A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes
|
|
|
- Rosa Ward
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes Song-Lak Kang Atmospheric Science Group, Texas Tech Univ. & George H. Bryan MMM, NCAR 20 th Symposium on Boundary Layer and Turbulence, Boston MA, 9-13 July 2012
2 Introduction This study investigates the sensitivity of moist convection initiation (CI) to the amplitudes of surface energy balance (SEB) heterogeneity on a scale of 10s of kilometers: 1) under a zero background wind 2) with a strong capping inversion of the CBL.
3 SEB Heterogeneity Warm and Dry Patch Cool and Moist Patch = Constant = 640 Wm -2 Surface sensible and latent heat fluxes are prescribed with the surface energy balance (SEB) constraint.
4 SEB Heterogeneity Warm and Dry Patch Cool and Moist Patch Surface sensible heat flux has a 180 degree phase lag relative to surface latent heat flux. Thus, warm and dry versus cool and moist surfaces are prescribed.
5 SEB Heterogeneity CASE A200B06 Warm and Dry Patch Cool and Moist Patch Amplitude = 200 Wm -2 This particular case has a SEB heterogeneity amplitude of 200 Wm -2.
6 SEB Heterogeneity CASE A200B06 Cool and Moist Patch Mean LE = 400 Wm -2 Mean SH = 240 Wm -2 Warm and Dry Patch Bowen ratio = SH/LE = 240 Wm -2 /400 Wm -2 = 0.6 This particular case has a domain average Bowen ratio of 0.6.
7 Numerical Experiment Cases The amplitude varies among 0 Wm -2 (homogeneous), 50 Wm -2 (weakly heterogeneous), and 200 Wm -2 (strongly heterogeneous).
8 Surface Flux Heterogeneity The domain-averaged Bowen ratio varies between 0.6 (wet surface) and 1.2 (dry surface).
9 Initial Atmospheric Condition Sounding modified from Weisman and Klemp (1982). - CBL with strong capping inversion - Drier than the original sounding CAPE: 230 J kg -1 CIN: 170 J kg -1 CBL height: 810 m LCL: 1.2 km
10 About Numerical Model and Domain Nonhydrostatic model of Bryan and Fritsch (2002) SFS model: TKE scheme Periodic LBCs Dx :100 m Dz : 40 m (lower than 4 km), m (4-6 km) 6 hour integration (Dt = 1 s; Output interval = 100 s) 6 km 32 km 8 km
11 Time evolutions of cloud water (colors) and rainwater (contours) mixing ratio 60 min. WET SFC. DRY SFC. Moist convection is randomly scattered throughout the domain Earlier start of moist convection and more cloud water over the WET SFC
12 Time evolutions of cloud water (shades) and rainwater (contours) mixing ratio WET SFC. DRY SFC. The transition from shallow convection into deep precipitating convection is identified. Within 6 hrs, neither the WET SFC nor the DRY SFC develops deep moist convection
13 Time evolutions of cloud water (colors) and rainwater (contours) mixing ratio 50 min. WET SFC. DRY SFC. Weakly Hete. Sfc.
14 Time evolutions of cloud water (colors) and rainwater (contours) mixing ratio WET SFC. DRY SFC. Over the WET SFC, moist convection grows to reach the height of 6 km at 345 min. However over the DRY SFC, moist convection does not reach the model top 6 km within 6 hours.
15 Time evolutions of cloud water (colors) and rainwater (contours) mixing ratio < 20 min. WET SFC. DRY SFC. Strongly Hete. Sfc.
16 Time evolutions of cloud water (colors) and rainwater (contours) mixing ratio WET SFC. DRY SFC. For both over the WET SFC and DRY SFC, moist convections grow to reach the height of 6 km at 230 min and 275 min respectively.
17 Mesoscale structure over the 30-min pre-ci period Spatially averaged over the y dimension and temporally averaged over the 30-min pre-ci period Water vapor mixing ratio : Colors Vertical Wind: Contours Horizontal Wind: Vectors White Solid Line: ABL height White Dotted Line: LCL
18 Mesoscale structure over the 30-min pre-ci period Spatially averaged over the y dimension and temporally averaged over the 30-min pre-ci period Water vapor mixing ratio : Colors Vertical Wind: Contours Horizontal Wind: Vectors White Solid Line: ABL height White Dotted Line: LCL
19 Mesoscale fluctuation structure over the 30-min pre-ci period Stronger Mesoscale Upward Motion Strongly Hete. Sfc. Weakly Hete. Sfc.
20 Mesoscale fluctuation structure over the 30-min pre-ci period Reduced effects of the entrainment: Less warming and drying Strongly Hete. Sfc. Weakly Hete. Sfc.
21 Mesoscale fluctuation structure over the 30-min pre-ci period Different characteristics of mesoscale moisture fluctuations
22 Spectra of θ and r at 140 m above ground averaged over the 30-min pre-ci period Potential temperature (θ) Water vapor mixing ratio ( r ) Black: The horizontally homogeneous ABL Blue: The ABL over weakly heterogeneous ABL Red: The ABL over strongly heterogeneous ABL
23 Spectra of θ and r at 140 m above ground averaged over the 30-min pre-ci period Potential temperature (θ) Water vapor mixing ratio ( r ) The spectral density peaks associated the ABL turbulence
24 Spectra of θ and r at 140 m above ground averaged over the 30-min pre-ci period Potential temperature (θ) Water vapor mixing ratio ( r ) The spectral density peaks associated the prescribed mesoscale surface heterogeneity
25 Spectra of θ and r at 140 m above ground averaged over the 30-min pre-ci period Potential temperature (θ) Water vapor mixing ratio ( r ) What are the third spectral density peaks existed only in the r spectra from cases the homogeneous ABL and the weakly heterogeneous ABL?
