Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches
|
|
|
- Sydney McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches LONG-TERM GOALS Joao Teixeira Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology MS , 48 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena, CA, 9119 phone: (818) Award Number: N1411IP269 The long term goals of this effort are (i) the development of a unified parameterization for the marine boundary layer; (ii) the implementation of this new parameterization in the US Navy NOGAPS model; and (iii) the transition of this new version of the NOGAPS model into operations at Fleet Numerical Meteorology and Oceanography Center (FNMOC). OBJECTIVES The objectives of this project are: i) to develop a unified parameterization for the Marine Boundary Layer (MBL) and ii) to implement and test this parameterization in the Navy Operational Global Atmospheric Prediction System (NOGAPS). This unified MBL parameterization will be based on two main components: (i) the Eddy-Diffusivity Mass-Flux (EDMF) parameterization of boundary layer mixing; and (ii) the Probability Density Function (PDF) cloud parameterization. APPROACH This unified boundary layer parameterization will be based on two main components: (i) the Eddy- Diffusivity Mass-Flux (EDMF) parameterization of turbulence and convective MBL mixing; and (ii) the Probability Density Function (PDF) cloud parameterization. Together these two concepts allow for the unification of MBL parameterization in one single scheme. They also allow for the development of physical parameterizations that lead to a resolution-dependent MBL parameterization that would adjust itself to the horizontal grid resolution. Key personnel: J. Teixeira (JPL/Caltech) uses his expertise in cloud and boundary layer parameterizations to guide the development and implementation of the EDMF/PDF parameterization. M. Peng (NRL) uses her expertise in global modeling to assist with the investigations related to NOGAPS within the context of this ONR DRI. K. Suselj (UCLA Research Associate) performs the development and implementation of the EDMF parameterization in the NOGAPS model. WORK COMPLETED Evaluation of new EDMF/PDF parameterization in Single Column Model (SCM): 1
2 i) New stochastic EDMF shallow convection parameterization was evaluated against observations and LES results for GEWEX Cloud Systems Studies (GCSS) case-studies (e.g. BOMEX, DYCOMS); ii) New stochastic EDMF shallow convection parameterization was evaluated against observations and LES results for GCSS cloud transition cases i.e. from stratocumulus to cumulus. Implementation and evaluation of new parameterizations in NOGAPS SCM: i) EDMF parameterization was implemented in NOGAPS SCM and tested for GEWEX Cloud Systems Studies (GCSS) case-studies (e.g. BOMEX, DYCOMS). RESULTS Introduction A parameterization which is suited to represent moist convective boundary layers is implemented in the NOGAPS single-column-model (SCM). The parameterization is based on a stochastic eddydiffusivity mass-flux (EDMF) approach. In the EDMF framework, turbulent fluxes are calculated as a sum of the down-gradient (eddy-diffusivity) based component and a mass flux component (e.g. Siebesma et al., 27). The eddy-diffusivity component is based on Louis et al., (1982), as implemented in the current version of the NOGAPS SCM, while the parameterization of the mass-flux component is new in NOGAPS. The mass-flux component is modeled as a fixed number of steady state plumes. In a dry boundary layer plumes represent the strongest thermals of the flow, and in the cumulus-dominated boundary layer they represent convective clouds. Therefore, the solutions have to account for a realistic representation of condensation within the plumes, and equally important of lateral entrainment into the plumes. We have shown (Sušelj et al. 212) that the EDMF model has the capability to capture the essential features of moist boundary layers, ranging from stratocumulus to shallow-cumulus regimes. The EDMF parameterization is implemented in the NOGAPS SCM. We show that the new parameterization improves the parameterization of convective boundary layers. The results from two sets of cases are shown: i) various dry convective boundary layer cases forced by a surface sensible heat flux, and ii) shallow moist convection (BOMEX case). In all simulations we use 91 vertical levels that correspond to ECMWF vertical levels. Results from NOGAPS-SCM Dry convective boundary layer The NOGAPS-SCM is first tested on a dry boundary layer forced by positive surface latent and sensible heat fluxes. We perform the same simulations as in Witek et al. (211). The initial conditions are described below. The well-mixed boundary layer has a height of 135 m. In the boundary layer, the potential temperature is constant ( K) and the total moisture at the surface is with a vertical gradient of km -1. Above the boundary layer height: km -1 and K km -1. Only a small wind speed is prescribed (u=.1 ms - 1 ). Three experiments are performed. They differ by the amount of prescribed surface sensible heat flux (see Tab. 1 for a list of experiments). The moisture flux was kept the same for all the experiments ( m s -1 ). The NOGAPS-SCM model results are compared to large-eddy simulation (LES) results (Figs. 1-3 compare the profiles of potential temperature and water vapor). The control NOGAPS-SCM does not 2
3 represent the boundary layer well. The turbulent mixing is too weak and confined to the shallow layer near the surface (boundary layer height is too low). Due to the prescribed surface fluxes, near surface temperatures and total water mixing ratios are too high. Part of the reason is that the Louis et al., (1982) scheme is not well suited to work in the limit of free (no shear) convection. In Louis et al., (1982) turbulent mixing is a function of bulk Richardson number which in the limit of free convection approaches infinity. The NOGAPS-SCM with EDMF shows an obvious improvement with respect to the control simulation in terms of the depth of the boundary layer as well as the stability in the boundary layer. The boundary layer height is better represented as well as the gradient of potential temperature and total water mixing ratio. Adjusting the eddy-diffusivity parameterization could eventually produce further improvements in the model. Simulation Sensible heat flux (Kms -1 ) A.3 B.6 C.12 Tab.1: List of dry convective boundary layer experiments θ [K] q 3 t x 1 Fig.1: Potential temperature (left) and total vapor mixing ratio (right) profiles for experiment A. Solid line LES results, dotted control NOGAPS, dashed EDMF NOGAPS. Results are for 1 hour (blue line), 3 hours (green) and 5 hours (red) after the simulation start q 3 θ [K] t x 1 Fig.2: Potential temperature (left) and total vapor mixing ratio (right) profiles for experiment B. Lines are 3
4 the same as in Fig q 3 θ [K] t x 1 Fig.3: Potential temperature (left) and total water mixing ratio (right) profiles for experiment C. Lines are the same as in Fig. 1except that they are for 1 hour (blue line), 2 hour (green) and 3 hour (red) after the simulation start. Shallow cumulus convection (BOMEX) The shallow convection case BOMEX was run with the NOGAPS-SCM with the new EDMF and the model results are compared to the LES results from Siebesma et al., (23). The BOMEX case is characterized by a dry well-mixed subcloud layer, reaching from the surface to around 6 m, topped by a non-precipitating shallow cumulus cloud layer. The boundary layer turbulence is forced mainly by buoyancy flux, the wind shear being small z [m] 15 z [m] θ L [K] q t [g kg 1 ] Fig.4: Liquid water potential temperature (left) and total water mixing ratio (right) from the EDMF NOGAPS-SCM (red line), LES (black line) and initial conditions (dashed black line). The shaded area represents the range from different LES models (see Siebesma 23 for details). Both the EDMF NOGAPS-SCM and LES results are after 3 hours of simulation. Fig. 4 shows the profiles of moist conserved variables from the EDMF NOGAPS-SCM and compares them to LES results. The turbulent fluxes in the subcloud layer should be mostly represented by the eddy-diffusivity parameterization and in the cloudy layer by the mass-flux part (Sušelj et al. 212). The profiles of moist conserved variables are well represented in the cloudy layer and less well in the subcloud layer. This indicates that the eddy-diffusivity part of the parameterization would need further improvements while the mass-flux part of the parameterization is well suited to represent the moist thermals (convective clouds). Fig. 5 shows the mean updraft area, vertical velocity and excesses 4
