surphs Mik Joson Dprtmnt o Computr Sin Univrsity o Clry Ltur #30 1 Introution 2 3 Dinition 4 Spnnin 5 6 Mik Joson (Univrsity o Clry) Computr Sin 331 Ltur #30 1 / 20 Mik
Outlin Computr Sin 331, Spnnin, n Surphs Mik Joson Dprtmnt o Computr Sin Univrsity o Clry Ltur #30 1 Introution 2 3 Dinition 4 Spnnin 5 6 Mik Joson (Univrsity o Clry) Computr Sin 331 Ltur #30 1 / 20 Mik
Exam 1 Solution. CS 542 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms 2/14/2013
 CS Avn Dt Struturs n Algorithms Exm Solution Jon Turnr //. ( points) Suppos you r givn grph G=(V,E) with g wights w() n minimum spnning tr T o G. Now, suppos nw g {u,v} is to G. Dsri (in wors) mtho or
CS Avn Dt Struturs n Algorithms Exm Solution Jon Turnr //. ( points) Suppos you r givn grph G=(V,E) with g wights w() n minimum spnning tr T o G. Now, suppos nw g {u,v} is to G. Dsri (in wors) mtho or
Constructive Geometric Constraint Solving
 Construtiv Gomtri Constrint Solving Antoni Soto i Rir Dprtmnt Llngutgs i Sistms Inormàtis Univrsitt Politèni Ctluny Brlon, Sptmr 2002 CGCS p.1/37 Prliminris CGCS p.2/37 Gomtri onstrint prolm C 2 D L BC
Construtiv Gomtri Constrint Solving Antoni Soto i Rir Dprtmnt Llngutgs i Sistms Inormàtis Univrsitt Politèni Ctluny Brlon, Sptmr 2002 CGCS p.1/37 Prliminris CGCS p.2/37 Gomtri onstrint prolm C 2 D L BC
CS 241 Analysis of Algorithms
 CS 241 Anlysis o Algorithms Prossor Eri Aron Ltur T Th 9:00m Ltur Mting Lotion: OLB 205 Businss HW6 u lry HW7 out tr Thnksgiving Ring: Ch. 22.1-22.3 1 Grphs (S S. B.4) Grphs ommonly rprsnt onntions mong
CS 241 Anlysis o Algorithms Prossor Eri Aron Ltur T Th 9:00m Ltur Mting Lotion: OLB 205 Businss HW6 u lry HW7 out tr Thnksgiving Ring: Ch. 22.1-22.3 1 Grphs (S S. B.4) Grphs ommonly rprsnt onntions mong
A Simple Code Generator. Code generation Algorithm. Register and Address Descriptors. Example 3/31/2008. Code Generation
 A Simpl Co Gnrtor Co Gnrtion Chptr 8 II Gnrt o for singl si lok How to us rgistrs? In most mhin rhitturs, som or ll of th oprnsmust in rgistrs Rgistrs mk goo tmporris Hol vlus tht r omput in on si lok
A Simpl Co Gnrtor Co Gnrtion Chptr 8 II Gnrt o for singl si lok How to us rgistrs? In most mhin rhitturs, som or ll of th oprnsmust in rgistrs Rgistrs mk goo tmporris Hol vlus tht r omput in on si lok
CSE303 - Introduction to the Theory of Computing Sample Solutions for Exercises on Finite Automata
 CSE303 - Introduction to th Thory of Computing Smpl Solutions for Exrciss on Finit Automt Exrcis 2.1.1 A dtrministic finit utomton M ccpts th mpty string (i.., L(M)) if nd only if its initil stt is finl
CSE303 - Introduction to th Thory of Computing Smpl Solutions for Exrciss on Finit Automt Exrcis 2.1.1 A dtrministic finit utomton M ccpts th mpty string (i.., L(M)) if nd only if its initil stt is finl
, each of which is a tree, and whose roots r 1. , respectively, are children of r. Data Structures & File Management
 nrl tr T is init st o on or mor nos suh tht thr is on sint no r, ll th root o T, n th rminin nos r prtition into n isjoint susts T, T,, T n, h o whih is tr, n whos roots r, r,, r n, rsptivly, r hilrn o
nrl tr T is init st o on or mor nos suh tht thr is on sint no r, ll th root o T, n th rminin nos r prtition into n isjoint susts T, T,, T n, h o whih is tr, n whos roots r, r,, r n, rsptivly, r hilrn o
temporally share the same FPGA Large circuit PI s micro-cycle one user cycle PO s
 Ciruit Prtitioning for Dynmilly Rongurl FPGAs Huiqun Liu n D. F. Wong Dprtmnt of Computr Sins Unirsity of Txs t Austin Austin, T 787 Emil: fhqliu, wongg@s.utxs.u Astrt Dynmilly rongurl FPGAs h th potntil
Ciruit Prtitioning for Dynmilly Rongurl FPGAs Huiqun Liu n D. F. Wong Dprtmnt of Computr Sins Unirsity of Txs t Austin Austin, T 787 Emil: fhqliu, wongg@s.utxs.u Astrt Dynmilly rongurl FPGAs h th potntil
Register Allocation and Binding for Low Power. Jui-Ming Chang and Massoud Pedram. function of signal statistics and correlations, and hence is
 Rgistr Allotion n ining or Low Powr Jui-Ming hng n Mssou Prm Dprtmnt o Eltril Enginring-Systms Univrsity o Southrn liorni Los Angls, A 989 Astrt This ppr sris thniqu or lulting th swithing tivity o st
Rgistr Allotion n ining or Low Powr Jui-Ming hng n Mssou Prm Dprtmnt o Eltril Enginring-Systms Univrsity o Southrn liorni Los Angls, A 989 Astrt This ppr sris thniqu or lulting th swithing tivity o st
Fundamental Algorithms for System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization
 Fundmntl Algorithms for Sstm Modling, Anlsis, nd Optimiztion Edwrd A. L, Jijt Rohowdhur, Snjit A. Sshi UC Brkl EECS 144/244 Fll 2011 Copright 2010-11, E. A. L, J. Rohowdhur, S. A. Sshi, All rights rsrvd
Fundmntl Algorithms for Sstm Modling, Anlsis, nd Optimiztion Edwrd A. L, Jijt Rohowdhur, Snjit A. Sshi UC Brkl EECS 144/244 Fll 2011 Copright 2010-11, E. A. L, J. Rohowdhur, S. A. Sshi, All rights rsrvd
Register Allocation. How to assign variables to finitely many registers? What to do when it can t be done? How to do so efficiently?
