Numbers and indices. 1.1 Fractions. GCSE C Example 1. Handy hint. Key point
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply y the reiprol of Cnel the ommon ftor : Bring the numertors together: Bring the enomintors together: So 7 Common ftors reue the size of the numers you re working with Without nelltion, this lultion is The rules for frtion rithmeti re: Frtions Wht you shoul lrey know: how to, sutrt, multiply n ivie y frtions how to onvert etween mie numers n top-hevy frtions In this setion you will lern: how to sustitute frtion into formul You must mke the enomintors equl efore you n or sutrt frtions In AS Mths, you will e epete to work onfiently with frtions They re often neee when simplifying, or fining the vlue of, n epression You will generlly fin it esier to work with top-hevy frtions rther thn mie numers For emple, it is not esy to work out the vlue of without lultor However, y writing s, you n esily work out this nswer () Moving on to AS Level Revisiting GCSE In GCSE Mths you performe lultions with frtions The numers involve my hve een top-hevy (or improper) frtions, suh s 7 or mie numers suh s You shoul e onfient in onverting mie numers into top-hevy frtions AS Level Emple Using the formul y, fin the vlue of y when You sustitute into the formul For emple, Use ommon enomintor of : 0 A the numertors: So NUMBERS AND INDICES Write s the top-hevy frtion Formul: y Cnel the ommon ftor : Simplify the prout: A the numertors: So y when Common error oes not equl To voi this type of error, write s NUMBERS AND INDICES
2 AS Level Emple Using the formul y, fin the vlue of y when You n write s, or simply s So the formul is y You sustitute into this formul Formul: y The oeffiient of is You n seprte the oeffiient from the -term You nee to know the rules of surs: The rules of surs re:, (where is not zero) These rules llow you to rek own sur For emple, It is not possile to rek own ny further using integers hs een epresse in simplifie sur form or et form 0 9 Sutrt the frtions y using ommon enomintor : Sutrt the frtions: So y when The epression n e written s, where n re ny numers,? 0 Tking it further You will nee to e onfient in using frtions s you progress through your ourse In prtiulr, you use them when working with stright-line equtions Surs Wht you shoul lrey know: how to re-write sur suh s how to rtionlise the enomintor of frtion suh s 0 In this setion you will lern: how to use the rules of surs to simplify more omple epressions how to rtionlise more omple enomintors in frtions how to lulte with numers n epressions involving surs the mening of et form Revisiting GCSE A sur is numer of the form where is not squre numer For emple, is sur A eiml pproimtion for is 7 ut you n never etly esrie sur using eimls However, 9 is not sur euse you n write own its et vlue, You shoul e fmilir with the squre numers:,, 9, 6,, 6 You n ssume 9 mens the positive squre root of 9 GCSE A Emple Epress in the form k where k is n integer Simplify y rtionlising the enomintor You nee to re-write using ftors of Re-write using ftors of hs lots of ftors Look for the gretest squre numer whih is ftor of (ie 6) 6 6 So, 6 (so k 6) The enomintor of is the sur You nee to fin frtion with the sme vlue s whih oes not hve sur in its enomintor Sine, you multiply the numertor n enomintor of this frtion y 7 Common error is NOT the sme s hek this on lultor Use squre numer whih is ftor of (ie ) Before nswering sur question, mke list of the first few squre numers (ie,, 9, 6, ) You n like surs You must multiply top n ottom y for ny numer > 0 Et form is the sme s giving n nswer in sur form 6 NUMBERS AND INDICES NUMBERS AND INDICES 7
3 Moving on to AS Level In AS Mths you will nee to e le to simplify epressions involving surs Also, you sometimes nee to give nswers in et form, rther thn using eimls AS Level Emple Show tht ( 7)( 7) is n integer, stting its vlue 7 Hene epress 7 in the form 7 where n re integers to e stte You nee to epn the rkets n then simplify the numers ( 7)( 7) , whih is n integer You nee to rtionlise the enomintor of the frtion 7 7 This n e one y multiplying the numertor n enomintor y ( 7) 7 ( 7 ) ( 7 ) So, 7 ( 7 ) ( 7 ) Comine numers n like surs: 7 7 Compre this nswer to the form 7 given in the question: 7 looks like 7 where, These re some efinitions for negtive n frtionl inies: for ny numer > 0 for ny numer 0 for ny numer, n for ny non-zero numer Prt oes not tell you how to strt Write 7 s 7 Use Prt is Hene question this mens you shoul mke use of prt You shoul use the result of prt to simplify the enomintor You must write own the vlue of n the vlue of, s irete y the question is the ue root of This is the numer suh tht = If n re integers, then ( )( ) is lso n integer, n equls N To rtionlise the enomintor of frtion of the form, multiply top n ottom y ( ) N To rtionlise the enomintor of frtion of the form, multiply top n ottom y ( ) Tking it further Surs pper in mny res of AS Mths, suh s solving qurti equtions n lulting istnes etween points Inies Wht you shoul lrey know: how to simplify epressions suh s ( ) how to lulte vlues suh s or In this setion you will lern: how to work out the vlue of more omplite epressions using the rules of inies Revisiting GCSE In GCSE Mths you woul hve use vrious rules of inies to simplify n epression For emple, in the epression you n the inies together so tht simplifies to This works euse ( ) ( ) Here re some results involving inies: m n m+n n m n for not zero ( m ) n ( n ) m mn n n () n n n n for not zero GCSE B Emple 6 Simplify (p q ) You n write rule s () n n n So (p q ) (p ) (q ) Use rule on eh rket: (p ) (q ) Simplify the inies: p 6 q So (p q ) simplifies to p 6 q You hve lso met the efinition of negtive n frtionl inies For emple, mens n so hs vlue Similrly, mens the positive squre root of, n so hs vlue Rule mens ( m ) n n ( n ) m re equl to eh other n re lso equl to mn Rule n e etene to three or more terms NUMBERS AND INDICES NUMBERS AND INDICES 9
4 GCSE A Emple 7 Fin the vlue of You pply the efinitions to eh epression 9 So 9 You must split the frtion up into two prts: Seprte the numers from the -terms: Use rules of inies: So Compre with n :,, n Common error is not Compring terms, = so = 9 Moving on to AS Level Here re some generl efinitions whih you nee to know for AS Mths 6 n n where n is ny integer 7 n n where n is ny positive integer In AS Mths you will e epete to evlute epressions involving inies, possily without the use of lultor m n ( n ) m n m When lulting m n it is usully esier to use the result ( n ) m rther thn n m Tking it further Inies pper in mny AS Mths topis, ut in prtiulr you will nee to e onfient in using them when stuying ifferentition n integrtion AS Level Emple Fin the vlue of 6 Simplify Epress in the form n, stting the vlue of the onstnts, n n Using rule 6 you n write 6 s 6 Now onentrte on the enomintor You n write 6 s 6 y using rule Now use rule 7: 6 ( 6) So 6 6 () 6 You n write s whih simplifies to 6 Now epress the enomintor s power of You n see tht the numers n epressions re more omple t this level You nee to omine severl rules of inies to nswer these questions Del with the negtive sign on the ine first Using rule, you oul lso work out 6 s (6 ), ut this woul men hving to fin 6 Although =, you shoul voi writing n ine using mie numer So 6 6 Use rule : 6 6 So simplifies to 6 0 NUMBERS AND INDICES NUMBERS AND INDICES
