short introduction to Practical on Shallow Convection
|
|
|
- Norma Peters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 short introduction to Practical on Shallow Convection Bart van Stratum Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg 26 June 2015 Alpine summer school, Valsaverenche, Italy
2 Goal practical Use the CLASS (mixed-layer) model to study shallow convection 1. What controls the formation of shallow cumuli? - (Talk Pierre): influence of surface / atmospheric conditions on mixed-layer top relative humidity 2. Can we represent shallow cumulus in something as simple as our mixed-layer model? ql h qt moist dry 1/10 q
3 1. What controls the formation of shallow cumuli?
4 1. What determines the formation of shallow cumulus? - Shallow-cumuli form as moist updrafts saturate at/near the ABL top - Horizontally averaged ABL top relative humidity close to, but less then 100% - We can use the relative humidity (RHtop) as an indicator for clouds - To keep things simple: assume that if RHtop, cumulus, RHtop = cumulus ql h qt moist dry 2/10 q
5 1. Mixed-layer top relative humidity RH = q ; RH top = hqi ; q sat = f (T, p) q sat q sat;h z (m) Reference Reference Moist ABL Reference Moist Cold ABL Moist Cold Deep Reference ABL (K) q (g kg 1 ) q/q sat ( ) - Processes / atmospheric tendencies influencing RH top : - Mixed-layer drying (- -) or moistening (++) - Mixed-layer cooling (++) or heating (- - ) - Mixed-layer top cooling as ABL grows (++) 3/10
6 1. Mixed-layer top relative humidity budget - These processes are strongly coupled in a convective ABL! - We can quantify the influence of each process by studying the budget of RHtop (Ek & Mahrt 1994, Chang & Ek, 1996) RH = q q sat ; drh dt = d dt q q sat! = {...} = f dhqi dt, dh i dt, dh! dt dhqi dt = w0 q 0 s h w 0 q 0 e h dh i dt = w0 0 s w 0 0 e h dh dt = w e van Heerwaarden et al, 2009, QJRMS Entrainment drying ABL growth Surface moistening ABL heating Each of these terms are available as output in CLASS (NOTE: keep the time step small when using this budget!) 4/10
7 1. First part exercises - Study the processes/conditions that influence the formation of shallow cumuli - Atmospheric (temperate, moisture, conditions free troposphere) - Surface (sensible and latent heat flux) - To simplify the setup: use prescribed fluxes - Mimic the influence of soil moisture by varying the evaporative fraction: Q net = S # S " +L # L "= LE + H (+ G) = constant EF = LE H + LE - High soil moisture content = high EF, and vice versa - We can repeat this with the land-surface scheme enabled 5/10
8 2. How can we represent shallow cumulus in our mixed-layer model?
9 2. Processes in the dry convective boundary layer - Convective mixing/transport limited to well-mixed layer 6/10
10 2. Processes in the cumulus-topped convective boundary layer - Small fraction of the convective plumes escape the well-mixed layer - Transport of mass, heat, moisture, to cloud layer: loss term in mixed-layer equations 7/10
11 2. Extension mixed-layer equations - Two options: - Fully describe multi-layer structure of ABL (e.g. Gentine et al., 2013) - Focus on well-mixed sub-cloud layer, include influence shallow cumuli on this layer - (This has a number of disadvantages ) q'>0 '>0 q'>0 '>0 8/10
12 2. Extension mixed-layer equations - Things we need to account for: - Mass transport from the sub-cloud layer: - Mass -flux: - Fraction: - Velocity: M = a c w c a c = f q sat q h, q;h 0 1 ghw 0 0 v w c w = B@ CA v - Scalar transport from the sub-cloud layer: 1/3 q'>0 '>0 q'>0 '>0 - Flux: w 0 q 0 M = M (q c q c hqi = q;h hqi) Modified ABL growth: Modified scalar tendency: q q sat dh dt = w e M dhqi dt = w0 q 0 s w 0 q 0 e w 0 q 0 M h Neggers et al., /10
13 1. Second part exercises - Study how shallow cumulus influences the development of the ABL - ARM-SGP case (Brown et al., 2002): diurnal cycle of shallow cumulus - Sensitivity studies enabling/disabling clouds, varying initial/boundary conditions, - Like exercise 1: we can repeat this case with the land-surface scheme enabled 10/10
14 Organization practical - You can work alone, in groups, on the first exercise, the second, combine them, - Discussion on Monday (15:00-16:00) - From this practical 1-2 presentations (~10 minutes each) - My suggestion: - Work on practical for ~1 hour - Discuss results and what to present on Monday - Continue 11/10
2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment
 Atmospheric Sciences 6150 Cloud System Modeling 2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment Arakawa (1969, 1972), W. Gray
Atmospheric Sciences 6150 Cloud System Modeling 2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment Arakawa (1969, 1972), W. Gray
BMeteorologische Zeitschrift, Vol.23, No. 5, (published online December 11, 2014)
