Chapter 5. Presenting Data
|
|
|
- Helen Owens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 5. Presenting Data Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 5-1 Basic principles of map design 5-2 1
2 Map Design Process 5-3 The map objective The first important design step Four key questions to answer What is the purpose? Who is the audience? What is the medium? Under what conditions will it be viewed? 5-4 2
3 Maps serve many purposes Locating Navigating Compiling Convincing Comparing Analyzing.? angepairs/index.html _sheet1.pdf s/highways_k12.jpg Audience Who will be viewing the map? What is their expected level of knowledge? About the subject matter About maps in general Do they have special requirements? Black and white? Color blindness, large print? 5-6 3
4 Medium Paper map Report? Wall map? Poster? Electronic files (pdf, gif, etc.) What format(s)? File sizes? Delivery method? Computer screen What size? Which types of computers? Projection screen Mobile devices/tablets/smartphones 5-7 Design for the medium Paper maps Static and unchanging Fixed paper size and scale High resolution May be complex with many levels of information Viewer is committed May serve multiple purposes Web maps Interactive Viewing size may vary by device screen Poor light/sunlight on mobile devices Short viewer attention span Competes for attention Should do one thing really well 5-8 4
5 Select 5-9 Selecting the data layers A good map tells a story Who are the lead players? Which layers play a supporting role? Do some layers distract from the story? Or obscure it?
6 Should you omit some data? Privacy issues Publishing parcel owner names Sensitive information Fossil or archeological sites (poaching issues) Endangered species locations Pipelines or climate stations (vandalism concerns) Unintended economic consequences Showing faults that intersect parcels Publishing water tests of private wells 5-11 Selecting within layers Sometimes need to simplify a data set for better performance on a map Known as cartographic generalization Adapt large-scale data to a smaller scale map
7 Using a query Show a subset of features Quakes > 4.0 Quakes > Cartographic generalization Refine Reclassify Simplify Typify Aggregate Displace Collapse Exaggerate
8 Selecting a map projection From Wikipedia: a map projection is a systematic transformation of the latitudes and longitudes of locations on the surface of a sphere (or an ellipsoid) into locations on a plane (a flat surface). Map projections are necessary for creating maps. More info: Selecting a map projection
9 Selecting a projection A map using a Geographic Coordinate system (GCS) (i.e. WGS 84) appears distorted. Always use a projected coordinate system for mapping Distortion All map projections distort the surface in some fashion. The four spatial properties subject to distortion in a projection are: Shape Area Distance Direction
10 Distortion
11 Distortion Unintended consequences Projection choice may affect the story Mercator maps make northern hemisphere look more important
12 Types of projections Cylindrical preserves shape and direction Conic preserves distance or area Azimuthal usually preserves distance 5-24 or area Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM)
13 State Plane 5-27 Graticule grids A north arrow is not appropriate for some projections because they distort direction. You should place graticule grids on the map instead.? Maps that distort distance should not have scale bars
14 Other types of map grids Measured grid (UTM meters) Reference grid 5-29 Arrange
15 Visual hierarchy The order in which a reader perceives the different objects in a design A good map establishes a clear pathway that highlights the important aspects Look at the map on the next slide for a few moments
16 Visual hierarchy What was the map about? What did you notice first? How did your eye move around the map? How was the path achieved? 5-33 Establishing a visual hierarchy Visual center Rule of thirds Balance Alignment Negative space Neatlines Symbolization Color Contrast Size/thickness Foreground/background
17 Visual center is higher than the geometric center Visual center 5-35 Composition rule for photographs Place important items at intersections Rule of thirds
18 Alignment Use columns Align edges 5-37 Balance it evenly Don t crowd elements Don t leave big empty spaces Use as another design element Subtle way to group things Negative space
19 Balancing elements 5-39 Symbolize
20 Symbolizing for hierarchy What stands out? How is it achieved? Color Contrast Foreground/background Size/thickness Symbol/font Spacing/grouping 5-41 Symbols and patterns The brain doesn t just observe, it tries to find patterns How do you make things stand out? Belong together? Show difference in quantity? Difference in category?
