Measurement of Three-Dimensional Rotational and Translational. Displacements using a Multi-Facet Mirror
|
|
|
- Britney Parsons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
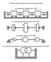
1 Mesurement of Three-Dimensionl Rottionl nd Trnsltionl Displements using Multi-Fet Mirror Won Shik Prk nd Hungsuk Cho Dept. of Mehnil Engineering, Kore Advned Institute of Siene nd Tehnolog 373-1, Kusong-dong, Yusong-gu, Tejeon , Kore ABSTRACT A mesurement sstem tht n mesure the si-degree-of-freedom motions of ritrr ojets is proposed. The mesurement sstem utilizes speil mirror looking like tringulr prmid nd hving three refletive lterl surfes, hih is to e mounted on the ojets of interest. One lser em illumintes the top of the mirror, the mirror reflets nd splits the em into three ems. These refleted ems re deteted three position-sensitive detetors (PSD), respetivel. Bsed on the signl outputs of the PSDs, the three-dimensionl position nd orienttion of the mirror n e omputed, hih, in turn, determines the three dimensionl position nd orienttion of the ojet. This pper proposes to options in ppling the mesurement priniple, one of hih hs its lser em soure fied in spe, nd the other ontrols the trnsltionl motion of the lser em soure to trk the mirror. In this pper, the priniple of the mesurement is proved to e vlid through theoretil nlsis nd eperiments. And the dvntges nd disdvntges of oth options re disussed. Keords: 3-dimensionl ojet pose, 6-DOF motion, 3-fet mirror, position-sensitive detetor (PSD) 1 INTRODUCTION Optil instruments suh s lser interferometers [1,2], lser doppler virometers [3], et. for mesuring miro or nno sle motions re idel used in vriet of industril res. These instruments, hih re sill for 1-D mesurement, sho ver high preision, even the order of nnometers in trnsltion. For higher dimensionl mesurement suh s 2- or 3-D position plus rottion, it is neessr to integrte severl lser interferometers nd lser doppler virometers, hih is ver diffiult tsk sine it eomes signifintl more diffiult to mesure the motions of n ojet ith inreses of even one-dof. Though there hve een gret dels of demnds for the mesurement methods to otin multi-degree-of-freedom, onl fe methods hve een developed for some limited pplitions. Lee et l. [4] investigted the possiilit of their ne optil sstem onsisting of lser soure, four qud-detetors, Prof. Hungsuk Cho(orrespondene), E-mil: hsho@l.kist..kr, WWW: Tel: , F: Optomehtroni Sstems IV, George K. Knopf, Editor, Proeedings of SPIE Vol (2003) 2003 SPIE X/03/$15.00
2 four em splitters, et. to mesure 6-DOF simultneousl. Their method mounts four em splitters on the ojet of interest to form light pth emitted from lser soure to four qud-detetors. Bsed on the preision of their quddetetors, the estimted the trnsltionl nd rottionl resolutions to e 0.05 µm nd 0.25 µrd, respetivel. But the mounting of four em splitters leds to lrge dditive eight of the ojet, thus the dnmi hrteristis of the ojet m e lrgel ffeted. In this pper, ne mesurement method is proposed tht n simultneousl mesure the 3-D position nd orienttion of rigid odies ith the preision order of mirometers nd mirordins. The sensor sstem utilizes lser soure, speill frited mirror, nd three PSDs. The speill frited mirror, lled three-fet mirror in this pper, looks like tringulr prmid hving n equilterl ross-setion. We mount this mirror on the ojets of interest, illuminte the mirror ith He-Ne lser em, nd then detet the ems refleted from the mirror ith PSDs. From the output signls of the PSDs, e n lulte the 3-D position nd orienttion of the three-fet mirror, thus enling us to otin the 3-D position nd orienttion of the ojets. This method utilizes smll nd light mirror, thus the mirror ffets the dnmi hrteristis of the ojet muh less thn tht of Lee et l. s method [4]. z lser soure z L lser em z s φ l PSD C z O su-em s su-em z s v l Lser em su-em ojet s τ z z O PSD B Q ψ ζ o o S ( ψ, ζ ) R ( ψ, ζ ) l o P (, ) p l l s M M M l t s P O PSD A PSD A O Figure 1 Shemti dring of the sensing sstem Figure 2 3-fet mirror nd PSD A 2 PRINCIPLE OF SENSOR SYSTEM 2.1 Sstem onfigurtion The shemti onfigurtion of the proposed sensor sstem is shon in Figure 1. In the figure, the sensor sstem is omposed of mirror of prmidl shpe, lser soure, nd three position-sensitive detetors (PSDs). The mirror hs n equilterl tringulr ross-setion, hih is referred to s three-fet mirror sine it hs three refletive lterl surfes. Its refletive surfes re inlined 45 to its ottom surfe, respetivel, nd the three ottom edges mke Pro. of SPIE Vol
3 equl ngle of 60 to eh other. As shon in Figure 2, one lser em illumintes the top of the three-fet mirror, the refletive surfes M, M, nd M split the lser em into three ems, hih re lled suems in this pper. And the suems impinge the sensitive res of the PSDs, from hih the PSDs detet the positions of the spots of the suems s ell s the inident light poers. If the three-fet mirror moves in n, the positions of the em spots on PSDs nd their inident light poers vr in some orresponding. If there eists some proper reltionship eteen the displements of the mirror nd the PSDs outputs, e m utilize this optil priniple to estimte the three-dimensionl displements of the mirror from the PSDs outputs. In the folloing setions, e onstrut mthemtil model of the reltionship nd sed upon this, theoretill hek if the proposed priniple is vlid. Figure 3 shos the plnr vie of the sensor sstem ith its lser soure omitted for presenttion. Here, the lser em is kept vertil to the referene plne of the sensor sstem, hih is defined three origins of the PSDs. As shon in the figure, three PSDs re loted t the sme distne R PSD from the origin of the sensor sstem o, round hih the origins of the PSDs mke n equl ngle 120 ith eh other. In the previous stud [5], it hs een presented tht the ngles eteen the PSDs θ nd θ re not so importnt, ut the distne from the enter to the PSDs R PSD ffets the ngulr resolution of the sensor. In this pper, the issues out the sstem prmeters nd their effets re not presented, ut e fous on the priniple nd its vritions tht properl dpt to given prolems. 2.2 Sensor model The PSDs re illuminted the suems nd provide the output signls out the 2-D positions nd inident light poers of the em spots. Within the em spots, irrdine distriutions look like pie-piees s shon in Figure 2. If the three-fet mirror trnsltes or rottes, the irrdine distriutions on the PSDs vr in generl so tht the PSDs provide the hnges in the 2-D oordintes nd inident light poer of the em spots. In this setion, the mthemtil reltionship eteen the 3-D pose of three-fet mirror nd the PSD outputs is derived, hih is funtion tht lultes the PSD outputs from given 3-D position nd orienttion of three-fet mirror. The derivtion is sed on light pth tring from the soure to the destintion, in hih lser em is regrded s set of stright lines. For simpliit of the model, diffrtive effet is negleted nd on ount of spe onsidertion, the derivtion for one detetor, PSD A, is presented in this pper. The sstem model epressed s J f relting the three-dimensionl pose of three-fet mirror to the outputs of three PSDs n e ξ = J f ( τ ) (1) here ξ nd τ represent the output nd input of the sensor, respetivel, defined s follos. ξ = ψ ζ Φ ψ ζ Φ ψ ζ Φ [ ] T (2) 86 Pro. of SPIE Vol. 5264
4 τ = [ t t t γ β α ] T. (3) z Here the omponents of ξ re the output signls provided the PSDs. (, ) the em spot impinging on PSD A ith respet to the oordinte sstem the inident light poer on the sme detetor. Similrl, ( ψ, ζ ), ψ ζ represents the 2-D oordinte of o defined on PSD A nd Φ, ( ψ, ζ ), nd PSD B nd C ith respet to their orresponding oordinte sstems o nd o. τ omponents of three-fet mirror. t, Φ represents Φ represent the outputs of onsists of the 6-DOF t, nd t z re the oordintes of the top of the mirror ith respet to the referene frme o nd γ, β, nd α re the roll, pith, nd ngles, respetivel. The definition of these si omponents orresponds to the reltive liner nd ngulr displement eteen the ojet frme o s defined t the verte of the mirror nd the referene frme o. It is noted tht the sensor input τ inludes (, ), hih is the 2- D oordinte of the lser em enter defined s the intersetion eteen the lser em enter nd -plne. This is represented ith respet to the referene frme o. The reson h τ inludes (, ) is sed on theoretil nlsis to e eplined in the folloing setion nd to present tht J f provides one-to-one mpping eteen ξ nd τ. PSD B o θ = R PSD =250mm o o PSD A D(J f )/D(τ) θ = PSD C o ε l Figure 3 Plnr vie of the sensor sstem Figure 4 Joins of J f J f hs eight input vriles nd nine output vriles. For one-to-one mpping eteen input vriles nd output vriles, it is neessr tht there should e onstrint tht redues the numer of independent output vriles. It is ovious tht the sum of the inident light poers on the PSDs is onstnt or rther the sme s the poer output of the lser soure if the ttenution t the mirror surfe is negligile. Thus, hih the numer of independent output vriles redues to eight. Φ +Φ +Φ = P, (4) To derive the model tht predits the PSDs output, ξ, from the mirror pose plus the lser em position, τ, e Pro. of SPIE Vol