5 Prtie: Frtions Numers n inies Work out these Give eh nswer in its simplest form 6 S D Work out these Give eh nswer in its simplest form 0 Convert these mie numers into top-hevy frtions 7 S D Simplify these Give eh nswer s tophevy frtion in its simplest form 7 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( 6) ( 9) By onverting mie numers to top-hevy frtions, fin the vlue of these Give eh nswer s frtion in its simplest form 6 ( 9 ) 6 6 Use these formule to fin the vlue of y for the given vlue of Give eh nswer for y s frtion in its simplest terms y, y, y, y, e y, f y 6, 7 A urve hs eqution y Fin the y-oorinte of the point on this urve where The formul for onverting the temperture C egrees Celsius into the temperture F egrees Fhrenheit is F 9C Wht is C in egrees Fhrenheit? The minimum overnight temperture in villge ws 7 C Wht ws this temperture in egrees Fhrenheit? 9 The formul for onverting the istne K kilometres into the istne M miles is M K How fr in miles is the istne 9 km? How fr in km is the istne miles? PRACTICE: NUMBERS AND INDICES 7
6 0 Solve these equtions Give eh nswer s frtion in its simplest form 7 A smll retngulr gren lwn hs length metres n with w metres The lwn hs re m w --- Show tht w Fin the perimeter of the lwn in metres Give your nswer s mie numer Surs Simplify these 0 ( ) e f 6 7 Epress these in simplifie sur form 0 7 By simplifying eh sur, fin the vlue 0 of 7 Simplify these epressions 6 e Epress these frtions in the form, where n re integers 6 Simplify these frtions Show tht 6 is n integer, stting its vlue Given tht D fin the vlue of D when i,, ii,, Give eh nswer in simplifie sur form Eplin why D oes not hve rel vlue when n 0 9 Epress these in simplifie sur form ABC is right-ngle tringle AB, AC C A + Fin the re of this tringle Show tht BC 6 Hene fin the et perimeter of this tringle Give your nswer in the form, where n re integers to e stte B Fin the gretest of these numers You my use lultor if you wish,, Show tht these three numers re sies of right-ngle tringle Fin the re of this tringle, giving your nswer in the form, where n re integers to e stte PQR is right-ngle tringle PQ, PR P + + Epn n then simplify Show tht QR R Q Using your nswer to prt, fin the et length QR Show tht the re n perimeter of this tringle re numerilly equl Inies Epress eh of these in the form n where n is n integer ( ) ( ) Epress these s frtions in their simplest terms Evlute these Evlute these Where pproprite, give nswers s frtions in their simplest form 7 e 6 f g h 6 By writing 6 s power of, or otherwise, solve the eqution 6 6 Solve these equtions Epress these terms in the form n where is rel numer e f g 6 h 0 Determine whether eh of these sttements is true or flse Use rules of inies to prove those whih you think re true For those sttements tht you think re flse, give n emple to show tht it is inorret n n n n n n mn m n n n e ( n ) n for ll numers n positive integers n for ll numers n n positive integers n for ll numers n positive integers m n n for ll non-zero numers n positive integers n for ll numers n positive integers n f 76 PRACTICE: NUMBERS AND INDICES PRACTICE: NUMBERS AND INDICES 77
7 9 Evlute these epression using the given vlue of Give nswers s top-hevy frtions where pproprite when when 9 6 when 6 when 6 e when f when 9 0 Epress in the form n, where, n n re onstnts Epress in the form, where, n re onstnts Epress these s sums of powers of ( )( ) ( ) 6 ( ) A urve C hs eqution y ( )( ) where 0 Epress y in the form, where, n re onstnts Eplin why, s inreses, the vlue of y pprohes 6 Is there point on this urve with y-oorinte 6? 7 PRACTICE: NUMBERS AND INDICES
Factorising FACTORISING.
 Ftorising FACTORISING www.mthletis.om.u Ftorising FACTORISING Ftorising is the opposite of expning. It is the proess of putting expressions into rkets rther thn expning them out. In this setion you will
Ftorising FACTORISING www.mthletis.om.u Ftorising FACTORISING Ftorising is the opposite of expning. It is the proess of putting expressions into rkets rther thn expning them out. In this setion you will
Surds and Indices. Surds and Indices. Curriculum Ready ACMNA: 233,
 Surs n Inies Surs n Inies Curriulum Rey ACMNA:, 6 www.mthletis.om Surs SURDS & & Inies INDICES Inies n surs re very losely relte. A numer uner (squre root sign) is lle sur if the squre root n t e simplifie.
Surs n Inies Surs n Inies Curriulum Rey ACMNA:, 6 www.mthletis.om Surs SURDS & & Inies INDICES Inies n surs re very losely relte. A numer uner (squre root sign) is lle sur if the squre root n t e simplifie.
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals
 AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
5. Every rational number have either terminating or repeating (recurring) decimal representation.
 CHAPTER NUMBER SYSTEMS Points to Rememer :. Numer used for ounting,,,,... re known s Nturl numers.. All nturl numers together with zero i.e. 0,,,,,... re known s whole numers.. All nturl numers, zero nd
CHAPTER NUMBER SYSTEMS Points to Rememer :. Numer used for ounting,,,,... re known s Nturl numers.. All nturl numers together with zero i.e. 0,,,,,... re known s whole numers.. All nturl numers, zero nd
6.5 Improper integrals
 Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
SIMPLE NONLINEAR GRAPHS
 S i m p l e N o n l i n e r G r p h s SIMPLE NONLINEAR GRAPHS www.mthletis.om.u Simple SIMPLE Nonliner NONLINEAR Grphs GRAPHS Liner equtions hve the form = m+ where the power of (n ) is lws. The re lle
S i m p l e N o n l i n e r G r p h s SIMPLE NONLINEAR GRAPHS www.mthletis.om.u Simple SIMPLE Nonliner NONLINEAR Grphs GRAPHS Liner equtions hve the form = m+ where the power of (n ) is lws. The re lle
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? IN THIS CHAPTER YOU WILL:
 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? 1 01 Squres, squre roots nd surds 1 02 Pythgors theorem 1 03 Finding the hypotenuse 1 04 Finding shorter side 1 05 Mixed prolems 1 06 Testing for right-ngled tringles
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? 1 01 Squres, squre roots nd surds 1 02 Pythgors theorem 1 03 Finding the hypotenuse 1 04 Finding shorter side 1 05 Mixed prolems 1 06 Testing for right-ngled tringles
x ) dx dx x sec x over the interval (, ).