 Rgistr Allotion Rgistr Allotion How to ssign vrils to initly mny rgistrs? Wht to o whn it n t on? How to o so iintly? Mony, Jun 3, 13 Mmory Wll Disprity twn CPU sp n mmory ss sp improvmnt Mony, Jun 3,
Rgistr Allotion Rgistr Allotion How to ssign vrils to initly mny rgistrs? Wht to o whn it n t on? How to o so iintly? Mony, Jun 3, 13 Mmory Wll Disprity twn CPU sp n mmory ss sp improvmnt Mony, Jun 3,
ECE COMBINATIONAL BUILDING BLOCKS - INVEST 13 DECODERS AND ENCODERS
 C 24 - COMBINATIONAL BUILDING BLOCKS - INVST 3 DCODS AND NCODS FALL 23 AP FLZ To o "wll" on this invstition you must not only t th riht nswrs ut must lso o nt, omplt n onis writups tht mk ovious wht h
C 24 - COMBINATIONAL BUILDING BLOCKS - INVST 3 DCODS AND NCODS FALL 23 AP FLZ To o "wll" on this invstition you must not only t th riht nswrs ut must lso o nt, omplt n onis writups tht mk ovious wht h
Chapter 16. 1) is a particular point on the graph of the function. 1. y, where x y 1
 Prctic qustions W now tht th prmtr p is dirctl rltd to th mplitud; thrfor, w cn find tht p. cos d [ sin ] sin sin Not: Evn though ou might not now how to find th prmtr in prt, it is lws dvisl to procd
Prctic qustions W now tht th prmtr p is dirctl rltd to th mplitud; thrfor, w cn find tht p. cos d [ sin ] sin sin Not: Evn though ou might not now how to find th prmtr in prt, it is lws dvisl to procd
Why the Junction Tree Algorithm? The Junction Tree Algorithm. Clique Potential Representation. Overview. Chris Williams 1.
 Why th Juntion Tr lgorithm? Th Juntion Tr lgorithm hris Willims 1 Shool of Informtis, Univrsity of Einurgh Otor 2009 Th JT is gnrl-purpos lgorithm for omputing (onitionl) mrginls on grphs. It os this y
Why th Juntion Tr lgorithm? Th Juntion Tr lgorithm hris Willims 1 Shool of Informtis, Univrsity of Einurgh Otor 2009 Th JT is gnrl-purpos lgorithm for omputing (onitionl) mrginls on grphs. It os this y
MULTIPLE-LEVEL LOGIC OPTIMIZATION II
 MUTIPE-EVE OGIC OPTIMIZATION II Booln mthos Eploit Booln proprtis Giovnni D Mihli Don t r onitions Stnfor Univrsit Minimition of th lol funtions Slowr lgorithms, ttr qulit rsults Etrnl on t r onitions
MUTIPE-EVE OGIC OPTIMIZATION II Booln mthos Eploit Booln proprtis Giovnni D Mihli Don t r onitions Stnfor Univrsit Minimition of th lol funtions Slowr lgorithms, ttr qulit rsults Etrnl on t r onitions
Problem solving by search
 Prolm solving y srh Tomáš voo Dprtmnt o Cyrntis, Vision or Roots n Autonomous ystms Mrh 5, 208 / 3 Outlin rh prolm. tt sp grphs. rh trs. trtgis, whih tr rnhs to hoos? trtgy/algorithm proprtis? Progrmming
Prolm solving y srh Tomáš voo Dprtmnt o Cyrntis, Vision or Roots n Autonomous ystms Mrh 5, 208 / 3 Outlin rh prolm. tt sp grphs. rh trs. trtgis, whih tr rnhs to hoos? trtgy/algorithm proprtis? Progrmming
Clustering for Processing Rate Optimization
 Clustring for Prossing Rt Optimiztion Chun Lin, Ji Wng, n Hi Zhou Eltril n Computr Enginring Northwstrn Univrsity Evnston, IL 60208 Astrt Clustring (or prtitioning) is ruil stp twn logi synthsis n physil
Clustring for Prossing Rt Optimiztion Chun Lin, Ji Wng, n Hi Zhou Eltril n Computr Enginring Northwstrn Univrsity Evnston, IL 60208 Astrt Clustring (or prtitioning) is ruil stp twn logi synthsis n physil
Formal Concept Analysis
 Forml Conpt Anlysis Conpt intnts s losd sts Closur Systms nd Implitions 4 Closur Systms 0.06.005 Nxt-Closur ws dvlopd y B. Gntr (984). Lt M = {,..., n}. A M is ltilly smllr thn B M, if B A if th smllst
Forml Conpt Anlysis Conpt intnts s losd sts Closur Systms nd Implitions 4 Closur Systms 0.06.005 Nxt-Closur ws dvlopd y B. Gntr (984). Lt M = {,..., n}. A M is ltilly smllr thn B M, if B A if th smllst
Announcements. These are Graphs. This is not a Graph. Graph Definitions. Applications of Graphs. Graphs & Graph Algorithms
 Grphs & Grph Algorithms Ltur CS Fll 5 Announmnts Upoming tlk h Mny Crrs o Computr Sintist Or how Computr Sin gr mpowrs you to o muh mor thn o Dn Huttnlohr, Prossor in th Dprtmnt o Computr Sin n Johnson
