MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)
|
|
|
- Ruth Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) 1. Which graph best represents the effect that heating has on air density in the atmosphere? 2. An empty 250-milliliter beaker has a mass of 50 grams. When 100 milliliters of a liquid is added to the beaker, the total mass is 140 grams. The density of the liquid is approximately (1) 1.7 g/ml (3) 0.9 g/ml (2) 1.4 g/ml (4) 0.6 g/ml The diagrams represent two different samples of the same type of solid material, both at sea level atmospheric pressure and both at the same temperature. 3. What is the approximate density of sample A, if its mass is 34 grams? (1) 1.25 g/cm 3 (3) 0.8 g/cm 3 (2) 2.0 g/cm 3 (4) 9.0 g/cm 3 4. The density of a mineral is found to be 1.50 grams per cubic centimeter. If the accepted value is 2.00 grams per cubic centimeter, the percent deviation (percent error) is (1) 25.0% (3) 40.0% (2) 33.3% (4) 50.0% 5. As viewed from the Earth, the Moon's phases have shown which type of changes over the past 50 years? (1) noncyclic and predictable (3) noncyclic and unpredictable (2) cyclic and predictable (4) cyclic and unpredictable 6. Which line best identifies the interface between the hydrosphere and the troposphere? (1) line A (2) line B (3) line C (4) line D
2 Use the graph to the right to answer questions 7 and The water temperature reached 50 C after the sample had been heated for approximately (1) 4 minutes (3) 6 minutes (2) 4.5 minutes (4) 6.5 minutes 8. Between which letters was water evaporating? (1) A and B (3) C and D (2) B and C (4) D and E 9. On the Generalized Bedrock Geology Map of New York State, what similar pattern is found at North latitude by 77 30' West longitude? 10. Which diagram best shows the altitude and direction of Polaris for an observer in New York City? 11. An observer on a moving ship notices that the altitude of Polaris increases each night. Local solar noon occurs at the same time each day. In what direction is the ship moving? (1) due east (3) due west (2) due south (4) due north 12. What do the tropopause, stratopause, and mesopause all have in common? (1) Each is an interface between two layers of the atmosphere. (2) Each is a point of maximum temperature in its layer of the atmosphere. (3) Each is a zone of decreasing water vapor content within the atmosphere. (4) Each is a region of increasing pressure within the atmosphere. 13. If atmospheric pressure measurements were taken at regular intervals from sea level to the stratopause, the measurements would most likely show that the pressure (1) decreases, only (2) increases, only (3) remains the same (4) decreases, then increases
3 Base your answers to questions on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the diagram of the Earth below, and your knowledge of earth science. Some of the latitude and longitude lines have been labeled. Points A through E represent locations on the Earth's surface. 14. What are the approximate latitude and longitude of location A? (1) 105 N, 25 W (3) 25 N, 105 E (2) 25 N, 105 W (4) 105 S, 25 E 15. What do locations A, B, and E have in common? (1) They are in the same season. (2) They have the same local time. (3) They have the same prevailing wind direction. (4) They are at the same latitude. 16. The latitude and longitude of which location are closest to those of New York State? 17. What is the approximate time at location D? (1) 6 a. m. (3) 6 p.m. (2) noon (4) midnight 18. What is the altitude of Polaris as viewed from location B? (1) 30 o (3) 60 o (2) 40 o (4) 100 o 19. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe began as an explosion and is still expanding. This theory is supported by observations that the stellar spectra of distant galaxies show a (1) concentration in the yellow portion of the spectrum (2) concentration in the green portion of the spectrum (3) shift toward the blue end of the spectrum (4) shift toward the red end of the spectrum 20. Compared to the Sun, a white dwarf star is (1) hotter and larger (3) cooler and larger (2) hotter and smaller (4) cooler and smaller
4 21. What factor determines whether a star will evolve into a white dwarf, a neutron star, or a black hole? (1) mass (3) percentage of carbon (2) percentage of helium (4) apparent brightness 22. The average temperature of the planets (1) increases with greater distance from the Sun (2) decreases with greater distance from the Sun (3) has no relationship to the distance from the Sun (4) depends only on the chemical composition of the atmosphere of each planet 23. Why do stars appear to move through the night sky at the rate of 15 degrees per hour? (1) The Earth actually moves around the Sun at a rate of 15 per hour. (2) The stars actually move around the center of the galaxy at a rate of 15 per hour. (3) The Earth actually rotates at a rate of 15 per hour. (4) The stars actually revolve around the Earth at a rate of 15 per hour. 24. Which diagram best represents the motions of celestial objects in a heliocentric model? 25. The gravitational attraction between the Earth and the Sun is greatest at the time when the (1) Earth is moving slowest in its orbit (2) Earth is moving fastest in its orbit (3) Northern Hemisphere is receiving maximum intensity of insolation (4) Northern Hemisphere is receiving maximum duration of insolation Use the diagram below to answer questions 26 through 28. The diagram below represents a model of the Sun's apparent path across the sky in New York State for selected dates. 26. For which path would daylight hours be greatest? 27. Which path could represent the apparent path of the Sun as seen on an equinox in New York State? 28. For which path would the noontime Sun create the longest shadows for objects on the surface of the Earth in this location?
