The Seasons. Description Position Description Position. March 21st B South Pole-24 Hrs of Dark C. June 21st C High Kinetic Energy A
|
|
|
- Edith Cole
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Seasons Description Position Description Position March 21st B South Pole-24 Hrs of Dark C June 21st C High Kinetic Energy A December 21st A Low Kinetic Energy C September 23rd D Earth Close to Sun A Northern Hemisphere Winter A Earth Far from Sun C Northern Hemisphere Spring B Southern Hemisphere Spring D North Hemisphere Summer C Southern Hemisphere Fall B Northern Hemisphere Fall D Southern Hemisphere Winter C Greatest Orbital Velocity A South Hemisphere Summer A Least Orbital Velocity C 9 Hrs of Day in NYS A 23 1/2 N-Zenith C 12 Hrs of Day in NYS D,B 0 (Equator)-Zenith D,B 15 Hrs of Day in NYS C 23 1/2 S-Zenith A Winter Solstice A North Pole-24 Hrs Day C Vernal Equinox B South Pole-24 Hrs Day A Autumnal Equinox D North Pole-24 Hrs Dark A Summer Solstice C
2 Sunʼs Path in NYS 1. What direction does the sun rise in summer? NE 2. What direction does the sun rise in winter? SE 3. What direction does the sun rise in fall/spring? E 4. How long is the sun out in fall/spring? How long is the sun out in winter? 9 6. How long is the sun out in summer? What direction do you look to see the noon time sun? S 8. What direction do you look to see polaris? N 9. From sunrise to noon, what happens to the length of a shadow? SMALLER 10. From noon to sunset, what happens to the length of a shadow? LONGER 11. From sunrise to noon, what happens to the angle of insolation and intensity of insolation? INREASES 12. From noon to sunset, what happens to the angle of insolation and intensity of insolation? DECREASES 13. What season does the sun have the greatest insolation? SUMMER 14. What season does the sun have the least insolation? WINTER 15. Does the sun ever reach the zenith in NYS? NO 16. What direction does the sun set during winter? SW 17. What direction does the sun set during fall/spring? W 18. What direction does the sun set during summer? NW 19. Does the sun physically move across the sky? NO Explain! ROTATION 20. From season to season, how many degrees does the noon time sun shift in the sky? Why is it so cold in NY during winter? TILT AWAY FROM SUN 22. Why is it so hot in NY during summer? TILT TOWARDS THE SUN 23. Why does the sun shift its position along the horizon with the changing seasons? EARTH_REVOLUTION 24. On the shadow diagram, what letter represents South? A
3 Station Models Temperature: 46 F Visibility: 1/4 MILE Variable Dew Point: 45 F Variable Wind Speed: 25 KNOTS Wind Direction: NE Cloud Cover: 75% Barometric Pressure: MB Precipitation:.15 INCHES Barometric Trend: FALLING 6.0 MB Current Weather: RAIN 1/ \.11 Variable Temperature-71 F Visibility-1/2 Mile Wind Direction-W Cloud Cover-100% Barometric Trend: -33\ Variable Dew Point-68 F Wind Speed-45 Knots Current Weather-T-Storms Barometric Pressure mb Precipitation Inches
4 Topographic Maps D C 1. What is the direction of stream flow for Maple Stream? SW 2. Provide an evidence that supports your answer. RIVERS FLOW FROM HIGH ELEVATION TO LOW ELEVATION 3. What is the highest possible elevation of Girard Hill? 539FT 4. Determine the gradient between points A and B. 3.2 FT/MILE 5. Create a profile between points C and D Elevation-Feet
5 Orographic Lifting 1. What side of the mountain will get the majority of the precipitation? WINDWARD_ 2. Tell me what the temperature and humidity will be like on the Windward side? WARM AND WET 3. What happens to the air mass as it begins to rise over the mountain? COOLS TO DEWPOINT 4. What temperature does the air mass cool to? DEWPOINT 5. As air rises, it cools and (expands or contracts)? EXPANDS 6. What phase change occurs as a cloud forms? CONDENSATION 7. When the air mass goes over the mountain, is the humidity high or low? HIGH 8. The Leeward side of the mountain has a phenomenon called The RAIN Shadow Effect 9. Tell me what the temperature and humidity will be like on the Leeward side? DRY AND HOT 10. As air sinks on the Leeward side it will warm due to (expansion or contraction?) CONTRACTION 11. What is orographic lifting? MTNS FORCE AIR TO RISE OVER IT 12. What is adiabatic temperature change? TEMPERATURE CHANGE DUE TO PRESSURE CHANGE
6 Index Fossils Identification Eospirifer Manticoceras Phacops Identification Letter Y G C Eon PHANEROZOIC PHANEROZOIC PHANEROZOIC Era PALEOZOIC PALEOZOIC PALEOZOIC Period SILURIAN DEVONIAN DEVONIAN Epoch EARLY MIDDLE MIDDLE Important Geo Event SALT/GYPSUM EROSION-ACADIAN EROSION-ACADIAN Landscape Where They Lived ERIE-ONTARIO LOWLANDS ALLEGHENY PLATEAU ALLEGHENY PLATEAU 1. Why are index fossils important in determining age of rocks? KNOW AGE OF THE FOSSIL...YOU KNOW THE AGE OF THE ROCK 2. What are the 2 criteria that is special to an index fossil? LIVE FOR SHORT PERIOD OF TIME AND OVER A BIG AREA 3. What was another method discussed in class (very similar to index fossils) that helps geologists determine age of rocks? VOLCANIC ASH
7 Correlation Activity 1. What rock layer is the oldest? SHALE (LOCATION W) 2. What rock layer is the youngest? CONGLOMERATE (LOCATION Z 3. What are the steps in determining unconformity AB? UPLIFT, WEATHERING, EROSION, DEPOSITION 4. What do the little lines coming off of the rock layers in locations W and Y represent? CONTACT METAMORPHISM 5. What is younger in location W: Intrusion or shale? INTRUSION 6. What is older in location X: Limestone or sandstone? SHALE 7. What happened most recent: Intrusion or bottom layer of shale? INTRUSION 8. What happened first: Breccia or Sandstone? _SANDSTONE 9. In location Y, what rock would form at the contact point between the intrusion and the sandstone? QUARTZITE
8 High and Low Pressure Characteristics High Pressure Characteristics Low Pressure Characteristics DRY CLOCKWISE SPIN OUTWARD COLD AIR SINKS DIVERGING AT THE SURFACE LITTLE MOISTURE GOOD WEATHER RELATIVELY NO CLOUDS MORE DENSE AIR WET COUNTERCLOCKWISE SPIN INWARD WARM AIR RISES CONVERGING AT THE SURFACE LOTS OF MOISTURE BAD WEATHER LOTS OF CLOUDS LESS DENSE AIR