Grphs & Grph Algorithms Ltur CS Fll 5 Announmnts Upoming tlk h Mny Crrs o Computr Sintist Or how Computr Sin gr mpowrs you to o muh mor thn o Dn Huttnlohr, Prossor in th Dprtmnt o Computr Sin n Johnson
Garnir Polynomial and their Properties
 Univrsity of Cliforni, Dvis Dprtmnt of Mthmtis Grnir Polynomil n thir Proprtis Author: Yu Wng Suprvisor: Prof. Gorsky Eugny My 8, 07 Grnir Polynomil n thir Proprtis Yu Wng mil: uywng@uvis.u. In this ppr,
Univrsity of Cliforni, Dvis Dprtmnt of Mthmtis Grnir Polynomil n thir Proprtis Author: Yu Wng Suprvisor: Prof. Gorsky Eugny My 8, 07 Grnir Polynomil n thir Proprtis Yu Wng mil: uywng@uvis.u. In this ppr,
CIVL 8/ D Boundary Value Problems - Rectangular Elements 1/7
 CIVL / -D Boundr Vlu Prolms - Rctngulr Elmnts / RECANGULAR ELEMENS - In som pplictions, it m mor dsirl to us n lmntl rprsnttion of th domin tht hs four sids, ithr rctngulr or qudriltrl in shp. Considr
CIVL / -D Boundr Vlu Prolms - Rctngulr Elmnts / RECANGULAR ELEMENS - In som pplictions, it m mor dsirl to us n lmntl rprsnttion of th domin tht hs four sids, ithr rctngulr or qudriltrl in shp. Considr
Implication Graphs and Logic Testing
 Implition Grphs n Logi Testing Vishwni D. Agrwl Jmes J. Dnher Professor Dept. of ECE, Auurn University Auurn, AL 36849 vgrwl@eng.uurn.eu www.eng.uurn.eu/~vgrwl Joint reserh with: K. K. Dve, ATI Reserh,
Implition Grphs n Logi Testing Vishwni D. Agrwl Jmes J. Dnher Professor Dept. of ECE, Auurn University Auurn, AL 36849 vgrwl@eng.uurn.eu www.eng.uurn.eu/~vgrwl Joint reserh with: K. K. Dve, ATI Reserh,
Outline. Computer Science 331. Computation of Min-Cost Spanning Trees. Costs of Spanning Trees in Weighted Graphs
 Outlin Computr Sin 33 Computtion o Minimum-Cost Spnnin Trs Prim s Mik Joson Dprtmnt o Computr Sin Univrsity o Clry Ltur #34 Introution Min-Cost Spnnin Trs 3 Gnrl Constrution 4 5 Trmintion n Eiiny 6 Aitionl
Outlin Computr Sin 33 Computtion o Minimum-Cost Spnnin Trs Prim s Mik Joson Dprtmnt o Computr Sin Univrsity o Clry Ltur #34 Introution Min-Cost Spnnin Trs 3 Gnrl Constrution 4 5 Trmintion n Eiiny 6 Aitionl
CS553 Lecture Register Allocation 1
 Low-Lvl Issus Lst ltur Livnss nlysis Rgistr llotion Toy Mor rgistr llotion Wnsy Common suxprssion limintion or PA2 Logistis PA1 is u PA2 hs n post Mony th 15 th, no lss u to LCPC in Orgon CS553 Ltur Rgistr
Low-Lvl Issus Lst ltur Livnss nlysis Rgistr llotion Toy Mor rgistr llotion Wnsy Common suxprssion limintion or PA2 Logistis PA1 is u PA2 hs n post Mony th 15 th, no lss u to LCPC in Orgon CS553 Ltur Rgistr
The University of Sydney MATH2969/2069. Graph Theory Tutorial 5 (Week 12) Solutions 2008
 Th Univrsity o Syny MATH2969/2069 Grph Thory Tutoril 5 (Wk 12) Solutions 2008 1. (i) Lt G th isonnt plnr grph shown. Drw its ul G, n th ul o th ul (G ). (ii) Show tht i G is isonnt plnr grph, thn G is
Th Univrsity o Syny MATH2969/2069 Grph Thory Tutoril 5 (Wk 12) Solutions 2008 1. (i) Lt G th isonnt plnr grph shown. Drw its ul G, n th ul o th ul (G ). (ii) Show tht i G is isonnt plnr grph, thn G is
CS 461, Lecture 17. Today s Outline. Example Run
 Prim s Algorithm CS 461, Ltur 17 Jr Si Univrsity o Nw Mxio In Prim s lgorithm, th st A mintin y th lgorithm orms singl tr. Th tr strts rom n ritrry root vrtx n grows until it spns ll th vrtis in V At h
Prim s Algorithm CS 461, Ltur 17 Jr Si Univrsity o Nw Mxio In Prim s lgorithm, th st A mintin y th lgorithm orms singl tr. Th tr strts rom n ritrry root vrtx n grows until it spns ll th vrtis in V At h
LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT
 LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT UT LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT UT LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT TU/ CWI UT LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT TU/ CWI UT TUD LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT TU/ Tnzni & Kny yr LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT Nw Zln.5
LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT UT LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT UT LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT TU/ CWI UT LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT TU/ CWI UT TUD LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT TU/ Tnzni & Kny yr LEO VAN IERSEL TU DELFT Nw Zln.5
5/7/13. Part 10. Graphs. Theorem Theorem Graphs Describing Precedence. Outline. Theorem 10-1: The Handshaking Theorem
 Thorm 10-1: Th Hnshkin Thorm Lt G=(V,E) n unirt rph. Thn Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Alorithms n Dt Struturs v V (v) = 2 E How mny s r thr in rph with 10 vrtis h of r six? 10 * 6 /2= 30 1 Thorm 10-2 An unirt
Thorm 10-1: Th Hnshkin Thorm Lt G=(V,E) n unirt rph. Thn Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Alorithms n Dt Struturs v V (v) = 2 E How mny s r thr in rph with 10 vrtis h of r six? 10 * 6 /2= 30 1 Thorm 10-2 An unirt
(2) If we multiplied a row of B by λ, then the value is also multiplied by λ(here lambda could be 0). namely
 . DETERMINANT.. Dtrminnt. Introution:I you think row vtor o mtrix s oorint o vtors in sp, thn th gomtri mning o th rnk o th mtrix is th imnsion o th prlllppi spnn y thm. But w r not only r out th imnsion,
. DETERMINANT.. Dtrminnt. Introution:I you think row vtor o mtrix s oorint o vtors in sp, thn th gomtri mning o th rnk o th mtrix is th imnsion o th prlllppi spnn y thm. But w r not only r out th imnsion,
GREEDY TECHNIQUE. Greedy method vs. Dynamic programming method:
 Dinition: GREEDY TECHNIQUE Gry thniqu is gnrl lgorithm sign strtgy, uilt on ollowing lmnts: onigurtions: irnt hois, vlus to in ojtiv untion: som onigurtions to ithr mximiz or minimiz Th mtho: Applil to
Dinition: GREEDY TECHNIQUE Gry thniqu is gnrl lgorithm sign strtgy, uilt on ollowing lmnts: onigurtions: irnt hois, vlus to in ojtiv untion: som onigurtions to ithr mximiz or minimiz Th mtho: Applil to
Present state Next state Q + M N
 Qustion 1. An M-N lip-lop works s ollows: I MN=00, th nxt stt o th lip lop is 0. I MN=01, th nxt stt o th lip-lop is th sm s th prsnt stt I MN=10, th nxt stt o th lip-lop is th omplmnt o th prsnt stt I
Qustion 1. An M-N lip-lop works s ollows: I MN=00, th nxt stt o th lip lop is 0. I MN=01, th nxt stt o th lip-lop is th sm s th prsnt stt I MN=10, th nxt stt o th lip-lop is th omplmnt o th prsnt stt I
Section 10.4 Connectivity (up to paths and isomorphism, not including)
 Toy w will isuss two stions: Stion 10.3 Rprsnting Grphs n Grph Isomorphism Stion 10.4 Conntivity (up to pths n isomorphism, not inluing) 1 10.3 Rprsnting Grphs n Grph Isomorphism Whn w r working on n lgorithm
Toy w will isuss two stions: Stion 10.3 Rprsnting Grphs n Grph Isomorphism Stion 10.4 Conntivity (up to pths n isomorphism, not inluing) 1 10.3 Rprsnting Grphs n Grph Isomorphism Whn w r working on n lgorithm
Basic Polyhedral theory
 Basic Polyhdral thory Th st P = { A b} is calld a polyhdron. Lmma 1. Eithr th systm A = b, b 0, 0 has a solution or thr is a vctorπ such that π A 0, πb < 0 Thr cass, if solution in top row dos not ist
Basic Polyhdral thory Th st P = { A b} is calld a polyhdron. Lmma 1. Eithr th systm A = b, b 0, 0 has a solution or thr is a vctorπ such that π A 0, πb < 0 Thr cass, if solution in top row dos not ist
COMPLEXITY OF COUNTING PLANAR TILINGS BY TWO BARS
 OMPLXITY O OUNTING PLNR TILINGS Y TWO RS KYL MYR strt. W show tht th prolm o trmining th numr o wys o tiling plnr igur with horizontl n vrtil r is #P-omplt. W uil o o th rsults o uquir, Nivt, Rmil, n Roson
OMPLXITY O OUNTING PLNR TILINGS Y TWO RS KYL MYR strt. W show tht th prolm o trmining th numr o wys o tiling plnr igur with horizontl n vrtil r is #P-omplt. W uil o o th rsults o uquir, Nivt, Rmil, n Roson
Numbering Boundary Nodes
 Numring Bounry Nos Lh MBri Empori Stt Univrsity August 10, 2001 1 Introution Th purpos of this ppr is to xplor how numring ltril rsistor ntworks ffts thir rspons mtrix, Λ. Morovr, wht n lrn from Λ out
