A study of the moist Entropy in Meteorology.
|
|
|
- Abigail Cox
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Workshop on the Atmospheric Modelling 8-10 February, 2011.Toulouse, France. A study of the moist Entropy in Meteorology. Pascal MARQUET (Météo-France. DPrévi / LABO)
2 Contents 1) Motivations : to study and compute the moist Entropy / why? 2) Theoretical results : s = Cste + c pd ln(θ s ) ; with θ s 3) Applications : Strato-cumulus FIRE-I ; [θ l ;θ E ; ] 4) Turbulence : 3D-diagrams non-conservative variables? 5) Conclusions - Outlooks 2
3 Contents 1) Motivations : to study and compute the moist Entropy / why? 2) Theoretical results : s = Cste + c pd ln(θ s ) ; with θ s 3) Applications : Strato-cumulus FIRE-I ; [θ l ;θ E ; ] 4) Turbulence : 3D-diagrams non-conservative variables? 5) Conclusions - Outlooks 3
4 Motivations (see the extended abstract) Work on Available Energy (LMD-Polytechnic school, ). «Exergy» and «Available Enthalpy» : (h h 0 ) T env (s s 0 ) Applications to the African Monsoon (?) ; «Lorenz Cycle» ; Impacts of a 2xCO2 ; Moist Norm but still with no answer to the question of Alan Thorpe (1990) : link Exergy & CAPE? 4
5 Motivations - A. Thorpe (1990) : Exergy & CAPE? T e = Cste Convection : w 2 /2 exergy? t t+dt t t+dt (e k ) in (e k ) out h in, s in W max? h out, s out θ v,env θ v, part θ v,env T e = Cste W max (h out h in ) +T e (s out s in ) [ (e k ) out (e k ) in ] Moist PBL & Turbulence W max = ( h T e s ) (e k ) A steam machine : the maximum shaft work W? B θ = D w D t v, part θ θ v, env w v, env w z D w D t ; 2 w 2 = z 2 D ( w 2 + a D t ( h Tenv s)? z h ) 0 5
6 Motivations There seems to be a need to compute the moist entropy But this has already be done! why another approach? Hauf & Höller (87), Marquet (93), Emanuel (94) : a weighted sum of partial entropies : but s r, c r, θ sr variables! s r, c r, θ sr constants Entering all the r t, q t et q d within the ln(...)? then θ s would becomes a true synonym of Entropy, even for varying r t q t q d... 6
7 Contents 1) Motivations : to study and compute the moist Entropy / why? 2) Theoretical results : s = Cste + c pd ln(θ s ) ; with θ s Marquet (QJRMS, 2011) 3) Applications : Strato-cumulus FIRE-I ; [θ l ;θ E ; ] 4) Turbulence : 3D-diagrams non-conservative variables? 5) Conclusions - Outlooks 7
8 Computations of : s θ s θ s complex? In fact, similar to HH87, M93 ou E94, except... 8
9 Computations of : s θ s The leading term : Generalization / A mixed of : absolute values of partial entropies The 3 rd Law 9
10 Contents 1) Motivations : to study and compute the moist Entropy / why? 2) Theoretical results : s = Cste + c pd ln(θ s ) ; with θ s 3) Applications : Strato-cumulus FIRE-I ; [θ l ;θ E ; ] A new formula : is there new consequences? is there new physical properties? if yes, a need of validations against measurements! 4) Turbulence : 3D-diagrams non-conservative variables? 5) Conclusions - Outlooks 10
11 Applications / FIRE-I : [ θ l ; q t ; q l ] RF03B-hom. Data flights NASA S. De Roode 10 K 6 g/kg θ l q t q l Same results as Roode & Wang (2007) clear-air cloud (entrain. region) Large jumps in θ l and q t (entrain. region) 11
12 Applications / FIRE-I : [ θ l ; q t ; q l ] RF03B-hom. θ l q t Unexpected results q l constant with z clear-air = cloud! for No jump in! 12
13 FIRE-I 03B 02B-04B-08B : OK + 3 other Sc cases : OK constant profiles for No (or small) jump (top-pbl) 13
14 Comparisons [θ l ;θ E ; ]? différent from all other Pot. Temp.! E94 TC81 GB81 L68 HH87 M93 θ E 2/3-1/3 between θ l & θ E θ l 14 K θ l 14
15 Contents 1) Motivations : to study and compute the moist Entropy / why? 2) Theoretical results : s = Cste + c pd ln(θ s ) ; with θ s 3) Applications : Strato-cumulus FIRE-I ; [θ l ;θ E ; ] 4) Turbulence : 3D-diagrams non-conservative variables? 5) Conclusions - Outlooks 15
16 Turbulent Fluxes : (θ l ; q t ) variables? θ s Approximated formula for the flux of moist entropy : Isentropic diffusion The fluxes of Betts variables would be linked (proportional) in the «moist isentropic case»? 16
17 Turbulent Fluxes : ( c pd T + φ ; L v q v ; L v q l ) variables? Flux de S m But how to go further? What are the links between entropy and turbulence? A crude idea: to replace S or θ l by S m or? But what about q t??? 17
18 z Thermodynamic Diagrams z Curve seen in profile! z θ l d ln = d ln(θ l ) + Λ dq t = θ l exp(λ q t ) d ln(θ X ) = d ln(θ l ) dq t /Λ q t θ l θ l θ X = θ l exp( q t /Λ) Maximum jump in θ X q t θ l Slope d q t /dθ l = 1 / (Λ θ l ) q t θ X 3D-Diagram: «conservatives» variables Mininum jump in Pascal MARQUET (june 2010) 18
19 Turbulents fluxes: the [ ; θ X ] variables? z = θ l exp(λ q t ) θ X = θ l exp( q t /Λ) θ l Isentropic mixing in : reduce the departure terms (grey lines) a relaxation? Mixing in θ X : other diabatic or irreversible physical processes (radiation, ) q t θ X A wish to switch to non-conservatives (natural) variables (θ, q v, q l )? 19
20 α = L v /(c pd T) Λ iso-q t in violet α q l Just like 2 slantwise roofs... q v θ l iso-θ l in green ln(θ l ) = ln(θ ) (α +Λ) q l q t =q v +q l ln = ln(θ ) + Λ q v α q l The iso- in red q v = 0 q l = 0 Pascal MARQUET (July 2010) A 3D-Diagram with the «non-conservatives» variables (θ, q v, q l ) : but how to represent θ l, q t,? θ The line iso - θ l iso - q t 20 20
