Worksheet #2 Math 285 Name: 1. Solve the following systems of linear equations. The prove that the solutions forms a subspace of
|
|
|
- Herbert Bates
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Worsheet # th Nme:. Sole the folloing sstems of liner equtions. he proe tht the solutions forms suspe of ) ). Find the neessr nd suffiient onditions of ll onstnts for the eistene of solution to the sstem:. Gien the mtri Wht must e true out nd if n e redued to the identit mtri.. Gien tht ) Sho tht is not inertile. ) Sole the homogenous sstem. Sole the sstem using the inerse of the oeffiient mtri.. Find the determinnt of the mtri Is inertile?. Let ) Find det ) For ht lue of ill he n inerse? ) For those suh tht eists find det. Use determinnts to find n eqution of the irle through points nd 9. Find ll lues of for hih the mtri is nonsingulr then find
2 g j. ssume tht d e f is suh tht det ) Is nonsingulr? If so ht is det ) Elute det( ) h det ) Let d e f g h j g h j. Find det().. roe the folloing: ) Let e n n n mtri nd n mtri suppose tht Y nd Z re to different n mtries for hih Y= nd Z=. i) Use this informtion to sho tht the sstem X= hs nontriil solution. ii) Conlude from prt (i) hether or not is inertile. ) Let e n n smmetri mtri nd e nother n n mtri then is lso smmetri. ) Eer inertile smmetri mtri hs smmetri inerse.. ) Let... e olletion of etors in etor spe V. n roe tht Spn is suspe of V. ) Let d e olletion of polnomils in n n. roe is suspe of n ) Let roe or disproe is suspe of n d) Let det. roe or disproe is suspe of e) d d. roe or disproe is suspe of f) Let e the etor spe of ll polnomils in ith rel oeffiients. Let S f ll the eponents of in f re een. Is S suspe of? Eplin. n. g) f f h) i) C. Whih of the folloing etors form sis for ) nd ) nd ) nd d) nd ' ' '?
3 . Find minimum set of tht spn() genertes the sme etor spe: ) 9 ) ). roe or disproe the folloing suset is suspe of. Find sis if suspe. ) ) Let ) d) Let e) f) Let g) d h). ) Let. Desrie the spe Spn. Does the etor lie in this spe? ) roe tht spns. ) For ht lues of if n is in the spn of d) In onsider N. Determine hether N is in the spn of e) If u is linerl independent suset of etor spe V. Sho tht u u is lso linerl independent set.
4 . ) roe or disproe: is sis for ) Consider the etor spe. Sho tht the folloing set of etors form sis for. hen find the oordinte etor (omponents) of the etors:. nd d ) Find the dimension of the suspe of nd spnned d d) roe tht the set S of S. is suspe of. hen find sis e) Find sis nd dimension of the suspe S re rel numers f) Find sis if the null spe of g) Find sis of S tr (tr()=sum of ll entries long the min digonl) h) Find sis of S.. ) Sho tht u u is n inner produt spe under the folloing definition of inner produt. u u ) Let nd u u u u nd define n opertion u u u u. Determine if this opertion is n inner produt on nd if it is not stte hih ondition fil. ) he tre of squre mtri is denoted tr nd is defined to e the sum of the entries on the min digonl of. Let nd e elements of n inner produt on n 9. Find sis for the rospe() nd olspe() here n. Sho tht tr defines
5 . Find sis of ernel nd rnge of the folloing liner trnsformtion. ) V V : defined for V. ) : defined ) is defined d) n : defined tr e) ) ( : i) Determine hether p is in the rnge of. ii) Determine hether p is in the ernel of.. Determine mtri of representtion of the folloing liner trnsformtion ith respeted to indited sis nd then determine sis of Ker() nd ng() ) : ith stndrd sis. ) : ith nd ) : ith nd d) d df f : ith stndrd ses.. Find the Eigenlues nd ssoited Eigenetors for the folloing mtries: ) ) ). Let ) Find ll eigenlues of. ) For eh eigenlue find s mn linerl independent eigenetors s possile. ) If is digonlile find nonsingulr mtri nd digonl mtri D suh tht D. Let ) Find digonl form of the mtri. ) Find n inertile mtri suh tht is digonl.
Matrix- System of rows and columns each position in a matrix has a purpose. 5 Ex: 5. Ex:
 Mtries Prelulus Mtri- Sstem of rows n olumns eh position in mtri hs purpose. Element- Eh vlue in the mtri mens the element in the n row, r olumn Dimensions- How mn rows b number of olumns Ientif the element:
Mtries Prelulus Mtri- Sstem of rows n olumns eh position in mtri hs purpose. Element- Eh vlue in the mtri mens the element in the n row, r olumn Dimensions- How mn rows b number of olumns Ientif the element:
Reference : Croft & Davison, Chapter 12, Blocks 1,2. A matrix ti is a rectangular array or block of numbers usually enclosed in brackets.