5 of moist conserved variables and compares them to LES results. In general the mass-flux part of the parameterization represents well the expected values from the LES model, except for the vertical velocity. Part of the problem in parameterizing the profile of the vertical velocity is that the surface conditions are not well represented. This can be improved by making the eddy-diffusivity part of the parameterization more realistic. Fig.5: Updraft properties for the BOMEX case. Blue lines represent the EDMF NOGAPS-SCM (full lines the moist updrafts, dashed lines the dry). Black and green lines represent the mean of the cloud and cloud cores from LES and dark (light) green and gray areas represent the inter-quartile (total) range from LES. Cloud and cloud cores represent different sampling of LES results (see Siebesma et al., 23 for details). The SCM results are expected to be between cloud and cloud core values. IMPACT/APPLICATIONS These results have an important potential future impact for the weather prediction capabilities of the US Navy after the implementation of these new parameterizations in the NOGAPS model. In addition it will be the first time that a unified parameterization of the marine boundary layer has ever been developed and implemented in a global weather prediction model. TRANSITIONS The new EDMF parameterization will be proposed for a transition at FNMOC after implementation and adequate testing in the NOGAPS model. RELATED PROJECTS This project is part of the Unified Physical Parameterizations for Seasonal Prediction Departmental Research Initiative. 5
6 REFERENCES Louis, J.F., M. Tiedtke and Geleyn, J.F. 1982: A short history of the operational PBL-parameterization at ECMWF, Workshop on Boundary layer parameterization, ECMWF, Reading, England. Siebesma, A., et al., 23: A large eddy simulation intercomparison study of shallow cumulus convection. J. Atmos. Sci., 6, Siebesma, A. P., P. M. M. Soares, and J. Teixeira, 27: A combined eddy-diffusivity mass flux approach for the convective boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci., 64, Sušelj, K., J. Teixeira and D. Chung, 212: A unified model for moist convective boundary layers based on a stochastic Eddy-Diffusivity/Mass-Flux parameterization. J. Atmos Sci., in press. Witek, M. L., J. Teixeira, and G. Matheou, 211b: An integrated TKE-based eddy diffusivity/massflux boundary layer closure for the dry convective boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci., 68, PUBLICATIONS Suselj, K., J. Teixeira, and D. Chung, 212: A unified model for moist convective boundary layers based on a stochastic Eddy-Diffusivity/Mass-Flux parameterization. J. Atmos. Sci., in press. de Rooy, W.C., P. Bechtold, K. Frohlich, C. Hohenegger, H. Jonker, D. Mironov, A. P. Siebesma, J. Teixeira and Jun-Ichi Yano, 212: Review Article, Entrainment and Detrainment in Cumulus Convection: An Overview. Quart. J. Roy. Meteo. Soc., in press. Karlsson, Johannes, and Joao Teixeira, 212: A simple stratocumulus-to-cumulus transition model derived from the climatological surface energy budget. Journal of Climate, in review. Suselj, K., J. Teixeira, and G. Matheou, 212: Eddy Diffusivity/Mass Flux and Shallow Cumulus Boundary Layer: An Updraft PDF Multiple Mass Flux Scheme. J. Atmos. Sci., 69, Witek, M.L, J. Teixeira, and G. Matheou, 211b: An eddy-diffusivity/mass-flux approach to the vertical transport of turbulent kinetic energy in convective boundary layers. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 68, Witek, M.L., J. Teixeira, and G. Matheou, 211a: An integrated TKE based eddy-diffusivity/massflux boundary layer scheme for the dry convective boundary layer. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 68,
Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches Joao Teixeira
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches Joao Teixeira
Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-Based Cloud Approaches
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-Based Cloud Approaches Joao Teixeira
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-Based Cloud Approaches Joao Teixeira
A framework to evaluate unified parameterizations for seasonal prediction: an LES/SCM parameterization test-bed
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A framework to evaluate unified parameterizations for seasonal prediction: an LES/SCM parameterization test-bed Joao Teixeira
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A framework to evaluate unified parameterizations for seasonal prediction: an LES/SCM parameterization test-bed Joao Teixeira
A Framework to Evaluate Unified Parameterizations for Seasonal Prediction: An LES/SCM Parameterization Test-Bed
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Framework to Evaluate Unified Parameterizations for Seasonal Prediction: An LES/SCM Parameterization Test-Bed Joao Teixeira
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Framework to Evaluate Unified Parameterizations for Seasonal Prediction: An LES/SCM Parameterization Test-Bed Joao Teixeira
From small-scale turbulence to large-scale convection: a unified scale-adaptive EDMF parameterization
 From small-scale turbulence to large-scale convection: a unified scale-adaptive EDMF parameterization Kay Sušelj 1, Joao Teixeira 1 and Marcin Kurowski 1,2 1 JET PROPULSION LABORATORY/CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE
From small-scale turbulence to large-scale convection: a unified scale-adaptive EDMF parameterization Kay Sušelj 1, Joao Teixeira 1 and Marcin Kurowski 1,2 1 JET PROPULSION LABORATORY/CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE
A Framework to Evaluate Unified Parameterizations for Seasonal Prediction: An LES/SCM Parameterization Test-Bed
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Framework to Evaluate Unified Parameterizations for Seasonal Prediction: An LES/SCM Parameterization Test-Bed Joao Teixeira
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Framework to Evaluate Unified Parameterizations for Seasonal Prediction: An LES/SCM Parameterization Test-Bed Joao Teixeira
A Framework to Evaluate Unified Parameterizations for Seasonal Prediction: An LES/SCM Parameterization Test-Bed
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Framework to Evaluate Unified Parameterizations for Seasonal Prediction: An LES/SCM Parameterization Test-Bed Joao Teixeira
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Framework to Evaluate Unified Parameterizations for Seasonal Prediction: An LES/SCM Parameterization Test-Bed Joao Teixeira
Cloud Structure and Entrainment in Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layers
 Cloud Structure and Entrainment in Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layers David C. Lewellen MAE Dept., PO Box 6106, West Virginia University Morgantown, WV, 26506-6106 phone: (304) 293-3111 (x2332) fax: (304)
Cloud Structure and Entrainment in Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layers David C. Lewellen MAE Dept., PO Box 6106, West Virginia University Morgantown, WV, 26506-6106 phone: (304) 293-3111 (x2332) fax: (304)
Cloud Feedbacks and Climate Models
 Cloud Feedbacks and Climate Models oão Teixeira, USA Together with many people including S. Cardoso (IDL/NCAR), A. Gettelman (NCAR), B. Kahn, S. Klein (LLNL), P. Miranda (IDL), A.P. Siebesma (KNMI), P.
