INTERNATIONAL LASER RANGING SERVICE
|
|
|
- Owen Randall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERNATIONAL LASER RANGING SERVICE R E P O R T June 2012 Edited by C. Noll and M. Pearlman Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD NASA/TP
2 Available From: NASA Center for Aerospace Information National Technical Information Service 7121 Standard Drive 5285 Port Royal Road Hanover, MD Springfield, VA Price Code: A17 Price Code: A10
3 Preface This volume is the sixth published report for the International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS). This edition once again concentrates on achievements and work in progress rather than ILRS organizational elements. This latest edition of the ILRS report is structured as follows: Section 1 Science Report examines the ILRS role in the ITRF, its synergy with the other geodetic techniques, and some interesting applications for both SLR and LLR. Section 2 About the ILRS, reviews the service, its mission, structure, and role in space geodesy. Section 3 ILRS Network, provides the current status and recent performance statistics of the international stations supporting the ILRS and offers a perspective on site surveys and system co-locations. An update on field engineering activities is also provided. Section 4 Supported Missions, gives information about many of the current and future missions supported by the ILRS. Section 5 Operations, discusses data center developments, satellite predictions, ILRS tracking priorities, recent developments in the area of dynamic priorities, and the flow of on-site normal points and full-rate data. Section 6 Analysis Activities, reviews the recent developments in the ILRS Analysis Working Group including the three pilot projects begun in 2002, Computation of Station Positions and EOPs, Orbits, and Software Benchmarking. Section 7 Reporting and Outreach, reviews website development, station performance reporting, and ILRS-related publications. Section 8 Working Group Reports, details the status of the ILRS Working Groups, recent accomplishments, and future plans. Section 9 Retroreflector Array Developments, includes ILRS standards in the area, performance modeling activities, and studies on future arrays. Section 10 Emerging Technologies, includes information about high repetition rate lasers and systems, detectors, timers and frequency standards, multi-wavelength ranging, and other hardware that will help advance the accuracy and automation of laser ranging systems. Also included are new applications for the SLR technique. Section 11 AC, AAC and Lunar AAC Reports, presents individual summaries from ILRS analysis, associate analysis, and lunar associate analysis centers. Section 12 Station Reports, includes information received from the stations contributing to the ILRS network. Section 13 Meeting Summaries, reviews ILRS-related meetings in and reports issued by the service over that period. Section 14 Bibliography, lists some of the papers and presentations about SLR and LLR science and technology made during Appendix ILRS Information, lists organizations participating in the ILRS and defines acronyms used in this report. This report is also available through the ILRS website at URL ILRS Annual Report i i
4 For further information, contact the ILRS Central Bureau: Carey Noll Secretary, ILRS Central Bureau NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Code Greenbelt, MD USA Michael Pearlman Director, ILRS Central Bureau Harvard/Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 60 Garden Street Cambridge, MA USA ILRS Web site: A complete list of ILRS associates can be found on the ILRS Web site at ii
5 Acknowledgement The editors would like to acknowledge the essential contributions from our ILRS colleagues to this edition of the ILRS report. iii
6
7 Table Of Contents Preface... i Acknowledgement... iii Dedication... 1 Introduction Chairman s Remarks... 7 Section 1 Science Report Section 2 About the ILRS Section 3 ILRS Network Section 4 Supported Missions Section 5 Operations Section 6 Analysis Report Section 7 Reporting and Outreach Section 8 Working Group Reports Section 9 Retroreflector Array Developments Section 10 Emerging Technologies Section 11 ILRS AC, AAC, and Lunar AAC Reports ILRS Analysis Center Reports Italian Space Agency/Space Geodesy Center G. Colombo (ASI/CGS) Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie (BKG) Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitute (DGFI) European Space Operation Center (ESOC) Geoscience Australia (GA) Helmholtz Centre Potsdam GeoForschungsZentrum German. Research Centre for Geosciences (GFZ) Groupe de Recherche en Geodesie Spatiale (GRGS) Joint Center for Earth Systems Technology/Goddard Space Flight Center (JCET/GSFC) Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) Space Geodesy Facility (NSGF) v
8 ILRS Associate Analysis Center Reports Center for Orbit Determination in Europe (CODE) The University of Texas Center for Space Research (CSR) Delft University of Technology (DUT) Forsvarets Forskningsinstitutt (FFI) Main Astronomical Observatory of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (GAOUA) Hitotsubashi University Information-Analytical Center (IAC) Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) National Institute of Geophysics, Geodesy and Geography (NIGGG, formerly CLG/BAS) Shanghai Astronomical Observatory (SHAO) ILRS Lunar Associate Analysis Center Reports Institut Fuer Erdmessung/Forschungseinrichtung Satellitengeodaesie (IFE/FESG) Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) Paris Observatory Lunar Analysis Center (POLAC) Section 12 ILRS Station Reports Arequipa, Peru Beijing, China Borowiec, Poland Changchun, China Concepción, Chile FTLRS and Grasse, France Graz, Austria Greenbelt MD (NGSLR), USA Haleakala HI, USA Hartebeesthoek, South Africa Helwan, Egypt Herstmonceux, UK Kiev, Ukraine Kunming, China Lviv, Ukraine McDonald TX, USA Metsähovi, Finland Monument Peak CA, USA Mount Stromlo, Australia Potsdam, Germany Riga, Latvia San Fernando, Spain San Juan, Argentina Shanghai, China vi
9 Simeiz, Ukraine Tahiti, French Polynesia Tanegashima, Japan Wettzell, Germany Yarragadee, Australia Zimmerwald, Switzerland Section 13 Meeting Summaries Section 14 Bibliography Appendix ILRS Information.... A-1 ILRS Contributing Organizations...A-1 Acronym List... A-3 vii
10
11 Dedication Wolfgang Seemueller ( ) DGFI Munich Wolfgang Seemueller ( ) The ILRS community sadly suffered another loss in Wolfgang Seemueller, head of the EUROLAS Data Center at the Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut, DGFI, in Munich, Germany, died from cancer on November 11, 2010 at the age of 64. Wolfgang studied Physics and Surveying Engineering at the Technical University in Munich from 1968 to In the following years, until 1981, he was a research assistant at the Technical University of Munich and joined DGFI in March From the beginning, his interest was focused on the problems of data management and archiving. He reorganized the data stored at DGFI, particularly the SLR data, into new structures. Shortly after the European Laser Stations (EUROLAS) Consortium was founded, Wolfgang joined the group to establish the new EUROLAS Data Center (EDC) since there was no common data management available at that time. Due to the reduced computer resources at DGFI he devoted a great portion of his time to create and run the operational data center for EUROLAS. Wolfgang dedicated all his heart and energy to this important task. His ideas to support the SLR community with rapid information on predictions, including time biases, and his effort to reduce the turn around time of data delivery are still in our memories. Since 1995 he also served as secretary of the EUROLAS Consortium and actively supported this group by setting up various infrastructure components including exploders. Wolfgang was a member of the SLR/CSTG Steering Committee, which was responsible for the establishment of the International Laser Ranging Service in Since the start of the ILRS, Wolfgang served on the Governing Board as its Data Center Representative. The EDC became part of the ILRS as a Global Data Center, parallel to CDDIS. His friendly rapport with the station operators and his willingness to solve any problem concerning predictions or data earned him the respect of the ILRS community. Because of his position at the EDC, Wolfgang was also a member of the Data Formats and Procedure Working Group of the ILRS, which he chaired from 2002 until his passing in The new CPF and CRD formats were formulated and applied under the direction of this working group during his tenure. Parallel to all his SLR activities, Wolfgang was involved in the GPS analysis of data from the stations in the SIRGAS (Geocentric Reference System of the Americas) network since June He was responsible for the SIRGAS RNAAC, the Regional Network Analysis Center for South America, and has combined the weekly solutions for this network as well as various combined SIRGAS coordinate solutions that are basis for national networks of those countries. Wolfgang Seemueller will be remembered as a competent member of the ILRS, a dear colleague, and a good friend. The ILRS wishes to dedicate this issue of the ILRS annual report series to the memory of Wolfgang Seemueller in the grateful recognition of his contribution to the ILRS and the entire SLR community. He will be missed. Horst Mueller, DGFI, Munich, Germany Mike Pearlman, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, USA 1
12