Numring Bounry Nos Lh MBri Empori Stt Univrsity August 10, 2001 1 Introution Th purpos of this ppr is to xplor how numring ltril rsistor ntworks ffts thir rspons mtrix, Λ. Morovr, wht n lrn from Λ out
Integration Continued. Integration by Parts Solving Definite Integrals: Area Under a Curve Improper Integrals
 Intgrtion Continud Intgrtion y Prts Solving Dinit Intgrls: Ar Undr Curv Impropr Intgrls Intgrtion y Prts Prticulrly usul whn you r trying to tk th intgrl o som unction tht is th product o n lgric prssion
Intgrtion Continud Intgrtion y Prts Solving Dinit Intgrls: Ar Undr Curv Impropr Intgrls Intgrtion y Prts Prticulrly usul whn you r trying to tk th intgrl o som unction tht is th product o n lgric prssion
CSCI Compiler Design
 CSCI 565 - Compilr Dsign Spring 2013 Sond Tst - Solution My 1, 2013 t 3.30 PM in Room RTH 115 Durtion: 2h 30 min. Pls ll ll pgs you turn in with your nm nd studnt numr. Nm: Numr: Grd: Prolm 1 [20 points]:
CSCI 565 - Compilr Dsign Spring 2013 Sond Tst - Solution My 1, 2013 t 3.30 PM in Room RTH 115 Durtion: 2h 30 min. Pls ll ll pgs you turn in with your nm nd studnt numr. Nm: Numr: Grd: Prolm 1 [20 points]:
Multi-Section Coupled Line Couplers
 /0/009 MultiSction Coupld Lin Couplrs /8 Multi-Sction Coupld Lin Couplrs W cn dd multipl coupld lins in sris to incrs couplr ndwidth. Figur 7.5 (p. 6) An N-sction coupld lin l W typiclly dsign th couplr
/0/009 MultiSction Coupld Lin Couplrs /8 Multi-Sction Coupld Lin Couplrs W cn dd multipl coupld lins in sris to incrs couplr ndwidth. Figur 7.5 (p. 6) An N-sction coupld lin l W typiclly dsign th couplr
m2 m3 m1 (a) (b) (c) n2 n3
 Outline LOGIC SYNTHESIS AND TWO-LEVEL LOGIC OPTIMIZATION Giovnni De Miheli Stnford University Overview of logi synthesis. Comintionl-logi design: { Bkground. { Two-level forms. Ext minimiztion. Covering
Outline LOGIC SYNTHESIS AND TWO-LEVEL LOGIC OPTIMIZATION Giovnni De Miheli Stnford University Overview of logi synthesis. Comintionl-logi design: { Bkground. { Two-level forms. Ext minimiztion. Covering
New challenges on Independent Gate FinFET Transistor Network Generation
 Nw hllngs on Inpnnt Gt FinFET Trnsistor Ntwork Gnrtion Viniius N. Possni, Anré I. Ris, Rnto P. Ris, Flip S. Mrqus, Lomr S. Ros Junior Thnology Dvlopmnt Cntr, Frl Univrsity o Plots, Plots, Brzil Institut
Nw hllngs on Inpnnt Gt FinFET Trnsistor Ntwork Gnrtion Viniius N. Possni, Anré I. Ris, Rnto P. Ris, Flip S. Mrqus, Lomr S. Ros Junior Thnology Dvlopmnt Cntr, Frl Univrsity o Plots, Plots, Brzil Institut
Quartets and unrooted level-k networks
 Phylogntis Workshop, Is Nwton Institut or Mthmtil Sins Cmrig 21/06/2011 Qurtts n unroot lvl-k ntworks Philipp Gmtt Outlin Astrt n xpliit phylognti ntworks Lvl-k ntworks Unroot lvl-1 ntworks n irulr split
Phylogntis Workshop, Is Nwton Institut or Mthmtil Sins Cmrig 21/06/2011 Qurtts n unroot lvl-k ntworks Philipp Gmtt Outlin Astrt n xpliit phylognti ntworks Lvl-k ntworks Unroot lvl-1 ntworks n irulr split
NP-Completeness. CS3230 (Algorithm) Traveling Salesperson Problem. What s the Big Deal? Given a Problem. What s the Big Deal? What s the Big Deal?
 NP-Compltnss 1. Polynomil tim lgorithm 2. Polynomil tim rution 3.P vs NP 4.NP-ompltnss (som slis y P.T. Um Univrsity o Txs t Dlls r us) Trvling Slsprson Prolm Fin minimum lngth tour tht visits h ity on
NP-Compltnss 1. Polynomil tim lgorithm 2. Polynomil tim rution 3.P vs NP 4.NP-ompltnss (som slis y P.T. Um Univrsity o Txs t Dlls r us) Trvling Slsprson Prolm Fin minimum lngth tour tht visits h ity on
Weighted Matching and Linear Programming
 Wightd Mtching nd Linr Progrmming Jonthn Turnr Mrch 19, 01 W v sn tht mximum siz mtchings cn b found in gnrl grphs using ugmnting pths. In principl, this sm pproch cn b pplid to mximum wight mtchings.
Wightd Mtching nd Linr Progrmming Jonthn Turnr Mrch 19, 01 W v sn tht mximum siz mtchings cn b found in gnrl grphs using ugmnting pths. In principl, this sm pproch cn b pplid to mximum wight mtchings.