Cloud Feedbacks and Climate Models oão Teixeira, USA Together with many people including S. Cardoso (IDL/NCAR), A. Gettelman (NCAR), B. Kahn, S. Klein (LLNL), P. Miranda (IDL), A.P. Siebesma (KNMI), P.
Improved Atmospheric Stable Boundary Layer Formulations for Navy Seasonal Forecasting
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Improved Atmospheric Stable Boundary Layer Formulations for Navy Seasonal Forecasting Michael Tjernström Department of
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Improved Atmospheric Stable Boundary Layer Formulations for Navy Seasonal Forecasting Michael Tjernström Department of
NAVGEM Platform Support
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. NAVGEM Platform Support Mr. Timothy Whitcomb Naval Research Laboratory 7 Grace Hopper Ave, MS2 Monterey, CA 93943 phone:
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. NAVGEM Platform Support Mr. Timothy Whitcomb Naval Research Laboratory 7 Grace Hopper Ave, MS2 Monterey, CA 93943 phone:
The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases
 The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Thorsten Mauritsen Max Planck Institute for Meteorology,
The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Thorsten Mauritsen Max Planck Institute for Meteorology,
A Dual Mass Flux Framework for Boundary Layer Convection. Part II: Clouds
 JUNE 2009 N E G G E R S 1489 A Dual Mass Flux Framework for Boundary Layer Convection. Part II: Clouds ROEL A. J. NEGGERS* European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, Reading, United Kingdom (Manuscript
JUNE 2009 N E G G E R S 1489 A Dual Mass Flux Framework for Boundary Layer Convection. Part II: Clouds ROEL A. J. NEGGERS* European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, Reading, United Kingdom (Manuscript
An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds: ECMWF
 An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds: EDMF @ ECMWF Martin Köhler ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Martin.Koehler@ecmwf.int 1 Introduction The importance of low
An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds: EDMF @ ECMWF Martin Köhler ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Martin.Koehler@ecmwf.int 1 Introduction The importance of low
Extending EDMF into the statistical modeling of boundary layer clouds
 Extending EDMF into the statistical modeling of boundary layer clouds Roel A. J. Neggers ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Roel.Neggers@ecmwf.int 1 Introduction The representation
Extending EDMF into the statistical modeling of boundary layer clouds Roel A. J. Neggers ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Roel.Neggers@ecmwf.int 1 Introduction The representation
Improving Mesoscale Prediction of Shallow Convection and Cloud Regime Transitions in NRL COAMPS
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Improving Mesoscale Prediction of Shallow Convection and Cloud Regime Transitions in NRL COAMPS David B. Mechem Atmospheric
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Improving Mesoscale Prediction of Shallow Convection and Cloud Regime Transitions in NRL COAMPS David B. Mechem Atmospheric
ECMWF now and future dry PBL stratocumulus shallow cumulus. ongoing work parcel numerics stratocumulus down-drafts shallow cumulus
 An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds Martin Köhler, ECMWF EDMF @ ECMWF now and future dry PBL stratocumulus shallow cumulus stratocumulus: evaluation against observations EPIC marine
An integral approach to modeling PBL transports and clouds Martin Köhler, ECMWF EDMF @ ECMWF now and future dry PBL stratocumulus shallow cumulus stratocumulus: evaluation against observations EPIC marine
NAVGEM Platform Support
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. NAVGEM Platform Support Mr. Timothy Whitcomb Naval Research Laboratory 7 Grace Hopper Ave, MS2 Monterey, CA 93943 phone:
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. NAVGEM Platform Support Mr. Timothy Whitcomb Naval Research Laboratory 7 Grace Hopper Ave, MS2 Monterey, CA 93943 phone:
ECMWF ARM Report Series
 ECMWF ARM Report Series 3. A dual mass flux framework for boundary layer convection. Part II: Clouds Roel A. J. Neggers European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Europäisches Zentrum für mittelfristige
ECMWF ARM Report Series 3. A dual mass flux framework for boundary layer convection. Part II: Clouds Roel A. J. Neggers European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Europäisches Zentrum für mittelfristige
Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch
 Improvements in CAM5 : Moist Turbulence, Shallow Convection, and Cloud Macrophysics AMWG Meeting Feb. 10. 2010 Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch CGD.NCAR University of Washington, Seattle,
Improvements in CAM5 : Moist Turbulence, Shallow Convection, and Cloud Macrophysics AMWG Meeting Feb. 10. 2010 Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch CGD.NCAR University of Washington, Seattle,
TURBULENT KINETIC ENERGY
 TURBULENT KINETIC ENERGY THE CLOSURE PROBLEM Prognostic Moment Equation Number Number of Ea. fg[i Q! Ilial.!.IokoQlI!!ol Ui au. First = at au.'u.' '_J_ ax j 3 6 ui'u/ au.'u.' a u.'u.'u k ' Second ' J =
TURBULENT KINETIC ENERGY THE CLOSURE PROBLEM Prognostic Moment Equation Number Number of Ea. fg[i Q! Ilial.!.IokoQlI!!ol Ui au. First = at au.'u.' '_J_ ax j 3 6 ui'u/ au.'u.' a u.'u.'u k ' Second ' J =
Shallow cumulus evaluated with the LASSO (ensemble LES) framework
 Shallow cumulus evaluated with the LASSO (ensemble LES) framework Wayne M. Angevine, Joe Olson, and Jaymes Kenyon CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Outline: What and why is LASSO? The shallow
Shallow cumulus evaluated with the LASSO (ensemble LES) framework Wayne M. Angevine, Joe Olson, and Jaymes Kenyon CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Outline: What and why is LASSO? The shallow
PALM - Cloud Physics. Contents. PALM group. last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015
 PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
Higher-order closures and cloud parameterizations
 Higher-order closures and cloud parameterizations Jean-Christophe Golaz National Research Council, Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA Vincent E. Larson Atmospheric Science Group, Dept. of Math Sciences
Higher-order closures and cloud parameterizations Jean-Christophe Golaz National Research Council, Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA Vincent E. Larson Atmospheric Science Group, Dept. of Math Sciences
Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute
A Parameterization of Dry Thermals and Shallow Cumuli for Mesoscale Numerical Weather Prediction
 Boundary-Layer Meteorol DOI 1.17/s1546-9-9388- ARTICLE A Parameterization of Dry Thermals and Shallow Cumuli for Mesoscale Numerical Weather Prediction Julien Pergaud Valéry Masson Sylvie Malardel Fleur
Boundary-Layer Meteorol DOI 1.17/s1546-9-9388- ARTICLE A Parameterization of Dry Thermals and Shallow Cumuli for Mesoscale Numerical Weather Prediction Julien Pergaud Valéry Masson Sylvie Malardel Fleur
Unified Boundary Layer and Convection Parameterization: The EDMF Approach
 Unified Bondary Layer and Convection Parameterization: The EDMF Approach João Teixeira, Kay Sselj and Marcin Krowski, California institte of Technology, Pasadena and JIFRESSE, University of California
Unified Bondary Layer and Convection Parameterization: The EDMF Approach João Teixeira, Kay Sselj and Marcin Krowski, California institte of Technology, Pasadena and JIFRESSE, University of California
Precipitating convection in cold air: Virtual potential temperature structure
 QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 133: 25 36 (2007) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).2 Precipitating convection in cold air:
QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 133: 25 36 (2007) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).2 Precipitating convection in cold air:
Differing Effects of Subsidence on Marine Boundary Layer Cloudiness
 Differing Effects of Subsidence on Marine Boundary Layer Cloudiness Joel Norris* Timothy Myers C. Seethala Scripps Institution of Oceanography *contact Information: jnorris@ucsd.edu Subsidence and Stratocumulus
Differing Effects of Subsidence on Marine Boundary Layer Cloudiness Joel Norris* Timothy Myers C. Seethala Scripps Institution of Oceanography *contact Information: jnorris@ucsd.edu Subsidence and Stratocumulus
Correspondence to: C. N. Franklin
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 14, 6557 6570, 2014 doi:10.5194/acp-14-6557-2014 Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. The effects of turbulent collision coalescence on precipitation formation and precipitation-dynamical
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 14, 6557 6570, 2014 doi:10.5194/acp-14-6557-2014 Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. The effects of turbulent collision coalescence on precipitation formation and precipitation-dynamical
Stable and transitional (and cloudy) boundary layers in WRF. Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL
 Stable and transitional (and cloudy) boundary layers in WRF Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL WRF PBL and Land Surface options Too many options! PBL here: MYJ (traditional,
Stable and transitional (and cloudy) boundary layers in WRF Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL WRF PBL and Land Surface options Too many options! PBL here: MYJ (traditional,
What you need to know in Ch. 12. Lecture Ch. 12. Atmospheric Heat Engine
 Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
NSF 2005 CPT Report. Jeffrey T. Kiehl & Cecile Hannay
 NSF 2005 CPT Report Jeffrey T. Kiehl & Cecile Hannay Introduction: The focus of our research is on the role of low tropical clouds in affecting climate sensitivity. Comparison of climate simulations between
NSF 2005 CPT Report Jeffrey T. Kiehl & Cecile Hannay Introduction: The focus of our research is on the role of low tropical clouds in affecting climate sensitivity. Comparison of climate simulations between
Simulation of shallow cumuli and their transition to deep convective clouds by cloud-resolving models with different third-order turbulence closures
 Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2006), 132, pp. 359 382 doi: 10.1256/qj.05.29 Simulation of shallow cumuli and their transition to deep convective clouds by cloud-resolving models with different third-order turbulence
Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (2006), 132, pp. 359 382 doi: 10.1256/qj.05.29 Simulation of shallow cumuli and their transition to deep convective clouds by cloud-resolving models with different third-order turbulence
P2.5 MODELING THE SUMMER DIURNAL CYCLE IN THE SW IBERIA (THE CICLUS EXPERIMENT)
 P2.5 MODELING THE SUMMER DIURNAL CYCLE IN THE SW IBERIA (THE CICLUS EXPERIMENT) Pedro M. M. Soares* University of Lisbon, Centro de Geofísica, Lisbon, Portugal ISEL, Department of Civil Engineering, Lisbon,
P2.5 MODELING THE SUMMER DIURNAL CYCLE IN THE SW IBERIA (THE CICLUS EXPERIMENT) Pedro M. M. Soares* University of Lisbon, Centro de Geofísica, Lisbon, Portugal ISEL, Department of Civil Engineering, Lisbon,
Performance of an Eddy Diffusivity Mass Flux Scheme for Shallow Cumulus Boundary Layers
 JULY 2010 A N G E V I N E E T A L. 2895 Performance of an Eddy Diffusivity Mass Flux Scheme for Shallow Cumulus Boundary Layers WAYNE M. ANGEVINE Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences,
JULY 2010 A N G E V I N E E T A L. 2895 Performance of an Eddy Diffusivity Mass Flux Scheme for Shallow Cumulus Boundary Layers WAYNE M. ANGEVINE Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences,
The role of shallow convection in ECMWFs Integrated Forecasting System
 725 The role of shallow convection in ECMWFs Integrated Forecasting System P. Bechtold, I. Sandu, D. Klocke, N. Semane, M. Ahlgrimm, A. Beljaars, R. Forbes, M. Rodwell Research Department July 9, 204 Series:
725 The role of shallow convection in ECMWFs Integrated Forecasting System P. Bechtold, I. Sandu, D. Klocke, N. Semane, M. Ahlgrimm, A. Beljaars, R. Forbes, M. Rodwell Research Department July 9, 204 Series:
What you need to know in Ch. 12. Lecture Ch. 12. Atmospheric Heat Engine. The Atmospheric Heat Engine. Atmospheric Heat Engine
 Lecture Ch. 1 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 1 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Lecture Ch. 1 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 1 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Atm S 547 Boundary Layer Meteorology
 Lecture 9. Nonlocal BL parameterizations for clear unstable boundary layers In tis lecture Nonlocal K-profile parameterization (e. g. WRF-YSU) for dry convective BLs EDMF parameterizations (e. g. ECMWF)
Lecture 9. Nonlocal BL parameterizations for clear unstable boundary layers In tis lecture Nonlocal K-profile parameterization (e. g. WRF-YSU) for dry convective BLs EDMF parameterizations (e. g. ECMWF)
2.1 Temporal evolution
 15B.3 ROLE OF NOCTURNAL TURBULENCE AND ADVECTION IN THE FORMATION OF SHALLOW CUMULUS Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands 1. MOTIVATION
15B.3 ROLE OF NOCTURNAL TURBULENCE AND ADVECTION IN THE FORMATION OF SHALLOW CUMULUS Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands 1. MOTIVATION
Simulation of Boundar y-layer Cumulus and Stratocumulus Clouds Using a Cloud-Resolving Model with Low- and Third-order Turbulence Closures
 November Journal of the 2008 Meteorological Society of Japan, A. Vol. CHENG 86A, pp. and 67 86, K.-M. 2008 XU 67 Simulation of Boundar y-layer Cumulus and Stratocumulus Clouds Using a Cloud-Resolving Model
November Journal of the 2008 Meteorological Society of Japan, A. Vol. CHENG 86A, pp. and 67 86, K.-M. 2008 XU 67 Simulation of Boundar y-layer Cumulus and Stratocumulus Clouds Using a Cloud-Resolving Model
A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes
 A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes Song-Lak Kang Atmospheric Science Group, Texas Tech Univ. & George H. Bryan MMM, NCAR 20 th Symposium on Boundary
A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes Song-Lak Kang Atmospheric Science Group, Texas Tech Univ. & George H. Bryan MMM, NCAR 20 th Symposium on Boundary
Testing and Improving Pacific NW PBL forecasts
 Testing and Improving Pacific NW PBL forecasts Chris Bretherton and Matt Wyant University of Washington Eric Grimit 3Tier NASA MODIS Image Testing and Improving Pacific NW PBL forecasts PBL-related forecast
Testing and Improving Pacific NW PBL forecasts Chris Bretherton and Matt Wyant University of Washington Eric Grimit 3Tier NASA MODIS Image Testing and Improving Pacific NW PBL forecasts PBL-related forecast
Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons)
 Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger How do we parameterize convec+on? Precipita)on response to soil moisture Increase
Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger How do we parameterize convec+on? Precipita)on response to soil moisture Increase
Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land
 Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land surfaces in the following ways: (a) Near surface air
Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land surfaces in the following ways: (a) Near surface air
3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme
 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme R. J. Keane and R. S. Plant 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme p.1/17 Outline Introduction to the Plant-Craig
3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme R. J. Keane and R. S. Plant 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme p.1/17 Outline Introduction to the Plant-Craig
Basic Concepts for Convection Parameterization in Weather Forecast and Climate Models: COST Action ES0905. Jun-Ichi Yano Meteo France
 Basic Concepts for Convection Parameterization in Weather Forecast and Climate Models: COST Action ES0905 Jun-Ichi Yano Meteo France COST Action (European Cooperation in Science and Technology): European
Basic Concepts for Convection Parameterization in Weather Forecast and Climate Models: COST Action ES0905 Jun-Ichi Yano Meteo France COST Action (European Cooperation in Science and Technology): European
Bulk Boundary-Layer Model
 Bulk Boundary-Layer Model David Randall Ball (1960) was the first to propose a model in which the interior of the planetary boundary layer (PBL) is well-mixed in the conservative variables, while the PBL
Bulk Boundary-Layer Model David Randall Ball (1960) was the first to propose a model in which the interior of the planetary boundary layer (PBL) is well-mixed in the conservative variables, while the PBL
Modified PM09 parameterizations in the shallow convection grey zone
 Modified PM09 parameterizations in the shallow convection grey zone LACE stay report Toulouse Centre National de Recherche Meteorologique, 02. February 2015 27. February 2015 Scientific supervisor: Rachel
Modified PM09 parameterizations in the shallow convection grey zone LACE stay report Toulouse Centre National de Recherche Meteorologique, 02. February 2015 27. February 2015 Scientific supervisor: Rachel
Cloud Structure and Entrainment in Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layers
 Cloud Structure and Entrainment in Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layers David C. Lewellen MAE Dept., PO Box 6106, West Virginia University Morgantown, WV, 26506-6106 Phone: (304) 293-3111 (x2332) Fax: (304)
Cloud Structure and Entrainment in Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layers David C. Lewellen MAE Dept., PO Box 6106, West Virginia University Morgantown, WV, 26506-6106 Phone: (304) 293-3111 (x2332) Fax: (304)
A brief overview of the scheme is given below, taken from the whole description available in Lopez (2002).
 Towards an operational implementation of Lopez s prognostic large scale cloud and precipitation scheme in ARPEGE/ALADIN NWP models F.Bouyssel, Y.Bouteloup, P. Marquet Météo-France, CNRM/GMAP, 42 av. G.