 Curve on 6 For -, () Evlute the integrl, n (b) check your nswer by ifferentiting. ( ). ( ). ( ).. 6. sin cos 7. sec csccot 8. sec (sec tn ) 9. sin csc. Evlute the integrl sin by multiplying the numertor
Curve on 6 For -, () Evlute the integrl, n (b) check your nswer by ifferentiting. ( ). ( ). ( ).. 6. sin cos 7. sec csccot 8. sec (sec tn ) 9. sin csc. Evlute the integrl sin by multiplying the numertor
A Study on the Properties of Rational Triangles
 Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
Bridging the gap: GCSE AS Level
 Bridging the gp: GCSE AS Level CONTENTS Chpter Removing rckets pge Chpter Liner equtions Chpter Simultneous equtions 8 Chpter Fctors 0 Chpter Chnge the suject of the formul Chpter 6 Solving qudrtic equtions
Bridging the gp: GCSE AS Level CONTENTS Chpter Removing rckets pge Chpter Liner equtions Chpter Simultneous equtions 8 Chpter Fctors 0 Chpter Chnge the suject of the formul Chpter 6 Solving qudrtic equtions
QUADRATIC EQUATION EXERCISE - 01 CHECK YOUR GRASP
 QUADRATIC EQUATION EXERCISE - 0 CHECK YOUR GRASP. Sine sum of oeffiients 0. Hint : It's one root is nd other root is 8 nd 5 5. tn other root 9. q 4p 0 q p q p, q 4 p,,, 4 Hene 7 vlues of (p, q) 7 equtions
QUADRATIC EQUATION EXERCISE - 0 CHECK YOUR GRASP. Sine sum of oeffiients 0. Hint : It's one root is nd other root is 8 nd 5 5. tn other root 9. q 4p 0 q p q p, q 4 p,,, 4 Hene 7 vlues of (p, q) 7 equtions
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL. Part 1. What and Why.?
 SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q5 of Paper 2
 Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
CARLETON UNIVERSITY. 1.0 Problems and Most Solutions, Sect B, 2005
 RLETON UNIVERSIT eprtment of Eletronis ELE 2607 Swithing iruits erury 28, 05; 0 pm.0 Prolems n Most Solutions, Set, 2005 Jn. 2, #8 n #0; Simplify, Prove Prolem. #8 Simplify + + + Reue to four letters (literls).
RLETON UNIVERSIT eprtment of Eletronis ELE 2607 Swithing iruits erury 28, 05; 0 pm.0 Prolems n Most Solutions, Set, 2005 Jn. 2, #8 n #0; Simplify, Prove Prolem. #8 Simplify + + + Reue to four letters (literls).
MCH T 111 Handout Triangle Review Page 1 of 3
 Hnout Tringle Review Pge of 3 In the stuy of sttis, it is importnt tht you e le to solve lgeri equtions n tringle prolems using trigonometry. The following is review of trigonometry sis. Right Tringle:
Hnout Tringle Review Pge of 3 In the stuy of sttis, it is importnt tht you e le to solve lgeri equtions n tringle prolems using trigonometry. The following is review of trigonometry sis. Right Tringle:
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1. Given a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
 1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
Logarithms LOGARITHMS.
 Logrithms LOGARITHMS www.mthletis.om.u Logrithms LOGARITHMS Logrithms re nother method to lulte nd work with eponents. Answer these questions, efore working through this unit. I used to think: In the
Logrithms LOGARITHMS www.mthletis.om.u Logrithms LOGARITHMS Logrithms re nother method to lulte nd work with eponents. Answer these questions, efore working through this unit. I used to think: In the
sec x over the interval (, ). x ) dx dx x 14. Use a graphing utility to generate some representative integral curves of the function Curve on 5
 Curve on Clcultor eperience Fin n ownlo (or type in) progrm on your clcultor tht will fin the re uner curve using given number of rectngles. Mke sure tht the progrm fins LRAM, RRAM, n MRAM. (You nee to
Curve on Clcultor eperience Fin n ownlo (or type in) progrm on your clcultor tht will fin the re uner curve using given number of rectngles. Mke sure tht the progrm fins LRAM, RRAM, n MRAM. (You nee to
Chapter Gauss Quadrature Rule of Integration
 Chpter 7. Guss Qudrture Rule o Integrtion Ater reding this hpter, you should e le to:. derive the Guss qudrture method or integrtion nd e le to use it to solve prolems, nd. use Guss qudrture method to
Chpter 7. Guss Qudrture Rule o Integrtion Ater reding this hpter, you should e le to:. derive the Guss qudrture method or integrtion nd e le to use it to solve prolems, nd. use Guss qudrture method to
Lesson 55 - Inverse of Matrices & Determinants
 // () Review Lesson - nverse of Mtries & Determinnts Mth Honors - Sntowski - t this stge of stuying mtries, we know how to, subtrt n multiply mtries i.e. if Then evlute: () + B (b) - () B () B (e) B n
// () Review Lesson - nverse of Mtries & Determinnts Mth Honors - Sntowski - t this stge of stuying mtries, we know how to, subtrt n multiply mtries i.e. if Then evlute: () + B (b) - () B () B (e) B n
Introduction to Olympiad Inequalities
 Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Polynomials. Polynomials. Curriculum Ready ACMNA:
 Polynomils Polynomils Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 66 www.mthletis.om Polynomils POLYNOMIALS A polynomil is mthemtil expression with one vrile whose powers re neither negtive nor frtions. The power in eh expression
Polynomils Polynomils Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 66 www.mthletis.om Polynomils POLYNOMIALS A polynomil is mthemtil expression with one vrile whose powers re neither negtive nor frtions. The power in eh expression
Chapter 8 Roots and Radicals
 Chpter 8 Roots nd Rdils 7 ROOTS AND RADICALS 8 Figure 8. Grphene is n inredily strong nd flexile mteril mde from ron. It n lso ondut eletriity. Notie the hexgonl grid pttern. (redit: AlexnderAIUS / Wikimedi
Chpter 8 Roots nd Rdils 7 ROOTS AND RADICALS 8 Figure 8. Grphene is n inredily strong nd flexile mteril mde from ron. It n lso ondut eletriity. Notie the hexgonl grid pttern. (redit: AlexnderAIUS / Wikimedi