21 α q l q t q v isentropes α = L v /(c pd T) Λ ln = ln(θ ) + Λ q v α q l Clear SBL Inversion & clear-air cloud The points are not scattered at random! Is it interesting for moist turbulence? q sat (T) is missing go from θ to T! Pascal MARQUET (January 2011) A 3D-diagram with nonconservatives variables Application : FIRE-I 03B? θ l clear q l = 0 cloud q l 0 along iso-(θ l, q t ) θ dry clear-air above the inversion 21 21
22 ln = (R d /c pd ) ln(p/p 0 ) + ln(t ) + Λ q v α q l T-ln(p) emagram FIRE-I / RF03B α = L v /(c pd T) Λ q v α q l Continuous + angular points! Proposition : (1) switch from black to red points define (T)* q v (on plane q l =0) ; (2) Mixing in (T)* q v with iso- (??) ; (3) If saturation: q l 0 => (T, q v, q l )(z) (T)* = T exp( α q l ) Pascal MARQUET (January 2011) A 3D-diagram with nonconservatives variables z p (q v ) sat (T,p) z p z p Go from θ to T T Slope of red lines : d(α q l )/dt = 1/T (with constant other terms). Unsolved problems : Be careful : homogeneous Sc N=100%? And what about : N<100 %? An the sub-grid variability: σ s? 22 22
23 Contents 1) Motivations : to study and compute the moist Entropy / why? 2) Theoretical results : s = Cste + c pd ln(θ s ) ; with θ s 3) Applications : Strato-cumulus FIRE-I ; [θ l ;θ E ; ] 4) Turbulence : 3D-diagrams non-conservative variables? 5) Conclusions - Outlooks : I will not show. 23
24 L.E.S. EUCAARI J.L. Brengier O. Thouron r l θ l r t 24
25 Radio Soundings : Bermuda θ w θ w Alignment! alignment
26 No influence at all of ( T r, p r, q r ) on s and θ s! 26
27 850 hpa 2D fields? (French Anasyg-Presyg) = 2K et 1g/kg θ w θ θ X q vap 27
28 Contents 1) Motivations : to study and compute the moist Entropy / why? 2) Theoretical results : s = Cste + c pd ln(θ s ) ; with θ s 3) Applications : Strato-cumulus FIRE-I ; [θ l ;θ E ; ] 4) Turbulence : 3D-diagrams non-conservative variables? 5) Conclusions - Outlooks : I will finish by. 28
29 Conclusions - Outlooks Get an analytical formulation for the moist entropy θ s Validations against observations (FIRE, EPIC, + R.S.) Paper accepted: QJRMS (2011) Sc analyses : global & local budget of (h, s) / IPCC? Improve Setup : LES CRM SCM NWP / GCM (Euclipse) NWP & GCM simulations : applications = moist turbulence θ X or for horizontal = front gradients : max in ; min in θ X θ l θ What about links ( s, θ s ) CAPE? Shallow? Deep? J. F. Geleyn + my own speculations : links Exergy S.V.? Q.G.? P.V.? 29
30 Thanks a lot for your attention Questions? J. W. GIBBS «A method of geometrical representation of the thermodynamic properties of substance by means of surfaces» - Gibbs (1873) 30
On the use of the moist entropy in parameterizations of the turbulence.
 AMA-2012 - Toulouse, 23 janvier 2012 Visit of Sergei Zilitinkevich (April 2012) On the use of the moist entropy in parameterizations of the turbulence. Pascal MARQUET (Météo-France. DPrévi / LABO) Jean-François
AMA-2012 - Toulouse, 23 janvier 2012 Visit of Sergei Zilitinkevich (April 2012) On the use of the moist entropy in parameterizations of the turbulence. Pascal MARQUET (Météo-France. DPrévi / LABO) Jean-François
Definition of a moist entropy potential temperature: application to FIRE-I data flights
 Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 137: 768 791, April 2011 A Definition of a moist entropy potential temperature: application to FIRE-I data flights Pascal Marquet
Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 137: 768 791, April 2011 A Definition of a moist entropy potential temperature: application to FIRE-I data flights Pascal Marquet
Beyond Dufour et Van Mieghem 1975, contribution of the Third Law to the thermodynamic of moist atmospheric open systems
 Beyond Dufour et Van Mieghem 1975, contribution of the Third Law to the thermodynamic of moist atmospheric open systems Jean-François GELEYN CNRM, Météo-France,Toulouse --- (many thanks to P. Marquet,
Beyond Dufour et Van Mieghem 1975, contribution of the Third Law to the thermodynamic of moist atmospheric open systems Jean-François GELEYN CNRM, Météo-France,Toulouse --- (many thanks to P. Marquet,
arxiv: v1 [physics.ao-ph] 12 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ao-ph] 12 Oct 2015 arxiv: v1 [physics.ao-ph] 12 Oct 2015](/thumbs/77/74746419.jpg) arxiv:1510.03239v1 [physics.ao-ph] 12 Oct 2015 Parameterization of Atmospheric Convection (COST-ES0905 book) in R. S. Plant and J.-I. Yano, editors. Vol. 2: Current issues and new theories. Chapter 22:
arxiv:1510.03239v1 [physics.ao-ph] 12 Oct 2015 Parameterization of Atmospheric Convection (COST-ES0905 book) in R. S. Plant and J.-I. Yano, editors. Vol. 2: Current issues and new theories. Chapter 22:
Moist thermodynamics and moist turbulence for modelling at the non-hydrostatic scales
 Moist thermodynamics and moist turbulence for modelling at the non-hydrostatic scales Jean-François Geleyn and Pascal Marquet Météo-France, Toulouse jean-francois.geleyn@meteo.fr Abstract The improvement
Moist thermodynamics and moist turbulence for modelling at the non-hydrostatic scales Jean-François Geleyn and Pascal Marquet Météo-France, Toulouse jean-francois.geleyn@meteo.fr Abstract The improvement
Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics
 Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics Reference Peixoto and Oort, Sec. 3.1, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5 (but skip the discussion of oceans until next week); Ch. 10 Thermodynamic
Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics Reference Peixoto and Oort, Sec. 3.1, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5 (but skip the discussion of oceans until next week); Ch. 10 Thermodynamic
