A 21st century HRRR-based approach to estimating probable maximum precipitation to enhance dam safety and community resilience
|
|
|
- Melvin Nichols
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 30 May 2017 FIRO Science Task Group Workshop A 21st century HRRR-based approach to estimating probable maximum precipitation to enhance dam safety and community resilience Courtesy Bill McCormick, Chief, CO Dam Safety Oroville Dam, Feb 2017 ( Kelly Mahoney, Eric James, Trevor Alcott, Rob Cifelli NOAA ESRL Physical Sciences Division NOAA ESRL Global Systems Division and CIRES/University of Colorado
2 Motivation Dams necessary to manage water in the West, but present risks Dam failures fatalities, disasters (Johnstown PA fatalities, 2017 Oroville Dam crisis) Probable Maximum Precipitation: Theoretical calculated maximum possible precipitation Important upper limit used for dam design, construction, operation Current PMP estimates lack recent storms, updated precipitation process understanding, technology HMR values often argued to be too high, especially in orographic areas In practice: subjective moving of storms, ad-hoc reductions: e.g., elevation-based decreases Can we do better with more modern data, tools, and methods? Dams in Colorado Taylor Park Dam, CO Existing documented PMP methods based on storms, science through 1970s 2
3 Exploring Dynamical Rainfall Forecast Modeling for PMP Estimation Goal: Perform a feasibility study to test and evaluate the potential benefits of adopting a high-resolution dynamical modeling-based framework for estimating the probable maximum precipitation (PMP) across Colorado and New Mexico. HMR 55A PMP for 72-hr, 10mi 2 storm: 45 inches over Boulder High resolution model terrain 3
4 Why is dynamical modeling a potentially desirable approach to PMP estimation? Scientific understanding of physical processes responsible for extreme storms enhanced since NOAA HMRs (PMP recipe books ) created Dynamical models solve physical equations of atmosphere: generate precipitation according to real-world environment, with continuity in space and time May alleviate need for many spatial, temporal, physical assumptions (e.g., storm transposition, storm templates, moisture maximization, etc.) Especially important in data-sparse regions of complex (& high-elevation) topography Processes and physical model elements that are represented in NWP models 4
5 What is the High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) model? The HRRR is a NOAA real-time 3-km resolution, hourly updated, cloud-resolving, convection-allowing atmospheric model, initialized by 3-km grids with 3-km radar assimilation. Radar data is assimilated in the HRRR every 15 min over a 1-h period adding further detail to that provided by the hourly data assimilation from the 13-km radar-enhanced Rapid Refresh. 5
6 Why is dynamical modeling a potentially desirable approach to PMP estimation? Experimental proof-of-concept: 1. Treat all available HRRR simulations as an effective long-term, running model ensemble ~15-hour forecasts run each hour, every day, for 5+ years Example of single 24-hour model ensemble max precipitation grid: (i.e., what is the most precipitation generated by any model ensemble member over the given period? ) 2. Create a running ensemble max precipitation grid to keep track of the most precipitation forecast by the HRRR model over the 5-y period of record. 3. Develop gridded 1-hour, 6-hour, 12-hour precipitation maxima fields using all available HRRR model data Max precip prototype: Integrate grids like this one to include many more forecasts: HRRR run every hour, every day, for 5+ years. 6
7 Is HRRR suitable for PMP estimation? Strengths High spatial resolution: 3-km grid allows for: Mostly explicit physics (atmospheric processes are simulated directly, rather than through statistical relationships) Realistic, physically-bounded estimates of heavy rainfall High temporal resolution: hourly forecasts over many years provide sample size of: 15(+) hour/cycle * 24 cycles/day* 365 days/year * 5 years ~ 31,000+ model runs Large spatial coverage (CONUS) Already operational at NOAA NCEP (institutional acceptance/approval) 7
8 What are HRRR s limitations? 5 years not long enough to sample all weather patterns that could occur at a given location No storm maximization taking place (also a strength) Biases relatively poorly understood at high elevations due to lack of verification data; work ongoing Proof of concept stage next up: How do patterns, qualitative findings compare to those of deterministic PMP estimation, precip/flood frequency analysis? When and where does dynamical modeling approach offer immediate, unique, and/or complementary benefits? Example near-term dataset benefit: Improved (model-derived) rain-vs-snow information 8
9 In progress & upcoming deliverables Using maximum precipitation prototype products, assess: How do results from the temporally-short but spatially-high resolution HRRR analysis compare with/augment previous observations-based studies of extreme precipitation climatologies? Do elevation-dependent precipitation thresholds exist? How can observations-based, longer-record precipitation climatologies be best combined with HRRR s high spatial, temporal resolution? How feasible is it for dynamically-based modeling framework to address PMP as stakeholders presently require the information? Example near-term dataset benefits: Improved understanding/data coverage related to (left to right) Seasonality of heavy precipitation; mean annual maximum precipitation; gridpoint max precip over 5-year record 9
10 For more information: Colorado-New Mexico Regional Extreme Precipitation Study (REPS) 10
11 11
12 Extra slides 12
13 Elevation-based precipitation reductions in practice Image courtesy B. Kappel, Applied Weather Associates Elevation-based precipitation reduction factors derived from HMRs Concept: reduce moisture as elevation increases based on adiabatic lapse rate: ~9%/1000 ft State of CO rules: historically reduced even further Are these PMP methods physically-realistic? Can we do better with more modern data, tools, and methods?
14 2013: Big Thompson Canyon (~7500 ft) washed out US 34 in floods Study objectives Examine approximations and assumptions currently used in PMP elevation adjustment factors Investigate role of elevation in 2013 Colorado Front Range floods Using a high-resolution numerical modeling framework, investigate: Model terrain sensitivities Storm environment effect on maximum elevations affected Evaluate potential benefit of state-of-the-art climate and weather modeling capabilities in PMP-based risk-assessment methods HMR 55A PMP for 72- hr, 10mi 2 storm: 45 inches over Boulder! WRF model terrain
15 2. What is the High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) model? The RAP and HRRR models are run EVERY HOUR of every day to provide updated forecasts using the latest observations DATA ASSIMILATION is the science of bringing in all the available weather observations (from radars, satellites, aircraft, surface weather stations, etc) to create an initial condition for the forecast The RAP is an hourly CYCLED system, meaning the 1-h forecast is used to provide a background for the data assimilation at the next hour; this allows us to cycle a physically-realistic atmospheric state 15
16 2. What is the High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) model? Part of the data assimilation step is a pre-forecast model integration bringing in radar reflectivity data every 15 min Model Pre-Forecast Time (min) Model Integrations Observed Radar Valid at -45 Valid at -30 Valid at -15 Valid at 0 GOAL: To create a starting point that is as realistic as possible, and allow for a good forecast 16
17 2. What is the High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) model? During the 1-hour pre-forecast, radar reflectivity observations are used to specify latent heating rates (atmospheric heat release due to precipitation formation) in each previous 15-min period: Observed Reflectivity 0 dbz : Zero heating rate to suppress spurious model precipitation. Observed Reflectivity 28 dbz : Positive heating rate to promote convective development. 0 dbz < Observed Reflectivity < 28 dbz : Model microphysics heating rate preserved. No radar coverage: Model microphysics heating rate preserved. This allows us to force the model to have realistic precipitation-related vertical motion at the starting point 17