21 Which map has a clear visual hierarchy? How is it achieved? 5-43 Base maps How does this base map establish visual hierarchy?
22 Review and edit 5-45 Reviewing the draft Check balance Visual hierarchy Print to check colors, if a paper map Spelling, grammar, details Are all required map elements present? Scale bar / north arrow / legend Did you remember your sources?
23 Pay attention to details! Crowded Unclear name Abbreviations Poor formatting Much better!!! 5-47 Review this map
24 5-49 Other Examples
25
26
27 External review Very helpful to have others review your map People similar to the intended audience People in your field Graphic designer (if you can find one) 5-55 Edit and improve Concentrate the message Simplify, simplify Experiment Test under conditions of use
28 You re done! (maybe )
GEOREFERENCING, PROJECTIONS Part I. PRESENTING DATA Part II
 Week 7 GEOREFERENCING, PROJECTIONS Part I PRESENTING DATA Part II topics of the week Georeferencing Coordinate systems Map Projections ArcMap and Projections Geo-referencing Geo-referencing is the process
Week 7 GEOREFERENCING, PROJECTIONS Part I PRESENTING DATA Part II topics of the week Georeferencing Coordinate systems Map Projections ArcMap and Projections Geo-referencing Geo-referencing is the process
Map Projections. Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps
 Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s class Map Projections: Why projections are needed Types of map projections Classification by type of projection Classification by characteristics of projection
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s class Map Projections: Why projections are needed Types of map projections Classification by type of projection Classification by characteristics of projection
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL. Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2
 Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
Geographers Perspectives on the World
 What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth. 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth. 3.1 Objectives
 Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS
 2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS What are geographic information systems and what are they used for? ArcGIS: ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcToolbox Vector data vs. raster data vs. attribute tables Polygons, polylines,
2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS What are geographic information systems and what are they used for? ArcGIS: ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcToolbox Vector data vs. raster data vs. attribute tables Polygons, polylines,
REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING
 GIS in Ecology SPATIAL REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING : :1 Where on earth? Early mapmakers recognized the need for a system that could locate features on the earth's surface.
GIS in Ecology SPATIAL REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING : :1 Where on earth? Early mapmakers recognized the need for a system that could locate features on the earth's surface.
Fri. Jan. 26, Demonstration of QGIS with GPS tracks. Types of data, simple vector (shapefile) formats
 Fri. Jan. 26, 2018 Demonstration of QGIS with GPS tracks Types of data, simple vector (shapefile) formats Map projections, Coordinate Reference Systems Demonstration of QGIS with geologic map 1 Raster
Fri. Jan. 26, 2018 Demonstration of QGIS with GPS tracks Types of data, simple vector (shapefile) formats Map projections, Coordinate Reference Systems Demonstration of QGIS with geologic map 1 Raster
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006
 I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
Basic principles of cartographic design. Makram Murad-al-shaikh M.S. Cartography Esri education delivery team
 Basic principles of cartographic design Makram Murad-al-shaikh M.S. Cartography Esri education delivery team Cartographic concepts Cartography defined The communication channel - Why maps fail Objectives
Basic principles of cartographic design Makram Murad-al-shaikh M.S. Cartography Esri education delivery team Cartographic concepts Cartography defined The communication channel - Why maps fail Objectives
Map Projections. What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL
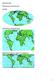 Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Understanding Projections for GIS
 Presented by John Schaeffer Juniper GIS Services, Inc. This PowerPoint is available at JuniperGIS.com Presentation Objectives To understand basic concepts on projections and coordinate systems for the
Presented by John Schaeffer Juniper GIS Services, Inc. This PowerPoint is available at JuniperGIS.com Presentation Objectives To understand basic concepts on projections and coordinate systems for the
Map image from the Atlas of Oregon (2nd. Ed.), Copyright 2001 University of Oregon Press
