Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes
|
|
|
- Warren Holt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes Tapio Schneider California Institute of Technology (based on Rev. Geophys. article with Xavier Levine and Paul O Gorman)
2 Water vapor dynamics in warming climate Facts Saturation vapor pressure increases with temperature at ~7%/K Relative humidity near the surface stays roughly constant Precipitable water q increases at ~7%/K with sfc. temperature Precipitation P increases more slowly, at ~2 3 %/K Water vapor cycling rate P/q decreases Common conjectures Tropical circulations (particularly Walker circulation) slow down Hadley circulation widens Extratropical storms become more energetic Precipitation extremes increase more rapidly than mean
3 Water vapor dynamics in warming climate Facts Saturation vapor pressure increases with temperature at ~7%/K Relative humidity near the surface stays roughly constant Precipitable water q increases at ~7%/K with sfc. temperature Precipitation P increases more slowly, at ~2 3 %/K Water vapor cycling rate P/q decreases Common conjectures Tropical circulations (particularly Walker circulation) slow down Hadley circulation widens Extratropical storms become more energetic Precipitation extremes increase more rapidly than mean
4 Water vapor dynamics in warming climate Facts Saturation vapor pressure increases with temperature at ~7%/K Relative humidity near the surface stays roughly constant Precipitable water q increases at ~7%/K with sfc. temperature Precipitation P increases more slowly, at ~2 3 %/K Water vapor cycling rate P/q decreases Common conjectures Tropical circulations (particularly Walker circulation) slow down Hadley circulation widens (?) Extratropical storms become more energetic Precipitation extremes increase more rapidly than mean
5 Water vapor dynamics in warming climate Facts Saturation vapor pressure increases with temperature at ~7%/K Relative humidity near the surface stays roughly constant Precipitable water q increases at ~7%/K with sfc. temperature Precipitation P increases more slowly, at ~2 3 %/K Water vapor cycling rate P/q decreases Common conjectures Tropical circulations (particularly Walker circulation) slow down Hadley circulation widens (?) Extratropical storms become more energetic Precipitation extremes increase more rapidly than mean
6 Water vapor dynamics in warming climate Facts Saturation vapor pressure increases with temperature at ~7%/K Relative humidity near the surface stays roughly constant Precipitable water q increases at ~7%/K with sfc. temperature Precipitation P increases more slowly, at ~2 3 %/K Water vapor cycling rate P/q decreases Common conjectures Tropical circulations (particularly Walker circulation) slow down Hadley circulation widens (?) Extratropical storms become more energetic Precipitation extremes increase more rapidly than mean
7 Simulations with idealized moist GCM Aquaplanet: uniform, water-covered surface; no ocean dynamics Built on GFDL FMS [similar to Frierson et al. (2006)] Only vapor-liquid phase transition considered (no ice) Radiative transfer of semi-gray atmosphere Climate varied by varying greenhouse gas concentrations : scaling of optical thickness of longwave absorber (by factor 12) Allows very large climate variations: Global-mean surface temperatures between 259 K and 316 K (!) (O Gorman & Schneider 2008)
8 A wide range of climates... a Potential temperature Streamfunction Relative humidity 0.2 σ b σ c σ Ice house Earth-like Hot house Latitude Latitude Latitude (O Gorman & Schneider 2008)
9 Saturation vapor pressure Clausius-Clapeyron relation between temperature T and saturation vapor pressure es δe s e s = L RT 2 δt For warming Earth, this implies increase in saturation vapor pressure of 7%/K, or 21% for 3K warming. (Boer 1993; Wentz & Schabel 2000; Trenberth 2003)
10 Near-surface relative humidity Evaporation (over ocean) is proportional to so, or RH~85% near surface, E 80 W/m 2, climate sensitivity ~0.8 K/(W m 2 ), so Near-surface RH changes strongly energetically constrained (Boer 1993; Held & Soden 2000)
11 Relative humidity (annual mean) Data source: ERA-40
12 Near-surface relative humidity Evaporation (over ocean) is proportional to so, or RH~85% near surface, E 80 W/m 2, climate sensitivity ~0.8 K/(W m 2 ), so Near-surface RH changes strongly energetically constrained (Boer 1993; Held & Soden 2000)
13 Precipitable water in idealized GCM RH=0.67 Earth-like (6.2%/K) Most water vapor near surface (Free-tropospheric RH does change) (O Gorman & Schneider 2008)
14 Precipitation in idealized GCM Earth-like (2.5%/K) Asymptotes to energetic bound (O Gorman & Schneider 2008)
15 Water vapor cycling rate Earth-like (-3.7%/K) Generally decreases (except in cold climates) (O Gorman & Schneider 2008; Schneider et al. 2009)
16 Tropical convective mass flux Moisture (or thermodynamic) balance in saturated updrafts where Mass-weighted vertical integral { } (avg d over convective system) (cf. Iribarne & Godson 1981; Schneider et al. 2009)
17 Scaling of convective mass flux General scaling behavior Case A Mass flux scales with inverse static stability (Betts & Harshvardhan 1987) Case B Mass flux scales with cycling rate (Betts 1998; Held & Soden 2006) (Schneider et al. 2009)
18 Scaling estimates are very different... At 290 K, Δq increases at 2.0%/K, q at 6.4%/K With δp/p~2.5%/k, mass flux increases under A, decreases under B! (Schneider et al. 2009)
19 Tropical mass flux in idealized GCM Gross mass flux Net mass flux (Hadley cell) Convective mass flux scales inversely with static stability, not with cycling rate; non-monotonic function of surface temperature (Schneider et al. 2009)
20 Precipitation extremes scale similarly... Precipitable water Precipitation extremes Based on IPCC 21st-century global warming simulations (O Gorman and Schneider 2009)
21 So the convective (gross) upward mass flux (zonally asymmetric) is thermally driven and depends on moistadiabatic static stability. It may increase or decrease as the climate warms. What does that imply about the net upward mass flux (Hadley circulation)?
