THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
|
|
|
- Silas Morton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM The Pythgoren Theorem is one of the most well-known nd widely used theorems in mthemtis. We will first look t n informl investigtion of the Pythgoren Theorem, nd then pply this theorem to find missing sides of right tringles s well s the distne etween two points. Finlly, we will provide proofs of the Pythgoren Theorem tht pply to vriety of lerning styles. Let us now turn to the lssi illustrtion of the Pythgoren Theorem, nd perform some mesurements s n investigtion. (The digrms nd mesurements from this illustrtion hve een reted using The Geometer s Skethpd softwre.) First, we rete right tringle ABC. The onvention for nming sides is tht side is loted ross from A, side is loted ross from B, nd side is loted ross from C. We then find the length of its sides, rounded to the nerest hundredth. B =.41 m = 4.00 m = 4.66 m C A Next, we onstrut squres on the three sides of ABC. We then mesure the re of eh of the squres (to the nerest hundredth), s shown elow. Wht do you notie? B Are of Squre t side = 5.80 m Are of squre t side = m Are of squre t side = 1.76 m C A
2 Notie tht the sum of the res of the two smller squres equls the re of the lrgest squre; this leds us to the more forml wording of the Pythgoren Theorem: The Pythgoren Theorem In right tringle, the sum of the squres of the lengths of the legs equls the squre of the length of the hypotenuse. In other words, if nd represent the lengths of the legs of right tringle, nd represents the length of the hypotenuse, the Pythgoren Theorem sttes tht: + = Exmples Find x. Write ll nswers in simplest rdil form. 1. Solution: The lengths of the legs re 6 nd 8, nd the x 8 length of the hypotenuse is x, so = x = x 100 = x 6 10 = x x = 10. Solution: 11 The lengths of the legs re 7 nd x, nd the x length of the hypotenuse is 11, so 7 + x = x = 11 7 x = 7 x = 7 x = 36 x = 6
3 3. Solution: 1 The lengths of the legs re x nd 3 5, nd 3 5 the length of the hypotenuse is 1, so x ( 3 5) 1 ( ) x + = x + = x = 144 x + 45 = 144 x = 99 x = 99 x = 9 11 x = 3 11 Exerises Find x. Write ll nswers in simplest rdil form x 5. x x
4 The Pythgoren Theorem nd the Distne Formul The Pythgoren Theorem n e used to find the distne etween two points, s shown elow. Exmples 1. Use the Pythgoren Theorem to find the distne etween the points A(, 3) nd B(7, 10). Write your nswer in simplest rdil form.. Use the Pythgoren Theorem to find the distne etween the points A(-3, 4) nd B(5, -6). Write your nswer in simplest rdil form. Solution to #1: We first plot the points A(, 3) nd B(7, 10) on the oordinte plne. We wnt to find the distne AB. Next, we drw right tringle ABC tht hs hypotenuse AB, s shown elow y A (, 3) B (7, 10) C (7, 3) x We n esily find the lengths of the legs of the tringle: AC = 5 (We n quikly ount the units or tke the solute vlue of the differene of the x-oordintes: 7 = 5, or equivlently 7 = 5.)
5 BC = 7 (We n quikly ount the units or tke the solute vlue of the differene of the y-oordintes: 10 3 = 7, or equivlently 3 10 = 7.) We n now use the Pythgoren Theorem: = ( AB) = ( AB) 74 = ( AB) AB = 74 (Note: This squre root n not e simplified ny further. For dditionl informtion on simplifying squre roots, refer to the Irrtionl Numers tutoril in the ppendix ) Solution to #: We first plot the points A(-3, 4) nd B(5, -6) on the oordinte plne. We wnt to find the distne AB. Next, we drw right tringle ABC tht hs hypotenuse AB, s shown elow. A (-3, 4) C (-3, -6) -7 B (5, -6) y x
6 We n esily find the lengths of the legs of the tringle: BC = 8 (We n quikly ount the units or find the solute vlue of the differene of the x-oordintes: 5 ( 3) = 8, or equivlently ( 3) 5 = 8.) AC = 10 (We n quikly ount the units or find the solute vlue of the differene of the y-oordintes; ( 6) 4 = 10, or equivlently 4 ( 6) = 10.) We n now use the Pythgoren Theorem: = ( AB) = ( AB) 164 = ( AB) AB = 164 AB = 4 41 AB = 41 (Note: For dditionl informtion on simplifying squre roots, refer to the Irrtionl Numers tutoril in the ppendix ) Now tht we hve used the Pythgoren Theorem, we will solve the sme prolems using the distne formul insted. The distne formul is shown elow. (An informl derivtion will e shown lter in this setion.) The Distne Formul Given two points Ax ( 1, y 1) nd B( x, y ), the distne d etween A nd B is ( ) ( ) 1 1 d = x x + y y Exmples 1. Use the distne formul to find the distne etween the points A(, 3) nd B(7, 10). Write your nswer in simplest rdil form.. Use the distne formul to find the distne etween the points A(-3, 4) nd B(5, -6). Write your nswer in simplest rdil form.
7 Solution to #1: ( ) ( ) 1 1 d = x x + y y ( 7 ) ( 10 3) d = + d = d = d = 74 Solution to #: ( 1) ( 1) ( 5 ( 3) ) ( 6 4) d = x x + y y d = + ( ) 8 10 d = + d = d = 164 = 4 41 = 41 Notie how the numers in this solutions ove orrespond to those in the previous set of exmples where we used the Pythgoren Theorem diretly. We will now show n informl derivtion of the distne formul. x y x represents the length of one leg of the tringle. 1 y represents the length of the other leg of the tringle. 1 Sine d represents the hypotenuse of the tringle, we n use the Pythgoren Theorem nd otin the following formul: ( 1 ) ( 1 ) x x + y y = d ( ) ( ) = x x y y d ( ) ( ) 1 1 d = x x + y y Exmples 1. Given the points A(3, 4) nd B(7, 1), ) Use the Pythgoren Theorem to find the distne from A to B. Write your nswer in simplest rdil form. ) Verify your nswer in prt () y using the distne formul.
8 . Given the points A(-1, 7) nd B(-4, -), ) Use the Pythgoren Theorem to find the distne from A to B. Write your nswer in simplest rdil form. ) Verify your nswer in prt () y using the distne formul.
9 Proofs of the Pythgoren Theorem We will now present four proofs of the Pythgoren Theorem. These prtiulr proofs hve een hosen euse s group, they ommodte vriety of lerning styles. The lerning styles re desried elow. Visul Visul lerners lern y seeing. They lern est from digrms, hrts, detiled written explntions, nd y tking detiled notes themselves. Auditory Auditory lerners lern y listening. When deling with written informtion, they lern muh etter when they n her the informtion eing explined to them. Ttile/Kinestheti Ttile/Kinestheti lerners lern y doing. They lern est when they n prtiipte in hnds-on tivities nd demonstrtions. After working through eh proof in detil, we will disuss the lerning style(s) tht pply most to tht prtiulr proof. Proof #1 The following proof is sed on the proof y Pythgors, ut we will first set up the proof in detil y sking the reder to help onstrut some digrms. We egin with the lssi illustrtion of the Pythgoren Theorem. We wish to show tht + =, or in other words, (the re of the squre t side ) + (the re of the squre t side ) = (the re of the squre t side ) B C A
10 We will now exmine the omined re of eh of the following groups of polygons. Group 1: The squre t side, the squre t side, nd four opies of the right tringle (with legs nd ). Group : The squre t side nd four opies of the right tringle (with legs nd ).