26 Spectra of θ and r at 140 m above ground averaged over the 30-min pre-ci period Potential temperature (θ) Water vapor mixing ratio ( r ) Meoscale fluctuations of r grown from turbulence (Jonker et al. 1999)
27 Spectra of θ and r at 140 m above ground averaged over the 30-min pre-ci period Potential temperature (θ) Water vapor mixing ratio ( r ) Characteristic length scale of r somewhat larger than that of θ (Couvreux et al. 2005; Mahrt 1991; LeMone and Meitin 1984)
28 Mesoscale fluctuation structure over the 30-min pre-ci period Mesoscale fluctuations of r on the sfc. heterogeneity scal Strongly Hete. Sfc.
29 Mesoscale fluctuation structure over the 30-min pre-ci period Mesoscale fluctuations of r on the sfc. heterogeneity scale and the scales smaller than the heterogeneity scale Weakly Hete. Sfc.
30 Conclusions 1. The mesoscale convergence zone of this circulation develops over the relatively warm surface, and this is where clouds first form. 2. With higher amplitude of the surface flux heterogeneity, CI occurs earlier in a more focused region over the center of the warm patch.
31 Conclusions 3. With the same amplitude of sensible heat flux heterogeneity, the relatively wet surface (lower Bowen ratio) yields earlier CI. 4. Over weakly heterogeneous and homogeneous surfaces, surface latent heat flux is especially significant for determining the development of deep moist convection.
32 Conclusions 5. Over strongly heterogeneous surfaces, moisture fluctuations on a scale larger than turbulence are generated only by the surface heterogeneity. 6. Over strongly heterogeneous surfaces, greater magnitude of mesoscale upward motion more significantly reduces the warming and drying effect by the entrainment of the free atmosphere into the CBL.
33 For the details, Please refer to Kang and Bryan, 2011: A Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Moist Convection Initiation over Heterogeneous Surface Fluxes, Mon. Wea. Review 139 :
14B.2 Relative humidity as a proxy for cloud formation over heterogeneous land surfaces
 14B.2 Relative humidity as a proxy for cloud formation over heterogeneous land surfaces Chiel C. van Heerwaarden and Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University,
14B.2 Relative humidity as a proxy for cloud formation over heterogeneous land surfaces Chiel C. van Heerwaarden and Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University,
PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues
 PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues Song-You Hong, Hyun-Joo Choi, Ji-Young Han, and Young-Cheol Kwon (Korea Institute of Atmospheric Prediction Systems: KIAPS) Overview of KIAPS (seminar
PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues Song-You Hong, Hyun-Joo Choi, Ji-Young Han, and Young-Cheol Kwon (Korea Institute of Atmospheric Prediction Systems: KIAPS) Overview of KIAPS (seminar
Land-surface response to shallow cumulus. Fabienne Lohou and Edward Patton
 Land-surface response to shallow cumulus Fabienne Lohou and Edward Patton Outline 1/ SEB response on average and locally ( Radiative and turbulent effects (not shown here)) Solar input Turbulence Radiative
Land-surface response to shallow cumulus Fabienne Lohou and Edward Patton Outline 1/ SEB response on average and locally ( Radiative and turbulent effects (not shown here)) Solar input Turbulence Radiative
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans
![Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans](/thumbs/96/128963638.jpg) Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Experiments with Idealized Supercell Simulations
 Latent Heat Nudging in almo: Experiments with Idealized Supercell Simulations Daniel Leuenberger and Andrea Rossa MeteoSwiss Talk Outline Introduction Supercell Storms Characteristics Reference simulation
Latent Heat Nudging in almo: Experiments with Idealized Supercell Simulations Daniel Leuenberger and Andrea Rossa MeteoSwiss Talk Outline Introduction Supercell Storms Characteristics Reference simulation
The perturbation pressure, p, can be represented as the sum of a hydrostatic pressure perturbation p h and a nonhydrostatic pressure perturbation p nh
 z = The perturbation pressure, p, can be represented as the sum of a hydrostatic pressure perturbation p h and a nonhydrostatic pressure perturbation p nh, that is, p = p h + p nh. (.1) The former arises
z = The perturbation pressure, p, can be represented as the sum of a hydrostatic pressure perturbation p h and a nonhydrostatic pressure perturbation p nh, that is, p = p h + p nh. (.1) The former arises
9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS
 9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS Ulrike Wissmeier, Robert Goler University of Munich, Germany 1 Introduction One does not associate severe storms with the tropics
9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS Ulrike Wissmeier, Robert Goler University of Munich, Germany 1 Introduction One does not associate severe storms with the tropics
z g + F w (2.56) p(x, y, z, t) = p(z) + p (x, y, z, t) (2.120) ρ(x, y, z, t) = ρ(z) + ρ (x, y, z, t), (2.121)
 = + dw dt = 1 ρ p z g + F w (.56) Let us describe the total pressure p and density ρ as the sum of a horizontally homogeneous base state pressure and density, and a deviation from this base state, that
= + dw dt = 1 ρ p z g + F w (.56) Let us describe the total pressure p and density ρ as the sum of a horizontally homogeneous base state pressure and density, and a deviation from this base state, that
11.B4 The influence of horizontal convective rolls on the morphology of low-level rotation in idealized simulations of supercell thunderstorms
 11.B4 The influence of horizontal convective rolls on the morphology of low-level rotation in idealized simulations of supercell thunderstorms CHRISTOPHER J. NOWOTARSKI, PAUL M. MARKOWSKI, AND YVETTE P.