22 A Hadley circulation is thermally driven, if... it conserves angular momentum m in upper branch v y m 0 Since y m f + ζ, this implies with local Rossby number it is energetically closed (no heat export) Classic theory is intuitively appealing, but is it adequate? (Schneider 1977; Schneider & Lindzen 1976, 1977; Held & Hou 1980)
23 Hadley cells and eddy momentum flux divergence EMFD S Angular (or zonal) momentum balance: Eddy driven if Ro<<1 (Schneider 2006; Schneider et al. 2009; data source: ERA-40)
24 Earth-like Hadley circulations... In the annual mean or during equinox are close to limit Ro 0 Do not respond directly to variations in thermal driving but respond via changes in eddy momentum fluxes We need to rethink Hadley circulation response, for example, to ENSO and global warming
25 Hadley cell strength in idealized GCM Ice house Earth-like Hot house Ro (Schneider et al. 2009)
26 Hadley cell strength Hadley cell strength (1e9 kg/s) Ice house dry Earth-like moist Surface Temperature (K) Non-monotonic function of surface temperature Hot house
27 Eddies mediate Hadley circulation response 0.03 EKE Energy (MJ m 2 ) MAPE dry moist Surface temperature (K) Eddy momentum flux scales with EKE, which is maximal near reference climate and scales with MAPE (O Gorman & Schneider 2008; Schneider & Walker 2008)
28 Eddies mediate Hadley circulation response 0.03 EKE Energy (MJ m 2 ) MAPE dry moist Surface temperature (K) Non-monotonic function of surface temperature (e.g., LGM less stormy?) (O Gorman & Schneider 2008; Schneider & Walker 2008)
29 Conclusions Precipitable water increases rapidly with temperature, precipitation less rapidly, water vapor cycling rate generally decreases, but... Gross upward mass flux in tropics may depend on static stability (increases slowly with temperature). Hadley cell during equinox, summer, and in annual mean controlled by eddy fluxes. Eddy scaling (non-monotonic) imprinted on Hadley cell response to climate change. Hadley cell and extratropical storms weaker in warmer and in (much) colder climates.
30 0.03 EKE Energy (MJ m 2 ) MAPE Surface temperature (K)
Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics
 Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH Zurich, Caltech (Source: CLAUS, http://badc.nerc.ac.uk/data/claus/) Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH
Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH Zurich, Caltech (Source: CLAUS, http://badc.nerc.ac.uk/data/claus/) Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH
arxiv: v2 [physics.ao-ph] 24 Nov 2009
![arxiv: v2 [physics.ao-ph] 24 Nov 2009 arxiv: v2 [physics.ao-ph] 24 Nov 2009](/thumbs/75/72853030.jpg) WATER VAPOR AND THE DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE CHANGES Tapio Schneider California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, USA Paul A. O Gorman Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts,
WATER VAPOR AND THE DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE CHANGES Tapio Schneider California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, USA Paul A. O Gorman Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts,
Water vapor and the dynamics of climate changes
 Water vapor and the dynamics of climate changes The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher Schneider,
Water vapor and the dynamics of climate changes The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher Schneider,
WATER VAPOR AND THE DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE CHANGES
 Click Here for Full Article WATER VAPOR AND THE DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE CHANGES Tapio Schneider, 1 Paul A. O Gorman, 2 and Xavier J. Levine 1 Received 29 June 2009; accepted 3 December 2009; published 2 July
Click Here for Full Article WATER VAPOR AND THE DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE CHANGES Tapio Schneider, 1 Paul A. O Gorman, 2 and Xavier J. Levine 1 Received 29 June 2009; accepted 3 December 2009; published 2 July
Radiative-Convective Models. The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation. Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1
 Climate Modeling Lecture 8 Radiative-Convective Models Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1 The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation Prepare for Mid-Term (Friday 9 am) Review Course Notes
Climate Modeling Lecture 8 Radiative-Convective Models Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1 The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation Prepare for Mid-Term (Friday 9 am) Review Course Notes
The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles. Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild
 The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild WCRP OSP, Denver, 27th October 2011 1 Motivation How will precipitation
The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild WCRP OSP, Denver, 27th October 2011 1 Motivation How will precipitation
Energy of Midlatitude Transient Eddies in Idealized Simulations of Changed Climates
 15 NOVEMBER 2008 O G O R M A N A N D S C H N E I D E R 5797 Energy of Midlatitude Transient Eddies in Idealized Simulations of Changed Climates PAUL A. O GORMAN* AND TAPIO SCHNEIDER California Institute
15 NOVEMBER 2008 O G O R M A N A N D S C H N E I D E R 5797 Energy of Midlatitude Transient Eddies in Idealized Simulations of Changed Climates PAUL A. O GORMAN* AND TAPIO SCHNEIDER California Institute
How closely do changes in surface and column water vapor follow Clausius-Clapeyron scaling in climate change simulations?