11 Proof #1: Ativity 1. Cut out the six piees from Group 1 elow.. Rerrnge the six piees nd ple them in suh wy tht they fit extly into the following squre of side length +.
12 This pge is intentionlly left lnk
13 3. Cut out the five piees from Group elow. 4. Rerrnge the six piees nd ple them in suh wy tht they fit extly into the following squre of side length +. Note: An extr opy of this tivity n e found on the next two pges (sine this one will e ll slied up fter you omplete the tivity). The solution to the tivity n e found on the pge fter tht No peeking until you hve figured it out yourself!!!
14 This pge is intentionlly left lnk
15 Proof #1: Ativity 1. Cut out the six piees from Group 1 elow.. Rerrnge the six piees nd ple them in suh wy tht they fit extly into the following squre of side length +.
16 This pge is intentionlly left lnk
17 3. Cut out the five piees from Group elow. 4. Rerrnge the five piees nd ple them in suh wy tht they fit extly into the following squre of side length +.
18 This pge is intentionlly left lnk
19 Solution to the Ativity for Proof #1: Arrngement of Group 1 Ojets: There re slight vritions of the rrngement of the ojets from Group 1, ut ll solutions hve the following hrteristis: The squre with side must e pled in one orner, the squre with side must e pled in the opposite orner, nd the four tringles must e pled in pirs to form two retngles to omprise the reminder of the digrm. Arrngement of Group Ojets: We will lern on the next pge why this result leds us to the onlusion of the Pythgoren Theorem
20 Justifition for Proof #1: We first find the re of eh of the individul ojets in Group 1: Are of squre with side : Are of squre with side : 1 Are of one tringle: (There re four suh tringles in the digrm.) We n now find the omined re of the Group 1 ojets y dding the individul res together: 1 Comined re of Group 1 Ojets ( ) = = + + We then find the re of eh of the individul ojets in Group : Are of squre with side : 1 Are of one tringle: (There re four suh tringles in the digrm.) We n now find the omined re of the Group ojets y dding the individul res together: 1 Comined re of Group Ojets ( ) = + 4 = + The omined re of the Group 1 ojets is equl to the omined re of the Group ojets (sine they oth omprise squre of length + ). Therefore, we n set the following quntities equl: Comined re of Group 1 Ojets = Comined re of Group Ojets + + = + We n then sutrt the quntity from oth sides of the eqution (whih is equivlent to removing the four tringles from eh of our digrms). We otin the following result, whih is the Pythgoren Theorem: + = Lerning Style Anlysis: Proof #1 would ppel primrily to the Kinestheti lerner. If presented in leture formt, the explntions would ppel to the Auditory lerner. The digrms nd equtions in this proof would lso ppel to the Visul lerner.
21 Proof # We egin with the lssi illustrtion of the Pythgoren Theorem. We wish to show tht + =, or in other words, (the re of the squre t side ) + (the re of the squre t side ) = (the re of the squre t side ) We will now onstrut two lines through the enter of the squre t side ; one whih is prllel to side, nd the other whih is perpendiulr to side, s shown elow.
22 Proof #: Ativity 1. Cut out the squre t side.. Cut out the squre t side, nd then ut long the thik lines inside this squre to divide it into four piees 3. Rerrnge the five piees (from squres nd ) nd ple them in suh wy tht they fit extly into the squre t side. Note: An extr opy of this tivity n e found on the next pge (sine this one will e ll slied up fter you omplete the tivity). The solution to the tivity n e found on the pge fter tht No peeking until you hve figured it out yourself!!!
23 This pge is intentionlly left lnk
24 Now perform the following tivity: 1. Cut out the squre t side.. Cut out the squre t side, nd then ut long the thik lines inside this squre to divide it into four piees 3. Rerrnge the five piees (from squres nd ) nd ple them in suh wy tht they fit extly into the squre t side.
25 This pge is intentionlly left lnk
26 Solution to Proof # (Perigl s Proof)
27 The previous proof is known s dissetion proof, nd is ttriuted to Henry Perigl, London stokroker who pulished the proof in 1873 (Bogomolny). The lgeri justifition of this proof is lengthy nd will not e shown in this text. Lerning Style Anlysis: Proof # would ppel primrily to the Kinestheti lerner. As with ll of our proofs of the Pythgoren Theorem, the digrms would lso ppel to the Visul lerner. Proof #3 The following proof ws disovered y President Grfield in 1876 (Bogomolny). Grfield s proof is sed on the formul for the re of trpezoid. His digrm is shown elow. If we find the re of the figure y using the formul for the re of trpezoid, h Are of trpezoid = se + se ( ) 1 + Are of trpezoid = + ( ) + + Are of trpezoid = = + + = Now we insted find the re of eh of the individul tringles, nd then dd them up to find the re of the entire figure:
28 1 Rememer tht the formul for the re of tringle is A= h. Tringle #1 Tringle # Tringle #3 A = A = A = 1 3 Adding up the res of the three tringles, we otin Totl re of tringles = A + A + A = + + = We now set the re of the trpezoid equl to the totl re of the tringles: Are of trpezoid = Totl re of tringles + + = We then sutrt from oth sides, nd otin the eqution + = Finlly, we multiply oth sides y, nd otin our desired result: + =. Lerning Style Anlysis: The digrms nd equtions in Proof #3 would ppel to the Visul lerner. If Proof #3 were to e presented in leture formt, the explntions would ppel to the Auditory lerner.
29 Prefe to Proof #4 We need to prefe our first proof with disussion out similrity. First, we drw right tringle ABC. C A B Next, we drw n ltitude from vertex C to the hypotenuse, AB, nd we lel the point of intersetion D. Notie tht the digrm elow ontins three tringles; the originl tringle s well s two smller tringles tht hve een formed y the ltitude. C A D B Let us suppose, for the purpose of illustrtion, tht B mesures 0 o. We then wnt to find the mesures of ll the other ngles in the digrm. (Note tht the digrm my not e drwn to sle.) C A D 0 o B
30 Sine the sum of the mesures of the ngles of tringle is 180 o, we n quikly otin the following ngle mesures. C 0 o 70 o A 70 o D 0 o B We now drw the three tringles seprtely nd lel the mesures of their ngles. C A 70 o 0 o B C C 0 o 70 o A 70 o D D 0 o B If three ngles of one tringle re ongruent to three orresponding ngles of nother tringle, then the tringles re similr. (This is lled AA Similrity, sine it is tully suffiient to just show tht two ngles of one tringle re ongruent to two orresponding ngles of nother tringle -- sine the third ngles must then e ongruent s well.) Sine eh of the ove tringles hve the sme set of ngle mesurements, the three tringles re similr to eh other. We must refully mth up the orresponding ngles s we nme them in the following similrity sttement. (We hve hosen to nme the 70 o ngle first, then the 0 o ngle, then the 90 o ngle.): ABC ACD CBD (The symol mens similr.)