9 Latitude and Longitude What is the latitude and longitude of point B? 40N, 120W 2. What is the latitude and longitude of point C? 30S, 70W 3. What is the latitude and longitude of point G? 45S, 70E 4. How many degrees separates each time zone? 15 DEGREES 5. How many degrees of longitude are in each time zone? 15 DEGREES 6. As you go east, the time does INCREASE 7. As you go west, the time gets LESS 8. If its 6:00am at point 1, what time is it at point 2? 9:00AM 9. If the altitude of polaris is 42 degrees, what is your latitude? 42N 10. If your latitude is 61 degrees North, what is your altitude of polaris? What is the altitude of polaris if you latitude is 41 degrees south? NONE 12. What latitude gets the most direct sun on June 21st? 23.5 N 13. What latitude gets the most direct sun on December 21st? 23.5 S 14. What latitude gets the most direct sun on March 21st? EQUATOR 15. What latitude gets the most direct sun on September 23rd? _EQUATOR
10 Weather Practice D Moon Phases 1. What is the name of the storm pictured above? MID LATITUDE CYCLONE 2. Is Low pressure dry weather or wet weather? WET 3. Draw in where the precipitation will be found for both the warm front and the cold front 4. Where does the mt airmass come from? GULF OF MEXICO 5. Where does the cp airmass come from? CANADA 6. In station model B, what does it mean when both the air temp and dew point temp are both 82 F? PRECIPITATION 7. What direction are the winds blowing around the low pressure? COUNTERCLOCWISE /INWARD 8. What station model just experienced torrential rains and a tornado warning? D 9. What station model has the driest air? C 10. What station model is experiencing slow steady precipitation? B 11. What station model has a slowly falling barometer? B 12. What 2 station models have a flood warning with very dangerous lightning? _A 13. What happened the pressure of station model D over the past hour? RISE 14. What direction will this low pressure center move over the next 24 hours? NE
11 Moon Phases Moon Phase # Name of the Phase Draw the Phase NEW MOON 2 WAXING CRESCENT 3 FIRST QUARTER WAXING GIBBOUS 5 FULL MOON 6 WANING GIBBOUS 7 THIRD QUARTER WANING CRESCENT 1. What 2 phases (name and number) provide a spring tide? 1,5 2. What 2 phases (name and number) provide a neap tide? 3,7 3. What phase (name and number) creates a solar eclipse? NEW MOON 1 4. What phase (name and number) creates a lunar eclipse? _FULL MOON 5 5. Why do we see the same side of the moon every day? ROTATION=REVOLUTION 6. What motion causes the phases of the moon? REVOLUTION
12 Fill in the blanks from the flowcharts below. SHALE RHYOLITE GNEISS Altitude of Polaris 1. What is the latitude of the observer? 52N 2. Can you see Polaris in the southern hemisphere? NO 3. What is the point directly above the observer called? ZENITH 4. As your latitude increases, what happens to your altitude of Polaris? _INCREASE 5. What type of relationship is that called? DIRECT 6. If one travels from NY to Chicago, what happens to their altitude of Polaris? _SAME
13 Sequence of Events 1 1. What layer of rock is the youngest? A 2. What layer of rock happened most recently? A 3. What layer of rock is the oldest? E 4. Which is older...shale or the Intrusion? SHALE 5. Name the rock found at point 1? MARBLE 6. Put the above sequence in order from oldest to youngest a. LIMESTONE b. SHALE c. INTRUSION d. EXTRUSION e. SANDSTONE f. CONGLOMERATE
14 Porosity, Permeability, Capillarity 1. Which sample has the greatest porosity? EQUAL 2. Which sample has the greatest permeability? LARGE 3. Which sample has the greatest capillarity? SMALL 4. Which sample will have the lowest permeability rate? _SMALL 5. Which sample will have the fastest infiltration time? LARGE 6. Which sample has the greatest surface area? SMALL Weathering Flow Chart CHEMICAL PHYSICAL MINERALS ICE
15 Earthquake Practice
16 Doppler Effect-Red Shift/Blue Shift 1. The doppler effect supports the idea that the universe is EXPANDING 2. Red shifts support the idea that objects are moving AWAY 3. Blue shifts support the idea that objects are moving TOWARDS 4. How long ago did the Big Bang occur? 13.7 BILLION YEARS 5. Infrared Radiation is on what side of the spectrum? RIGHT 6. Ultraviolet Radiation is on what side of the spectrum? LEFT 7. The Red end of the spectrum is (long or short) wavelength? LONG 8. The Blue end of the spectrum is (long or short) wavelength? SHORT 9. What is the name of the galaxy that we live in? MILK WAY 10. What type of galaxy do we live in? SPIRAL 11. The farther an object is red-shifted, what do we know about itʼs distance? FARTHER AWAY 12. The farther an object is red-shifted, what do we know about itʼs speed? TRAVELING FASTER
17 Radioactive Decay 1 Half Life 2 Half Lives 1. If the half life above is 5700 years, how many years have gone by? 11,400YRS 2. In the example above, what percentage of original sample is left? 25% 3. What isotope is used to date young, organic material? CARBON Name an isotope used to date a trilobite fossil? POTASSIUM In the above example, if you start out with 1000 g of K40, how much Ar40 is left after 2 half lives? 250G 6. In the previous example, how many years have passed over 2 half lives? 2.6 BY CONVERGENT PULL APART SAN ANDREAS FAULT CONT-CONT JUAN DE FUCA/ NA
18 Sunʼs Path and Altitude of Polaris 1. What season is shown in the diagram above? FALL/SPRING 2. What is the altitude of the noon sun? What direction would the noon shadow of the observer point? NORTH 4. What is the altitude of Polaris? Name a city in NYS that would see Polaris at this altitude? ELMIRA 6. What would the altitude of the noon sun be in Summer? What is the zenith? _POINT DIRECTLY ABOVE OBSERVER 8. Does the noon sun ever reach the zenith in NYS? _NO 9. Explain why the zenith is never reached in NYS. NY NOT IN THE TROPICS 10. What happens to the length of the shadow from sunrise to noon? _DECREASES 11. What happens to the length of the shadow from noon to sunset? _INCREASES 12. What season has the longest noon shadow? WINTER 13. What season has the greatest angle of insolation? SUMMER 14. What season has the shortest noon shadow? SUMMER 15. What season has the lowest angle of insolation? WINTER
19 Stars 1. What is the luminosity and temperature of Betelgeuse? _500,000 X BRIGHTER/3500C_ 2. What is the temperature and luminosity of Rigel? 400,000X BRIGHTER/12,000C 3. What is the name of the reaction that produces light within a star? FUSION 4. What is the fuel of the sun? HYDROGEN 5. The majority of stars fit into what category? MAIN SEQUENCE 6. Our own sun is considered a (what group of star?) _MAIN SEQUENCE 7. In 5 billion years, our sun is going to turn into a RED GIANT 8. We can see Orion in December...why canʼt we see Orion in June? EARTH REVOLVES AROUND THE SUN 9. What color star is Sirius? WHITE/BLUE-WHITE 10. What group of stars does Aldebaran belong to? GIANT