 How closely do changes in surface and column water vapor follow Clausius-Clapeyron scaling in climate change simulations? The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
How closely do changes in surface and column water vapor follow Clausius-Clapeyron scaling in climate change simulations? The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
The Effective Static Stability Experienced by Eddies in a Moist Atmosphere
 JANUARY 2011 O G O R M A N 75 The Effective Static Stability Experienced by Eddies in a Moist Atmosphere PAUL A. O GORMAN Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts (Manuscript received
JANUARY 2011 O G O R M A N 75 The Effective Static Stability Experienced by Eddies in a Moist Atmosphere PAUL A. O GORMAN Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts (Manuscript received
Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms
 Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms Basic radiative feedbacks (Plank, Water Vapor, Lapse-Rate Feedbacks) Ice albedo & Vegetation-Climate feedback Cloud feedback Biogeochemical feedbacks
Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms Basic radiative feedbacks (Plank, Water Vapor, Lapse-Rate Feedbacks) Ice albedo & Vegetation-Climate feedback Cloud feedback Biogeochemical feedbacks
Land Ocean Warming Contrast over a Wide Range of Climates: Convective Quasi-Equilibrium Theory and Idealized Simulations
 4000 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 26 Land Ocean Warming Contrast over a Wide Range of Climates: Convective Quasi-Equilibrium Theory and Idealized Simulations MICHAEL P. BYRNE AND PAUL A. O GORMAN
4000 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 26 Land Ocean Warming Contrast over a Wide Range of Climates: Convective Quasi-Equilibrium Theory and Idealized Simulations MICHAEL P. BYRNE AND PAUL A. O GORMAN
ATS 421/521. Climate Modeling. Spring 2015
 ATS 421/521 Climate Modeling Spring 2015 Lecture 9 Hadley Circulation (Held and Hou, 1980) General Circulation Models (tetbook chapter 3.2.3; course notes chapter 5.3) The Primitive Equations (tetbook
ATS 421/521 Climate Modeling Spring 2015 Lecture 9 Hadley Circulation (Held and Hou, 1980) General Circulation Models (tetbook chapter 3.2.3; course notes chapter 5.3) The Primitive Equations (tetbook
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport. Recall that the most primitive equilibrium climate model can be written
 2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans
![Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans](/thumbs/96/128963638.jpg) Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback
 Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
Carbon dioxide s direct weakening of the tropical circulation: from comprehensive climate models to axisymmetric Hadley cell theory
 Carbon dioxide s direct weakening of the tropical circulation: from comprehensive climate models to axisymmetric Hadley cell theory Timothy M. Merlis McGill University Key point The spatial structure of
Carbon dioxide s direct weakening of the tropical circulation: from comprehensive climate models to axisymmetric Hadley cell theory Timothy M. Merlis McGill University Key point The spatial structure of
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do?
 Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
Presentation A simple model of multiple climate regimes
 A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS
 Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation
 Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C
An Interconnected Planet
 An Interconnected Planet How Clouds, Aerosols, and the Ocean Cause Distant Rainfall Anomalies Dargan M. W. Frierson University of Washington CESM Workshop, 6-15-15 New Connections Recent research has uncovered
An Interconnected Planet How Clouds, Aerosols, and the Ocean Cause Distant Rainfall Anomalies Dargan M. W. Frierson University of Washington CESM Workshop, 6-15-15 New Connections Recent research has uncovered
Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 2: Tropical General Circulation
 Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 2: Tropical General Circulation DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES 1-28-16 Today What determines
Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 2: Tropical General Circulation DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES 1-28-16 Today What determines
The effective static stability experienced by eddies in a moist atmosphere. Paul A. O Gorman
 Generated using V3. of the official AMS LATEX template The effective static stability experienced by eddies in a moist atmosphere Paul A. O Gorman Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Generated using V3. of the official AMS LATEX template The effective static stability experienced by eddies in a moist atmosphere Paul A. O Gorman Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Dynamics of Earth s Hadley Circulation
 Dynamics of Earth s Hadley Circulation Thesis by Xavier J. Levine In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute of Technology Pasadena, California
Dynamics of Earth s Hadley Circulation Thesis by Xavier J. Levine In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute of Technology Pasadena, California
The Arctic Energy Budget
 The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
A Gray-Radiation Aquaplanet Moist GCM. Part II: Energy Transports in Altered Climates
 1680 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 64 A Gray-Radiation Aquaplanet Moist GCM. Part II: Energy Transports in Altered Climates DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON University of Chicago,
1680 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 64 A Gray-Radiation Aquaplanet Moist GCM. Part II: Energy Transports in Altered Climates DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON University of Chicago,
Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet
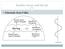 Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet A Barotropic Model Stochastic stirring + linear damping Force barotropic vort. eqn. with white noise in storm
Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet A Barotropic Model Stochastic stirring + linear damping Force barotropic vort. eqn. with white noise in storm
Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean*
 JUNE 2013 W U A N D P A U L U I S 1649 Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean* YUTIAN WU AND OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant
JUNE 2013 W U A N D P A U L U I S 1649 Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean* YUTIAN WU AND OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant
Lecture 10a: The Hadley Cell
 Lecture 10a: The Hadley Cell Geoff Vallis; notes by Jim Thomas and Geoff J. Stanley June 27 In this short lecture we take a look at the general circulation of the atmosphere, and in particular the Hadley
Lecture 10a: The Hadley Cell Geoff Vallis; notes by Jim Thomas and Geoff J. Stanley June 27 In this short lecture we take a look at the general circulation of the atmosphere, and in particular the Hadley
Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate
 Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate Geostrophic balance Zonal-mean circulation Transients and eddies Meridional energy transport Moist static energy Angular momentum balance Atmosphere
Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate Geostrophic balance Zonal-mean circulation Transients and eddies Meridional energy transport Moist static energy Angular momentum balance Atmosphere
no eddies eddies Figure 3. Simulated surface winds. Surface winds no eddies u, v m/s φ0 =12 φ0 =0
 References Held, Isaac M., and Hou, A. Y., 1980: Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 515-533. Held, Isaac M., and Suarez, M. J., 1994: A proposal
References Held, Isaac M., and Hou, A. Y., 1980: Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 515-533. Held, Isaac M., and Suarez, M. J., 1994: A proposal
Chapter 4 Water Vapor
 Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Understanding Climate Feedbacks Using Radiative Kernels
 Understanding Climate Feedbacks Using Radiative Kernels Brian Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric Science University of Miami Overview of radiative kernels Recent advances in understanding
Understanding Climate Feedbacks Using Radiative Kernels Brian Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric Science University of Miami Overview of radiative kernels Recent advances in understanding
Climate Models & Climate Sensitivity: A Review
 Climate Models & Climate Sensitivity: A Review Stroeve et al. 2007, BBC Paul Kushner Department of Physics, University of Toronto Recent Carbon Dioxide Emissions 2 2 0 0 0 0 7 6 x x Raupach et al. 2007
Climate Models & Climate Sensitivity: A Review Stroeve et al. 2007, BBC Paul Kushner Department of Physics, University of Toronto Recent Carbon Dioxide Emissions 2 2 0 0 0 0 7 6 x x Raupach et al. 2007