18 2. What is the High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) model? A HYDROMETEOR analysis is also carried out as part of the data assimilation step to ensure a realistic analysis: Variables Updated Add to model? Remove from model? Which observations are used? cloud water, cloud ice, temperature, water vapor Yes, below 1.2 km AGL Yes Satellite cloud top, Ceilometers Rain water, snow water Yes, If 2m T < 5 C: add to full column, Else: add at observed maximum reflectivity level and where obs dbz Yes Radar reflectivity 18
19 What are HRRR s limitations? Spring 2015: Maximum HRRR 6-h QPF Spring 2015: Maximum 6-h Stage-IV QPE Overall physical representation of precipitation is good, but biases are evident Observations (QPE) have obvious limitations too (radar coverage) over Western US complex terrain 19
20 What are HRRR s limitations? Spring 2015: HRRR 6-h QPF vs Stage-IV QPE High Bias Ideal Low Bias We can examine the frequency of occurrence of different precipitation amount in the HRRR to a QPE analysis Based on 6-h forecasts, HRRR produces: (1) too many heavy rainfall events (2) too few extreme events (1) is related to the initial push from radar data being a bit too strong (2) is related to resolution. The strongest storms on a 3-km grid still aren t quite strong enough 20
21 What are HRRR s limitations? High Bias Ideal Good news: Short term: both issues can be addressed ex post facto, through statistical bias correction, using a moving window of the most recent forecasts (a few weeks of HRRR runs) Low Bias Long term: planned improvements to HRRR model physics will reduce these biases in the model itself inches per 6 h 21
22 What are possible workarounds to HRRR s limitations? Bias correction using trusted QPE analyses and/or point observations Group together grid points with similar overall climatologies, but different 5-year maximum values; i.e., an intelligent neighborhood technique Combine multiple HRRR runs with overlapping valid times into an ensemble to place error bars on predicted rainfall Many other ideas to explore along the way 22
23 Is HRRR suitable for PMP estimation? QPF statistics for 2016 so far: Forecast Bias Western US 12-h QPF Western US 6-h QPF Eastern US 12-h QPF Eastern US 6-h QPF Critical Success Index (CSI) Thresholds: 1: 0.10 inch 2: 0.25 inch 3: 0.50 inch 4: 1.00 inch 5: 1.50 inch 6: 2.00 inch 7: 3.00 inch Thresholds: 1: 0.10 inch 2: 0.25 inch 3: 0.50 inch 4: 1.00 inch 5: 1.50 inch 6: 2.00 inch 7: 3.00 inch 23
24 RAP/HRRR wiring diagram 24
25 Current RAP/HRRR configuration 25
26 Observations used in the data assimilation 26
27 WRF Model experiments What is the precipitation sensitivity to terrain elevation? How sensitive to storm environment are maximum elevations affected by heavy precipitation? 1. Control 2. No_Terrain m_All_Terrain 4. Half_Terrain 5. Bulldoze Rockies 6. Terrainx1.25 Experiments: 1. Control Terrain modifications: 2. No-Terrain (Domain flattened, terrain HGT=0) 3. Terrain-All-1610m (Domain flattened, terrain HGT=1610 m) 4. Terrain-1/2-height (Domain terrain HGT=HGT orig /2) 5. Terrain-Bulldoze-Rockies (Domain terrain capped at 1610 m) 6. Terrainx1.25 (Domain terrain HGT increased by 25%) Environment modifications: 7. +RH_10%: Increase initial, lateral boundary environmental humidity by 10% 8. -RH_10%: Decrease initial, lateral boundary environmental humidity by 10% 9. +RH_50%: Increase initial, lateral boundary environmental humidity by 50% 10. +RH_100%: Increase initial, lateral boundary environmental humidity to 100%
28 Results: 72-hour precipitation Control No_Terrain 1610m_All_Terrain Half_Terrain Bulldoze Rockies Terrainx1.25 +RH_10% -RH_10% Flat terrain simulations show impact of dynamics-only Increasing terrain height by 25% decreases max precip by ~10 20%; similar max location Increasing RH diffuses maxima, increases average precipitation
29 Precipitation vs. elevation: Max precip cross-section example 72-hour rainfall over terrain: CTRL Total rainfall along x-sect: CTRL Terrain height along x- sect CTRL simulation elevation vs. precipitation: rainfall max m ( ~8000 feet)
30 Precipitation vs. elevation: Max precip cross-section example 72-hour rainfall over terrain: RH+10% Total rainfall along x-sect: CTRL Terrain height along x- sect CTRL simulation elevation vs. precipitation: precip max ~8500 ft (2590m) +RH_10%: max precip: amount less, but location moves over higher Front Range terrain (~3000m) What about over the whole domain?
31 Precipitation vs. elevation: Moisture-increased experiments Moisture-modified runs show variable precip-elevation relationships Domain-wide analysis (all gridpoints) Median rainfall vs. elevation +RH_100% +RH_50% +RH_10% CTRL Elevation (ft) Max rainfall vs. elevation +RH_100% Distribution of median, max precip shifts as moisture increases Generally upward trend in 50%, 100% increases, but not consistently Variability indicates localized nature of terrain effects, casespecific dynamical details More cases needed for systematic relationships; proof-ofconcept demonstrates potential benefit to extreme precipitation estimation in complex terrain +RH_50% +RH_10% CTRL Elevation (ft)
32 Precipitation vs. elevation: Comparison to reduction factors Current practices: linear reduction factors; solely dependent on terrain height Max precip across all simulations Reality: Extreme precipitation systems nonlinear dynamical nature & terrain effects extremely localized (Proof of concept; single case) High variability across model realizations of this event Many cases, more perturbed realizations, post-processing techniques needed to see systematic extreme precipitation/elevation relationships Dynamics, weather climatology still dictate that precipitation changes will not vary with elevation alone; dynamical model results over sufficiently long period can highlight relative controls of local dynamics vs. elevation
33 Summary and future work 2013 Colorado floods exceeded 7500-foot terrain limit for flood potential Some dams stressed but no major failures. PMP is conservatively safe but inefficient Modeling case study: model terrain, storm environment experiments emphasize sensitivity of amount and distribution of heavy precipitation Role of terrain in CO floods complex: Terrain focused/enhanced precipitation in Front Range Dynamics produced considerable precipitation - even in absence of terrain Terrain role complex: Rockies vs. Front Range vs. Palmer Divide (Morales et al. 2015)) Elevation adjustment factors used today draw on overly-simplified, average conditions and do not account for real-world dynamics; new data and tools are available and should be considered for application Estes Park, CO flooding 13 Sept 2013: Elevation 7820 ft (Walt Hester) Dynamical model output ex: Control simulation precipitable water as 3D surface
34 Summary and future work Future Work Participate in multi-agency CO/NM PMP study to assess new PMP methods including dynamical modeling Connect state-of-the-art climate and weather modeling capabilities with currently-used risk-assessment approaches Work toward ideal long-term solution: long-running model ensembles using perturbations that allow confidence in improved PMP and elimination of adjustment factors HMR 55A PMP for 72- hr, 10mi 2 storm: 45 inches over Boulder! Evaluate use of state-of-the-art modeling datasets in PMP estimation (e.g., HRRR) (Image RAP model NCEI)
Using a high-resolution ensemble modeling method to inform risk-based decision-making at Taylor Park Dam, Colorado
 Using a high-resolution ensemble modeling method to inform risk-based decision-making at Taylor Park Dam, Colorado Michael J. Mueller 1, Kelly Mahoney 2, Kathleen Holman 3, David Gochis 4 1 Cooperative
Using a high-resolution ensemble modeling method to inform risk-based decision-making at Taylor Park Dam, Colorado Michael J. Mueller 1, Kelly Mahoney 2, Kathleen Holman 3, David Gochis 4 1 Cooperative
Aircraft-based Observations: Impact on weather forecast model performance