 BMeteorologische Zeitschrift, Vol.23, No. 5, 491 51 (published online December 11, 214) 214 The authors Open Access Article The effect of soil moisture and atmospheric conditions on the development of
BMeteorologische Zeitschrift, Vol.23, No. 5, 491 51 (published online December 11, 214) 214 The authors Open Access Article The effect of soil moisture and atmospheric conditions on the development of
2.1 Temporal evolution
 15B.3 ROLE OF NOCTURNAL TURBULENCE AND ADVECTION IN THE FORMATION OF SHALLOW CUMULUS Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands 1. MOTIVATION
15B.3 ROLE OF NOCTURNAL TURBULENCE AND ADVECTION IN THE FORMATION OF SHALLOW CUMULUS Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands 1. MOTIVATION
Land-surface response to shallow cumulus. Fabienne Lohou and Edward Patton
 Land-surface response to shallow cumulus Fabienne Lohou and Edward Patton Outline 1/ SEB response on average and locally ( Radiative and turbulent effects (not shown here)) Solar input Turbulence Radiative
Land-surface response to shallow cumulus Fabienne Lohou and Edward Patton Outline 1/ SEB response on average and locally ( Radiative and turbulent effects (not shown here)) Solar input Turbulence Radiative
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans
![Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans](/thumbs/96/128963638.jpg) Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica
 Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme
 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme R. J. Keane and R. S. Plant 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme p.1/17 Outline Introduction to the Plant-Craig
3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme R. J. Keane and R. S. Plant 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme p.1/17 Outline Introduction to the Plant-Craig
Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence)
 1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes
 A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes Song-Lak Kang Atmospheric Science Group, Texas Tech Univ. & George H. Bryan MMM, NCAR 20 th Symposium on Boundary
A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes Song-Lak Kang Atmospheric Science Group, Texas Tech Univ. & George H. Bryan MMM, NCAR 20 th Symposium on Boundary
Aerosol effect on the evolution of the thermodynamic properties of warm convective cloud fields
 Supporting Information for Aerosol effect on the evolution of the thermodynamic properties of warm convective cloud fields Guy Dagan, Ilan Koren*, Orit Altaratz and Reuven H. Heiblum Department of Earth
Supporting Information for Aerosol effect on the evolution of the thermodynamic properties of warm convective cloud fields Guy Dagan, Ilan Koren*, Orit Altaratz and Reuven H. Heiblum Department of Earth
Surface and Atmospheric Controls on the Onset of Moist Convection over Land
 OCTOBER 2013 G E N T I N E E T A L. 1443 Surface and Atmospheric Controls on the Onset of Moist Convection over Land PIERRE GENTINE Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering, Columbia University,
OCTOBER 2013 G E N T I N E E T A L. 1443 Surface and Atmospheric Controls on the Onset of Moist Convection over Land PIERRE GENTINE Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering, Columbia University,
14B.2 Relative humidity as a proxy for cloud formation over heterogeneous land surfaces
 14B.2 Relative humidity as a proxy for cloud formation over heterogeneous land surfaces Chiel C. van Heerwaarden and Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University,
14B.2 Relative humidity as a proxy for cloud formation over heterogeneous land surfaces Chiel C. van Heerwaarden and Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University,
MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016
 MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016 We have reviewed the reasons why NWP models need to
MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016 We have reviewed the reasons why NWP models need to
Chapter 4 Water Vapor
 Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Quantifying the transport of subcloud layer reactants by shallow cumulus clouds over the Amazon
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: AMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 13,041 13,059, doi:10.1002/2013jd020431, 2013 Quantifying the transport of subcloud layer reactants by shallow cumulus clouds over the Amazon H. G.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: AMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 13,041 13,059, doi:10.1002/2013jd020431, 2013 Quantifying the transport of subcloud layer reactants by shallow cumulus clouds over the Amazon H. G.