31 The 0 o nd 70 o ngles were used solely for the purpose of illustrtion; the ove exmple n e generlized to ny right tringle, s will e shown in Proof #1. The similr tringles will e used to prove the Pythgoren Theorem. Proof #4 We egin with right tringle ABC. We need to prove tht ( AC) ( BC) ( AB) C + =. A B We then drw n ltitude to the hypotenuse, with point of intersetion D. C A D B There re three different tringles in the digrm ove. Their ongruent ngles re mrked elow. C A C C B A D D B
32 The three tringles re similr y AA Similrity; therefore ABC ACD CBD Sine the tringles re similr, their orresponding sides re proportionl. Using the ft tht ABC ACD, we n sy tht AC AB AD =. AC Cross multiplying, we otin the eqution AC AC = AB AD. (1) Using the ft tht ABC CBD, we n sy tht BC BD =. AB BC Cross multiplying, we otin the eqution BC BC = AB BD. () Adding equtions (1) nd (), we otin AC AC+ BC BC = AB AD+ AB BD ( AC) + ( BC) = AB( AD+ BD) C Sine AD + BD = AB (see digrm t right), ( ) ( ) AC + BC = AB AB, so A D B ( AC) + ( BC) = ( AB) Lerning Style Anlysis: If Proof #4 were to e presented in leture formt, the explntions would ppel to the Auditory lerner. The digrms nd equtions would ppel to the Visul lerner. Online Resoure The following wepge ontins n wrd-winning Jv pplet whih ws written y Jim Morey. This pplet is n exellent visul demonstrtion of the Pythgoren Theorem: gors.html
33 Works Cited Bogomolny, Alexnder. Pythgoren Theorem CTK Softwre, In. <wester.ommnet.edu/ml/online.shtml>
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1. Given a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
 1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? IN THIS CHAPTER YOU WILL:
 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? 1 01 Squres, squre roots nd surds 1 02 Pythgors theorem 1 03 Finding the hypotenuse 1 04 Finding shorter side 1 05 Mixed prolems 1 06 Testing for right-ngled tringles
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? 1 01 Squres, squre roots nd surds 1 02 Pythgors theorem 1 03 Finding the hypotenuse 1 04 Finding shorter side 1 05 Mixed prolems 1 06 Testing for right-ngled tringles
12.4 Similarity in Right Triangles
 Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday 17 October 2012 Geometry II: Side Lengths
 Intermedite Mth Cirles Wednesdy 17 Otoer 01 Geometry II: Side Lengths Lst week we disussed vrious ngle properties. As we progressed through the evening, we proved mny results. This week, we will look t
Intermedite Mth Cirles Wednesdy 17 Otoer 01 Geometry II: Side Lengths Lst week we disussed vrious ngle properties. As we progressed through the evening, we proved mny results. This week, we will look t
Section 1.3 Triangles
 Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
GM1 Consolidation Worksheet
 Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
Proving the Pythagorean Theorem
 Proving the Pythgoren Theorem W. Bline Dowler June 30, 2010 Astrt Most people re fmilir with the formul 2 + 2 = 2. However, in most ses, this ws presented in lssroom s n solute with no ttempt t proof or
Proving the Pythgoren Theorem W. Bline Dowler June 30, 2010 Astrt Most people re fmilir with the formul 2 + 2 = 2. However, in most ses, this ws presented in lssroom s n solute with no ttempt t proof or
Comparing the Pre-image and Image of a Dilation
 hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
Lesson 2: The Pythagorean Theorem and Similar Triangles. A Brief Review of the Pythagorean Theorem.
 27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
Part I: Study the theorem statement.
 Nme 1 Nme 2 Nme 3 A STUDY OF PYTHAGORAS THEOREM Instrutions: Together in groups of 2 or 3, fill out the following worksheet. You my lift nswers from the reding, or nswer on your own. Turn in one pket for
Nme 1 Nme 2 Nme 3 A STUDY OF PYTHAGORAS THEOREM Instrutions: Together in groups of 2 or 3, fill out the following worksheet. You my lift nswers from the reding, or nswer on your own. Turn in one pket for
Proportions: A ratio is the quotient of two numbers. For example, 2 3
 Proportions: rtio is the quotient of two numers. For exmple, 2 3 is rtio of 2 n 3. n equlity of two rtios is proportion. For exmple, 3 7 = 15 is proportion. 45 If two sets of numers (none of whih is 0)
Proportions: rtio is the quotient of two numers. For exmple, 2 3 is rtio of 2 n 3. n equlity of two rtios is proportion. For exmple, 3 7 = 15 is proportion. 45 If two sets of numers (none of whih is 0)
April 8, 2017 Math 9. Geometry. Solving vector problems. Problem. Prove that if vectors and satisfy, then.
 pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 9: Roots, Real Numbers and The Pythagorean Theorem
 HS Pre-Alger Notes Unit 9: Roots, Rel Numers nd The Pythgoren Theorem Roots nd Cue Roots Syllus Ojetive 5.4: The student will find or pproximte squre roots of numers to 4. CCSS 8.EE.-: Evlute squre roots
HS Pre-Alger Notes Unit 9: Roots, Rel Numers nd The Pythgoren Theorem Roots nd Cue Roots Syllus Ojetive 5.4: The student will find or pproximte squre roots of numers to 4. CCSS 8.EE.-: Evlute squre roots
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
Similar Right Triangles
 Geometry V1.noteook Ferury 09, 2012 Similr Right Tringles Cn I identify similr tringles in right tringle with the ltitude? Cn I identify the proportions in right tringles? Cn I use the geometri mens theorems
Geometry V1.noteook Ferury 09, 2012 Similr Right Tringles Cn I identify similr tringles in right tringle with the ltitude? Cn I identify the proportions in right tringles? Cn I use the geometri mens theorems
Proving the Pythagorean Theorem. Proving the Pythagorean Theorem and the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem
 .5 Proving the Pythgoren Theorem Proving the Pythgoren Theorem nd the Converse of the Pythgoren Theorem Lerning Gols In this lesson, you will: Prove the Pythgoren Theorem using similr tringles. Prove the
.5 Proving the Pythgoren Theorem Proving the Pythgoren Theorem nd the Converse of the Pythgoren Theorem Lerning Gols In this lesson, you will: Prove the Pythgoren Theorem using similr tringles. Prove the
9.1 Day 1 Warm Up. Solve the equation = x x 2 = March 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythagorean Theorem 1
 9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
A Study on the Properties of Rational Triangles
 Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
Activities. 4.1 Pythagoras' Theorem 4.2 Spirals 4.3 Clinometers 4.4 Radar 4.5 Posting Parcels 4.6 Interlocking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes and Solutions
 MEP: Demonstrtion Projet UNIT 4: Trigonometry UNIT 4 Trigonometry tivities tivities 4. Pythgors' Theorem 4.2 Spirls 4.3 linometers 4.4 Rdr 4.5 Posting Prels 4.6 Interloking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes nd
MEP: Demonstrtion Projet UNIT 4: Trigonometry UNIT 4 Trigonometry tivities tivities 4. Pythgors' Theorem 4.2 Spirls 4.3 linometers 4.4 Rdr 4.5 Posting Prels 4.6 Interloking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes nd
= x x 2 = 25 2
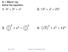 9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