 Aircraft-based Observations: Impact on weather forecast model performance Stephen S. Weygandt Eric James, Stan Benjamin, Bill Moninger, Brian Jamison, Geoff Manikin* NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory
Aircraft-based Observations: Impact on weather forecast model performance Stephen S. Weygandt Eric James, Stan Benjamin, Bill Moninger, Brian Jamison, Geoff Manikin* NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory
Weather Hazard Modeling Research and development: Recent Advances and Plans
 Weather Hazard Modeling Research and development: Recent Advances and Plans Stephen S. Weygandt Curtis Alexander, Stan Benjamin, Geoff Manikin*, Tanya Smirnova, Ming Hu NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory
Weather Hazard Modeling Research and development: Recent Advances and Plans Stephen S. Weygandt Curtis Alexander, Stan Benjamin, Geoff Manikin*, Tanya Smirnova, Ming Hu NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory
Updating Probable Maximum Precipitation for the Tennessee Valley Authority
 Updating Probable Maximum Precipitation for the Tennessee Valley Authority Bill Kappel, President/Senior Meteorologist Applied Weather Associates, Monument, CO www.appliedweatherassociates.com Mike Eiffe,
Updating Probable Maximum Precipitation for the Tennessee Valley Authority Bill Kappel, President/Senior Meteorologist Applied Weather Associates, Monument, CO www.appliedweatherassociates.com Mike Eiffe,
Development of High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) Ensemble Data Assimilation, Forecasts and Post Processing
 7 th Ensemble Users Workshop Ensemble Development I Development of High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) Ensemble Data Assimilation, Forecasts and Post Processing 14 June 2016 Curtis Alexander, David Dowell,
7 th Ensemble Users Workshop Ensemble Development I Development of High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) Ensemble Data Assimilation, Forecasts and Post Processing 14 June 2016 Curtis Alexander, David Dowell,
2012 and changes to the Rapid Refresh and HRRR weather forecast models
 2012 and 2013-15 changes to the Rapid Refresh and HRRR weather forecast models 31 October 2012 Stan Benjamin Steve Weygandt Curtis Alexander NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory Boulder, CO FPAW - 2012
2012 and 2013-15 changes to the Rapid Refresh and HRRR weather forecast models 31 October 2012 Stan Benjamin Steve Weygandt Curtis Alexander NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory Boulder, CO FPAW - 2012
Kelly Mahoney NOAA ESRL Physical Sciences Division
 The role of gray zone convective model physics in highresolution simulations of the 2013 Colorado Front Range Flood WRF model simulated precipitation over terrain in CO Front Range Kelly Mahoney NOAA ESRL
The role of gray zone convective model physics in highresolution simulations of the 2013 Colorado Front Range Flood WRF model simulated precipitation over terrain in CO Front Range Kelly Mahoney NOAA ESRL
Weather Forecasting: Lecture 2
 Weather Forecasting: Lecture 2 Dr. Jeremy A. Gibbs Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah Spring 2017 1 / 40 Overview 1 Forecasting Techniques 2 Forecast Tools 2 / 40 Forecasting Techniques
Weather Forecasting: Lecture 2 Dr. Jeremy A. Gibbs Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah Spring 2017 1 / 40 Overview 1 Forecasting Techniques 2 Forecast Tools 2 / 40 Forecasting Techniques
A new mesoscale NWP system for Australia
 A new mesoscale NWP system for Australia www.cawcr.gov.au Peter Steinle on behalf of : Earth System Modelling (ESM) and Weather&Environmental Prediction (WEP) Research Programs, CAWCR Data Assimilation
A new mesoscale NWP system for Australia www.cawcr.gov.au Peter Steinle on behalf of : Earth System Modelling (ESM) and Weather&Environmental Prediction (WEP) Research Programs, CAWCR Data Assimilation
NOAA s Severe Weather Forecasting System: HRRR to WoF to FACETS
 NOAA s Severe Weather Forecasting System: HRRR to WoF to FACETS David D NOAA / Earth System Research Laboratory / Global Systems Division Nowcasting and Mesoscale Research Working Group Meeting World Meteorological
NOAA s Severe Weather Forecasting System: HRRR to WoF to FACETS David D NOAA / Earth System Research Laboratory / Global Systems Division Nowcasting and Mesoscale Research Working Group Meeting World Meteorological
Canadian Meteorological and Oceanographic Society and American Meteorological Society 21 st Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction 31 May 2012
 Canadian Meteorological and Oceanographic Society and American Meteorological Society 21 st Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction 31 May 2012 The High Resolution Rapid Refresh (): An hourly updating
Canadian Meteorological and Oceanographic Society and American Meteorological Society 21 st Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction 31 May 2012 The High Resolution Rapid Refresh (): An hourly updating
Extreme precipitation events in the. southeast U.S.
 Extreme precipitation events in the Southeast US A preliminary investigation of operational forecast challenges related to moisture sources and transport TN flooding May 2010 Asheville, NC 2004 State Climate
Extreme precipitation events in the Southeast US A preliminary investigation of operational forecast challenges related to moisture sources and transport TN flooding May 2010 Asheville, NC 2004 State Climate
Areal Reduction Factors for the Colorado Front Range and Analysis of the September 2013 Colorado Storm
 Areal Reduction Factors for the Colorado Front Range and Analysis of the September 2013 Colorado Storm Doug Hultstrand, Bill Kappel, Geoff Muhlestein Applied Weather Associates, LLC - Monument, Colorado
Areal Reduction Factors for the Colorado Front Range and Analysis of the September 2013 Colorado Storm Doug Hultstrand, Bill Kappel, Geoff Muhlestein Applied Weather Associates, LLC - Monument, Colorado
weather forecast Improving NOAA models for energy Stan Benjamin, Boulder, CO USA Joseph Olson, Curtis Alexander, Eric James,
 Lamont, OK X Obs radar 5h HRRR Forecast Improving NOAA weather forecast models for energy Stan Benjamin, Joseph Olson, Curtis Alexander, Eric James, Dave Turner, Melinda Marquis NOAA Earth System Research
Lamont, OK X Obs radar 5h HRRR Forecast Improving NOAA weather forecast models for energy Stan Benjamin, Joseph Olson, Curtis Alexander, Eric James, Dave Turner, Melinda Marquis NOAA Earth System Research
Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) CU-Boulder 2. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
 Moisture transport during the inland penetrating atmospheric river of early November 006 in the Pacific Northwest: A high-resolution model-based study Michael J. Mueller 1 and Kelly Mahoney 1 Cooperative
Moisture transport during the inland penetrating atmospheric river of early November 006 in the Pacific Northwest: A high-resolution model-based study Michael J. Mueller 1 and Kelly Mahoney 1 Cooperative
Verifying Ensemble Forecasts Using A Neighborhood Approach
 Verifying Ensemble Forecasts Using A Neighborhood Approach Craig Schwartz NCAR/MMM schwartz@ucar.edu Thanks to: Jack Kain, Ming Xue, Steve Weiss Theory, Motivation, and Review Traditional Deterministic
Verifying Ensemble Forecasts Using A Neighborhood Approach Craig Schwartz NCAR/MMM schwartz@ucar.edu Thanks to: Jack Kain, Ming Xue, Steve Weiss Theory, Motivation, and Review Traditional Deterministic
A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS
 A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS Wei Yu, Yubao Liu, Tom Warner, Randy Bullock, Barbara Brown and
A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS Wei Yu, Yubao Liu, Tom Warner, Randy Bullock, Barbara Brown and
Verification of ensemble and probability forecasts
 Verification of ensemble and probability forecasts Barbara Brown NCAR, USA bgb@ucar.edu Collaborators: Tara Jensen (NCAR), Eric Gilleland (NCAR), Ed Tollerud (NOAA/ESRL), Beth Ebert (CAWCR), Laurence Wilson
Verification of ensemble and probability forecasts Barbara Brown NCAR, USA bgb@ucar.edu Collaborators: Tara Jensen (NCAR), Eric Gilleland (NCAR), Ed Tollerud (NOAA/ESRL), Beth Ebert (CAWCR), Laurence Wilson