 I MATRIX ALGEBRA INTRODUCTION TO MATRICES Referene : Croft & Dvison, Chpter, Blos, A mtri ti is retngulr rr or lo of numers usull enlosed in rets. A m n mtri hs m rows nd n olumns. Mtri Alger Pge If the
I MATRIX ALGEBRA INTRODUCTION TO MATRICES Referene : Croft & Dvison, Chpter, Blos, A mtri ti is retngulr rr or lo of numers usull enlosed in rets. A m n mtri hs m rows nd n olumns. Mtri Alger Pge If the
Pre-Lie algebras, rooted trees and related algebraic structures
 Pre-Lie lgers, rooted trees nd relted lgeri strutures Mrh 23, 2004 Definition 1 A pre-lie lger is vetor spe W with mp : W W W suh tht (x y) z x (y z) = (x z) y x (z y). (1) Exmple 2 All ssoitive lgers
Pre-Lie lgers, rooted trees nd relted lgeri strutures Mrh 23, 2004 Definition 1 A pre-lie lger is vetor spe W with mp : W W W suh tht (x y) z x (y z) = (x z) y x (z y). (1) Exmple 2 All ssoitive lgers
Vibration with more (than one) degrees of freedom (DOF) a) longitudinal vibration with 3 DOF. b) rotational (torsional) vibration with 3 DOF
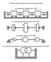 irtion with ore (thn one) degrees of freedo (DOF) ) longitudinl irtion with DOF ) rottionl (torsionl) irtion with DOF ) ending irtion with DOF d) the D (plnr) irtion of the fleil supported rigid od with
irtion with ore (thn one) degrees of freedo (DOF) ) longitudinl irtion with DOF ) rottionl (torsionl) irtion with DOF ) ending irtion with DOF d) the D (plnr) irtion of the fleil supported rigid od with
Chapter 5 Determinants
 hpter 5 Determinnts 5. Introduction Every squre mtri hs ssocited with it sclr clled its determinnt. Given mtri, we use det() or to designte its determinnt. We cn lso designte the determinnt of mtri by
hpter 5 Determinnts 5. Introduction Every squre mtri hs ssocited with it sclr clled its determinnt. Given mtri, we use det() or to designte its determinnt. We cn lso designte the determinnt of mtri by
Worksheet : Class XII Matrices & Determinants
 Worksheet : Clss XII Mtries & Determinnts Prepred B:Mr. durhimn K Mth Teher l-hej Interntionl Shool, Jeddh (IGCSE). rhmnrk@gmil.om #00966007900# MTHEMTICS WKSHEET I Nme: Mrh 0. If 8 LGEBR (Mtries nd Determinnts)
Worksheet : Clss XII Mtries & Determinnts Prepred B:Mr. durhimn K Mth Teher l-hej Interntionl Shool, Jeddh (IGCSE). rhmnrk@gmil.om #00966007900# MTHEMTICS WKSHEET I Nme: Mrh 0. If 8 LGEBR (Mtries nd Determinnts)
Matrices and Determinants
 Nme Chpter 8 Mtrices nd Determinnts Section 8.1 Mtrices nd Systems of Equtions Objective: In this lesson you lerned how to use mtrices, Gussin elimintion, nd Guss-Jordn elimintion to solve systems of liner
Nme Chpter 8 Mtrices nd Determinnts Section 8.1 Mtrices nd Systems of Equtions Objective: In this lesson you lerned how to use mtrices, Gussin elimintion, nd Guss-Jordn elimintion to solve systems of liner
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL. Part 1. What and Why.?
 SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
Chapter 3 MATRIX. In this chapter: 3.1 MATRIX NOTATION AND TERMINOLOGY
 Chpter 3 MTRIX In this chpter: Definition nd terms Specil Mtrices Mtrix Opertion: Trnspose, Equlity, Sum, Difference, Sclr Multipliction, Mtrix Multipliction, Determinnt, Inverse ppliction of Mtrix in
Chpter 3 MTRIX In this chpter: Definition nd terms Specil Mtrices Mtrix Opertion: Trnspose, Equlity, Sum, Difference, Sclr Multipliction, Mtrix Multipliction, Determinnt, Inverse ppliction of Mtrix in
April 8, 2017 Math 9. Geometry. Solving vector problems. Problem. Prove that if vectors and satisfy, then.
 pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
Linear Algebra Introduction
 Introdution Wht is Liner Alger out? Liner Alger is rnh of mthemtis whih emerged yers k nd ws one of the pioneer rnhes of mthemtis Though, initilly it strted with solving of the simple liner eqution x +
Introdution Wht is Liner Alger out? Liner Alger is rnh of mthemtis whih emerged yers k nd ws one of the pioneer rnhes of mthemtis Though, initilly it strted with solving of the simple liner eqution x +
TOPIC: LINEAR ALGEBRA MATRICES
 Interntionl Blurete LECTUE NOTES for FUTHE MATHEMATICS Dr TOPIC: LINEA ALGEBA MATICES. DEFINITION OF A MATIX MATIX OPEATIONS.. THE DETEMINANT deta THE INVESE A -... SYSTEMS OF LINEA EQUATIONS. 8. THE AUGMENTED
Interntionl Blurete LECTUE NOTES for FUTHE MATHEMATICS Dr TOPIC: LINEA ALGEBA MATICES. DEFINITION OF A MATIX MATIX OPEATIONS.. THE DETEMINANT deta THE INVESE A -... SYSTEMS OF LINEA EQUATIONS. 8. THE AUGMENTED
Tutorial Worksheet. 1. Find all solutions to the linear system by following the given steps. x + 2y + 3z = 2 2x + 3y + z = 4.
 Mth 5 Tutoril Week 1 - Jnury 1 1 Nme Setion Tutoril Worksheet 1. Find ll solutions to the liner system by following the given steps x + y + z = x + y + z = 4. y + z = Step 1. Write down the rgumented mtrix
Mth 5 Tutoril Week 1 - Jnury 1 1 Nme Setion Tutoril Worksheet 1. Find ll solutions to the liner system by following the given steps x + y + z = x + y + z = 4. y + z = Step 1. Write down the rgumented mtrix
CHAPTER 4: DETERMINANTS
 CHAPTER 4: DETERMINANTS MARKS WEIGHTAGE 0 mrks NCERT Importnt Questions & Answers 6. If, then find the vlue of. 8 8 6 6 Given tht 8 8 6 On epnding both determinnts, we get 8 = 6 6 8 36 = 36 36 36 = 0 =
CHAPTER 4: DETERMINANTS MARKS WEIGHTAGE 0 mrks NCERT Importnt Questions & Answers 6. If, then find the vlue of. 8 8 6 6 Given tht 8 8 6 On epnding both determinnts, we get 8 = 6 6 8 36 = 36 36 36 = 0 =
( ) { } [ ] { } [ ) { } ( ] { }
![( ) { } [ ] { } [ ) { } ( ] { } ( ) { } [ ] { } [ ) { } ( ] { }](/thumbs/96/129291861.jpg) Mth 65 Prelulus Review Properties of Inequlities 1. > nd > >. > + > +. > nd > 0 > 4. > nd < 0 < Asolute Vlue, if 0, if < 0 Properties of Asolute Vlue > 0 1. < < > or
Mth 65 Prelulus Review Properties of Inequlities 1. > nd > >. > + > +. > nd > 0 > 4. > nd < 0 < Asolute Vlue, if 0, if < 0 Properties of Asolute Vlue > 0 1. < < > or
Matrices SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & BUILT ENVIRONMENT. Mathematics (c) 1. Definition of a Matrix
 tries Definition of tri mtri is regulr rry of numers enlosed inside rkets SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & UIL ENVIRONEN Emple he following re ll mtries: ), ) 9, themtis ), d) tries Definition of tri Size of tri
tries Definition of tri mtri is regulr rry of numers enlosed inside rkets SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & UIL ENVIRONEN Emple he following re ll mtries: ), ) 9, themtis ), d) tries Definition of tri Size of tri
( ) 1. 1) Let f( x ) = 10 5x. Find and simplify f( 2) and then state the domain of f(x).