12.4 Similarity in Right Triangles
 Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
Section 2.3. Matrix Inverses
 Mtri lger Mtri nverses Setion.. Mtri nverses hree si opertions on mtries, ition, multiplition, n sutrtion, re nlogues for mtries of the sme opertions for numers. n this setion we introue the mtri nlogue
Mtri lger Mtri nverses Setion.. Mtri nverses hree si opertions on mtries, ition, multiplition, n sutrtion, re nlogues for mtries of the sme opertions for numers. n this setion we introue the mtri nlogue
50 AMC Lectures Problem Book 2 (36) Substitution Method
 0 AMC Letures Prolem Book Sustitution Metho PROBLEMS Prolem : Solve for rel : 9 + 99 + 9 = Prolem : Solve for rel : 0 9 8 8 Prolem : Show tht if 8 Prolem : Show tht + + if rel numers,, n stisf + + = Prolem
0 AMC Letures Prolem Book Sustitution Metho PROBLEMS Prolem : Solve for rel : 9 + 99 + 9 = Prolem : Solve for rel : 0 9 8 8 Prolem : Show tht if 8 Prolem : Show tht + + if rel numers,, n stisf + + = Prolem
Green s Theorem. (2x e y ) da. (2x e y ) dx dy. x 2 xe y. (1 e y ) dy. y=1. = y e y. y=0. = 2 e
 Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
UNCORRECTED SAMPLE PAGES. surds NUMBER AND ALGEBRA
 Chpter Wht you will lern A Irrtionl numers n surs (0A) B Aing n sutrting surs (0A) C Multiplying n iviing surs (0A) D Binomil prouts (0A) E Rtionlising the enomintor (0A) F Review of inex lws (Consoliting)
Chpter Wht you will lern A Irrtionl numers n surs (0A) B Aing n sutrting surs (0A) C Multiplying n iviing surs (0A) D Binomil prouts (0A) E Rtionlising the enomintor (0A) F Review of inex lws (Consoliting)
Algebra 2 Semester 1 Practice Final
 Alger 2 Semester Prtie Finl Multiple Choie Ientify the hoie tht est ompletes the sttement or nswers the question. To whih set of numers oes the numer elong?. 2 5 integers rtionl numers irrtionl numers
Alger 2 Semester Prtie Finl Multiple Choie Ientify the hoie tht est ompletes the sttement or nswers the question. To whih set of numers oes the numer elong?. 2 5 integers rtionl numers irrtionl numers
Chapter 1: Logarithmic functions and indices
 Chpter : Logrithmic functions nd indices. You cn simplify epressions y using rules of indices m n m n m n m n ( m ) n mn m m m m n m m n Emple Simplify these epressions: 5 r r c 4 4 d 6 5 e ( ) f ( ) 4
Chpter : Logrithmic functions nd indices. You cn simplify epressions y using rules of indices m n m n m n m n ( m ) n mn m m m m n m m n Emple Simplify these epressions: 5 r r c 4 4 d 6 5 e ( ) f ( ) 4
Algebraic fractions. This unit will help you to work with algebraic fractions and solve equations. rs r s 2. x x.
 Get strted 25 Algeri frtions This unit will help you to work with lgeri frtions nd solve equtions. AO1 Flueny hek 1 Ftorise 2 2 5 2 25 2 6 5 d 2 2 6 2 Simplify 2 6 3 rs r s 2 d 8 2 y 3 6 y 2 3 Write s
Get strted 25 Algeri frtions This unit will help you to work with lgeri frtions nd solve equtions. AO1 Flueny hek 1 Ftorise 2 2 5 2 25 2 6 5 d 2 2 6 2 Simplify 2 6 3 rs r s 2 d 8 2 y 3 6 y 2 3 Write s
Mathematics Number: Logarithms
 plce of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Deprtment of Curriculum nd Pedgogy Mthemtics Numer: Logrithms Science nd Mthemtics Eduction Reserch Group Supported y UBC Teching nd Lerning Enhncement
plce of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Deprtment of Curriculum nd Pedgogy Mthemtics Numer: Logrithms Science nd Mthemtics Eduction Reserch Group Supported y UBC Teching nd Lerning Enhncement
Integration. antidifferentiation
 9 Integrtion 9A Antidifferentition 9B Integrtion of e, sin ( ) nd os ( ) 9C Integrtion reognition 9D Approimting res enlosed funtions 9E The fundmentl theorem of integrl lulus 9F Signed res 9G Further
9 Integrtion 9A Antidifferentition 9B Integrtion of e, sin ( ) nd os ( ) 9C Integrtion reognition 9D Approimting res enlosed funtions 9E The fundmentl theorem of integrl lulus 9F Signed res 9G Further
Section 1.3 Triangles
 Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
Using integration tables
 Using integrtion tbles Integrtion tbles re inclue in most mth tetbooks, n vilble on the Internet. Using them is nother wy to evlute integrls. Sometimes the use is strightforwr; sometimes it tkes severl
Using integrtion tbles Integrtion tbles re inclue in most mth tetbooks, n vilble on the Internet. Using them is nother wy to evlute integrls. Sometimes the use is strightforwr; sometimes it tkes severl
5.2 Exponent Properties Involving Quotients
 5. Eponent Properties Involving Quotients Lerning Objectives Use the quotient of powers property. Use the power of quotient property. Simplify epressions involving quotient properties of eponents. Use
5. Eponent Properties Involving Quotients Lerning Objectives Use the quotient of powers property. Use the power of quotient property. Simplify epressions involving quotient properties of eponents. Use
Project 6: Minigoals Towards Simplifying and Rewriting Expressions
 MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
21.1 Using Formulae Construct and Use Simple Formulae Revision of Negative Numbers Substitution into Formulae
 MEP Jmi: STRAND G UNIT 1 Formule: Student Tet Contents STRAND G: Alger Unit 1 Formule Student Tet Contents Setion 1.1 Using Formule 1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule 1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers 1.4
MEP Jmi: STRAND G UNIT 1 Formule: Student Tet Contents STRAND G: Alger Unit 1 Formule Student Tet Contents Setion 1.1 Using Formule 1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule 1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers 1.4
Lesson 2: The Pythagorean Theorem and Similar Triangles. A Brief Review of the Pythagorean Theorem.