11.B4 The influence of horizontal convective rolls on the morphology of low-level rotation in idealized simulations of supercell thunderstorms CHRISTOPHER J. NOWOTARSKI, PAUL M. MARKOWSKI, AND YVETTE P.
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
Diurnal Timescale Feedbacks in the Tropical Cumulus Regime
 DYNAMO Sounding Array Diurnal Timescale Feedbacks in the Tropical Cumulus Regime James Ruppert Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany GEWEX CPCM, Tropical Climate Part 1 8 September 2016
DYNAMO Sounding Array Diurnal Timescale Feedbacks in the Tropical Cumulus Regime James Ruppert Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany GEWEX CPCM, Tropical Climate Part 1 8 September 2016
MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016
 MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016 We have reviewed the reasons why NWP models need to
MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016 We have reviewed the reasons why NWP models need to
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR
 CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches LONG-TERM
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches LONG-TERM
Isentropic analysis and atmospheric circulation.
 Isentropic analysis and atmospheric circulation. Olivier Pauluis Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Thanks to Arnaud Czaja, Robert Korty and Frederic Laliberte Sept. 1, 2009 Keck Institute for
Isentropic analysis and atmospheric circulation. Olivier Pauluis Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Thanks to Arnaud Czaja, Robert Korty and Frederic Laliberte Sept. 1, 2009 Keck Institute for
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget
 The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
1.3 HIGH-RESOLUTION MESOSCALE SIMULATIONS ON THE ROLE OF SHALLOW AND DEEP CONVECTION ON DUST EMISSION AND TRANSPORT IN A DESERT AREA.
 1.3 HIGH-RESOLUTION MESOSCALE SIMULATIONS ON THE ROLE OF SHALLOW AND DEEP CONVECTION ON DUST EMISSION AND TRANSPORT IN A DESERT AREA Tetsuya Takemi Dept. of Environmental Science and Technology, Tokyo
1.3 HIGH-RESOLUTION MESOSCALE SIMULATIONS ON THE ROLE OF SHALLOW AND DEEP CONVECTION ON DUST EMISSION AND TRANSPORT IN A DESERT AREA Tetsuya Takemi Dept. of Environmental Science and Technology, Tokyo
Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land
 Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land surfaces in the following ways: (a) Near surface air
Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land surfaces in the following ways: (a) Near surface air
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
GEOG 402. Soil Temperature and Soil Heat Conduction. Summit of Haleakalā. Surface Temperature. 20 Soil Temperature at 5.0 cm.
 GEOG 40 Soil Temperature and Soil Heat Conduction 35 30 5 Summit of Haleakalā Surface Temperature Soil Temperature at.5 cm 0 Soil Temperature at 5.0 cm 5 0 Air Temp 5 0 0:00 3:00 6:00 9:00 :00 5:00 8:00
GEOG 40 Soil Temperature and Soil Heat Conduction 35 30 5 Summit of Haleakalā Surface Temperature Soil Temperature at.5 cm 0 Soil Temperature at 5.0 cm 5 0 Air Temp 5 0 0:00 3:00 6:00 9:00 :00 5:00 8:00
The Impact of Observed Deforestation on the Mesoscale Distribution of Rainfall and Clouds in Amazonia
 JUNE 2000 WANG ET AL. 267 The Impact of Observed Deforestation on the Mesoscale Distribution of Rainfall and Clouds in Amazonia JINGFENG WANG, RAFAEL L. BRAS, AND ELFATIH A. B. ELTAHIR Department of Civil
JUNE 2000 WANG ET AL. 267 The Impact of Observed Deforestation on the Mesoscale Distribution of Rainfall and Clouds in Amazonia JINGFENG WANG, RAFAEL L. BRAS, AND ELFATIH A. B. ELTAHIR Department of Civil
What is the Mechanism for the Modification of Convective Cloud Distributions by Land Surface Induced Flows?