Diabatic Processes. Diabatic processes are non-adiabatic processes such as. entrainment and mixing. radiative heating or cooling
 Diabatic Processes Diabatic processes are non-adiabatic processes such as precipitation fall-out entrainment and mixing radiative heating or cooling Parcel Model dθ dt dw dt dl dt dr dt = L c p π (C E
Diabatic Processes Diabatic processes are non-adiabatic processes such as precipitation fall-out entrainment and mixing radiative heating or cooling Parcel Model dθ dt dw dt dl dt dr dt = L c p π (C E
Impact of Turbulence on the Intensity of Hurricanes in Numerical Models* Richard Rotunno NCAR
 Impact of Turbulence on the Intensity of Hurricanes in Numerical Models* Richard Rotunno NCAR *Based on: Bryan, G. H., and R. Rotunno, 2009: The maximum intensity of tropical cyclones in axisymmetric numerical
Impact of Turbulence on the Intensity of Hurricanes in Numerical Models* Richard Rotunno NCAR *Based on: Bryan, G. H., and R. Rotunno, 2009: The maximum intensity of tropical cyclones in axisymmetric numerical
Lecture Ch. 6. Condensed (Liquid) Water. Cloud in a Jar Demonstration. How does saturation occur? Saturation of Moist Air. Saturation of Moist Air
 Lecture Ch. 6 Saturation of moist air Relationship between humidity and dewpoint Clausius-Clapeyron equation Dewpoint Temperature Depression Isobaric cooling Moist adiabatic ascent of air Equivalent temperature
Lecture Ch. 6 Saturation of moist air Relationship between humidity and dewpoint Clausius-Clapeyron equation Dewpoint Temperature Depression Isobaric cooling Moist adiabatic ascent of air Equivalent temperature
Radiative-Convective Instability. Kerry Emanuel Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 Radiative-Convective Instability Kerry Emanuel Massachusetts Institute of Technology Program Basic radiative-convective equilibrium Macro-instability of the RC state Some consequences Radiative Equilibrium
Radiative-Convective Instability Kerry Emanuel Massachusetts Institute of Technology Program Basic radiative-convective equilibrium Macro-instability of the RC state Some consequences Radiative Equilibrium
Meteorology 6150 Cloud System Modeling
 Meteorology 6150 Cloud System Modeling Steve Krueger Spring 2009 1 Fundamental Equations 1.1 The Basic Equations 1.1.1 Equation of motion The movement of air in the atmosphere is governed by Newton s Second
Meteorology 6150 Cloud System Modeling Steve Krueger Spring 2009 1 Fundamental Equations 1.1 The Basic Equations 1.1.1 Equation of motion The movement of air in the atmosphere is governed by Newton s Second
short introduction to Practical on Shallow Convection
 short introduction to Practical on Shallow Convection Bart van Stratum Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg 26 June 2015 Alpine summer school, Valsaverenche, Italy Goal practical Use the CLASS
short introduction to Practical on Shallow Convection Bart van Stratum Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg 26 June 2015 Alpine summer school, Valsaverenche, Italy Goal practical Use the CLASS
PALM - Cloud Physics. Contents. PALM group. last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015
 PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study
 The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
GEF2200 Atmosfærefysikk 2012
 GEF2200 Atmosfærefysikk 2012 Løsningsforslag til oppgavesett 4 WH06 3.46 (WH 2.49) The air parcel has the properties p = 1000hPa, T = 15 C and T d = 4 C. b Lifting the air parcel to p 2 = 900hPa, T 2 we
GEF2200 Atmosfærefysikk 2012 Løsningsforslag til oppgavesett 4 WH06 3.46 (WH 2.49) The air parcel has the properties p = 1000hPa, T = 15 C and T d = 4 C. b Lifting the air parcel to p 2 = 900hPa, T 2 we
Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches LONG-TERM
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches LONG-TERM
3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme
 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme R. J. Keane and R. S. Plant 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme p.1/17 Outline Introduction to the Plant-Craig
3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme R. J. Keane and R. S. Plant 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme p.1/17 Outline Introduction to the Plant-Craig
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation
 Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016
 MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016 We have reviewed the reasons why NWP models need to
MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016 We have reviewed the reasons why NWP models need to
Parcel Model. Meteorology September 3, 2008
 Parcel Model Meteorology 5210 September 3, 2008 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature, θ, mixing
Parcel Model Meteorology 5210 September 3, 2008 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature, θ, mixing
Parcel Model. Atmospheric Sciences September 30, 2012
 Parcel Model Atmospheric Sciences 6150 September 30, 2012 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature,
Parcel Model Atmospheric Sciences 6150 September 30, 2012 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature,
Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches Joao Teixeira
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches Joao Teixeira
Earth s flattening : which impact for meteorology and climatology?