5 Base your answers to questions 29 through 31 on your knowledge of Earth Science and on the diagram below. The diagram represents the Earth at a specific time in its orbit with dash lines indicating radiation from the Sun and points A through H, locations on the Earth's surface. 29. What is the season in the Northern Hemisphere when the Earth is in the position shown in the diagram? (1) spring (3) fall (2) summer (4) winter 30. When the Sun is in the position shown in the diagram, how many hours of daylight would occur at the North Pole during one complete rotation? (1) 0 (3) 12 (2) 8 (4) Which latitude would be receiving the most direct rays of the Sun? (1) the Equator (3) the Tropic of Cancer (2) the North Pole (4) the Tropic of Capricorn Base your answers to questions on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the diagram below, and your knowledge of Earth Science, The diagram shows the system of star Alpha and planet X, Points A, B, C, and D indicate four orbital positions of planet X. 32. At which position does planet X travel fastest? 33. Which graph shows the star's apparent diameter, as viewed from planet X?
6 Base your answers to questions on the diagram below. The diagram is a model of the orbit of an imaginary planet Q around a star. Points A, B, C, and D indicate four orbital positions of planet Q. 34. What is the approximate eccentricity of planet Q's orbit? (1) 0.06 (3) 0.67 (2) 0.15 (4) How would a scale drawing of the Earth's orbit around the Sun compare to the drawing shown of planet Q's orbit? (1) Earth's orbit would appear to have a more circular shape than planet Q's. (2) Earth's orbit would appear to have a more eccentric shape than planet Q's. (3) Earth's orbit would appear to be the same shape as planet Q's. 36. Some stars that can be seen in New York State on a summer night cannot be seen on a winter night. This fact is a result of the (1) rotation of the Earth on its axis (2) rotation of the stars around Polaris (3) revolution of Polaris around the Earth (4) revolution of the Earth around the Sun 37. The Foucault pendulum provides evidence that the Earth (1) rotates on its axis (3) revolves around the Sun (2) has a spherical shape (4) is inclined on its axis 38. What causes the Coriolis Effect? (1) high and low-pressure belts (3) the Earth's revolution (2) the equatorial calms (4) the Earth's rotation 39. Which real motion causes the Sun to appear to rise in the east and set in the west? (1) the Sun's revolution (3) the Earth's revolution (2) the Sun's rotation (4) the Earth's rotation The diagram represents a side view of the Milky Way Galaxy. 40. At approximately which position is Earth s Solar System located?
7 Base your answers to questions on the diagram below. The diagram represents the Moon in various positions in its orbit around the Earth. Letters A through E represent five of the Moon's positions. 41. The Moon would not be visible from Earth when the Moon is at position (2) E (4) D 42. Which diagram best represents the appearance of the Moon to an observer on the Earth when the Moon is at position B? 43. Why would an observer on Earth see a complete cycle of phases of the Moon in approximately 1 month? 1 The Moon rotates on its axis. 2 The Moon revolves around the Earth. 3 The Earth rotates on its axis. 4 The Earth revolves around the Sun. 44. A spring tide would be experienced on Earth when the Moon is located at position (2) B (4) E 45. A solar eclipse could be viewed on Earth when the Moon is located at position 46. The process by which energy can travel through outer space is known as (1) absorption (3) convection (2) conduction (4) radiation 47. Infrared, ultraviolet, and visible light are all part of the solar spectrum. The basic difference between them is their (1) wavelength (3) source (2) speed (4) temperature 48. Which substance will heat up the quickest? (1) 1 gram of liquid water (3) 1 gram of basalt (2) 1 gram of iron (4) 1 gram of granite
8 49. The energy gained by water during evaporation is later released by the water during the process of (1) transpiration (3) melting (2) convection (4) condensation Directions: Base your answers to the questions on your knowledge of earth science and on the diagram below. The diagram represents a temperature field for a vertical cross section of a room from ceiling to floor with points A -H at different locations within the room. 50. What is the temperature at point B? (1) 10 C (3) 20 C (2) 16 C (4) 28 C 51. At which point would the air have the least density? (1) A (3) H (2) E (4) D 52. If a heat source is located at point A, which diagram best represents the probable direction of air movement in this room? 53. Heat energy will circulate through the air in the room by the process of (1) absorption (3) convection (2) conduction (4) radiation 54. The diagram below shows temperature values at various points in a solid piece of aluminum. Toward which point will heat flow from point P? (1) A (2) B (3) C (4) D