 Mth 15 Fettermn/DeSmet Gustfson/Finl Em Review 1) Let f( ) = 10 5. Find nd simplif f( ) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = +. Find nd simplif f(1) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = 8.
Mth 15 Fettermn/DeSmet Gustfson/Finl Em Review 1) Let f( ) = 10 5. Find nd simplif f( ) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = +. Find nd simplif f(1) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = 8.
m A 1 1 A ! and AC 6
 REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
12.4 Similarity in Right Triangles
 Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
MATHEMATICS FOR MANAGEMENT BBMP1103
 T o p i c M T R I X MTHEMTICS FOR MNGEMENT BBMP Ojectives: TOPIC : MTRIX. Define mtri. ssess the clssifictions of mtrices s well s know how to perform its opertions. Clculte the determinnt for squre mtri
T o p i c M T R I X MTHEMTICS FOR MNGEMENT BBMP Ojectives: TOPIC : MTRIX. Define mtri. ssess the clssifictions of mtrices s well s know how to perform its opertions. Clculte the determinnt for squre mtri
Section 2.3. Matrix Inverses
 Mtri lger Mtri nverses Setion.. Mtri nverses hree si opertions on mtries, ition, multiplition, n sutrtion, re nlogues for mtries of the sme opertions for numers. n this setion we introue the mtri nlogue
Mtri lger Mtri nverses Setion.. Mtri nverses hree si opertions on mtries, ition, multiplition, n sutrtion, re nlogues for mtries of the sme opertions for numers. n this setion we introue the mtri nlogue
Solutions Manual for Introductory Linear Algebra
 جايعت انقذس ان فتىحت QUDS OPEN UNIVESITY Solutions Mnul for Introdutor iner lger uthordrmhmoud l-bei l-quds Open Universit SolutionsMnul forintrodutor iner lger uthordrmhmoud l-bei Evlutor DrMuhtr l-shellh
جايعت انقذس ان فتىحت QUDS OPEN UNIVESITY Solutions Mnul for Introdutor iner lger uthordrmhmoud l-bei l-quds Open Universit SolutionsMnul forintrodutor iner lger uthordrmhmoud l-bei Evlutor DrMuhtr l-shellh
Things to Memorize: A Partial List. January 27, 2017
 Things to Memorize: A Prtil List Jnury 27, 2017 Chpter 2 Vectors - Bsic Fcts A vector hs mgnitude (lso clled size/length/norm) nd direction. It does not hve fixed position, so the sme vector cn e moved
Things to Memorize: A Prtil List Jnury 27, 2017 Chpter 2 Vectors - Bsic Fcts A vector hs mgnitude (lso clled size/length/norm) nd direction. It does not hve fixed position, so the sme vector cn e moved
H (2a, a) (u 2a) 2 (E) Show that u v 4a. Explain why this implies that u v 4a, with equality if and only u a if u v 2a.
 Chpter Review 89 IGURE ol hord GH of the prol 4. G u v H (, ) (A) Use the distne formul to show tht u. (B) Show tht G nd H lie on the line m, where m ( )/( ). (C) Solve m for nd sustitute in 4, otining
Chpter Review 89 IGURE ol hord GH of the prol 4. G u v H (, ) (A) Use the distne formul to show tht u. (B) Show tht G nd H lie on the line m, where m ( )/( ). (C) Solve m for nd sustitute in 4, otining
MATRICES AND VECTORS SPACE
 MATRICES AND VECTORS SPACE MATRICES AND MATRIX OPERATIONS SYSTEM OF LINEAR EQUATIONS DETERMINANTS VECTORS IN -SPACE AND -SPACE GENERAL VECTOR SPACES INNER PRODUCT SPACES EIGENVALUES, EIGENVECTORS LINEAR
MATRICES AND VECTORS SPACE MATRICES AND MATRIX OPERATIONS SYSTEM OF LINEAR EQUATIONS DETERMINANTS VECTORS IN -SPACE AND -SPACE GENERAL VECTOR SPACES INNER PRODUCT SPACES EIGENVALUES, EIGENVECTORS LINEAR
INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ME Applied Mthemtics for Mechnicl Engineers INTRODUCTION TO INEAR AGEBRA Mtrices nd Vectors Prof. Dr. Bülent E. Pltin Spring Sections & / ME Applied Mthemtics for Mechnicl Engineers INTRODUCTION TO INEAR
ME Applied Mthemtics for Mechnicl Engineers INTRODUCTION TO INEAR AGEBRA Mtrices nd Vectors Prof. Dr. Bülent E. Pltin Spring Sections & / ME Applied Mthemtics for Mechnicl Engineers INTRODUCTION TO INEAR
Lecture Notes No. 10
 2.6 System Identifition, Estimtion, nd Lerning Leture otes o. Mrh 3, 26 6 Model Struture of Liner ime Invrint Systems 6. Model Struture In representing dynmil system, the first step is to find n pproprite
2.6 System Identifition, Estimtion, nd Lerning Leture otes o. Mrh 3, 26 6 Model Struture of Liner ime Invrint Systems 6. Model Struture In representing dynmil system, the first step is to find n pproprite
CS434a/541a: Pattern Recognition Prof. Olga Veksler. Lecture 2
 CS434/54: Pttern Recognition Prof. Olg Veksler Lecture Outline Review of Liner Algebr vectors nd mtrices products nd norms vector spces nd liner trnsformtions eigenvlues nd eigenvectors Introduction to