 Earth s flattening : which impact for meteorology and climatology? Pierre Bénard Météo-France CNRM/GMAP CNRS 16 21 Aug. 2014, Montreal P. Bénard (Météo-France) Earth s flattening : which impact? 16/21
Earth s flattening : which impact for meteorology and climatology? Pierre Bénard Météo-France CNRM/GMAP CNRS 16 21 Aug. 2014, Montreal P. Bénard (Météo-France) Earth s flattening : which impact? 16/21
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models
 An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
Adiabatic expansion Isothermal compression Adiabatic compression
 Tropical Cyclones: Steady State Physics 1 Energy Production 2 Carnot Theorem: Maximum efficiency results from a pa rticular energy e cycle: Isothermal expansion Adiabatic expansion Isothermal compression
Tropical Cyclones: Steady State Physics 1 Energy Production 2 Carnot Theorem: Maximum efficiency results from a pa rticular energy e cycle: Isothermal expansion Adiabatic expansion Isothermal compression
Hurricanes are intense vortical (rotational) storms that develop over the tropical oceans in regions of very warm surface water.
 Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment
 Atmospheric Sciences 6150 Cloud System Modeling 2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment Arakawa (1969, 1972), W. Gray
Atmospheric Sciences 6150 Cloud System Modeling 2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment Arakawa (1969, 1972), W. Gray
UNRESOLVED ISSUES. 1. Spectral broadening through different growth histories 2. Entrainment and mixing 3. In-cloud activation
 URESOLVED ISSUES. Spectral broadening through different growth histories 2. Entrainment and mixing. In-cloud activation /4 dr dt ξ ( S ) r, ξ F D + F K 2 dr dt 2ξ ( S ) For a given thermodynamic conditions
URESOLVED ISSUES. Spectral broadening through different growth histories 2. Entrainment and mixing. In-cloud activation /4 dr dt ξ ( S ) r, ξ F D + F K 2 dr dt 2ξ ( S ) For a given thermodynamic conditions
Activities on model error at Météo- France
 Activities on model error at Météo- France Philippe Arbogast, Marie Boisserie (CNRM-GAME, Toulouse) With contributions by I. Beau, H. Douville, F. Bouyssel, CH. Lac, D. Ricard, Y. Seity, R. Honnert, L.
Activities on model error at Météo- France Philippe Arbogast, Marie Boisserie (CNRM-GAME, Toulouse) With contributions by I. Beau, H. Douville, F. Bouyssel, CH. Lac, D. Ricard, Y. Seity, R. Honnert, L.
Isentropic analysis and atmospheric circulation.
 Isentropic analysis and atmospheric circulation. Olivier Pauluis Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Thanks to Arnaud Czaja, Robert Korty and Frederic Laliberte Sept. 1, 2009 Keck Institute for
Isentropic analysis and atmospheric circulation. Olivier Pauluis Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Thanks to Arnaud Czaja, Robert Korty and Frederic Laliberte Sept. 1, 2009 Keck Institute for
SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT
 SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT Progress Reports should be 2 to 10 pages in length, depending on importance of the project. All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Reporting year
SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT Progress Reports should be 2 to 10 pages in length, depending on importance of the project. All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Reporting year
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition. SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club
 Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club Mar 01, 2006 AGCM5 of the GFD-DENNOU CLUB edition is a three-dimensional primitive system on a sphere (Swamp Project,
Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club Mar 01, 2006 AGCM5 of the GFD-DENNOU CLUB edition is a three-dimensional primitive system on a sphere (Swamp Project,
An Introduction to Climate Modeling
 An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Numerical modelling of the interaction of soil moisture with planetary boundary layer features and convection over West Africa
 Numerical modelling of the interaction of soil moisture with planetary boundary layer features and convection over West Africa Leonhard Gantner, Norbert Kalthoff, and Martin Kohler Photo: J. Schwendike
Numerical modelling of the interaction of soil moisture with planetary boundary layer features and convection over West Africa Leonhard Gantner, Norbert Kalthoff, and Martin Kohler Photo: J. Schwendike
Sub-grid parametrization in the ECMWF model
 Sub-grid parametrization in the ECMWF model Anton Beljaars Thanks to: Gianpaolo Balsamo, Peter Bechtold, Richard Forbes, Thomas Haiden, Marta Janiskova and Irina Sandu WWOSC: Parametrization at ECMWF Slide
Sub-grid parametrization in the ECMWF model Anton Beljaars Thanks to: Gianpaolo Balsamo, Peter Bechtold, Richard Forbes, Thomas Haiden, Marta Janiskova and Irina Sandu WWOSC: Parametrization at ECMWF Slide
A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes
 A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes Song-Lak Kang Atmospheric Science Group, Texas Tech Univ. & George H. Bryan MMM, NCAR 20 th Symposium on Boundary
A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes Song-Lak Kang Atmospheric Science Group, Texas Tech Univ. & George H. Bryan MMM, NCAR 20 th Symposium on Boundary
Department: Machines and equipments. Stage: First Stage Title: Thermodynamic week: 19
 Department: Machines and equipments Stage: First Stage Title: Thermodynamic week: 19 Entropy, changes on closed systems and temperature entropy plane Entropy is an extensive property of a system and sometimes
Department: Machines and equipments Stage: First Stage Title: Thermodynamic week: 19 Entropy, changes on closed systems and temperature entropy plane Entropy is an extensive property of a system and sometimes