13 Dedication Yang FuMin ( ) Shanghai Obs., China Yang FuMin ( ) I am honored to write this dedication on behalf of my longtime SLR colleague and friend, Professor Yang FuMin. I wish to express my gratitude to Yang s son, Jun, and to his SLR colleague in Shanghai, Zhang Zhongping, for filling in the gaps in my knowledge of Yang s life history and accomplishments. Yang FuMin was born on 24 December 1942 in Chongqing City, China. His family later moved to the city of Guang-zhou in Guang-dong Province, where he spent his childhood years. In 1961, he began his studies at the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory and, in 1964, was the one of the Observatory s first Master s Degree candidates. Following his graduation in 1968, he carried out research on astrometry and celestial mechanics for the Chinese Academy of Sciences. By 1971, Yang had become interested in SLR technology, and, from 1978 to 1985, he led the development of multiple generations of China s SLR stations and software for precision orbit determination. From 1985 to 1988, Yang was a Visiting Scholar in the Quantum Electronics Group at the University of Maryland College Park in the USA. The group was led by my Ph.D. thesis advisor, Professor Carroll Alley, who first introduced me to Yang. Shortly after I was appointed Deputy Manager of NASA s Crustal Dynamics Project in 1989, my wife and I were invited by Yang and Madame Ye to tour the Chinese SLR sites. It was during our first visit to China in 1991 that Yang invited us to their apartment in Shanghai, where we were introduced to his lovely and gracious wife, Hu Miaoying, and to their affable teenage son, Jun. Over the years, Yang and I continued to correspond. When Yang traveled to the USA, I often met with him in Washington DC and Adele and I were happy to have the opportunity to host him in our home. As a researcher, Yang published 70 papers and reports and, in 1992, was elected one of China s National Outstanding Experts and went on to win three national science prizes, six Shanghai prizes, among others. In 1995, he was elected Deputy Chairman of the Chinese Astronomical Society. He also served as a professor, doctoral thesis advisor, Deputy Director of the Shanghai Observatory, and Chair of the Shanghai Astronomical Society. Within the ILRS community, Yang served as a member of the ILRS Governing Board, Chairman of the WPLTN Executive Committee, and Chairman of 10th ILRS Workshop Scientific Committee. Perhaps most importantly, after nearly 40 years of Yang s leadership, the Chinese SLR stations now rank among the top performing stations in the world. Within the past decade, Yang conducted research on uncooperative space targets and Laser Time Transfer (LTT). Using a 40W laser, laser returns from an uncooperative space target were first obtained by the Shanghai station on July 7, In 2007, an LTT experiment, between a ground-based hydrogen maser and space-qualified rubidium clocks on the Chinese Experimental Compass M1 Navigation satellite, successfully monitored the performance of Chinese-made atomic clocks onboard. Furthermore, in 2008, the high cross-section laser retro-reflector arrays (LRAs), also designed by Yang, were successfully tracked by the ILRS network. 3
14 Yang retired from the Observatory in November 2008, but continued to work with his SLR colleagues in China until his untimely death from heart disease on February 9, Yang FuMin will be remembered as a kind-hearted, hardworking, and soft-spoken consummate gentleman. He will long be missed by his family and his colleagues in the ILRS community. Rest in peace, my friend. Dr. John Degnan, Chief Scientist, Sigma Space Corporation 4
15 Introduction The Importance of Satellite Laser Ranging to the International Terrestrial Reference Frame Since its inception, space geodesy has brought a new era of global measurements allowing us to quantify changes of the Earth system in space and time: Earth rotation, its gravity field and their irregularities, global and regional sea level variation, tectonic motion and deformation, post-glacial rebound, geocenter motion, large scale deformation due to Earthquakes, local subsidence and other ruptures and crustal dislocations. All these geosciences applications, together with precise satellite orbit determination and other practical applications in geo-information, fundamentally depend on the availability of a truly global reference system that only space geodesy is able realize. Geodetic observations collected at stations with measurement systems of Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR), Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI), Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) and Doppler Orbitography Radiopositioning Integrated by Satellite (DORIS), are the main ingredients of the construction of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF), recommended as a standard by the International Unions for Earth science applications. As the ITRF becomes widely used and needed, the science requirement becomes more demanding and stringent, aiming for a precise reference frame at the level of 1 mm and 0.1 mm/year stability over decades. SLR is playing a major, yet a critical role in the ITRF definition, currently being the most precise satellite technique for realizing the physical center of mass of the whole Earth system, chosen as a natural origin for the ITRF. SLR, together with VLBI, contributes to the ITRF scale definition. These two physical parameters (origin and scale) are of fundamental importance in Earth science applications, such as the currently under-debate societal issue of how much sea level is rising due to ice sheet melting and its ramification with global warming and climate change. An ITRF origin drift of 2 mm/year would cause an error of 0.3 mm/year in the estimated rate of global sea level rise as determined by satellite altimetry. This bias would be more amplified in the estimated regional sea level rise, and in particular at high latitudes, reaching up to 1.8 mm/year. An ITRF origin drift in the Z direction of 2 mm/year generates a change in the north velocity, as a function the cosine of the latitude (2 mm/year at the equator and zero at the pole), and a vertical velocity change as a function of the sine of the latitude (zero at the equator and +2 and -2 mm/year at the North and South poles, respectively). A scale drift of 0.1 ppb/year (10-9, or 6.3 mm/year at the equator) translates to a drift of 0.6 mm/year in the estimated rate of sea level rise, as determined by tide gauge records, and causes vertical velocity changes by the same amount. Such origin and scale drifts would be critical, not only for sea level rise investigation, but also for plate motion and Post Glacial Rebound estimates by space geodesy. Our current assessment of the accuracy of the ITRF origin and scale (ITRF2008 results) is roughly 1 cm over the time span of the available observations. As we aim for a stable ITRF over decades, we still need to improve the reference frame by at least a factor of ten in order to meet the science requirement. As long as we need to improve the reference frame, we still need to continue tracking LAGEOS and other satellites, but we also need to upgrade the aging SLR and other technique ground instruments to new generation of observing systems. Zuheir Altamimi Institut Géographique National President of IAG Commission 1 ( ) May 21,
16
17 Chairman s Remarks The period of time covered by this bi-annual ILRS Report is, in my opinion, a very exciting time to be involved in Satellite Laser Ranging and in Space Geodesy in general. The inclusion of the ILRS as a Service within the International Association of Geodesy s Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) brings us into firm scientific context alongside our sister Services, the IGS, IVS and IDS. With GGOS itself a sub-task within the Inter-governmental GEO (Group for Earth Observation), our work to support a wide range of geophysical investigations, many of them of direct interest to policy makers and the general public, has never had such a high profile. Of course, along with that impact on such areas of interest as climate change, sea-level rise, etc., comes the responsibility to ensure that our underpinning observations and the products derived from them are of the highest possible quality. The GGOS goal is to realize a global reference frame of accuracy 1mm and stability 0.1mm y-1 [Gross, et al, in: The Global Geodetic Observing System: Meeting the Requirements of a Global Society on a Changing Planet in 2020, edited by H.- P. Plag and M. Pearlman, Springer, Berlin, 2009], so we cannot afford to take our eyes off the ball in terms of continuing efforts to drive down systematic errors in our calibration and satellite range measurements and to improve the models used in our analyses. My predecessor, the late and sadly missed Prof. Werner Gurtner, wrote in his introduction to the ILRS Report that a disappointment during that period was the discovery of small but significant range errors detected at a number of stations that used a particular time-of-flight counter. Hopefully, with the evident migration at several stations to high-quality event timers to support high repetition ranging, such discoveries will become rare and of dwindling magnitude. But many stations continue to be in need of upgrade and the hope is that their responsible agencies will consider this as a matter of urgency. In some respects of course, such discoveries of range errors do show that a healthy dialogue is in place between the ILRS observing teams, technologists, and analysts such that there can be no hiding place for bad data. The ILRS continues to increase its impact on a wide variety of new missions. Many hours of one-way tracking have been recorded by the mission from a subset of the ILRS network to NASA s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), in orbit a few tens of km above the lunar surface. Very impressive and crucial to tracking success is the web-interface that gives observers near real-time feedback on whether or not their photons are being detected on board. The CNES/OCA Time Transfer by Laser Link (T2L2) project on board Jason-2 