20 Minerals 1. What is the hardness and composition of quartz? 7/SIO2 2. What is the luster and form of breakage of halite? NONMETALLIC/CLEAVAGE 3. What makes quartz different from halite? _INTERNAL ARRANGEMENT OF ATOMS_ 4. What mineral has a metallic luster, hardness of 6.5 and is a brassy yellow color? PYRITE 5. What mineral has a non-metallic luster, has cleavage and bubbles with acid? CALCITE 6. What mineral has a greasy feel and and is used in ceramics? TALC Eccentricity 1. What is the eccentricity of this ellipse? When the planet gets close to the star, what happens to the velocity? _INCREASES_ 3. The more elliptical this ellipse gets...what happens to eccentriciy? _GETS HIGHER_ 4. Low eccentricity is what shape orbit...round or oval? ROUND
21 Sedimentary Rocks 1. Which rocks above are clastic? A,B,C,D 2. Which rock is organic? E-LIMESTONE 3. Which rock is a chemical rock? F-ROCK SALT 4. What are the 2 ways a chemical rock can form? _PRECIPITATION/EVAPORATION_ 5. Describe the process for the formation of a clastic rock? _WEATHERING/EROSION/DEPOSITION/COMPRESSION/COMPACTION/LITHIFICATION_ 6. What is the particle size for a sandstone rock? CM 7. What is the difference between a conglomerate and breccia rock? ANGLED/ROUNDED FRAGMENTS 8. Which rock had particles that traveled further...conglomerate or breccia? CONGLOMERATE-ROUNDED FRAGMENTS 9. Which rock is made of particles with a diameter of cm? _SANDSTONE 10. Which bioclastic rock is made from dead plants? BITUMINOUS COAL 11. What is the composition of rock gypsum? GYPSUM 12. How are clastic sedimentary rocks classified? GRAIN SIZE 13. How are chemical rocks classified? COMPOSITION
22 Earth Rotation 1. The Earth rotates in what direction? COUNTERCLOCKWISE 2. What direction do wind and water currents deflect towards in the northern hemisphere? RIGHT 3. What direction do wind and water currents deflect towards in the southern hemisphere? LEFT 4. The coriolis effect is caused by what? EARTH ROTATION 5. The Foucault Pendulum supports the idea that the Earth does what? _ROTATES 6. The Earth rotates how many degrees per hour? 15 DEGREES 7. What does rotation give us on the planet? DAY/NIGHT 8. What does revolution give us on the planet? SEASONS
23 Metamorphic Rocks 1. What rock is shown in the picture above? GNEISS 2. What 2 processes produce a metamorphic rock? HEAT/PRESSURE 3. What does foliation mean? MINERAL ALIGNMENT 4. What type of foliation does Gneiss show? BANDING 5. What are the 2 types of metamorphism? REGIONAL/CONTACT 6. What sedimentary rock forms into Anthracite Coal? BITUMINOUS COAL 7. What sedimentary rock forms into Quartzite? SANDSTONE 8. What sedimentary rock forms into Marble? LIMESTONE 9. What metamorphic rock shows the lowest grade of metamorphism? SLATE 10. What metamorphic rock shows the highest grade of metamorphism? _GNEISS 11. How are nonfoliated rocks classified? COMPOSITION 12. What metamorphic rock is made of platy mica crystals? SCHIST 13. What metamorphic rock can be made from various other rocks through the contact of magma? HORNFELS 14. What metamorphic rock is made from shale? SLATE
24 Igneous Rocks 1. What 2 processes produce an igneous rock? MELTING/SOLIDIFICATION 2. Rocks that form inside the earth are...intrusive or extrusive? INTRUSIVE 3. Rocks that form at or near the surface are...intrusive or extrusive? EXTRUSIVE 4. Igneous rocks are classified how? TEXTURE 5. Very coarse rocks are created where? _INSIDE THE EARTH 6. What is the color, density and composition of Granite? LIGHT/LOW AND FELSIC 7. What is the color, density and composition of Basalt? DARK/HIGH AND MAFIC 8. Name a coarse grained rock that contains the mineral pyroxene? GABBRO 9. Name a vesicular rock that is glassy and floats in water? PUMICE 10. Name an igneous rock that contains a lot of quartz? GRANITE 11. Rocks that have large crystals formed...quickly or slowly? SLOW 12. Rocks that have very small crystals formed...quickly or slowly? QUICK 13. How are the crystals described with igneous rocks? INTERLOCKING
25 Weathering Conditions 1. Describe the climate needed for chemical weathering to be dominant. WET AND HOT 2. Describe the climate needed for physical weathering to be dominant. WET AND TEMPS ABOVE/BELOW FREEZING 3. Provide a few examples of physical weathering. FROST ACTION 4. Provide a few examples of chemical weathering. CARBONATION 5. Describe what a chemical weathering landscape would look like. ROUNDED HILLS, THICK VEGETATION, THICK SOIL 6. Describe what a physical weathering landscape would look like. STEEP, SHARP CLIFFS, THIN SOIL, NO VEGETATION
26 Plate Boundary Diagrams B C A 1. Name the type of plate boundary for diagram A TRANSFORM 2. Name the type of plate boundary for diagram B CONVERGENT 3. Name the type of plate boundary for diagram C DIVERGENT 4. Provide an example from your reference table where you would find diagram A. SAN ANDREAS FAULT 5. Provide an example from your reference table where you would find diagram B. NAZCA/SOUTH AMERICAN PLATES 6. Provide an example from your reference table where you would find diagram C. MID ATLANTIC RIDGE 7. What is convection and what layer of Earth would you find it? DENSITY CIRCULATION WITHIN THE ASTHENOSPHERE 8. Describe the geologic features that you would get with diagram A. MASSIVE EARTHQUAKES 9. Describe what the + and - signs mean with diagram C. REVERSAL OF MAGNETIC POLARITY
27 The Water Cycle 1. Label the processes from the diagram above... i. EVAPORATION ii. TRANSPORATION iii. CONDENSATION iv. PRECIPITATION v. RUNOFF vi. INFILTRATION 2. Provide the necessary ground conditions for runoff. IMPERMEABLE SOIL THAT IS SATURATED 3. What does the term saturated? FILLRD WITH WATER 4. Provide the necessary ground conditions for infiltration. UNSATURATED SOIL THAT IS PERMEABLE 5. Clouds form from what process? CONDENSATION 6. Water enters the atmosphere through 2 processes...what are the? EVAPORATION/TRANSPORATION 7. What are the 2 groundwater zones? ZONES OF SATURATION AND AERATION
28 Winds A B 1. Winds in the northern hemisphere travel in what direction? RIGHT 2. Winds in the southern hemisphere travel in what direction? LEFT 3. Winds that converge at the surface do what? RISE AND COOL 4. Winds that diverge at the surface do what? SINK AND WARM 5. Which diagram shows a land breeze? B 6. What time of day does a land breeze occur? NIGHT TIME 7. Which diagram shows a sea breeze? A 8. What time of day does a sea breeze occur? AFTERNOON 9. Winds are caused by differences in what? PRESSURE_DIFFERENCES 10. What are lines of equal pressure called? ISOBARS 11. How do you determine where the strongest winds are on a weather map? ISOBARS CLOSE TOGETHER