Key Feedbacks in the Climate System
 Key Feedbacks in the Climate System With a Focus on Climate Sensitivity SOLAS Summer School 12 th of August 2009 Thomas Schneider von Deimling, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Why do Climate
Key Feedbacks in the Climate System With a Focus on Climate Sensitivity SOLAS Summer School 12 th of August 2009 Thomas Schneider von Deimling, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Why do Climate
Intensification of precipitation extremes with warming in a cloud resolving model. Larissa E. Back
 Generated using V3.0 of the official AMS LATEX template journal page layout FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! Intensification of precipitation extremes with warming in a cloud resolving model Caroline
Generated using V3.0 of the official AMS LATEX template journal page layout FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! Intensification of precipitation extremes with warming in a cloud resolving model Caroline
Intensification of precipitation extremes with warming in a cloud resolving model
 Intensification of precipitation extremes with warming in a cloud resolving model The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Intensification of precipitation extremes with warming in a cloud resolving model The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
The meteorology of monsoons
 978--521-84799-5 - The Asian Monsoon: Causes, History and Effects 1 The meteorology of monsoons 1.1 Introduction Monsoon circulations are major features of the tropical atmosphere, which, primarily through
978--521-84799-5 - The Asian Monsoon: Causes, History and Effects 1 The meteorology of monsoons 1.1 Introduction Monsoon circulations are major features of the tropical atmosphere, which, primarily through
Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere
![Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere](/thumbs/72/66535634.jpg) Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Vertical temperature profile Total atmospheric mass: ~5.15x10
Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Vertical temperature profile Total atmospheric mass: ~5.15x10
Eddy-Mediated Regime Transitions in the Seasonal Cycle of a Hadley Circulation and Implications for Monsoon Dynamics
 Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences (to appear) Eddy-Mediated Regime Transitions in the Seasonal Cycle of a Hadley Circulation and Implications for Monsoon Dynamics TAPIO SCHNEIDER California Institute
Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences (to appear) Eddy-Mediated Regime Transitions in the Seasonal Cycle of a Hadley Circulation and Implications for Monsoon Dynamics TAPIO SCHNEIDER California Institute
Aquaplanet warming experiments with CAM: a tale of the subtropics
 Aquaplanet warming experiments with CAM: a tale of the subtropics AMWG meeting, 12 February 2018, NCAR Thomas Toniazzo Uni Research (?) & Bjerknes Centre Bergen, Norway Plan of this talk A) Intro B) Slab
Aquaplanet warming experiments with CAM: a tale of the subtropics AMWG meeting, 12 February 2018, NCAR Thomas Toniazzo Uni Research (?) & Bjerknes Centre Bergen, Norway Plan of this talk A) Intro B) Slab
Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence)
 1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
Link between land-ocean warming contrast and surface relative humidities in simulations with coupled climate models
 Link between land-ocean warming contrast and surface relative humidities in simulations with coupled climate models The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
Link between land-ocean warming contrast and surface relative humidities in simulations with coupled climate models The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS PART II
 Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS PART II The next chapter in the story: How differences in INSOLATION between low and high latitudes drive atmospheric circulation! pp 64 in Class Notes THE RADIATION BALANCE
Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS PART II The next chapter in the story: How differences in INSOLATION between low and high latitudes drive atmospheric circulation! pp 64 in Class Notes THE RADIATION BALANCE
The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet ABSTRACT
 Climate Dynamics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) 1 2 The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments. 3 Aaron Donohoe Dargan Frierson 4 5 Manuscript
Climate Dynamics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) 1 2 The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments. 3 Aaron Donohoe Dargan Frierson 4 5 Manuscript
The Global Atmospheric Circulation in Moist Isentropic Coordinates
 1JUNE 2010 P A U L U I S E T A L. 3077 The Global Atmospheric Circulation in Moist Isentropic Coordinates OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University New York New York
1JUNE 2010 P A U L U I S E T A L. 3077 The Global Atmospheric Circulation in Moist Isentropic Coordinates OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University New York New York
Large-scale changes in the atmospheric water cycle in models and observations
 Large-scale changes in the atmospheric water cycle in models and observations Richard Allan University of Reading Strength of Feedback (Wm-2/oC) Uncertainty in strength of cloud feedback Total range Range
Large-scale changes in the atmospheric water cycle in models and observations Richard Allan University of Reading Strength of Feedback (Wm-2/oC) Uncertainty in strength of cloud feedback Total range Range
1) The energy balance at the TOA is: 4 (1 α) = σt (1 0.3) = ( ) 4. (1 α) 4σ = ( S 0 = 255 T 1