The role of testbeds in NOAA for transitioning NWP research to operations
 ECMWF Workshop on Operational Systems November 18, 2013 The role of testbeds in NOAA for transitioning NWP research to operations Ligia Bernardet 1* and Zoltan Toth 1 1 NOAA ESRL Global Systems Division,
ECMWF Workshop on Operational Systems November 18, 2013 The role of testbeds in NOAA for transitioning NWP research to operations Ligia Bernardet 1* and Zoltan Toth 1 1 NOAA ESRL Global Systems Division,
A Cycled GSI+EnKF and Storm-Scale Ensemble Forecasting (SSEF) Experiment
 A Cycled GSI+EnKF and Storm-Scale Ensemble Forecasting (SSEF) Experiment Fanyou Kong, Ming Xue, Youngsun Jung, Keith A. Brewster, Gang Zhao Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms University of Oklahoma
A Cycled GSI+EnKF and Storm-Scale Ensemble Forecasting (SSEF) Experiment Fanyou Kong, Ming Xue, Youngsun Jung, Keith A. Brewster, Gang Zhao Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms University of Oklahoma
Areal Reduction Factors for the Colorado Front Range and Analysis of the September 2013 Colorado Storm
 Areal Reduction Factors for the Colorado Front Range and Analysis of the September 2013 Colorado Storm Doug Hultstrand, Bill Kappel, Geoff Muhlestein Applied Weather Associates, LLC - Monument, Colorado
Areal Reduction Factors for the Colorado Front Range and Analysis of the September 2013 Colorado Storm Doug Hultstrand, Bill Kappel, Geoff Muhlestein Applied Weather Associates, LLC - Monument, Colorado
Thunderstorm-Scale EnKF Analyses Verified with Dual-Polarization, Dual-Doppler Radar Data
 Thunderstorm-Scale EnKF Analyses Verified with Dual-Polarization, Dual-Doppler Radar Data David Dowell and Wiebke Deierling National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO Ensemble Data Assimilation
Thunderstorm-Scale EnKF Analyses Verified with Dual-Polarization, Dual-Doppler Radar Data David Dowell and Wiebke Deierling National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO Ensemble Data Assimilation
Presented by Jerry A. Gomez, P.E. National Hydropower Association Northeast Regional Meeting - September 17, 2009
 Presented by Jerry A. Gomez, P.E. National Hydropower Association Northeast Regional Meeting - September 17, 2009 Defining Probable Maximum Precipitation (PMP) PMP is the theoretically greatest depth of
Presented by Jerry A. Gomez, P.E. National Hydropower Association Northeast Regional Meeting - September 17, 2009 Defining Probable Maximum Precipitation (PMP) PMP is the theoretically greatest depth of
Linking the Hydrologic and Atmospheric Communities Through Probabilistic Flash Flood Forecasting
 Linking the Hydrologic and Atmospheric Communities Through Probabilistic Flash Flood Forecasting Wallace Hogsett Science and Operations Officer NOAA/NWS/Weather Prediction Center with numerous contributions
Linking the Hydrologic and Atmospheric Communities Through Probabilistic Flash Flood Forecasting Wallace Hogsett Science and Operations Officer NOAA/NWS/Weather Prediction Center with numerous contributions
FAA Weather Research Plans
 FAA Weather Research Plans Presented to: Friends /Partners in Aviation Weather Vision Forum By: Ray Moy FAA Aviation Weather Office Date: Aviation Weather Research Program (AWRP) Purpose: Applied Research
FAA Weather Research Plans Presented to: Friends /Partners in Aviation Weather Vision Forum By: Ray Moy FAA Aviation Weather Office Date: Aviation Weather Research Program (AWRP) Purpose: Applied Research
The general procedure for estimating 24-hour PMP includes the following steps:
 14th Conference on Applied Climatology Abstract # 71520 Using PRISM Climate Grids and GIS for Extreme Precipitation Mapping George H. Taylor and Christopher Daly Oregon State University Corvallis Oregon
14th Conference on Applied Climatology Abstract # 71520 Using PRISM Climate Grids and GIS for Extreme Precipitation Mapping George H. Taylor and Christopher Daly Oregon State University Corvallis Oregon
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies
 Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
3B.3: Climate Controls on the Extreme Rainstorms in the Contiguous US:
 97 th AMS Annual Meeting 3B.3: Climate Controls on the Extreme Rainstorms in the Contiguous US: 1979-2015 Xiaodong Chen and Faisal Hossain Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of
97 th AMS Annual Meeting 3B.3: Climate Controls on the Extreme Rainstorms in the Contiguous US: 1979-2015 Xiaodong Chen and Faisal Hossain Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of
The NEXRAD Revolution: Scientific Basis for Updating the HMR-49 Statistical Storm Intensities and PMPs
 The NEXRAD Revolution: Scientific Basis for Updating the HMR-49 Statistical Storm Intensities and PMPs Bill Kappel, Senior Meteorologist/President Applied Weather Associates, Monument, CO www.appliedweatherassociates.com
The NEXRAD Revolution: Scientific Basis for Updating the HMR-49 Statistical Storm Intensities and PMPs Bill Kappel, Senior Meteorologist/President Applied Weather Associates, Monument, CO www.appliedweatherassociates.com
Denver International Airport MDSS Demonstration Verification Report for the Season
 Denver International Airport MDSS Demonstration Verification Report for the 2015-2016 Season Prepared by the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research Research Applications Division (RAL) Seth Linden
Denver International Airport MDSS Demonstration Verification Report for the 2015-2016 Season Prepared by the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research Research Applications Division (RAL) Seth Linden
Applications in situational awareness high-resolution NWP -- Ideas for the Blueprint DA discussion
 Applications in situational awareness high-resolution NWP -- Ideas for the Blueprint DA discussion 8 March 2016 Stan Benjamin, David Dowell, Curtis Alexander NOAA/ESRL/GLOBAL SYSTEMS DIVISION Situational
Applications in situational awareness high-resolution NWP -- Ideas for the Blueprint DA discussion 8 March 2016 Stan Benjamin, David Dowell, Curtis Alexander NOAA/ESRL/GLOBAL SYSTEMS DIVISION Situational
Further dynamical downscaling of NARCCAP using WRF:
 Further dynamical downscaling of NARCCAP using WRF: High-resolution simulations of extreme precipitation events in future NARCCAP climate scenarios Kelly Mahoney (UCAR-PACE) Michael Alexander, Jamie Scott,
Further dynamical downscaling of NARCCAP using WRF: High-resolution simulations of extreme precipitation events in future NARCCAP climate scenarios Kelly Mahoney (UCAR-PACE) Michael Alexander, Jamie Scott,
Bill Kappel. Doug Hultstrand. Applied Weather Associates
 Cool-Season PMP/PMF Meteorological Time Series for Snow Melt Calculations Bill Kappel Senior Meteorologist/Vice President Doug Hultstrand Hydrometeorologist Applied Weather Associates www.appliedweatherassociates.com
Cool-Season PMP/PMF Meteorological Time Series for Snow Melt Calculations Bill Kappel Senior Meteorologist/Vice President Doug Hultstrand Hydrometeorologist Applied Weather Associates www.appliedweatherassociates.com
Understanding Weather and Climate Risk. Matthew Perry Sharing an Uncertain World Conference The Geological Society, 13 July 2017
 Understanding Weather and Climate Risk Matthew Perry Sharing an Uncertain World Conference The Geological Society, 13 July 2017 What is risk in a weather and climate context? Hazard: something with the
Understanding Weather and Climate Risk Matthew Perry Sharing an Uncertain World Conference The Geological Society, 13 July 2017 What is risk in a weather and climate context? Hazard: something with the
Development of an Hourly- Updated NAM Forecast System
 Development of an Hourly- Updated NAM Forecast System Jacob Carley ab, Eric Rogers b, Shun Liu ab, Brad Ferrier ab, Eric Aligo ab, Matthew Pyle b, and Geoff DiMego b a IMSG, b NOAA/NWS/NCEP/EMC jacob.carley@noaa.gov
Development of an Hourly- Updated NAM Forecast System Jacob Carley ab, Eric Rogers b, Shun Liu ab, Brad Ferrier ab, Eric Aligo ab, Matthew Pyle b, and Geoff DiMego b a IMSG, b NOAA/NWS/NCEP/EMC jacob.carley@noaa.gov
Minor Winter Flooding Event in northwestern Pennsylvania January 2017