29 The Greenhouse Effect 1. What type of radiation enters the greenhouse (provide wavelength and names of waves) SHORT AND UV 2. What type of radiation tries to escape the greenhouse (provide wavelength and names of waves) LONG AND IR 3. Provide a few examples of greenhouse gases. CO2, METHANE 4. The glass in the greenhouse is equivalent to which greenhouse gas? CO2_ 5. What are some possible reasons for the increased amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? BURNING OF FOSSIL FUELS, DEFORESTATION 6. Dark colors are good at doing what? ABSORBING/RADIATING 7. The electromagnetic spectrum is organized by what? WAVELENGTH
30 Deposition 1. What is deposition? SEDIMENTS DROPPED OFF 2. What is erosion? TRANSPORTATION OF SEDIMENTS 3. The diagram at the left, which positions will show erosion? A/D 4. The diagram at the left, which positions will show deposition? B/C 5. What is carrying power? _ABILITY TO MOVE SEDIMENT 6. What is discharge? VOLUME 7. What is velocity? SPEED 8. What are meanders? TURNS 9. The diagram on the right shows horizontal sorting...what are some of the factors that effect deposition? SIZE, SHAPE, DENSITY 10. What is the relationship between velocity and slope? DIRECT 11. In a straight channel stream, where does water travel the fastest? CENTER 12. Why does water erode more on the outside of a meander? FAST WATER 13. Why does water deposit more on the inside of a meander? SLOW WATER
31 Climatic Conditions A B C D 1. In diagram A, explain why the 2 cities have very different temperature curves? 1 INLAND AND ONE COASTAL 2. Explain the summers and winters of an inland region. HOT SUMMERS/COLD WINTERS 3. Explain the summers and winters of a coastal region. COOL SUMMERS/WARM WINTERS 4. What substance has the highest specific heat on the planet? _WATER 5. Describe the differences in heating/cooling for substances that have high or low specific heats. HIGH-SLOW HEATING/COOLING...LOW-FAST HEATING/COOLING 6. In diagrams B and C, explain the difference in temperature curves for Arica and Rio de Janeiro. Both cities are at the same latitude. COLD CURRENT-COLD AIR...WARM CURRENT-WARM AIR 7. In diagram D, explain the difference in climate for positions A and B. A-WINDWARD...B-LEEWARD
32 Temperature and Dew Point 1. Low pressure is going to bring in what type of weather? RAINY 2. High pressure is going to bring in what type of weather? DRY 3. As the air temperature approaches the dew point, what happens outside? PRECIPITATION 4. As the air temperature and dew point get farther apart, what happens to the weather outside? BEAUTIFUL WEATHER 5. Clouds form when warm air rises, expands, cools to the DEW POINT 6. In the diagram above, what 2 time blocks represent the best chance for precipitation? 7-11AM...11PM-12AM 7. As air temperature approaches the dew point, what happens to the relative humidity? INCREASES 8. Air that is saturated is said to have what type of humidity? 100%
33 Index Fossils and Correlation 1. What are the 2 criteria for a fossil to be considered an index fossil? LIVED FOR SHORT PERIOD...OVER A HUGE AREA 2. What is line XY called? UNCONFORMITY 3. What does line XY represent? GAP IN GEOLOGIC ROCK RECORD 4. Provide the steps needed to create line XY UPLIFT, WEATHERING, EROSION, SUBSIDENCE 5. What is rock layer A? INTRUSION 6. Why are these fossils useful in determining the relative age of these rocks? AGE OF FOSSIL=AGE OF ROCK 7. Put the sequence in order... a. SHALE b. SHALE c. SHALE d. LIMESTONE e. INTRUSION f. UPLIFT g. W + E h. SUBSIDENCE i. SANDSTONE
34 Landscapes Match the landscapes on the left with the drainage patterns to the right
35 Oceans 1. When looking at the groin, what compass direction will the largest beach? E 2. Sediment is carried parallel to the shoreline by LONGSHORE CURRENTS 3. Ocean currents follow the same path as WIND CURRENTS 4. What direction is the current flowing? WEST Mass Wasting 1. What is the major force behind all 4 types of erosion shown above? _GRAVITY 2. Mass wasting produces what type of sediment? UNSORTED 3. Glaciers/gravity produce unsorted sediment, wind and water produce SORTED 4. Which one of the 4 diagrams above has the greatest velocity? ROCK FALL
The Seasons. Description Position Description Position. North Pole-24 Hrs Dark. 23 1/2 N-Zenith 12 Hrs of Day in NYS
 The Seasons Description Position Description Position March 21st June 21st December 21st September 23rd Northern Hemisphere Winter Northern Hemisphere Spring North Hemisphere Summer Northern Hemisphere
The Seasons Description Position Description Position March 21st June 21st December 21st September 23rd Northern Hemisphere Winter Northern Hemisphere Spring North Hemisphere Summer Northern Hemisphere
Weather Review. What is the relative humidity when the temperature equals the dew point?
 Weather Review A measures dew point and relative humidity. What is another name for the DRY BULB? Why is the wet bulb NEVER higher than the dry bulb? What is the dew point? What is the relative humidity?
Weather Review A measures dew point and relative humidity. What is another name for the DRY BULB? Why is the wet bulb NEVER higher than the dry bulb? What is the dew point? What is the relative humidity?
Earth Science SOL Study Guide due DAY of SOL (test grade)
 Name: DAY OF MY TEST: Block: Earth Science SOL Study Guide due DAY of SOL (test grade) Introductory Science: What s the difference between the independent and dependent variable? What is the control in
Name: DAY OF MY TEST: Block: Earth Science SOL Study Guide due DAY of SOL (test grade) Introductory Science: What s the difference between the independent and dependent variable? What is the control in
Which rock unit is youngest in age? A) A B) B C) C D) D
 1. The Catskills landscape region is classified as a plateau because it has A) low elevations and mostly faulted or folded bedrock B) low elevations and mostly horizontal bedrock C) high elevations and
1. The Catskills landscape region is classified as a plateau because it has A) low elevations and mostly faulted or folded bedrock B) low elevations and mostly horizontal bedrock C) high elevations and
1. How wide is this sheet of paper, to the nearest 0.1 cm? meters?
 Earrtth Sciience 22001111--22001122 REGENTS WEEKLY REVIEW HANDOUT #4 ESRT Name Reference Table Page 1 1. How wide is this sheet of paper, to the nearest 0.1 cm? meters? 2. Which of the radioactive substances
Earrtth Sciience 22001111--22001122 REGENTS WEEKLY REVIEW HANDOUT #4 ESRT Name Reference Table Page 1 1. How wide is this sheet of paper, to the nearest 0.1 cm? meters? 2. Which of the radioactive substances
Monday, May 24, Things to Know...