5 (7) should (1) identif the shpe of the em spot, (2) otin the irrdine distriution, nd (3) lulte the mss nd enter of mss of the irrdine distriution ithin the spot for eh PSD. These proedures re to e desried in the folloings. Shpes of em spots on the detetors Figure 2 shos sitution, in hih suem refleted from M impinges on PSD A to form spot resemling piee of pie, P. In the figure, the dotted ellipse L is the imginr ross-setion of the lser em s if the lser em ere not split the three-fet mirror ut normll refleted plnr mirror hose pose is the sme s tht of M. S is the enter of the dotted ellipse P, l nd l L nd lso the projeted imge of the enter of the lser em. To edges of, re the projeted imges of the edges of the 3-fet mirror, l nd l. L inluding the r of P is defined s the projeted imge of the oundr of the lser em defined em dimeter φ l. Q, the intersetion of l nd l, is the point projeted from the top of the mirror, s shon in the figure. If the enter of lser em oinides ith the mirror top, then Q nd S re loted t the sme position. R is the light entroid of P, hih is the reding of the 2-D position of the em spot on PSD A. More detils on the predition of the P inluding R, Q nd S re referred to the previous literture [5, 6]. Intensit distriutions on the detetors First, e model the originl lser em of Gussin intensit distriution from soure hose diretion vetor is vl nd the position of soure point is. As desried ove, the diretion of the lser em is kept vertil. Thus, n e epressed s v l v = [0 0 1] l T (5) The intensit distriution ithin the em is distriuted in Gussin funtionl form given 2 8P 8r Ir () = ep 2 2 πφl φl. (6) Here, P represents the poer of the lser em, φ l the dimeter of the lser em, nd r the rdil distne from the enter is of the lser em to n point of interest. As shon in Figure 2, the irulr ross-setionl profile of the Gussin em is someht hnged into n elliptil one, hih depends on the ngle of inidene of the suem. The irrdine distriution ithin the elliptil em profile of P n e epressed s follos: p I( r) = I( r) p here is the unit surfe norml vetor of PSD A nd p = [ p p p ] T z is the diretion vetor of the suem 88 Pro. of SPIE Vol. 5264
6 A ith respet to o, hih n e otined ppling the refletion l [7] to the diretion vetor of the originl lser em. And it should e noted tht r is not the rdil distne s used in Eq. (6), ut someht different term, lled modified rdil distnes in this pper nd defined s follos: p r z 2 2 o 2 o 2 = ( ψ) + ( ) 2 2 ζ 2 2 p + p p + pz p (8) Mss nd enter of mss of the irrdine distriution As desried ove, the lotions ( ψ, ζ ), ( ψ, ζ ), nd ( ψ, ζ ) re the enters of mss of the irrdine distriution ithin P, P, nd P. For PSD A, ( ψ, ζ ) n e omputed s follos: I ( r ) d dz z I ( r ) d dz P P ψ =, ζ = I ( r) ddz I ( r) ddz P P At this stge, e hve ompleted modeling the reltionship eteen the 3-dimensionl pose, t, t, tz, γ, β, nd α, nd the PSD outputs, ( ψ, ζ, Φ ), ( ψ, ζ, Φ ), nd ( ψ, ζ, Φ ). The 2-dimensionl position of the lser em (, ) tkes prt ith in the input side of the model, hile it is not so importnt s others. When tul mesurement is performed ith the proposed sensor sstem, it is neessr to perform n inversion of the ove model, i.e., lultion of t, t, tz, γ, β, nd α ith given ( ψ, ζ, Φ ), ( ψ, ζ, Φ ), nd ( ψ, ζ, Φ ). The inversion is performed through numeril, the Neton s method [8], through hih e hve suessfull otined the solution, t, t, tz, γ, β, nd α, from given ( ψ, ζ, Φ ), ( ψ, ζ, Φ ), nd ( ψ, ζ, Φ ) in the eperiments to e eplined in setion 3. (9) 2.3 Eistene of the inverse funtion of the sensor model In this setion, the eistene nd uniqueness of the inverse funtion of J f is emined. For the emintion, inverse funtion theorem [9] is pplied. For the purpose, it should e shon tht there eists set of funtions { f1,, f8} tht is suset of the PSD outputs { ψ, ζ, Φ, ψ, ζ, Φ, ψ, ζ, Φ } stisfing ( f1,, f8) ( t,, ) τ f1 f1 ( τ) ( τ) t = 0 f1 f1 ( τ) ( τ) t (10) for ever τ in mesurement rnge. From (4), it is epeted tht one of Φ, Φ, nd Φ is redundnt for unique τ if the poer of lser em P is onstnt, hih is resonle ondition if e use some properl stilized lser soure. Here, Φ is omitted nd then to hek the ondition in Eq. (10) s follos: Pro. of SPIE Vol
7 ( ψ,, ζ) ( t,, ) τ = ψ ψ ( τ) ( τ) t ζ ζ ( τ) ( τ) t. (11) Figure 4 shos the determinnt vlues in Eq. (11) ith respet to the reltive distne eteen the lser em enter nd the verte of three-fet mirror ε l defined s ε = {( t ) + ( t ) }. (12) 2 2 1/2 l In the evlution, the sstem prmeters re given s in Figure 3 nd Tle 1 eept lser poer P nd em dimeter φ l. Here the lser poer P is ssumed to e 1mW nd the em dimeter φ l is to e 1mm. And τ, the 6-DOF pose of three-fet mirror nd 2-dimensionl position of the lser em, hs een hosen rndomlithin the mesurement rnge ondition. As shon in Figure 4, the join is negtive definite over the rnge, thus the sensor model J f is proved to hve unique inverse funtion ithin the mesurement rnge. The numer of points rndoml emined is over , hose neighorhoods re epeted to suffiientl over the input spe. Tle 1 Speifitions of the eperimentl sstem Components He-Ne Lser 3-fet mirror PSD Speifitions Poer 0.3 mw Bem dimeter 0.85 mm Bem orienttion t 3-fet mirror Vertil (onst.) Azimuth of surfe norml 45 Longitudinl distne eteen surfe normls 120 Surfe fltness λ/10 t nm Size of sensitive re 13 mm 13 mm Rdil distne from the sstem origin 250 mm Longitudinl distne eteen PSDs 120 Lout Orienttions See Figure 3 3 EXPERIMENTS In order to verif the priniple nd effetiveness of the proposed mesurement method, e hve implemented n eperimentl sstem nd performed series of eperiments. The onfigurtion of the eperimentl sstem is shon s in Figure 3 nd Tle 1. Figure 5 shos the tul pperne of the eperimentl sstem nd loser look of threefet mirror. As shon in setion 2.3, the proposed method n estimte the 6-DOF of three-fet mirror from the PSD outputs, regrdless of the 2-D position of the lser em, if the em illumintes the top of the mirror. In this setion, 90 Pro. of SPIE Vol. 5264
8 e present to kinds of vrition of the proposed method, one of hih uses lser em of fied position nd the other ontrols the lser em to trk the top of the mirror. The former is dvntgeous for fst ojets nd the ltter is for lrger mesurement rnge. lser soure mirror lser em 3-fet mirror PSD B PSD C 3-fet mirror 6-is stge PSD A Figure 5 Photogrph of the eperimentl sstem DOF pose estimtion ith fied lser em If e need to mesure some motion of smll rnge tht n e overed the ross-setionl re of the lser em, the lser em ould e etter to e fied t position hile its orienttion is lso fied s vertil. It is quite nturl to lote the lser em t the enter of the sensor sstem so tht (, ) = (0, 0). Figure 6 shos some mesurement rnges of the sensor sstem hen its lser em is fied t the enter, in hih eh plot presents mesurement rnge of some 2-DOF motion hile the rest 4-DOF omponents re set to zero. In the plot shoing the rnge of plnr motion, e n see the mesurement rnge is muh smller thn the lser em profile. This is euse s the top of the mirror moves outrd the em, some of the three PSDs ill get so ek inident light tht its signl-to-noise rtio gets too lo. Thus, the mesurement rnge in -diretion is limited the S/N rtio of the PSDs. On the other hnd, the other motions suh s z -trnsltion nd rottions re limited the size of sensitive re of PSD mm mrd mrd mm β (mrd) mrd α (mrd) mrd γ (mrd) β (mrd) Figure 6 Mesurement rnge ith fied lser em Pro. of SPIE Vol