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1
 Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
A "New" Mechanism for the Diurnal Variation of Convection over the Tropical Western Pacific Ocean
 A "New" Mechanism for the Diurnal Variation of Convection over the Tropical Western Pacific Ocean D. B. Parsons Atmospheric Technology Division National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Boulder,
A "New" Mechanism for the Diurnal Variation of Convection over the Tropical Western Pacific Ocean D. B. Parsons Atmospheric Technology Division National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Boulder,
A Probabilistic Bulk Model of Coupled Mixed Layer and Convection. Part II: Shallow Convection Case
 JUNE 2013 G E N T I N E E T A L. 1557 A Probabilistic Bulk Model of Coupled Mixed Layer and Convection. Part II: Shallow Convection Case PIERRE GENTINE,* ALAN K. BETTS, 1 BENJAMIN R. LINTNER, # KIRSTEN
JUNE 2013 G E N T I N E E T A L. 1557 A Probabilistic Bulk Model of Coupled Mixed Layer and Convection. Part II: Shallow Convection Case PIERRE GENTINE,* ALAN K. BETTS, 1 BENJAMIN R. LINTNER, # KIRSTEN
Shallow convection over land: a mesoscale modelling study based on idealized WRF experiments
 Tethys, 6, 51 66, 2009 Journal of Weather & Climate of the Western Mediterranean www.tethys.cat ISSN-1697-1523 eissn-1139-3394 DOI:10.3369/tethys.2009.6.04 Journal edited by ACAM (Associació Catalana de
Tethys, 6, 51 66, 2009 Journal of Weather & Climate of the Western Mediterranean www.tethys.cat ISSN-1697-1523 eissn-1139-3394 DOI:10.3369/tethys.2009.6.04 Journal edited by ACAM (Associació Catalana de
Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance
 Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance Instructor: Prof. Johnny Luo http://www.sci.ccny.cuny.edu/~luo Surface Energy Balance 1. Factors affecting surface energy balance 2. Surface heat storage 3. Surface
Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance Instructor: Prof. Johnny Luo http://www.sci.ccny.cuny.edu/~luo Surface Energy Balance 1. Factors affecting surface energy balance 2. Surface heat storage 3. Surface
+ Validation of a simplified land surface model and
 + Validation of a simplified land surface model and its application to the case of shallow cumulus convection development Colorado State University January 2013 Marat Khairoutdinov Jungmin Lee Simplified
+ Validation of a simplified land surface model and its application to the case of shallow cumulus convection development Colorado State University January 2013 Marat Khairoutdinov Jungmin Lee Simplified
Dry Season Shallow Cumulus Clouds in the Amazon Rainforest
 Master s Thesis of Climate Studies Dry Season Shallow Cumulus Clouds in the Amazon Rainforest WAGENINGEN U NIVERSITY M ETEOROLOGY AND A IR Q UALITY Author: Xuemei Wang Supervisor: Prof. Jordi Vila -Guerau
Master s Thesis of Climate Studies Dry Season Shallow Cumulus Clouds in the Amazon Rainforest WAGENINGEN U NIVERSITY M ETEOROLOGY AND A IR Q UALITY Author: Xuemei Wang Supervisor: Prof. Jordi Vila -Guerau
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
Radiative convective equilibrium over a land. surface
 1 2 Radiative convective equilibrium over a land surface 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Nicolas Rochetin Columbia University New York, NY 10027 Benjamin R. Lintner Rutgers, the
1 2 Radiative convective equilibrium over a land surface 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Nicolas Rochetin Columbia University New York, NY 10027 Benjamin R. Lintner Rutgers, the
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
1. CLIMATOLOGY: 2. ATMOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY:
 What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
Atmospheric Boundary Layers
 Lecture for International Summer School on the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Les Houches, France, June 17, 2008 Atmospheric Boundary Layers Bert Holtslag Introducing the latest developments in theoretical
Lecture for International Summer School on the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Les Houches, France, June 17, 2008 Atmospheric Boundary Layers Bert Holtslag Introducing the latest developments in theoretical
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 14: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 14: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Today, HW#5 is posted Quiz Today on Chapter 3, too. Mid Term
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 14: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Today, HW#5 is posted Quiz Today on Chapter 3, too. Mid Term
Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons)
 Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger How do we parameterize convec+on? Precipita)on response to soil moisture Increase
Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger How do we parameterize convec+on? Precipita)on response to soil moisture Increase
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERIC MOISTURE Atmospheric Moisture The Nature of Water The Hydrologic Cycle Evaporation Measures of Humidity Condensation The Buoyancy of Air Precipitation
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERIC MOISTURE Atmospheric Moisture The Nature of Water The Hydrologic Cycle Evaporation Measures of Humidity Condensation The Buoyancy of Air Precipitation
The Water Cycle. Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site:
 Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Latent Heat Evaporation & Saturation Relative Humidity Dew Point Lecture 11 Oct 2 2018
Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Latent Heat Evaporation & Saturation Relative Humidity Dew Point Lecture 11 Oct 2 2018
From small-scale turbulence to large-scale convection: a unified scale-adaptive EDMF parameterization
 From small-scale turbulence to large-scale convection: a unified scale-adaptive EDMF parameterization Kay Sušelj 1, Joao Teixeira 1 and Marcin Kurowski 1,2 1 JET PROPULSION LABORATORY/CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE
From small-scale turbulence to large-scale convection: a unified scale-adaptive EDMF parameterization Kay Sušelj 1, Joao Teixeira 1 and Marcin Kurowski 1,2 1 JET PROPULSION LABORATORY/CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE
TURBULENT KINETIC ENERGY
 TURBULENT KINETIC ENERGY THE CLOSURE PROBLEM Prognostic Moment Equation Number Number of Ea. fg[i Q! Ilial.!.IokoQlI!!ol Ui au. First = at au.'u.' '_J_ ax j 3 6 ui'u/ au.'u.' a u.'u.'u k ' Second ' J =
TURBULENT KINETIC ENERGY THE CLOSURE PROBLEM Prognostic Moment Equation Number Number of Ea. fg[i Q! Ilial.!.IokoQlI!!ol Ui au. First = at au.'u.' '_J_ ax j 3 6 ui'u/ au.'u.' a u.'u.'u k ' Second ' J =
Role of nocturnal turbulence and advection in the formation of shallow cumulus over land
 QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 133: 1615 1627 (2007) Published online 5 September 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).138 Role of nocturnal
QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 133: 1615 1627 (2007) Published online 5 September 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).138 Role of nocturnal
The influence of wind speed on shallow marine cumulus convection
 Generated using V3.0 of the official AMS LATEX template journal page layout FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! The influence of wind speed on shallow marine cumulus convection Louise Nuijens and
Generated using V3.0 of the official AMS LATEX template journal page layout FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! The influence of wind speed on shallow marine cumulus convection Louise Nuijens and
Kelvin Effect. Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics
 Kelvin Effect Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Vapor Pressure (e) e < e # e = e # Vapor Pressure e > e # Relative humidity RH =
Kelvin Effect Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Vapor Pressure (e) e < e # e = e # Vapor Pressure e > e # Relative humidity RH =
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110, D15S16, doi: /2004jd005109, 2005
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004jd005109, 2005 Moisture and temperature balances at the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Southern Great Plains Site in forecasts with the Community
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004jd005109, 2005 Moisture and temperature balances at the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Southern Great Plains Site in forecasts with the Community
Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches Joao Teixeira
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches Joao Teixeira
Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch
 Improvements in CAM5 : Moist Turbulence, Shallow Convection, and Cloud Macrophysics AMWG Meeting Feb. 10. 2010 Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch CGD.NCAR University of Washington, Seattle,
Improvements in CAM5 : Moist Turbulence, Shallow Convection, and Cloud Macrophysics AMWG Meeting Feb. 10. 2010 Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch CGD.NCAR University of Washington, Seattle,
Diabatic Processes. Diabatic processes are non-adiabatic processes such as. entrainment and mixing. radiative heating or cooling
 Diabatic Processes Diabatic processes are non-adiabatic processes such as precipitation fall-out entrainment and mixing radiative heating or cooling Parcel Model dθ dt dw dt dl dt dr dt = L c p π (C E
Diabatic Processes Diabatic processes are non-adiabatic processes such as precipitation fall-out entrainment and mixing radiative heating or cooling Parcel Model dθ dt dw dt dl dt dr dt = L c p π (C E
Clouds associated with cold and warm fronts. Whiteman (2000)
 Clouds associated with cold and warm fronts Whiteman (2000) Dalton s law of partial pressures! The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases equals the sum of the partial pressure of the gases! Partial
Clouds associated with cold and warm fronts Whiteman (2000) Dalton s law of partial pressures! The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases equals the sum of the partial pressure of the gases! Partial
Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP
 Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP Paul Earnshaw and Sean Milton Met Office, UK Crown copyright 2005 Page 1 Overview Production and use of CEOP data Results SGP Seasonal & Diurnal cycles Other extratopical
Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP Paul Earnshaw and Sean Milton Met Office, UK Crown copyright 2005 Page 1 Overview Production and use of CEOP data Results SGP Seasonal & Diurnal cycles Other extratopical
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015
 The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015 The effects of moisture conditions on the organization and intensity
The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015 The effects of moisture conditions on the organization and intensity
Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches LONG-TERM
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches LONG-TERM
Global Water Cycle. Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere. Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40.