Interaction of boundary-layer turbulence and convection in the AROME model: Preliminary results
 Interaction of boundary-layer turbulence and convection in the AROME model: Preliminary results Balázs Szintai Hungarian Meteorological Service COST ES0905 Workshop Cambridge, England 23 March 2010 Outline
Interaction of boundary-layer turbulence and convection in the AROME model: Preliminary results Balázs Szintai Hungarian Meteorological Service COST ES0905 Workshop Cambridge, England 23 March 2010 Outline
DANO, Burkina Faso. Instruments Data set Status Highlights. Norbert Kalthoff and Juliane Schwendike. Institut für Meteorologie und Klimaforschung
 DANO, Burkina Faso Instruments Data set Status Highlights by Norbert Kalthoff and Juliane Schwendike Dano (super-)site in Burkina Faso Dreyer Foundation Dano Dano Bontioli Measurements at Bontioli site
DANO, Burkina Faso Instruments Data set Status Highlights by Norbert Kalthoff and Juliane Schwendike Dano (super-)site in Burkina Faso Dreyer Foundation Dano Dano Bontioli Measurements at Bontioli site
Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes)
 10/12/06 ATS 541 - Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Cloud Physics 1 Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes) ATS 541 students: Answer all questions ATS 441 students: You may delete problem 3 or problem 5 1. [10
10/12/06 ATS 541 - Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Cloud Physics 1 Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes) ATS 541 students: Answer all questions ATS 441 students: You may delete problem 3 or problem 5 1. [10
An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds: ECMWF
 An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds: EDMF @ ECMWF Martin Köhler ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Martin.Koehler@ecmwf.int 1 Introduction The importance of low
An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds: EDMF @ ECMWF Martin Köhler ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Martin.Koehler@ecmwf.int 1 Introduction The importance of low
ECMWF now and future dry PBL stratocumulus shallow cumulus. ongoing work parcel numerics stratocumulus down-drafts shallow cumulus
 An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds Martin Köhler, ECMWF EDMF @ ECMWF now and future dry PBL stratocumulus shallow cumulus stratocumulus: evaluation against observations EPIC marine
An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds Martin Köhler, ECMWF EDMF @ ECMWF now and future dry PBL stratocumulus shallow cumulus stratocumulus: evaluation against observations EPIC marine
Improved rainfall and cloud-radiation interaction with Betts-Miller-Janjic cumulus scheme in the tropics
 Improved rainfall and cloud-radiation interaction with Betts-Miller-Janjic cumulus scheme in the tropics Tieh-Yong KOH 1 and Ricardo M. FONSECA 2 1 Singapore University of Social Sciences, Singapore 2
Improved rainfall and cloud-radiation interaction with Betts-Miller-Janjic cumulus scheme in the tropics Tieh-Yong KOH 1 and Ricardo M. FONSECA 2 1 Singapore University of Social Sciences, Singapore 2
Description and Preliminary Results of the 9-level UCLA General Circulation Model
 July 6, 003 :08 am Description and Preliminary Results of the 9-level UCLA General Circulation Model Max J. Suarez, Akio Arakawa This manuscript has been re-typed from: Suarez, M. J. and A. Arakawa, 979:
July 6, 003 :08 am Description and Preliminary Results of the 9-level UCLA General Circulation Model Max J. Suarez, Akio Arakawa This manuscript has been re-typed from: Suarez, M. J. and A. Arakawa, 979:
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models
 Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Development of a stochastic convection scheme
 Development of a stochastic convection scheme R. J. Keane, R. S. Plant, N. E. Bowler, W. J. Tennant Development of a stochastic convection scheme p.1/45 Mini-ensemble of rainfall forecasts Development
Development of a stochastic convection scheme R. J. Keane, R. S. Plant, N. E. Bowler, W. J. Tennant Development of a stochastic convection scheme p.1/45 Mini-ensemble of rainfall forecasts Development
Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate
 Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans
![Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans](/thumbs/96/128963638.jpg) Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Some remarks on climate modeling
 Some remarks on climate modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Selected overheads by Doug Nychka Outline Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Some remarks on climate modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Selected overheads by Doug Nychka Outline Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Mid-Level Vorticity, Moisture, and Gross Moist Stability in the Tropical Atmosphere
 Mid-Level Vorticity, Moisture, and Gross Moist Stability in the Tropical Atmosphere David Raymond, Saška Gjorgjievska, Sharon Sessions, Carlos López, Željka Fuchs Physics Department and Geophysical Research
Mid-Level Vorticity, Moisture, and Gross Moist Stability in the Tropical Atmosphere David Raymond, Saška Gjorgjievska, Sharon Sessions, Carlos López, Željka Fuchs Physics Department and Geophysical Research
Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch
 Improvements in CAM5 : Moist Turbulence, Shallow Convection, and Cloud Macrophysics AMWG Meeting Feb. 10. 2010 Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch CGD.NCAR University of Washington, Seattle,
Improvements in CAM5 : Moist Turbulence, Shallow Convection, and Cloud Macrophysics AMWG Meeting Feb. 10. 2010 Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch CGD.NCAR University of Washington, Seattle,
ECMWF Overview. The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts is an international. organisation supported by 23 European States.