 1. Overview Minor Winter Flooding Event in northwestern Pennsylvania 12-13 January 2017 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A combination of snow melt, frozen ground, and areas
1. Overview Minor Winter Flooding Event in northwestern Pennsylvania 12-13 January 2017 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A combination of snow melt, frozen ground, and areas
Heavy Rainfall Event of June 2013
 Heavy Rainfall Event of 10-11 June 2013 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A 500 hpa short-wave moved over the eastern United States (Fig. 1) brought a surge of
Heavy Rainfall Event of 10-11 June 2013 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A 500 hpa short-wave moved over the eastern United States (Fig. 1) brought a surge of
CAPS Storm-Scale Ensemble Forecasting (SSEF) System
 CAPS Storm-Scale Ensemble Forecasting (SSEF) System Fanyou Kong, Ming Xue, Xuguang Wang, Keith Brewster Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms University of Oklahoma (collaborated with NSSL, SPC,
CAPS Storm-Scale Ensemble Forecasting (SSEF) System Fanyou Kong, Ming Xue, Xuguang Wang, Keith Brewster Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms University of Oklahoma (collaborated with NSSL, SPC,
Improving Reservoir Management Using the Storm Precipitation Analysis System (SPAS) and NEXRAD Weather Radar
 Improving Reservoir Management Using the Storm Precipitation Analysis System (SPAS) and NEXRAD Weather Radar Bill D. Kappel, Applied Weather Associates, LLC, Monument, CO Edward M. Tomlinson, Ph.D., Applied
Improving Reservoir Management Using the Storm Precipitation Analysis System (SPAS) and NEXRAD Weather Radar Bill D. Kappel, Applied Weather Associates, LLC, Monument, CO Edward M. Tomlinson, Ph.D., Applied
Talk Overview. Concepts. Climatology. Monitoring. Applications
 Atmospheric Rivers Talk Overview Concepts Climatology Monitoring Applications Satellite View Where is the storm? Where is the impact? Atmospheric Rivers Plume or fire hose of tropical moisture Heavy precipitation
Atmospheric Rivers Talk Overview Concepts Climatology Monitoring Applications Satellite View Where is the storm? Where is the impact? Atmospheric Rivers Plume or fire hose of tropical moisture Heavy precipitation
MET Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16)
 MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
Multi Radar Multi Sensor NextGen Weather Program. Presentation materials sourced from: Ken Howard HydroMet Research Group NSSL Warning R&D Division
 Multi Radar Multi Sensor NextGen Weather Program Presentation materials sourced from: Ken Howard HydroMet Research Group NSSL Warning R&D Division What is Multiple Radar Multi Sensor System () is the world
Multi Radar Multi Sensor NextGen Weather Program Presentation materials sourced from: Ken Howard HydroMet Research Group NSSL Warning R&D Division What is Multiple Radar Multi Sensor System () is the world
Convection-Resolving NWP with WRF. Section coordinator Ming Xue University of Oklahoma
 Convection-Resolving NWP with WRF Section coordinator Ming Xue University of Oklahoma Convection-resolving NWP Is NWP that explicitly treats moist convective systems ranging from organized MCSs to individual
Convection-Resolving NWP with WRF Section coordinator Ming Xue University of Oklahoma Convection-resolving NWP Is NWP that explicitly treats moist convective systems ranging from organized MCSs to individual
The Impact of Horizontal Resolution and Ensemble Size on Probabilistic Forecasts of Precipitation by the ECMWF EPS
 The Impact of Horizontal Resolution and Ensemble Size on Probabilistic Forecasts of Precipitation by the ECMWF EPS S. L. Mullen Univ. of Arizona R. Buizza ECMWF University of Wisconsin Predictability Workshop,
The Impact of Horizontal Resolution and Ensemble Size on Probabilistic Forecasts of Precipitation by the ECMWF EPS S. L. Mullen Univ. of Arizona R. Buizza ECMWF University of Wisconsin Predictability Workshop,
0-6 hour Weather Forecast Guidance at The Weather Company. Steven Honey, Joseph Koval, Cathryn Meyer, Peter Neilley The Weather Company
 1 0-6 hour Weather Forecast Guidance at The Weather Company Steven Honey, Joseph Koval, Cathryn Meyer, Peter Neilley The Weather Company TWC Forecasts: Widespread Adoption 2 0-6 Hour Forecast Details 3
1 0-6 hour Weather Forecast Guidance at The Weather Company Steven Honey, Joseph Koval, Cathryn Meyer, Peter Neilley The Weather Company TWC Forecasts: Widespread Adoption 2 0-6 Hour Forecast Details 3
Hydrologic Research Laboratory Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of California, Davis
 Physically-Based Estimation of Maximum Precipitation: Preliminary Results on Application to American River Basin for the December,1996-January,1997 Flood Event Hydrologic Research Laboratory Department
Physically-Based Estimation of Maximum Precipitation: Preliminary Results on Application to American River Basin for the December,1996-January,1997 Flood Event Hydrologic Research Laboratory Department
Hurricane Harvey the Name says it all. by Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service office State College, PA
 Hurricane Harvey the Name says it all by Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service office State College, PA 16803. 1. Overview Hurricane Harvey crossed the Texas coast (Fig. 1) as a category
Hurricane Harvey the Name says it all by Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service office State College, PA 16803. 1. Overview Hurricane Harvey crossed the Texas coast (Fig. 1) as a category
Operational Perspectives on Hydrologic Model Data Assimilation
 Operational Perspectives on Hydrologic Model Data Assimilation Rob Hartman Hydrologist in Charge NOAA / National Weather Service California-Nevada River Forecast Center Sacramento, CA USA Outline Operational
Operational Perspectives on Hydrologic Model Data Assimilation Rob Hartman Hydrologist in Charge NOAA / National Weather Service California-Nevada River Forecast Center Sacramento, CA USA Outline Operational
Introduction to NCEP's time lagged North American Rapid Refresh Ensemble Forecast System (NARRE-TL)
 Introduction to NCEP's time lagged North American Rapid Refresh Ensemble Forecast System (NARRE-TL) Binbin Zhou 1,2, Jun Du 2, Geoff Manikin 2 & Geoff DiMego 2 1. I.M. System Group 2. EMC/NCEP/NWS/NOAA
Introduction to NCEP's time lagged North American Rapid Refresh Ensemble Forecast System (NARRE-TL) Binbin Zhou 1,2, Jun Du 2, Geoff Manikin 2 & Geoff DiMego 2 1. I.M. System Group 2. EMC/NCEP/NWS/NOAA
Motivation & Goal. We investigate a way to generate PDFs from a single deterministic run
 Motivation & Goal Numerical weather prediction is limited by errors in initial conditions, model imperfections, and nonlinearity. Ensembles of an NWP model provide forecast probability density functions
Motivation & Goal Numerical weather prediction is limited by errors in initial conditions, model imperfections, and nonlinearity. Ensembles of an NWP model provide forecast probability density functions
An Overview of Operations at the West Gulf River Forecast Center Gregory Waller Service Coordination Hydrologist NWS - West Gulf River Forecast Center
 National Weather Service West Gulf River Forecast Center An Overview of Operations at the West Gulf River Forecast Center Gregory Waller Service Coordination Hydrologist NWS - West Gulf River Forecast
National Weather Service West Gulf River Forecast Center An Overview of Operations at the West Gulf River Forecast Center Gregory Waller Service Coordination Hydrologist NWS - West Gulf River Forecast
Adaptation by Design: The Impact of the Changing Climate on Infrastructure
 Adaptation by Design: The Impact of the Changing Climate on Infrastructure Heather Auld, J Klaassen, S Fernandez, S Eng, S Cheng, D MacIver, N Comer Adaptation and Impacts Research Division Environment
Adaptation by Design: The Impact of the Changing Climate on Infrastructure Heather Auld, J Klaassen, S Fernandez, S Eng, S Cheng, D MacIver, N Comer Adaptation and Impacts Research Division Environment
Remote Sensing of Precipitation
 Lecture Notes Prepared by Prof. J. Francis Spring 2003 Remote Sensing of Precipitation Primary reference: Chapter 9 of KVH I. Motivation -- why do we need to measure precipitation with remote sensing instruments?