continues successfully with several tracking campaigns organized by the mission, including one involving the Observatoire de Paris and the French transportable laser ranging system. It was very exciting to see that, following very high resolution imaging from LRO that re-discovered on the surface of the Moon the long-lost Russian Lunokod-2 rover, the Apache Point Observatory LLR Operation obtained a strong series of returns from the vehicle. It is to be hoped that such high-profile work will re-invigorate this very valuable lunar component of the ILRS. Future to-be supported missions include the Russian RadioAstron astrophysical VLBI satellite that will challenge even the Lunar-capable stations, the proposed highly-novel JPL mission, Geodetic Reference Antenna in Space (GRASP), that is set to revolutionize from orbit the accuracy with which stations inter-technique ground ties can be determined and monitored for all the key geodetic systems, and the new ASI/ESA geodetic and relativity sphere LARES. More speculatively, but approved by the ILRS for transponder support, is the far-future international GETEMME mission to Mars and its two moons. A very successful Technical Workshop on SLR Tracking of GNSS Constellations was held in Metsovo, Greece in September The meeting discussed many aspects of both the scientific advantages and practical issues surrounding the requirement for the ILRS network to track increasing numbers of GNSS satellites, including those from the GLONASS, COMPASS and emerging Galileo constellations, as well as plans for future GPS satellites. A follow-on Technical Workshop is to be held in Italy in late Events surrounding the planned 17th International Workshop on Laser Ranging in Concepcion Chile, served as a stark reminder of the forces that our geodetic observations seek 7
18 to understand. The magnitude 8.8 earthquake that struck and caused extensive damage to the region in March 2010 prevented the University of Concepcion from hosting the workshop in late Our colleagues at the Wettzell station are to be thanked for offering at short notice to host the re-arranged workshop in Koetzting in May From the many sections of this report it is clear that the ILRS continues as a vibrant, essential service with many new technological and analytical advances and new scientific applications. New missions that need precise tracking to underpin their scientific goals are always welcome to apply for support, and it is very encouraging that the network stations, operations, and data centers continue to cope with the increasing workload without any apparent negative impact on the more traditional geodetic targets LAGEOS and Etalon that ensure that the ILRS continues to play an important role in fundamental geodesy. Graham Appleby ILRS Governing Board Chairman NERC Space Geodesy Facility United Kingdom 8
INTERNATIONAL SLR SERVICE
 ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES, Vol. 46, No. 4 2011 DOI: 10.2478/v10018-012-0004-z INTERNATIONAL SLR SERVICE Stanisław Schillak Space Research Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences Astrogeodynamic Observatory, Borowiec
ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES, Vol. 46, No. 4 2011 DOI: 10.2478/v10018-012-0004-z INTERNATIONAL SLR SERVICE Stanisław Schillak Space Research Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences Astrogeodynamic Observatory, Borowiec
3.4.2 International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS)
 3 Reports of IERS components 3.4 Technique Centres 3.4.2 International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS) Introduction Network The International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS), established in 1998, is responsible
3 Reports of IERS components 3.4 Technique Centres 3.4.2 International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS) Introduction Network The International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS), established in 1998, is responsible
Fundamental Station Wettzell - geodetic observatory -
 Fundamental Station Wettzell - geodetic observatory - Wolfgang Schlüter Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Fundamental Station Wettzell Germany Radiometer Workshop, Wettzell, 10.10.06 Evolvement
Fundamental Station Wettzell - geodetic observatory - Wolfgang Schlüter Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Fundamental Station Wettzell Germany Radiometer Workshop, Wettzell, 10.10.06 Evolvement
From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed?
 From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed? Zuheir ALTAMIMI Institut National de l Information Géographique et Forestière, France Vice-President,
From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed? Zuheir ALTAMIMI Institut National de l Information Géographique et Forestière, France Vice-President,
The Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) of the International Association of Geodesy, IAG
 The Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) of the International Association of Geodesy, IAG Hans-Peter Plag (1), Markus Rothacher (2), Richard Gross (3), Srinivas Bettadpur (4) (1) Nevada Bureau of Mines
The Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) of the International Association of Geodesy, IAG Hans-Peter Plag (1), Markus Rothacher (2), Richard Gross (3), Srinivas Bettadpur (4) (1) Nevada Bureau of Mines
GGOS The Global Geodetic Observing System of the International Association of Geodesy (IAG)
 GGOS The Global Geodetic Observing System of the International Association of Geodesy (IAG) Hansjörg KUTTERER, Germany Key words: Geodetic Reference Frames, Global Geodetic Observing System, International
GGOS The Global Geodetic Observing System of the International Association of Geodesy (IAG) Hansjörg KUTTERER, Germany Key words: Geodetic Reference Frames, Global Geodetic Observing System, International
Geodetic Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI)
 Geodetic Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) A brief Note compiled by: Prof. Madhav N. Kulkarni, IIT Bombay Since the inception of the Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) system in 1967, this
Geodetic Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) A brief Note compiled by: Prof. Madhav N. Kulkarni, IIT Bombay Since the inception of the Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) system in 1967, this
A Unique Reference Frame: Basis of the Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) for Geodynamics and Global Change
 SRTM (InSAR) A Unique Reference Frame: Basis of the Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) for Geodynamics and Global Change Hermann Drewes President IAG Commission 1 Reference Frames Deutsches Geodätisches
SRTM (InSAR) A Unique Reference Frame: Basis of the Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) for Geodynamics and Global Change Hermann Drewes President IAG Commission 1 Reference Frames Deutsches Geodätisches
Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, NAWI Graz Technische Universität Graz
 GGOS and Reference Systems Introduction 2015-10-12 Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, NAWI Graz Technische Universität Graz Torsten Mayer-Gürr 1 Course and exam Lecture Monday 14:00 16:00, A111 (ST01044)
GGOS and Reference Systems Introduction 2015-10-12 Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, NAWI Graz Technische Universität Graz Torsten Mayer-Gürr 1 Course and exam Lecture Monday 14:00 16:00, A111 (ST01044)
Lecture 2 Measurement Systems. GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy
 Lecture 2 Measurement Systems GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy VLBI and SLR VLBI Very Long Baseline Interferometry SLR Satellite Laser Ranging Very Long Baseline Interferometry VLBI Geometric Delay δg S Baseline
Lecture 2 Measurement Systems GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy VLBI and SLR VLBI Very Long Baseline Interferometry SLR Satellite Laser Ranging Very Long Baseline Interferometry VLBI Geometric Delay δg S Baseline
New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts
 Fourth Swarm science meeting and geodetic missions workshop ESA, 20-24 March 2017, Banff, Alberta, Canada New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts Richard
Fourth Swarm science meeting and geodetic missions workshop ESA, 20-24 March 2017, Banff, Alberta, Canada New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts Richard
SECOND ANNOUNCEMENT International Technical Laser Workshop 2012 (ITLW-12)
 SECOND ANNOUNCEMENT International Technical Laser Workshop 2012 (ITLW-12) Version 31/Oct/12 Satellite, Lunar and Planetary Laser Ranging: characterizing the space segment Frascati National Laboratories
SECOND ANNOUNCEMENT International Technical Laser Workshop 2012 (ITLW-12) Version 31/Oct/12 Satellite, Lunar and Planetary Laser Ranging: characterizing the space segment Frascati National Laboratories
GGOS The Global Geodetic Observing System of the International Association of Geodesy
 GGOS The Global Geodetic Observing System of the International Association of Geodesy Presented at the FIG Working Week 2017, May 29 - June 2, 2017 in Helsinki, Finland Hansjörg Kutterer BKG, Germany Content
GGOS The Global Geodetic Observing System of the International Association of Geodesy Presented at the FIG Working Week 2017, May 29 - June 2, 2017 in Helsinki, Finland Hansjörg Kutterer BKG, Germany Content
REGIONAL REFERENCE FRAMES: THE IAG PERSPECTIVE
 REGIONAL REFERENCE FRAMES: THE IAG PERSPECTIVE João Agria Torres SPUIAGG IAG Sub-commission 1.3: Regional Reference Frames jatorres@iol.pt 1. About the IAG CONTENT 2. Objectives and organization of SC
REGIONAL REFERENCE FRAMES: THE IAG PERSPECTIVE João Agria Torres SPUIAGG IAG Sub-commission 1.3: Regional Reference Frames jatorres@iol.pt 1. About the IAG CONTENT 2. Objectives and organization of SC