9 Figure 7 - Figure 9 present some of our eperimentl results for single is motions nd multi-is motions, hile the errors in 6-DOF re lso presented. From the error plots, e n see tht the proposed method suessfull otins the trnsltionl nd rottionl displements from the PSD signls ith limited ross-il errors ε 0.15 ε 0.12 ε z 0.09 ε γ ε β ε α Mesurement error Mesurement error (mrd) Figure 7 Trnsltion in -is ε ε γ 15 ε ε β ε z 0.09 ε α α (mrd) Mesurement error Mesurement error (mrd) α (mrd) Figure 8 Rottion round z -is α (mrd) 0.20 α (mrd) Figure 9 Multi-DOF motions 92 Pro. of SPIE Vol. 5264
10 3.2 6-DOF pose estimtion ith em position djustment The proposed method n e esil modified to hieve lrger mesurement rnge in -diretion. The lser em soure is mounted on to-is trnsltion stge so tht the em n trk the top of three-fet mirror. In this method, e dopt feedk loop to djust the 2-D position of the lser em to three-fet mirror. The error signls inditing the offset eteen the enter of the lser em nd the top of three-fet mirror re otined ompring the inident light poer shres mong the PSDs. This is sed on tht (, ) ( t, t ) if Φ =Φ =Φ nd if γ, β, α < ε. (13) For emple, if ll of roll, pith, nd ngles re smller thn 10mrd, hih is degree, then e hve the trking error, the offset eteen the lser em enter nd the top of the mirror, less thn 0.89µm. For n tul feedk signl, e define some indies s follos: χ Φ +Φ os120 = +Φ os120 o o Φ +Φ +Φ, χ Φ sin120 = Φ sin120 o o Φ +Φ +Φ. (14) If χ is positive, e hve to djust the lser em in negtive -diretion, or if χ is negtive, the em should go in positive -diretion. And for χ, similr of djustment is used. And the mgnitude of χ nd χ represent the distne eteen the lser em enter nd the top of the mirror. Thus it n e used s the proportionl gin for P-ontrol lgorithm. Figure 10 shos the mesurement rnge in -diretion hieved through the mirror trking, in hih the sstem prmeters re the sme s those of the method using fied lser em s shon in Figure 3 nd Tle 1. As shon in the figure, the mesurement rnge in -diretion hs een remrkl enlrged. In this method, the mesurement rnge is not defined the S/N rtio of the PSDs ut the size of sensitive re of the PSDs mm mm Figure 10 Mesurement rnge in -plne motion ith em position djustment Figure 11 shos the eperimentl results for nd -diretion. As shon in the figure, the proposed method ith mirror trking hs suessfull mesured the motions in lrger rnge thn tht ith fied lser em, hile the Pro. of SPIE Vol
11 mesured rnge is restrited ithin smller rnge thn tht shon in Figure 10 due to some limittion of eperimentl hrdre. (mesurement, mm) 0.3 men -σ 0.2 +σ min. 0.1 m error men -σ +σ min. m (mesurement, mm) 0.3 men -σ 0.2 +σ min. 0.1 m error 0.03 men -σ +σ 0.02 min. m Figure 11 Eperimentl results for the motions in nd -diretion ith mirror trking 3.3 Sensor evlution In generl, sensors n e evluted their mesurement rnge nd resolution. The sensor presented in this pper hs not een optimized ut n eperimentl setup. Hoever, e n roughl understnd its possiilit nd ppliilit to n prolems tht e m hve to solve. Tle 2 shos the mesurement rnges nd resolutions of the eperimentl sstem onstruted in this pper. In the mesurement method proposed in this pper, mesurement rnge nd resolution in 6-DOF m not e simpl presented s shon in the tle. The numers listed in the tle n e regrded s n outline on its performne. The mesurement rnge in eh is hs een tken s the mimum distne in the diretion of interest, hile other es ere set to their origin. Thus the rnges m vrhen other es re elsehere. The resolutions in eh is lso m vrith respet to the 6-DOF pose of the mirror. Thus to otin the most representtive quntit out the resolutions for si es, e otin numer of repeted mesurement for eh point in 6-DOF spe, lulte the stndrd devitions for eh point, nd finll tke the mimum of the stndrd devitions for eh is. The resolutions hve een defined, in this pper, s the tie s the mimum stndrd devitions for eh is, hih is, in other ord, root-men-squred error. 94 Pro. of SPIE Vol. 5264
12 Tle 2 Summr of eperimentl results z γ β α Rnge (mm, mrd) 0.36 / / Resolution (µm, µrd) Mesurement rnge hieved mirror trking, otherise fied lser em 4 CONCLUSIONS The proposed priniple hs een proved to e vlid in oth theoretil nd eperimentl s. In theoretil nlsis, e onstruted sensor model nd emined it hether its Join mtri is nonsingulr. And in eperiments, to different pprohes, depending on hether the position of the lser em trks the mirror or not, hve een emined. The one hose lser em is not ontrolled hs so tin mesurement rnge for in-plne motions tht it n over t most 0.25mm 0.25mm squre re ut dvntgeous to fst ojets of round 3kHz in ndidth. And the other, of hih the lser em trks the mirror, hs muh lrger mesurement rnge overing over 8mm 8mm for motions in -diretion ut not suitle for fst ojets euse it needs mehnil servoing. The mesurement preisions hieved in our eperiments re t most 2.8µm for trnsltion nd 13.0µrd for rottion. REFERENCES 1 L. M. Smith nd C. C. Doson, Asolute displement mesurement using modultion of the spetrum of hite light in Mihelson interferometer, Appl. Opt., Vol. 28, pp , S. Hosoe, Lser interferometri sstem for displement mesurement ith high preision, Nnotehnolog, Vol. 2, pp , J. R. Bell nd S. J. Rotherg, Lser virometers nd ontting trnsduers, trget rottion nd si degree-offreedom virtion: ht do e rell mesure? J. Sound Vi., Vol. 237, No. 2, pp , N. Lee, Y. Ci, nd A. Jonej, High-resolution multidimensionl displement monitoring sstem, Opt. Eng., Vol. 36, No. 8, pp , W. S. Prk, Mesurement of 6-dof motions of rigid odies through splitting lser em, Ph.D. thesis, Kore Advned Institute of Siene nd Tehnolog, W. S. Prk nd H. S. Cho, Mesurement of fine 6-degrees-of-freedom displement of rigid odies through splitting lser em: eperimentl investigtion, Optil Engineering, Vol. 41, No.4, pp , April M. Bss, E. W. Strlnd, D. R. Willims, W. L. Wolfe, Hndook of Optis, 2nd Ed., vol. 1, MGr-Hill, W. H. Press, S. A. Teukolsk, W. T. Vetterling, nd B. P. Flnner, Numeril Reipes in C, 2nd Ed., Cmridge Universit Press, Jerrold E. Mrden nd Anthorn J. Trom, Vetor lulus, 2 nd Ed., Freemn, Pro. of SPIE Vol
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL. Part 1. What and Why.?
 SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
Reflection Property of a Hyperbola
 Refletion Propert of Hperol Prefe The purpose of this pper is to prove nltill nd to illustrte geometrill the propert of hperol wherein r whih emntes outside the onvit of the hperol, tht is, etween the
Refletion Propert of Hperol Prefe The purpose of this pper is to prove nltill nd to illustrte geometrill the propert of hperol wherein r whih emntes outside the onvit of the hperol, tht is, etween the
Comparing the Pre-image and Image of a Dilation
 hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
The Ellipse. is larger than the other.
 The Ellipse Appolonius of Perg (5 B.C.) disovered tht interseting right irulr one ll the w through with plne slnted ut is not perpendiulr to the is, the intersetion provides resulting urve (oni setion)
The Ellipse Appolonius of Perg (5 B.C.) disovered tht interseting right irulr one ll the w through with plne slnted ut is not perpendiulr to the is, the intersetion provides resulting urve (oni setion)
GM1 Consolidation Worksheet
 Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF AN ISOLATED MASS WITH SIX DEGREES OF FREEDOM Revision G
 B Tom Irvine Emil: tom@virtiondt.om Jnur 8, 3 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF AN ISOLATED MASS WITH SIX DEGREES OF FREEDOM Revision G Introdution An vionis omponent m e mounted with isoltor grommets, whih t s soft
B Tom Irvine Emil: tom@virtiondt.om Jnur 8, 3 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF AN ISOLATED MASS WITH SIX DEGREES OF FREEDOM Revision G Introdution An vionis omponent m e mounted with isoltor grommets, whih t s soft
THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
 MD THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY CA CB C Coordintes of point in spe There re infinite numer of points in spe We wnt to identif eh nd ever point of spe with the help of three mutull perpendiulr oordintes es
MD THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY CA CB C Coordintes of point in spe There re infinite numer of points in spe We wnt to identif eh nd ever point of spe with the help of three mutull perpendiulr oordintes es
Reference : Croft & Davison, Chapter 12, Blocks 1,2. A matrix ti is a rectangular array or block of numbers usually enclosed in brackets.