 117 Things to Know... 117 Things to Know... The same substance always has the same density. 2As pressure increases, density increases 3As temperature increases, density decreases 4Water expands when it
117 Things to Know... 117 Things to Know... The same substance always has the same density. 2As pressure increases, density increases 3As temperature increases, density decreases 4Water expands when it
3. This room is located in a building in New York State. On which side of the building is the window located? (1) north (3) east (2) south (4) west
 1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
Name Period Date 8R MIDTERM REVIEW I. ASTRONOMY 1. Most stars are made mostly of. 2. The dark, cooler areas on the sun s surface are
 Name Period Date 8R MIDTERM REVIEW I. ASTRONOMY 1. Most stars are made mostly of 2. The dark, cooler areas on the sun s surface are 3. When hydrogen nuclei fuse they form 4. Einstein s equation is 5. The
Name Period Date 8R MIDTERM REVIEW I. ASTRONOMY 1. Most stars are made mostly of 2. The dark, cooler areas on the sun s surface are 3. When hydrogen nuclei fuse they form 4. Einstein s equation is 5. The
As compaction and cementation of these sediments eventually occur, which area will become siltstone? A) A B) B C) C D) D
 1. A student obtains a cup of quartz sand from a beach. A saltwater solution is poured into the sand and allowed to evaporate. The mineral residue from the saltwater solution cements the sand grains together,
1. A student obtains a cup of quartz sand from a beach. A saltwater solution is poured into the sand and allowed to evaporate. The mineral residue from the saltwater solution cements the sand grains together,
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Complete the following using your ESRT. Remember to show work and use units as appropriate.
 Name: The ESRT Review Guide Complete the following using your ESRT. Remember to show work and use units as appropriate. Page 1 1. Write the half life of Uranium-238 as a standard number 2. What substance
Name: The ESRT Review Guide Complete the following using your ESRT. Remember to show work and use units as appropriate. Page 1 1. Write the half life of Uranium-238 as a standard number 2. What substance
New Paltz Central School District Earth Science
 UNIT 1: MEASUREMENT AND DENSITY Measure volume, length, weight, and rate of Practicum during exam How do you accurately measure length, weight, change. Full lab write-up of density determination of and
UNIT 1: MEASUREMENT AND DENSITY Measure volume, length, weight, and rate of Practicum during exam How do you accurately measure length, weight, change. Full lab write-up of density determination of and
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals
 Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
4) Graphing an indirect relationship, as X-axis increases, Y-axis decreases.
 THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW FOR THE REGENTS CHAPTER 1 1) An observation uses your senses, an instrument extends your senses; an inference (prediction) is a conclusion based on observations. 2) Classification
THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW FOR THE REGENTS CHAPTER 1 1) An observation uses your senses, an instrument extends your senses; an inference (prediction) is a conclusion based on observations. 2) Classification
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
Observations vs. Inferences. Density. Rate of Change / Gradient
 Observations vs. Inferences Observations: perceptions/facts that can be seen or measured with senses or instruments In addition to this review, study ALL previous TESTS, Quizzes, labs, handouts and notes.
Observations vs. Inferences Observations: perceptions/facts that can be seen or measured with senses or instruments In addition to this review, study ALL previous TESTS, Quizzes, labs, handouts and notes.
WEATHER. Review Note Cards
 WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
A) its rotation D) Sun, the Moon, and some stars C) an oblate sphere D) troposphere B) hydrosphere and troposphere B) less dense and more felsic
 1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its molten core 2. The Earth's actual shape
1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its molten core 2. The Earth's actual shape
2nd Grade Changing of Earth
 Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Weather Cycles The Rock Cycle Defined Events Gradual
Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Weather Cycles The Rock Cycle Defined Events Gradual
2nd Grade. Earth and Moon Cycles. Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133. Slide 3 / 133. Slide 4 / 133. Slide 5 / 133. Slide 6 / 133.
 Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Slide 4 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Click on the topic to go to that
Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Slide 4 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Click on the topic to go to that
CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: PROLOGUE The Local Environment... 1 Observation, Inference, Classification Properties of the Environment...
 CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: PROLOGUE The Local Environment... 1 Observation, Inference, Classification Properties of the Environment... 3 Measurement, Percent Deviation From Accepted Value Density... 6 Density
CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: PROLOGUE The Local Environment... 1 Observation, Inference, Classification Properties of the Environment... 3 Measurement, Percent Deviation From Accepted Value Density... 6 Density
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
Page 1. Name: 1) Which diagram best shows the grain size of some common sedimentary rocks?
 Name: 1) Which diagram best shows the grain size of some common sedimentary rocks? 1663-1 - Page 1 5) The flowchart below illustrates the change from melted rock to basalt. 2) Which processes most likely
Name: 1) Which diagram best shows the grain size of some common sedimentary rocks? 1663-1 - Page 1 5) The flowchart below illustrates the change from melted rock to basalt. 2) Which processes most likely
Which rock is shown? A) slate B) dunite C) gneiss D) quartzite
 1. Which metamorphic rock will have visible mica crystals and a foliated texture? A) marble B) quartzite C) schist D) slate 2. The recrystallization of unmelted material under high temperature and pressure
1. Which metamorphic rock will have visible mica crystals and a foliated texture? A) marble B) quartzite C) schist D) slate 2. The recrystallization of unmelted material under high temperature and pressure
YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO... (by Charles Burrows)
 YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO... (by Charles Burrows) COMPOSITION OF THE EARTH S CRUST 1. Identify the characteristics of matter. 2. Explain the importance of chemical bonds. 3. Identify the characteristics of
YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO... (by Charles Burrows) COMPOSITION OF THE EARTH S CRUST 1. Identify the characteristics of matter. 2. Explain the importance of chemical bonds. 3. Identify the characteristics of
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
1) What is the theory of plate tectonics? a. The lithosphere (top layer) floats on top of the partially molten layer under it (asthenosphere).
 1) What is the theory of plate tectonics? a. The lithosphere (top layer) floats on top of the partially molten layer under it (asthenosphere). Convection currents underneath are the main cause for the
1) What is the theory of plate tectonics? a. The lithosphere (top layer) floats on top of the partially molten layer under it (asthenosphere). Convection currents underneath are the main cause for the
Weather Final Review Page 1
 Weather Final Review Name 1. Which change would cause a decrease in the amount of insolation absorbed at Earths surface? A) a decrease in cloud cover B) a decrease in atmospheric transparency C) an increase
Weather Final Review Name 1. Which change would cause a decrease in the amount of insolation absorbed at Earths surface? A) a decrease in cloud cover B) a decrease in atmospheric transparency C) an increase
Which sample best shows the physical properties normally associated with regional metamorphism? (1) A (3) C (2) B (4) D
 1 Compared to felsic igneous rocks, mafic igneous rocks contain greater amounts of (1) white quartz (3) pink feldspar (2) aluminum (4) iron 2 The diagram below shows how a sample of the mineral mica breaks
1 Compared to felsic igneous rocks, mafic igneous rocks contain greater amounts of (1) white quartz (3) pink feldspar (2) aluminum (4) iron 2 The diagram below shows how a sample of the mineral mica breaks
117 Ways to Pass the Earth Science Regents
 117 Ways to Pass the Earth Science Regents 1. The same substance always has the same density 2. As pressure increases, density increases 3. As temperature increases, density decreases 6. Water is most
117 Ways to Pass the Earth Science Regents 1. The same substance always has the same density 2. As pressure increases, density increases 3. As temperature increases, density decreases 6. Water is most
The rock probably formed 200million years ago. The mineral sample is purple.