CS434/54: Pttern Recognition Prof. Olg Veksler Lecture Outline Review of Liner Algebr vectors nd mtrices products nd norms vector spces nd liner trnsformtions eigenvlues nd eigenvectors Introduction to
A Primer on Continuous-time Economic Dynamics
 Eonomis 205A Fll 2008 K Kletzer A Primer on Continuous-time Eonomi Dnmis A Liner Differentil Eqution Sstems (i) Simplest se We egin with the simple liner first-orer ifferentil eqution The generl solution
Eonomis 205A Fll 2008 K Kletzer A Primer on Continuous-time Eonomi Dnmis A Liner Differentil Eqution Sstems (i) Simplest se We egin with the simple liner first-orer ifferentil eqution The generl solution
Lesson 4.1 Triangle Sum Conjecture
 Lesson 4.1 ringle um onjeture me eriod te n erises 1 9, determine the ngle mesures. 1. p, q 2., 3., 31 82 p 98 q 28 53 17 79 23 50 4. r, s, 5., 6. t t s r 100 85 100 30 4 7 31 7. s 8. m 9. m s 76 35 m
Lesson 4.1 ringle um onjeture me eriod te n erises 1 9, determine the ngle mesures. 1. p, q 2., 3., 31 82 p 98 q 28 53 17 79 23 50 4. r, s, 5., 6. t t s r 100 85 100 30 4 7 31 7. s 8. m 9. m s 76 35 m
GRAND PLAN. Visualizing Quaternions. I: Fundamentals of Quaternions. Andrew J. Hanson. II: Visualizing Quaternion Geometry. III: Quaternion Frames
 Visuliing Quternions Andrew J. Hnson Computer Siene Deprtment Indin Universit Siggrph Tutoril GRAND PLAN I: Fundmentls of Quternions II: Visuliing Quternion Geometr III: Quternion Frmes IV: Clifford Algers
Visuliing Quternions Andrew J. Hnson Computer Siene Deprtment Indin Universit Siggrph Tutoril GRAND PLAN I: Fundmentls of Quternions II: Visuliing Quternion Geometr III: Quternion Frmes IV: Clifford Algers
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA IIT KANPUR HOME ASSIGNMENTS FOR SUMMER VACATIONS CLASS - XII MATHEMATICS (Relations and Functions & Binary Operations)
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA IIT KANPUR HOME ASSIGNMENTS FOR SUMMER VACATIONS 6-7 CLASS - XII MATHEMATICS (Reltions nd Funtions & Binry Opertions) For Slow Lerners: - A Reltion is sid to e Reflexive if.. every A
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA IIT KANPUR HOME ASSIGNMENTS FOR SUMMER VACATIONS 6-7 CLASS - XII MATHEMATICS (Reltions nd Funtions & Binry Opertions) For Slow Lerners: - A Reltion is sid to e Reflexive if.. every A
CSCI 5525 Machine Learning
 CSCI 555 Mchine Lerning Some Deini*ons Qudrtic Form : nn squre mtri R n n : n vector R n the qudrtic orm: It is sclr vlue. We oten implicitly ssume tht is symmetric since / / I we write it s the elements
CSCI 555 Mchine Lerning Some Deini*ons Qudrtic Form : nn squre mtri R n n : n vector R n the qudrtic orm: It is sclr vlue. We oten implicitly ssume tht is symmetric since / / I we write it s the elements
308K. 1 Section 3.2. Zelaya Eufemia. 1. Example 1: Multiplication of Matrices: X Y Z R S R S X Y Z. By associativity we have to choices:
 8K Zely Eufemi Section 2 Exmple : Multipliction of Mtrices: X Y Z T c e d f 2 R S X Y Z 2 c e d f 2 R S 2 By ssocitivity we hve to choices: OR: X Y Z R S cr ds er fs X cy ez X dy fz 2 R S 2 Suggestion
8K Zely Eufemi Section 2 Exmple : Multipliction of Mtrices: X Y Z T c e d f 2 R S X Y Z 2 c e d f 2 R S 2 By ssocitivity we hve to choices: OR: X Y Z R S cr ds er fs X cy ez X dy fz 2 R S 2 Suggestion
Algebra Of Matrices & Determinants
 lgebr Of Mtrices & Determinnts Importnt erms Definitions & Formule 0 Mtrix - bsic introduction: mtrix hving m rows nd n columns is clled mtrix of order m n (red s m b n mtrix) nd mtrix of order lso in
lgebr Of Mtrices & Determinnts Importnt erms Definitions & Formule 0 Mtrix - bsic introduction: mtrix hving m rows nd n columns is clled mtrix of order m n (red s m b n mtrix) nd mtrix of order lso in
Operations with Matrices
 Section. Equlit of Mtrices Opertions with Mtrices There re three ws to represent mtri.. A mtri cn be denoted b n uppercse letter, such s A, B, or C.. A mtri cn be denoted b representtive element enclosed
Section. Equlit of Mtrices Opertions with Mtrices There re three ws to represent mtri.. A mtri cn be denoted b n uppercse letter, such s A, B, or C.. A mtri cn be denoted b representtive element enclosed
8.3 THE HYPERBOLA OBJECTIVES
 8.3 THE HYPERBOLA OBJECTIVES 1. Define Hperol. Find the Stndrd Form of the Eqution of Hperol 3. Find the Trnsverse Ais 4. Find the Eentriit of Hperol 5. Find the Asmptotes of Hperol 6. Grph Hperol HPERBOLAS
8.3 THE HYPERBOLA OBJECTIVES 1. Define Hperol. Find the Stndrd Form of the Eqution of Hperol 3. Find the Trnsverse Ais 4. Find the Eentriit of Hperol 5. Find the Asmptotes of Hperol 6. Grph Hperol HPERBOLAS
A Lower Bound for the Length of a Partial Transversal in a Latin Square, Revised Version