3 Angle Geometry. 3.1 Measuring Angles. 1. Using a protractor, measure the marked angles.
 3 ngle Geometry MEP Prtie ook S3 3.1 Mesuring ngles 1. Using protrtor, mesure the mrked ngles. () () (d) (e) (f) 2. Drw ngles with the following sizes. () 22 () 75 120 (d) 90 (e) 153 (f) 45 (g) 180 (h)
3 ngle Geometry MEP Prtie ook S3 3.1 Mesuring ngles 1. Using protrtor, mesure the mrked ngles. () () (d) (e) (f) 2. Drw ngles with the following sizes. () 22 () 75 120 (d) 90 (e) 153 (f) 45 (g) 180 (h)
Non Right Angled Triangles
 Non Right ngled Tringles Non Right ngled Tringles urriulum Redy www.mthletis.om Non Right ngled Tringles NON RIGHT NGLED TRINGLES sin i, os i nd tn i re lso useful in non-right ngled tringles. This unit
Non Right ngled Tringles Non Right ngled Tringles urriulum Redy www.mthletis.om Non Right ngled Tringles NON RIGHT NGLED TRINGLES sin i, os i nd tn i re lso useful in non-right ngled tringles. This unit
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q5 of Paper 2
 Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
ILLUSTRATING THE EXTENSION OF A SPECIAL PROPERTY OF CUBIC POLYNOMIALS TO NTH DEGREE POLYNOMIALS
 ILLUSTRATING THE EXTENSION OF A SPECIAL PROPERTY OF CUBIC POLYNOMIALS TO NTH DEGREE POLYNOMIALS Dvid Miller West Virgini University P.O. BOX 6310 30 Armstrong Hll Morgntown, WV 6506 millerd@mth.wvu.edu
ILLUSTRATING THE EXTENSION OF A SPECIAL PROPERTY OF CUBIC POLYNOMIALS TO NTH DEGREE POLYNOMIALS Dvid Miller West Virgini University P.O. BOX 6310 30 Armstrong Hll Morgntown, WV 6506 millerd@mth.wvu.edu
Plotting Ordered Pairs Using Integers
 SAMPLE Plotting Ordered Pirs Using Integers Ple two elsti nds on geoord to form oordinte xes shown on the right to help you solve these prolems.. Wht letter of the lphet does eh set of pirs nme?. (, )
SAMPLE Plotting Ordered Pirs Using Integers Ple two elsti nds on geoord to form oordinte xes shown on the right to help you solve these prolems.. Wht letter of the lphet does eh set of pirs nme?. (, )
Math Lesson 4-5 The Law of Cosines
 Mth-1060 Lesson 4-5 The Lw of osines Solve using Lw of Sines. 1 17 11 5 15 13 SS SSS Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. We need nother eqution. h Drop nd ltitude
Mth-1060 Lesson 4-5 The Lw of osines Solve using Lw of Sines. 1 17 11 5 15 13 SS SSS Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. We need nother eqution. h Drop nd ltitude
Trigonometry and Constructive Geometry
 Trigonometry nd Construtive Geometry Trining prolems for M2 2018 term 1 Ted Szylowie tedszy@gmil.om 1 Leling geometril figures 1. Prtie writing Greek letters. αβγδɛθλµπψ 2. Lel the sides, ngles nd verties
Trigonometry nd Construtive Geometry Trining prolems for M2 2018 term 1 Ted Szylowie tedszy@gmil.om 1 Leling geometril figures 1. Prtie writing Greek letters. αβγδɛθλµπψ 2. Lel the sides, ngles nd verties
CHENG Chun Chor Litwin The Hong Kong Institute of Education
 PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
Reflection Property of a Hyperbola
 Refletion Propert of Hperol Prefe The purpose of this pper is to prove nltill nd to illustrte geometrill the propert of hperol wherein r whih emntes outside the onvit of the hperol, tht is, etween the
Refletion Propert of Hperol Prefe The purpose of this pper is to prove nltill nd to illustrte geometrill the propert of hperol wherein r whih emntes outside the onvit of the hperol, tht is, etween the
Geometry of the Circle - Chords and Angles. Geometry of the Circle. Chord and Angles. Curriculum Ready ACMMG: 272.
 Geometry of the irle - hords nd ngles Geometry of the irle hord nd ngles urriulum Redy MMG: 272 www.mthletis.om hords nd ngles HRS N NGLES The irle is si shpe nd so it n e found lmost nywhere. This setion
Geometry of the irle - hords nd ngles Geometry of the irle hord nd ngles urriulum Redy MMG: 272 www.mthletis.om hords nd ngles HRS N NGLES The irle is si shpe nd so it n e found lmost nywhere. This setion
MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS 1.6
 MTHMTIS N STTISTIS 1.6 pply geometri resoning in solving prolems ternlly ssessed 4 redits S 91031 inding unknown ngles When finding the size of unknown ngles in figure, t lest two steps of resoning will
MTHMTIS N STTISTIS 1.6 pply geometri resoning in solving prolems ternlly ssessed 4 redits S 91031 inding unknown ngles When finding the size of unknown ngles in figure, t lest two steps of resoning will
In right-angled triangles the square on the side subtending the right angle is equal to the squares on the sides containing the right angle.
 Mth 3329-Uniform Geometries Leture 06 1. Review of trigonometry While we re looking t Eulid s Elements, I d like to look t some si trigonometry. Figure 1. The Pythgoren theorem sttes tht if = 90, then
Mth 3329-Uniform Geometries Leture 06 1. Review of trigonometry While we re looking t Eulid s Elements, I d like to look t some si trigonometry. Figure 1. The Pythgoren theorem sttes tht if = 90, then
Pythagoras Theorem. Pythagoras Theorem. Curriculum Ready ACMMG: 222, 245.
 Pythgors Theorem Pythgors Theorem Curriulum Redy ACMMG:, 45 www.mthletis.om Fill in these spes with ny other interesting fts you n find out Pythgors. In the world of Mthemtis, Pythgors is legend. He lived
Pythgors Theorem Pythgors Theorem Curriulum Redy ACMMG:, 45 www.mthletis.om Fill in these spes with ny other interesting fts you n find out Pythgors. In the world of Mthemtis, Pythgors is legend. He lived
Chapter 8 Roots and Radicals
 Chpter 8 Roots nd Rdils 7 ROOTS AND RADICALS 8 Figure 8. Grphene is n inredily strong nd flexile mteril mde from ron. It n lso ondut eletriity. Notie the hexgonl grid pttern. (redit: AlexnderAIUS / Wikimedi
Chpter 8 Roots nd Rdils 7 ROOTS AND RADICALS 8 Figure 8. Grphene is n inredily strong nd flexile mteril mde from ron. It n lso ondut eletriity. Notie the hexgonl grid pttern. (redit: AlexnderAIUS / Wikimedi
Introduction to Olympiad Inequalities
 Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Vectors. a Write down the vector AB as a column vector ( x y ). A (3, 2) x point C such that BC = 3. . Go to a OA = a
 Streth lesson: Vetors Streth ojetives efore you strt this hpter, mrk how onfident you feel out eh of the sttements elow: I n lulte using olumn vetors nd represent the sum nd differene of two vetors grphilly.