 EAS488/B8800 Climate & Climate Change Homework 2: Atmospheric Radiation and Climate, surface energy balance, and atmospheric general circulation Posted: 3/12/18; due: 3/26/18 Answer keys 1. (10 points)
EAS488/B8800 Climate & Climate Change Homework 2: Atmospheric Radiation and Climate, surface energy balance, and atmospheric general circulation Posted: 3/12/18; due: 3/26/18 Answer keys 1. (10 points)
COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION
 COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER CHRIS BRIERLEY Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences 5. Human
COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER CHRIS BRIERLEY Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences 5. Human
Electromagnetic Radiation. Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance. Electromagnetic Spectrum of the Sun
 Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Solar radiation warms the planet Conversion of solar energy at the surface Absorption and emission by the atmosphere The greenhouse
Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Solar radiation warms the planet Conversion of solar energy at the surface Absorption and emission by the atmosphere The greenhouse
The General Circulation of the Atmosphere
 Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2006. 34:655 88 The Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Science is online at earth.annualreviews.org doi: 10.1146/ annurev.earth.34.031405.125144 Copyright c 2006 by Annual
Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2006. 34:655 88 The Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Science is online at earth.annualreviews.org doi: 10.1146/ annurev.earth.34.031405.125144 Copyright c 2006 by Annual
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation
 Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Course Outline CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION. 1. Current climate. 2. Changing climate. 3. Future climate change
 COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER CHRIS BRIERLEY Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences 5. Human
COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER CHRIS BRIERLEY Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences 5. Human
Isentropic flows and monsoonal circulations
 Isentropic flows and monsoonal circulations Olivier Pauluis (NYU) Monsoons- Past, Present and future May 20th, 2015 Caltech, Pasadena Outline Introduction Global monsoon in isentropic coordinates Dry ventilation
Isentropic flows and monsoonal circulations Olivier Pauluis (NYU) Monsoons- Past, Present and future May 20th, 2015 Caltech, Pasadena Outline Introduction Global monsoon in isentropic coordinates Dry ventilation
Width of the Hadley cell in simple and comprehensive general circulation models
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L18804, doi:10.1029/2007gl031115, 2007 Width of the Hadley cell in simple and comprehensive general circulation models Dargan M. W. Frierson,
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L18804, doi:10.1029/2007gl031115, 2007 Width of the Hadley cell in simple and comprehensive general circulation models Dargan M. W. Frierson,
Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~
 2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
Course , General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 4: Water Vapor Budget
 Course 12.812, General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 4: Water Vapor Budget Water Vapor Distribution First let us look at the distribution of specific humidity, q. The
Course 12.812, General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 4: Water Vapor Budget Water Vapor Distribution First let us look at the distribution of specific humidity, q. The
Today s Lecture (Lecture 5): General circulation of the atmosphere
 Climate Dynamics (Summer Semester 2017) J. Mülmenstädt Today s Lecture (Lecture 5): General circulation of the atmosphere Reference Hartmann, Global Physical Climatology (1994), Ch. 2, 3, 6 Peixoto and
Climate Dynamics (Summer Semester 2017) J. Mülmenstädt Today s Lecture (Lecture 5): General circulation of the atmosphere Reference Hartmann, Global Physical Climatology (1994), Ch. 2, 3, 6 Peixoto and
A last saturation diagnosis of subtropical water vapor response to global warming
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042316, 2010 A last saturation diagnosis of subtropical water vapor response to global warming John V. Hurley 1 and
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042316, 2010 A last saturation diagnosis of subtropical water vapor response to global warming John V. Hurley 1 and
Hemispherical Asymmetry of Tropical Precipitation in ECHAM5/MPI-OM during El Niño and under Global Warming
 15 MARCH 2008 C H O U A N D T U 1309 Hemispherical Asymmetry of Tropical Precipitation in ECHAM5/MPI-OM during El Niño and under Global Warming CHIA CHOU Research Center for Environmental Changes, Academia
15 MARCH 2008 C H O U A N D T U 1309 Hemispherical Asymmetry of Tropical Precipitation in ECHAM5/MPI-OM during El Niño and under Global Warming CHIA CHOU Research Center for Environmental Changes, Academia
Expansion of the Hadley cell under global warming
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L06805, doi:10.1029/2006gl028443, 2007 Expansion of the Hadley cell under global warming Jian Lu, 1,2 Gabriel A. Vecchi, 3 and Thomas
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L06805, doi:10.1029/2006gl028443, 2007 Expansion of the Hadley cell under global warming Jian Lu, 1,2 Gabriel A. Vecchi, 3 and Thomas
Transient and Eddy. Transient/Eddy Flux. Flux Components. Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance. Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean
 Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
The role of land-sea contrast in the circulation response to seasonal insolation and global warming
 The role of land-sea contrast in the circulation response to seasonal insolation and global warming Tiffany A. Shaw Columbia University University of Chicago Thanks to A. Voigt, I Simpson, R. Seager What
The role of land-sea contrast in the circulation response to seasonal insolation and global warming Tiffany A. Shaw Columbia University University of Chicago Thanks to A. Voigt, I Simpson, R. Seager What
Dynamics of the Atmosphere
 12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere Course description: Discusses the dynamics of the atmosphere, with emphasis on the large scale. Instructor: Paul O Gorman Email: pog@mit.edu Office: 54-1712 Questions:
12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere Course description: Discusses the dynamics of the atmosphere, with emphasis on the large scale. Instructor: Paul O Gorman Email: pog@mit.edu Office: 54-1712 Questions:
Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture
 Chapter 1: Properties of Atmosphere Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture Thickness of the Atmosphere (from Meteorology Today) 90% 70% The thickness of the atmosphere is only about 2% of Earth s thickness
Chapter 1: Properties of Atmosphere Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture Thickness of the Atmosphere (from Meteorology Today) 90% 70% The thickness of the atmosphere is only about 2% of Earth s thickness
Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Science 2 nd Edition: Article Template
 Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Science 2 nd Edition: Article Template Hadley Circulation (revised from I N James) Jian Lu 4400 University Drive MS 2B3 George Mason University Fairfax, VA 20330 USA E- mail:
Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Science 2 nd Edition: Article Template Hadley Circulation (revised from I N James) Jian Lu 4400 University Drive MS 2B3 George Mason University Fairfax, VA 20330 USA E- mail:
ATMO 436a. The General Circulation. Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it
 ATMO 436a The General Circulation Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it Scales of Atmospheric Motion vs. Lifespan The general circulation Atmospheric oscillations
ATMO 436a The General Circulation Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it Scales of Atmospheric Motion vs. Lifespan The general circulation Atmospheric oscillations
Midlatitude Static Stability in Simple and. Comprehensive General Circulation Models
 Midlatitude Static Stability in Simple and Comprehensive General Circulation Models Dargan M. W. Frierson 1 University of Chicago June 7 1 Department of Geophysical Sciences, University of Chicago, 5734
Midlatitude Static Stability in Simple and Comprehensive General Circulation Models Dargan M. W. Frierson 1 University of Chicago June 7 1 Department of Geophysical Sciences, University of Chicago, 5734
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
Understanding decreases in land relative humidity with global warming: conceptual model and GCM simulations
 Generated using the official AMS LATEX template two-column layout. FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E Understanding decreases in land relative humidity with global
Generated using the official AMS LATEX template two-column layout. FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E Understanding decreases in land relative humidity with global
A High Latitude Convective Cloud Feedback and Equable Climates
 A High Latitude Convective Cloud Feedback and Equable Climates Dorian S. Abbot, Eli Tziperman Recent SPCAM updates: with David Randall, Mark Branson Hadrosaurus Cretaceous [Karen Carr] [Abbot, Tziperman
A High Latitude Convective Cloud Feedback and Equable Climates Dorian S. Abbot, Eli Tziperman Recent SPCAM updates: with David Randall, Mark Branson Hadrosaurus Cretaceous [Karen Carr] [Abbot, Tziperman
Four perspectives on climate feedbacks
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL., 7 11, doi:1.1/grl.5711, 13 Four perspectives on climate feedbacks N. Feldl 1 andg.h.roe Received 7 May 13; revised 7 June 13; accepted 8 June 13; published 3 July 13.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL., 7 11, doi:1.1/grl.5711, 13 Four perspectives on climate feedbacks N. Feldl 1 andg.h.roe Received 7 May 13; revised 7 June 13; accepted 8 June 13; published 3 July 13.
Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development
 Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development R. S. Plant (With thanks to: I. A. Boutle and S. E. Belcher) 28th May 2010 University of East Anglia Outline Introduction and background Baroclinic
Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development R. S. Plant (With thanks to: I. A. Boutle and S. E. Belcher) 28th May 2010 University of East Anglia Outline Introduction and background Baroclinic
Lecture 2: Light And Air
 Lecture 2: Light And Air Earth s Climate System Earth, Mars, and Venus Compared Solar Radiation Greenhouse Effect Thermal Structure of the Atmosphere Atmosphere Ocean Solid Earth Solar forcing Land Energy,
Lecture 2: Light And Air Earth s Climate System Earth, Mars, and Venus Compared Solar Radiation Greenhouse Effect Thermal Structure of the Atmosphere Atmosphere Ocean Solid Earth Solar forcing Land Energy,
Course Outline. About Me. Today s Outline CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION. 1. Current climate. 2.
 Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER 5. Human impacts 6.
Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER 5. Human impacts 6.