Towards an operational implementation of Lopez s prognostic large scale cloud and precipitation scheme in ARPEGE/ALADIN NWP models F.Bouyssel, Y.Bouteloup, P. Marquet Météo-France, CNRM/GMAP, 42 av. G.
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5
 Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Méso-NH simulations of Fog and Stratocumulus Clouds in Los Angeles
 Méso-NH simulations of Fog and Stratocumulus Clouds in Los Angeles Rui Salgado (Univ. Évora) João Teixeira, Marcin Kurowski and Kay Suselj (JPL) 1/17 Motivation May Grey and June Gloom In California, people
Méso-NH simulations of Fog and Stratocumulus Clouds in Los Angeles Rui Salgado (Univ. Évora) João Teixeira, Marcin Kurowski and Kay Suselj (JPL) 1/17 Motivation May Grey and June Gloom In California, people
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
Super-Parameterization of Boundary Layer Roll Vortices in Tropical Cyclone Models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-Parameterization of Boundary Layer Roll Vortices in Tropical Cyclone Models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-Parameterization of Boundary Layer Roll Vortices in Tropical Cyclone Models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
Assessing Land Surface Albedo Bias in Models of Tropical Climate
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Assessing Land Surface Albedo Bias in Models of Tropical Climate William R. Boos (PI) Yale University PO Box 208109 New
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Assessing Land Surface Albedo Bias in Models of Tropical Climate William R. Boos (PI) Yale University PO Box 208109 New
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model
 Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models
 Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
A Unified Convection Scheme : UNICON
 A Unified Convection Scheme : UNICON HFIP Meeting. Washington D.C. Aug. 9. 2011 Sungsu Park AMP. CGD. NESL. NCAR. Boulder. CO. The Unicorn is the only fabulous beast that does not seem to have been conceived
A Unified Convection Scheme : UNICON HFIP Meeting. Washington D.C. Aug. 9. 2011 Sungsu Park AMP. CGD. NESL. NCAR. Boulder. CO. The Unicorn is the only fabulous beast that does not seem to have been conceived
Numerical simulation of marine stratocumulus clouds Andreas Chlond
 Numerical simulation of marine stratocumulus clouds Andreas Chlond Marine stratus and stratocumulus cloud (MSC), which usually forms from 500 to 1000 m above the ocean surface and is a few hundred meters
Numerical simulation of marine stratocumulus clouds Andreas Chlond Marine stratus and stratocumulus cloud (MSC), which usually forms from 500 to 1000 m above the ocean surface and is a few hundred meters
Improved prediction of boundary layer clouds
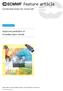 from Newsletter Number 14 Summer 25 METEOROLOGY Improved prediction of boundary layer clouds doi:1.21957/812mkwz37 This article appeared in the Meteorology section of ECMWF Newsletter No. 14 Summer 25,
from Newsletter Number 14 Summer 25 METEOROLOGY Improved prediction of boundary layer clouds doi:1.21957/812mkwz37 This article appeared in the Meteorology section of ECMWF Newsletter No. 14 Summer 25,
4.4 DRIZZLE-INDUCED MESOSCALE VARIABILITY OF BOUNDARY LAYER CLOUDS IN A REGIONAL FORECAST MODEL. David B. Mechem and Yefim L.
 4.4 DRIZZLE-INDUCED MESOSCALE VARIABILITY OF BOUNDARY LAYER CLOUDS IN A REGIONAL FORECAST MODEL David B. Mechem and Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies University
4.4 DRIZZLE-INDUCED MESOSCALE VARIABILITY OF BOUNDARY LAYER CLOUDS IN A REGIONAL FORECAST MODEL David B. Mechem and Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies University
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model
 Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
Quantifying Uncertainty through Global and Mesoscale Ensembles
 Quantifying Uncertainty through Global and Mesoscale Ensembles Teddy R. Holt Naval Research Laboratory Monterey CA 93943-5502 phone: (831) 656-4740 fax: (831) 656-4769 e-mail: holt@nrlmry.navy.mil Award
Quantifying Uncertainty through Global and Mesoscale Ensembles Teddy R. Holt Naval Research Laboratory Monterey CA 93943-5502 phone: (831) 656-4740 fax: (831) 656-4769 e-mail: holt@nrlmry.navy.mil Award
Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition. SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club
 Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club Mar 01, 2006 AGCM5 of the GFD-DENNOU CLUB edition is a three-dimensional primitive system on a sphere (Swamp Project,
Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club Mar 01, 2006 AGCM5 of the GFD-DENNOU CLUB edition is a three-dimensional primitive system on a sphere (Swamp Project,
Evaluation of Forecasted Southeast Pacific Stratocumulus in the NCAR, GFDL, and ECMWF Models
 1JUNE 2009 H A N N A Y E T A L. 2871 Evaluation of Forecasted Southeast Pacific Stratocumulus in the NCAR, GFDL, and ECMWF Models CÉCILE HANNAY, DAVID L. WILLIAMSON, JAMES J. HACK, JEFFREY T. KIEHL, AND
1JUNE 2009 H A N N A Y E T A L. 2871 Evaluation of Forecasted Southeast Pacific Stratocumulus in the NCAR, GFDL, and ECMWF Models CÉCILE HANNAY, DAVID L. WILLIAMSON, JAMES J. HACK, JEFFREY T. KIEHL, AND
Bells and whistles of convection parameterization
 Bells and whistles of convection parameterization Article Accepted Version Yano, J. I., Machulskaya, E., Bechtold, P. and Plant, R. S. (2013) Bells and whistles of convection parameterization. Bulletin
Bells and whistles of convection parameterization Article Accepted Version Yano, J. I., Machulskaya, E., Bechtold, P. and Plant, R. S. (2013) Bells and whistles of convection parameterization. Bulletin
PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues
 PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues Song-You Hong, Hyun-Joo Choi, Ji-Young Han, and Young-Cheol Kwon (Korea Institute of Atmospheric Prediction Systems: KIAPS) Overview of KIAPS (seminar
PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues Song-You Hong, Hyun-Joo Choi, Ji-Young Han, and Young-Cheol Kwon (Korea Institute of Atmospheric Prediction Systems: KIAPS) Overview of KIAPS (seminar
JI NIE. Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts ZHIMING KUANG
 1936 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Responses of Shallow Cumulus Convection to Large-Scale Temperature and Moisture Perturbations: A Comparison of Large-Eddy Simulations
1936 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Responses of Shallow Cumulus Convection to Large-Scale Temperature and Moisture Perturbations: A Comparison of Large-Eddy Simulations