 ECMWF Overview The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts is an international organisation supported by 3 European States. The center was established in 1973 by a Convention and the real-time
ECMWF Overview The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts is an international organisation supported by 3 European States. The center was established in 1973 by a Convention and the real-time
The Relationship Between Atmospheric Boundary Layer Structure and Refractivity
 The Relationship Between Atmospheric Boundary Layer Structure and Refractivity Robert E. Marshall, PhD Atmospheric Scientist / RF Engineer NSWCDD Q32 10 March 2011 Distribu(on Statement A: Approved for
The Relationship Between Atmospheric Boundary Layer Structure and Refractivity Robert E. Marshall, PhD Atmospheric Scientist / RF Engineer NSWCDD Q32 10 March 2011 Distribu(on Statement A: Approved for
Mass Conserving Courant Number Independent Eulerian Advection of the Moisture Quantities for the LMK
 Mass Conserving Courant Number Independent Eulerian Advection of the Moisture Quantities for the LMK Jochen Förstner, Michael Baldauf, Axel Seifert Deutscher Wetterdienst, Kaiserleistraße 29/35, 63067
Mass Conserving Courant Number Independent Eulerian Advection of the Moisture Quantities for the LMK Jochen Förstner, Michael Baldauf, Axel Seifert Deutscher Wetterdienst, Kaiserleistraße 29/35, 63067
The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases
 The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Thorsten Mauritsen Max Planck Institute for Meteorology,
The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Thorsten Mauritsen Max Planck Institute for Meteorology,
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR
 CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
Météo-France Physics (AROME & ARPEGE) Eric Bazile, Yves Bouteloup, Rachel Honnert,
 Recent developments in Météo-France Physics (AROME & ARPEGE Eric Bazile, Yves Bouteloup, Rachel Honnert, Sébastien Riette, Yann Seity 34th Ewglam & 19th SRNWP joined meetings Helsinki 8-11 october 2012
Recent developments in Météo-France Physics (AROME & ARPEGE Eric Bazile, Yves Bouteloup, Rachel Honnert, Sébastien Riette, Yann Seity 34th Ewglam & 19th SRNWP joined meetings Helsinki 8-11 october 2012
Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic]
![Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic]](/thumbs/81/83694823.jpg) Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Entropy 1. (Thermodynamics) a thermodynamic quantity that changes in a
Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Entropy 1. (Thermodynamics) a thermodynamic quantity that changes in a
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
Tropical Cyclone Formation: Results
 Tropical Cyclone Formation: Results from PREDICT (PRE Depression Investigation of Cloud systems in the Tropics) collaborator on this presentation: Dave Ahijevych (NCAR) Chris Davis National Center for
Tropical Cyclone Formation: Results from PREDICT (PRE Depression Investigation of Cloud systems in the Tropics) collaborator on this presentation: Dave Ahijevych (NCAR) Chris Davis National Center for
THERMODYNAMICS 1 /43
 THERMODYNAMICS 1 Atmosphere A multi-component Multi-Phase System The gas phase atmospheric cons1tuents; major gases; fixed propor1ons by volume (dry air) Nitrogen (N 2 ) 78,08 % Oxygen (O 2 ) 29,05 % Argon
THERMODYNAMICS 1 Atmosphere A multi-component Multi-Phase System The gas phase atmospheric cons1tuents; major gases; fixed propor1ons by volume (dry air) Nitrogen (N 2 ) 78,08 % Oxygen (O 2 ) 29,05 % Argon
Fluid dynamics and moist thermodynamics
 Chapter 1 Fluid dynamics and moist thermodynamics In this chapter we review the equations that represent the physical laws governing atmospheric motion. Rigorous derivations of the equations may be found
Chapter 1 Fluid dynamics and moist thermodynamics In this chapter we review the equations that represent the physical laws governing atmospheric motion. Rigorous derivations of the equations may be found
Atmospheric Boundary Layers
 Lecture for International Summer School on the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Les Houches, France, June 17, 2008 Atmospheric Boundary Layers Bert Holtslag Introducing the latest developments in theoretical
Lecture for International Summer School on the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Les Houches, France, June 17, 2008 Atmospheric Boundary Layers Bert Holtslag Introducing the latest developments in theoretical
Clouds and atmospheric convection
 Clouds and atmospheric convection Caroline Muller CNRS/Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique (LMD) Département de Géosciences ENS M2 P7/ IPGP 1 What are clouds? Clouds and atmospheric convection 3 What
Clouds and atmospheric convection Caroline Muller CNRS/Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique (LMD) Département de Géosciences ENS M2 P7/ IPGP 1 What are clouds? Clouds and atmospheric convection 3 What
Robert J. Trapp Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana
 10.6 DO SUPERCELL THUNDERSTORMS PLAY A ROLE IN THE EQUILIBRATION OF THE LARGE-SCALE ATMOSPHERE? Robert J. Trapp Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana Charles A. Doswell, III Cooperative Institute
10.6 DO SUPERCELL THUNDERSTORMS PLAY A ROLE IN THE EQUILIBRATION OF THE LARGE-SCALE ATMOSPHERE? Robert J. Trapp Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana Charles A. Doswell, III Cooperative Institute
A brief overview of the scheme is given below, taken from the whole description available in Lopez (2002).
 Towards an operational implementation of Lopez s prognostic large scale cloud and precipitation scheme in ARPEGE/ALADIN NWP models F.Bouyssel, Y.Bouteloup, P. Marquet Météo-France, CNRM/GMAP, 42 av. G.
Towards an operational implementation of Lopez s prognostic large scale cloud and precipitation scheme in ARPEGE/ALADIN NWP models F.Bouyssel, Y.Bouteloup, P. Marquet Météo-France, CNRM/GMAP, 42 av. G.
PV Generation in the Boundary Layer
 1 PV Generation in the Boundary Layer Robert Plant 18th February 2003 (With thanks to S. Belcher) 2 Introduction How does the boundary layer modify the behaviour of weather systems? Often regarded as a
1 PV Generation in the Boundary Layer Robert Plant 18th February 2003 (With thanks to S. Belcher) 2 Introduction How does the boundary layer modify the behaviour of weather systems? Often regarded as a
The Tropical Atmosphere: Hurricane Incubator
 The Tropical Atmosphere: Hurricane Incubator Images from journals published by the American Meteorological Society are copyright AMS and used with permission. A One-Dimensional Description of the Tropical
The Tropical Atmosphere: Hurricane Incubator Images from journals published by the American Meteorological Society are copyright AMS and used with permission. A One-Dimensional Description of the Tropical
...Thermodynamics. Entropy: The state function for the Second Law. Entropy ds = d Q. Central Equation du = TdS PdV
 ...Thermodynamics Entropy: The state function for the Second Law Entropy ds = d Q T Central Equation du = TdS PdV Ideal gas entropy s = c v ln T /T 0 + R ln v/v 0 Boltzmann entropy S = klogw Statistical
...Thermodynamics Entropy: The state function for the Second Law Entropy ds = d Q T Central Equation du = TdS PdV Ideal gas entropy s = c v ln T /T 0 + R ln v/v 0 Boltzmann entropy S = klogw Statistical
Where does the memory of convection stem from? Why can it be useful for parameterizations?