Streth lesson: Vetors Streth ojetives efore you strt this hpter, mrk how onfident you feel out eh of the sttements elow: I n lulte using olumn vetors nd represent the sum nd differene of two vetors grphilly.
Pythagoras Theorem. The area of the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides
 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry Pythgors Theorem The hypotenuse of right-ngled tringle is the longest side The hypotenuse is lwys opposite the right-ngle 2 = 2 + 2 or 2 = 2-2 or 2 = 2-2 The re of the
Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry Pythgors Theorem The hypotenuse of right-ngled tringle is the longest side The hypotenuse is lwys opposite the right-ngle 2 = 2 + 2 or 2 = 2-2 or 2 = 2-2 The re of the
I1 = I2 I1 = I2 + I3 I1 + I2 = I3 + I4 I 3
 2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
LESSON 11: TRIANGLE FORMULAE
 . THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
. THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
QUADRATIC EQUATION. Contents
 QUADRATIC EQUATION Contents Topi Pge No. Theory 0-04 Exerise - 05-09 Exerise - 09-3 Exerise - 3 4-5 Exerise - 4 6 Answer Key 7-8 Syllus Qudrti equtions with rel oeffiients, reltions etween roots nd oeffiients,
QUADRATIC EQUATION Contents Topi Pge No. Theory 0-04 Exerise - 05-09 Exerise - 09-3 Exerise - 3 4-5 Exerise - 4 6 Answer Key 7-8 Syllus Qudrti equtions with rel oeffiients, reltions etween roots nd oeffiients,
Something found at a salad bar
 Nme PP Something found t sld r 4.7 Notes RIGHT TRINGLE hs extly one right ngle. To solve right tringle, you n use things like SOH-H-TO nd the Pythgoren Theorem. n OLIQUE TRINGLE hs no right ngles. To solve
Nme PP Something found t sld r 4.7 Notes RIGHT TRINGLE hs extly one right ngle. To solve right tringle, you n use things like SOH-H-TO nd the Pythgoren Theorem. n OLIQUE TRINGLE hs no right ngles. To solve
STRAND J: TRANSFORMATIONS, VECTORS and MATRICES
 Mthemtics SKE: STRN J STRN J: TRNSFORMTIONS, VETORS nd MTRIES J3 Vectors Text ontents Section J3.1 Vectors nd Sclrs * J3. Vectors nd Geometry Mthemtics SKE: STRN J J3 Vectors J3.1 Vectors nd Sclrs Vectors
Mthemtics SKE: STRN J STRN J: TRNSFORMTIONS, VETORS nd MTRIES J3 Vectors Text ontents Section J3.1 Vectors nd Sclrs * J3. Vectors nd Geometry Mthemtics SKE: STRN J J3 Vectors J3.1 Vectors nd Sclrs Vectors
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL. Part 1. What and Why.?
 SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
MCH T 111 Handout Triangle Review Page 1 of 3
 Hnout Tringle Review Pge of 3 In the stuy of sttis, it is importnt tht you e le to solve lgeri equtions n tringle prolems using trigonometry. The following is review of trigonometry sis. Right Tringle:
Hnout Tringle Review Pge of 3 In the stuy of sttis, it is importnt tht you e le to solve lgeri equtions n tringle prolems using trigonometry. The following is review of trigonometry sis. Right Tringle:
5. Every rational number have either terminating or repeating (recurring) decimal representation.
 CHAPTER NUMBER SYSTEMS Points to Rememer :. Numer used for ounting,,,,... re known s Nturl numers.. All nturl numers together with zero i.e. 0,,,,,... re known s whole numers.. All nturl numers, zero nd
CHAPTER NUMBER SYSTEMS Points to Rememer :. Numer used for ounting,,,,... re known s Nturl numers.. All nturl numers together with zero i.e. 0,,,,,... re known s whole numers.. All nturl numers, zero nd
2.4 Linear Inequalities and Interval Notation
 .4 Liner Inequlities nd Intervl Nottion We wnt to solve equtions tht hve n inequlity symol insted of n equl sign. There re four inequlity symols tht we will look t: Less thn , Less thn or
.4 Liner Inequlities nd Intervl Nottion We wnt to solve equtions tht hve n inequlity symol insted of n equl sign. There re four inequlity symols tht we will look t: Less thn , Less thn or
1 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA and GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE
 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA nd GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE Directions: Study the exmples, work the prolems, then check your nswers t the end of ech topic. If you don t get the nswer given, check
ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA nd GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE Directions: Study the exmples, work the prolems, then check your nswers t the end of ech topic. If you don t get the nswer given, check
Section 2.1 Special Right Triangles
 Se..1 Speil Rigt Tringles 49 Te --90 Tringle Setion.1 Speil Rigt Tringles Te --90 tringle (or just 0-60-90) is so nme euse of its ngle mesures. Te lengts of te sies, toug, ve very speifi pttern to tem
Se..1 Speil Rigt Tringles 49 Te --90 Tringle Setion.1 Speil Rigt Tringles Te --90 tringle (or just 0-60-90) is so nme euse of its ngle mesures. Te lengts of te sies, toug, ve very speifi pttern to tem
Figure 1. The left-handed and right-handed trefoils
 The Knot Group A knot is n emedding of the irle into R 3 (or S 3 ), k : S 1 R 3. We shll ssume our knots re tme, mening the emedding n e extended to solid torus, K : S 1 D 2 R 3. The imge is lled tuulr
The Knot Group A knot is n emedding of the irle into R 3 (or S 3 ), k : S 1 R 3. We shll ssume our knots re tme, mening the emedding n e extended to solid torus, K : S 1 D 2 R 3. The imge is lled tuulr