 27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
Pythagoras Theorem PYTHAGORAS THEOREM.
 Pthgors Theorem PYTHAGORAS THEOREM www.mthletis.om.u How oes it work? Solutions Pthgors Theorem Pge 3 questions Right-ngle tringles D E x z Hotenuse is sie: F Hotenuse is sie: DF Q k j l Hotenuse is sie:
Pthgors Theorem PYTHAGORAS THEOREM www.mthletis.om.u How oes it work? Solutions Pthgors Theorem Pge 3 questions Right-ngle tringles D E x z Hotenuse is sie: F Hotenuse is sie: DF Q k j l Hotenuse is sie:
Equivalent fractions have the same value but they have different denominators. This means they have been divided into a different number of parts.
 Frtions equivlent frtions Equivlent frtions hve the sme vlue ut they hve ifferent enomintors. This mens they hve een ivie into ifferent numer of prts. Use the wll to fin the equivlent frtions: Wht frtions
Frtions equivlent frtions Equivlent frtions hve the sme vlue ut they hve ifferent enomintors. This mens they hve een ivie into ifferent numer of prts. Use the wll to fin the equivlent frtions: Wht frtions
Pythagoras theorem and surds
 HPTER Mesurement nd Geometry Pythgors theorem nd surds In IE-EM Mthemtis Yer 8, you lernt out the remrkle reltionship etween the lengths of the sides of right-ngled tringle. This result is known s Pythgors
HPTER Mesurement nd Geometry Pythgors theorem nd surds In IE-EM Mthemtis Yer 8, you lernt out the remrkle reltionship etween the lengths of the sides of right-ngled tringle. This result is known s Pythgors
Math Lesson 4-5 The Law of Cosines
 Mth-1060 Lesson 4-5 The Lw of osines Solve using Lw of Sines. 1 17 11 5 15 13 SS SSS Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. We need nother eqution. h Drop nd ltitude
Mth-1060 Lesson 4-5 The Lw of osines Solve using Lw of Sines. 1 17 11 5 15 13 SS SSS Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. We need nother eqution. h Drop nd ltitude
Mathematics SKE: STRAND F. F1.1 Using Formulae. F1.2 Construct and Use Simple Formulae. F1.3 Revision of Negative Numbers
 Mthemtis SKE: STRAND F UNIT F1 Formule: Tet STRAND F: Alger F1 Formule Tet Contents Setion F1.1 Using Formule F1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule F1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers F1.4 Sustitution into Formule
Mthemtis SKE: STRAND F UNIT F1 Formule: Tet STRAND F: Alger F1 Formule Tet Contents Setion F1.1 Using Formule F1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule F1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers F1.4 Sustitution into Formule
A-Level Mathematics Transition Task (compulsory for all maths students and all further maths student)
 A-Level Mthemtics Trnsition Tsk (compulsory for ll mths students nd ll further mths student) Due: st Lesson of the yer. Length: - hours work (depending on prior knowledge) This trnsition tsk provides revision
A-Level Mthemtics Trnsition Tsk (compulsory for ll mths students nd ll further mths student) Due: st Lesson of the yer. Length: - hours work (depending on prior knowledge) This trnsition tsk provides revision
Improper Integrals. Introduction. Type 1: Improper Integrals on Infinite Intervals. When we defined the definite integral.
 Improper Integrls Introduction When we defined the definite integrl f d we ssumed tht f ws continuous on [, ] where [, ] ws finite, closed intervl There re t lest two wys this definition cn fil to e stisfied:
Improper Integrls Introduction When we defined the definite integrl f d we ssumed tht f ws continuous on [, ] where [, ] ws finite, closed intervl There re t lest two wys this definition cn fil to e stisfied:
Calculus Cheat Sheet. Integrals Definitions. where F( x ) is an anti-derivative of f ( x ). Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. dx = f x dx g x dx
 Clulus Chet Sheet Integrls Definitions Definite Integrl: Suppose f ( ) is ontinuous Anti-Derivtive : An nti-derivtive of f ( ) on [, ]. Divide [, ] into n suintervls of is funtion, F( ), suh tht F = f.
Clulus Chet Sheet Integrls Definitions Definite Integrl: Suppose f ( ) is ontinuous Anti-Derivtive : An nti-derivtive of f ( ) on [, ]. Divide [, ] into n suintervls of is funtion, F( ), suh tht F = f.
Now we must transform the original model so we can use the new parameters. = S max. Recruits
 MODEL FOR VARIABLE RECRUITMENT (ontinue) Alterntive Prmeteriztions of the pwner-reruit Moels We n write ny moel in numerous ifferent ut equivlent forms. Uner ertin irumstnes it is onvenient to work with
MODEL FOR VARIABLE RECRUITMENT (ontinue) Alterntive Prmeteriztions of the pwner-reruit Moels We n write ny moel in numerous ifferent ut equivlent forms. Uner ertin irumstnes it is onvenient to work with
QUADRATIC EQUATION. Contents
 QUADRATIC EQUATION Contents Topi Pge No. Theory 0-04 Exerise - 05-09 Exerise - 09-3 Exerise - 3 4-5 Exerise - 4 6 Answer Key 7-8 Syllus Qudrti equtions with rel oeffiients, reltions etween roots nd oeffiients,
QUADRATIC EQUATION Contents Topi Pge No. Theory 0-04 Exerise - 05-09 Exerise - 09-3 Exerise - 3 4-5 Exerise - 4 6 Answer Key 7-8 Syllus Qudrti equtions with rel oeffiients, reltions etween roots nd oeffiients,
for all x in [a,b], then the area of the region bounded by the graphs of f and g and the vertical lines x = a and x = b is b [ ( ) ( )] A= f x g x dx
![for all x in [a,b], then the area of the region bounded by the graphs of f and g and the vertical lines x = a and x = b is b [ ( ) ( )] A= f x g x dx for all x in [a,b], then the area of the region bounded by the graphs of f and g and the vertical lines x = a and x = b is b [ ( ) ( )] A= f x g x dx](/thumbs/74/70408252.jpg) Applitions of Integrtion Are of Region Between Two Curves Ojetive: Fin the re of region etween two urves using integrtion. Fin the re of region etween interseting urves using integrtion. Desrie integrtion
Applitions of Integrtion Are of Region Between Two Curves Ojetive: Fin the re of region etween two urves using integrtion. Fin the re of region etween interseting urves using integrtion. Desrie integrtion
Goals: Determine how to calculate the area described by a function. Define the definite integral. Explore the relationship between the definite
 Unit #8 : The Integrl Gols: Determine how to clculte the re described by function. Define the definite integrl. Eplore the reltionship between the definite integrl nd re. Eplore wys to estimte the definite
Unit #8 : The Integrl Gols: Determine how to clculte the re described by function. Define the definite integrl. Eplore the reltionship between the definite integrl nd re. Eplore wys to estimte the definite
Chapters Five Notes SN AA U1C5
 Chpters Five Notes SN AA U1C5 Nme Period Section 5-: Fctoring Qudrtic Epressions When you took lger, you lerned tht the first thing involved in fctoring is to mke sure to fctor out ny numers or vriles
Chpters Five Notes SN AA U1C5 Nme Period Section 5-: Fctoring Qudrtic Epressions When you took lger, you lerned tht the first thing involved in fctoring is to mke sure to fctor out ny numers or vriles
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
 PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
Geometry of the Circle - Chords and Angles. Geometry of the Circle. Chord and Angles. Curriculum Ready ACMMG: 272.