More Foundations. Undirected Graphs. Degree. A Theorem. Graphs, Products, & Relations
 Mr Funtins Grphs, Pruts, & Rltins Unirt Grphs An unirt grph is pir f 1. A st f ns 2. A st f gs (whr n g is st f tw ns*) Friy, Sptmr 2, 2011 Ring: Sipsr 0.2 ginning f 0.4; Stughtn 1.1.5 ({,,,,}, {{,}, {,},
Mr Funtins Grphs, Pruts, & Rltins Unirt Grphs An unirt grph is pir f 1. A st f ns 2. A st f gs (whr n g is st f tw ns*) Friy, Sptmr 2, 2011 Ring: Sipsr 0.2 ginning f 0.4; Stughtn 1.1.5 ({,,,,}, {{,}, {,},
Seven-Segment Display Driver
 7-Smnt Disply Drivr, Ron s in 7-Smnt Disply Drivr, Ron s in Prolm 62. 00 0 0 00 0000 000 00 000 0 000 00 0 00 00 0 0 0 000 00 0 00 BCD Diits in inry Dsin Drivr Loi 4 inputs, 7 outputs 7 mps, h with 6 on
7-Smnt Disply Drivr, Ron s in 7-Smnt Disply Drivr, Ron s in Prolm 62. 00 0 0 00 0000 000 00 000 0 000 00 0 00 00 0 0 0 000 00 0 00 BCD Diits in inry Dsin Drivr Loi 4 inputs, 7 outputs 7 mps, h with 6 on
Graph Contraction and Connectivity
 Chptr 17 Grph Contrtion n Conntivity So r w hv mostly ovr thniqus or solving prolms on grphs tht wr vlop in th ontxt o squntil lgorithms. Som o thm r sy to prllliz whil othrs r not. For xmpl, w sw tht
Chptr 17 Grph Contrtion n Conntivity So r w hv mostly ovr thniqus or solving prolms on grphs tht wr vlop in th ontxt o squntil lgorithms. Som o thm r sy to prllliz whil othrs r not. For xmpl, w sw tht
Prefix-Free Regular-Expression Matching
 Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing Yo-Su Hn, Yjun Wng nd Derik Wood Deprtment of Computer Siene HKUST Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing p.1/15 Pttern Mthing Given pttern P nd text T, find ll sustrings
Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing Yo-Su Hn, Yjun Wng nd Derik Wood Deprtment of Computer Siene HKUST Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing p.1/15 Pttern Mthing Given pttern P nd text T, find ll sustrings
CSE 373: AVL trees. Warmup: Warmup. Interlude: Exploring the balance invariant. AVL Trees: Invariants. AVL tree invariants review
 rmup CSE 7: AVL trs rmup: ht is n invrint? Mihl L Friy, Jn 9, 0 ht r th AVL tr invrints, xtly? Disuss with your nighor. AVL Trs: Invrints Intrlu: Exploring th ln invrint Cor i: xtr invrint to BSTs tht
rmup CSE 7: AVL trs rmup: ht is n invrint? Mihl L Friy, Jn 9, 0 ht r th AVL tr invrints, xtly? Disuss with your nighor. AVL Trs: Invrints Intrlu: Exploring th ln invrint Cor i: xtr invrint to BSTs tht
Instructions for Section 1
 Instructions for Sction 1 Choos th rspons tht is corrct for th qustion. A corrct nswr scors 1, n incorrct nswr scors 0. Mrks will not b dductd for incorrct nswrs. You should ttmpt vry qustion. No mrks
Instructions for Sction 1 Choos th rspons tht is corrct for th qustion. A corrct nswr scors 1, n incorrct nswr scors 0. Mrks will not b dductd for incorrct nswrs. You should ttmpt vry qustion. No mrks
A 4-state solution to the Firing Squad Synchronization Problem based on hybrid rule 60 and 102 cellular automata
 A 4-stt solution to th Firing Squ Synhroniztion Prolm s on hyri rul 60 n 102 llulr utomt LI Ning 1, LIANG Shi-li 1*, CUI Shung 1, XU Mi-ling 1, ZHANG Ling 2 (1. Dprtmnt o Physis, Northst Norml Univrsity,
A 4-stt solution to th Firing Squ Synhroniztion Prolm s on hyri rul 60 n 102 llulr utomt LI Ning 1, LIANG Shi-li 1*, CUI Shung 1, XU Mi-ling 1, ZHANG Ling 2 (1. Dprtmnt o Physis, Northst Norml Univrsity,
Metodologie di progetto HW Technology Mapping. Last update: 19/03/09
 Metodologie di progetto HW Tehnology Mpping Lst updte: 19/03/09 Tehnology Mpping 2 Tehnology Mpping Exmple: t 1 = + b; t 2 = d + e; t 3 = b + d; t 4 = t 1 t 2 + fg; t 5 = t 4 h + t 2 t 3 ; F = t 5 ; t
Metodologie di progetto HW Tehnology Mpping Lst updte: 19/03/09 Tehnology Mpping 2 Tehnology Mpping Exmple: t 1 = + b; t 2 = d + e; t 3 = b + d; t 4 = t 1 t 2 + fg; t 5 = t 4 h + t 2 t 3 ; F = t 5 ; t
Multipoint Alternate Marking method for passive and hybrid performance monitoring
 Multipoint Altrnt Mrkin mtho or pssiv n hyri prormn monitorin rt-iool-ippm-multipoint-lt-mrk-00 Pru, Jul 2017, IETF 99 Giuspp Fiool (Tlom Itli) Muro Coilio (Tlom Itli) Amo Spio (Politnio i Torino) Riro
Multipoint Altrnt Mrkin mtho or pssiv n hyri prormn monitorin rt-iool-ippm-multipoint-lt-mrk-00 Pru, Jul 2017, IETF 99 Giuspp Fiool (Tlom Itli) Muro Coilio (Tlom Itli) Amo Spio (Politnio i Torino) Riro
Final Exam Solutions
 CS 2 Advancd Data Structurs and Algorithms Final Exam Solutions Jonathan Turnr /8/20. (0 points) Suppos that r is a root of som tr in a Fionacci hap. Assum that just for a dltmin opration, r has no childrn