 MARCH 2011 G A R C I A - C A R R E R A S E T A L. 619 What is the Mechanism for the Modification of Convective Cloud Distributions by Land Surface Induced Flows? LUIS GARCIA-CARRERAS AND DOUGLAS J. PARKER
MARCH 2011 G A R C I A - C A R R E R A S E T A L. 619 What is the Mechanism for the Modification of Convective Cloud Distributions by Land Surface Induced Flows? LUIS GARCIA-CARRERAS AND DOUGLAS J. PARKER
May 3, :41 AOGS - AS 9in x 6in b951-v16-ch13 LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING DATA
 Advances in Geosciences Vol. 16: Atmospheric Science (2008) Eds. Jai Ho Oh et al. c World Scientific Publishing Company LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING
Advances in Geosciences Vol. 16: Atmospheric Science (2008) Eds. Jai Ho Oh et al. c World Scientific Publishing Company LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
A Study of Convective Initiation Failure on 22 Oct 2004
 A Study of Convective Initiation Failure on 22 Oct 2004 Jennifer M. Laflin Philip N. Schumacher NWS Sioux Falls, SD August 6 th, 2011 Introduction Forecasting challenge: strong forcing for ascent and large
A Study of Convective Initiation Failure on 22 Oct 2004 Jennifer M. Laflin Philip N. Schumacher NWS Sioux Falls, SD August 6 th, 2011 Introduction Forecasting challenge: strong forcing for ascent and large
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
short introduction to Practical on Shallow Convection
 short introduction to Practical on Shallow Convection Bart van Stratum Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg 26 June 2015 Alpine summer school, Valsaverenche, Italy Goal practical Use the CLASS
short introduction to Practical on Shallow Convection Bart van Stratum Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg 26 June 2015 Alpine summer school, Valsaverenche, Italy Goal practical Use the CLASS
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity
 The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
 Convective Fluxes: Sensible and Latent Heat Convective Fluxes Convective fluxes require Vertical gradient of temperature / water AND Turbulence ( mixing ) Vertical gradient, but no turbulence: only very
Convective Fluxes: Sensible and Latent Heat Convective Fluxes Convective fluxes require Vertical gradient of temperature / water AND Turbulence ( mixing ) Vertical gradient, but no turbulence: only very
Analysis of the role of the planetary boundary layer schemes during a severe convective storm
 Annales Geophysicae (2004) 22: 1861 1874 SRef-ID: 1432-0576/ag/2004-22-1861 European Geosciences Union 2004 Annales Geophysicae Analysis of the role of the planetary boundary layer schemes during a severe
Annales Geophysicae (2004) 22: 1861 1874 SRef-ID: 1432-0576/ag/2004-22-1861 European Geosciences Union 2004 Annales Geophysicae Analysis of the role of the planetary boundary layer schemes during a severe
Atmospheric Boundary Layers
 Lecture for International Summer School on the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Les Houches, France, June 17, 2008 Atmospheric Boundary Layers Bert Holtslag Introducing the latest developments in theoretical
Lecture for International Summer School on the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Les Houches, France, June 17, 2008 Atmospheric Boundary Layers Bert Holtslag Introducing the latest developments in theoretical
Temperature fronts and vortical structures in turbulent stably stratified atmospheric boundary layers
 VIIIth International Symposium on Stratified Flows August 29 - September 1 2016, San Diego, CA Temperature fronts and vortical structures in turbulent stably stratified atmospheric boundary layers Peter
VIIIth International Symposium on Stratified Flows August 29 - September 1 2016, San Diego, CA Temperature fronts and vortical structures in turbulent stably stratified atmospheric boundary layers Peter
Glaciology HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION
 HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION A Heat Budget 1 Black body radiation Definition. A perfect black body is defined as a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on it. The intensity of radiation emitted by a
HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION A Heat Budget 1 Black body radiation Definition. A perfect black body is defined as a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on it. The intensity of radiation emitted by a
2.1 Temporal evolution
 15B.3 ROLE OF NOCTURNAL TURBULENCE AND ADVECTION IN THE FORMATION OF SHALLOW CUMULUS Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands 1. MOTIVATION
15B.3 ROLE OF NOCTURNAL TURBULENCE AND ADVECTION IN THE FORMATION OF SHALLOW CUMULUS Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano Meteorology and Air Quality Section, Wageningen University, The Netherlands 1. MOTIVATION
Hurricanes are intense vortical (rotational) storms that develop over the tropical oceans in regions of very warm surface water.
 Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
1.4 CONNECTIONS BETWEEN PV INTRUSIONS AND TROPICAL CONVECTION. Beatriz M. Funatsu* and Darryn Waugh The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD
 1.4 CONNECTIONS BETWEEN PV INTRUSIONS AND TROPICAL CONVECTION Beatriz M. Funatsu* and Darryn Waugh The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD 1. INTRODUCTION Stratospheric intrusions into the tropical
1.4 CONNECTIONS BETWEEN PV INTRUSIONS AND TROPICAL CONVECTION Beatriz M. Funatsu* and Darryn Waugh The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD 1. INTRODUCTION Stratospheric intrusions into the tropical
Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate
 Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Idealized Nonhydrostatic Supercell Simulations in the Global MPAS
 Idealized Nonhydrostatic Supercell Simulations in the Global Joe Klemp, Bill Skamarock, and Sang-Hun Park National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Typical characteristics: Supercell Thunderstorms
Idealized Nonhydrostatic Supercell Simulations in the Global Joe Klemp, Bill Skamarock, and Sang-Hun Park National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Typical characteristics: Supercell Thunderstorms
ScienceDirect. Numerical modeling of atmospheric water content and probability evaluation. Part I
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 70 ( 2014 ) 321 329 12th International Conference on Computing and Control for the Water Industry, CCWI2013 Numerical modeling
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 70 ( 2014 ) 321 329 12th International Conference on Computing and Control for the Water Industry, CCWI2013 Numerical modeling
Modified PM09 parameterizations in the shallow convection grey zone
 Modified PM09 parameterizations in the shallow convection grey zone LACE stay report Toulouse Centre National de Recherche Meteorologique, 02. February 2015 27. February 2015 Scientific supervisor: Rachel
Modified PM09 parameterizations in the shallow convection grey zone LACE stay report Toulouse Centre National de Recherche Meteorologique, 02. February 2015 27. February 2015 Scientific supervisor: Rachel
Turbulent transport of the energy in the entrainment interface layer
 Turbulent transport of the energy in the entrainment interface layer Marta K. Kopec 1, S. P. Malinowski1, Z. P. Piotrowski2 1 nstitute 2 nstitute of Geophysics, Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw,
Turbulent transport of the energy in the entrainment interface layer Marta K. Kopec 1, S. P. Malinowski1, Z. P. Piotrowski2 1 nstitute 2 nstitute of Geophysics, Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw,
Chapter 4 Water Vapor
 Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
2σ e s (r,t) = e s (T)exp( rr v ρ l T ) = exp( ) 2σ R v ρ l Tln(e/e s (T)) e s (f H2 O,r,T) = f H2 O
 Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
that individual/local amplitudes of Ro can reach O(1).