 Geometry of the irle - hords nd ngles Geometry of the irle hord nd ngles urriulum Redy MMG: 272 www.mthletis.om hords nd ngles HRS N NGLES The irle is si shpe nd so it n e found lmost nywhere. This setion
Geometry of the irle - hords nd ngles Geometry of the irle hord nd ngles urriulum Redy MMG: 272 www.mthletis.om hords nd ngles HRS N NGLES The irle is si shpe nd so it n e found lmost nywhere. This setion
List all of the possible rational roots of each equation. Then find all solutions (both real and imaginary) of the equation. 1.
 Mth Anlysis CP WS 4.X- Section 4.-4.4 Review Complete ech question without the use of grphing clcultor.. Compre the mening of the words: roots, zeros nd fctors.. Determine whether - is root of 0. Show
Mth Anlysis CP WS 4.X- Section 4.-4.4 Review Complete ech question without the use of grphing clcultor.. Compre the mening of the words: roots, zeros nd fctors.. Determine whether - is root of 0. Show
x dx does exist, what does the answer look like? What does the answer to
 Review Guie or MAT Finl Em Prt II. Mony Decemer th 8:.m. 9:5.m. (or the 8:3.m. clss) :.m. :5.m. (or the :3.m. clss) Prt is worth 5% o your Finl Em gre. NO CALCULATORS re llowe on this portion o the Finl
Review Guie or MAT Finl Em Prt II. Mony Decemer th 8:.m. 9:5.m. (or the 8:3.m. clss) :.m. :5.m. (or the :3.m. clss) Prt is worth 5% o your Finl Em gre. NO CALCULATORS re llowe on this portion o the Finl
Calculus Module C21. Areas by Integration. Copyright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technology All Rights Reserved.
 Clculus Module C Ares Integrtion Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 7. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Mrch, 9 Introduction to Ares Integrtion Sttement of Prerequisite
Clculus Module C Ares Integrtion Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 7. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Mrch, 9 Introduction to Ares Integrtion Sttement of Prerequisite
GM1 Consolidation Worksheet
 Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
APPENDIX. Precalculus Review D.1. Real Numbers and the Real Number Line
 APPENDIX D Preclculus Review APPENDIX D.1 Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Orer n Inequlities Asolute Vlue n Distnce Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel numers cn e represente
APPENDIX D Preclculus Review APPENDIX D.1 Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Orer n Inequlities Asolute Vlue n Distnce Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel numers cn e represente
Introduction to Algebra - Part 2
 Alger Module A Introduction to Alger - Prt Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Oct., 008 Introduction to Alger - Prt Sttement of Prerequisite
Alger Module A Introduction to Alger - Prt Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Oct., 008 Introduction to Alger - Prt Sttement of Prerequisite
Lecture 6: Coding theory
 Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
1 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA and GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE
 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA nd GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE Directions: Study the exmples, work the prolems, then check your nswers t the end of ech topic. If you don t get the nswer given, check
ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA nd GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE Directions: Study the exmples, work the prolems, then check your nswers t the end of ech topic. If you don t get the nswer given, check
4.5 THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS
 4.5 The Funmentl Theorem of Clculus Contemporry Clculus 4.5 THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS This section contins the most importnt n most use theorem of clculus, THE Funmentl Theorem of Clculus. Discovere
4.5 The Funmentl Theorem of Clculus Contemporry Clculus 4.5 THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS This section contins the most importnt n most use theorem of clculus, THE Funmentl Theorem of Clculus. Discovere
The First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. If f(x) is continuous on [a, b] and F (x) is any antiderivative. f(x) dx = F (b) F (a).