 A Lower Bound for the Length of Prtil Trnsversl in Ltin Squre, Revised Version Pooy Htmi nd Peter W. Shor Deprtment of Mthemtil Sienes, Shrif University of Tehnology, P.O.Bo 11365-9415, Tehrn, Irn Deprtment
A Lower Bound for the Length of Prtil Trnsversl in Ltin Squre, Revised Version Pooy Htmi nd Peter W. Shor Deprtment of Mthemtil Sienes, Shrif University of Tehnology, P.O.Bo 11365-9415, Tehrn, Irn Deprtment
Matrix Algebra. Matrix Addition, Scalar Multiplication and Transposition. Linear Algebra I 24
 Mtrix lger Mtrix ddition, Sclr Multipliction nd rnsposition Mtrix lger Section.. Mtrix ddition, Sclr Multipliction nd rnsposition rectngulr rry of numers is clled mtrix ( the plurl is mtrices ) nd the
Mtrix lger Mtrix ddition, Sclr Multipliction nd rnsposition Mtrix lger Section.. Mtrix ddition, Sclr Multipliction nd rnsposition rectngulr rry of numers is clled mtrix ( the plurl is mtrices ) nd the
Introduction To Matrices MCV 4UI Assignment #1
 Introduction To Mtrices MCV UI Assignment # INTRODUCTION: A mtrix plurl: mtrices) is rectngulr rry of numbers rrnged in rows nd columns Exmples: ) b) c) [ ] d) Ech number ppering in the rry is sid to be
Introduction To Mtrices MCV UI Assignment # INTRODUCTION: A mtrix plurl: mtrices) is rectngulr rry of numbers rrnged in rows nd columns Exmples: ) b) c) [ ] d) Ech number ppering in the rry is sid to be
Connectivity in Graphs. CS311H: Discrete Mathematics. Graph Theory II. Example. Paths. Connectedness. Example
 Connetiit in Grphs CSH: Disrete Mthemtis Grph Theor II Instrtor: Işıl Dillig Tpil qestion: Is it possile to get from some noe to nother noe? Emple: Trin netork if there is pth from to, possile to tke trin
Connetiit in Grphs CSH: Disrete Mthemtis Grph Theor II Instrtor: Işıl Dillig Tpil qestion: Is it possile to get from some noe to nother noe? Emple: Trin netork if there is pth from to, possile to tke trin
How do we solve these things, especially when they get complicated? How do we know when a system has a solution, and when is it unique?
 XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk bout solving systems of liner equtions. These re problems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6 2 3 7 4
XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk bout solving systems of liner equtions. These re problems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6 2 3 7 4
Unit-VII: Linear Algebra-I. To show what are the matrices, why they are useful, how they are classified as various types and how they are solved.
 Unit-VII: Liner lger-i Purpose of lession : To show wht re the mtries, wh the re useful, how the re lssified s vrious tpes nd how the re solved. Introdution: Mtries is powerful tool of modern Mthemtis
Unit-VII: Liner lger-i Purpose of lession : To show wht re the mtries, wh the re useful, how the re lssified s vrious tpes nd how the re solved. Introdution: Mtries is powerful tool of modern Mthemtis
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1. Given a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
 1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
Bases for Vector Spaces
 Bses for Vector Spces 2-26-25 A set is independent if, roughly speking, there is no redundncy in the set: You cn t uild ny vector in the set s liner comintion of the others A set spns if you cn uild everything
Bses for Vector Spces 2-26-25 A set is independent if, roughly speking, there is no redundncy in the set: You cn t uild ny vector in the set s liner comintion of the others A set spns if you cn uild everything
1.3 SCALARS AND VECTORS
 Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
Chapter 3. Vector Spaces. 3.1 Images and Image Arithmetic
 Chpter 3 Vetor Spes In Chpter 2, we sw tht the set of imges possessed numer of onvenient properties. It turns out tht ny set tht possesses similr onvenient properties n e nlyzed in similr wy. In liner
Chpter 3 Vetor Spes In Chpter 2, we sw tht the set of imges possessed numer of onvenient properties. It turns out tht ny set tht possesses similr onvenient properties n e nlyzed in similr wy. In liner
The Ellipse. is larger than the other.
 The Ellipse Appolonius of Perg (5 B.C.) disovered tht interseting right irulr one ll the w through with plne slnted ut is not perpendiulr to the is, the intersetion provides resulting urve (oni setion)
The Ellipse Appolonius of Perg (5 B.C.) disovered tht interseting right irulr one ll the w through with plne slnted ut is not perpendiulr to the is, the intersetion provides resulting urve (oni setion)
How do we solve these things, especially when they get complicated? How do we know when a system has a solution, and when is it unique?
 XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk out solving systems of liner equtions. These re prolems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6= x + x 7=
XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk out solving systems of liner equtions. These re prolems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6= x + x 7=
Math 520 Final Exam Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xiao/Dumas/Liaw) Spring 2008
 Mth 520 Finl Exm Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xio/Dums/Liw) Spring 2008 The finl exm will be held on Tuesdy, My 13, 2-5pm in 117 McMilln Wht will be covered The finl exm will cover the mteril from ll of
Mth 520 Finl Exm Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xio/Dums/Liw) Spring 2008 The finl exm will be held on Tuesdy, My 13, 2-5pm in 117 McMilln Wht will be covered The finl exm will cover the mteril from ll of
Introduction to Determinants. Remarks. Remarks. The determinant applies in the case of square matrices
 Introduction to Determinnts Remrks The determinnt pplies in the cse of squre mtrices squre mtrix is nonsingulr if nd only if its determinnt not zero, hence the term determinnt Nonsingulr mtrices re sometimes
Introduction to Determinnts Remrks The determinnt pplies in the cse of squre mtrices squre mtrix is nonsingulr if nd only if its determinnt not zero, hence the term determinnt Nonsingulr mtrices re sometimes
Chapter 3. Vector Spaces
 3.4 Liner Trnsformtions 1 Chpter 3. Vector Spces 3.4 Liner Trnsformtions Note. We hve lredy studied liner trnsformtions from R n into R m. Now we look t liner trnsformtions from one generl vector spce
3.4 Liner Trnsformtions 1 Chpter 3. Vector Spces 3.4 Liner Trnsformtions Note. We hve lredy studied liner trnsformtions from R n into R m. Now we look t liner trnsformtions from one generl vector spce
Lesson 2.1 Inductive Reasoning
 Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
September 13 Homework Solutions
 College of Engineering nd Computer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprtment Mechnicl Engineering 5A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll Ticket: 5966 Instructor: Lrry Cretto Septemer Homework Solutions. Are
College of Engineering nd Computer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprtment Mechnicl Engineering 5A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll Ticket: 5966 Instructor: Lrry Cretto Septemer Homework Solutions. Are
+ = () i =, find the values of x & y. 4. Write the function in the simplifies from. ()tan i. x x. 5. Find the derivative of. 6.
 Summer vtions Holid Home Work 7-8 Clss-XII Mths. Give the emple of reltion, whih is trnsitive ut neither refleive nor smmetri.. Find the vlues of unknown quntities if. + + () i =, find the vlues of & 7
Summer vtions Holid Home Work 7-8 Clss-XII Mths. Give the emple of reltion, whih is trnsitive ut neither refleive nor smmetri.. Find the vlues of unknown quntities if. + + () i =, find the vlues of & 7
The Algebra (al-jabr) of Matrices
 Section : Mtri lgebr nd Clculus Wshkewicz College of Engineering he lgebr (l-jbr) of Mtrices lgebr s brnch of mthemtics is much broder thn elementry lgebr ll of us studied in our high school dys. In sense
Section : Mtri lgebr nd Clculus Wshkewicz College of Engineering he lgebr (l-jbr) of Mtrices lgebr s brnch of mthemtics is much broder thn elementry lgebr ll of us studied in our high school dys. In sense
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 Dte :... IIT/AIEEE APPEARING 0 MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS PART & PART Red the following Instrutions very refully efore you proeed for PART Time : hrs. M.M. : 40 There re 0 questions in totl. Questions to
Dte :... IIT/AIEEE APPEARING 0 MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS PART & PART Red the following Instrutions very refully efore you proeed for PART Time : hrs. M.M. : 40 There re 0 questions in totl. Questions to
MTH 5102 Linear Algebra Practice Exam 1 - Solutions Feb. 9, 2016
 Nme (Lst nme, First nme): MTH 502 Liner Algebr Prctice Exm - Solutions Feb 9, 206 Exm Instructions: You hve hour & 0 minutes to complete the exm There re totl of 6 problems You must show your work Prtil
Nme (Lst nme, First nme): MTH 502 Liner Algebr Prctice Exm - Solutions Feb 9, 206 Exm Instructions: You hve hour & 0 minutes to complete the exm There re totl of 6 problems You must show your work Prtil
Numbers and indices. 1.1 Fractions. GCSE C Example 1. Handy hint. Key point
 GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
Why symmetry? Symmetry is often argued from the requirement that the strain energy must be positive. (e.g. Generalized 3-D Hooke s law)
 Why symmetry? Symmetry is oten rgued rom the requirement tht the strin energy must be positie. (e.g. Generlized -D Hooke s lw) One o the derities o energy principles is the Betti- Mxwell reciprocity theorem.
Why symmetry? Symmetry is oten rgued rom the requirement tht the strin energy must be positie. (e.g. Generlized -D Hooke s lw) One o the derities o energy principles is the Betti- Mxwell reciprocity theorem.
8 THREE PHASE A.C. CIRCUITS
 8 THREE PHSE.. IRUITS The signls in hpter 7 were sinusoidl lternting voltges nd urrents of the so-lled single se type. n emf of suh type n e esily generted y rotting single loop of ondutor (or single winding),
8 THREE PHSE.. IRUITS The signls in hpter 7 were sinusoidl lternting voltges nd urrents of the so-lled single se type. n emf of suh type n e esily generted y rotting single loop of ondutor (or single winding),
Discrete Structures, Test 2 Monday, March 28, 2016 SOLUTIONS, VERSION α
 Disrete Strutures, Test 2 Mondy, Mrh 28, 2016 SOLUTIONS, VERSION α α 1. (18 pts) Short nswer. Put your nswer in the ox. No prtil redit. () Consider the reltion R on {,,, d with mtrix digrph of R.. Drw
Disrete Strutures, Test 2 Mondy, Mrh 28, 2016 SOLUTIONS, VERSION α α 1. (18 pts) Short nswer. Put your nswer in the ox. No prtil redit. () Consider the reltion R on {,,, d with mtrix digrph of R.. Drw
Computational Biology Lecture 18: Genome rearrangements, finding maximal matches Saad Mneimneh