9 55. A temperature of 104 o F is equal to a temperature of (1) 40 o C (2) 72 o C (3) 104 o C (4) 136 o C Base your answers to questions on your knowledge of Earth Science and the diagram below which represents a temperature field map of the air near the ceiling of a room. The letters represent points in the field. 56. The most likely direction of heat flow is from (1) F to A (3) C to E (2) B to D (4) E to F 57. The greatest temperature gradient exists between (1) A and D (3) C and E (2) B and D (4) E and F 58. The average temperature gradient between points x and y is closest to (1) 0.5 degree per meter (3) 3.0 degrees per meter (2) 2.0 degrees per meter (4) 1.5 degrees per meter 59. Which graph best represents the temperature change along the isotherm from point F to point A? 60. In general, good absorbers of electromagnetic energy are also good (1) refractors (3) reflectors (2) radiators (4) convectors 61. Which form of electromagnetic energy is radiated from Earth s surface with the greatest intensity? (1) X-rays (3) ultraviolet rays (2) infrared rays (4) visible light rays
10 Base your answers to questions on the diagram and data below. The diagram represents a closed glass greenhouse. The data table shows the air temperatures inside and outside the greenhouse from 6 a.m. to 6 p.m. on a particular day. 62. The highest temperature was recorded at (1) 12 noon outside the greenhouse (3) 12 noon inside the greenhouse (2) 2 p.m. outside the greenhouse (4) 2 p.m. inside the greenhouse 63. By which process does air circulate inside the greenhouse due to differences in air temperature and air density? (1) absorption (3) convection (2) radiation (4) conduction 64. Several objects made of the same material, but with different surface characteristics, are tested in the greenhouse to determine which object will absorb the most sunlight. The object that absorbs the most sunlight most likely has a surface that is (1) dark-colored and smooth (3) light-colored and smooth (2) dark-colored and rough (4) light-colored and rough 65. Which statement best explains what happens to the insolation reaching the greenhouse? (1) Most of the insolation is absorbed by the glass. (2) All of the insolation is reflected by the glass. (3) Insolation absorbed inside the greenhouse is reradiated as longer wavelengths. (4) Insolation absorbed inside the greenhouse is reradiated as shorter wavelengths. 66. At approximately what rate did the temperature rise inside the greenhouse between 8 a.m. and 10 a.m.? (1) 1.0 o C/hr (3) 0.5 o C/hr (2) 2.0 o C/hr (4) 12.0 o C/hr 67. Infrared radiation is absorbed in the atmosphere mainly by (1) nitrogen and oxygen (2) argon and radon (3) ice crystals and water vapor (4) carbon dioxide and water vapor 68. Which statement describes how the insolation changes in New York State from May 21 to June 21? (1) The intensity and duration of insolation both decrease. (2) The intensity and duration of insolation both increase. (3) The intensity of insolation decreases and duration of insolation increases. (4) The intensity of insolation increases and duration of insolation decreases.
11 69. Compared to polar areas, why are equatorial areas of equal size heated much more intensely by the Sun? (1) The Sun s rays are more nearly perpendicular at the Equator than at the poles. (2) The equatorial areas contain more water than the polar areas do. (3) More hours of daylight occur at the Equator than at the poles. (4) The equatorial areas are nearer to the Sun than the polar areas are. The activity shown in the diagram below was used to test the effect of the angle of insolation on temperature. A student place four thermometers (A, B, C, and D) on a large globe. The bulb of each thermometer was placed against a black plastic square directly on a line representing latitude. The thermometers were then exposed to direct sunlight for 10 minutes at the angles shown. 70. Which thermometer will show the greatest increase in temperature? 71. Ozone gas in the Earth s atmosphere helps to protect life on the Earth. This protection is due to the ability of ozone to absorb (1) radio waves (3) gamma radiation (2) ultraviolet radiation (4) visible radiation 72. Which layer of the atmosphere has the smallest distance from the bottom to the top of its zone? (1) troposphere (3) mesosphere (2) stratosphere (4) thermosphere 73. What is the most abundant element in the troposphere? (1) helium (3) hydrogen (2) nitrogen (4) oxygen 74. The temperature of the stratosphere ranges from approximately (1) -55 o F to 0 o F (3) 10 o F to 35 o F (2) -55 o C to 0 o C (4) 10 o C to 50 o C 75. The diagram to the right shows the flow of air over a mountain from point A to point C. Which graph best shows the approximate temperature change of the rising and descending air due to the adiabatic process?