 Map Layout and Cartographic Design with ArcGIS Desktop Matthew Baker ESRI Educational Services Redlands, CA Education UC 2008 1 Seminar overview General map design principles Working with map elements
Map Layout and Cartographic Design with ArcGIS Desktop Matthew Baker ESRI Educational Services Redlands, CA Education UC 2008 1 Seminar overview General map design principles Working with map elements
ch02.pdf chap2.pdf chap02.pdf
 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
Working with georeferenced data. What is georeferencing? Coordinate Systems. Geographic and Projected Coordinate System
 GIS501 Fundamentals of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) Coordinate Systems Working with georeferenced data What is georeferencing? Geographically referenced data which is, in some way, referenced
GIS501 Fundamentals of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) Coordinate Systems Working with georeferenced data What is georeferencing? Geographically referenced data which is, in some way, referenced
Chapter 7: Making Maps with GIS. 7.1 The Parts of a Map 7.2 Choosing a Map Type 7.3 Designing the Map
 Chapter 7: Making Maps with GIS 7.1 The Parts of a Map 7.2 Choosing a Map Type 7.3 Designing the Map What is a map? A graphic depiction of all or part of a geographic realm in which the real-world features
Chapter 7: Making Maps with GIS 7.1 The Parts of a Map 7.2 Choosing a Map Type 7.3 Designing the Map What is a map? A graphic depiction of all or part of a geographic realm in which the real-world features
PROJECTIONS AND COORDINATES EXPLORED THROUGH GOOGLE EARTH EXERCISE (SOLUTION SHEET)
 PROJECTIONS AND COORDINATES EXPLORED THROUGH GOOGLE EARTH EXERCISE (SOLUTION SHEET) Name: Date: Period: Note: Correct answers on some problems are indicated with a yellow highlight. PROJECTIONS 1. Here
PROJECTIONS AND COORDINATES EXPLORED THROUGH GOOGLE EARTH EXERCISE (SOLUTION SHEET) Name: Date: Period: Note: Correct answers on some problems are indicated with a yellow highlight. PROJECTIONS 1. Here
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Eight: Comparing Map Projections
 Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Eight: Comparing Map Projections In this activity, you will do a series of projection comparisons using maps at different scales and geographic extents. In this
Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Eight: Comparing Map Projections In this activity, you will do a series of projection comparisons using maps at different scales and geographic extents. In this
Exercise 6: Coordinate Systems
 Exercise 6: Coordinate Systems This exercise will teach you the fundamentals of Coordinate Systems within QGIS. In this exercise you will learn: How to determine the coordinate system of a layer How the
Exercise 6: Coordinate Systems This exercise will teach you the fundamentals of Coordinate Systems within QGIS. In this exercise you will learn: How to determine the coordinate system of a layer How the
Georeferencing. Place names Postal addresses Postal codes Coordinate systems (lat/long, UTM, etc.)
 Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems
 Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017 1 Why? Laying the Earth Flat Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveying instruments measure
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017 1 Why? Laying the Earth Flat Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveying instruments measure
Performing Map Cartography. using Esri Production Mapping
 AGENDA Performing Map Cartography Presentation Title using Esri Production Mapping Name of Speaker Company Name Kannan Jayaraman Agenda Introduction What s New in ArcGIS 10.1 ESRI Production Mapping Mapping
AGENDA Performing Map Cartography Presentation Title using Esri Production Mapping Name of Speaker Company Name Kannan Jayaraman Agenda Introduction What s New in ArcGIS 10.1 ESRI Production Mapping Mapping
Version 1.1 GIS Syllabus
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION Version 1.1 GIS Syllabus Endorsed 1 Version 1 January 2007 GIS Certification Programme 1. Target The GIS certification is aimed at: Those who wish to demonstrate
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION Version 1.1 GIS Syllabus Endorsed 1 Version 1 January 2007 GIS Certification Programme 1. Target The GIS certification is aimed at: Those who wish to demonstrate
Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections
 Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections SHAPE OF THE EARTH Earth's Shape Geoid: shape of earth minus topographic features (irregular due to local variations in gravity) Ellipsoid: elongated
Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections SHAPE OF THE EARTH Earth's Shape Geoid: shape of earth minus topographic features (irregular due to local variations in gravity) Ellipsoid: elongated
How does an ellipsoid differ from a sphere in approximating the shape and size of the Earth?