 Computtionl Biology Leture 8: Genome rerrngements, finding miml mthes Sd Mneimneh We hve seen how to rerrnge genome to otin nother one sed on reversls nd the knowledge of the preserved loks or genes. Now
Computtionl Biology Leture 8: Genome rerrngements, finding miml mthes Sd Mneimneh We hve seen how to rerrnge genome to otin nother one sed on reversls nd the knowledge of the preserved loks or genes. Now
Introduction to Matrix Algebra
 Itrodutio to Mtri Alger George H Olso, Ph D Dotorl Progrm i Edutiol Ledership Applhi Stte Uiversit Septemer Wht is mtri? Dimesios d order of mtri A p q dimesioed mtri is p (rows) q (olums) rr of umers,
Itrodutio to Mtri Alger George H Olso, Ph D Dotorl Progrm i Edutiol Ledership Applhi Stte Uiversit Septemer Wht is mtri? Dimesios d order of mtri A p q dimesioed mtri is p (rows) q (olums) rr of umers,
M344 - ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS
 M3 - ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS Lecture 18: Lplce s Eqution, Anltic nd Numericl Solution Our emple of n elliptic prtil differentil eqution is Lplce s eqution, lso clled the Diffusion Eqution. If
M3 - ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS Lecture 18: Lplce s Eqution, Anltic nd Numericl Solution Our emple of n elliptic prtil differentil eqution is Lplce s eqution, lso clled the Diffusion Eqution. If
Lecture Solution of a System of Linear Equation
 ChE Lecture Notes, Dept. of Chemicl Engineering, Univ. of TN, Knoville - D. Keffer, 5/9/98 (updted /) Lecture 8- - Solution of System of Liner Eqution 8. Why is it importnt to e le to solve system of liner
ChE Lecture Notes, Dept. of Chemicl Engineering, Univ. of TN, Knoville - D. Keffer, 5/9/98 (updted /) Lecture 8- - Solution of System of Liner Eqution 8. Why is it importnt to e le to solve system of liner
THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
 MD THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY CA CB C Coordintes of point in spe There re infinite numer of points in spe We wnt to identif eh nd ever point of spe with the help of three mutull perpendiulr oordintes es
MD THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY CA CB C Coordintes of point in spe There re infinite numer of points in spe We wnt to identif eh nd ever point of spe with the help of three mutull perpendiulr oordintes es
QUADRATIC EQUATION. Contents
 QUADRATIC EQUATION Contents Topi Pge No. Theory 0-04 Exerise - 05-09 Exerise - 09-3 Exerise - 3 4-5 Exerise - 4 6 Answer Key 7-8 Syllus Qudrti equtions with rel oeffiients, reltions etween roots nd oeffiients,
QUADRATIC EQUATION Contents Topi Pge No. Theory 0-04 Exerise - 05-09 Exerise - 09-3 Exerise - 3 4-5 Exerise - 4 6 Answer Key 7-8 Syllus Qudrti equtions with rel oeffiients, reltions etween roots nd oeffiients,
are coplanar. ˆ ˆ ˆ and iˆ
 SML QUSTION Clss XII Mthemtis Time llowed: hrs Mimum Mrks: Generl Instrutions: i ll questions re ompulsor ii The question pper onsists of 6 questions divided into three Setions, B nd C iii Question No
SML QUSTION Clss XII Mthemtis Time llowed: hrs Mimum Mrks: Generl Instrutions: i ll questions re ompulsor ii The question pper onsists of 6 questions divided into three Setions, B nd C iii Question No
Lecture 1 - Introduction and Basic Facts about PDEs
 * 18.15 - Introdution to PDEs, Fll 004 Prof. Gigliol Stffilni Leture 1 - Introdution nd Bsi Fts bout PDEs The Content of the Course Definition of Prtil Differentil Eqution (PDE) Liner PDEs VVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVV
* 18.15 - Introdution to PDEs, Fll 004 Prof. Gigliol Stffilni Leture 1 - Introdution nd Bsi Fts bout PDEs The Content of the Course Definition of Prtil Differentil Eqution (PDE) Liner PDEs VVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVV
The University of Nottingham SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE A LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER MACHINES AND THEIR LANGUAGES ANSWERS
 The University of ottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTR SCIC A LVL 2 MODUL, SPRIG SMSTR 2015 2016 MACHIS AD THIR LAGUAGS ASWRS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my omplete the front over of their nswer ook nd sign their
The University of ottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTR SCIC A LVL 2 MODUL, SPRIG SMSTR 2015 2016 MACHIS AD THIR LAGUAGS ASWRS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my omplete the front over of their nswer ook nd sign their
Here we consider the matrix transformation for a square matrix from a geometric point of view.
 Section. he Mgnifiction Fctor In Section.5 we iscusse the mtri trnsformtion etermine mtri A. For n m n mtri A the function f(c) = Ac provies corresponence etween vectors in R n n R m. Here we consier the
Section. he Mgnifiction Fctor In Section.5 we iscusse the mtri trnsformtion etermine mtri A. For n m n mtri A the function f(c) = Ac provies corresponence etween vectors in R n n R m. Here we consier the
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
 PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
Lecture 8 Wrap-up Part1, Matlab
 Lecture 8 Wrp-up Prt1, Mtlb Homework Polic Plese stple our homework (ou will lose 10% credit if not stpled or secured) Submit ll problems in order. This mens to plce ever item relting to problem 3 (our
Lecture 8 Wrp-up Prt1, Mtlb Homework Polic Plese stple our homework (ou will lose 10% credit if not stpled or secured) Submit ll problems in order. This mens to plce ever item relting to problem 3 (our
Lesson 2.1 Inductive Reasoning
 Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Quotient Rule: am a n = am n (a 0) Negative Exponents: a n = 1 (a 0) an Power Rules: (a m ) n = a m n (ab) m = a m b m
 Formuls nd Concepts MAT 099: Intermedite Algebr repring for Tests: The formuls nd concepts here m not be inclusive. You should first tke our prctice test with no notes or help to see wht mteril ou re comfortble
Formuls nd Concepts MAT 099: Intermedite Algebr repring for Tests: The formuls nd concepts here m not be inclusive. You should first tke our prctice test with no notes or help to see wht mteril ou re comfortble
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals
 AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
Probability. b a b. a b 32.