![The First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. If f(x) is continuous on [a, b] and F (x) is any antiderivative. f(x) dx = F (b) F (a). The First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. If f(x) is continuous on [a, b] and F (x) is any antiderivative. f(x) dx = F (b) F (a).](/thumbs/78/77467690.jpg) The Fundmentl Theorems of Clculus Mth 4, Section 0, Spring 009 We now know enough bout definite integrls to give precise formultions of the Fundmentl Theorems of Clculus. We will lso look t some bsic emples
The Fundmentl Theorems of Clculus Mth 4, Section 0, Spring 009 We now know enough bout definite integrls to give precise formultions of the Fundmentl Theorems of Clculus. We will lso look t some bsic emples
Study Guide and Intervention
 - Stud Guide nd Intervention with the Sme Sign The quotient of two integers with the sme sign is positive. Emple. 7 The dividend nd the divisor hve the sme sign. b. () The dividend nd divisor hve the sme
- Stud Guide nd Intervention with the Sme Sign The quotient of two integers with the sme sign is positive. Emple. 7 The dividend nd the divisor hve the sme sign. b. () The dividend nd divisor hve the sme
Introduction to Differentiation
 Introution to Differentition Introution to Differentition Curriulum Rey www.mtletis.om Copyrigt 009 P Lerning. All rigts reserve. First eition printe 009 in Austrli. A tlogue reor for tis ook is ville
Introution to Differentition Introution to Differentition Curriulum Rey www.mtletis.om Copyrigt 009 P Lerning. All rigts reserve. First eition printe 009 in Austrli. A tlogue reor for tis ook is ville
Solids of Revolution
 Solis of Revolution Solis of revolution re rete tking n re n revolving it roun n is of rottion. There re two methos to etermine the volume of the soli of revolution: the isk metho n the shell metho. Disk
Solis of Revolution Solis of revolution re rete tking n re n revolving it roun n is of rottion. There re two methos to etermine the volume of the soli of revolution: the isk metho n the shell metho. Disk
Lesson 2.1 Inductive Reasoning
 Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Mathematical Proofs Table of Contents
 Mthemtil Proofs Tle of Contents Proof Stnr Pge(s) Are of Trpezoi 7MG. Geometry 8.0 Are of Cirle 6MG., 9 6MG. 7MG. Geometry 8.0 Volume of Right Cirulr Cyliner 6MG. 4 7MG. Geometry 8.0 Volume of Sphere Geometry
Mthemtil Proofs Tle of Contents Proof Stnr Pge(s) Are of Trpezoi 7MG. Geometry 8.0 Are of Cirle 6MG., 9 6MG. 7MG. Geometry 8.0 Volume of Right Cirulr Cyliner 6MG. 4 7MG. Geometry 8.0 Volume of Sphere Geometry
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE
 SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
1B40 Practical Skills
 B40 Prcticl Skills Comining uncertinties from severl quntities error propgtion We usully encounter situtions where the result of n experiment is given in terms of two (or more) quntities. We then need
B40 Prcticl Skills Comining uncertinties from severl quntities error propgtion We usully encounter situtions where the result of n experiment is given in terms of two (or more) quntities. We then need
Lesson 2.1 Inductive Reasoning
 Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
m A 1 1 A ! and AC 6
 REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
K 7. Quadratic Equations. 1. Rewrite these polynomials in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0. Identify the values of a, b and c:
 Qudrti Equtions The Null Ftor Lw Let's sy there re two numers nd. If # = then = or = (or oth re ) This mens tht if the produt of two epressions is zero, then t lest one of the epressions must e equl to
Qudrti Equtions The Null Ftor Lw Let's sy there re two numers nd. If # = then = or = (or oth re ) This mens tht if the produt of two epressions is zero, then t lest one of the epressions must e equl to
A Primer on Continuous-time Economic Dynamics
 Eonomis 205A Fll 2008 K Kletzer A Primer on Continuous-time Eonomi Dnmis A Liner Differentil Eqution Sstems (i) Simplest se We egin with the simple liner first-orer ifferentil eqution The generl solution
Eonomis 205A Fll 2008 K Kletzer A Primer on Continuous-time Eonomi Dnmis A Liner Differentil Eqution Sstems (i) Simplest se We egin with the simple liner first-orer ifferentil eqution The generl solution
Mid-Term Examination - Spring 2014 Mathematical Programming with Applications to Economics Total Score: 45; Time: 3 hours
 Mi-Term Exmintion - Spring 0 Mthemtil Progrmming with Applitions to Eonomis Totl Sore: 5; Time: hours. Let G = (N, E) e irete grph. Define the inegree of vertex i N s the numer of eges tht re oming into
Mi-Term Exmintion - Spring 0 Mthemtil Progrmming with Applitions to Eonomis Totl Sore: 5; Time: hours. Let G = (N, E) e irete grph. Define the inegree of vertex i N s the numer of eges tht re oming into
Algebra Basics. Algebra Basics. Curriculum Ready ACMNA: 133, 175, 176, 177, 179.
 Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 33 75 76 77 79 www.mthletis.om Fill in the spes with nything you lredy know out Alger Creer Opportunities: Arhitets eletriins plumers et. use it to do importnt lultions. Give this
Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 33 75 76 77 79 www.mthletis.om Fill in the spes with nything you lredy know out Alger Creer Opportunities: Arhitets eletriins plumers et. use it to do importnt lultions. Give this
Core 2 Logarithms and exponentials. Section 1: Introduction to logarithms
 Core Logrithms nd eponentils Setion : Introdution to logrithms Notes nd Emples These notes ontin subsetions on Indies nd logrithms The lws of logrithms Eponentil funtions This is n emple resoure from MEI
Core Logrithms nd eponentils Setion : Introdution to logrithms Notes nd Emples These notes ontin subsetions on Indies nd logrithms The lws of logrithms Eponentil funtions This is n emple resoure from MEI
For a, b, c, d positive if a b and. ac bd. Reciprocal relations for a and b positive. If a > b then a ab > b. then
 Slrs-7.2-ADV-.7 Improper Definite Integrls 27.. D.dox Pge of Improper Definite Integrls Before we strt the min topi we present relevnt lger nd it review. See Appendix J for more lger review. Inequlities:
Slrs-7.2-ADV-.7 Improper Definite Integrls 27.. D.dox Pge of Improper Definite Integrls Before we strt the min topi we present relevnt lger nd it review. See Appendix J for more lger review. Inequlities:
Solving Radical Equations
 Solving dil Equtions Equtions with dils: A rdil eqution is n eqution in whih vrible ppers in one or more rdinds. Some emples o rdil equtions re: Solution o dil Eqution: The solution o rdil eqution is the
Solving dil Equtions Equtions with dils: A rdil eqution is n eqution in whih vrible ppers in one or more rdinds. Some emples o rdil equtions re: Solution o dil Eqution: The solution o rdil eqution is the
ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS. The real numbers have the following properties: a b c ab ac
 REVIEW OF ALGEBRA Here we review the bsic rules nd procedures of lgebr tht you need to know in order to be successful in clculus. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS The rel numbers hve the following properties: b b
REVIEW OF ALGEBRA Here we review the bsic rules nd procedures of lgebr tht you need to know in order to be successful in clculus. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS The rel numbers hve the following properties: b b
10. AREAS BETWEEN CURVES
 . AREAS BETWEEN CURVES.. Ares etween curves So res ove the x-xis re positive nd res elow re negtive, right? Wrong! We lied! Well, when you first lern out integrtion it s convenient fiction tht s true in
. AREAS BETWEEN CURVES.. Ares etween curves So res ove the x-xis re positive nd res elow re negtive, right? Wrong! We lied! Well, when you first lern out integrtion it s convenient fiction tht s true in
CS 491G Combinatorial Optimization Lecture Notes
 CS 491G Comintoril Optimiztion Leture Notes Dvi Owen July 30, August 1 1 Mthings Figure 1: two possile mthings in simple grph. Definition 1 Given grph G = V, E, mthing is olletion of eges M suh tht e i,
CS 491G Comintoril Optimiztion Leture Notes Dvi Owen July 30, August 1 1 Mthings Figure 1: two possile mthings in simple grph. Definition 1 Given grph G = V, E, mthing is olletion of eges M suh tht e i,