 I MATRIX ALGEBRA INTRODUCTION TO MATRICES Referene : Croft & Dvison, Chpter, Blos, A mtri ti is retngulr rr or lo of numers usull enlosed in rets. A m n mtri hs m rows nd n olumns. Mtri Alger Pge If the
I MATRIX ALGEBRA INTRODUCTION TO MATRICES Referene : Croft & Dvison, Chpter, Blos, A mtri ti is retngulr rr or lo of numers usull enlosed in rets. A m n mtri hs m rows nd n olumns. Mtri Alger Pge If the
12.4 Similarity in Right Triangles
 Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
Matrices SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & BUILT ENVIRONMENT. Mathematics (c) 1. Definition of a Matrix
 tries Definition of tri mtri is regulr rry of numers enlosed inside rkets SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & UIL ENVIRONEN Emple he following re ll mtries: ), ) 9, themtis ), d) tries Definition of tri Size of tri
tries Definition of tri mtri is regulr rry of numers enlosed inside rkets SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & UIL ENVIRONEN Emple he following re ll mtries: ), ) 9, themtis ), d) tries Definition of tri Size of tri
Worksheet #2 Math 285 Name: 1. Solve the following systems of linear equations. The prove that the solutions forms a subspace of
 Worsheet # th Nme:. Sole the folloing sstems of liner equtions. he proe tht the solutions forms suspe of ) ). Find the neessr nd suffiient onditions of ll onstnts for the eistene of solution to the sstem:.
Worsheet # th Nme:. Sole the folloing sstems of liner equtions. he proe tht the solutions forms suspe of ) ). Find the neessr nd suffiient onditions of ll onstnts for the eistene of solution to the sstem:.
Activities. 4.1 Pythagoras' Theorem 4.2 Spirals 4.3 Clinometers 4.4 Radar 4.5 Posting Parcels 4.6 Interlocking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes and Solutions
 MEP: Demonstrtion Projet UNIT 4: Trigonometry UNIT 4 Trigonometry tivities tivities 4. Pythgors' Theorem 4.2 Spirls 4.3 linometers 4.4 Rdr 4.5 Posting Prels 4.6 Interloking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes nd
MEP: Demonstrtion Projet UNIT 4: Trigonometry UNIT 4 Trigonometry tivities tivities 4. Pythgors' Theorem 4.2 Spirls 4.3 linometers 4.4 Rdr 4.5 Posting Prels 4.6 Interloking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes nd
m m m m m m m m P m P m ( ) m m P( ) ( ). The o-ordinte of the point P( ) dividing the line segment joining the two points ( ) nd ( ) eternll in the r
 CO-ORDINTE GEOMETR II I Qudrnt Qudrnt (-.+) (++) X X - - - 0 - III IV Qudrnt - Qudrnt (--) - (+-) Region CRTESIN CO-ORDINTE SSTEM : Retngulr Co-ordinte Sstem : Let X' OX nd 'O e two mutull perpendiulr
CO-ORDINTE GEOMETR II I Qudrnt Qudrnt (-.+) (++) X X - - - 0 - III IV Qudrnt - Qudrnt (--) - (+-) Region CRTESIN CO-ORDINTE SSTEM : Retngulr Co-ordinte Sstem : Let X' OX nd 'O e two mutull perpendiulr
Parabola and Catenary Equations for Conductor Height Calculation
 ELECTROTEHNICĂ, ELECTRONICĂ, AUTOMATICĂ, 6 (), nr. 3 9 Prbol nd Ctenr Equtions for Condutor Height Clultion Alen HATIBOVIC Abstrt This pper presents new equtions for ondutor height lultion bsed on the
ELECTROTEHNICĂ, ELECTRONICĂ, AUTOMATICĂ, 6 (), nr. 3 9 Prbol nd Ctenr Equtions for Condutor Height Clultion Alen HATIBOVIC Abstrt This pper presents new equtions for ondutor height lultion bsed on the
1.3 SCALARS AND VECTORS
 Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
Due to gravity and wind load, the post supporting the sign shown is subjected simultaneously to compression, bending, and torsion.
 ue to grvit nd wind lod, the post supporting the sign shown is sujeted simultneousl to ompression, ending, nd torsion. In this hpter ou will lern to determine the stresses reted suh omined lodings in strutures
ue to grvit nd wind lod, the post supporting the sign shown is sujeted simultneousl to ompression, ending, nd torsion. In this hpter ou will lern to determine the stresses reted suh omined lodings in strutures
GRAND PLAN. Visualizing Quaternions. I: Fundamentals of Quaternions. Andrew J. Hanson. II: Visualizing Quaternion Geometry. III: Quaternion Frames
 Visuliing Quternions Andrew J. Hnson Computer Siene Deprtment Indin Universit Siggrph Tutoril GRAND PLAN I: Fundmentls of Quternions II: Visuliing Quternion Geometr III: Quternion Frmes IV: Clifford Algers
Visuliing Quternions Andrew J. Hnson Computer Siene Deprtment Indin Universit Siggrph Tutoril GRAND PLAN I: Fundmentls of Quternions II: Visuliing Quternion Geometr III: Quternion Frmes IV: Clifford Algers
Integration. antidifferentiation
 9 Integrtion 9A Antidifferentition 9B Integrtion of e, sin ( ) nd os ( ) 9C Integrtion reognition 9D Approimting res enlosed funtions 9E The fundmentl theorem of integrl lulus 9F Signed res 9G Further
9 Integrtion 9A Antidifferentition 9B Integrtion of e, sin ( ) nd os ( ) 9C Integrtion reognition 9D Approimting res enlosed funtions 9E The fundmentl theorem of integrl lulus 9F Signed res 9G Further
m A 1 1 A ! and AC 6
 REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
H (2a, a) (u 2a) 2 (E) Show that u v 4a. Explain why this implies that u v 4a, with equality if and only u a if u v 2a.
 Chpter Review 89 IGURE ol hord GH of the prol 4. G u v H (, ) (A) Use the distne formul to show tht u. (B) Show tht G nd H lie on the line m, where m ( )/( ). (C) Solve m for nd sustitute in 4, otining
Chpter Review 89 IGURE ol hord GH of the prol 4. G u v H (, ) (A) Use the distne formul to show tht u. (B) Show tht G nd H lie on the line m, where m ( )/( ). (C) Solve m for nd sustitute in 4, otining
Ellipses. The second type of conic is called an ellipse.
 Ellipses The seond type of oni is lled n ellipse. Definition of Ellipse An ellipse is the set of ll points (, y) in plne, the sum of whose distnes from two distint fied points (foi) is onstnt. (, y) d
Ellipses The seond type of oni is lled n ellipse. Definition of Ellipse An ellipse is the set of ll points (, y) in plne, the sum of whose distnes from two distint fied points (foi) is onstnt. (, y) d
Generalization of 2-Corner Frequency Source Models Used in SMSIM
 Generliztion o 2-Corner Frequeny Soure Models Used in SMSIM Dvid M. Boore 26 Mrh 213, orreted Figure 1 nd 2 legends on 5 April 213, dditionl smll orretions on 29 My 213 Mny o the soure spetr models ville
Generliztion o 2-Corner Frequeny Soure Models Used in SMSIM Dvid M. Boore 26 Mrh 213, orreted Figure 1 nd 2 legends on 5 April 213, dditionl smll orretions on 29 My 213 Mny o the soure spetr models ville
EXTENSION OF THE GCD STAR OF DAVID THEOREM TO MORE THAN TWO GCDS CALVIN LONG AND EDWARD KORNTVED
 EXTENSION OF THE GCD STAR OF DAVID THEOREM TO MORE THAN TWO GCDS CALVIN LONG AND EDWARD KORNTVED Astrt. The GCD Str of Dvi Theorem n the numerous ppers relte to it hve lrgel een evote to shoing the equlit
EXTENSION OF THE GCD STAR OF DAVID THEOREM TO MORE THAN TWO GCDS CALVIN LONG AND EDWARD KORNTVED Astrt. The GCD Str of Dvi Theorem n the numerous ppers relte to it hve lrgel een evote to shoing the equlit
Novel Fiber-Optical Refractometric Sensor Employing Hemispherically-Shaped Detection Element
 Novel Fier-Optil Refrtometri Sensor Employing Hemispherilly-Shped Detetion Element SERGEI KHOTIAINTSEV, VLADIMIR SVIRID Deprtment of Eletril Engineering, Fulty of Engineering Ntionl Autonomous University
Novel Fier-Optil Refrtometri Sensor Employing Hemispherilly-Shped Detetion Element SERGEI KHOTIAINTSEV, VLADIMIR SVIRID Deprtment of Eletril Engineering, Fulty of Engineering Ntionl Autonomous University
April 8, 2017 Math 9. Geometry. Solving vector problems. Problem. Prove that if vectors and satisfy, then.
 pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
Chapter Gauss Quadrature Rule of Integration
 Chpter 7. Guss Qudrture Rule o Integrtion Ater reding this hpter, you should e le to:. derive the Guss qudrture method or integrtion nd e le to use it to solve prolems, nd. use Guss qudrture method to
Chpter 7. Guss Qudrture Rule o Integrtion Ater reding this hpter, you should e le to:. derive the Guss qudrture method or integrtion nd e le to use it to solve prolems, nd. use Guss qudrture method to
for all x in [a,b], then the area of the region bounded by the graphs of f and g and the vertical lines x = a and x = b is b [ ( ) ( )] A= f x g x dx
![for all x in [a,b], then the area of the region bounded by the graphs of f and g and the vertical lines x = a and x = b is b [ ( ) ( )] A= f x g x dx for all x in [a,b], then the area of the region bounded by the graphs of f and g and the vertical lines x = a and x = b is b [ ( ) ( )] A= f x g x dx](/thumbs/74/70408252.jpg) Applitions of Integrtion Are of Region Between Two Curves Ojetive: Fin the re of region etween two urves using integrtion. Fin the re of region etween interseting urves using integrtion. Desrie integrtion
Applitions of Integrtion Are of Region Between Two Curves Ojetive: Fin the re of region etween two urves using integrtion. Fin the re of region etween interseting urves using integrtion. Desrie integrtion
6.5 Plate Problems in Rectangular Coordinates
 6.5 lte rolems in Rectngulr Coordintes In this section numer of importnt plte prolems ill e emined ug Crte coordintes. 6.5. Uniform ressure producing Bending in One irection Consider first the cse of plte
6.5 lte rolems in Rectngulr Coordintes In this section numer of importnt plte prolems ill e emined ug Crte coordintes. 6.5. Uniform ressure producing Bending in One irection Consider first the cse of plte
A Lower Bound for the Length of a Partial Transversal in a Latin Square, Revised Version
 A Lower Bound for the Length of Prtil Trnsversl in Ltin Squre, Revised Version Pooy Htmi nd Peter W. Shor Deprtment of Mthemtil Sienes, Shrif University of Tehnology, P.O.Bo 11365-9415, Tehrn, Irn Deprtment
A Lower Bound for the Length of Prtil Trnsversl in Ltin Squre, Revised Version Pooy Htmi nd Peter W. Shor Deprtment of Mthemtil Sienes, Shrif University of Tehnology, P.O.Bo 11365-9415, Tehrn, Irn Deprtment
Exercise sheet 6: Solutions
 Eerise sheet 6: Solutions Cvet emptor: These re merel etended hints, rther thn omplete solutions. 1. If grph G hs hromti numer k > 1, prove tht its verte set n e prtitioned into two nonempt sets V 1 nd
Eerise sheet 6: Solutions Cvet emptor: These re merel etended hints, rther thn omplete solutions. 1. If grph G hs hromti numer k > 1, prove tht its verte set n e prtitioned into two nonempt sets V 1 nd
5. Every rational number have either terminating or repeating (recurring) decimal representation.
 CHAPTER NUMBER SYSTEMS Points to Rememer :. Numer used for ounting,,,,... re known s Nturl numers.. All nturl numers together with zero i.e. 0,,,,,... re known s whole numers.. All nturl numers, zero nd
CHAPTER NUMBER SYSTEMS Points to Rememer :. Numer used for ounting,,,,... re known s Nturl numers.. All nturl numers together with zero i.e. 0,,,,,... re known s whole numers.. All nturl numers, zero nd
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1. Given a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
 1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
Lecture Notes No. 10
 2.6 System Identifition, Estimtion, nd Lerning Leture otes o. Mrh 3, 26 6 Model Struture of Liner ime Invrint Systems 6. Model Struture In representing dynmil system, the first step is to find n pproprite
2.6 System Identifition, Estimtion, nd Lerning Leture otes o. Mrh 3, 26 6 Model Struture of Liner ime Invrint Systems 6. Model Struture In representing dynmil system, the first step is to find n pproprite
Green s Theorem. (2x e y ) da. (2x e y ) dx dy. x 2 xe y. (1 e y ) dy. y=1. = y e y. y=0. = 2 e
 Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
Forces on curved surfaces Buoyant force Stability of floating and submerged bodies
 Stti Surfe ores Stti Surfe ores 8m wter hinge? 4 m ores on plne res ores on urved surfes Buont fore Stbilit of floting nd submerged bodies ores on Plne res Two tpes of problems Horizontl surfes (pressure
Stti Surfe ores Stti Surfe ores 8m wter hinge? 4 m ores on plne res ores on urved surfes Buont fore Stbilit of floting nd submerged bodies ores on Plne res Two tpes of problems Horizontl surfes (pressure
50 AMC Lectures Problem Book 2 (36) Substitution Method
 0 AMC Letures Prolem Book Sustitution Metho PROBLEMS Prolem : Solve for rel : 9 + 99 + 9 = Prolem : Solve for rel : 0 9 8 8 Prolem : Show tht if 8 Prolem : Show tht + + if rel numers,, n stisf + + = Prolem
0 AMC Letures Prolem Book Sustitution Metho PROBLEMS Prolem : Solve for rel : 9 + 99 + 9 = Prolem : Solve for rel : 0 9 8 8 Prolem : Show tht if 8 Prolem : Show tht + + if rel numers,, n stisf + + = Prolem
KINEMATICS OF RIGID BODIES
 KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES Introduction In rigid body kinemtics, e use the reltionships governing the displcement, velocity nd ccelertion, but must lso ccount for the rottionl motion of the body. Description
KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES Introduction In rigid body kinemtics, e use the reltionships governing the displcement, velocity nd ccelertion, but must lso ccount for the rottionl motion of the body. Description
Appendix C Partial discharges. 1. Relationship Between Measured and Actual Discharge Quantities
 Appendi Prtil dishrges. Reltionship Between Mesured nd Atul Dishrge Quntities A dishrging smple my e simply represented y the euilent iruit in Figure. The pplied lternting oltge V is inresed until the
Appendi Prtil dishrges. Reltionship Between Mesured nd Atul Dishrge Quntities A dishrging smple my e simply represented y the euilent iruit in Figure. The pplied lternting oltge V is inresed until the
are coplanar. ˆ ˆ ˆ and iˆ
 SML QUSTION Clss XII Mthemtis Time llowed: hrs Mimum Mrks: Generl Instrutions: i ll questions re ompulsor ii The question pper onsists of 6 questions divided into three Setions, B nd C iii Question No
SML QUSTION Clss XII Mthemtis Time llowed: hrs Mimum Mrks: Generl Instrutions: i ll questions re ompulsor ii The question pper onsists of 6 questions divided into three Setions, B nd C iii Question No
] dx (3) = [15x] 2 0
![] dx (3) = [15x] 2 0 ] dx (3) = [15x] 2 0](/thumbs/80/81916477.jpg) Leture 6. Double Integrls nd Volume on etngle Welome to Cl IV!!!! These notes re designed to be redble nd desribe the w I will eplin the mteril in lss. Hopefull the re thorough, but it s good ide to hve
Leture 6. Double Integrls nd Volume on etngle Welome to Cl IV!!!! These notes re designed to be redble nd desribe the w I will eplin the mteril in lss. Hopefull the re thorough, but it s good ide to hve
Learning Objectives of Module 2 (Algebra and Calculus) Notes:
 67 Lerning Ojetives of Module (Alger nd Clulus) Notes:. Lerning units re grouped under three res ( Foundtion Knowledge, Alger nd Clulus ) nd Further Lerning Unit.. Relted lerning ojetives re grouped under
67 Lerning Ojetives of Module (Alger nd Clulus) Notes:. Lerning units re grouped under three res ( Foundtion Knowledge, Alger nd Clulus ) nd Further Lerning Unit.. Relted lerning ojetives re grouped under
(h+ ) = 0, (3.1) s = s 0, (3.2)
 Chpter 3 Nozzle Flow Qusistedy idel gs flow in pipes For the lrge vlues of the Reynolds number typilly found in nozzles, the flow is idel. For stedy opertion with negligible body fores the energy nd momentum
Chpter 3 Nozzle Flow Qusistedy idel gs flow in pipes For the lrge vlues of the Reynolds number typilly found in nozzles, the flow is idel. For stedy opertion with negligible body fores the energy nd momentum
Unit-VII: Linear Algebra-I. To show what are the matrices, why they are useful, how they are classified as various types and how they are solved.