 Supplementary Figure. (a)-(b) As Figures c-d but for Rossby number Ro at the surface, defined as the relative vorticity ζ divided by the Coriolis frequency f. The equatorial band (os-on) is not shown due
Supplementary Figure. (a)-(b) As Figures c-d but for Rossby number Ro at the surface, defined as the relative vorticity ζ divided by the Coriolis frequency f. The equatorial band (os-on) is not shown due
Dry Season Shallow Cumulus Clouds in the Amazon Rainforest
 Master s Thesis of Climate Studies Dry Season Shallow Cumulus Clouds in the Amazon Rainforest WAGENINGEN U NIVERSITY M ETEOROLOGY AND A IR Q UALITY Author: Xuemei Wang Supervisor: Prof. Jordi Vila -Guerau
Master s Thesis of Climate Studies Dry Season Shallow Cumulus Clouds in the Amazon Rainforest WAGENINGEN U NIVERSITY M ETEOROLOGY AND A IR Q UALITY Author: Xuemei Wang Supervisor: Prof. Jordi Vila -Guerau
An Intercomparison of Single-Column Model Simulations of Summertime Midlatitude Continental Convection
 An Intercomparison of Single-Column Model Simulations of Summertime Midlatitude Continental Convection S. J. Ghan Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Richland, Washington D. A. Randall, K.-M. Xu, and
An Intercomparison of Single-Column Model Simulations of Summertime Midlatitude Continental Convection S. J. Ghan Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Richland, Washington D. A. Randall, K.-M. Xu, and
Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration
 Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration Climatological and hydrological field work Figure 1: Estimate of the Earth s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the incoming
Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration Climatological and hydrological field work Figure 1: Estimate of the Earth s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the incoming
Convective self-aggregation, cold pools, and domain size
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 1 5, doi:10.1002/grl.50204, 2013 Convective self-aggregation, cold pools, and domain size Nadir Jeevanjee, 1,2 and David M. Romps, 1,3 Received 14 December 2012;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 1 5, doi:10.1002/grl.50204, 2013 Convective self-aggregation, cold pools, and domain size Nadir Jeevanjee, 1,2 and David M. Romps, 1,3 Received 14 December 2012;
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2)
 Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) The ABL, though turbulent, is not homogeneous, and a critical role of turbulence is transport and mixing of air properties, especially in the
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) The ABL, though turbulent, is not homogeneous, and a critical role of turbulence is transport and mixing of air properties, especially in the
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004
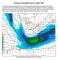 Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium
 A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium A. Parodi(1), K. Emanuel(2) (2) CIMA Research Foundation,Savona, Italy (3) EAPS, MIT, Boston, USA True dynamics: turbulent, moist, non-boussinesq,
A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium A. Parodi(1), K. Emanuel(2) (2) CIMA Research Foundation,Savona, Italy (3) EAPS, MIT, Boston, USA True dynamics: turbulent, moist, non-boussinesq,
A R C T E X Results of the Arctic Turbulence Experiments Long-term Monitoring of Heat Fluxes at a high Arctic Permafrost Site in Svalbard
 A R C T E X Results of the Arctic Turbulence Experiments www.arctex.uni-bayreuth.de Long-term Monitoring of Heat Fluxes at a high Arctic Permafrost Site in Svalbard 1 A R C T E X Results of the Arctic
A R C T E X Results of the Arctic Turbulence Experiments www.arctex.uni-bayreuth.de Long-term Monitoring of Heat Fluxes at a high Arctic Permafrost Site in Svalbard 1 A R C T E X Results of the Arctic
Synoptic Meteorology I: Skew-T Diagrams and Thermodynamic Properties
 Synoptic Meteorology I: Skew-T Diagrams and Thermodynamic Properties For Further Reading Most information contained within these lecture notes is drawn from Chapters 1, 2, 4, and 6 of The Use of the Skew
Synoptic Meteorology I: Skew-T Diagrams and Thermodynamic Properties For Further Reading Most information contained within these lecture notes is drawn from Chapters 1, 2, 4, and 6 of The Use of the Skew
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Evolution and Maintenance of the June 2003 Nocturnal Convection
 Evolution and Maintenance of the 22-23 June 2003 Nocturnal Convection Jerilyn Billings NOAA/NWS Wichita, KS August 6 th, 2011 Work Completed at North Carolina State University for MS Thesis During the
Evolution and Maintenance of the 22-23 June 2003 Nocturnal Convection Jerilyn Billings NOAA/NWS Wichita, KS August 6 th, 2011 Work Completed at North Carolina State University for MS Thesis During the
The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015
 The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015 The effects of moisture conditions on the organization and intensity
The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015 The effects of moisture conditions on the organization and intensity
( ) = 1005 J kg 1 K 1 ;
 Problem Set 3 1. A parcel of water is added to the ocean surface that is denser (heavier) than any of the waters in the ocean. Suppose the parcel sinks to the ocean bottom; estimate the change in temperature
Problem Set 3 1. A parcel of water is added to the ocean surface that is denser (heavier) than any of the waters in the ocean. Suppose the parcel sinks to the ocean bottom; estimate the change in temperature
Forecasting Convective Downburst Potential Over The United States Great Plains
 Forecasting Convective Downburst Potential Over The United States Great Plains Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS), Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA Abstract A favorable
Forecasting Convective Downburst Potential Over The United States Great Plains Kenneth L. Pryor Center for Satellite Applications and Research (NOAA/NESDIS), Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA Abstract A favorable