International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS)
 International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS) http://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov E. C. Pavlis 1, M. R. Pearlman 2, C. E. Noll 3, G. Appleby 4, J. Müller 5 Overview The ILRS is the international source that provides
International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS) http://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov E. C. Pavlis 1, M. R. Pearlman 2, C. E. Noll 3, G. Appleby 4, J. Müller 5 Overview The ILRS is the international source that provides
The Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) of the International Association of Geodesy (IAG)
 The Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) of the International Association of Geodesy (IAG) Hermann Drewes Representative of the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG) to the Cartographic
The Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) of the International Association of Geodesy (IAG) Hermann Drewes Representative of the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG) to the Cartographic
Report for 15th PCGIAP Meeting at 18th UNRCC-AP Working Group 1 Regional Geodesy
 Report for 15th PCGIAP Meeting at 18th UNRCC-AP Working Group 1 Regional Geodesy Chairman Shigeru Matsuzaka, Japan - shigeru@gsi.go.jp Vice Chairman Prof. Pengfei Cheng, China - chengpf@casm.ac.cn John
Report for 15th PCGIAP Meeting at 18th UNRCC-AP Working Group 1 Regional Geodesy Chairman Shigeru Matsuzaka, Japan - shigeru@gsi.go.jp Vice Chairman Prof. Pengfei Cheng, China - chengpf@casm.ac.cn John
Progress Report on the WLRS: Getting ready for GGOS, LLR and Time Transfer
 13-0219 Progress Report on the WLRS: Getting ready for GGOS, LLR and Time Transfer G. Herold (1), J. Eckl (1), M. Mühlbauer (1), A. Leidig (1), J. Kodet (2), U. Schreiber (2) (1) Geodetic Observatory Wettzell,
13-0219 Progress Report on the WLRS: Getting ready for GGOS, LLR and Time Transfer G. Herold (1), J. Eckl (1), M. Mühlbauer (1), A. Leidig (1), J. Kodet (2), U. Schreiber (2) (1) Geodetic Observatory Wettzell,
Overview of the ILRS contribution to the development of ITRF2013
 Overview of the ILRS contribution to the development of ITRF203 V. Luceri, E. C. Pavlis 2, B. Pace, D. König 2, M. Kuzmicz-Cieslak 2, G. Bianco 3 ) e-geos S.p.A., Centro di Geodesia Spaziale, Matera, Italy
Overview of the ILRS contribution to the development of ITRF203 V. Luceri, E. C. Pavlis 2, B. Pace, D. König 2, M. Kuzmicz-Cieslak 2, G. Bianco 3 ) e-geos S.p.A., Centro di Geodesia Spaziale, Matera, Italy
SENTINEL-3 SLR YEARLY REPORT
 SENTINEL-3 SLR YEARLY REPORT - 2017 SENTINELSPOD Prepared by: X L. J. Gallardo Project Engineer Firmado por: Luis Javier Gallardo Amézquita Approved by: X Authorised by: X J. Aguilar Quality Manager Firmado
SENTINEL-3 SLR YEARLY REPORT - 2017 SENTINELSPOD Prepared by: X L. J. Gallardo Project Engineer Firmado por: Luis Javier Gallardo Amézquita Approved by: X Authorised by: X J. Aguilar Quality Manager Firmado
Update on the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) : ITRF2014. Zuheir Altamimi
 Update on the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) : ITRF2014 Zuheir Altamimi Head of the IERS ITRF Product Center IAG Vice President IGN, France E-mail: zuheir.altamimi@ign.fr Key Points Introduction:
Update on the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) : ITRF2014 Zuheir Altamimi Head of the IERS ITRF Product Center IAG Vice President IGN, France E-mail: zuheir.altamimi@ign.fr Key Points Introduction:
GG S. Internal Vision of GGOS. Markus Rothacher. GFZ Potsdam
 Internal Vision of GGOS Markus Rothacher GFZ Potsdam GGOS Retreat DGFI in Munich February 15-16, 2006 Contents Motivation Four Levels of Products of the IAG Services: First Level: Raw Data Collection Second
Internal Vision of GGOS Markus Rothacher GFZ Potsdam GGOS Retreat DGFI in Munich February 15-16, 2006 Contents Motivation Four Levels of Products of the IAG Services: First Level: Raw Data Collection Second
Challenges and Perspectives for TRF and CRF Determination
 , IVS 2012 General Meeting Proceedings, p.309 313 http://ivscc.gsfc.nasa.gov/publications/gm2012/boehm.pdf Johannes Böhm 1, Zinovy Malkin 2, Sebastien Lambert 3, Chopo Ma 4 1) Vienna University of Technology
, IVS 2012 General Meeting Proceedings, p.309 313 http://ivscc.gsfc.nasa.gov/publications/gm2012/boehm.pdf Johannes Böhm 1, Zinovy Malkin 2, Sebastien Lambert 3, Chopo Ma 4 1) Vienna University of Technology
Assessment of the International Terrestrial Reference System 2014 realizations by Precise Orbit Determination of SLR Satellites
 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI-TUM) Technische Universität München Assessment of the International Terrestrial Reference System 2014 realizations by Precise Orbit Determination of SLR
Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI-TUM) Technische Universität München Assessment of the International Terrestrial Reference System 2014 realizations by Precise Orbit Determination of SLR
DETERMINATION OF THE STATION COORDINATES FOR QUALITY CONTROL OF THE SATELLITE LASER RANGING DATA S.
 DETERMINATION OF THE STATION COORDINATES FOR QUALITY CONTROL OF THE SATELLITE LASER RANGING DATA S. Schillak Space Research Centre of the Polish Academy of Sciences. Astrogeodynamic Observatory, Borowiec
DETERMINATION OF THE STATION COORDINATES FOR QUALITY CONTROL OF THE SATELLITE LASER RANGING DATA S. Schillak Space Research Centre of the Polish Academy of Sciences. Astrogeodynamic Observatory, Borowiec
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA
 Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), 199-206 Contributed paper REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA D. BLAGOJEVIĆ and V. VASILIĆ Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), 199-206 Contributed paper REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA D. BLAGOJEVIĆ and V. VASILIĆ Faculty of Civil Engineering,
GGOS Bureau for Standards and Conventions
 GGOS D. Angermann (1), T. Gruber (2), J. Bouman (1), M. Gerstl (1), R. Heinkelmann (1), U. Hugentobler (2), L. Sánchez (1), P. Steigenberger (2) (1) Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI), München
GGOS D. Angermann (1), T. Gruber (2), J. Bouman (1), M. Gerstl (1), R. Heinkelmann (1), U. Hugentobler (2), L. Sánchez (1), P. Steigenberger (2) (1) Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI), München
SLR Graz: khz Satellite Laser Ranging & Co
 Graz in Space 2014 KFU Graz 4. 5. September 2014 SLR Graz: khz Satellite Laser Ranging & Co Georg Kirchner, Franz Koidl, Oliver Baur Space Research Institute Austrian Academy of Sciences Outline What is
Graz in Space 2014 KFU Graz 4. 5. September 2014 SLR Graz: khz Satellite Laser Ranging & Co Georg Kirchner, Franz Koidl, Oliver Baur Space Research Institute Austrian Academy of Sciences Outline What is
International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics. Resolutions
 International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics Resolutions ADOPTED BY THE COUNCIL AT THE XXVI GENERAL ASSEMBLY PRAGUE, CZECH REPUBLIC (22 JUNE 2 JULY 2015) 0 Page Resolution 1: Role of Ocean in Climate
International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics Resolutions ADOPTED BY THE COUNCIL AT THE XXVI GENERAL ASSEMBLY PRAGUE, CZECH REPUBLIC (22 JUNE 2 JULY 2015) 0 Page Resolution 1: Role of Ocean in Climate
GGOS INFORMATION MODELS: ANALYSIS OF INTERRELATIONS BETWEEN OBSERVATION TECHNIQUES AND THE EARTH GRAVITY FIELD
 GGOS INFORMATION MODELS: ANALYSIS OF INTERRELATIONS BETWEEN OBSERVATION TECHNIQUES AND THE EARTH GRAVITY FIELD Wojciech Pachelski 1) Małgorzata Paśnicka-Pawłowska 2) Karolina Szafranek 3) Agnieszka Zwirowicz
GGOS INFORMATION MODELS: ANALYSIS OF INTERRELATIONS BETWEEN OBSERVATION TECHNIQUES AND THE EARTH GRAVITY FIELD Wojciech Pachelski 1) Małgorzata Paśnicka-Pawłowska 2) Karolina Szafranek 3) Agnieszka Zwirowicz
Working Group 1. Geodetic Reference Frame. Activity Report. for. The UN-GGIM-AP Plenary Meeting
 Regional Committee of United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific (UN-GGIM-AP) Established by a United Nations Resolution Working Group 1 Geodetic Reference Frame Activity
Regional Committee of United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific (UN-GGIM-AP) Established by a United Nations Resolution Working Group 1 Geodetic Reference Frame Activity
GG S Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS): Status and Future. Markus Rothacher, Ruth Neilan, Hans-Peter Plag
 2020 Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS): Status and Future Markus Rothacher, Ruth Neilan, Hans-Peter Plag GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam (GFZ) Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) University of Nevada, Reno
2020 Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS): Status and Future Markus Rothacher, Ruth Neilan, Hans-Peter Plag GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam (GFZ) Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) University of Nevada, Reno
SIRGAS: Basis for Geosciences, Geodata, and Navigation in Latin America
 SIRGAS: Basis for Geosciences, Geodata, and Navigation in Latin America Claudio Brunini President of SIRGAS Universidad Nacional de La Plata, Argentina María Virginia Mackern President of SIRGAS/WG-I:
SIRGAS: Basis for Geosciences, Geodata, and Navigation in Latin America Claudio Brunini President of SIRGAS Universidad Nacional de La Plata, Argentina María Virginia Mackern President of SIRGAS/WG-I:
Reduction and analysis of one-way laser ranging data from ILRS ground stations to LRO
 Reduction and analysis of one-way laser ranging data from ILRS ground stations to LRO S. Bauer 1, J. Oberst 1,2, H. Hussmann 1, P. Gläser 2, U. Schreiber 3, D. Mao 4, G.A. Neumann 5, E. Mazarico 5, M.H.