 Unit-VII: Liner lger-i Purpose of lession : To show wht re the mtries, wh the re useful, how the re lssified s vrious tpes nd how the re solved. Introdution: Mtries is powerful tool of modern Mthemtis
Unit-VII: Liner lger-i Purpose of lession : To show wht re the mtries, wh the re useful, how the re lssified s vrious tpes nd how the re solved. Introdution: Mtries is powerful tool of modern Mthemtis
Plate Theory. Section 11: PLATE BENDING ELEMENTS
 Section : PLATE BENDING ELEMENTS Plte Theor A plte is structurl element hose mid surfce lies in flt plne. The dimension in the direction norml to the plne is referred to s the thickness of the plte. A
Section : PLATE BENDING ELEMENTS Plte Theor A plte is structurl element hose mid surfce lies in flt plne. The dimension in the direction norml to the plne is referred to s the thickness of the plte. A
Similar Right Triangles
 Geometry V1.noteook Ferury 09, 2012 Similr Right Tringles Cn I identify similr tringles in right tringle with the ltitude? Cn I identify the proportions in right tringles? Cn I use the geometri mens theorems
Geometry V1.noteook Ferury 09, 2012 Similr Right Tringles Cn I identify similr tringles in right tringle with the ltitude? Cn I identify the proportions in right tringles? Cn I use the geometri mens theorems
6.5 Improper integrals
 Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
CHENG Chun Chor Litwin The Hong Kong Institute of Education
 PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
 THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM The Pythgoren Theorem is one of the most well-known nd widely used theorems in mthemtis. We will first look t n informl investigtion of the Pythgoren Theorem, nd then pply this
THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM The Pythgoren Theorem is one of the most well-known nd widely used theorems in mthemtis. We will first look t n informl investigtion of the Pythgoren Theorem, nd then pply this
Vibration with more (than one) degrees of freedom (DOF) a) longitudinal vibration with 3 DOF. b) rotational (torsional) vibration with 3 DOF
 irtion with ore (thn one) degrees of freedo (DOF) ) longitudinl irtion with DOF ) rottionl (torsionl) irtion with DOF ) ending irtion with DOF d) the D (plnr) irtion of the fleil supported rigid od with
irtion with ore (thn one) degrees of freedo (DOF) ) longitudinl irtion with DOF ) rottionl (torsionl) irtion with DOF ) ending irtion with DOF d) the D (plnr) irtion of the fleil supported rigid od with
Structural Systems. Structural Engineering
 101-305 Theor of Strutures 1-1 Instrutor: ST, P, J nd TPS Struturl Engineering 101-305 Theor of Strutures 1 - Instrutor: ST, P, J nd TPS Struturl Sstems Struture the tion of building: ONSTUTION Struturl
101-305 Theor of Strutures 1-1 Instrutor: ST, P, J nd TPS Struturl Engineering 101-305 Theor of Strutures 1 - Instrutor: ST, P, J nd TPS Struturl Sstems Struture the tion of building: ONSTUTION Struturl
2. There are an infinite number of possible triangles, all similar, with three given angles whose sum is 180.
 SECTION 8-1 11 CHAPTER 8 Setion 8 1. There re n infinite numer of possile tringles, ll similr, with three given ngles whose sum is 180. 4. If two ngles α nd β of tringle re known, the third ngle n e found
SECTION 8-1 11 CHAPTER 8 Setion 8 1. There re n infinite numer of possile tringles, ll similr, with three given ngles whose sum is 180. 4. If two ngles α nd β of tringle re known, the third ngle n e found
Applications of Definite Integral
 Chpter 5 Applitions of Definite Integrl 5.1 Are Between Two Curves In this setion we use integrls to find res of regions tht lie between the grphs of two funtions. Consider the region tht lies between
Chpter 5 Applitions of Definite Integrl 5.1 Are Between Two Curves In this setion we use integrls to find res of regions tht lie between the grphs of two funtions. Consider the region tht lies between
SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION OF Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 FILMS
 SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION OF Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 FILMS IN-SITU PROBING OF DOMAIN POLING IN Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 THIN FILMS BY OPTICAL SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION YANIV BARAD, VENKATRAMAN GOPALAN Mterils Reserh Lortory
SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION OF Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 FILMS IN-SITU PROBING OF DOMAIN POLING IN Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 THIN FILMS BY OPTICAL SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION YANIV BARAD, VENKATRAMAN GOPALAN Mterils Reserh Lortory
8 THREE PHASE A.C. CIRCUITS
 8 THREE PHSE.. IRUITS The signls in hpter 7 were sinusoidl lternting voltges nd urrents of the so-lled single se type. n emf of suh type n e esily generted y rotting single loop of ondutor (or single winding),
8 THREE PHSE.. IRUITS The signls in hpter 7 were sinusoidl lternting voltges nd urrents of the so-lled single se type. n emf of suh type n e esily generted y rotting single loop of ondutor (or single winding),
Applications of Definite Integral
 Chpter 5 Applitions of Definite Integrl 5.1 Are Between Two Curves In this setion we use integrls to find res of regions tht lie between the grphs of two funtions. Consider the region tht lies between
Chpter 5 Applitions of Definite Integrl 5.1 Are Between Two Curves In this setion we use integrls to find res of regions tht lie between the grphs of two funtions. Consider the region tht lies between
Lecture Summaries for Multivariable Integral Calculus M52B
 These leture summries my lso be viewed online by liking the L ion t the top right of ny leture sreen. Leture Summries for Multivrible Integrl Clulus M52B Chpter nd setion numbers refer to the 6th edition.
These leture summries my lso be viewed online by liking the L ion t the top right of ny leture sreen. Leture Summries for Multivrible Integrl Clulus M52B Chpter nd setion numbers refer to the 6th edition.
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals
 AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
Algorithms & Data Structures Homework 8 HS 18 Exercise Class (Room & TA): Submitted by: Peer Feedback by: Points:
 Eidgenössishe Tehnishe Hohshule Zürih Eole polytehnique fédérle de Zurih Politenio federle di Zurigo Federl Institute of Tehnology t Zurih Deprtement of Computer Siene. Novemer 0 Mrkus Püshel, Dvid Steurer
Eidgenössishe Tehnishe Hohshule Zürih Eole polytehnique fédérle de Zurih Politenio federle di Zurigo Federl Institute of Tehnology t Zurih Deprtement of Computer Siene. Novemer 0 Mrkus Püshel, Dvid Steurer
The Trapezoidal Rule
 _.qd // : PM Pge 9 SECTION. Numericl Integrtion 9 f Section. The re of the region cn e pproimted using four trpezoids. Figure. = f( ) f( ) n The re of the first trpezoid is f f n. Figure. = Numericl Integrtion
_.qd // : PM Pge 9 SECTION. Numericl Integrtion 9 f Section. The re of the region cn e pproimted using four trpezoids. Figure. = f( ) f( ) n The re of the first trpezoid is f f n. Figure. = Numericl Integrtion
Math 32B Discussion Session Week 8 Notes February 28 and March 2, f(b) f(a) = f (t)dt (1)
 Green s Theorem Mth 3B isussion Session Week 8 Notes Februry 8 nd Mrh, 7 Very shortly fter you lerned how to integrte single-vrible funtions, you lerned the Fundmentl Theorem of lulus the wy most integrtion
Green s Theorem Mth 3B isussion Session Week 8 Notes Februry 8 nd Mrh, 7 Very shortly fter you lerned how to integrte single-vrible funtions, you lerned the Fundmentl Theorem of lulus the wy most integrtion
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
 PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
Calculus Cheat Sheet. Integrals Definitions. where F( x ) is an anti-derivative of f ( x ). Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. dx = f x dx g x dx
 Clulus Chet Sheet Integrls Definitions Definite Integrl: Suppose f ( ) is ontinuous Anti-Derivtive : An nti-derivtive of f ( ) on [, ]. Divide [, ] into n suintervls of is funtion, F( ), suh tht F = f.
Clulus Chet Sheet Integrls Definitions Definite Integrl: Suppose f ( ) is ontinuous Anti-Derivtive : An nti-derivtive of f ( ) on [, ]. Divide [, ] into n suintervls of is funtion, F( ), suh tht F = f.
Plate Theory. Section 13: PLATE BENDING ELEMENTS
 Section : PLATE BENDING ELEENTS Wshkeic College of Engineering Plte Theor A plte is structurl element hose mid surfce lies in flt plne. The dimension in the direction norml to the plne is referred to s
Section : PLATE BENDING ELEENTS Wshkeic College of Engineering Plte Theor A plte is structurl element hose mid surfce lies in flt plne. The dimension in the direction norml to the plne is referred to s
SIMPLE NONLINEAR GRAPHS
 S i m p l e N o n l i n e r G r p h s SIMPLE NONLINEAR GRAPHS www.mthletis.om.u Simple SIMPLE Nonliner NONLINEAR Grphs GRAPHS Liner equtions hve the form = m+ where the power of (n ) is lws. The re lle
S i m p l e N o n l i n e r G r p h s SIMPLE NONLINEAR GRAPHS www.mthletis.om.u Simple SIMPLE Nonliner NONLINEAR Grphs GRAPHS Liner equtions hve the form = m+ where the power of (n ) is lws. The re lle
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q5 of Paper 2
 Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
This enables us to also express rational numbers other than natural numbers, for example:
 Overview Study Mteril Business Mthemtis 05-06 Alger The Rel Numers The si numers re,,3,4, these numers re nturl numers nd lso lled positive integers. The positive integers, together with the negtive integers
Overview Study Mteril Business Mthemtis 05-06 Alger The Rel Numers The si numers re,,3,4, these numers re nturl numers nd lso lled positive integers. The positive integers, together with the negtive integers
Can one hear the shape of a drum?