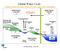 Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
Radiative-Convective Models. The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation. Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1
 Climate Modeling Lecture 8 Radiative-Convective Models Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1 The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation Prepare for Mid-Term (Friday 9 am) Review Course Notes
Climate Modeling Lecture 8 Radiative-Convective Models Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1 The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation Prepare for Mid-Term (Friday 9 am) Review Course Notes
A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium
 A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium A. Parodi(1), K. Emanuel(2) (2) CIMA Research Foundation,Savona, Italy (3) EAPS, MIT, Boston, USA True dynamics: turbulent, moist, non-boussinesq,
A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium A. Parodi(1), K. Emanuel(2) (2) CIMA Research Foundation,Savona, Italy (3) EAPS, MIT, Boston, USA True dynamics: turbulent, moist, non-boussinesq,
AOSC 614. Chapter 4 Junjie Liu Oct. 26, 2006
 AOSC 614 Chapter 4 Junjie Liu Oct. 26, 2006 The role of parameterization in the numerical model Why do we need parameterization process? Chapter 2 discussed the governing equations. Chapter 3 discussed
AOSC 614 Chapter 4 Junjie Liu Oct. 26, 2006 The role of parameterization in the numerical model Why do we need parameterization process? Chapter 2 discussed the governing equations. Chapter 3 discussed
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
Chapter 5. Atmospheric Moisture
 Chapter 5 Atmospheric Moisture hydrologic cycle--movement of water in all forms between earth & atmosphere Humidity: amount of water vapor in air vapor pressure saturation vapor pressure absolute humidity
Chapter 5 Atmospheric Moisture hydrologic cycle--movement of water in all forms between earth & atmosphere Humidity: amount of water vapor in air vapor pressure saturation vapor pressure absolute humidity
Thunderstorms and Severe Weather. (Chapt 15)
 Thunderstorms and Severe Weather (Chapt 15) The Big Picture We ve emphasized horizontal transport of energy to balance the planetary energy budget: Hadley Cell Subtropical divergence Midlatitude cyclones
Thunderstorms and Severe Weather (Chapt 15) The Big Picture We ve emphasized horizontal transport of energy to balance the planetary energy budget: Hadley Cell Subtropical divergence Midlatitude cyclones
Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001
 Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please be sure to read each question CAREFULLY
Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please be sure to read each question CAREFULLY
Climate change with an iris-effect. Thorsten Mauritsen and Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg
 Climate change with an iris-effect! Thorsten Mauritsen and Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg AR4 Temperature anomaly ( C) w.r.t. 1961 1990 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 } AR4 CMIP3 } Observations
Climate change with an iris-effect! Thorsten Mauritsen and Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg AR4 Temperature anomaly ( C) w.r.t. 1961 1990 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 } AR4 CMIP3 } Observations
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study
 The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate
 Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
ENTRAINMENT-MIXING IN SHALLOW CUMULUS AND THE ONSET OF PRECIPITATION
 ENTRAINMENT-MIXING IN SHALLOW CUMULUS AND THE ONSET OF PRECIPITATION Frédéric Burnet & Jean-Louis Brenguier Météo-France CNRM-GAME Experimental and Instrumental Research Group Objectives What are the controling
ENTRAINMENT-MIXING IN SHALLOW CUMULUS AND THE ONSET OF PRECIPITATION Frédéric Burnet & Jean-Louis Brenguier Météo-France CNRM-GAME Experimental and Instrumental Research Group Objectives What are the controling
Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology
 S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
( ) = 1005 J kg 1 K 1 ;
 Problem Set 3 1. A parcel of water is added to the ocean surface that is denser (heavier) than any of the waters in the ocean. Suppose the parcel sinks to the ocean bottom; estimate the change in temperature
Problem Set 3 1. A parcel of water is added to the ocean surface that is denser (heavier) than any of the waters in the ocean. Suppose the parcel sinks to the ocean bottom; estimate the change in temperature
777 GROUNDSCHOOL Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms
 777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
Atmospheric Processes
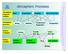 Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
PALM - Cloud Physics. Contents. PALM group. last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015
 PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
 Convective Fluxes: Sensible and Latent Heat Convective Fluxes Convective fluxes require Vertical gradient of temperature / water AND Turbulence ( mixing ) Vertical gradient, but no turbulence: only very
Convective Fluxes: Sensible and Latent Heat Convective Fluxes Convective fluxes require Vertical gradient of temperature / water AND Turbulence ( mixing ) Vertical gradient, but no turbulence: only very
Greenhouse Steady State Energy Balance Model
 Greenhouse Steady State Energy Balance Model The energy balance for the greenhouse was obtained by applying energy conservation to the greenhouse system as a control volume and identifying the energy terms.
Greenhouse Steady State Energy Balance Model The energy balance for the greenhouse was obtained by applying energy conservation to the greenhouse system as a control volume and identifying the energy terms.