 Midterm Study Guide 1) Intro to Earth Science (Chapters 1& 2) a) Fact (observation) vs. Inference (assumption/hypothesis) Recognize whether a statement is a fact or an inference. For example: The rock
Midterm Study Guide 1) Intro to Earth Science (Chapters 1& 2) a) Fact (observation) vs. Inference (assumption/hypothesis) Recognize whether a statement is a fact or an inference. For example: The rock
Earth Space EOC Review Test #1
 Earth Space EOC Review Test #1 NAME: Use test for questions 1 and 2 Jack studied the effects of light pollution on turtles and their offspring. He observed that areas with a high amounts of light pollution
Earth Space EOC Review Test #1 NAME: Use test for questions 1 and 2 Jack studied the effects of light pollution on turtles and their offspring. He observed that areas with a high amounts of light pollution
Earth Science Physical Setting Relationship Review Sketch all graphs in pencil. Density. Average Temperature. Gravitational Force.
 except water Water For a uniform material For a uniform material Volume (cm3) 0 4 10 Volume (cm3) ( C) Altitude of Polaris Average Gradient 0 4 5 90 0 4 5 90 Distance Between Isolines Latitude ( N) Latitude
except water Water For a uniform material For a uniform material Volume (cm3) 0 4 10 Volume (cm3) ( C) Altitude of Polaris Average Gradient 0 4 5 90 0 4 5 90 Distance Between Isolines Latitude ( N) Latitude
Version 1 Page 1 Barnard/George/Ward
 The Great Mineral & Rock Test 1. Base your answer to the following question on the table below which provides information about the crystal sizes and the mineral compositions of four igneous rocks, A,
The Great Mineral & Rock Test 1. Base your answer to the following question on the table below which provides information about the crystal sizes and the mineral compositions of four igneous rocks, A,
2/22/ Atmospheric Characteristics
 17.1 Atmospheric Characteristics Atmosphere: the gaseous layer that surrounds the Earth I. In the past, gases came from volcanic eruptions A. Water vapor was a major component of outgassing B. Other gases
17.1 Atmospheric Characteristics Atmosphere: the gaseous layer that surrounds the Earth I. In the past, gases came from volcanic eruptions A. Water vapor was a major component of outgassing B. Other gases
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Identify and explain monthly patterns in the phases of the Moon.
 (NGSS in Parentheses) Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards The phases of the Moon are caused by the orbit of the moon around the Earth. (ESS1.A) The phases
(NGSS in Parentheses) Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards The phases of the Moon are caused by the orbit of the moon around the Earth. (ESS1.A) The phases
Earth Science Physical Setting Relationship Review Sketch all graphs in pencil For a uniform material. Density. Average Temperature
 except water Water For a uniform material Volume For a uniform material Volume (cm3) 0 4 10 Volume (cm3) ( C) 0 4 5 90 0 4 5 90 Distance Between Isolines Latitude ( N) Latitude ( N) Number of Isolines
except water Water For a uniform material Volume For a uniform material Volume (cm3) 0 4 10 Volume (cm3) ( C) 0 4 5 90 0 4 5 90 Distance Between Isolines Latitude ( N) Latitude ( N) Number of Isolines
UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
 UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE After Unit 12 you should be able to: o Effectively use the charts Average Chemical Composition of Earth s Crust, Hydrosphere and Troposphere, Selected Properties of Earth
UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE After Unit 12 you should be able to: o Effectively use the charts Average Chemical Composition of Earth s Crust, Hydrosphere and Troposphere, Selected Properties of Earth
3. The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth as viewed from above the North Pole.
 1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision Sheet. Grade
 Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Climate versus Weather
 Climate versus Weather What is climate? Climate is the average weather usually taken over a 30-year time period for a particular region and time period. Climate is not the same as weather, but rather,
Climate versus Weather What is climate? Climate is the average weather usually taken over a 30-year time period for a particular region and time period. Climate is not the same as weather, but rather,
Earth Science final exam study guide (Semester 2)
 Earth Science final exam study guide (Semester 2) Chapter 22: astronomy, sun-earth-moon system Define the following vocabulary and answer the questions that follow Earth-Sun-Moon 1. Define nebula: 2. Identify
Earth Science final exam study guide (Semester 2) Chapter 22: astronomy, sun-earth-moon system Define the following vocabulary and answer the questions that follow Earth-Sun-Moon 1. Define nebula: 2. Identify
8 th Grade Science Tutoring. Earth Space, Ms. Winkle
 8 th Grade Science Tutoring Earth Space, Ms. Winkle List of Topics PART ONE Atoms, molecules, elements, mixtures, compounds Density Physical vs chemical changes Weathering, Erosion, Deposition (include
8 th Grade Science Tutoring Earth Space, Ms. Winkle List of Topics PART ONE Atoms, molecules, elements, mixtures, compounds Density Physical vs chemical changes Weathering, Erosion, Deposition (include
Practice Test Rocks and Minerals. Name. Page 1
 Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
The Atmosphere. All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere
 The Atmosphere Structure/Layers Contains 4 major layers See E.S.R.T pg 14 o Troposphere All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere o Stratosphere Contains
The Atmosphere Structure/Layers Contains 4 major layers See E.S.R.T pg 14 o Troposphere All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere o Stratosphere Contains
2. What are the four most common gasses in the atmosphere and their percentages?
 Meteorology Review Directions: Answer the following open ended review questions. Utilize a diagram where appropriate and do make sure that you label and describe the drawing. Atmospheric Composition 1.
Meteorology Review Directions: Answer the following open ended review questions. Utilize a diagram where appropriate and do make sure that you label and describe the drawing. Atmospheric Composition 1.