 Cn one her the shpe of drum? After M. K, C. Gordon, D. We, nd S. Wolpert Corentin Lén Università Degli Studi di Torino Diprtimento di Mtemti Giuseppe Peno UNITO Mthemtis Ph.D Seminrs Mondy 23 My 2016 Motivtion:
Cn one her the shpe of drum? After M. K, C. Gordon, D. We, nd S. Wolpert Corentin Lén Università Degli Studi di Torino Diprtimento di Mtemti Giuseppe Peno UNITO Mthemtis Ph.D Seminrs Mondy 23 My 2016 Motivtion:
Chapter 3. Vector Spaces. 3.1 Images and Image Arithmetic
 Chpter 3 Vetor Spes In Chpter 2, we sw tht the set of imges possessed numer of onvenient properties. It turns out tht ny set tht possesses similr onvenient properties n e nlyzed in similr wy. In liner
Chpter 3 Vetor Spes In Chpter 2, we sw tht the set of imges possessed numer of onvenient properties. It turns out tht ny set tht possesses similr onvenient properties n e nlyzed in similr wy. In liner
8.6 The Hyperbola. and F 2. is a constant. P F 2. P =k The two fixed points, F 1. , are called the foci of the hyperbola. The line segments F 1
 8. The Hperol Some ships nvigte using rdio nvigtion sstem clled LORAN, which is n cronm for LOng RAnge Nvigtion. A ship receives rdio signls from pirs of trnsmitting sttions tht send signls t the sme time.
8. The Hperol Some ships nvigte using rdio nvigtion sstem clled LORAN, which is n cronm for LOng RAnge Nvigtion. A ship receives rdio signls from pirs of trnsmitting sttions tht send signls t the sme time.
ECE Microwave Engineering. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 8. Waveguides Part 5: Coaxial Cable
 ECE 5317-6351 Mirowve Engineering Fll 17 Prof. Dvid R. Jkson Dept. of ECE Notes 8 Wveguides Prt 5: Coil Cle 1 Coil Line: TEM Mode To find the TEM mode fields, we need to solve: ( ρφ) Φ, ; Φ ( ) V Φ ( )
ECE 5317-6351 Mirowve Engineering Fll 17 Prof. Dvid R. Jkson Dept. of ECE Notes 8 Wveguides Prt 5: Coil Cle 1 Coil Line: TEM Mode To find the TEM mode fields, we need to solve: ( ρφ) Φ, ; Φ ( ) V Φ ( )
KINEMATICS OF RIGID BODIES
 KINEMTICS OF RIGI OIES Introduction In rigid body kinemtics, e use the reltionships governing the displcement, velocity nd ccelertion, but must lso ccount for the rottionl motion of the body. escription
KINEMTICS OF RIGI OIES Introduction In rigid body kinemtics, e use the reltionships governing the displcement, velocity nd ccelertion, but must lso ccount for the rottionl motion of the body. escription
THE INFLUENCE OF MODEL RESOLUTION ON AN EXPRESSION OF THE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER IN A SINGLE-COLUMN MODEL
 THE INFLUENCE OF MODEL RESOLUTION ON AN EXPRESSION OF THE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER IN A SINGLE-COLUMN MODEL P3.1 Kot Iwmur*, Hiroto Kitgw Jpn Meteorologil Ageny 1. INTRODUCTION Jpn Meteorologil Ageny
THE INFLUENCE OF MODEL RESOLUTION ON AN EXPRESSION OF THE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER IN A SINGLE-COLUMN MODEL P3.1 Kot Iwmur*, Hiroto Kitgw Jpn Meteorologil Ageny 1. INTRODUCTION Jpn Meteorologil Ageny
The Double Integral. The Riemann sum of a function f (x; y) over this partition of [a; b] [c; d] is. f (r j ; t k ) x j y k
![The Double Integral. The Riemann sum of a function f (x; y) over this partition of [a; b] [c; d] is. f (r j ; t k ) x j y k The Double Integral. The Riemann sum of a function f (x; y) over this partition of [a; b] [c; d] is. f (r j ; t k ) x j y k](/thumbs/86/94790710.jpg) The Double Integrl De nition of the Integrl Iterted integrls re used primrily s tool for omputing double integrls, where double integrl is n integrl of f (; y) over region : In this setion, we de ne double
The Double Integrl De nition of the Integrl Iterted integrls re used primrily s tool for omputing double integrls, where double integrl is n integrl of f (; y) over region : In this setion, we de ne double
Iowa Training Systems Trial Snus Hill Winery Madrid, IA
 Iow Trining Systems Tril Snus Hill Winery Mdrid, IA Din R. Cohrn nd Gil R. Nonneke Deprtment of Hortiulture, Iow Stte University Bkground nd Rtionle: Over the lst severl yers, five sttes hve een evluting
Iow Trining Systems Tril Snus Hill Winery Mdrid, IA Din R. Cohrn nd Gil R. Nonneke Deprtment of Hortiulture, Iow Stte University Bkground nd Rtionle: Over the lst severl yers, five sttes hve een evluting
Polyphase Systems. Objectives 23.1 INTRODUCTION
 Polyphse Systems 23 Ojetives eome fmilir with the opertion of threephse genertor nd the mgnitude nd phse reltionship etween the three phse voltges. e le to lulte the voltges nd urrents for three-phse Y-onneted
Polyphse Systems 23 Ojetives eome fmilir with the opertion of threephse genertor nd the mgnitude nd phse reltionship etween the three phse voltges. e le to lulte the voltges nd urrents for three-phse Y-onneted
THE ASYMMETRY OF COASTAL WATER LEVEL RESPONSE TO LANDFALLING HURRICANES SIMULATED BY A THREE-DIMENSIONAL STORM SURGE MODEL
 THE ASYMMETRY OF COASTAL WATER LEVEL RESPONSE TO LANDFALLING HURRICANES SIMULATED BY A THREE-DIMENSIONAL STORM SURGE MODEL Mhun Peng *, Lin Xie nd Leonrd J. Pietrfes Deprtment of Mrine, Erth nd Atmospheri
THE ASYMMETRY OF COASTAL WATER LEVEL RESPONSE TO LANDFALLING HURRICANES SIMULATED BY A THREE-DIMENSIONAL STORM SURGE MODEL Mhun Peng *, Lin Xie nd Leonrd J. Pietrfes Deprtment of Mrine, Erth nd Atmospheri
6.3.2 Spectroscopy. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 NO 2 CH 3. CH 3 C a. NMR spectroscopy. Different types of NMR
 6.. Spetrosopy NMR spetrosopy Different types of NMR NMR spetrosopy involves intertion of mterils with the lowenergy rdiowve region of the eletromgneti spetrum NMR spetrosopy is the sme tehnology s tht
6.. Spetrosopy NMR spetrosopy Different types of NMR NMR spetrosopy involves intertion of mterils with the lowenergy rdiowve region of the eletromgneti spetrum NMR spetrosopy is the sme tehnology s tht
Chapter 2. Vectors. 1 vv 2 c 2.
 Chpter 2 Vetors CHAPTER 2 VECTORS In the first hpter on Einstein s speil theor of reltivit, we sw how muh we ould lern from the simple onept of uniform motion. Everthing in the speil theor n e derived
Chpter 2 Vetors CHAPTER 2 VECTORS In the first hpter on Einstein s speil theor of reltivit, we sw how muh we ould lern from the simple onept of uniform motion. Everthing in the speil theor n e derived
M344 - ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS
 M3 - ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS Lecture 18: Lplce s Eqution, Anltic nd Numericl Solution Our emple of n elliptic prtil differentil eqution is Lplce s eqution, lso clled the Diffusion Eqution. If
M3 - ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS Lecture 18: Lplce s Eqution, Anltic nd Numericl Solution Our emple of n elliptic prtil differentil eqution is Lplce s eqution, lso clled the Diffusion Eqution. If
ANALYSIS AND MODELLING OF RAINFALL EVENTS
 Proeedings of the 14 th Interntionl Conferene on Environmentl Siene nd Tehnology Athens, Greee, 3-5 Septemer 215 ANALYSIS AND MODELLING OF RAINFALL EVENTS IOANNIDIS K., KARAGRIGORIOU A. nd LEKKAS D.F.
Proeedings of the 14 th Interntionl Conferene on Environmentl Siene nd Tehnology Athens, Greee, 3-5 Septemer 215 ANALYSIS AND MODELLING OF RAINFALL EVENTS IOANNIDIS K., KARAGRIGORIOU A. nd LEKKAS D.F.
THE ANALYSIS AND CALCULATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD AROUND OVERHEAD POWER LINE HongWang Yang
 5th Interntionl Conferene on Advned Mterils nd Computer Siene (ICAMCS 6) THE ANALYSIS AN CALCULATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIEL AROUN OVERHEA POWER LINE HongWng Yng eprtment of eletril engineering, North
5th Interntionl Conferene on Advned Mterils nd Computer Siene (ICAMCS 6) THE ANALYSIS AN CALCULATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIEL AROUN OVERHEA POWER LINE HongWng Yng eprtment of eletril engineering, North
Logarithms LOGARITHMS.