 Chapter 02 Test Bank Worksheet Questions 1. What is a map projection? Topic: Map Projection 2. How does an ellipsoid differ from a sphere in approximating the shape and size of the Earth? Topic: Ellipsoid
Chapter 02 Test Bank Worksheet Questions 1. What is a map projection? Topic: Map Projection 2. How does an ellipsoid differ from a sphere in approximating the shape and size of the Earth? Topic: Ellipsoid
Lecture 2. Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 2 Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Map Projections Map projections are mathematical formulas
Lecture 2 Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Map Projections Map projections are mathematical formulas
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab
 Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections.
 Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections. 1 It is extremely important that you gain an understanding of coordinate systems and map projections. GIS works with spatial data, and,
Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections. 1 It is extremely important that you gain an understanding of coordinate systems and map projections. GIS works with spatial data, and,
How not to give a poster: Some suggestions based on years of experience. D. Lund (credit to J. Granger)
 How not to give a poster: Some suggestions based on years of experience D. Lund (credit to J. Granger) Purpose of a Poster Summarize research concisely and attractively Help publicize it and generate discussion
How not to give a poster: Some suggestions based on years of experience D. Lund (credit to J. Granger) Purpose of a Poster Summarize research concisely and attractively Help publicize it and generate discussion
Where on Earth are We? Projections and Coordinate Reference Systems
 Where on Earth are We? Projections and Coordinate Reference Systems Nick Eubank February 11, 2018 If I told you that there was a treasure chest buried at the coordinates p2, 5q, your first response might
Where on Earth are We? Projections and Coordinate Reference Systems Nick Eubank February 11, 2018 If I told you that there was a treasure chest buried at the coordinates p2, 5q, your first response might
1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. a. True *b. False
 Chapter 2 Where in the Geospatial World Are You? 1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. 2. For geospatial technology to work, every location on Earth must be: a. inhabited
Chapter 2 Where in the Geospatial World Are You? 1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. 2. For geospatial technology to work, every location on Earth must be: a. inhabited
Introduction to GIS Sarah Watson University of Kentucky Libraries March 6, 2017
 Introduction to GIS Sarah Watson sarahwatson@uky.edu University of Kentucky Libraries March 6, 2017 Outline Overview of various terms Quick overview of ArcGIS and QGIS Geocoding Activity Considering Map
Introduction to GIS Sarah Watson sarahwatson@uky.edu University of Kentucky Libraries March 6, 2017 Outline Overview of various terms Quick overview of ArcGIS and QGIS Geocoding Activity Considering Map
Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E. Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections
 Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections What is Geodesy? The science of geodesy determines: Earth s shape and Interrelation of different points on earth s surface The
Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections What is Geodesy? The science of geodesy determines: Earth s shape and Interrelation of different points on earth s surface The
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections
 Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
Shape e o f f the e Earth
 1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
Introduction to Geography
 Introduction to Geography What is geography? Geography comes from the Greek word Geographia. Geo means earth and graphia means to describe or chart. Geographers study the earth in relation to space and
Introduction to Geography What is geography? Geography comes from the Greek word Geographia. Geo means earth and graphia means to describe or chart. Geographers study the earth in relation to space and
Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP)
 Workshop on : Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP) 14-15 April 2016 Venue: Tehran, Iran GIS definitions GIS: A simplified view of the real
Workshop on : Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP) 14-15 April 2016 Venue: Tehran, Iran GIS definitions GIS: A simplified view of the real
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography
 EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
GIST 3300 / Geographic Information Systems. Last Time. Today
 GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook Chang 2006 and the practical manual)
 Introduction Geo-information Science (GRS-10306) Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook 2006 and the practical manual) Introduction Chapter 1 Geographic information system (GIS) Geographically
Introduction Geo-information Science (GRS-10306) Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook 2006 and the practical manual) Introduction Chapter 1 Geographic information system (GIS) Geographically
Overview. GIS Data Output Methods
 Overview GIS Output Formats ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
Overview GIS Output Formats ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS. Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output
 ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output Overview GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements GIS Output Formats Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output Overview GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements GIS Output Formats Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
Lecture 4. Coordinate Systems & Projections
 Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
12/26/2012. Geographic Information Systems * * * * GIS (... yrezaei
 ( - Geographic Information Systems ( ( 1 2 3 Information System Data base DB IS IS DB (Knowledge ( ( (System (Information System - (Georefrence Analysis Data + Knowledge ======== Information 4 5 ( < 10%
( - Geographic Information Systems ( ( 1 2 3 Information System Data base DB IS IS DB (Knowledge ( ( (System (Information System - (Georefrence Analysis Data + Knowledge ======== Information 4 5 ( < 10%
Introduction to Geoinformatics I
 Introduction to Geoinformatics I MAP CONCEPT Definition: 1) A map is a visual representation of an area a symbolic depiction highlighting relationships between elements of that space such as objects, regions,
Introduction to Geoinformatics I MAP CONCEPT Definition: 1) A map is a visual representation of an area a symbolic depiction highlighting relationships between elements of that space such as objects, regions,
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
Chapter 1: The World of Geography
 Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Susan Cutter et al. Aug, 2002, The Professional Geographer, 54(3): David Tenenbaum GEOG 070 UNC-CH Spring 2005
 What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts. -Coordinate Systems -Datum
 Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Geographic coordinate systems
 1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
Georeferencing. datum. projection. scale. The next few lectures will introduce you to these elements. on the Earth, you ll need to understand how
 Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity
 Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
Projections and Coordinate Systems
 Projections and Coordinate Systems Overview Projections Examples of different projections Coordinate systems Datums Projections Overview Projections and Coordinate Systems GIS must accurately represent
Projections and Coordinate Systems Overview Projections Examples of different projections Coordinate systems Datums Projections Overview Projections and Coordinate Systems GIS must accurately represent
What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps
 Mapping with GIS What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps Reference maps showing reference features such as roads, locations, political boundaries, cities etc. Thematic
Mapping with GIS What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps Reference maps showing reference features such as roads, locations, political boundaries, cities etc. Thematic
Using Maps. Using Maps. Using Maps. Using Maps
 A is a visual representation, or model, of part or all of the earth. lines are imaginary lines that run east to west around the globe; they are also known as parallels. They show distances in degrees north
A is a visual representation, or model, of part or all of the earth. lines are imaginary lines that run east to west around the globe; they are also known as parallels. They show distances in degrees north
Introduction to Geography
 Introduction to Geography ropic of Cancer 3½ N Arctic Circle 90 N Prime Meridian 0 Arctic Ocean Mississippi R. Appalachian Mts. Europe Rocky Mountains N. America Atlantic Gulf of Ocean Mexico Caribbean
Introduction to Geography ropic of Cancer 3½ N Arctic Circle 90 N Prime Meridian 0 Arctic Ocean Mississippi R. Appalachian Mts. Europe Rocky Mountains N. America Atlantic Gulf of Ocean Mexico Caribbean
The World of Geography Pre-Test/Study Guide Chapter 1 Test
 Read each statement or question. On the lines below write the letter of the best answer. 1. Geographers look at the Earth 5. What are the two specific A. by studying cities first. measurements of Earth
Read each statement or question. On the lines below write the letter of the best answer. 1. Geographers look at the Earth 5. What are the two specific A. by studying cities first. measurements of Earth
What is a Map Projection?
 What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools
 Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
Mapping Earth. How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled?
 Name Mapping Earth How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about maps Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Name Mapping Earth How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about maps Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Coordinate Systems. Location on earth is defined by coordinates
 Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006
 Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006 I. Common Projections There are several areas where maps are commonly used and a few projections dominate these fields. An
Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006 I. Common Projections There are several areas where maps are commonly used and a few projections dominate these fields. An
Map Makeovers: How to Make Your Map Great!
 Esri International User Conference San Diego, CA Technical Workshops Map Makeovers: How to Make Your Map Great! Charlie Frye, Esri, Redlands, Jim Herries, Esri, Redlands Session Goals Demonstrate cartographic
Esri International User Conference San Diego, CA Technical Workshops Map Makeovers: How to Make Your Map Great! Charlie Frye, Esri, Redlands, Jim Herries, Esri, Redlands Session Goals Demonstrate cartographic
Outline. Shape of the Earth. Geographic Coordinates (φ, λ, z) Ellipsoid or Spheroid Rotate an ellipse around an axis. Ellipse.
 Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections
 Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
An Information Model for Maps: Towards Cartographic Production from GIS Databases
 An Information Model for s: Towards Cartographic Production from GIS Databases Aileen Buckley, Ph.D. and Charlie Frye Senior Cartographic Researchers, ESRI Barbara Buttenfield, Ph.D. Professor, University
An Information Model for s: Towards Cartographic Production from GIS Databases Aileen Buckley, Ph.D. and Charlie Frye Senior Cartographic Researchers, ESRI Barbara Buttenfield, Ph.D. Professor, University
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems.
 Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
Cartography and Geovisualization. Chapters 12 and 13 of your textbook
 Cartography and Geovisualization Chapters 12 and 13 of your textbook Why cartography? Maps are the principle means of displaying spatial data Exploration: visualization, leading to conceptualization of
Cartography and Geovisualization Chapters 12 and 13 of your textbook Why cartography? Maps are the principle means of displaying spatial data Exploration: visualization, leading to conceptualization of
Theory, Concepts and Terminology
 GIS Workshop: Theory, Concepts and Terminology 1 Theory, Concepts and Terminology Suggestion: Have Maptitude with a map open on computer so that we can refer to it for specific menu and interface items.
GIS Workshop: Theory, Concepts and Terminology 1 Theory, Concepts and Terminology Suggestion: Have Maptitude with a map open on computer so that we can refer to it for specific menu and interface items.
An interactive tool for teaching map projections
 An interactive tool for teaching map projections Map projections are one of the fundamental concepts of geographic information science and cartography. An understanding of the different variants and properties
An interactive tool for teaching map projections Map projections are one of the fundamental concepts of geographic information science and cartography. An understanding of the different variants and properties
CHAPTER 9 DATA DISPLAY AND CARTOGRAPHY
 CHAPTER 9 DATA DISPLAY AND CARTOGRAPHY 9.1 Cartographic Representation 9.1.1 Spatial Features and Map Symbols 9.1.2 Use of Color 9.1.3 Data Classification 9.1.4 Generalization Box 9.1 Representations 9.2
CHAPTER 9 DATA DISPLAY AND CARTOGRAPHY 9.1 Cartographic Representation 9.1.1 Spatial Features and Map Symbols 9.1.2 Use of Color 9.1.3 Data Classification 9.1.4 Generalization Box 9.1 Representations 9.2
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map
 What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
Pool Canvas. Add. Creation Settings. Chapter 1--Objectives and Tools of World Regional Geography. Description Instructions.
 1 of 6 TEST BANK > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add Question drop-down list and click Go to add questions. Use
1 of 6 TEST BANK > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add Question drop-down list and click Go to add questions. Use
Wed. Apr. 25, 2018 GIS DEMO. Reading: Ch Comparing Image Types (Death Valley) Treat as review of techniques already studied
 Wed. Apr. 25, 2018 GIS DEMO Reading: Ch. 14 -- Comparing Image Types (Death Valley) Treat as review of techniques already studied 1 GIS: Geographic Information Systems Way to organize data obtained by
Wed. Apr. 25, 2018 GIS DEMO Reading: Ch. 14 -- Comparing Image Types (Death Valley) Treat as review of techniques already studied 1 GIS: Geographic Information Systems Way to organize data obtained by
Introduction to Geographic Information Science. Updates/News. Last Lecture. Geography 4103 / Map Projections and Coordinate Systems
 Geography 4103 / 5103 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Map Projections and Coordinate Systems Updates/News Thursday s lecture Reading discussion 1 find the readings online open questions,
Geography 4103 / 5103 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Map Projections and Coordinate Systems Updates/News Thursday s lecture Reading discussion 1 find the readings online open questions,
Military Map Reading 201
 Military Map Reading 201 This information paper is designed to resolve the confusion between the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) and the Military Grid Reference System (MGRS) coordinates. The two systems
Military Map Reading 201 This information paper is designed to resolve the confusion between the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) and the Military Grid Reference System (MGRS) coordinates. The two systems
Map Projections. is about presenting the round Earth on a flat surface.map Projections: Vermeer s Cartographer
 Map Projections is about presenting the round Earth on a flat surface.map Projections: Vermeer s Cartographer What is a map projection? A projection is a way to make a flat representation of the Earth
Map Projections is about presenting the round Earth on a flat surface.map Projections: Vermeer s Cartographer What is a map projection? A projection is a way to make a flat representation of the Earth
APC Part I Workshop. Mapping and Cartography. 14 November 2014
 APC Part I Workshop Mapping and Cartography 14 November 2014 Cartography Cartography is the discipline dealing with the conception, production, dissemination and study of maps in all forms (ICA) A holistic
APC Part I Workshop Mapping and Cartography 14 November 2014 Cartography Cartography is the discipline dealing with the conception, production, dissemination and study of maps in all forms (ICA) A holistic
AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are?
 AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are? Studying Human Geography Physical Geography Physical geography deals with Earth s natural
AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are? Studying Human Geography Physical Geography Physical geography deals with Earth s natural
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections
 NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
Different types of maps and how to read them.
 Different types of maps and how to read them. A map is a picture or representation of the Earth's surface, showing how things are related to each other by distance, direction, and size. Maps have been
Different types of maps and how to read them. A map is a picture or representation of the Earth's surface, showing how things are related to each other by distance, direction, and size. Maps have been
What is Geography? *Mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world into one field of study.
 World Geography What is Geography? *It is the study of the earth *Mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world into one field of study. *Shows the relationship between people and the environment.
World Geography What is Geography? *It is the study of the earth *Mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world into one field of study. *Shows the relationship between people and the environment.
Multiple Representations with Overrides, and their relationship to DLM/DCM Generalization. Paul Hardy Dan Lee
 Multiple Representations with Overrides, and their relationship to DLM/DCM Generalization Paul Hardy Dan Lee phardy@esri.com dlee@esri.com 1 Context This is a forward-looking presentation, and much of
Multiple Representations with Overrides, and their relationship to DLM/DCM Generalization Paul Hardy Dan Lee phardy@esri.com dlee@esri.com 1 Context This is a forward-looking presentation, and much of
Lab#3: GIS Projections and Coordinate Systems. Start Arcmap and create a data frame for each of the above coordinate systems.
 NRM338 Fall 2017 Lab#3 Page#1 of 18 In this lab, you will Lab#3: GIS Projections and Coordinate Systems 1) Define the geographic coordinate system of two GIS themes. 2) Determine the geographic coordinates
NRM338 Fall 2017 Lab#3 Page#1 of 18 In this lab, you will Lab#3: GIS Projections and Coordinate Systems 1) Define the geographic coordinate system of two GIS themes. 2) Determine the geographic coordinates
1/28/16. EGM101 Skills Toolbox. Oblate spheroid. The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections. Geoid
 EGM101 Skills Toolbox Oblate spheroid The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections The geoid is the shape that the surface of the oceans would take under the influence of Earth's gravitation
EGM101 Skills Toolbox Oblate spheroid The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections The geoid is the shape that the surface of the oceans would take under the influence of Earth's gravitation
Trouble-Shooting Coordinate System Problems
 Trouble-Shooting Coordinate System Problems Written by Barbara M. Parmenter. Revised on October 2, 2018 OVERVIEW OF THE EXERCISE... 1 COPYING THE MAP PROJECTION EXERCISE FOLDER TO YOUR H: DRIVE OR DESKTOP...
Trouble-Shooting Coordinate System Problems Written by Barbara M. Parmenter. Revised on October 2, 2018 OVERVIEW OF THE EXERCISE... 1 COPYING THE MAP PROJECTION EXERCISE FOLDER TO YOUR H: DRIVE OR DESKTOP...
Lab #3 Map Projections.
 Lab #3 Map Projections http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/earth/geography/cartography/map-projections.jpg Map Projections Projection: a systematic arrangement of parallels and meridians on a plane
Lab #3 Map Projections http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/earth/geography/cartography/map-projections.jpg Map Projections Projection: a systematic arrangement of parallels and meridians on a plane
MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts.
 MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts. Types of Maps General Purpose Topographic Thematic/Choropleth Dot Graduated Circle Isometric/Isolines Isopleth Mental Maps Scale Small-scale
MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts. Types of Maps General Purpose Topographic Thematic/Choropleth Dot Graduated Circle Isometric/Isolines Isopleth Mental Maps Scale Small-scale
Intro to GIS Summer 2012 Data Visualization
 Intro to GIS Summer 2012 Data Visualization UNDERSTANDING YOUR MAP DATA Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data Qualitative Data classified by category e.g. Soil types, Animal Species Quantitative Data grouped
Intro to GIS Summer 2012 Data Visualization UNDERSTANDING YOUR MAP DATA Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data Qualitative Data classified by category e.g. Soil types, Animal Species Quantitative Data grouped
Observe Reflect Question What type of document is this?
 Appendix 2 An Empty Primary Source Analysis Tool and a Full Primary Source Analysis Tool with Guiding Questions Observe Reflect Question What type of document is this? What is the purpose of this document?
Appendix 2 An Empty Primary Source Analysis Tool and a Full Primary Source Analysis Tool with Guiding Questions Observe Reflect Question What type of document is this? What is the purpose of this document?
APC PART I WORKSHOP MAPPING AND CARTOGRAPHY
 APC PART I WORKSHOP MAPPING AND CARTOGRAPHY 5 June 2015 MAPPING The act or process of making a map. A matching process where the points of one set are matched against the points of another set. Graphical
APC PART I WORKSHOP MAPPING AND CARTOGRAPHY 5 June 2015 MAPPING The act or process of making a map. A matching process where the points of one set are matched against the points of another set. Graphical
EN5302. US ARMY ENGINEER SCHOOL CARTOGRAPHY II Grid Construction, Plotting and Projection Graticules
 SUBCOURSE EN5302 EDITION 6 US ARMY ENGINEER SCHOOL CARTOGRAPHY II Grid Construction, Plotting and Projection Graticules TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE INTRODUCTION... iii GRADING AND CERTIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS...
SUBCOURSE EN5302 EDITION 6 US ARMY ENGINEER SCHOOL CARTOGRAPHY II Grid Construction, Plotting and Projection Graticules TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE INTRODUCTION... iii GRADING AND CERTIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS...
2. What does the map scale tell the map reader? a ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the length given to that distance on a map
 AP Human Geography - Damon Name Unit 1 - Intro to Human Geography Hour Map and Globe Skills Review Note: All links in this packet are found on our Wikispace under Map and Globe Skills Review First, read
AP Human Geography - Damon Name Unit 1 - Intro to Human Geography Hour Map and Globe Skills Review Note: All links in this packet are found on our Wikispace under Map and Globe Skills Review First, read
Creating an Illustrated Map: New Zealand
 S T U D E N T H A N D O U T A Creating an Illustrated Map: New Zealand You will work in a group of four to create an illustrated map of one type of Pacific island: a continental island. Your illustrated
S T U D E N T H A N D O U T A Creating an Illustrated Map: New Zealand You will work in a group of four to create an illustrated map of one type of Pacific island: a continental island. Your illustrated
MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY
 MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY BYOD BRING YOUR OWN DEVICE IN SMALL GROUPS (3-4), USE YOUR ELECTRONIC DEVICE(S) AND DEFINE THE FOLLOWING VOCAB. WORDS 1. GEOGRAPHY 2.
MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY BYOD BRING YOUR OWN DEVICE IN SMALL GROUPS (3-4), USE YOUR ELECTRONIC DEVICE(S) AND DEFINE THE FOLLOWING VOCAB. WORDS 1. GEOGRAPHY 2.
Spatial locations. Spatial locations. Spatial locations. Spatial locations
 Where am I? sounds simple, but definitely not huge amount of picky detail Cartographers make a career from the details focus on the minimum you need to know c Philip M. Dixon (Iowa State Univ.) Spatial
Where am I? sounds simple, but definitely not huge amount of picky detail Cartographers make a career from the details focus on the minimum you need to know c Philip M. Dixon (Iowa State Univ.) Spatial