Formative Test. 4 th Grading in Science VII
 Formative Test 4 th Grading in Science VII I. Latitude and Longitude 1. It is an imaginary line that divides the northern and southern hemispheres. A. Latitude B. Equator C. Longitude D. Tropic of Cancer
Formative Test 4 th Grading in Science VII I. Latitude and Longitude 1. It is an imaginary line that divides the northern and southern hemispheres. A. Latitude B. Equator C. Longitude D. Tropic of Cancer
Objective 3: Earth and Space Systems
 Name Class Period: Objective 3: Earth and Space Systems 1. The diagram above shows the orbit of the moon around Earth. At which point in the moon s orbit will a person standing on Earth see a waxing crescent
Name Class Period: Objective 3: Earth and Space Systems 1. The diagram above shows the orbit of the moon around Earth. At which point in the moon s orbit will a person standing on Earth see a waxing crescent
The Atmosphere. Characteristics of the Atmosphere. Section 23.1 Objectives. Chapter 23. Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science. Section 1
 The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
Study Guide for Earth Science Final 11-12
 Study Guide for Earth Science Final 11-12 SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. What are the steps involved in the scientific method? 2. What is a control? 3. What is the difference between an independent and dependent
Study Guide for Earth Science Final 11-12 SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. What are the steps involved in the scientific method? 2. What is a control? 3. What is the difference between an independent and dependent
Chapter 3 Packet. and causes seasons Earth tilted at 23.5 / 365 1/4 days = one year or revolution
 Name Chapter 3 Packet Sequence Section 1 Seasons and Weather : and causes seasons Earth tilted at 23.5 / 365 1/4 days = one year or revolution solstice - begins summer in N. hemisphere, longest day winter
Name Chapter 3 Packet Sequence Section 1 Seasons and Weather : and causes seasons Earth tilted at 23.5 / 365 1/4 days = one year or revolution solstice - begins summer in N. hemisphere, longest day winter
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS. Subtitle
 THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
astronomy A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
Weather and Climate A B1
 Weather and Climate A B1 1. What causes the Coriolis effect? (1) Earth s tilt on its axis (2) the spin of Earth on its axis (3) the orbital motion of the Moon around Earth (4) the orbital motion of Earth
Weather and Climate A B1 1. What causes the Coriolis effect? (1) Earth s tilt on its axis (2) the spin of Earth on its axis (3) the orbital motion of the Moon around Earth (4) the orbital motion of Earth
8 th Grade Science. Reporting Category 3 STAAR
 8 th Grade Science Reporting Category 3 STAAR Which letter on the model illustrates rotation on an axis? This length of time takes one day. Which letter on the model illustrates a revolution around the
8 th Grade Science Reporting Category 3 STAAR Which letter on the model illustrates rotation on an axis? This length of time takes one day. Which letter on the model illustrates a revolution around the
The Atmosphere - Chapter Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Answers. Rocks. Year 8 Science Chapter 8
 Answers Rocks Year 8 Science Chapter 8 p171 1 Rocks are made up of minerals such as quartz, feldspars, micas, and calcite. Different rocks are made up of different combinations of minerals. 2 Igneous,
Answers Rocks Year 8 Science Chapter 8 p171 1 Rocks are made up of minerals such as quartz, feldspars, micas, and calcite. Different rocks are made up of different combinations of minerals. 2 Igneous,
B) color B) Sediment must be compacted and cemented before it can change to sedimentary rock. D) igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks
 1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
RR#4 - Multiple Choice
 1. The map below shows the amount of snowfall, in inches, produced by a lake-effect snowstorm in central New York State. The wind that produced this snowfall pattern most likely came from the 1) northeast
1. The map below shows the amount of snowfall, in inches, produced by a lake-effect snowstorm in central New York State. The wind that produced this snowfall pattern most likely came from the 1) northeast
MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)
 MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) 1. Which graph best represents the effect that heating has on air density in the atmosphere? 2. An empty 250-milliliter beaker has a
MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) 1. Which graph best represents the effect that heating has on air density in the atmosphere? 2. An empty 250-milliliter beaker has a
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #9 ROCK IDENTIFICATION
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #9 ROCK IDENTIFICATION **NOTE TO TEACHERS: THIS LAB CAN BE DONE AS ONE BIG LAB OR DIVIDED INTO THREE SEPARATE LABS (9A, 9B, AND 9C)** INTRODUCTION The three main types
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #9 ROCK IDENTIFICATION **NOTE TO TEACHERS: THIS LAB CAN BE DONE AS ONE BIG LAB OR DIVIDED INTO THREE SEPARATE LABS (9A, 9B, AND 9C)** INTRODUCTION The three main types
Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere
 14. Day Breezes H L Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere Questions Pages 177 179 1. (3) 2. (4) 3. (4) 4. (3) 5. (2) 6. (3) 7. (2) 8. (2) 9. (3) 10. (1) 11. (4) 12. (2) Questions Pages 186 188 13. (3)
14. Day Breezes H L Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere Questions Pages 177 179 1. (3) 2. (4) 3. (4) 4. (3) 5. (2) 6. (3) 7. (2) 8. (2) 9. (3) 10. (1) 11. (4) 12. (2) Questions Pages 186 188 13. (3)
Astronomy Review. Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4.
 Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
1. Base your answer to the following question on on the photographs and news article below. Old Man s Loss Felt in New Hampshire
 UNIT 3 EXAM ROCKS AND MINERALS NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on on the photographs and news article below. Old Man s Loss Felt in New Hampshire FRANCONIA, N.H. Crowds
UNIT 3 EXAM ROCKS AND MINERALS NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on on the photographs and news article below. Old Man s Loss Felt in New Hampshire FRANCONIA, N.H. Crowds
A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at different times in August.
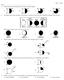 Name: 1) Which weather station model indicates the highest relative humidity? 8605-1 - Page 1 A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at
Name: 1) Which weather station model indicates the highest relative humidity? 8605-1 - Page 1 A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) What is the approximate density of a mineral with a mass of 262.2 grams that displaces 46 cubic centimeters of water? A) 6.1 g/cm 3 C) 1.8 g/cm 3 B) 5.7 g/cm 3 D) 12.2 g/cm 3 2) In which two Earth
Name: 1) What is the approximate density of a mineral with a mass of 262.2 grams that displaces 46 cubic centimeters of water? A) 6.1 g/cm 3 C) 1.8 g/cm 3 B) 5.7 g/cm 3 D) 12.2 g/cm 3 2) In which two Earth
The map shows ocean currents in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Which location most likely has the warmest climate?
 6 th Grade Final Exam Study Guide 1. Use the map below to answer this question. The map shows ocean currents in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Which location most likely has the warmest climate? 2. Daylight
6 th Grade Final Exam Study Guide 1. Use the map below to answer this question. The map shows ocean currents in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Which location most likely has the warmest climate? 2. Daylight
The Cycling of Matter. Day 1
 The Cycling of Matter Day 1 Objective I will learn the rock cycle is the series of processes in which rock changes from one form to another. I will learn in the water cycle, water condenses, precipitates
The Cycling of Matter Day 1 Objective I will learn the rock cycle is the series of processes in which rock changes from one form to another. I will learn in the water cycle, water condenses, precipitates
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS
 UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS REFER TO CHAPTER 2 IN YOUR MANUAL
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Section: Pre-Lab and Introduction to Physical Properties of Rocks Assignment for: Common Rocks (Chapter 2) For this assignment, you will require:
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Section: Pre-Lab and Introduction to Physical Properties of Rocks Assignment for: Common Rocks (Chapter 2) For this assignment, you will require:
Week: Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: EVEN Period: Week: 28 30 Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2 O 3 E *Vocabulary *Water in the Atmosphere and Clouds Notes *Cloud Drawings
clementaged.weebly.com Name: EVEN Period: Week: 28 30 Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2 O 3 E *Vocabulary *Water in the Atmosphere and Clouds Notes *Cloud Drawings
MASTERY ASSIGNMENT 2015
 Climate & Meteorology MASTERY ASSIGNMENT 2015 Directions: You must submit this document via Google Docs to lzimmerman@wcpss.net. The document must include the questions and pictures must be hand drawn
Climate & Meteorology MASTERY ASSIGNMENT 2015 Directions: You must submit this document via Google Docs to lzimmerman@wcpss.net. The document must include the questions and pictures must be hand drawn
C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increase.
 1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way.
 Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way. All rocks fit into one of three categories: Igneous- formed by the cooling and hardening of hot molten rock Sedimentary- formed
Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way. All rocks fit into one of three categories: Igneous- formed by the cooling and hardening of hot molten rock Sedimentary- formed
2 Igneous Rock. How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture of igneous rock? BEFORE YOU READ. Rocks: Mineral Mixtures
 CHAPTER 4 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
CHAPTER 4 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
Evolution of the Earth
 Evolution of the Earth http://static.newworldencyclopedia.org/f/fe/geologic_clock.jpg Evolution of the Earth Solar system, 4.6 byr Collapse of a nebula Star forms as gravity concentrates material at center
Evolution of the Earth http://static.newworldencyclopedia.org/f/fe/geologic_clock.jpg Evolution of the Earth Solar system, 4.6 byr Collapse of a nebula Star forms as gravity concentrates material at center
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars
 Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
Amazing Earth Science Facts. Scientific Investigation Facts. 1. Density = mass/volume The S.I. units for Density are: grams/cm 3
 Amazing Earth Science Facts Scientific Investigation Facts 1. Density = mass/volume The S.I. units for Density are: grams/cm 3 or g/ml 2. Volume for irregular shaped objects is found by water displacement.
Amazing Earth Science Facts Scientific Investigation Facts 1. Density = mass/volume The S.I. units for Density are: grams/cm 3 or g/ml 2. Volume for irregular shaped objects is found by water displacement.
L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment
 Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
RR#7 - Multiple Choice
 1. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? 1) hematite 2) fluorite 3) galena 4) talc 2. Which rock is composed of the mineral halite that formed when seawater evaporated? 1) limestone 2) dolostone
1. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? 1) hematite 2) fluorite 3) galena 4) talc 2. Which rock is composed of the mineral halite that formed when seawater evaporated? 1) limestone 2) dolostone
Fluid Circulation Review. Vocabulary. - Dark colored surfaces absorb more energy.
 Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
Solar System Glossary. The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting
 Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
b. The boundary between two different air masses is called a.
 NAME Earth Science Weather WebQuest Part 1. Air Masses 1. Find out what an air mass is. http://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/airmasses.html a. What is an air mass? An air mass is b. The boundary
NAME Earth Science Weather WebQuest Part 1. Air Masses 1. Find out what an air mass is. http://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/airmasses.html a. What is an air mass? An air mass is b. The boundary
Rocks. Rocks are composed of 1 or more minerals. Rocks are classified based on how they formed (origin). 3 classes of rocks:
 ROCKS Rocks If a mineral is a naturally occurring homogeneous solid, inorganically formed, with a definite chemical composi:on and a crystalline structure then what is a rock? Rocks Rocks are composed
ROCKS Rocks If a mineral is a naturally occurring homogeneous solid, inorganically formed, with a definite chemical composi:on and a crystalline structure then what is a rock? Rocks Rocks are composed
Syosset High School Midterm Review
 Mass (g) Romano Name Syosset High School Midterm Review Topic 1 - Measurement and Graphing 1. As the temperature of a body of air increases, its density and the air will. (increases, decreases, remains
Mass (g) Romano Name Syosset High School Midterm Review Topic 1 - Measurement and Graphing 1. As the temperature of a body of air increases, its density and the air will. (increases, decreases, remains
Give me one example of: Benthos. Diagram Upwelling. Explain a Convection Cell. What does it mean to have a high albedo?
 The surface will reflect a lot of the sun s radiation. What does it mean to have a high albedo? Warmer, less dense materials rise while cooler more dense materials sink. Explain a Convection Cell What
The surface will reflect a lot of the sun s radiation. What does it mean to have a high albedo? Warmer, less dense materials rise while cooler more dense materials sink. Explain a Convection Cell What
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres Pressure Composition Greenhouse effect Atmospheric structure Color of the sky 1 Atmospheres
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres Pressure Composition Greenhouse effect Atmospheric structure Color of the sky 1 Atmospheres
Rock Identification Lab, 60 Points This is a BIG lab! Work carefully and thoroughly
 Rock Identification Lab, 60 Points This is a BIG lab! Work carefully and thoroughly Name: Date: Period: Lab Skills and Objectives 1. You will examine, classify, and identify several samples of igneous,
Rock Identification Lab, 60 Points This is a BIG lab! Work carefully and thoroughly Name: Date: Period: Lab Skills and Objectives 1. You will examine, classify, and identify several samples of igneous,
Example Quiz on Earthquakes
 Example Quizzes, Tests, and Review Information A Example Quiz on Earthquakes Quizzes such as this one are given at the beginning of each lab. 1. The point beneath the Earth s surface at which an earthquake
Example Quizzes, Tests, and Review Information A Example Quiz on Earthquakes Quizzes such as this one are given at the beginning of each lab. 1. The point beneath the Earth s surface at which an earthquake
Rocks are made from Minerals
 Rocks and Minerals Rocks are made from Minerals Rocks are nothing more than a mixture of different mineral crystals. ***All three minerals are combined in a Granite rock Granite Quartz + Biotite + Feldspar
Rocks and Minerals Rocks are made from Minerals Rocks are nothing more than a mixture of different mineral crystals. ***All three minerals are combined in a Granite rock Granite Quartz + Biotite + Feldspar
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather
 Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Weather Notes. Chapter 16, 17, & 18
 Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Chapter 10. Chapter Rocks and the Rock Cycle. Rocks. Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Earth/Space Honors EOC Pacing Guide
 Lesson Vocabulary NGSSS Minerals Understand the physical and chemical properties that define and identify a mineral. Chemical formula Luster Cleavage Fracture Hardness Streak Specific gravity Solid Inorganic
Lesson Vocabulary NGSSS Minerals Understand the physical and chemical properties that define and identify a mineral. Chemical formula Luster Cleavage Fracture Hardness Streak Specific gravity Solid Inorganic
Ocean s Influence on Weather and Climate
 Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Earth Moon Motions A B1
 Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Earth Science. Explain how Earth's biogeochemical cycles create a balance of materials. Examine the importance of biogeochemical cycles.
 Unit 1: DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF EARTH Introduction to Understand that earth science is based upon the four sciences of astronomy, geology, meteorology, and oceanography. Identify topics studied within the
Unit 1: DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF EARTH Introduction to Understand that earth science is based upon the four sciences of astronomy, geology, meteorology, and oceanography. Identify topics studied within the
Apparent Motion. How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky?
 Apparent Motion How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky? 1 Apparent Motions Geocentric Universe - idea that Earth was at the center of the solar system Stars all rotate around the Earth
Apparent Motion How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky? 1 Apparent Motions Geocentric Universe - idea that Earth was at the center of the solar system Stars all rotate around the Earth
EARTH SCIENCE REVIEW. Name:
 EARTH SCIENCE REVIEW Name: 1 Topic 1: Earth s Dimensions: Layers of the Earth, Latitude/Longitude, Contour Maps (ESRT p 14, 15) Layers of Earth Lithosphere Solid (made of crust and rigid mantle) Oxygen
EARTH SCIENCE REVIEW Name: 1 Topic 1: Earth s Dimensions: Layers of the Earth, Latitude/Longitude, Contour Maps (ESRT p 14, 15) Layers of Earth Lithosphere Solid (made of crust and rigid mantle) Oxygen