Super-Parameterization of Boundary Layer Roll Vortices in Tropical Cyclone Models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-Parameterization of Boundary Layer Roll Vortices in Tropical Cyclone Models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-Parameterization of Boundary Layer Roll Vortices in Tropical Cyclone Models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
Sensitivity to the PBL and convective schemes in forecasts with CAM along the Pacific Cross-section
 Sensitivity to the PBL and convective schemes in forecasts with CAM along the Pacific Cross-section Cécile Hannay, Jeff Kiehl, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Jim Hack, Richard Neale and Chris Bretherton*
Sensitivity to the PBL and convective schemes in forecasts with CAM along the Pacific Cross-section Cécile Hannay, Jeff Kiehl, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Jim Hack, Richard Neale and Chris Bretherton*
Boundary layer processes. Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg
 Boundary layer processes Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg The Atmospheric Boundary Layer (ABL) An Abstraction (Wippermann 76) The bottom 100-3000 m of the Troposphere (Stull
Boundary layer processes Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg The Atmospheric Boundary Layer (ABL) An Abstraction (Wippermann 76) The bottom 100-3000 m of the Troposphere (Stull
Chapter (3) TURBULENCE KINETIC ENERGY
 Chapter (3) TURBULENCE KINETIC ENERGY 3.1 The TKE budget Derivation : The definition of TKE presented is TKE/m= e = 0.5 ( u 2 + v 2 + w 2 ). we recognize immediately that TKE/m is nothing more than the
Chapter (3) TURBULENCE KINETIC ENERGY 3.1 The TKE budget Derivation : The definition of TKE presented is TKE/m= e = 0.5 ( u 2 + v 2 + w 2 ). we recognize immediately that TKE/m is nothing more than the
Evaluation of Forecasted Southeast Pacific Stratocumulus in the NCAR, GFDL and ECMWF Models.
 Evaluation of Forecasted Southeast Pacific Stratocumulus in the NCAR, GFDL and ECMWF Models. Cécile Hannay, David L Williamson, James J Hack, Jeffrey T Kiehl, Jerry G Olson, National Center for Atmospheric
Evaluation of Forecasted Southeast Pacific Stratocumulus in the NCAR, GFDL and ECMWF Models. Cécile Hannay, David L Williamson, James J Hack, Jeffrey T Kiehl, Jerry G Olson, National Center for Atmospheric
Turbulent transport of the energy in the entrainment interface layer
 Turbulent transport of the energy in the entrainment interface layer Marta K. Kopec 1, S. P. Malinowski1, Z. P. Piotrowski2 1 nstitute 2 nstitute of Geophysics, Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw,
Turbulent transport of the energy in the entrainment interface layer Marta K. Kopec 1, S. P. Malinowski1, Z. P. Piotrowski2 1 nstitute 2 nstitute of Geophysics, Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw,
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.1002/2016MS000634 Key Points: A scale-aware parameterization is proposed which includes stochastic sampling and convective
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.1002/2016MS000634 Key Points: A scale-aware parameterization is proposed which includes stochastic sampling and convective
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans
![Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans](/thumbs/96/128963638.jpg) Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Evaluation of Statistical Distributions for the Parametrization of Subgrid Boundary-Layer Clouds
 Boundary-Layer Meteorol (2011) 140:263 294 DOI 10.1007/s10546-011-9607-3 ARTICLE Evaluation of Statistical Distributions for the Parametrization of Subgrid Boundary-Layer Clouds Emilie Perraud Fleur Couvreux
Boundary-Layer Meteorol (2011) 140:263 294 DOI 10.1007/s10546-011-9607-3 ARTICLE Evaluation of Statistical Distributions for the Parametrization of Subgrid Boundary-Layer Clouds Emilie Perraud Fleur Couvreux
Errors caused by draft fraction in cumulus parameterization
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L17802, doi:10.1029/2009gl039100, 2009 Errors caused by draft fraction in cumulus parameterization Akihiko Murata 1 Received 24 May 2009; revised 16 July 2009; accepted
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L17802, doi:10.1029/2009gl039100, 2009 Errors caused by draft fraction in cumulus parameterization Akihiko Murata 1 Received 24 May 2009; revised 16 July 2009; accepted
Near-surface Measurements In Support of Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Study
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Near-surface Measurements In Support of Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Study Qing Wang Meteorology Department, Naval
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Near-surface Measurements In Support of Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Study Qing Wang Meteorology Department, Naval
Northern Arabian Sea Circulation Autonomous Research (NASCar) DRI: A Study of Vertical Mixing Processes in the Northern Arabian Sea
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Northern Arabian Sea Circulation Autonomous Research (NASCar) DRI: A Study of Vertical Mixing Processes in the Northern
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Northern Arabian Sea Circulation Autonomous Research (NASCar) DRI: A Study of Vertical Mixing Processes in the Northern
Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China
 Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION Convective rain occurs over southern
Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION Convective rain occurs over southern
Introduction to climate modeling. ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008
 Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
On the Fidelity of Large-Eddy Simulation of Shallow Precipitating Cumulus Convection
 2918 M O N T H L Y W E A T H E R R E V I E W VOLUME 139 On the Fidelity of Large-Eddy Simulation of Shallow Precipitating Cumulus Convection GEORGIOS MATHEOU AND DANIEL CHUNG Jet Propulsion Laboratory,
2918 M O N T H L Y W E A T H E R R E V I E W VOLUME 139 On the Fidelity of Large-Eddy Simulation of Shallow Precipitating Cumulus Convection GEORGIOS MATHEOU AND DANIEL CHUNG Jet Propulsion Laboratory,
Shallow cumulus convection: A validation of large-eddy simulation against aircraft and Landsat observations
 Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (3), 9, pp. 67 696 doi:.56/qj..93 Shallow cumulus convection: A validation of large-eddy simulation against aircraft and Landsat observations By R. A. J. NEGGERS, P. G. DUYNKERKE
Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. (3), 9, pp. 67 696 doi:.56/qj..93 Shallow cumulus convection: A validation of large-eddy simulation against aircraft and Landsat observations By R. A. J. NEGGERS, P. G. DUYNKERKE
A Probabilistic Bulk Model of Coupled Mixed Layer and Convection. Part II: Shallow Convection Case
 JUNE 2013 G E N T I N E E T A L. 1557 A Probabilistic Bulk Model of Coupled Mixed Layer and Convection. Part II: Shallow Convection Case PIERRE GENTINE,* ALAN K. BETTS, 1 BENJAMIN R. LINTNER, # KIRSTEN
JUNE 2013 G E N T I N E E T A L. 1557 A Probabilistic Bulk Model of Coupled Mixed Layer and Convection. Part II: Shallow Convection Case PIERRE GENTINE,* ALAN K. BETTS, 1 BENJAMIN R. LINTNER, # KIRSTEN
Interagency Earth System Predic;on Capability (ESPC) Navy ESPC PM: D. Eleuterio (ONR)
 US Navy Coupled System Research and Development under the Earth System Predic;on Capability C. Reynolds, N. Barton, M. Flatau, J. Ridout, NRL, Monterey, CA Interagency Earth System Predic;on Capability
US Navy Coupled System Research and Development under the Earth System Predic;on Capability C. Reynolds, N. Barton, M. Flatau, J. Ridout, NRL, Monterey, CA Interagency Earth System Predic;on Capability
Prediction of clouds and precipitation in atmospheric models
 Prediction of clouds and precipitation in atmospheric models Cumulus congestus. Sønderjylland, 2002. Foto: Flemming Byg. B. H. Sass NetFam Summer School July 2008 outline Basic definitions and characteristics
Prediction of clouds and precipitation in atmospheric models Cumulus congestus. Sønderjylland, 2002. Foto: Flemming Byg. B. H. Sass NetFam Summer School July 2008 outline Basic definitions and characteristics
Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken during DYNAMO
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken
Annual Report for Blue Waters Allocation: Sonia Lasher-Trapp, Oct 2017
 Annual Report for Blue Waters Allocation: Sonia Lasher-Trapp, Oct 2017 Project Information: Untangling Entrainment Effects on Hail and Rain in Deep Convective Clouds o Sonia Lasher-Trapp, UIUC, slasher@illinois.edu
Annual Report for Blue Waters Allocation: Sonia Lasher-Trapp, Oct 2017 Project Information: Untangling Entrainment Effects on Hail and Rain in Deep Convective Clouds o Sonia Lasher-Trapp, UIUC, slasher@illinois.edu
Development and Implementation of Universal Cloud/Radiation Parameterizations in Navy Operational Forecast Models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Development and Implementation of Universal Cloud/Radiation Parameterizations in Navy Operational Forecast Models Harshvardhan
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Development and Implementation of Universal Cloud/Radiation Parameterizations in Navy Operational Forecast Models Harshvardhan
2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment
 Atmospheric Sciences 6150 Cloud System Modeling 2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment Arakawa (1969, 1972), W. Gray
Atmospheric Sciences 6150 Cloud System Modeling 2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment Arakawa (1969, 1972), W. Gray
Using Cloud-Resolving Models for Parameterization Development
 Using Cloud-Resolving Models for Parameterization Development Steven K. Krueger University of Utah! 16th CMMAP Team Meeting January 7-9, 2014 What is are CRMs and why do we need them? Range of scales diagram
Using Cloud-Resolving Models for Parameterization Development Steven K. Krueger University of Utah! 16th CMMAP Team Meeting January 7-9, 2014 What is are CRMs and why do we need them? Range of scales diagram
Warm rain variability and its association with cloud mesoscalestructure t and cloudiness transitions. Photo: Mingxi Zhang
 Warm rain variability and its association with cloud mesoscalestructure t and cloudiness transitions Robert Wood, Universityof Washington with help and data from Louise Leahy (UW), Matt Lebsock (JPL),
Warm rain variability and its association with cloud mesoscalestructure t and cloudiness transitions Robert Wood, Universityof Washington with help and data from Louise Leahy (UW), Matt Lebsock (JPL),
J3.2 TRANSPORT AND CHEMICAL TRANSFORMATIONS INFLUENCED BY SHALLOW CUMULUS OVER LAND
 J3.2 TRANSPORT AND CHEMICAL TRANSFORMATIONS INFLUENCED BY SHALLOW CUMULUS OVER LAND Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorlogy and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands Si-Wan Kim,
J3.2 TRANSPORT AND CHEMICAL TRANSFORMATIONS INFLUENCED BY SHALLOW CUMULUS OVER LAND Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorlogy and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands Si-Wan Kim,
Atmospheric Boundary Layers
 Lecture for International Summer School on the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Les Houches, France, June 17, 2008 Atmospheric Boundary Layers Bert Holtslag Introducing the latest developments in theoretical
Lecture for International Summer School on the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Les Houches, France, June 17, 2008 Atmospheric Boundary Layers Bert Holtslag Introducing the latest developments in theoretical
Impact of Resolution on Extended-Range Multi-Scale Simulations
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Impact of Resolution on Extended-Range Multi-Scale Simulations Carolyn A. Reynolds Naval Research Laboratory Monterey,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Impact of Resolution on Extended-Range Multi-Scale Simulations Carolyn A. Reynolds Naval Research Laboratory Monterey,
Atm S 547 Boundary-Layer Meteorology. Lecture 15. Subtropical stratocumulus-capped boundary layers. In this lecture
 Atm S 547 Boundary-Layer Meteorology Bretherton Lecture 15. Subtropical stratocumulus-capped boundary layers In this lecture Physical processes and their impact on Sc boundary layer structure Mixed-layer
Atm S 547 Boundary-Layer Meteorology Bretherton Lecture 15. Subtropical stratocumulus-capped boundary layers In this lecture Physical processes and their impact on Sc boundary layer structure Mixed-layer
A Discussion on The Effect of Mesh Resolution on Convective Boundary Layer Statistics and Structures Generated by Large-Eddy Simulation by Sullivan
 耶鲁 - 南京信息工程大学大气环境中心 Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment A Discussion on The Effect of Mesh Resolution on Convective Boundary Layer Statistics and Structures Generated by Large-Eddy Simulation
耶鲁 - 南京信息工程大学大气环境中心 Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment A Discussion on The Effect of Mesh Resolution on Convective Boundary Layer Statistics and Structures Generated by Large-Eddy Simulation