Reduction and analysis of one-way laser ranging data from ILRS ground stations to LRO S. Bauer 1, J. Oberst 1,2, H. Hussmann 1, P. Gläser 2, U. Schreiber 3, D. Mao 4, G.A. Neumann 5, E. Mazarico 5, M.H.
Strategy for the Realization of the International Height Reference System (IHRS)
 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI-TUM) Technische Universität München Strategy for the Realization of the International Height Reference System (IHRS) Laura Sánchez 1, Johannes Ihde 2, Roland
Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI-TUM) Technische Universität München Strategy for the Realization of the International Height Reference System (IHRS) Laura Sánchez 1, Johannes Ihde 2, Roland
El proyecto Sistema de Observación Geodésico Global [Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS)] de la Asociación Internacional de Geodesia (IAG)
![El proyecto Sistema de Observación Geodésico Global [Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS)] de la Asociación Internacional de Geodesia (IAG) El proyecto Sistema de Observación Geodésico Global [Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS)] de la Asociación Internacional de Geodesia (IAG)](/thumbs/79/79010389.jpg) El proyecto Sistema de Observación Geodésico Global [Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS)] de la Asociación Internacional de Geodesia (IAG) Hermann Drewes Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI)
El proyecto Sistema de Observación Geodésico Global [Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS)] de la Asociación Internacional de Geodesia (IAG) Hermann Drewes Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI)
Analysis and application of 1-way laser ranging data to LRO
 www.dlr.de Chart 1 WLRS ranging to LRO Analysis and application of 1-way laser ranging data to LRO S. Bauer (1), J. Oberst (1,2), H. Hussmann (1), P. Gläser (2), U. Schreiber (3), D. Mao (4), G. Neumann
www.dlr.de Chart 1 WLRS ranging to LRO Analysis and application of 1-way laser ranging data to LRO S. Bauer (1), J. Oberst (1,2), H. Hussmann (1), P. Gläser (2), U. Schreiber (3), D. Mao (4), G. Neumann
The e-vlbi Progress in Chinese VLBI Network
 The e-vlbi Progress in Chinese VLBI Network Zhang Xiuzhong, CAS 1 Nov 2005 CANS 2005 Outline: 1. About VLBI 2. e-vlbi progress 3. The e-vlbi test in CVN 4. The near future plan of e-vlbi for CVN Traditional
The e-vlbi Progress in Chinese VLBI Network Zhang Xiuzhong, CAS 1 Nov 2005 CANS 2005 Outline: 1. About VLBI 2. e-vlbi progress 3. The e-vlbi test in CVN 4. The near future plan of e-vlbi for CVN Traditional
GGOS. Global Geodetic Observing System. Carey Noll NASA GSFC (on behalf of GGOS) WDS Forum September 11, 2016
 https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?r=20160011397 2018-12-07T18:04:29+00:00Z GGOS Global Geodetic Observing System Carey Noll NASA GSFC (on behalf of GGOS) WDS Forum September 11, 2016 Global Geodetic Observing
https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?r=20160011397 2018-12-07T18:04:29+00:00Z GGOS Global Geodetic Observing System Carey Noll NASA GSFC (on behalf of GGOS) WDS Forum September 11, 2016 Global Geodetic Observing
Global Geodetic Reference Frame GGRF & Implications for GNSS
 Global Geodetic Reference Frame GGRF & Implications for GNSS On behalf of Gary Johnston Chair GIAC, Ruth Neilan Vice Chair, Global Geodetic Observing System ICG-9 Prague, 10 November 2014 UN GGRF Working
Global Geodetic Reference Frame GGRF & Implications for GNSS On behalf of Gary Johnston Chair GIAC, Ruth Neilan Vice Chair, Global Geodetic Observing System ICG-9 Prague, 10 November 2014 UN GGRF Working
Role and importance of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame for sustainable development
 Role and importance of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame for sustainable development This report is provided for the benefit of participants of the UNRCC-PCGIAP Informal Geodetic Consultation,
Role and importance of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame for sustainable development This report is provided for the benefit of participants of the UNRCC-PCGIAP Informal Geodetic Consultation,
Towards a Rigorous Combination of Space Geodetic Techniques
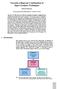 Towards a Rigorous Combination of Space Geodetic Techniques Markus Rothacher Forschungseinrichtung Satellitengeodäsie, TU Munich, Germany Abstract: The with all its different components and products, ranging
Towards a Rigorous Combination of Space Geodetic Techniques Markus Rothacher Forschungseinrichtung Satellitengeodäsie, TU Munich, Germany Abstract: The with all its different components and products, ranging
3.4.2 International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS)
 3 Reports of IERS components 3.4 Technique Centres 3.4.2 International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS) Introduction Network The International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS), established in 1998, is responsible
3 Reports of IERS components 3.4 Technique Centres 3.4.2 International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS) Introduction Network The International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS), established in 1998, is responsible
Contributions of Geodesy to Oceanography
 Contributions of Geodesy to Oceanography B. Tapley and J. Ries Center for Space Research, The University of Texas at Austin Dynamic Planet 2005 Cairns, Australia August 22-26, 2005 August 22-26, 2005 Dynam
Contributions of Geodesy to Oceanography B. Tapley and J. Ries Center for Space Research, The University of Texas at Austin Dynamic Planet 2005 Cairns, Australia August 22-26, 2005 August 22-26, 2005 Dynam
Ludwig Combrinck HartRAO 3rd Space Geodesy Workshop 16 March 2009 Matjiesfontein
 Space Geodesy and Space Science Ludwig Combrinck HartRAO 3rd Space Geodesy Workshop 16 March 2009 Matjiesfontein DST s Concept of Space Science SA Space Agency, commercial applications, CSIR Satellite
Space Geodesy and Space Science Ludwig Combrinck HartRAO 3rd Space Geodesy Workshop 16 March 2009 Matjiesfontein DST s Concept of Space Science SA Space Agency, commercial applications, CSIR Satellite
Global & National Geodesy, GNSS Surveying & CORS Infrastructure
 Global & National Geodesy, GNSS Surveying & CORS Infrastructure Chris Rizos School of Surveying & Spatial Information Systems University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia President-elect, International
Global & National Geodesy, GNSS Surveying & CORS Infrastructure Chris Rizos School of Surveying & Spatial Information Systems University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia President-elect, International
Geodetic Observing Systems: tools in observing the Glacial Isostatic Adjustment. Markku Poutanen Finnish Geodetic Institute
 Geodetic Observing Systems: tools in observing the Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Markku Poutanen Finnish Geodetic Institute Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Land uplift is just one consequence of the physical
Geodetic Observing Systems: tools in observing the Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Markku Poutanen Finnish Geodetic Institute Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Land uplift is just one consequence of the physical
The International Terrestrial Reference Frame. What is a Terrestrial Reference Frame?