Lecture Notes Prepared by Prof. J. Francis Spring 2003 Remote Sensing of Precipitation Primary reference: Chapter 9 of KVH I. Motivation -- why do we need to measure precipitation with remote sensing instruments?
Tangent-linear and adjoint models in data assimilation
 Tangent-linear and adjoint models in data assimilation Marta Janisková and Philippe Lopez ECMWF Thanks to: F. Váňa, M.Fielding 2018 Annual Seminar: Earth system assimilation 10-13 September 2018 Tangent-linear
Tangent-linear and adjoint models in data assimilation Marta Janisková and Philippe Lopez ECMWF Thanks to: F. Váňa, M.Fielding 2018 Annual Seminar: Earth system assimilation 10-13 September 2018 Tangent-linear
Southern Heavy rain and floods of 8-10 March 2016 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16803
 Southern Heavy rain and floods of 8-10 March 2016 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. Introduction Heavy rains (Fig. 1) produced record flooding in northeastern Texas
Southern Heavy rain and floods of 8-10 March 2016 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. Introduction Heavy rains (Fig. 1) produced record flooding in northeastern Texas
Enhancing Weather Information with Probability Forecasts. An Information Statement of the American Meteorological Society
 Enhancing Weather Information with Probability Forecasts An Information Statement of the American Meteorological Society (Adopted by AMS Council on 12 May 2008) Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 89 Summary This
Enhancing Weather Information with Probability Forecasts An Information Statement of the American Meteorological Society (Adopted by AMS Council on 12 May 2008) Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 89 Summary This
Probable Maximum Precipitation Study
 Probable Maximum Precipitation Study Virginia Floodplain Management Association Workshop Thursday, October 29, 2015 Robert T. Bennett, PE, RA, CFM DCR Dam Safety & Floodplain Management Definition (4VAC50-20-50.H)
Probable Maximum Precipitation Study Virginia Floodplain Management Association Workshop Thursday, October 29, 2015 Robert T. Bennett, PE, RA, CFM DCR Dam Safety & Floodplain Management Definition (4VAC50-20-50.H)
Using PRISM Climate Grids and GIS for Extreme Precipitation Mapping
 Using PRISM Climate Grids and GIS for Extreme Precipitation Mapping George H. Taylor, State Climatologist Oregon Climate Service 316 Strand Ag Hall Oregon State University Corvallis OR 97331-2209 Tel:
Using PRISM Climate Grids and GIS for Extreme Precipitation Mapping George H. Taylor, State Climatologist Oregon Climate Service 316 Strand Ag Hall Oregon State University Corvallis OR 97331-2209 Tel:
Development of High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) Ensemble Data Assimilation, Forecast and Post-Processing
 CORP Science Symposium, July 18-19, 2016, Fort Collins Development of High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) Ensemble Data Assimilation, Forecast and Post-Processing Isidora Jankov, Curtis Alexander, David
CORP Science Symposium, July 18-19, 2016, Fort Collins Development of High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) Ensemble Data Assimilation, Forecast and Post-Processing Isidora Jankov, Curtis Alexander, David
Justin Arnott and Michael Evans NOAA National Weather Service, Binghamton, NY. Richard Grumm NOAA National Weather Service, State College, PA
 3A.5 REGIONAL SCALE ENSEMBLE FORECAST OF THE LAKE EFFECT SNOW EVENT OF 7 FEBRUARY 2007 Justin Arnott and Michael Evans NOAA National Weather Service, Binghamton, NY Richard Grumm NOAA National Weather
3A.5 REGIONAL SCALE ENSEMBLE FORECAST OF THE LAKE EFFECT SNOW EVENT OF 7 FEBRUARY 2007 Justin Arnott and Michael Evans NOAA National Weather Service, Binghamton, NY Richard Grumm NOAA National Weather
Forecasting of Optical Turbulence in Support of Realtime Optical Imaging and Communication Systems
 Forecasting of Optical Turbulence in Support of Realtime Optical Imaging and Communication Systems Randall J. Alliss and Billy Felton Northrop Grumman Corporation, 15010 Conference Center Drive, Chantilly,
Forecasting of Optical Turbulence in Support of Realtime Optical Imaging and Communication Systems Randall J. Alliss and Billy Felton Northrop Grumman Corporation, 15010 Conference Center Drive, Chantilly,
Comparison of the NCEP and DTC Verification Software Packages
 Comparison of the NCEP and DTC Verification Software Packages Point of Contact: Michelle Harrold September 2011 1. Introduction The National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) and the Developmental
Comparison of the NCEP and DTC Verification Software Packages Point of Contact: Michelle Harrold September 2011 1. Introduction The National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) and the Developmental
Lightning Data Assimilation using an Ensemble Kalman Filter
 Lightning Data Assimilation using an Ensemble Kalman Filter G.J. Hakim, P. Regulski, Clifford Mass and R. Torn University of Washington, Department of Atmospheric Sciences Seattle, United States 1. INTRODUCTION
Lightning Data Assimilation using an Ensemble Kalman Filter G.J. Hakim, P. Regulski, Clifford Mass and R. Torn University of Washington, Department of Atmospheric Sciences Seattle, United States 1. INTRODUCTION
Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change: Historical Trends and Future Projections
 Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change: Historical Trends and Future Projections Thomas R. Knutson Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory / NOAA, Princeton, NJ U.S.A. IOGP/JCOMM/WCRP Workshop September 25-27,
Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change: Historical Trends and Future Projections Thomas R. Knutson Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory / NOAA, Princeton, NJ U.S.A. IOGP/JCOMM/WCRP Workshop September 25-27,
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING. GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13
 ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
NRC Workshop Probabilistic Flood Hazard Assessment (PFHA) Jan 29-31, Mel Schaefer Ph.D. P.E. MGS Engineering Consultants, Inc.