Lecture 10. Surface Energy Balance (Garratt )
 Lecture 10. Surface Energy Balance (Garratt 5.1-5.2) The balance of energy at the earth s surface is inextricably linked to the overlying atmospheric boundary layer. In this lecture, we consider the energy
Lecture 10. Surface Energy Balance (Garratt 5.1-5.2) The balance of energy at the earth s surface is inextricably linked to the overlying atmospheric boundary layer. In this lecture, we consider the energy
Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons)
 Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger How do we parameterize convec+on? Precipita)on response to soil moisture Increase
Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger How do we parameterize convec+on? Precipita)on response to soil moisture Increase
Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment. Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS)
 Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS) Introduction Balance of lower-tropospheric wind shear and strength of evaporation-generated
Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS) Introduction Balance of lower-tropospheric wind shear and strength of evaporation-generated
Snow II: Snowmelt and energy balance
 Snow II: Snowmelt and energy balance The are three basic snowmelt phases 1) Warming phase: Absorbed energy raises the average snowpack temperature to a point at which the snowpack is isothermal (no vertical
Snow II: Snowmelt and energy balance The are three basic snowmelt phases 1) Warming phase: Absorbed energy raises the average snowpack temperature to a point at which the snowpack is isothermal (no vertical
Clouds and turbulent moist convection
 Clouds and turbulent moist convection Lecture 2: Cloud formation and Physics Caroline Muller Les Houches summer school Lectures Outline : Cloud fundamentals - global distribution, types, visualization
Clouds and turbulent moist convection Lecture 2: Cloud formation and Physics Caroline Muller Les Houches summer school Lectures Outline : Cloud fundamentals - global distribution, types, visualization
Impacts of oasis on the atmospheric hydrological cycle over the nearby desert
 Vol., No.7, 1-7 (1) http://dx.doi.org/1.3/ns.1.7 Natural Science Impacts of oasis on the atmospheric hydrological cycle over the nearby desert Qiang Zhang 1,,3*, Yuhe Nan, Sheng Wang 1,3 1 Key Laboratory
Vol., No.7, 1-7 (1) http://dx.doi.org/1.3/ns.1.7 Natural Science Impacts of oasis on the atmospheric hydrological cycle over the nearby desert Qiang Zhang 1,,3*, Yuhe Nan, Sheng Wang 1,3 1 Key Laboratory
Study of the impacts of grid spacing and physical parameterizations on WRF simulations of convective system rainfall and morphology
 Study of the impacts of grid spacing and physical parameterizations on WRF simulations of convective system rainfall and morphology Introduction Report on WRF-DTC Visit of W. Gallus, I. Jankov and E. Aligo
Study of the impacts of grid spacing and physical parameterizations on WRF simulations of convective system rainfall and morphology Introduction Report on WRF-DTC Visit of W. Gallus, I. Jankov and E. Aligo
2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment
 Atmospheric Sciences 6150 Cloud System Modeling 2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment Arakawa (1969, 1972), W. Gray
Atmospheric Sciences 6150 Cloud System Modeling 2.1 Effects of a cumulus ensemble upon the large scale temperature and moisture fields by induced subsidence and detrainment Arakawa (1969, 1972), W. Gray
Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition. SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club
 Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club Mar 01, 2006 AGCM5 of the GFD-DENNOU CLUB edition is a three-dimensional primitive system on a sphere (Swamp Project,
Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club Mar 01, 2006 AGCM5 of the GFD-DENNOU CLUB edition is a three-dimensional primitive system on a sphere (Swamp Project,
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
Convectively Generated Gravity Waves and Their Effect on the Cloud Environment
 15 AUGUST 2001 LANE AND REEDER 2427 Convectively Generated Gravity Waves and Their Effect on the Cloud Environment TODD P. LANE AND MICHAEL J. REEDER Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Monash University,
15 AUGUST 2001 LANE AND REEDER 2427 Convectively Generated Gravity Waves and Their Effect on the Cloud Environment TODD P. LANE AND MICHAEL J. REEDER Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Monash University,
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting. Primer on organized convection
 Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
1) The energy balance at the TOA is: 4 (1 α) = σt (1 0.3) = ( ) 4. (1 α) 4σ = ( S 0 = 255 T 1
 EAS488/B8800 Climate & Climate Change Homework 2: Atmospheric Radiation and Climate, surface energy balance, and atmospheric general circulation Posted: 3/12/18; due: 3/26/18 Answer keys 1. (10 points)
EAS488/B8800 Climate & Climate Change Homework 2: Atmospheric Radiation and Climate, surface energy balance, and atmospheric general circulation Posted: 3/12/18; due: 3/26/18 Answer keys 1. (10 points)
PALM - Cloud Physics. Contents. PALM group. last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015
 PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM. I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop
 Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop Motivation The Earth s atmosphere is an extremely thin sheet of air
Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop Motivation The Earth s atmosphere is an extremely thin sheet of air
The Arctic Energy Budget
 The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
The Relationship Between Cloud And Rain Cells And The Role Of The Environment In Convective Processes During CHUVA-GoAmazon2014/5
 The Relationship Between Cloud And Rain Cells And The Role Of The Environment In Convective Processes During CHUVA-GoAmazon2014/5 Cristiano W. Eichholz 1, Courtney Schumacher 2, Luiz A. T. Machado 1 1.