 The International Terrestrial Reference Frame As early as the 15th century, Swedes noticed that rocks in their harbors were slowly rising out of the sea [Ekman, 1991]. These local observations were not
The International Terrestrial Reference Frame As early as the 15th century, Swedes noticed that rocks in their harbors were slowly rising out of the sea [Ekman, 1991]. These local observations were not
ESTIMATION OF NUTATION TERMS USING GPS
 ESTIMATION OF NUTATION TERMS USING GPS Markus Rothacher, Gerhard Beutler Astronomical Institute, University of Berne CH-3012 Berne, Switzerland ABSTRACT Satellite space-geodetic measurements have been
ESTIMATION OF NUTATION TERMS USING GPS Markus Rothacher, Gerhard Beutler Astronomical Institute, University of Berne CH-3012 Berne, Switzerland ABSTRACT Satellite space-geodetic measurements have been
Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study
 Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study B. Männel, M. Rothacher ETH Zürich, Geodesy and Geodynamics Lab 7 th IGS General Meeting, Madrid 212 1 Reference frame and local ties
Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study B. Männel, M. Rothacher ETH Zürich, Geodesy and Geodynamics Lab 7 th IGS General Meeting, Madrid 212 1 Reference frame and local ties
Reference frames and positioning
 The APREF Project: an Improved Geodetic Infrastructure for Asia and the Pacific (4861) John Dawson (Australia), Graeme Blick (New Zealand), Manoj Deo, Guorong Hu and Gary Johnston (Australia) Reference
The APREF Project: an Improved Geodetic Infrastructure for Asia and the Pacific (4861) John Dawson (Australia), Graeme Blick (New Zealand), Manoj Deo, Guorong Hu and Gary Johnston (Australia) Reference
Status. EUREF TWG Meeting November 8 9, 2004, Praha
 ECGN was initiated by IAG Sub-Commission for Europe EUREF (SC1.3a) and IAG Sub-Commission for Europe of the International Gravity and Geoid Commission (IGGC) with relationship to Joint Research Centre
ECGN was initiated by IAG Sub-Commission for Europe EUREF (SC1.3a) and IAG Sub-Commission for Europe of the International Gravity and Geoid Commission (IGGC) with relationship to Joint Research Centre
Riccardo Giacconi Papers,
 , 1955-2002 Finding aid prepared by Smithsonian Institution Archives Smithsonian Institution Archives Washington, D.C. Contact us at osiaref@si.edu Table of Contents Collection Overview... 1 Administrative
, 1955-2002 Finding aid prepared by Smithsonian Institution Archives Smithsonian Institution Archives Washington, D.C. Contact us at osiaref@si.edu Table of Contents Collection Overview... 1 Administrative
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Seitz M., Steigenberger P., Artz T. (2xx) Consistent adjustment of combined terrestrial and celestial reference frames, Earth on the Edge: Science for a Sustainable Planet, IAG
Originally published as: Seitz M., Steigenberger P., Artz T. (2xx) Consistent adjustment of combined terrestrial and celestial reference frames, Earth on the Edge: Science for a Sustainable Planet, IAG
GGSP: Realisation of the Galileo Terrestrial Reference Frame
 Galileo Geodetic Service Provider Prototype GGSP: Realisation of the Galileo Terrestrial Reference Frame Wolfgang Söhne, Johannes Ihde Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy Gerd Gendt, Markus Rothacher
Galileo Geodetic Service Provider Prototype GGSP: Realisation of the Galileo Terrestrial Reference Frame Wolfgang Söhne, Johannes Ihde Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy Gerd Gendt, Markus Rothacher
GGOS, ECGN and NGOS: Global and regional geodetic observing systems. Markku Poutanen Finish Geodetic Institute
 GGOS, ECGN and NGOS: Global and regional geodetic observing systems Markku Poutanen Finish Geodetic Institute Contents GGOS, ECGN, NGOS Why? How? Future? (geodesy) GGOS Structure GGOS Structure European
GGOS, ECGN and NGOS: Global and regional geodetic observing systems Markku Poutanen Finish Geodetic Institute Contents GGOS, ECGN, NGOS Why? How? Future? (geodesy) GGOS Structure GGOS Structure European
Common Realization of Terrestrial and Celestial Reference Frame
 Common Realization of Terrestrial and Celestial Reference Frame M. Seitz, R. Heinkelmann, P. Steigenberger, T. Artz Abstract The realization of the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) and the
Common Realization of Terrestrial and Celestial Reference Frame M. Seitz, R. Heinkelmann, P. Steigenberger, T. Artz Abstract The realization of the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) and the
Graz in Space Graz SLR System. Daniel Kucharski. IWF / SatGeo
 Graz in Space 2008 Graz SLR System Daniel Kucharski IWF / SatGeo Satellite Laser Ranging Range measurements to the satellites - time of flight of the ultrashort laser pulses - mm precision station-satellite
Graz in Space 2008 Graz SLR System Daniel Kucharski IWF / SatGeo Satellite Laser Ranging Range measurements to the satellites - time of flight of the ultrashort laser pulses - mm precision station-satellite
Frequent epoch reference frames instead of instant station positions and constant velocities
 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut Technische Universität München (DGFI-TUM) Frequent epoch reference frames instead of instant station positions and constant velocities Hermann Drewes Deutsches
Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut Technische Universität München (DGFI-TUM) Frequent epoch reference frames instead of instant station positions and constant velocities Hermann Drewes Deutsches
GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy. Jeff Freymueller Elvey 413B, x7286
 GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller jfreymueller@alaska.edu Elvey 413B, x7286 Application of Geodesy to Tectonics Uncertainties < 1 mm/y Blue: stable part of tectonic plates Red: deforming zones
GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller jfreymueller@alaska.edu Elvey 413B, x7286 Application of Geodesy to Tectonics Uncertainties < 1 mm/y Blue: stable part of tectonic plates Red: deforming zones
Impact of Earth Radiation Pressure on LAGEOS Orbits and on the Global Scale
 13-Po-22 Impact of Earth Radiation Pressure on LAGEOS Orbits and on the Global Scale Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Carlos Javier Rodríguez-Solano (2), Daniela Thaller (3), Adrian Jäggi (1), Rolf Dach (1), Gerhard
13-Po-22 Impact of Earth Radiation Pressure on LAGEOS Orbits and on the Global Scale Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Carlos Javier Rodríguez-Solano (2), Daniela Thaller (3), Adrian Jäggi (1), Rolf Dach (1), Gerhard
Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites
 Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Adrian Jäggi (1), Daniela Thaller (2), Ulrich Meyer (1), Gerhard Beutler (1), Rolf Dach (1) (1) Astronomical Institute,
Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Adrian Jäggi (1), Daniela Thaller (2), Ulrich Meyer (1), Gerhard Beutler (1), Rolf Dach (1) (1) Astronomical Institute,
The 2008 Local-tie Survey at the Onsala Space Observatory
 The 2008 Local-tie Survey at the Onsala Space Observatory M. Lösler, Geodetic Institute of the University of Karlsruhe (TH), DE-76128 Karlsruhe, Germany R. Haas Department of Radio and Space Science, Chalmers
The 2008 Local-tie Survey at the Onsala Space Observatory M. Lösler, Geodetic Institute of the University of Karlsruhe (TH), DE-76128 Karlsruhe, Germany R. Haas Department of Radio and Space Science, Chalmers
PERFORMANCE. 1 Scheduled and successfully completed observing time
 PERFORMANCE INDICATORS The ATNF assesses its performance through key performance indicators, based on those used generally by CSIRO but adapted to be appropriate for a National Facility. Unless otherwise
PERFORMANCE INDICATORS The ATNF assesses its performance through key performance indicators, based on those used generally by CSIRO but adapted to be appropriate for a National Facility. Unless otherwise
Effects of Climate Change on Earth s Parameters An Example of Exabyte-sized System
 Effects of Climate Change on Earth s Parameters An Example of Exabyte-sized System Giampiero Sindoni 1, Erricos. C. Pavlis 2, Claudio Paris 3,1, Antonio Paolozzi 1,3 and Ignazio Ciufolini 4,3 1 Scuola
Effects of Climate Change on Earth s Parameters An Example of Exabyte-sized System Giampiero Sindoni 1, Erricos. C. Pavlis 2, Claudio Paris 3,1, Antonio Paolozzi 1,3 and Ignazio Ciufolini 4,3 1 Scuola
What are the social, technical, environmental and economic benefits and opportunities of accessing and sharing geodetic data?