8/21/08. Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 4: Equatorial Wave Dynamics. Moisture and Equatorial Waves
 Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 4: Equatorial Wave Dynamics D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P
Modeling the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Topic 4: Equatorial Wave Dynamics D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P
Moist Recirculation and Water Vapor Transport on Dry Isentropes*
 MARCH 212 L A L I B E R T É ET AL. 875 Moist Recirculation and Water Vapor Transport on Dry Isentropes* FRÉDÉRIC LALIBERTÉ Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada TIFFANY
MARCH 212 L A L I B E R T É ET AL. 875 Moist Recirculation and Water Vapor Transport on Dry Isentropes* FRÉDÉRIC LALIBERTÉ Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada TIFFANY
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES. Weather. atmosphere. Weather and climate
 GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
Sensitivity of Intertropical Convergence Zone Movement to the Latitudinal Position of Thermal Forcing
 15 APRIL 2014 S E O E T A L. 3035 Sensitivity of Intertropical Convergence Zone Movement to the Latitudinal Position of Thermal Forcing JEONGBIN SEO AND SARAH M. KANG School of Urban and Environmental
15 APRIL 2014 S E O E T A L. 3035 Sensitivity of Intertropical Convergence Zone Movement to the Latitudinal Position of Thermal Forcing JEONGBIN SEO AND SARAH M. KANG School of Urban and Environmental
Dynamics and Kinematics
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Temperature Change. Heat (Q) Latent Heat. Latent Heat. Heat Fluxes Transfer of heat in/out of the ocean Flux = Quantity/(Area Time) Latent heat
 Heat (Q) 1 calorie = 4.18 Joule Heat : Total Kinetic Energy Temperature: Average Kinetic Energy Heat that causes a change in temperature: Sensible Heat Temperature Change ΔQ = m c water ΔT Q in Joules
Heat (Q) 1 calorie = 4.18 Joule Heat : Total Kinetic Energy Temperature: Average Kinetic Energy Heat that causes a change in temperature: Sensible Heat Temperature Change ΔQ = m c water ΔT Q in Joules
Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics
 Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics M 1 ( ) e R ε er Tropical v Midlatitude Meteorology Why is the general circulation and synoptic weather systems in the tropics different to the those in the
Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics M 1 ( ) e R ε er Tropical v Midlatitude Meteorology Why is the general circulation and synoptic weather systems in the tropics different to the those in the
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228)
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
Course , General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 9: Numerical Models
 Course 1.81, General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 9: Numerical Models Phillips Numerical Experiment: We are going to discuss Phillips (1956) original numerical experiment
Course 1.81, General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 9: Numerical Models Phillips Numerical Experiment: We are going to discuss Phillips (1956) original numerical experiment
Climate Warming Related Strengthening of the Tropical Hydrological Cycle
 562 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 26 Climate Warming Related Strengthening of the Tropical Hydrological Cycle MATTHIAS ZAHN AND RICHARD P. ALLAN University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom
562 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 26 Climate Warming Related Strengthening of the Tropical Hydrological Cycle MATTHIAS ZAHN AND RICHARD P. ALLAN University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom
Climate of an Earth- like Aquaplanet: the high- obliquity case and the <dally- locked case
 Climate of an Earth- like Aquaplanet: the high- obliquity case and the
Climate of an Earth- like Aquaplanet: the high- obliquity case and the
The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments
 The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Table of Contents. Chapter: Atmosphere. Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere. Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere. Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer
Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS continued (Part II) pp in Class Notes
 Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS continued (Part II) pp 61-67 in Class Notes To drive the circulation, the initial source of energy is from the Sun: Not to scale! EARTH- SUN Relationships 4 Things to Know
Topic # 11 HOW CLIMATE WORKS continued (Part II) pp 61-67 in Class Notes To drive the circulation, the initial source of energy is from the Sun: Not to scale! EARTH- SUN Relationships 4 Things to Know
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 20: More Ocean: Chapter 7
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 20: More Ocean: Chapter 7 Community Business Quiz discussion Next Topic will be Chapter 8, Natural Climate variability in the instrumental record. Homework
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 20: More Ocean: Chapter 7 Community Business Quiz discussion Next Topic will be Chapter 8, Natural Climate variability in the instrumental record. Homework
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models
 An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
Dynamics of the Atmosphere. General circulation of the atmosphere
 12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere 1 Spinup of the general circulation in an idealized model Fig. 1 Schneider, General circulation of the atmosphere, 2006 2 Sigma 0.2
12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere 1 Spinup of the general circulation in an idealized model Fig. 1 Schneider, General circulation of the atmosphere, 2006 2 Sigma 0.2
On the role of planetary-scale waves in the abrupt seasonal. transition of the Northern Hemisphere general circulation. Tiffany A.
 Generated using version 3.2 of the official AMS L A TEX template 1 On the role of planetary-scale waves in the abrupt seasonal 2 transition of the Northern Hemisphere general circulation 3 Tiffany A. Shaw
Generated using version 3.2 of the official AMS L A TEX template 1 On the role of planetary-scale waves in the abrupt seasonal 2 transition of the Northern Hemisphere general circulation 3 Tiffany A. Shaw
The tropical precipitation response to orbital precession
 Generated using V3.1.2 of the official AMS LATEX template journal page layout FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! The tropical precipitation response to orbital precession Timothy M. Merlis Princeton
Generated using V3.1.2 of the official AMS LATEX template journal page layout FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! The tropical precipitation response to orbital precession Timothy M. Merlis Princeton
Impact of sea surface temperatures on African climate. Alessandra Giannini
 Impact of sea surface temperatures on African climate Alessandra Giannini alesall@iri.columbia.edu Outline: Intro/Motivation: demand-driven science, use of seasonal climate prediction, adaptation to climate
Impact of sea surface temperatures on African climate Alessandra Giannini alesall@iri.columbia.edu Outline: Intro/Motivation: demand-driven science, use of seasonal climate prediction, adaptation to climate
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