The Relationship Between Cloud And Rain Cells And The Role Of The Environment In Convective Processes During CHUVA-GoAmazon2014/5 Cristiano W. Eichholz 1, Courtney Schumacher 2, Luiz A. T. Machado 1 1.
Shallow convection over land: a mesoscale modelling study based on idealized WRF experiments
 Tethys, 6, 51 66, 2009 Journal of Weather & Climate of the Western Mediterranean www.tethys.cat ISSN-1697-1523 eissn-1139-3394 DOI:10.3369/tethys.2009.6.04 Journal edited by ACAM (Associació Catalana de
Tethys, 6, 51 66, 2009 Journal of Weather & Climate of the Western Mediterranean www.tethys.cat ISSN-1697-1523 eissn-1139-3394 DOI:10.3369/tethys.2009.6.04 Journal edited by ACAM (Associació Catalana de
Environmental stability control of the intensity of squall lines under low-level shear conditions
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2007jd008793, 2007 Environmental stability control of the intensity of squall lines under low-level shear conditions Tetsuya Takemi 1 Received 12
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2007jd008793, 2007 Environmental stability control of the intensity of squall lines under low-level shear conditions Tetsuya Takemi 1 Received 12
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters
 Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
Presentation A simple model of multiple climate regimes
 A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries
 11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
Løsningsforslag: oppgavesett kap. 9 (2 av 3) GEF2200
 Løsningsforslag: oppgavesett kap. 9 (2 av 3) GEF2200 s.m.blichner@geo.uio.no Oppgave 1 a) The turbulent vertical flux of sensible heat (Q H ) in the atmospheric boundary layer often takes place through
Løsningsforslag: oppgavesett kap. 9 (2 av 3) GEF2200 s.m.blichner@geo.uio.no Oppgave 1 a) The turbulent vertical flux of sensible heat (Q H ) in the atmospheric boundary layer often takes place through
1 Introduction to Governing Equations 2 1a Methodology... 2
 Contents 1 Introduction to Governing Equations 2 1a Methodology............................ 2 2 Equation of State 2 2a Mean and Turbulent Parts...................... 3 2b Reynolds Averaging.........................
Contents 1 Introduction to Governing Equations 2 1a Methodology............................ 2 2 Equation of State 2 2a Mean and Turbulent Parts...................... 3 2b Reynolds Averaging.........................
Q. Deng a, NYU Abu Dhabi G. Hernandez-Duenas b, UNAM A. Majda, Courant S. Stechmann, UW-Madison L.M. Smith, UW-Madison
 Minimal Models for Precipitating Turbulent Convection Q. Deng a, NYU Abu Dhabi G. Hernandez-Duenas b, UNAM A. Majda, Courant S. Stechmann, UW-Madison L.M. Smith, UW-Madison Contours of rain water in a
Minimal Models for Precipitating Turbulent Convection Q. Deng a, NYU Abu Dhabi G. Hernandez-Duenas b, UNAM A. Majda, Courant S. Stechmann, UW-Madison L.M. Smith, UW-Madison Contours of rain water in a
Properties of a simulated convective boundary layer over inhomogeneous vegetation
 Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 137: 99 117, January 2011 Part A Properties of a simulated convective boundary layer over inhomogeneous vegetation Chan Wang,
Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 137: 99 117, January 2011 Part A Properties of a simulated convective boundary layer over inhomogeneous vegetation Chan Wang,
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study
 The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
Global Water Cycle. Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere. Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40.