 What are the social, technical, environmental and economic benefits and opportunities of accessing and sharing geodetic data? Graeme Blick Group Manager Positioning and Resilience Land Information New
What are the social, technical, environmental and economic benefits and opportunities of accessing and sharing geodetic data? Graeme Blick Group Manager Positioning and Resilience Land Information New
GNSS-specific local effects at the Geodetic Observatory Wettzell
 GNSS-specific local effects at the Geodetic Observatory Wettzell Peter Steigenberger, Urs Hugentobler, Ralf Schmid Technische Universität München (TUM) Uwe Hessels, Thomas Klügel Bundesamt für Kartographie
GNSS-specific local effects at the Geodetic Observatory Wettzell Peter Steigenberger, Urs Hugentobler, Ralf Schmid Technische Universität München (TUM) Uwe Hessels, Thomas Klügel Bundesamt für Kartographie
Frames for the Future New Datum Definitions for Modernization of the U.S. National Spatial Reference System
 Figure 10. Horizontal position differences (in meters) between NAD 83 and ITRF 08 at time 2022.00 (January 1, 2022). Positional differences are shown for the North American and Pacific tectonic plates.
Figure 10. Horizontal position differences (in meters) between NAD 83 and ITRF 08 at time 2022.00 (January 1, 2022). Positional differences are shown for the North American and Pacific tectonic plates.
Application of ECGS to host the direction of the
 Président d honneur: Son Altesse Royale Le Grand Duc Henri Président Secrétaire J-M. Goerens E. Buttini ECGS 19, Rue Josy Welter L-7256 Walferdange http://www.ecgs.lu To the International Association of
Président d honneur: Son Altesse Royale Le Grand Duc Henri Président Secrétaire J-M. Goerens E. Buttini ECGS 19, Rue Josy Welter L-7256 Walferdange http://www.ecgs.lu To the International Association of
3.6 ITRS Combination Centres
 3 Reports of IERS components 3.6.1 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI) In 2010, the focus of the ITRS Combination Centre at DGFI was on the finalization of the ITRS realization DTRF2008, internal
3 Reports of IERS components 3.6.1 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI) In 2010, the focus of the ITRS Combination Centre at DGFI was on the finalization of the ITRS realization DTRF2008, internal
The Kinematic Reference Frame for ITRF
 The Kinematic Reference Frame for ITRF Hermann Drewes and Barbara Meisel Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut Munich, Germany IERS Workshop, Potsdam, 10.10.2005 Motivation and Objectives The kinematic
The Kinematic Reference Frame for ITRF Hermann Drewes and Barbara Meisel Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut Munich, Germany IERS Workshop, Potsdam, 10.10.2005 Motivation and Objectives The kinematic
The Interactions between IGS and GGOS
 The Interactions between IGS and GGOS Markus Rothacher Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP) ETH Zurich, Switzerland 2012 IGS Workshop July 23-27, 2012, Olsztyn, Poland Overview GGOS Vision, Mission
The Interactions between IGS and GGOS Markus Rothacher Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP) ETH Zurich, Switzerland 2012 IGS Workshop July 23-27, 2012, Olsztyn, Poland Overview GGOS Vision, Mission
Background Document: Report of the Regional Committee of United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific
 Background Document: Report of the Regional Committee of United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific 1. Summary 1. This report highlights the activities carried out
Background Document: Report of the Regional Committee of United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific 1. Summary 1. This report highlights the activities carried out
The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part II : ITRS & ETRS89 relationship
 The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part II : ITRS & ETRS89 relationship Zuheir ALTAMIMI Laboratoire de Recherche en Géodésie Institut national de l information géographique et forestière
The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part II : ITRS & ETRS89 relationship Zuheir ALTAMIMI Laboratoire de Recherche en Géodésie Institut national de l information géographique et forestière
Precise Orbital and Geodetic Parameter Estimation using SLR Observations for ILRS AAC
 Research Paper J. Astron. Space Sci. 30(4), 269277 (203) http://dx.doi.org/0.540/jass.203.30.4.269 Precise Orbital and Geodetic Parameter Estimation using SLR Observations for ILRS AAC YoungRok Kim, Eunseo
Research Paper J. Astron. Space Sci. 30(4), 269277 (203) http://dx.doi.org/0.540/jass.203.30.4.269 Precise Orbital and Geodetic Parameter Estimation using SLR Observations for ILRS AAC YoungRok Kim, Eunseo
Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites
 13-01-08 Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Adrian Jäggi (1), Daniela Thaller (2), Ulrich Meyer (1), Christian Baumann (1), Rolf Dach (1), Gerhard
13-01-08 Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Adrian Jäggi (1), Daniela Thaller (2), Ulrich Meyer (1), Christian Baumann (1), Rolf Dach (1), Gerhard
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 18 July 2016 Original: English Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Sixth session New York, 3-5 August 2016 Item 2
United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 18 July 2016 Original: English Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Sixth session New York, 3-5 August 2016 Item 2
Connecting terrestrial to celestial reference frames
 Russian Academy of Sciences Central Astronomical Observatory at Pulkovo IAU XXVIII General Assembly, Joint Discussion 7, Beijing, China, August 28, 2012 Connecting terrestrial to celestial reference frames
Russian Academy of Sciences Central Astronomical Observatory at Pulkovo IAU XXVIII General Assembly, Joint Discussion 7, Beijing, China, August 28, 2012 Connecting terrestrial to celestial reference frames
Update on IPWG Activities
 Update on IPWG Activities Paul Kucera National Center for Atmospheric Research Research Applications Laboratory Boulder, Colorado, USA Bozena Lapeta Satellite Remote Sensing Centre Institute of Meteorology
Update on IPWG Activities Paul Kucera National Center for Atmospheric Research Research Applications Laboratory Boulder, Colorado, USA Bozena Lapeta Satellite Remote Sensing Centre Institute of Meteorology
Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations. Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis
 Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis Observatoire de Paris SYRTE, 61 av. de l'observatoire, 7514 Paris Introduction Gravity field
Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis Observatoire de Paris SYRTE, 61 av. de l'observatoire, 7514 Paris Introduction Gravity field
EUREF Technical Note 1: Relationship and Transformation between the International and the European Terrestrial Reference Systems
 EUREF Technical Note 1: Relationship and Transformation between the International and the European Terrestrial Reference Systems Zuheir Altamimi Institut National de l Information Géographique et Forestière
EUREF Technical Note 1: Relationship and Transformation between the International and the European Terrestrial Reference Systems Zuheir Altamimi Institut National de l Information Géographique et Forestière
Lunar Discovery and Exploration program
 Lunar Discovery and Exploration program Space Policy Directive-1 (December 11, 2017) amends the National Space Policy to include the following paragraph: Lead an innovative and sustainable program of exploration
Lunar Discovery and Exploration program Space Policy Directive-1 (December 11, 2017) amends the National Space Policy to include the following paragraph: Lead an innovative and sustainable program of exploration
UN Resolution on GGRF ( and its implementation in Europe)
 Presented at the FIG Working Week 2017, UN Resolution on GGRF ( and its implementation in Europe) May 29 - June 2, 2017 in Helsinki, Finland Markku Poutanen, FGI Contents Global Geodetic Reference Frame