Understanding the Daily Cycle of Evapotranspiration: A Method to Quantify the Influence of Forcings and Feedbacks
 DECEMBER 2010 V A N H E E R W A A R D E N E T A L. 1405 Understanding the Daily Cycle of Evapotranspiration: A Method to Quantify the Influence of Forcings and Feedbacks CHIEL C. VAN HEERWAARDEN AND JORDI
DECEMBER 2010 V A N H E E R W A A R D E N E T A L. 1405 Understanding the Daily Cycle of Evapotranspiration: A Method to Quantify the Influence of Forcings and Feedbacks CHIEL C. VAN HEERWAARDEN AND JORDI
Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM. I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop
 Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop Motivation The Earth s atmosphere is an extremely thin sheet of air
Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop Motivation The Earth s atmosphere is an extremely thin sheet of air
INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH
 INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH WEATHER PATTERNS Extratropical cyclones (low pressure core) and anticyclones (high pressure core) Cold fronts and warm fronts Jet stream
INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH WEATHER PATTERNS Extratropical cyclones (low pressure core) and anticyclones (high pressure core) Cold fronts and warm fronts Jet stream
4.4 EVALUATION OF AN IMPROVED CONVECTION TRIGGERING MECHANISM IN THE NCAR COMMUNITY ATMOSPHERE MODEL CAM2 UNDER CAPT FRAMEWORK
 . EVALUATION OF AN IMPROVED CONVECTION TRIGGERING MECHANISM IN THE NCAR COMMUNITY ATMOSPHERE MODEL CAM UNDER CAPT FRAMEWORK Shaocheng Xie, James S. Boyle, Richard T. Cederwall, and Gerald L. Potter Atmospheric
. EVALUATION OF AN IMPROVED CONVECTION TRIGGERING MECHANISM IN THE NCAR COMMUNITY ATMOSPHERE MODEL CAM UNDER CAPT FRAMEWORK Shaocheng Xie, James S. Boyle, Richard T. Cederwall, and Gerald L. Potter Atmospheric
Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land
 Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land surfaces in the following ways: (a) Near surface air
Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land surfaces in the following ways: (a) Near surface air
Cumulus parameterization in non-convection-resolving models
 Cumulus parameterization in non-convection-resolving models Given a column profile of model variables*, what convective tendencies will* occur? Hard questions: *1 is mean thermo. sounding enough information?»if
Cumulus parameterization in non-convection-resolving models Given a column profile of model variables*, what convective tendencies will* occur? Hard questions: *1 is mean thermo. sounding enough information?»if
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport. Recall that the most primitive equilibrium climate model can be written
 2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
Improved Atmospheric Stable Boundary Layer Formulations for Navy Seasonal Forecasting
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Improved Atmospheric Stable Boundary Layer Formulations for Navy Seasonal Forecasting Michael Tjernström Department of
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Improved Atmospheric Stable Boundary Layer Formulations for Navy Seasonal Forecasting Michael Tjernström Department of
Thunderstorm: a cumulonimbus cloud or collection of cumulonimbus clouds featuring vigorous updrafts, precipitation and lightning
 Thunderstorm: a cumulonimbus cloud or collection of cumulonimbus clouds featuring vigorous updrafts, precipitation and lightning Thunderstorms are responsible for most of what we refer to as severe weather,
Thunderstorm: a cumulonimbus cloud or collection of cumulonimbus clouds featuring vigorous updrafts, precipitation and lightning Thunderstorms are responsible for most of what we refer to as severe weather,
The prognostic deep convection parametrization for operational forecast in horizontal resolutions of 8, 4 and 2 km
 The prognostic deep convection parametrization for operational forecast in horizontal resolutions of 8, 4 and 2 km Martina Tudor, Stjepan Ivatek-Šahdan and Antonio Stanešić tudor@cirus.dhz.hr Croatian
The prognostic deep convection parametrization for operational forecast in horizontal resolutions of 8, 4 and 2 km Martina Tudor, Stjepan Ivatek-Šahdan and Antonio Stanešić tudor@cirus.dhz.hr Croatian
Annual Report for Blue Waters Allocation: Sonia Lasher-Trapp, Oct 2017
 Annual Report for Blue Waters Allocation: Sonia Lasher-Trapp, Oct 2017 Project Information: Untangling Entrainment Effects on Hail and Rain in Deep Convective Clouds o Sonia Lasher-Trapp, UIUC, slasher@illinois.edu
Annual Report for Blue Waters Allocation: Sonia Lasher-Trapp, Oct 2017 Project Information: Untangling Entrainment Effects on Hail and Rain in Deep Convective Clouds o Sonia Lasher-Trapp, UIUC, slasher@illinois.edu
An Intercomparison of Single-Column Model Simulations of Summertime Midlatitude Continental Convection