 Logrithms LOGARITHMS www.mthletis.om.u Logrithms LOGARITHMS Logrithms re nother method to lulte nd work with eponents. Answer these questions, efore working through this unit. I used to think: In the
Logrithms LOGARITHMS www.mthletis.om.u Logrithms LOGARITHMS Logrithms re nother method to lulte nd work with eponents. Answer these questions, efore working through this unit. I used to think: In the
Review Topic 14: Relationships between two numerical variables
 Review Topi 14: Reltionships etween two numeril vriles Multiple hoie 1. Whih of the following stterplots est demonstrtes line of est fit? A B C D E 2. The regression line eqution for the following grph
Review Topi 14: Reltionships etween two numeril vriles Multiple hoie 1. Whih of the following stterplots est demonstrtes line of est fit? A B C D E 2. The regression line eqution for the following grph
Mathematics. Area under Curve.
 Mthemtics Are under Curve www.testprepkrt.com Tle of Content 1. Introduction.. Procedure of Curve Sketching. 3. Sketching of Some common Curves. 4. Are of Bounded Regions. 5. Sign convention for finding
Mthemtics Are under Curve www.testprepkrt.com Tle of Content 1. Introduction.. Procedure of Curve Sketching. 3. Sketching of Some common Curves. 4. Are of Bounded Regions. 5. Sign convention for finding
Numbers and indices. 1.1 Fractions. GCSE C Example 1. Handy hint. Key point
 GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
8.3 THE HYPERBOLA OBJECTIVES
 8.3 THE HYPERBOLA OBJECTIVES 1. Define Hperol. Find the Stndrd Form of the Eqution of Hperol 3. Find the Trnsverse Ais 4. Find the Eentriit of Hperol 5. Find the Asmptotes of Hperol 6. Grph Hperol HPERBOLAS
8.3 THE HYPERBOLA OBJECTIVES 1. Define Hperol. Find the Stndrd Form of the Eqution of Hperol 3. Find the Trnsverse Ais 4. Find the Eentriit of Hperol 5. Find the Asmptotes of Hperol 6. Grph Hperol HPERBOLAS
A Primer on Continuous-time Economic Dynamics
 Eonomis 205A Fll 2008 K Kletzer A Primer on Continuous-time Eonomi Dnmis A Liner Differentil Eqution Sstems (i) Simplest se We egin with the simple liner first-orer ifferentil eqution The generl solution
Eonomis 205A Fll 2008 K Kletzer A Primer on Continuous-time Eonomi Dnmis A Liner Differentil Eqution Sstems (i) Simplest se We egin with the simple liner first-orer ifferentil eqution The generl solution
ES.182A Topic 32 Notes Jeremy Orloff
 ES.8A Topic 3 Notes Jerem Orloff 3 Polr coordintes nd double integrls 3. Polr Coordintes (, ) = (r cos(θ), r sin(θ)) r θ Stndrd,, r, θ tringle Polr coordintes re just stndrd trigonometric reltions. In
ES.8A Topic 3 Notes Jerem Orloff 3 Polr coordintes nd double integrls 3. Polr Coordintes (, ) = (r cos(θ), r sin(θ)) r θ Stndrd,, r, θ tringle Polr coordintes re just stndrd trigonometric reltions. In
Polyphase Systems 22.1 INTRODUCTION
 22 Polyphse Systems 22.1 INTRODUTION n genertor designed to develop single sinusoidl voltge for eh rottion of the shft (rotor) is referred to s single-phse genertor. If the numer of oils on the rotor is
22 Polyphse Systems 22.1 INTRODUTION n genertor designed to develop single sinusoidl voltge for eh rottion of the shft (rotor) is referred to s single-phse genertor. If the numer of oils on the rotor is
Nondeterministic Automata vs Deterministic Automata
 Nondeterministi Automt vs Deterministi Automt We lerned tht NFA is onvenient model for showing the reltionships mong regulr grmmrs, FA, nd regulr expressions, nd designing them. However, we know tht n
Nondeterministi Automt vs Deterministi Automt We lerned tht NFA is onvenient model for showing the reltionships mong regulr grmmrs, FA, nd regulr expressions, nd designing them. However, we know tht n
Lesson 2: The Pythagorean Theorem and Similar Triangles. A Brief Review of the Pythagorean Theorem.
 27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
HOMEWORK FOR CLASS XII ( )
 HOMEWORK FOR CLASS XII 8-9 Show tht the reltion R on the set Z of ll integers defined R,, Z,, is, divisile,, is n equivlene reltion on Z Let f: R R e defined if f if Is f one-one nd onto if If f, g : R
HOMEWORK FOR CLASS XII 8-9 Show tht the reltion R on the set Z of ll integers defined R,, Z,, is, divisile,, is n equivlene reltion on Z Let f: R R e defined if f if Is f one-one nd onto if If f, g : R
Proving the Pythagorean Theorem
 Proving the Pythgoren Theorem W. Bline Dowler June 30, 2010 Astrt Most people re fmilir with the formul 2 + 2 = 2. However, in most ses, this ws presented in lssroom s n solute with no ttempt t proof or
Proving the Pythgoren Theorem W. Bline Dowler June 30, 2010 Astrt Most people re fmilir with the formul 2 + 2 = 2. However, in most ses, this ws presented in lssroom s n solute with no ttempt t proof or
( ) { } [ ] { } [ ) { } ( ] { }
![( ) { } [ ] { } [ ) { } ( ] { } ( ) { } [ ] { } [ ) { } ( ] { }](/thumbs/96/129291861.jpg) Mth 65 Prelulus Review Properties of Inequlities 1. > nd > >. > + > +. > nd > 0 > 4. > nd < 0 < Asolute Vlue, if 0, if < 0 Properties of Asolute Vlue > 0 1. < < > or
Mth 65 Prelulus Review Properties of Inequlities 1. > nd > >. > + > +. > nd > 0 > 4. > nd < 0 < Asolute Vlue, if 0, if < 0 Properties of Asolute Vlue > 0 1. < < > or
6.3.2 Spectroscopy. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 NO 2 H 3 CH3 C. NMR spectroscopy. Different types of NMR
 6.. Spetrosopy NMR spetrosopy Different types of NMR NMR spetrosopy involves intertion of mterils with the lowenergy rdiowve region of the eletromgneti spetrum NMR spetrosopy is the sme tehnology s tht
6.. Spetrosopy NMR spetrosopy Different types of NMR NMR spetrosopy involves intertion of mterils with the lowenergy rdiowve region of the eletromgneti spetrum NMR spetrosopy is the sme tehnology s tht
Global alignment. Genome Rearrangements Finding preserved genes. Lecture 18
 Computt onl Biology Leture 18 Genome Rerrngements Finding preserved genes We hve seen before how to rerrnge genome to obtin nother one bsed on: Reversls Knowledge of preserved bloks (or genes) Now we re
Computt onl Biology Leture 18 Genome Rerrngements Finding preserved genes We hve seen before how to rerrnge genome to obtin nother one bsed on: Reversls Knowledge of preserved bloks (or genes) Now we re
Electromagnetism Notes, NYU Spring 2018
 Eletromgnetism Notes, NYU Spring 208 April 2, 208 Ation formultion of EM. Free field desription Let us first onsider the free EM field, i.e. in the bsene of ny hrges or urrents. To tret this s mehnil system
Eletromgnetism Notes, NYU Spring 208 April 2, 208 Ation formultion of EM. Free field desription Let us first onsider the free EM field, i.e. in the bsene of ny hrges or urrents. To tret this s mehnil system
UNCORRECTED SAMPLE PAGES. Australian curriculum NUMBER AND ALGEBRA
 7A 7B 7C 7D 7E 7F 7G 7H 7I 7J 7K Chpter Wht ou will lern 7Prols nd other grphs Eploring prols Skething prols with trnsformtions Skething prols using ftoristion Skething ompleting the squre Skething using
7A 7B 7C 7D 7E 7F 7G 7H 7I 7J 7K Chpter Wht ou will lern 7Prols nd other grphs Eploring prols Skething prols with trnsformtions Skething prols using ftoristion Skething ompleting the squre Skething using
ENERGY AND PACKING. Outline: MATERIALS AND PACKING. Crystal Structure
 EERGY AD PACKIG Outline: Crstlline versus morphous strutures Crstl struture - Unit ell - Coordintion numer - Atomi pking ftor Crstl sstems on dense, rndom pking Dense, regulr pking tpil neighor ond energ
EERGY AD PACKIG Outline: Crstlline versus morphous strutures Crstl struture - Unit ell - Coordintion numer - Atomi pking ftor Crstl sstems on dense, rndom pking Dense, regulr pking tpil neighor ond energ