 Where does the memory of convection stem from? Why can it be useful for parameterizations? D'où vient la mémoire de la convection? En quoi cela peut-il être utile pour les paramétrisations? Maxime Colin,
Where does the memory of convection stem from? Why can it be useful for parameterizations? D'où vient la mémoire de la convection? En quoi cela peut-il être utile pour les paramétrisations? Maxime Colin,
Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-Based Cloud Approaches
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-Based Cloud Approaches Joao Teixeira
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-Based Cloud Approaches Joao Teixeira
Sensitivity to the PBL and convective schemes in forecasts with CAM along the Pacific Cross-section
 Sensitivity to the PBL and convective schemes in forecasts with CAM along the Pacific Cross-section Cécile Hannay, Jeff Kiehl, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Jim Hack, Richard Neale and Chris Bretherton*
Sensitivity to the PBL and convective schemes in forecasts with CAM along the Pacific Cross-section Cécile Hannay, Jeff Kiehl, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Jim Hack, Richard Neale and Chris Bretherton*
WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica
 Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
Diurnal cycle Coupling Experiment (DICE) GLASS / GASS joint project. Martin Best and Adrian Lock Crown copyright Met Office
 Diurnal cycle Coupling Experiment (DICE) GLASS / GASS joint project Martin Best and Adrian Lock Courtesy of Mike Ek GLACE hotspot regions Koster et al (2006) Outline of the 3 stages of DICE LSM and SCM
Diurnal cycle Coupling Experiment (DICE) GLASS / GASS joint project Martin Best and Adrian Lock Courtesy of Mike Ek GLACE hotspot regions Koster et al (2006) Outline of the 3 stages of DICE LSM and SCM
Large-scale disturbances and convection. Željka Fuchs, University of Split
 Large-scale disturbances and convection Željka Fuchs, University of Split Huatulco airport Tropical disturbances Tropical cyclones Monsoons Easterly waves Madden-Julian oscillation Convectively
Large-scale disturbances and convection Željka Fuchs, University of Split Huatulco airport Tropical disturbances Tropical cyclones Monsoons Easterly waves Madden-Julian oscillation Convectively
MODEL UNIFICATION my latest research excitement Akio Arakawa
 MODEL UNIFICATION my latest research excitement Akio Arakawa Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, UCLA CMMAP, January 7, 24 Wayne Schubert ` 7 Cumulus/ L-S interaction David Randall Wayne Schubert
MODEL UNIFICATION my latest research excitement Akio Arakawa Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, UCLA CMMAP, January 7, 24 Wayne Schubert ` 7 Cumulus/ L-S interaction David Randall Wayne Schubert
Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China
 Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION Convective rain occurs over southern
Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION Convective rain occurs over southern
Feedback and Sensitivity in Climate
 Feedback and Sensitivity in Climate Frédéric Hourdin June 19, 2009 2 Boundary layer processes in climate 2 Boundary layer processes in climate ps2pdf OK. Figure: ClimSI WV feedback model responses. 0-0.45-3
Feedback and Sensitivity in Climate Frédéric Hourdin June 19, 2009 2 Boundary layer processes in climate 2 Boundary layer processes in climate ps2pdf OK. Figure: ClimSI WV feedback model responses. 0-0.45-3
Convection in the Unified Model
 Convection in the Unified Model Martin S. Singh Honours Thesis submitted as part of the B.Sc. (Honours) degree in the School of Mathematical Sciences, Monash University. Supervisor: Prof. Christian Jakob
Convection in the Unified Model Martin S. Singh Honours Thesis submitted as part of the B.Sc. (Honours) degree in the School of Mathematical Sciences, Monash University. Supervisor: Prof. Christian Jakob
Structure of Mass-Flux Convection Paprameterization. by Jun-Ichi Yano Meteo France Toulouse
 Structure of Mass-Flux Convection Paprameterization by Jun-Ichi Yano Meteo France Toulouse One cannot be a successful scientist without realizing that, in contrast to the popular conception supported by
Structure of Mass-Flux Convection Paprameterization by Jun-Ichi Yano Meteo France Toulouse One cannot be a successful scientist without realizing that, in contrast to the popular conception supported by
Simplified Microphysics. condensation evaporation. evaporation
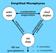 Simplified Microphysics water vapor condensation evaporation cloud droplets evaporation condensation collection rain drops fall out (precipitation) = 0 (reversible) = (irreversible) Simplified Microphysics
Simplified Microphysics water vapor condensation evaporation cloud droplets evaporation condensation collection rain drops fall out (precipitation) = 0 (reversible) = (irreversible) Simplified Microphysics
Response of convection to relative SST: Cloud-resolving simulations in 2D and 3D
 1 2 Response of convection to relative SST: Cloud-resolving simulations in 2D and 3D S. Wang, 1 and A. H. Sobel 2 -------------- Shuguang Wang, Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics, Columbia
1 2 Response of convection to relative SST: Cloud-resolving simulations in 2D and 3D S. Wang, 1 and A. H. Sobel 2 -------------- Shuguang Wang, Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics, Columbia
What you need to know in Ch. 12. Lecture Ch. 12. Atmospheric Heat Engine
 Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
LECTURE 28. The Planetary Boundary Layer
 LECTURE 28 The Planetary Boundary Layer The planetary boundary layer (PBL) [also known as atmospheric boundary layer (ABL)] is the lower part of the atmosphere in which the flow is strongly influenced
LECTURE 28 The Planetary Boundary Layer The planetary boundary layer (PBL) [also known as atmospheric boundary layer (ABL)] is the lower part of the atmosphere in which the flow is strongly influenced
Convective self-aggregation, cold pools, and domain size
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 1 5, doi:10.1002/grl.50204, 2013 Convective self-aggregation, cold pools, and domain size Nadir Jeevanjee, 1,2 and David M. Romps, 1,3 Received 14 December 2012;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 1 5, doi:10.1002/grl.50204, 2013 Convective self-aggregation, cold pools, and domain size Nadir Jeevanjee, 1,2 and David M. Romps, 1,3 Received 14 December 2012;
Fundamentals of Weather and Climate
 Fundamentals of Weather and Climate ROBIN McILVEEN Environmental Science Division Institute of Environmental and Biological Sciences Lancaster University CHAPMAN & HALL London Glasgow Weinheim New York
Fundamentals of Weather and Climate ROBIN McILVEEN Environmental Science Division Institute of Environmental and Biological Sciences Lancaster University CHAPMAN & HALL London Glasgow Weinheim New York
Simulations with different convection parameterizations in the LM
 Simulations with different convection parameterizations in the LM Linda Smoydzin Almut Gassmann Andreas Bott Marco Arpagaus (Meteo Swiss) Meteorological Institute of the University of Bonn, Germany Aims
Simulations with different convection parameterizations in the LM Linda Smoydzin Almut Gassmann Andreas Bott Marco Arpagaus (Meteo Swiss) Meteorological Institute of the University of Bonn, Germany Aims
Presentation A simple model of multiple climate regimes
 A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
USING PROGRAM HURRICANE. Download all the files, including the (empty) output subdirectory into a new folder on your machine.