Energy and Insolation Review 2
 Energy and Insolation Review 2 The diagram below shows a container of water that is being heated. 1. The movement of water shown by the arrows is most likely caused by (1) density differences (2) insolation
Energy and Insolation Review 2 The diagram below shows a container of water that is being heated. 1. The movement of water shown by the arrows is most likely caused by (1) density differences (2) insolation
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
1 A 3 C 2 B 4 D. 5. During which month does the minimum duration of insolation occur in New York State? 1 February 3 September 2 July 4 December
 INSOLATION REVIEW 1. The map below shows isolines of average daily insolation received in calories per square centimeter per minute at the Earth s surface. If identical solar collectors are placed at the
INSOLATION REVIEW 1. The map below shows isolines of average daily insolation received in calories per square centimeter per minute at the Earth s surface. If identical solar collectors are placed at the
Syosset High School Midterm Review
 Mass (g) Romano Name Syosset High School Midterm Review Topic 1 - Measurement and Graphing 1. As the temperature of a body of air increases, its density and the air will. (increases, decreases, remains
Mass (g) Romano Name Syosset High School Midterm Review Topic 1 - Measurement and Graphing 1. As the temperature of a body of air increases, its density and the air will. (increases, decreases, remains
astronomy A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
3. The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth as viewed from above the North Pole.
 1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
C) wavelength C) eastern horizon B) the angle of insolation is high B) increases, only D) thermosphere D) receive low-angle insolation
 1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
Which Earth latitude receives the greatest intensity of insolation when Earth is at the position shown in the diagram? A) 0 B) 23 N C) 55 N D) 90 N
 1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
4. Which object best represents a true scale model of the shape of the Earth? A) a Ping-Pong ball B) a football C) an egg D) a pear
 Name Test on Friday 1. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional shape of the Earth? A) B) C) D) Date Review Sheet 4. Which object best represents a true scale model of the shape of the Earth?
Name Test on Friday 1. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional shape of the Earth? A) B) C) D) Date Review Sheet 4. Which object best represents a true scale model of the shape of the Earth?
2/22/ Atmospheric Characteristics
 17.1 Atmospheric Characteristics Atmosphere: the gaseous layer that surrounds the Earth I. In the past, gases came from volcanic eruptions A. Water vapor was a major component of outgassing B. Other gases
17.1 Atmospheric Characteristics Atmosphere: the gaseous layer that surrounds the Earth I. In the past, gases came from volcanic eruptions A. Water vapor was a major component of outgassing B. Other gases
Midterm Review #3-2018
 1. The reaction below represents an energy-producing process. The reaction represents how energy is produced A) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere B) during nuclear decay C) from the movement of
1. The reaction below represents an energy-producing process. The reaction represents how energy is produced A) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere B) during nuclear decay C) from the movement of
Topic 5 Practice Test
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which represents the greenhouse effect in which heat energy is trapped in Earth's atmosphere 1. The Earth surface that best absorbs short-wave
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which represents the greenhouse effect in which heat energy is trapped in Earth's atmosphere 1. The Earth surface that best absorbs short-wave
3. Which color of the visible light has the shortest wavelength? A) violet B) green C) yellow D) red
 Name: Topic 6 Test 1. Which process is responsible for the greatest loss of energy from Earth's surface into space on a clear night? A) condensation B) conduction C) radiation D) convection 2. Base your
Name: Topic 6 Test 1. Which process is responsible for the greatest loss of energy from Earth's surface into space on a clear night? A) condensation B) conduction C) radiation D) convection 2. Base your
C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increase.
 1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
3. This room is located in a building in New York State. On which side of the building is the window located? (1) north (3) east (2) south (4) west
 1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE. Tarbuck Lutgens
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 17 The Atmosphere: Structure and Temperature 17.1 Atmosphere Characteristics Composition of the Atmosphere Weather is constantly changing, and it refers
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 17 The Atmosphere: Structure and Temperature 17.1 Atmosphere Characteristics Composition of the Atmosphere Weather is constantly changing, and it refers
Name Period Date 8R MIDTERM REVIEW I. ASTRONOMY 1. Most stars are made mostly of. 2. The dark, cooler areas on the sun s surface are
 Name Period Date 8R MIDTERM REVIEW I. ASTRONOMY 1. Most stars are made mostly of 2. The dark, cooler areas on the sun s surface are 3. When hydrogen nuclei fuse they form 4. Einstein s equation is 5. The
Name Period Date 8R MIDTERM REVIEW I. ASTRONOMY 1. Most stars are made mostly of 2. The dark, cooler areas on the sun s surface are 3. When hydrogen nuclei fuse they form 4. Einstein s equation is 5. The
Earth Moon Motions A B1
 Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Which table correctly shows the dates on which the apparent paths of the Sun were observed? A) B) C) D)
 1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
1. The diagram below represents the horizon and the Sun's apparent paths, A, B, and C, on three different dates, as viewed from the same location in New York State. Which table correctly shows the dates
Astronomy Review. Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4.
 Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Meteorology Pretest on Chapter 2
 Meteorology Pretest on Chapter 2 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The earth emits terrestrial radiation a) only at night b) all the time c) only during winter d) only over the continents 2. If an imbalance occurs between
Meteorology Pretest on Chapter 2 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The earth emits terrestrial radiation a) only at night b) all the time c) only during winter d) only over the continents 2. If an imbalance occurs between
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS
 UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
Chapter 2. Heating Earth's Surface & Atmosphere
 Chapter 2 Heating Earth's Surface & Atmosphere Topics Earth-Sun Relationships Energy, Heat and Temperature Mechanisms of Heat Transfer What happens to Incoming Solar Radiation? Radiation Emitted by the
Chapter 2 Heating Earth's Surface & Atmosphere Topics Earth-Sun Relationships Energy, Heat and Temperature Mechanisms of Heat Transfer What happens to Incoming Solar Radiation? Radiation Emitted by the
Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date
 Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date Base your answers to questions 1 through 5 on diagram below, which represents the Sun s apparent paths and the solar noon positions for an observer at 42 N latitude on
Name Regents Review Packet #2 Date Base your answers to questions 1 through 5 on diagram below, which represents the Sun s apparent paths and the solar noon positions for an observer at 42 N latitude on
5. In which diagram is the observer experiencing the greatest intensity of insolation? A) B)
 1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test
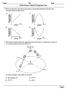 Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test 1) Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature? 2) The diagram below shows the apparent path
Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test 1) Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature? 2) The diagram below shows the apparent path
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline. Heating the Atmosphere
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline Heating the Atmosphere They are still here! Focus on the Atmosphere Weather Occurs over a short period of time Constantly changing Climate Averaged over a long period of time
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline Heating the Atmosphere They are still here! Focus on the Atmosphere Weather Occurs over a short period of time Constantly changing Climate Averaged over a long period of time
November 20, NOTES ES Rotation, Rev, Tilt.notebook. vertically. night. night. counterclockwise. counterclockwise. East. Foucault.
 NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely
 CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH
 L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH 1. The graph below shows air temperatures on a clear summer day from 7 a.m. to 12 noon at two locations, one in Florida
L.O: THE ANGLE OF INSOLATION ANGLE INSOLATION: THE ANGLE SUNLIGHT HITS THE EARTH 1. The graph below shows air temperatures on a clear summer day from 7 a.m. to 12 noon at two locations, one in Florida
Practice Seasons Moon Quiz
 1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
Energy Transfer Packet 9
 Energy Transfer Packet 9 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 2 Performance Indicator 2.2 Explain how incoming solar radiation, ocean currents, and land masses affect weather and climate.
Energy Transfer Packet 9 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 2 Performance Indicator 2.2 Explain how incoming solar radiation, ocean currents, and land masses affect weather and climate.
EARTH MOON SUN REVIEW
 1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
ATMOSPHERE PACKET CHAPTER 22 PAGES Section 1 page 546
 Name: Period: ATMOSPHERE PACKET CHAPTER 22 PAGES 546-564 Section 1 page 546 1. Identify five main components of the atmosphere 2. Explain the cause of atmospheric pressure. 3. Why is atmospheric pressure
Name: Period: ATMOSPHERE PACKET CHAPTER 22 PAGES 546-564 Section 1 page 546 1. Identify five main components of the atmosphere 2. Explain the cause of atmospheric pressure. 3. Why is atmospheric pressure
Which graph best shows the relationship between intensity of insolation and position on the Earth's surface? A) B) C) D)
 1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
D. most intense and of longest duration C. D.
 Astronomy Take Home Test Answer on a separate sheet of paper In complete sentences justify your answer Name: 1. The Moon s cycle of phases can be observed from Earth because the Moon 4. The accompanying
Astronomy Take Home Test Answer on a separate sheet of paper In complete sentences justify your answer Name: 1. The Moon s cycle of phases can be observed from Earth because the Moon 4. The accompanying
2. The diagram below represents the apparent path of the Sun as seen by an observer at 65 N on March 21.
 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
Practice Questions: Seasons #1
 1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
Most of the energy from the light sources was transferred to the sand by the process of A) conduction B) convection C) radiation D) transpiration
 1. Light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation are given off by stars using energy released during A) nuclear fusion B) conduction C) convection D) radioactive decay 2. At which temperature would
1. Light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation are given off by stars using energy released during A) nuclear fusion B) conduction C) convection D) radioactive decay 2. At which temperature would
In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. as waves. thermosphere
 Skills Worksheet Concept Review In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. layers of the atmosphere 2. radiation 3. conduction 4. convection 5.
Skills Worksheet Concept Review In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. layers of the atmosphere 2. radiation 3. conduction 4. convection 5.
EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE. 1. The graph below shows the average concentration of ozone in Earth's atmosphere over Arizona during 4 months of the year.
 EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE 1. The graph below shows the average concentration of ozone in Earth's atmosphere over Arizona during 4 months of the year. Which layer of Earth's atmosphere contains the greatest concentration
EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE 1. The graph below shows the average concentration of ozone in Earth's atmosphere over Arizona during 4 months of the year. Which layer of Earth's atmosphere contains the greatest concentration
17. According to the data below, what is the exact shape of the Earth?
 1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its molten core 2. Which diagram most accurately
1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its molten core 2. Which diagram most accurately
ATMOSPHERIC ENERGY REVIEW QUESTIONS
 1. Which process is responsible for the greatest loss of energy from Earth's surface into space on a clear night? A) condensation B) conduction C) radiation D) convection 2. Which type of land surface
1. Which process is responsible for the greatest loss of energy from Earth's surface into space on a clear night? A) condensation B) conduction C) radiation D) convection 2. Which type of land surface
COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Characteristics of the Atmosphere 1. Define atmosphere. 2. Describe two important functions served by Earth s atmosphere. COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE 3. The
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Characteristics of the Atmosphere 1. Define atmosphere. 2. Describe two important functions served by Earth s atmosphere. COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE 3. The
A) its rotation D) Sun, the Moon, and some stars C) an oblate sphere D) troposphere B) hydrosphere and troposphere B) less dense and more felsic
 1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its molten core 2. The Earth's actual shape
1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its molten core 2. The Earth's actual shape
A) usually less B) dark colored and rough D) light colored with a smooth surface A) transparency of the atmosphere D) rough, black surface
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which shows two identical houses, A and B, in a city in North Carolina. One house was built on the east side of a factory, and the other
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which shows two identical houses, A and B, in a city in North Carolina. One house was built on the east side of a factory, and the other
HEATING THE ATMOSPHERE
 HEATING THE ATMOSPHERE Earth and Sun 99.9% of Earth s heat comes from Sun But
HEATING THE ATMOSPHERE Earth and Sun 99.9% of Earth s heat comes from Sun But
Name: Midterm Practice
 Name: Midterm Practice 1. The map below shows the path of an ash cloud that resulted from the Mount St. Helens volcanic eruption. The map was developed from satellite photographs. The path of the ash cloud
Name: Midterm Practice 1. The map below shows the path of an ash cloud that resulted from the Mount St. Helens volcanic eruption. The map was developed from satellite photographs. The path of the ash cloud
RR#3- Multiple Choice
 1. Which type of land surface will most likely absorb the greatest amount of incoming solar radiation? 1) rough, dark-colored surface 2) rough, light-colored surface 3) smooth, dark-colored surface 4)
1. Which type of land surface will most likely absorb the greatest amount of incoming solar radiation? 1) rough, dark-colored surface 2) rough, light-colored surface 3) smooth, dark-colored surface 4)
The Atmosphere: Structure and Temperature
 Chapter The Atmosphere: Structure and Temperature Geologists have uncovered evidence of when Earth was first able to support oxygenrich atmosphere similar to what we experience today and more so, take
Chapter The Atmosphere: Structure and Temperature Geologists have uncovered evidence of when Earth was first able to support oxygenrich atmosphere similar to what we experience today and more so, take
drinking straw, protractor, string, and rock. observer on Earth. Sun across the sky on March 21 as seen by an
 1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
Name and Student ID Section Day/Time:
 AY2 - Overview of the Universe - Midterm #1 - Instructor: Maria F. Duran Name and Student ID Section Day/Time: 1) Imagine we ve discovered a planet orbiting another star at 1 AU every 6 months. The planet
AY2 - Overview of the Universe - Midterm #1 - Instructor: Maria F. Duran Name and Student ID Section Day/Time: 1) Imagine we ve discovered a planet orbiting another star at 1 AU every 6 months. The planet
C) D) 2. The model below shows the apparent path of the Sun as seen by an observer in New York State on the first day of one of the four seasons.
 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER)
 L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
1. The diagram below represents a Foucault pendulum that is swinging back and forth.
 1. The diagram below represents a Foucault pendulum that is swinging back and forth. Which diagram best represents the change in the motion of a Foucault pendulum that provides evidence of Earth's rotation?
1. The diagram below represents a Foucault pendulum that is swinging back and forth. Which diagram best represents the change in the motion of a Foucault pendulum that provides evidence of Earth's rotation?
Directed Reading. Section: Solar Energy and the Atmosphere RADIATION. identical point on the next wave. waves
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Solar Energy and the Atmosphere 1. How is Earth s atmosphere heated? 2. Name the two primary sources of heat in the atmosphere. RADIATION In the space provided,
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Solar Energy and the Atmosphere 1. How is Earth s atmosphere heated? 2. Name the two primary sources of heat in the atmosphere. RADIATION In the space provided,
The Universe. 3. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents the bright-line spectrum for an element.
 A) B) The Universe 1. According to the Big Bang theory, which graph hest represents the relationship between time and the size of the universe from the beginning of the universe to the present? C) D) 2.
A) B) The Universe 1. According to the Big Bang theory, which graph hest represents the relationship between time and the size of the universe from the beginning of the universe to the present? C) D) 2.