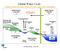 Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
FORECAST UNCERTAINTY UNDER
 FORECAST UNCERTAINTY UNDER DIFFERENT LAND-ATMOSPHERE COUPLING REGIMES Hyo-Jong Song and Craig R. Ferguson Atmospheric Sciences Research Center, University at Albany, SUNY, Albany, NY BACKGROUND Takeaways
FORECAST UNCERTAINTY UNDER DIFFERENT LAND-ATMOSPHERE COUPLING REGIMES Hyo-Jong Song and Craig R. Ferguson Atmospheric Sciences Research Center, University at Albany, SUNY, Albany, NY BACKGROUND Takeaways
Vertical resolution of numerical models. Atm S 547 Lecture 8, Slide 1
 Vertical resolution of numerical models Atm S 547 Lecture 8, Slide 1 M-O and Galperin stability factors Atm S 547 Lecture 8, Slide 2 Profile vs. forcing-driven turbulence parameterization Mellor-Yamada
Vertical resolution of numerical models Atm S 547 Lecture 8, Slide 1 M-O and Galperin stability factors Atm S 547 Lecture 8, Slide 2 Profile vs. forcing-driven turbulence parameterization Mellor-Yamada
Weather Research and Forecasting Model. Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004
 Weather Research and Forecasting Model Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004 Outline What does WRF model do? WRF Standard Initialization WRF Dynamics Conservation Equations Grid staggering
Weather Research and Forecasting Model Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004 Outline What does WRF model do? WRF Standard Initialization WRF Dynamics Conservation Equations Grid staggering
Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China
 Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION Convective rain occurs over southern
Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION Convective rain occurs over southern
Radiative-Convective Models. The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation. Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1
 Climate Modeling Lecture 8 Radiative-Convective Models Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1 The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation Prepare for Mid-Term (Friday 9 am) Review Course Notes
Climate Modeling Lecture 8 Radiative-Convective Models Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1 The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation Prepare for Mid-Term (Friday 9 am) Review Course Notes
PENETRATIVE TURBULENCE ASSOCIATED WITH MESOSCALE SURFACE HEAT FLUX VARIATIONS
 PENETRATIVE TURBULENCE ASSOCIATED WITH MESOSCALE SURFACE HEAT FLUX VARIATIONS Jahrul M. Alam and M. Alamgir Hossain Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Memorial University of Newfoundland, Prince
PENETRATIVE TURBULENCE ASSOCIATED WITH MESOSCALE SURFACE HEAT FLUX VARIATIONS Jahrul M. Alam and M. Alamgir Hossain Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Memorial University of Newfoundland, Prince
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. College of Earth and Mineral Sciences THE EFFECTS OF MESOSCALE SURFACE HETEROGENEITY ON THE
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Earth and Mineral Sciences THE EFFECTS OF MESOSCALE SURFACE HETEROGENEITY ON THE FAIR-WEATHER CONVECTIVE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER AThesisin
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Earth and Mineral Sciences THE EFFECTS OF MESOSCALE SURFACE HETEROGENEITY ON THE FAIR-WEATHER CONVECTIVE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER AThesisin
Numerical modelling of the interaction of soil moisture with planetary boundary layer features and convection over West Africa
 Numerical modelling of the interaction of soil moisture with planetary boundary layer features and convection over West Africa Leonhard Gantner, Norbert Kalthoff, and Martin Kohler Photo: J. Schwendike
Numerical modelling of the interaction of soil moisture with planetary boundary layer features and convection over West Africa Leonhard Gantner, Norbert Kalthoff, and Martin Kohler Photo: J. Schwendike
Mid-Level Vorticity, Moisture, and Gross Moist Stability in the Tropical Atmosphere
 Mid-Level Vorticity, Moisture, and Gross Moist Stability in the Tropical Atmosphere David Raymond, Saška Gjorgjievska, Sharon Sessions, Carlos López, Željka Fuchs Physics Department and Geophysical Research
Mid-Level Vorticity, Moisture, and Gross Moist Stability in the Tropical Atmosphere David Raymond, Saška Gjorgjievska, Sharon Sessions, Carlos López, Željka Fuchs Physics Department and Geophysical Research
The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science
 The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science Outline Basic Dynamical Equations Numerical Methods Initialization
The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science Outline Basic Dynamical Equations Numerical Methods Initialization
THE IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS SLANT-PATH WET DELAY MEASUREMENTS ON SHORT-RANGE PREDICTION OF A PREFRONTAL SQUALL LINE
 JP1.17 THE IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS SLANT-PATH WET DELAY MEASUREMENTS ON SHORT-RANGE PREDICTION OF A PREFRONTAL SQUALL LINE So-Young Ha *1,, Ying-Hwa Kuo 1, Gyu-Ho Lim 1 National Center for Atmospheric
JP1.17 THE IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS SLANT-PATH WET DELAY MEASUREMENTS ON SHORT-RANGE PREDICTION OF A PREFRONTAL SQUALL LINE So-Young Ha *1,, Ying-Hwa Kuo 1, Gyu-Ho Lim 1 National Center for Atmospheric
The Transfer of Heat
 The Transfer of Heat Outcomes: S2-4-03 Explain effects of heat transfer within the atmosphere and hydrosphere on the development and movement of wind and ocean currents. Coriolis Effect In our ecology
The Transfer of Heat Outcomes: S2-4-03 Explain effects of heat transfer within the atmosphere and hydrosphere on the development and movement of wind and ocean currents. Coriolis Effect In our ecology
Reduced Complexity Frameworks for Exploring Physics Dynamics Coupling Sensitivities
 Reduced Complexity Frameworks for Exploring Physics Dynamics Coupling Sensitivities Kevin A. Reed & Adam R. Herrington School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New
Reduced Complexity Frameworks for Exploring Physics Dynamics Coupling Sensitivities Kevin A. Reed & Adam R. Herrington School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New