2. There are an infinite number of possible triangles, all similar, with three given angles whose sum is 180.
 SECTION 8-1 11 CHAPTER 8 Setion 8 1. There re n infinite numer of possile tringles, ll similr, with three given ngles whose sum is 180. 4. If two ngles α nd β of tringle re known, the third ngle n e found
SECTION 8-1 11 CHAPTER 8 Setion 8 1. There re n infinite numer of possile tringles, ll similr, with three given ngles whose sum is 180. 4. If two ngles α nd β of tringle re known, the third ngle n e found
3.1 Review of Sine, Cosine and Tangent for Right Angles
 Foundtions of Mth 11 Section 3.1 Review of Sine, osine nd Tngent for Right Tringles 125 3.1 Review of Sine, osine nd Tngent for Right ngles The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigon,
Foundtions of Mth 11 Section 3.1 Review of Sine, osine nd Tngent for Right Tringles 125 3.1 Review of Sine, osine nd Tngent for Right ngles The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigon,
Shape and measurement
 C H A P T E R 5 Shpe nd mesurement Wht is Pythgors theorem? How do we use Pythgors theorem? How do we find the perimeter of shpe? How do we find the re of shpe? How do we find the volume of shpe? How do
C H A P T E R 5 Shpe nd mesurement Wht is Pythgors theorem? How do we use Pythgors theorem? How do we find the perimeter of shpe? How do we find the re of shpe? How do we find the volume of shpe? How do
m A 1 1 A ! and AC 6
 REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
 PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
UNIT 31 Angles and Symmetry: Data Sheets
 UNIT 31 Angles nd Symmetry Dt Sheets Dt Sheets 31.1 Line nd Rottionl Symmetry 31.2 Angle Properties 31.3 Angles in Tringles 31.4 Angles nd Prllel Lines: Results 31.5 Angles nd Prllel Lines: Exmple 31.6
UNIT 31 Angles nd Symmetry Dt Sheets Dt Sheets 31.1 Line nd Rottionl Symmetry 31.2 Angle Properties 31.3 Angles in Tringles 31.4 Angles nd Prllel Lines: Results 31.5 Angles nd Prllel Lines: Exmple 31.6
A study of Pythagoras Theorem
 CHAPTER 19 A study of Pythgors Theorem Reson is immortl, ll else mortl. Pythgors, Diogenes Lertius (Lives of Eminent Philosophers) Pythgors Theorem is proly the est-known mthemticl theorem. Even most nonmthemticins
CHAPTER 19 A study of Pythgors Theorem Reson is immortl, ll else mortl. Pythgors, Diogenes Lertius (Lives of Eminent Philosophers) Pythgors Theorem is proly the est-known mthemticl theorem. Even most nonmthemticins
Triangles The following examples explore aspects of triangles:
 Tringles The following exmples explore spects of tringles: xmple 1: ltitude of right ngled tringle + xmple : tringle ltitude of the symmetricl ltitude of n isosceles x x - 4 +x xmple 3: ltitude of the
Tringles The following exmples explore spects of tringles: xmple 1: ltitude of right ngled tringle + xmple : tringle ltitude of the symmetricl ltitude of n isosceles x x - 4 +x xmple 3: ltitude of the
Project 6: Minigoals Towards Simplifying and Rewriting Expressions
 MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
NON-DETERMINISTIC FSA
 Tw o types of non-determinism: NON-DETERMINISTIC FS () Multiple strt-sttes; strt-sttes S Q. The lnguge L(M) ={x:x tkes M from some strt-stte to some finl-stte nd ll of x is proessed}. The string x = is
Tw o types of non-determinism: NON-DETERMINISTIC FS () Multiple strt-sttes; strt-sttes S Q. The lnguge L(M) ={x:x tkes M from some strt-stte to some finl-stte nd ll of x is proessed}. The string x = is
Polynomials. Polynomials. Curriculum Ready ACMNA:
 Polynomils Polynomils Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 66 www.mthletis.om Polynomils POLYNOMIALS A polynomil is mthemtil expression with one vrile whose powers re neither negtive nor frtions. The power in eh expression
Polynomils Polynomils Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 66 www.mthletis.om Polynomils POLYNOMIALS A polynomil is mthemtil expression with one vrile whose powers re neither negtive nor frtions. The power in eh expression
CS311 Computational Structures Regular Languages and Regular Grammars. Lecture 6
 CS311 Computtionl Strutures Regulr Lnguges nd Regulr Grmmrs Leture 6 1 Wht we know so fr: RLs re losed under produt, union nd * Every RL n e written s RE, nd every RE represents RL Every RL n e reognized
CS311 Computtionl Strutures Regulr Lnguges nd Regulr Grmmrs Leture 6 1 Wht we know so fr: RLs re losed under produt, union nd * Every RL n e written s RE, nd every RE represents RL Every RL n e reognized
Green s Theorem. (2x e y ) da. (2x e y ) dx dy. x 2 xe y. (1 e y ) dy. y=1. = y e y. y=0. = 2 e
 Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
5: The Definite Integral
 5: The Definite Integrl 5.: Estimting with Finite Sums Consider moving oject its velocity (meters per second) t ny time (seconds) is given y v t = t+. Cn we use this informtion to determine the distnce
5: The Definite Integrl 5.: Estimting with Finite Sums Consider moving oject its velocity (meters per second) t ny time (seconds) is given y v t = t+. Cn we use this informtion to determine the distnce
Calculus Module C21. Areas by Integration. Copyright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technology All Rights Reserved.
 Clculus Module C Ares Integrtion Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 7. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Mrch, 9 Introduction to Ares Integrtion Sttement of Prerequisite
Clculus Module C Ares Integrtion Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 7. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Mrch, 9 Introduction to Ares Integrtion Sttement of Prerequisite
Symmetrical Components 1
 Symmetril Components. Introdution These notes should e red together with Setion. of your text. When performing stedy-stte nlysis of high voltge trnsmission systems, we mke use of the per-phse equivlent
Symmetril Components. Introdution These notes should e red together with Setion. of your text. When performing stedy-stte nlysis of high voltge trnsmission systems, we mke use of the per-phse equivlent
The University of Nottingham SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE A LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER MACHINES AND THEIR LANGUAGES ANSWERS
 The University of ottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTR SCIC A LVL 2 MODUL, SPRIG SMSTR 2015 2016 MACHIS AD THIR LAGUAGS ASWRS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my omplete the front over of their nswer ook nd sign their
The University of ottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTR SCIC A LVL 2 MODUL, SPRIG SMSTR 2015 2016 MACHIS AD THIR LAGUAGS ASWRS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my omplete the front over of their nswer ook nd sign their
Identifying and Classifying 2-D Shapes
 Ientifying n Clssifying -D Shpes Wht is your sign? The shpe n olour of trffi signs let motorists know importnt informtion suh s: when to stop onstrution res. Some si shpes use in trffi signs re illustrte
Ientifying n Clssifying -D Shpes Wht is your sign? The shpe n olour of trffi signs let motorists know importnt informtion suh s: when to stop onstrution res. Some si shpes use in trffi signs re illustrte
Ellipses. The second type of conic is called an ellipse.