Chapter 26 Section 1 pages Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe
 Name: Period: Chapter 26 Section 1 pages 659-666 Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 2. What is the main reason people study the
Name: Period: Chapter 26 Section 1 pages 659-666 Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 2. What is the main reason people study the
The following terms are some of the vocabulary that students should be familiar with in order to fully master this lesson.
 Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
Name Period Date L.O: SWBAT DESCRIBE THE PROPERTIES OF THE ATMOSPHERE.(
 Name Period Date L.O: SWBAT DESCRIBE THE PROPERTIES OF THE ATMOSPHERE.( 1. Scientists have inferred that Earth s original atmosphere was formed by the A) outgassing from Earth s interior B) erosion of
Name Period Date L.O: SWBAT DESCRIBE THE PROPERTIES OF THE ATMOSPHERE.( 1. Scientists have inferred that Earth s original atmosphere was formed by the A) outgassing from Earth s interior B) erosion of
Explain the Big Bang Theory and give two pieces of evidence which support it.
 Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: asteroid, celestial object, comet, constellation, Doppler effect, eccentricity, eclipse, ellipse, focus, Foucault Pendulum, galaxy, geocentric model, heliocentric model,
Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: asteroid, celestial object, comet, constellation, Doppler effect, eccentricity, eclipse, ellipse, focus, Foucault Pendulum, galaxy, geocentric model, heliocentric model,
The Atmosphere. Characteristics of the Atmosphere. Section 23.1 Objectives. Chapter 23. Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science. Section 1
 The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision Sheet. Grade
 Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Energy and Seasons A B1. 9. Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature?
 Energy and Seasons A B1 1. Which type of surface absorbs the greatest amount of electromagnetic energy from the Sun? (1) smooth, shiny, and light colored (2) smooth, shiny, and dark colored (3) rough,
Energy and Seasons A B1 1. Which type of surface absorbs the greatest amount of electromagnetic energy from the Sun? (1) smooth, shiny, and light colored (2) smooth, shiny, and dark colored (3) rough,
Chapter 9 Atmosphere Study Guide
 Science Chapter 9 Atmosphere Study Guide Name Due 1. What is the definition for: a. Conduction: The transfer of thermal energy by collisions between particles in matter. (Heats air close to Earth s surface)
Science Chapter 9 Atmosphere Study Guide Name Due 1. What is the definition for: a. Conduction: The transfer of thermal energy by collisions between particles in matter. (Heats air close to Earth s surface)
Observations vs. Inferences. Density. Rate of Change / Gradient
 Observations vs. Inferences Observations: perceptions/facts that can be seen or measured with senses or instruments In addition to this review, study ALL previous TESTS, Quizzes, labs, handouts and notes.
Observations vs. Inferences Observations: perceptions/facts that can be seen or measured with senses or instruments In addition to this review, study ALL previous TESTS, Quizzes, labs, handouts and notes.
8R EARTH'S SHAPE PRACTICE
 1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
10-20 billion years old
 Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Practice Questions: Seasons #2
 1. How many degrees does the Sun appear to move across the sky in four hours? A) 60 B) 45 C) 15 D) 4 Practice Questions: Seasons #2 2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which
1. How many degrees does the Sun appear to move across the sky in four hours? A) 60 B) 45 C) 15 D) 4 Practice Questions: Seasons #2 2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which
The Atmosphere - Chapter Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Earth Motions Packet 14
 Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe
 Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Solar System Glossary. The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting
 Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice
 A) B) Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's
A) B) Regents Review Packet #2 Multiple Choice 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's
Bring pencils and a calculator. You may prepare & use 1 handwritten 4 x 6 note card.
 Name: Singler ES2 Midyear Topic Outline Midyear Date: Friday 1/19/2018 8:00 a.m. Location: Room B446 Bring pencils and a calculator. You may prepare & use 1 handwritten 4 x 6 note card. UNIT 1 Intro to
Name: Singler ES2 Midyear Topic Outline Midyear Date: Friday 1/19/2018 8:00 a.m. Location: Room B446 Bring pencils and a calculator. You may prepare & use 1 handwritten 4 x 6 note card. UNIT 1 Intro to
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
EARTHS SHAPE AND POLARIS PRACTICE 2017
 1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
1. In the diagram below, letters A through D represent the locations of four observers on the Earth's surface. Each observer has the same mass. 3. Which diagram most accurately shows the cross-sectional
A. the spinning of Earth on its axis B. the path of the Sun around Earth
 stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
Apparent Motion. How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky?
 Apparent Motion How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky? 1 Apparent Motions Geocentric Universe - idea that Earth was at the center of the solar system Stars all rotate around the Earth
Apparent Motion How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky? 1 Apparent Motions Geocentric Universe - idea that Earth was at the center of the solar system Stars all rotate around the Earth
1. The diagram below shows Earth, four different positions of the Moon, and the direction of incoming sunlight.
 G8 Semester I MCAS Pre-Test Please answer on Scantron Card; not on this test form Standard: 9 - Describe lunar and solar eclipses, the observed moon phases, and tides. Relate them to the relative positions
G8 Semester I MCAS Pre-Test Please answer on Scantron Card; not on this test form Standard: 9 - Describe lunar and solar eclipses, the observed moon phases, and tides. Relate them to the relative positions
Fluid Circulation Review. Vocabulary. - Dark colored surfaces absorb more energy.
 Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
Day, Night, Year, and Seasons
 Welcome Astronomers to the Sun, Moon, and Earth! The relationship between the Sun, Moon, and Earth is very important to the existence of life on Earth. Our quest is to find out how their relationships
Welcome Astronomers to the Sun, Moon, and Earth! The relationship between the Sun, Moon, and Earth is very important to the existence of life on Earth. Our quest is to find out how their relationships
Mr. Lanik Practice Test Name:
 Mr. Lanik Practice Test Name: 1. New York State s Catskills are classified as which type of landscape region? mountain plateau Adirondacks Catskills lowland plain 2. In which New York State landscape region
Mr. Lanik Practice Test Name: 1. New York State s Catskills are classified as which type of landscape region? mountain plateau Adirondacks Catskills lowland plain 2. In which New York State landscape region
The diagram below shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in space.
 Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: 3653-1 - Page 1 The diagram below shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in
Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: 3653-1 - Page 1 The diagram below shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in
Brock University. Test 1, May 2014 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01 Number of Students: 500 Date of Examination: May 21, 2014
 Brock University Test 1, May 2014 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01 Number of Students: 500 Date of Examination: May 21, 2014 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 14:00 14:50 Instructor: B.Mitrović
Brock University Test 1, May 2014 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01 Number of Students: 500 Date of Examination: May 21, 2014 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 14:00 14:50 Instructor: B.Mitrović
The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Energy Chapter 3 and 4
 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Energy Chapter 3 and 4 Size of the Earth s Atmosphere Atmosphere produced over 4.6 billion years of development Protects us from radiation Completely surrounds the earth
The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Energy Chapter 3 and 4 Size of the Earth s Atmosphere Atmosphere produced over 4.6 billion years of development Protects us from radiation Completely surrounds the earth
Astronomy Part 1 Regents Questions
 Regents Questions 1. The Sun revolves around the center of A) Polaris B) Aldebaran C) Earth D) the Milky Way Galaxy 4. In which sequence are the items listed from least total mass to greatest total mass?
Regents Questions 1. The Sun revolves around the center of A) Polaris B) Aldebaran C) Earth D) the Milky Way Galaxy 4. In which sequence are the items listed from least total mass to greatest total mass?
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System
 CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
Directed Reading. Section: Viewing the Universe THE VALUE OF ASTRONOMY. Skills Worksheet. 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Scientists observe the environment around them using their five senses.
 Earth Science Notes Topics 1: Observation and Measurement Topic 2: The Changing Environment Review book pages 1-38 Scientists observe the environment around them using their five senses. When scientists
Earth Science Notes Topics 1: Observation and Measurement Topic 2: The Changing Environment Review book pages 1-38 Scientists observe the environment around them using their five senses. When scientists
Science Period. Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7
 Name: Date: Science Period Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7 Directions: Write the letter of the BEST answer on the appropriate space on the answer sheet. 2 points each 1.The model in which SUN is
Name: Date: Science Period Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7 Directions: Write the letter of the BEST answer on the appropriate space on the answer sheet. 2 points each 1.The model in which SUN is
9/1/14. Chapter 2: Heating Earth s Surface and Atmosphere. The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th. Lutgens Tarbuck
 Chapter 2: Heating Earth s Surface and Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University! Earth s two principal
Chapter 2: Heating Earth s Surface and Atmosphere The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University! Earth s two principal
Geography Class 6 Chapters 3 and
 CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
Midterm Review #2-2018
 1. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) Base your answers to questions
1. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) Base your answers to questions
The rock probably formed 200million years ago. The mineral sample is purple.
 Midterm Study Guide 1) Intro to Earth Science (Chapters 1& 2) a) Fact (observation) vs. Inference (assumption/hypothesis) Recognize whether a statement is a fact or an inference. For example: The rock
Midterm Study Guide 1) Intro to Earth Science (Chapters 1& 2) a) Fact (observation) vs. Inference (assumption/hypothesis) Recognize whether a statement is a fact or an inference. For example: The rock
Which letter on the timeline best represents the time when scientists estimate that the Big Bang occurred? A) A B) B C) C D) D
 1. The red shift of light from most galaxies is evidence that A) most galaxies are moving away from Earth B) a majority of stars in most galaxies are red giants C) the light slows down as it nears Earth
1. The red shift of light from most galaxies is evidence that A) most galaxies are moving away from Earth B) a majority of stars in most galaxies are red giants C) the light slows down as it nears Earth