2. There are an infinite number of possible triangles, all similar, with three given angles whose sum is 180.
 SECTION 8-1 11 CHAPTER 8 Setion 8 1. There re n infinite numer of possile tringles, ll similr, with three given ngles whose sum is 180. 4. If two ngles α nd β of tringle re known, the third ngle n e found
SECTION 8-1 11 CHAPTER 8 Setion 8 1. There re n infinite numer of possile tringles, ll similr, with three given ngles whose sum is 180. 4. If two ngles α nd β of tringle re known, the third ngle n e found
Section 6: Area, Volume, and Average Value
 Chpter The Integrl Applied Clculus Section 6: Are, Volume, nd Averge Vlue Are We hve lredy used integrls to find the re etween the grph of function nd the horizontl xis. Integrls cn lso e used to find
Chpter The Integrl Applied Clculus Section 6: Are, Volume, nd Averge Vlue Are We hve lredy used integrls to find the re etween the grph of function nd the horizontl xis. Integrls cn lso e used to find
Directed Numbers. Directed Numbers. Curriculum Ready.
 Direte Numers Curriulum Rey www.mthletis.om Numers ome in ll sizes n forms. They n e positive or negtive, whole numers, frtions or eimls n rtionl or irrtionl. Before you strt, investigte these terms n
Direte Numers Curriulum Rey www.mthletis.om Numers ome in ll sizes n forms. They n e positive or negtive, whole numers, frtions or eimls n rtionl or irrtionl. Before you strt, investigte these terms n
Antiderivatives Introduction
 Antierivtives 0. Introuction So fr much of the term hs been sent fining erivtives or rtes of chnge. But in some circumstnces we lrey know the rte of chnge n we wish to etermine the originl function. For
Antierivtives 0. Introuction So fr much of the term hs been sent fining erivtives or rtes of chnge. But in some circumstnces we lrey know the rte of chnge n we wish to etermine the originl function. For
CHENG Chun Chor Litwin The Hong Kong Institute of Education
 PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
Example 3 Find the tangent line to the following function at.
 Emple Given n fin eh of the following. () () () () Emple Given fin. Emple Fin the tngent line to the following funtion t. Now ll tht we nee is the funtion vlue n erivtive (for the slope) t. The tngent
Emple Given n fin eh of the following. () () () () Emple Given fin. Emple Fin the tngent line to the following funtion t. Now ll tht we nee is the funtion vlue n erivtive (for the slope) t. The tngent
9.1 Day 1 Warm Up. Solve the equation = x x 2 = March 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythagorean Theorem 1
 9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday 17 October 2012 Geometry II: Side Lengths
 Intermedite Mth Cirles Wednesdy 17 Otoer 01 Geometry II: Side Lengths Lst week we disussed vrious ngle properties. As we progressed through the evening, we proved mny results. This week, we will look t
Intermedite Mth Cirles Wednesdy 17 Otoer 01 Geometry II: Side Lengths Lst week we disussed vrious ngle properties. As we progressed through the evening, we proved mny results. This week, we will look t
BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I)
 /0 BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I) SAMPLE TEST PLACEMENT EXAMINATION Downlod the omplete Study Pket: http://www.glendle.edu/studypkets Students who hve tken yer of high shool lger or its equivlent with grdes
/0 BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I) SAMPLE TEST PLACEMENT EXAMINATION Downlod the omplete Study Pket: http://www.glendle.edu/studypkets Students who hve tken yer of high shool lger or its equivlent with grdes
Solutions for HW9. Bipartite: put the red vertices in V 1 and the black in V 2. Not bipartite!
 Solutions for HW9 Exerise 28. () Drw C 6, W 6 K 6, n K 5,3. C 6 : W 6 : K 6 : K 5,3 : () Whih of the following re iprtite? Justify your nswer. Biprtite: put the re verties in V 1 n the lk in V 2. Biprtite:
Solutions for HW9 Exerise 28. () Drw C 6, W 6 K 6, n K 5,3. C 6 : W 6 : K 6 : K 5,3 : () Whih of the following re iprtite? Justify your nswer. Biprtite: put the re verties in V 1 n the lk in V 2. Biprtite:
Pythagoras Theorem. The area of the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides
 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry Pythgors Theorem The hypotenuse of right-ngled tringle is the longest side The hypotenuse is lwys opposite the right-ngle 2 = 2 + 2 or 2 = 2-2 or 2 = 2-2 The re of the
Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry Pythgors Theorem The hypotenuse of right-ngled tringle is the longest side The hypotenuse is lwys opposite the right-ngle 2 = 2 + 2 or 2 = 2-2 or 2 = 2-2 The re of the
APPROXIMATION AND ESTIMATION MATHEMATICAL LANGUAGE THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF ARITHMETIC LAWS OF ALGEBRA ORDER OF OPERATIONS
 TOPIC 2: MATHEMATICAL LANGUAGE NUMBER AND ALGEBRA You shoul unerstn these mthemtil terms, n e le to use them ppropritely: ² ition, sutrtion, multiplition, ivision ² sum, ifferene, prout, quotient ² inex
TOPIC 2: MATHEMATICAL LANGUAGE NUMBER AND ALGEBRA You shoul unerstn these mthemtil terms, n e le to use them ppropritely: ² ition, sutrtion, multiplition, ivision ² sum, ifferene, prout, quotient ² inex
Section 4: Integration ECO4112F 2011
 Reding: Ching Chpter Section : Integrtion ECOF Note: These notes do not fully cover the mteril in Ching, ut re ment to supplement your reding in Ching. Thus fr the optimistion you hve covered hs een sttic
Reding: Ching Chpter Section : Integrtion ECOF Note: These notes do not fully cover the mteril in Ching, ut re ment to supplement your reding in Ching. Thus fr the optimistion you hve covered hs een sttic
= x x 2 = 25 2
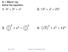 9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
Gauss Quadrature Rule of Integration
 Guss Qudrture Rule o Integrtion Mjor: All Engineering Mjors Authors: Autr Kw, Chrlie Brker http://numerilmethods.eng.us.edu Trnsorming Numeril Methods Edution or STEM Undergrdutes /0/00 http://numerilmethods.eng.us.edu
Guss Qudrture Rule o Integrtion Mjor: All Engineering Mjors Authors: Autr Kw, Chrlie Brker http://numerilmethods.eng.us.edu Trnsorming Numeril Methods Edution or STEM Undergrdutes /0/00 http://numerilmethods.eng.us.edu
LESSON 11: TRIANGLE FORMULAE
 . THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
. THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