 An Intercomparison of Single-Column Model Simulations of Summertime Midlatitude Continental Convection S. J. Ghan Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Richland, Washington D. A. Randall, K.-M. Xu, and
An Intercomparison of Single-Column Model Simulations of Summertime Midlatitude Continental Convection S. J. Ghan Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Richland, Washington D. A. Randall, K.-M. Xu, and
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5
 Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Moist Convection. Chapter 6
 Moist Convection Chapter 6 1 2 Trade Cumuli Afternoon cumulus over land 3 Cumuls congestus Convectively-driven weather systems Deep convection plays an important role in the dynamics of tropical weather
Moist Convection Chapter 6 1 2 Trade Cumuli Afternoon cumulus over land 3 Cumuls congestus Convectively-driven weather systems Deep convection plays an important role in the dynamics of tropical weather
Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance
 Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance Instructor: Prof. Johnny Luo http://www.sci.ccny.cuny.edu/~luo Total: 50 pts Absorption of IR radiation O 3 band ~ 9.6 µm Vibration-rotation interaction of CO 2 ~
Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance Instructor: Prof. Johnny Luo http://www.sci.ccny.cuny.edu/~luo Total: 50 pts Absorption of IR radiation O 3 band ~ 9.6 µm Vibration-rotation interaction of CO 2 ~
1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents
 CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
UNRESOLVED ISSUES. 1. Spectral broadening through different growth histories 2. Entrainment and mixing 3. In-cloud activation
 URESOLVED ISSUES. Spectral broadening through different growth histories 2. Entrainment and mixing. In-cloud activation /4 dr dt ξ ( S ) r, ξ F D + F K 2 dr dt 2ξ ( S ) For a given thermodynamic conditions
URESOLVED ISSUES. Spectral broadening through different growth histories 2. Entrainment and mixing. In-cloud activation /4 dr dt ξ ( S ) r, ξ F D + F K 2 dr dt 2ξ ( S ) For a given thermodynamic conditions
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting. Primer on organized convection
 Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment. Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS)
 Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS) Introduction Balance of lower-tropospheric wind shear and strength of evaporation-generated
Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS) Introduction Balance of lower-tropospheric wind shear and strength of evaporation-generated
Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration
 Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration Climatological and hydrological field work Figure 1: Estimate of the Earth s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the incoming
Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration Climatological and hydrological field work Figure 1: Estimate of the Earth s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the incoming
JI NIE. Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts ZHIMING KUANG
 1936 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Responses of Shallow Cumulus Convection to Large-Scale Temperature and Moisture Perturbations: A Comparison of Large-Eddy Simulations
1936 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Responses of Shallow Cumulus Convection to Large-Scale Temperature and Moisture Perturbations: A Comparison of Large-Eddy Simulations
Reading. What meteorological conditions precede a thunderstorm? Thunderstorms: ordinary or single cell storms, multicell storms, supercell storms
 Thunderstorms: ordinary or single cell storms, multicell storms, supercell storms Reading Ahrens, Chapter 14: Thunderstorms and Tornadoes This lecture + next (Lightning, tornadoes) will cover the topic.
Thunderstorms: ordinary or single cell storms, multicell storms, supercell storms Reading Ahrens, Chapter 14: Thunderstorms and Tornadoes This lecture + next (Lightning, tornadoes) will cover the topic.
Chapter 7. Water and Atmospheric Moisture. Water on Earth Unique Properties of Water Humidity Atmospheric Stability Clouds and Fog
 Chapter 7 Water and Atmospheric Moisture Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Water kept both the terrestrial and marine ecosystems closely linked with the atmosphere. (1) Air carries water vapor and
Chapter 7 Water and Atmospheric Moisture Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Water kept both the terrestrial and marine ecosystems closely linked with the atmosphere. (1) Air carries water vapor and
Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes
 Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes Tapio Schneider California Institute of Technology (based on Rev. Geophys. article with Xavier Levine and Paul O Gorman) Water vapor dynamics in warming
Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes Tapio Schneider California Institute of Technology (based on Rev. Geophys. article with Xavier Levine and Paul O Gorman) Water vapor dynamics in warming