 USING PROGRAM HURRICANE Download all the files, including the (empty) output subdirectory into a new folder on your machine. QuickStart: First compile hurr.f. Modify the first column of the input file
USING PROGRAM HURRICANE Download all the files, including the (empty) output subdirectory into a new folder on your machine. QuickStart: First compile hurr.f. Modify the first column of the input file
PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues
 PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues Song-You Hong, Hyun-Joo Choi, Ji-Young Han, and Young-Cheol Kwon (Korea Institute of Atmospheric Prediction Systems: KIAPS) Overview of KIAPS (seminar
PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues Song-You Hong, Hyun-Joo Choi, Ji-Young Han, and Young-Cheol Kwon (Korea Institute of Atmospheric Prediction Systems: KIAPS) Overview of KIAPS (seminar
Modified PM09 parameterizations in the shallow convection grey zone
 Modified PM09 parameterizations in the shallow convection grey zone LACE stay report Toulouse Centre National de Recherche Meteorologique, 02. February 2015 27. February 2015 Scientific supervisor: Rachel
Modified PM09 parameterizations in the shallow convection grey zone LACE stay report Toulouse Centre National de Recherche Meteorologique, 02. February 2015 27. February 2015 Scientific supervisor: Rachel
Thermodynamic Energy Equation
 Thermodynamic Energy Equation The temperature tendency is = u T x v T y w T z + dt dt (1) where dt/dt is the individual derivative of temperature. This temperature change experienced by the air parcel
Thermodynamic Energy Equation The temperature tendency is = u T x v T y w T z + dt dt (1) where dt/dt is the individual derivative of temperature. This temperature change experienced by the air parcel
df dz = dp dt Essentially, this is just a statement of the first law in one of the forms we derived earlier (expressed here in W m 3 ) dq p dt dp
 A problem with using entropy as a variable is that it is not a particularly intuitive concept. The mechanics of using entropy for evaluating system evolution is well developed, but it sometimes feels a
A problem with using entropy as a variable is that it is not a particularly intuitive concept. The mechanics of using entropy for evaluating system evolution is well developed, but it sometimes feels a
Cloud Feedbacks and Climate Models
 Cloud Feedbacks and Climate Models oão Teixeira, USA Together with many people including S. Cardoso (IDL/NCAR), A. Gettelman (NCAR), B. Kahn, S. Klein (LLNL), P. Miranda (IDL), A.P. Siebesma (KNMI), P.
Cloud Feedbacks and Climate Models oão Teixeira, USA Together with many people including S. Cardoso (IDL/NCAR), A. Gettelman (NCAR), B. Kahn, S. Klein (LLNL), P. Miranda (IDL), A.P. Siebesma (KNMI), P.
Neva Pristov. LACE area leader for physics
 ALARO Physics Developments Neva Pristov LACE area leader for physics Main developments TOUCANS turbulence scheme Radiation Convection Ivan Baštak Duran, Jean-Francois Geleyn, Filip Vana Jan Mašek, Radmila
ALARO Physics Developments Neva Pristov LACE area leader for physics Main developments TOUCANS turbulence scheme Radiation Convection Ivan Baštak Duran, Jean-Francois Geleyn, Filip Vana Jan Mašek, Radmila
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5
 Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM. I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop
 Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop Motivation The Earth s atmosphere is an extremely thin sheet of air
Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop Motivation The Earth s atmosphere is an extremely thin sheet of air
Daehyun Kim. *GCRM (global cloud resolving model): Next talk
 Daehyun Kim *GCRM (global cloud resolving model): Next talk No satisfactory theory that everyone agrees Inadequate simulation capability in most of the standard GCMs Slingo et al. 1996: models are poor
Daehyun Kim *GCRM (global cloud resolving model): Next talk No satisfactory theory that everyone agrees Inadequate simulation capability in most of the standard GCMs Slingo et al. 1996: models are poor
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS
 INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS C.G. Georgiev1 and P. Santurette2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Tsarigradsko chaussee 66, 1784 Sofia, Bulgaria 2 Météo-France, 42,
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS C.G. Georgiev1 and P. Santurette2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Tsarigradsko chaussee 66, 1784 Sofia, Bulgaria 2 Météo-France, 42,