Presented at the FIG Working Week 2017, UN Resolution on GGRF ( and its implementation in Europe) May 29 - June 2, 2017 in Helsinki, Finland Markku Poutanen, FGI Contents Global Geodetic Reference Frame
Development of Laser Measurement to Space Debris at Shanghai SLR Station
 Abstract Development of Laser Measurement to Space Debris at Shanghai SLR Station Zhang Zhongping, Deng Huarong, Tang Kai, Wu Zhibo, Zhang Haifeng (Shanghai Astronomical Observatory of Chinese Academy
Abstract Development of Laser Measurement to Space Debris at Shanghai SLR Station Zhang Zhongping, Deng Huarong, Tang Kai, Wu Zhibo, Zhang Haifeng (Shanghai Astronomical Observatory of Chinese Academy
Towards an improved ILRS TRF contribution
 Towards an improved ILRS TRF contribution Erricos C. Pavlis ILRS Analysis Coordinator JCET/ & NASA Goddard IERS Workshop on Conventions 2007 20-21 Sept. 2007, Sèvres, France Overview The ILRS Network Geometry
Towards an improved ILRS TRF contribution Erricos C. Pavlis ILRS Analysis Coordinator JCET/ & NASA Goddard IERS Workshop on Conventions 2007 20-21 Sept. 2007, Sèvres, France Overview The ILRS Network Geometry
Economic and Social Council 2 July 2015
 ADVANCE UNEDITED VERSION UNITED NATIONS E/C.20/2015/11/Add.1 Economic and Social Council 2 July 2015 Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Fifth session New York, 5-7 August
ADVANCE UNEDITED VERSION UNITED NATIONS E/C.20/2015/11/Add.1 Economic and Social Council 2 July 2015 Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Fifth session New York, 5-7 August
Home Page Vatican Observatory
 HOME WHO ARE RESEARCH SCIENCE, RELIGION, SUMMER SCHOOLS PUBLICATIONS NEWS WORKSHOP WE? SOCIETY (VOSS) LEMAITRE Home Page Vatican Observatory Poster VOSS2018 On March 14, 1891, exactly 125 years ago, Pope
HOME WHO ARE RESEARCH SCIENCE, RELIGION, SUMMER SCHOOLS PUBLICATIONS NEWS WORKSHOP WE? SOCIETY (VOSS) LEMAITRE Home Page Vatican Observatory Poster VOSS2018 On March 14, 1891, exactly 125 years ago, Pope
Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission
 Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission Sergei Rudenko (1,2), Saskia Esselborn (1), Tilo Schöne (1) (1) GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences,
Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission Sergei Rudenko (1,2), Saskia Esselborn (1), Tilo Schöne (1) (1) GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences,
Establishment of a Global Absolute Gravity Network
 Establishment of a Global Absolute Gravity Network H. Wilmes 1), H. Wziontek 1), R. Falk 1), J. Ihde 1), S. Bonvalot 2), R. Forsberg 3), S. Kenyon 4), L. Vitushkin 5) 1) Federal Agency for Cartography
Establishment of a Global Absolute Gravity Network H. Wilmes 1), H. Wziontek 1), R. Falk 1), J. Ihde 1), S. Bonvalot 2), R. Forsberg 3), S. Kenyon 4), L. Vitushkin 5) 1) Federal Agency for Cartography
Recent and Anticipated Changes to the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) Conventions
 Recent and Anticipated Changes to the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) Conventions Brian Luzum, U.S. Naval Observatory BIOGRAPHY Brian Luzum began full-time employment
Recent and Anticipated Changes to the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) Conventions Brian Luzum, U.S. Naval Observatory BIOGRAPHY Brian Luzum began full-time employment
Operational Support by ESOC s GRAS Ground Support Network - Status and Outlook
 ESA UNCLASSIFIED Releasable to the public Operational Support by ESOC s GRAS Ground Support Network - Status and Outlook R. Zandbergen, F.Wollenweber, C.Marquardt, W. Enderle and the ESOC and EUMETSAT
ESA UNCLASSIFIED Releasable to the public Operational Support by ESOC s GRAS Ground Support Network - Status and Outlook R. Zandbergen, F.Wollenweber, C.Marquardt, W. Enderle and the ESOC and EUMETSAT
UN-GGIM: Europe GRF-Europe. Markku Poutanen
 UN-GGIM: Europe GRF-Europe Markku Poutanen Global Geodetic Reference Frame GGRF The UN Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management (UN-GGIM) decided in July 2013 to formulate and facilitate
UN-GGIM: Europe GRF-Europe Markku Poutanen Global Geodetic Reference Frame GGRF The UN Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management (UN-GGIM) decided in July 2013 to formulate and facilitate
Global reference systems and Earth rotation
 current realizations and scientific problems Aleksander Brzeziński 1,2, Tomasz Liwosz 1, Jerzy Rogowski 1, Jan Kryński 3 1 Department of Geodesy and Geodetic Astronomy Warsaw University of Technology 2
current realizations and scientific problems Aleksander Brzeziński 1,2, Tomasz Liwosz 1, Jerzy Rogowski 1, Jan Kryński 3 1 Department of Geodesy and Geodetic Astronomy Warsaw University of Technology 2
ICRF-3: ROADMAP TO THE NEXT GENERATION ICRF
 ICRF-3: ROADMAP TO THE NEXT GENERATION ICRF C.S. JACOBS 1, F. ARIAS 2, D. BOBOLTZ 3, J. BOEHM 4, S. BOLOTIN 5, G. BOURDA 6,7, P. CHARLOT 6,7, A. DE WITT 8, A. FEY 9, R. GAUME 9, D. GORDON 5, R. HEINKELMANN
ICRF-3: ROADMAP TO THE NEXT GENERATION ICRF C.S. JACOBS 1, F. ARIAS 2, D. BOBOLTZ 3, J. BOEHM 4, S. BOLOTIN 5, G. BOURDA 6,7, P. CHARLOT 6,7, A. DE WITT 8, A. FEY 9, R. GAUME 9, D. GORDON 5, R. HEINKELMANN
The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data
 The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data J. Boehm, A. Niell, P. Tregoning, H. Schuh Troposphere mapping functions are used in the analyses
The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data J. Boehm, A. Niell, P. Tregoning, H. Schuh Troposphere mapping functions are used in the analyses
FOSTERING GNSS SCIENCE WITH GALILEO AND GALILEO SATELLITE METADATA
 FOSTERING GNSS SCIENCE WITH GALILEO AND GALILEO SATELLITE METADATA Dr Javier Ventura-Traveset, Galileo Navigation Science Office, ESA D. Blonski, Galileo Project Office, ESA ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official
FOSTERING GNSS SCIENCE WITH GALILEO AND GALILEO SATELLITE METADATA Dr Javier Ventura-Traveset, Galileo Navigation Science Office, ESA D. Blonski, Galileo Project Office, ESA ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official
Modernization of National Geodetic Datum in China *
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.102/IP.16 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Nineteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 29 October 1 November 2012 Item 6(b) of the provisional
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.102/IP.16 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Nineteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 29 October 1 November 2012 Item 6(b) of the provisional
EUMETSAT. A global operational satellite agency at the heart of Europe. Presentation for the Spanish Industry Day Madrid, 15 March 2012
 EUMETSAT A global operational satellite agency at the heart of Europe Presentation for the Spanish Industry Day Madrid, Angiolo Rolli EUMETSAT Director of Administration EUMETSAT objectives The primary
EUMETSAT A global operational satellite agency at the heart of Europe Presentation for the Spanish Industry Day Madrid, Angiolo Rolli EUMETSAT Director of Administration EUMETSAT objectives The primary
Report of PCGIAP to the 18 th United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific (UNRCC-AP) for the period
 Permanent Committee on GIS Infrastructure for Asia and the Pacific (PCGIAP) Established in 1995 by a United Nations Resolution Report of PCGIAP to the 18 th United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference
Permanent Committee on GIS Infrastructure for Asia and the Pacific (PCGIAP) Established in 1995 by a United Nations Resolution Report of PCGIAP to the 18 th United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference
Incorporation of the Caribbean to the Geocentric Reference System for the Americas SIRGAS
 Incorporation of the Caribbean to the Geocentric Reference System for the Americas SIRGAS W. Martínez M. V. Mackern V. Cioce R. Rodino S.R. De Freitas UN-GGIM: Americas Third Session, October 5 2016, Mexico
Incorporation of the Caribbean to the Geocentric Reference System for the Americas SIRGAS W. Martínez M. V. Mackern V. Cioce R. Rodino S.R. De Freitas UN-GGIM: Americas Third Session, October 5 2016, Mexico