GEO1010 tirsdag
 GEO1010 tirsdag 31.08.2010 Jørn Kristiansen; jornk@met.no I dag: Først litt repetisjon Stråling (kap. 4) Atmosfærens sirkulasjon (kap. 6) Latitudinal Geographic Zones Figure 1.12 jkl TØRR ATMOSFÆRE Temperature
GEO1010 tirsdag 31.08.2010 Jørn Kristiansen; jornk@met.no I dag: Først litt repetisjon Stråling (kap. 4) Atmosfærens sirkulasjon (kap. 6) Latitudinal Geographic Zones Figure 1.12 jkl TØRR ATMOSFÆRE Temperature
The moist boundary layer under a midlatitude
 The moist boundary layer under a midlatitude weather system Article Accepted Version Boutle, I., Beare, R.J., Belcher, S. E., Brown, A.R. and Plant, R. S. (1) The moist boundary layer under a mid latitude
The moist boundary layer under a midlatitude weather system Article Accepted Version Boutle, I., Beare, R.J., Belcher, S. E., Brown, A.R. and Plant, R. S. (1) The moist boundary layer under a mid latitude
Description of the ET of Super Typhoon Choi-Wan (2009) based on the YOTC-dataset
 High Impact Weather PANDOWAE Description of the ET of Super Typhoon Choi-Wan (2009) based on the YOTC-dataset ¹, D. Anwender¹, S. C. Jones2, J. Keller2, L. Scheck¹ 2 ¹Karlsruhe Institute of Technology,
High Impact Weather PANDOWAE Description of the ET of Super Typhoon Choi-Wan (2009) based on the YOTC-dataset ¹, D. Anwender¹, S. C. Jones2, J. Keller2, L. Scheck¹ 2 ¹Karlsruhe Institute of Technology,
Investigating the Impact of Land-PBL Coupling on the Water and Energy Cycle in NASA Model and Observation Products
 Investigating the Impact of Land-PBL Coupling on the Water and Energy Cycle in NASA Model and Observation Products PI: Joseph A. Santanello, Jr. Hydrological Sciences Laboratory NASA-GSFC, Greenbelt, MD
Investigating the Impact of Land-PBL Coupling on the Water and Energy Cycle in NASA Model and Observation Products PI: Joseph A. Santanello, Jr. Hydrological Sciences Laboratory NASA-GSFC, Greenbelt, MD
A study of the moist Entropy in Meteorology.
 Workshop on the Atmospheric Modelling 8-10 February, 2011.Toulouse, France. A study of the moist Entropy in Meteorology. Pascal MARQUET (Météo-France. DPrévi / LABO) Contents 1) Motivations : to study
Workshop on the Atmospheric Modelling 8-10 February, 2011.Toulouse, France. A study of the moist Entropy in Meteorology. Pascal MARQUET (Météo-France. DPrévi / LABO) Contents 1) Motivations : to study
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR
 CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
ECMWF now and future dry PBL stratocumulus shallow cumulus. ongoing work parcel numerics stratocumulus down-drafts shallow cumulus
 An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds Martin Köhler, ECMWF EDMF @ ECMWF now and future dry PBL stratocumulus shallow cumulus stratocumulus: evaluation against observations EPIC marine
An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds Martin Köhler, ECMWF EDMF @ ECMWF now and future dry PBL stratocumulus shallow cumulus stratocumulus: evaluation against observations EPIC marine
J3.2 TRANSPORT AND CHEMICAL TRANSFORMATIONS INFLUENCED BY SHALLOW CUMULUS OVER LAND
 J3.2 TRANSPORT AND CHEMICAL TRANSFORMATIONS INFLUENCED BY SHALLOW CUMULUS OVER LAND Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorlogy and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands Si-Wan Kim,
J3.2 TRANSPORT AND CHEMICAL TRANSFORMATIONS INFLUENCED BY SHALLOW CUMULUS OVER LAND Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorlogy and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands Si-Wan Kim,
ESCI 485 Air/Sea Interaction Lesson 1 Stresses and Fluxes Dr. DeCaria
 ESCI 485 Air/Sea Interaction Lesson 1 Stresses and Fluxes Dr DeCaria References: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, Holton MOMENTUM EQUATIONS The momentum equations governing the ocean or atmosphere
ESCI 485 Air/Sea Interaction Lesson 1 Stresses and Fluxes Dr DeCaria References: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, Holton MOMENTUM EQUATIONS The momentum equations governing the ocean or atmosphere
A Multi-year Hindcast Experiment for Cloud and Precipitation Studies
 A Multi-year Hindcast Experiment for Cloud and Precipitation Studies Hsi-Yen Ma Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory with Stephen Klein, Shaocheng Xie, Zhou Chen, Cathy Chuang, Tom Phillips, Xue Zheng,
A Multi-year Hindcast Experiment for Cloud and Precipitation Studies Hsi-Yen Ma Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory with Stephen Klein, Shaocheng Xie, Zhou Chen, Cathy Chuang, Tom Phillips, Xue Zheng,
Shallow cumulus evaluated with the LASSO (ensemble LES) framework
 Shallow cumulus evaluated with the LASSO (ensemble LES) framework Wayne M. Angevine, Joe Olson, and Jaymes Kenyon CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Outline: What and why is LASSO? The shallow
Shallow cumulus evaluated with the LASSO (ensemble LES) framework Wayne M. Angevine, Joe Olson, and Jaymes Kenyon CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Outline: What and why is LASSO? The shallow