 Stochastic Event Flood Model (SEFM) Stochastic Modeling of Extreme Floods A Hydrological Tool for Analysis of Extreme Floods Mel Schaefer Ph.D. P.E. MGS Engineering Consultants, Inc. Olympia, WA NRC Workshop
Stochastic Event Flood Model (SEFM) Stochastic Modeling of Extreme Floods A Hydrological Tool for Analysis of Extreme Floods Mel Schaefer Ph.D. P.E. MGS Engineering Consultants, Inc. Olympia, WA NRC Workshop
Convective-scale NWP for Singapore
 Convective-scale NWP for Singapore Hans Huang and the weather modelling and prediction section MSS, Singapore Dale Barker and the SINGV team Met Office, Exeter, UK ECMWF Symposium on Dynamical Meteorology
Convective-scale NWP for Singapore Hans Huang and the weather modelling and prediction section MSS, Singapore Dale Barker and the SINGV team Met Office, Exeter, UK ECMWF Symposium on Dynamical Meteorology
Dynamic Ensemble Model Evaluation of Elevated Thunderstorms sampled by PRECIP
 Dynamic Ensemble Model Evaluation of Elevated Thunderstorms sampled by PRECIP Joshua S. Kastman, Patrick S. Market, and Neil Fox, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO Session 8B - Numerical Weather Prediction
Dynamic Ensemble Model Evaluation of Elevated Thunderstorms sampled by PRECIP Joshua S. Kastman, Patrick S. Market, and Neil Fox, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO Session 8B - Numerical Weather Prediction
The Use of GPS Radio Occultation Data for Tropical Cyclone Prediction. Bill Kuo and Hui Liu UCAR
 The Use of GPS Radio Occultation Data for Tropical Cyclone Prediction Bill Kuo and Hui Liu UCAR Current capability of the National Hurricane Center Good track forecast improvements. Errors cut in half
The Use of GPS Radio Occultation Data for Tropical Cyclone Prediction Bill Kuo and Hui Liu UCAR Current capability of the National Hurricane Center Good track forecast improvements. Errors cut in half
Toward improved initial conditions for NCAR s real-time convection-allowing ensemble. Ryan Sobash, Glen Romine, Craig Schwartz, and Kate Fossell
 Toward improved initial conditions for NCAR s real-time convection-allowing ensemble Ryan Sobash, Glen Romine, Craig Schwartz, and Kate Fossell Storm-scale ensemble design Can an EnKF be used to initialize
Toward improved initial conditions for NCAR s real-time convection-allowing ensemble Ryan Sobash, Glen Romine, Craig Schwartz, and Kate Fossell Storm-scale ensemble design Can an EnKF be used to initialize
Assimilation of cloud/precipitation data at regional scales
 Assimilation of cloud/precipitation data at regional scales Thomas Auligné National Center for Atmospheric Research auligne@ucar.edu Acknowledgments to: Steven Cavallo, David Dowell, Aimé Fournier, Hans
Assimilation of cloud/precipitation data at regional scales Thomas Auligné National Center for Atmospheric Research auligne@ucar.edu Acknowledgments to: Steven Cavallo, David Dowell, Aimé Fournier, Hans
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System January 15, 2019
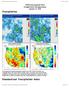 NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System January 15, 2019 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and
NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System January 15, 2019 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and
WRF Historical and PGW Simulations over Alaska
 WRF Historical and PGW Simulations over Alaska Andrew J. Newman 1, Andrew J. Monaghan 2, Martyn P. Clark 1, Kyoko Ikeda 1, Lulin Xue 1, and Jeff R. Arnold 3 GEWEX CPCM Workshop II 1 National Center for
WRF Historical and PGW Simulations over Alaska Andrew J. Newman 1, Andrew J. Monaghan 2, Martyn P. Clark 1, Kyoko Ikeda 1, Lulin Xue 1, and Jeff R. Arnold 3 GEWEX CPCM Workshop II 1 National Center for
Verification Methods for High Resolution Model Forecasts
 Verification Methods for High Resolution Model Forecasts Barbara Brown (bgb@ucar.edu) NCAR, Boulder, Colorado Collaborators: Randy Bullock, John Halley Gotway, Chris Davis, David Ahijevych, Eric Gilleland,
Verification Methods for High Resolution Model Forecasts Barbara Brown (bgb@ucar.edu) NCAR, Boulder, Colorado Collaborators: Randy Bullock, John Halley Gotway, Chris Davis, David Ahijevych, Eric Gilleland,
Project Summary 2015 DTC Task MM5: Test of an Expanded WRF-ARW Domain
 1. Introduction Project Summary 2015 DTC Task MM5: Test of an Expanded WRF-ARW Domain Trevor Alcott Ligia Bernardet Isidora Jankov The High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) model represents a major step
1. Introduction Project Summary 2015 DTC Task MM5: Test of an Expanded WRF-ARW Domain Trevor Alcott Ligia Bernardet Isidora Jankov The High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) model represents a major step
Report on EN2 DTC Ensemble Task 2015: Testing of Stochastic Physics for use in NARRE
 Report on EN2 DTC Ensemble Task 2015: Testing of Stochastic Physics for use in NARRE Motivation: With growing evidence that initial- condition uncertainties are not sufficient to entirely explain forecast
Report on EN2 DTC Ensemble Task 2015: Testing of Stochastic Physics for use in NARRE Motivation: With growing evidence that initial- condition uncertainties are not sufficient to entirely explain forecast
The enduring Louisiana rain and flooding of August 2016 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16803
 1. Introduction The enduring Louisiana rain and flooding of August 2016 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 Historic flooding impacted Louisiana on 12-15 August 2016 (TWC
1. Introduction The enduring Louisiana rain and flooding of August 2016 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 Historic flooding impacted Louisiana on 12-15 August 2016 (TWC
Atmospheric Moisture, Precipitation, and Weather Systems
 Atmospheric Moisture, Precipitation, and Weather Systems 6 Chapter Overview The atmosphere is a complex system, sometimes described as chaotic in nature. In this chapter we examine one of the principal
Atmospheric Moisture, Precipitation, and Weather Systems 6 Chapter Overview The atmosphere is a complex system, sometimes described as chaotic in nature. In this chapter we examine one of the principal
The Impacts of GPS Radio Occultation Data on the Analysis and Prediction of Tropical Cyclones. Bill Kuo, Xingqin Fang, and Hui Liu UCAR COSMIC
 The Impacts of GPS Radio Occultation Data on the Analysis and Prediction of Tropical Cyclones Bill Kuo, Xingqin Fang, and Hui Liu UCAR COSMIC GPS Radio Occultation α GPS RO observations advantages for
The Impacts of GPS Radio Occultation Data on the Analysis and Prediction of Tropical Cyclones Bill Kuo, Xingqin Fang, and Hui Liu UCAR COSMIC GPS Radio Occultation α GPS RO observations advantages for
HIGH RESOLUTION RAPID REFRESH COUPLED WITH SMOKE (HRRR- SMOKE): REAL-TIME AIR QUALITY MODELING SYSTEM AND ITS APPLICATION TO CASE STUDIES
 HIGH RESOLUTION RAPID REFRESH COUPLED WITH SMOKE (HRRR- SMOKE): REAL-TIME AIR QUALITY MODELING SYSTEM AND ITS APPLICATION TO CASE STUDIES Ravan Ahmadov 1,2 (ravan.ahmadov@noaa.gov) Acknowledgement: G.
HIGH RESOLUTION RAPID REFRESH COUPLED WITH SMOKE (HRRR- SMOKE): REAL-TIME AIR QUALITY MODELING SYSTEM AND ITS APPLICATION TO CASE STUDIES Ravan Ahmadov 1,2 (ravan.ahmadov@noaa.gov) Acknowledgement: G.
FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic areas for Risk mitigation in the Alpine space
 Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
Deterministic and Ensemble Storm scale Lightning Data Assimilation
 LI Mission Advisory Group & GOES-R Science Team Workshop 27-29 May 2015 Deterministic and Ensemble Storm scale Lightning Data Assimilation Don MacGorman, Ted Mansell (NOAA/National Severe Storms Lab) Alex
LI Mission Advisory Group & GOES-R Science Team Workshop 27-29 May 2015 Deterministic and Ensemble Storm scale Lightning Data Assimilation Don MacGorman, Ted Mansell (NOAA/National Severe Storms Lab) Alex
USSD Conference, Denver 2016
 USSD Conference, Denver 2016 M Schaefer, MGS Engineering Consultants K Neff, TVA River Operations C Jawdy, TVA River Operations S Carney, Riverside Technology B Barker, MGS Engineering Consultants G Taylor,
USSD Conference, Denver 2016 M Schaefer, MGS Engineering Consultants K Neff, TVA River Operations C Jawdy, TVA River Operations S Carney, Riverside Technology B Barker, MGS Engineering Consultants G Taylor,
QPF? So it s a Land-falling Atmospheric River, Can That Help the Forecaster Make a Better. David W. Reynolds
 So it s a Land-falling Atmospheric River, Can That Help the Forecaster Make a Better QPF? David W. Reynolds Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences Boulder, CO Brian Kawzenuk Center
So it s a Land-falling Atmospheric River, Can That Help the Forecaster Make a Better QPF? David W. Reynolds Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences Boulder, CO Brian Kawzenuk Center
MIDWEST PROBABLE MAXIMUM PRECIPITATION STUDIES
 MIDWEST PROBABLE MAXIMUM PRECIPITATION STUDIES Bill Kappel Senior Meteorologist/Vice President Ed Tomlinson, PhD Chief Meteorologist/President Applied Weather Associates www.appliedweatherassociates.com
MIDWEST PROBABLE MAXIMUM PRECIPITATION STUDIES Bill Kappel Senior Meteorologist/Vice President Ed Tomlinson, PhD Chief Meteorologist/President Applied Weather Associates www.appliedweatherassociates.com
Pseudo-Global warming approach using 4KM WRF model
 Pseudo-Global warming approach using 4KM WRF model S. Kurkute 1,2 Y. Li 1,2 1 School of Environment and Sustainability University of Saskatchewan 2 Global Institute of Water Security University of Saskatchewan
Pseudo-Global warming approach using 4KM WRF model S. Kurkute 1,2 Y. Li 1,2 1 School of Environment and Sustainability University of Saskatchewan 2 Global Institute of Water Security University of Saskatchewan
High Resolution Numerical Weather Prediction for High Impact and Extreme Weather Events in 2014 across Southern California
 High Resolution Numerical Weather Prediction for High Impact and Extreme Weather Events in 2014 across Southern California Alex Tardy Alexander.Tardy@noaa.gov NWS San Diego Warning Coordination Meteorologist
High Resolution Numerical Weather Prediction for High Impact and Extreme Weather Events in 2014 across Southern California Alex Tardy Alexander.Tardy@noaa.gov NWS San Diego Warning Coordination Meteorologist
A WRF-based rapid updating cycling forecast system of. BMB and its performance during the summer and Olympic. Games 2008
 A WRF-based rapid updating cycling forecast system of BMB and its performance during the summer and Olympic Games 2008 Min Chen 1, Shui-yong Fan 1, Jiqin Zhong 1, Xiang-yu Huang 2, Yong-Run Guo 2, Wei
A WRF-based rapid updating cycling forecast system of BMB and its performance during the summer and Olympic Games 2008 Min Chen 1, Shui-yong Fan 1, Jiqin Zhong 1, Xiang-yu Huang 2, Yong-Run Guo 2, Wei
Strategic Radar Enhancement Project (SREP) Forecast Demonstration Project (FDP) The future is here and now
 Strategic Radar Enhancement Project (SREP) Forecast Demonstration Project (FDP) The future is here and now Michael Berechree National Manager Aviation Weather Services Australian Bureau of Meteorology
Strategic Radar Enhancement Project (SREP) Forecast Demonstration Project (FDP) The future is here and now Michael Berechree National Manager Aviation Weather Services Australian Bureau of Meteorology
Recent Data Assimilation Activities at Environment Canada
 Recent Data Assimilation Activities at Environment Canada Major upgrade to global and regional deterministic prediction systems (now in parallel run) Sea ice data assimilation Mark Buehner Data Assimilation
Recent Data Assimilation Activities at Environment Canada Major upgrade to global and regional deterministic prediction systems (now in parallel run) Sea ice data assimilation Mark Buehner Data Assimilation
Impact of Targeted Dropsonde Data on Mid-latitude Numerical Weather Forecasts during the 2011 Winter Storms Reconnaissance Program
 ESRL Impact of Targeted Dropsonde Data on Mid-latitude Numerical Weather Forecasts during the 2011 Winter Storms Reconnaissance Program Presented by Tom Hamill Forecasts and assimilations : Carla Cardinali,
ESRL Impact of Targeted Dropsonde Data on Mid-latitude Numerical Weather Forecasts during the 2011 Winter Storms Reconnaissance Program Presented by Tom Hamill Forecasts and assimilations : Carla Cardinali,
HRRR-AK: Status and Future of a High- Resolu8on Forecast Model for Alaska
 HRRR-AK: Status and Future of a High- Resolu8on Forecast Model for Alaska Trevor Alco* 1, Jiang Zhu 2, Don Morton 3, Ming Hu 4, Cur8s Alexander 1 1 ESRL Global Systems Division, Boulder, CO 2 GINA/UAF,
HRRR-AK: Status and Future of a High- Resolu8on Forecast Model for Alaska Trevor Alco* 1, Jiang Zhu 2, Don Morton 3, Ming Hu 4, Cur8s Alexander 1 1 ESRL Global Systems Division, Boulder, CO 2 GINA/UAF,
NRC Workshop - Probabilistic Flood Hazard Assessment Jan 2013
 Regional Precipitation-Frequency Analysis And Extreme Storms Including PMP Current State of Understanding/Practice Mel Schaefer Ph.D. P.E. MGS Engineering Consultants, Inc. Olympia, WA NRC Workshop - Probabilistic
Regional Precipitation-Frequency Analysis And Extreme Storms Including PMP Current State of Understanding/Practice Mel Schaefer Ph.D. P.E. MGS Engineering Consultants, Inc. Olympia, WA NRC Workshop - Probabilistic
Applications/Users for Improved S2S Forecasts
 Applications/Users for Improved S2S Forecasts Nolan Doesken Colorado Climate Center Colorado State University WSWC Precipitation Forecasting Workshop June 7-9, 2016 San Diego, CA First -- A short background
Applications/Users for Improved S2S Forecasts Nolan Doesken Colorado Climate Center Colorado State University WSWC Precipitation Forecasting Workshop June 7-9, 2016 San Diego, CA First -- A short background
AMPS Update June 2017
 AMPS Update June 2017 Kevin W. Manning Jordan G. Powers Mesoscale and Microscale Meteorology Laboratory National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO 12th Workshop on Antarctic Meteorology and Climate
AMPS Update June 2017 Kevin W. Manning Jordan G. Powers Mesoscale and Microscale Meteorology Laboratory National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO 12th Workshop on Antarctic Meteorology and Climate
The National Weather Service of the Future: Building a Weather-Ready Nation
 The of the Future: Building a Weather-Ready Nation Dr. Louis W. Uccellini Director, NOAA Assistant Administrator for Weather Services NCEP Production Suite Review December 2, 2014 Outline Building a Weather-Ready
The of the Future: Building a Weather-Ready Nation Dr. Louis W. Uccellini Director, NOAA Assistant Administrator for Weather Services NCEP Production Suite Review December 2, 2014 Outline Building a Weather-Ready
Amy Harless. Jason Levit, David Bright, Clinton Wallace, Bob Maxson. Aviation Weather Center Kansas City, MO
 Amy Harless Jason Levit, David Bright, Clinton Wallace, Bob Maxson Aviation Weather Center Kansas City, MO AWC Mission Decision Support for Traffic Flow Management Ensemble Applications at AWC Testbed
Amy Harless Jason Levit, David Bright, Clinton Wallace, Bob Maxson Aviation Weather Center Kansas City, MO AWC Mission Decision Support for Traffic Flow Management Ensemble Applications at AWC Testbed
Implementation and evaluation of a regional data assimilation system based on WRF-LETKF
 Implementation and evaluation of a regional data assimilation system based on WRF-LETKF Juan José Ruiz Centro de Investigaciones del Mar y la Atmosfera (CONICET University of Buenos Aires) With many thanks
Implementation and evaluation of a regional data assimilation system based on WRF-LETKF Juan José Ruiz Centro de Investigaciones del Mar y la Atmosfera (CONICET University of Buenos Aires) With many thanks
CONDUIT Update Cooperative Opportunity for NCEP Data using IDD Technology Rebecca Cosgrove NCEP/NCO/Production Management Branch September 15, 2014
 CONDUIT Update Cooperative Opportunity for NCEP Data using IDD Technology Rebecca Cosgrove NCEP/NCO/Production Management Branch September 15, 2014 Agenda Technology Refresh Data available today NOAAPORT/SBN
CONDUIT Update Cooperative Opportunity for NCEP Data using IDD Technology Rebecca Cosgrove NCEP/NCO/Production Management Branch September 15, 2014 Agenda Technology Refresh Data available today NOAAPORT/SBN
IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST. (a) (b) (c)
 9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