 Ellipses The seond type of oni is lled n ellipse. Definition of Ellipse An ellipse is the set of ll points (, y) in plne, the sum of whose distnes from two distint fied points (foi) is onstnt. (, y) d
Ellipses The seond type of oni is lled n ellipse. Definition of Ellipse An ellipse is the set of ll points (, y) in plne, the sum of whose distnes from two distint fied points (foi) is onstnt. (, y) d
TOPIC: LINEAR ALGEBRA MATRICES
 Interntionl Blurete LECTUE NOTES for FUTHE MATHEMATICS Dr TOPIC: LINEA ALGEBA MATICES. DEFINITION OF A MATIX MATIX OPEATIONS.. THE DETEMINANT deta THE INVESE A -... SYSTEMS OF LINEA EQUATIONS. 8. THE AUGMENTED
Interntionl Blurete LECTUE NOTES for FUTHE MATHEMATICS Dr TOPIC: LINEA ALGEBA MATICES. DEFINITION OF A MATIX MATIX OPEATIONS.. THE DETEMINANT deta THE INVESE A -... SYSTEMS OF LINEA EQUATIONS. 8. THE AUGMENTED
4. Statements Reasons
 Chpter 9 Answers Prentie-Hll In. Alterntive Ativity 9-. Chek students work.. Opposite sides re prllel. 3. Opposite sides re ongruent. 4. Opposite ngles re ongruent. 5. Digonls iset eh other. 6. Students
Chpter 9 Answers Prentie-Hll In. Alterntive Ativity 9-. Chek students work.. Opposite sides re prllel. 3. Opposite sides re ongruent. 4. Opposite ngles re ongruent. 5. Digonls iset eh other. 6. Students
Numbers and indices. 1.1 Fractions. GCSE C Example 1. Handy hint. Key point
 GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
2.1 ANGLES AND THEIR MEASURE. y I
 .1 ANGLES AND THEIR MEASURE Given two interseting lines or line segments, the mount of rottion out the point of intersetion (the vertex) required to ring one into orrespondene with the other is lled the
.1 ANGLES AND THEIR MEASURE Given two interseting lines or line segments, the mount of rottion out the point of intersetion (the vertex) required to ring one into orrespondene with the other is lled the
Bridging the gap: GCSE AS Level
 Bridging the gp: GCSE AS Level CONTENTS Chpter Removing rckets pge Chpter Liner equtions Chpter Simultneous equtions 8 Chpter Fctors 0 Chpter Chnge the suject of the formul Chpter 6 Solving qudrtic equtions
Bridging the gp: GCSE AS Level CONTENTS Chpter Removing rckets pge Chpter Liner equtions Chpter Simultneous equtions 8 Chpter Fctors 0 Chpter Chnge the suject of the formul Chpter 6 Solving qudrtic equtions
Pythagoras theorem and surds
 HPTER Mesurement nd Geometry Pythgors theorem nd surds In IE-EM Mthemtis Yer 8, you lernt out the remrkle reltionship etween the lengths of the sides of right-ngled tringle. This result is known s Pythgors
HPTER Mesurement nd Geometry Pythgors theorem nd surds In IE-EM Mthemtis Yer 8, you lernt out the remrkle reltionship etween the lengths of the sides of right-ngled tringle. This result is known s Pythgors
Section 4: Integration ECO4112F 2011
 Reding: Ching Chpter Section : Integrtion ECOF Note: These notes do not fully cover the mteril in Ching, ut re ment to supplement your reding in Ching. Thus fr the optimistion you hve covered hs een sttic
Reding: Ching Chpter Section : Integrtion ECOF Note: These notes do not fully cover the mteril in Ching, ut re ment to supplement your reding in Ching. Thus fr the optimistion you hve covered hs een sttic
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals
 AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
CS 573 Automata Theory and Formal Languages
 Non-determinism Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Leture # 3 Septemer 6, 2 To hieve our gol, we need the onept of Non-deterministi Finite Automton with -moves (NFA) An NFA is tuple
Non-determinism Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Leture # 3 Septemer 6, 2 To hieve our gol, we need the onept of Non-deterministi Finite Automton with -moves (NFA) An NFA is tuple
Factorising FACTORISING.
 Ftorising FACTORISING www.mthletis.om.u Ftorising FACTORISING Ftorising is the opposite of expning. It is the proess of putting expressions into rkets rther thn expning them out. In this setion you will
Ftorising FACTORISING www.mthletis.om.u Ftorising FACTORISING Ftorising is the opposite of expning. It is the proess of putting expressions into rkets rther thn expning them out. In this setion you will
Chapter17. Congruence and transformations. Contents: A Transformations B Congruent figures C Congruent triangles D Proof using congruence
 hpter17 ongruene nd trnsfortions ontents: Trnsfortions ongruent figures ongruent tringles Proof using ongruene 352 ONGRUENE N TRNSFORMTIONS (hpter 17) Opening prole Jne ut two tringulr slies of heeseke,
hpter17 ongruene nd trnsfortions ontents: Trnsfortions ongruent figures ongruent tringles Proof using ongruene 352 ONGRUENE N TRNSFORMTIONS (hpter 17) Opening prole Jne ut two tringulr slies of heeseke,
SAMPLE EVALUATION ONLY
 mesurement nd geometry topic 5 Geometry 5.1 Overview Why lern this? Geometry llows us to explore our world in very preise wy. uilders, rhitets, surveyors nd engineers use knowledge of geometry to ensure
mesurement nd geometry topic 5 Geometry 5.1 Overview Why lern this? Geometry llows us to explore our world in very preise wy. uilders, rhitets, surveyors nd engineers use knowledge of geometry to ensure
S2 (2.2) Pythagoras.notebook March 04, 2016
 S2 (2.2) Pythgors.noteook Mrh 04, 2016 Dily Prtie 16.12.2015 Q1. Multiply out nd simplify 9x 3(2x + 1) Q2. Solve the eqution 3(2x + 4) = 18 Q3. If 1 = $1.30, how muh is 50 in dollrs? Tody we will e lerning
S2 (2.2) Pythgors.noteook Mrh 04, 2016 Dily Prtie 16.12.2015 Q1. Multiply out nd simplify 9x 3(2x + 1) Q2. Solve the eqution 3(2x + 4) = 18 Q3. If 1 = $1.30, how muh is 50 in dollrs? Tody we will e lerning
Lesson 8.1 Graphing Parametric Equations
 Lesson 8.1 Grphing Prmetric Equtions 1. rete tle for ech pir of prmetric equtions with the given vlues of t.. x t 5. x t 3 c. x t 1 y t 1 y t 3 y t t t {, 1, 0, 1, } t {4,, 0,, 4} t {4, 0,, 4, 8}. Find
Lesson 8.1 Grphing Prmetric Equtions 1. rete tle for ech pir of prmetric equtions with the given vlues of t.. x t 5. x t 3 c. x t 1 y t 1 y t 3 y t t t {, 1, 0, 1, } t {4,, 0,, 4} t {4, 0,, 4, 8}. Find
Computing data with spreadsheets. Enter the following into the corresponding cells: A1: n B1: triangle C1: sqrt
 Computing dt with spredsheets Exmple: Computing tringulr numers nd their squre roots. Rell, we showed 1 ` 2 ` `n npn ` 1q{2. Enter the following into the orresponding ells: A1: n B1: tringle C1: sqrt A2:
Computing dt with spredsheets Exmple: Computing tringulr numers nd their squre roots. Rell, we showed 1 ` 2 ` `n npn ` 1q{2. Enter the following into the orresponding ells: A1: n B1: tringle C1: sqrt A2:
Chapter 9 Definite Integrals
 Chpter 9 Definite Integrls In the previous chpter we found how to tke n ntiderivtive nd investigted the indefinite integrl. In this chpter the connection etween ntiderivtives nd definite integrls is estlished
Chpter 9 Definite Integrls In the previous chpter we found how to tke n ntiderivtive nd investigted the indefinite integrl. In this chpter the connection etween ntiderivtives nd definite integrls is estlished
Bravais lattices and crystal systems
 3 Brvis ltties nd rystl systems 3. Introdution The definitions of the motif, the repeting unit of pttern, nd the lttie, n rry of points in spe in whih eh point hs n identil environment, hold in three dimensions
3 Brvis ltties nd rystl systems 3. Introdution The definitions of the motif, the repeting unit of pttern, nd the lttie, n rry of points in spe in whih eh point hs n identil environment, hold in three dimensions
Topics Covered: Pythagoras Theorem Definition of sin, cos and tan Solving right-angle triangles Sine and cosine rule
 Trigonometry Topis overed: Pythgors Theorem Definition of sin, os nd tn Solving right-ngle tringles Sine nd osine rule Lelling right-ngle tringle Opposite (Side opposite the ngle θ) Hypotenuse (Side opposite
Trigonometry Topis overed: Pythgors Theorem Definition of sin, os nd tn Solving right-ngle tringles Sine nd osine rule Lelling right-ngle tringle Opposite (Side opposite the ngle θ) Hypotenuse (Side opposite
Basic Angle Rules 5. A Short Hand Geometric Reasons. B Two Reasons. 1 Write in full the meaning of these short hand geometric reasons.
 si ngle Rules 5 6 Short Hnd Geometri Resons 1 Write in full the mening of these short hnd geometri resons. Short Hnd Reson Full Mening ) se s isos Δ re =. ) orr s // lines re =. ) sum s t pt = 360. d)
si ngle Rules 5 6 Short Hnd Geometri Resons 1 Write in full the mening of these short hnd geometri resons. Short Hnd Reson Full Mening ) se s isos Δ re =. ) orr s // lines re =. ) sum s t pt = 360. d)
1.3 SCALARS AND VECTORS
 Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
Algebra Basics. Algebra Basics. Curriculum Ready ACMNA: 133, 175, 176, 177, 179.
 Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 33 75 76 77 79 www.mthletis.om Fill in the spes with nything you lredy know out Alger Creer Opportunities: Arhitets eletriins plumers et. use it to do importnt lultions. Give this
Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 33 75 76 77 79 www.mthletis.om Fill in the spes with nything you lredy know out Alger Creer Opportunities: Arhitets eletriins plumers et. use it to do importnt lultions. Give this
The Ellipse. is larger than the other.
 The Ellipse Appolonius of Perg (5 B.C.) disovered tht interseting right irulr one ll the w through with plne slnted ut is not perpendiulr to the is, the intersetion provides resulting urve (oni setion)
The Ellipse Appolonius of Perg (5 B.C.) disovered tht interseting right irulr one ll the w through with plne slnted ut is not perpendiulr to the is, the intersetion provides resulting urve (oni setion)
Vectors. Chapter14. Syllabus reference: 4.1, 4.2, 4.5 Contents:
 hpter Vetors Syllus referene:.,.,.5 ontents: D E F G H I J K Vetors nd slrs Geometri opertions with vetors Vetors in the plne The mgnitude of vetor Opertions with plne vetors The vetor etween two points
hpter Vetors Syllus referene:.,.,.5 ontents: D E F G H I J K Vetors nd slrs Geometri opertions with vetors Vetors in the plne The mgnitude of vetor Opertions with plne vetors The vetor etween two points
Similarity and Congruence
 Similrity nd ongruence urriculum Redy MMG: 201, 220, 221, 243, 244 www.mthletics.com SIMILRITY N ONGRUN If two shpes re congruent, it mens thy re equl in every wy ll their corresponding sides nd ngles
Similrity nd ongruence urriculum Redy MMG: 201, 220, 221, 243, 244 www.mthletics.com SIMILRITY N ONGRUN If two shpes re congruent, it mens thy re equl in every wy ll their corresponding sides nd ngles
Naming the sides of a right-angled triangle
 6.2 Wht is trigonometry? The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigonon (tringle) nd metron (mesurement). Thus, it literlly mens to mesure tringle. Trigonometry dels with the reltionship
6.2 Wht is trigonometry? The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigonon (tringle) nd metron (mesurement). Thus, it literlly mens to mesure tringle. Trigonometry dels with the reltionship
S56 (5.3) Vectors.notebook January 29, 2016
 Dily Prctice 15.1.16 Q1. The roots of the eqution (x 1)(x + k) = 4 re equl. Find the vlues of k. Q2. Find the rte of chnge of 剹 x when x = 1 / 8 Tody we will e lerning out vectors. Q3. Find the eqution
Dily Prctice 15.1.16 Q1. The roots of the eqution (x 1)(x + k) = 4 re equl. Find the vlues of k. Q2. Find the rte of chnge of 剹 x when x = 1 / 8 Tody we will e lerning out vectors. Q3. Find the eqution
Things to Memorize: A Partial List. January 27, 2017
 Things to Memorize: A Prtil List Jnury 27, 2017 Chpter 2 Vectors - Bsic Fcts A vector hs mgnitude (lso clled size/length/norm) nd direction. It does not hve fixed position, so the sme vector cn e moved
Things to Memorize: A Prtil List Jnury 27, 2017 Chpter 2 Vectors - Bsic Fcts A vector hs mgnitude (lso clled size/length/norm) nd direction. It does not hve fixed position, so the sme vector cn e moved
8Similarity UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS. 8.1 Kick off with CAS 8.2 Similar objects 8.3 Linear scale factors. 8.4 Area and volume scale factors 8.
 8.1 Kick off with S 8. Similr ojects 8. Liner scle fctors 8Similrity 8. re nd volume scle fctors 8. Review U N O R R E TE D P G E PR O O FS 8.1 Kick off with S Plese refer to the Resources t in the Prelims
8.1 Kick off with S 8. Similr ojects 8. Liner scle fctors 8Similrity 8. re nd volume scle fctors 8. Review U N O R R E TE D P G E PR O O FS 8.1 Kick off with S Plese refer to the Resources t in the Prelims
Pre-AP Geometry Worksheet 5.2: Similar Right Triangles
 ! re-a Geometr Worksheet 5.2: Similr Right Tringles Nme: te: eriod: Solve. Show ll work. Leve nswers s simplified rdicls on #1-5. For #6, round to the nerer tenth. 12!! 6! 1) =! 8! 6! 2) = 18! 8! w!+!9!
! re-a Geometr Worksheet 5.2: Similr Right Tringles Nme: te: eriod: Solve. Show ll work. Leve nswers s simplified rdicls on #1-5. For #6, round to the nerer tenth. 12!! 6! 1) =! 8! 6! 2) = 18! 8! w!+!9!
BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I)
 /0 BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I) SAMPLE TEST PLACEMENT EXAMINATION Downlod the omplete Study Pket: http://www.glendle.edu/studypkets Students who hve tken yer of high shool lger or its equivlent with grdes
/0 BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I) SAMPLE TEST PLACEMENT EXAMINATION Downlod the omplete Study Pket: http://www.glendle.edu/studypkets Students who hve tken yer of high shool lger or its equivlent with grdes
Trigonometry. Trigonometry. labelling conventions. Evaluation of areas of non-right-angled triangles using the formulas A = 1 ab sin (C )
 8 8 Pythgors theorem 8 Pythgoren trids 8 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 8D Trigonometri rtios 8E The sine rule 8F miguous se of the sine rule 8G The osine rule 8H Speil tringles 8I re of tringles res
8 8 Pythgors theorem 8 Pythgoren trids 8 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 8D Trigonometri rtios 8E The sine rule 8F miguous se of the sine rule 8G The osine rule 8H Speil tringles 8I re of tringles res
Precalculus Notes: Unit 6 Law of Sines & Cosines, Vectors, & Complex Numbers. A can be rewritten as
 Dte: 6.1 Lw of Sines Syllus Ojetie: 3.5 Te student will sole pplition prolems inoling tringles (Lw of Sines). Deriing te Lw of Sines: Consider te two tringles. C C In te ute tringle, sin In te otuse tringle,
Dte: 6.1 Lw of Sines Syllus Ojetie: 3.5 Te student will sole pplition prolems inoling tringles (Lw of Sines). Deriing te Lw of Sines: Consider te two tringles. C C In te ute tringle, sin In te otuse tringle,