CS 2 Advancd Data Structurs and Algorithms Final Exam Solutions Jonathan Turnr /8/20. (0 points) Suppos that r is a root of som tr in a Fionacci hap. Assum that just for a dltmin opration, r has no childrn
XML and Databases. Outline. Recall: Top-Down Evaluation of Simple Paths. Recall: Top-Down Evaluation of Simple Paths. Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW
 Smll Pth Quiz ML n Dtss Cn you giv n xprssion tht rturns th lst / irst ourrn o h istint pri lmnt? Ltur 8 Strming Evlution: how muh mmory o you n? Sstin Mnth NICTA n UNSW
Smll Pth Quiz ML n Dtss Cn you giv n xprssion tht rturns th lst / irst ourrn o h istint pri lmnt? Ltur 8 Strming Evlution: how muh mmory o you n? Sstin Mnth NICTA n UNSW
Self-Adjusting Top Trees
 Th Polm Sl-jsting Top Ts ynmi ts: ol: mintin n n-tx ost tht hngs o tim. link(,w): ts n g twn tis n w. t(,w): lts g (,w). pplition-spii t ssoit with gs n/o tis. ont xmpls: in minimm-wight g in th pth twn
Th Polm Sl-jsting Top Ts ynmi ts: ol: mintin n n-tx ost tht hngs o tim. link(,w): ts n g twn tis n w. t(,w): lts g (,w). pplition-spii t ssoit with gs n/o tis. ont xmpls: in minimm-wight g in th pth twn
Multi-Way VLSI Circuit Partitioning Based on Dual Net Representation
 Multi-Wy VLSI Ciruit Prtitioning Bs on Dul Nt Rprsnttion Json Cong Dprtmnt of Computr Sin Univrsity of Cliforni, Los Angls, CA 90024 Wilurt Lio n Nrynn Shivkumr Dprtmnt of Computr Sin Stnfor Univrsity,
Multi-Wy VLSI Ciruit Prtitioning Bs on Dul Nt Rprsnttion Json Cong Dprtmnt of Computr Sin Univrsity of Cliforni, Los Angls, CA 90024 Wilurt Lio n Nrynn Shivkumr Dprtmnt of Computr Sin Stnfor Univrsity,
Design Optimization Based on Diagnosis Techniques
 Dsign Optimiztion Bs on Dignosis Thniqus Anrs Vnris Mgy S. Air Irhim N. Hjj Univrsity of Toronto Motorol Univrsity of Illinois ECE Dprtmnt 77 W. Prmr ECE Dprtmnt n CSL Toronto, ON M5S 34 Austin, T 78729
Dsign Optimiztion Bs on Dignosis Thniqus Anrs Vnris Mgy S. Air Irhim N. Hjj Univrsity of Toronto Motorol Univrsity of Illinois ECE Dprtmnt 77 W. Prmr ECE Dprtmnt n CSL Toronto, ON M5S 34 Austin, T 78729
HIGHER ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Prof Enriqu Mtus Nivs PhD in Mthmtis Edution IGER ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS omognous linr qutions with onstnt offiints of ordr two highr Appl rdution mthod to dtrmin solution of th nonhomognous qution
Prof Enriqu Mtus Nivs PhD in Mthmtis Edution IGER ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS omognous linr qutions with onstnt offiints of ordr two highr Appl rdution mthod to dtrmin solution of th nonhomognous qution
TOPIC 5: INTEGRATION
 TOPIC 5: INTEGRATION. Th indfinit intgrl In mny rspcts, th oprtion of intgrtion tht w r studying hr is th invrs oprtion of drivtion. Dfinition.. Th function F is n ntidrivtiv (or primitiv) of th function
TOPIC 5: INTEGRATION. Th indfinit intgrl In mny rspcts, th oprtion of intgrtion tht w r studying hr is th invrs oprtion of drivtion. Dfinition.. Th function F is n ntidrivtiv (or primitiv) of th function
Computational Biology, Phylogenetic Trees. Consensus methods
 Computtionl Biology, Phylognti Trs Consnsus mthos Asgr Bruun & Bo Simonsn Th 16th of Jnury 2008 Dprtmnt of Computr Sin Th univrsity of Copnhgn 0 Motivtion Givn olltion of Trs Τ = { T 0,..., T n } W wnt
Computtionl Biology, Phylognti Trs Consnsus mthos Asgr Bruun & Bo Simonsn Th 16th of Jnury 2008 Dprtmnt of Computr Sin Th univrsity of Copnhgn 0 Motivtion Givn olltion of Trs Τ = { T 0,..., T n } W wnt
FSA. CmSc 365 Theory of Computation. Finite State Automata and Regular Expressions (Chapter 2, Section 2.3) ALPHABET operations: U, concatenation, *
 CmSc 365 Thory of Computtion Finit Stt Automt nd Rgulr Exprssions (Chptr 2, Sction 2.3) ALPHABET oprtions: U, conctntion, * otin otin Strings Form Rgulr xprssions dscri Closd undr U, conctntion nd * (if
CmSc 365 Thory of Computtion Finit Stt Automt nd Rgulr Exprssions (Chptr 2, Sction 2.3) ALPHABET oprtions: U, conctntion, * otin otin Strings Form Rgulr xprssions dscri Closd undr U, conctntion nd * (if
EE1000 Project 4 Digital Volt Meter
 Ovrviw EE1000 Projt 4 Diitl Volt Mtr In this projt, w mk vi tht n msur volts in th rn o 0 to 4 Volts with on iit o ury. Th input is n nlo volt n th output is sinl 7-smnt iit tht tlls us wht tht input s
Ovrviw EE1000 Projt 4 Diitl Volt Mtr In this projt, w mk vi tht n msur volts in th rn o 0 to 4 Volts with on iit o ury. Th input is n nlo volt n th output is sinl 7-smnt iit tht tlls us wht tht input s
QUESTIONS BEGIN HERE!
 Points miss: Stunt's Nm: Totl sor: /100 points Est Tnnss Stt Univrsity Dprtmnt of Computr n Informtion Sins CSCI 710 (Trnoff) Disrt Struturs TEST for Fll Smstr, 00 R this for strtin! This tst is los ook
Points miss: Stunt's Nm: Totl sor: /100 points Est Tnnss Stt Univrsity Dprtmnt of Computr n Informtion Sins CSCI 710 (Trnoff) Disrt Struturs TEST for Fll Smstr, 00 R this for strtin! This tst is los ook
WORKSHOP 6 BRIDGE TRUSS
 WORKSHOP 6 BRIDGE TRUSS WS6-2 Workshop Ojtivs Lrn to msh lin gomtry to gnrt CBAR lmnts Bom fmilir with stting up th CBAR orinttion vtor n stion proprtis Lrn to st up multipl lo ss Lrn to viw th iffrnt
WORKSHOP 6 BRIDGE TRUSS WS6-2 Workshop Ojtivs Lrn to msh lin gomtry to gnrt CBAR lmnts Bom fmilir with stting up th CBAR orinttion vtor n stion proprtis Lrn to st up multipl lo ss Lrn to viw th iffrnt
1 Introduction to Modulo 7 Arithmetic
 1 Introution to Moulo 7 Arithmti Bor w try our hn t solvin som hr Moulr KnKns, lt s tk los look t on moulr rithmti, mo 7 rithmti. You ll s in this sminr tht rithmti moulo prim is quit irnt rom th ons w
1 Introution to Moulo 7 Arithmti Bor w try our hn t solvin som hr Moulr KnKns, lt s tk los look t on moulr rithmti, mo 7 rithmti. You ll s in this sminr tht rithmti moulo prim is quit irnt rom th ons w
Technology Mapping Method for Low Power Consumption and High Performance in General-Synchronous Framework
 R-17 SASIMI 015 Proeeings Tehnology Mpping Metho for Low Power Consumption n High Performne in Generl-Synhronous Frmework Junki Kwguhi Yukihie Kohir Shool of Computer Siene, the University of Aizu Aizu-Wkmtsu
R-17 SASIMI 015 Proeeings Tehnology Mpping Metho for Low Power Consumption n High Performne in Generl-Synhronous Frmework Junki Kwguhi Yukihie Kohir Shool of Computer Siene, the University of Aizu Aizu-Wkmtsu
Outline. Binary Tree
 Outlin Similrity Srh Th Binry Brnh Distn Nikolus Austn nikolus.ustn@s..t Dpt. o Computr Sins Univrsity o Slzur http://rsrh.uni-slzur.t 1 Binry Brnh Distn Binry Rprsnttion o Tr Binry Brnhs Lowr Boun or
Outlin Similrity Srh Th Binry Brnh Distn Nikolus Austn nikolus.ustn@s..t Dpt. o Computr Sins Univrsity o Slzur http://rsrh.uni-slzur.t 1 Binry Brnh Distn Binry Rprsnttion o Tr Binry Brnhs Lowr Boun or
Ch 1.2: Solutions of Some Differential Equations
 Ch 1.2: Solutions of Som Diffrntil Equtions Rcll th fr fll nd owl/mic diffrntil qutions: v 9.8.2v, p.5 p 45 Ths qutions hv th gnrl form y' = y - b W cn us mthods of clculus to solv diffrntil qutions of
Ch 1.2: Solutions of Som Diffrntil Equtions Rcll th fr fll nd owl/mic diffrntil qutions: v 9.8.2v, p.5 p 45 Ths qutions hv th gnrl form y' = y - b W cn us mthods of clculus to solv diffrntil qutions of
I. The Connection between Spectroscopy and Quantum Mechanics
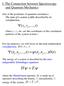 I. Th Connction twn Spctroscopy nd Quntum Mchnics On of th postults of quntum mchnics: Th stt of systm is fully dscrid y its wvfunction, Ψ( r1, r,..., t) whr r 1, r, tc. r th coordints of th constitunt
I. Th Connction twn Spctroscopy nd Quntum Mchnics On of th postults of quntum mchnics: Th stt of systm is fully dscrid y its wvfunction, Ψ( r1, r,..., t) whr r 1, r, tc. r th coordints of th constitunt
minimize c'x subject to subject to subject to
 z ' sut to ' M ' M N uostrd N z ' sut to ' z ' sut to ' sl vrls vtor of : vrls surplus vtor of : uostrd s s s s s s z sut to whr : ut ost of :out of : out of ( ' gr of h food ( utrt : rqurt for h utrt
z ' sut to ' M ' M N uostrd N z ' sut to ' z ' sut to ' sl vrls vtor of : vrls surplus vtor of : uostrd s s s s s s z sut to whr : ut ost of :out of : out of ( ' gr of h food ( utrt : rqurt for h utrt