 Proility If n event n hppen in '' wys nd fil in '' wys, nd eh of these wys is eqully likely, then proility or the hne, or its hppening is, nd tht of its filing is eg, If in lottery there re prizes nd lnks,
Proility If n event n hppen in '' wys nd fil in '' wys, nd eh of these wys is eqully likely, then proility or the hne, or its hppening is, nd tht of its filing is eg, If in lottery there re prizes nd lnks,
ECE Microwave Engineering. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 8. Waveguides Part 5: Coaxial Cable
 ECE 5317-6351 Mirowve Engineering Fll 17 Prof. Dvid R. Jkson Dept. of ECE Notes 8 Wveguides Prt 5: Coil Cle 1 Coil Line: TEM Mode To find the TEM mode fields, we need to solve: ( ρφ) Φ, ; Φ ( ) V Φ ( )
ECE 5317-6351 Mirowve Engineering Fll 17 Prof. Dvid R. Jkson Dept. of ECE Notes 8 Wveguides Prt 5: Coil Cle 1 Coil Line: TEM Mode To find the TEM mode fields, we need to solve: ( ρφ) Φ, ; Φ ( ) V Φ ( )
Chapter 2. Determinants
 Chpter Determinnts The Determinnt Function Recll tht the X mtrix A c b d is invertible if d-bc0. The expression d-bc occurs so frequently tht it hs nme; it is clled the determinnt of the mtrix A nd is
Chpter Determinnts The Determinnt Function Recll tht the X mtrix A c b d is invertible if d-bc0. The expression d-bc occurs so frequently tht it hs nme; it is clled the determinnt of the mtrix A nd is
Electromagnetism Notes, NYU Spring 2018
 Eletromgnetism Notes, NYU Spring 208 April 2, 208 Ation formultion of EM. Free field desription Let us first onsider the free EM field, i.e. in the bsene of ny hrges or urrents. To tret this s mehnil system
Eletromgnetism Notes, NYU Spring 208 April 2, 208 Ation formultion of EM. Free field desription Let us first onsider the free EM field, i.e. in the bsene of ny hrges or urrents. To tret this s mehnil system
Ch. 2.3 Counting Sample Points. Cardinality of a Set
 Ch..3 Counting Smple Points CH 8 Crdinlity of Set Let S e set. If there re extly n distint elements in S, where n is nonnegtive integer, we sy S is finite set nd n is the rdinlity of S. The rdinlity of
Ch..3 Counting Smple Points CH 8 Crdinlity of Set Let S e set. If there re extly n distint elements in S, where n is nonnegtive integer, we sy S is finite set nd n is the rdinlity of S. The rdinlity of
Calculus Cheat Sheet. Integrals Definitions. where F( x ) is an anti-derivative of f ( x ). Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. dx = f x dx g x dx
 Clulus Chet Sheet Integrls Definitions Definite Integrl: Suppose f ( ) is ontinuous Anti-Derivtive : An nti-derivtive of f ( ) on [, ]. Divide [, ] into n suintervls of is funtion, F( ), suh tht F = f.
Clulus Chet Sheet Integrls Definitions Definite Integrl: Suppose f ( ) is ontinuous Anti-Derivtive : An nti-derivtive of f ( ) on [, ]. Divide [, ] into n suintervls of is funtion, F( ), suh tht F = f.
Chapter 14. Matrix Representations of Linear Transformations
 Chpter 4 Mtrix Representtions of Liner Trnsformtions When considering the Het Stte Evolution, we found tht we could describe this process using multipliction by mtrix. This ws nice becuse computers cn
Chpter 4 Mtrix Representtions of Liner Trnsformtions When considering the Het Stte Evolution, we found tht we could describe this process using multipliction by mtrix. This ws nice becuse computers cn
CS311 Computational Structures Regular Languages and Regular Grammars. Lecture 6
 CS311 Computtionl Strutures Regulr Lnguges nd Regulr Grmmrs Leture 6 1 Wht we know so fr: RLs re losed under produt, union nd * Every RL n e written s RE, nd every RE represents RL Every RL n e reognized
CS311 Computtionl Strutures Regulr Lnguges nd Regulr Grmmrs Leture 6 1 Wht we know so fr: RLs re losed under produt, union nd * Every RL n e written s RE, nd every RE represents RL Every RL n e reognized
Matrix Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors September 13, 2017
 Mtri Eigenvlues nd Eigenvectors September, 7 Mtri Eigenvlues nd Eigenvectors Lrry Cretto Mechnicl Engineering 5A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis September, 7 Outline Review lst lecture Definition of eigenvlues
Mtri Eigenvlues nd Eigenvectors September, 7 Mtri Eigenvlues nd Eigenvectors Lrry Cretto Mechnicl Engineering 5A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis September, 7 Outline Review lst lecture Definition of eigenvlues
Matrices. Elementary Matrix Theory. Definition of a Matrix. Matrix Elements:
 Mtrices Elementry Mtrix Theory It is often desirble to use mtrix nottion to simplify complex mthemticl expressions. The simplifying mtrix nottion usully mkes the equtions much esier to hndle nd mnipulte.
Mtrices Elementry Mtrix Theory It is often desirble to use mtrix nottion to simplify complex mthemticl expressions. The simplifying mtrix nottion usully mkes the equtions much esier to hndle nd mnipulte.
MATH34032: Green s Functions, Integral Equations and the Calculus of Variations 1. 1 [(y ) 2 + yy + y 2 ] dx,
![MATH34032: Green s Functions, Integral Equations and the Calculus of Variations 1. 1 [(y ) 2 + yy + y 2 ] dx, MATH34032: Green s Functions, Integral Equations and the Calculus of Variations 1. 1 [(y ) 2 + yy + y 2 ] dx,](/thumbs/89/98261542.jpg) MATH3403: Green s Funtions, Integrl Equtions nd the Clulus of Vritions 1 Exmples 5 Qu.1 Show tht the extreml funtion of the funtionl I[y] = 1 0 [(y ) + yy + y ] dx, where y(0) = 0 nd y(1) = 1, is y(x)
MATH3403: Green s Funtions, Integrl Equtions nd the Clulus of Vritions 1 Exmples 5 Qu.1 Show tht the extreml funtion of the funtionl I[y] = 1 0 [(y ) + yy + y ] dx, where y(0) = 0 nd y(1) = 1, is y(x)
LESSON 11: TRIANGLE FORMULAE
 . THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
. THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
HOMEWORK FOR CLASS XII ( )
 HOMEWORK FOR CLASS XII 8-9 Show tht the reltion R on the set Z of ll integers defined R,, Z,, is, divisile,, is n equivlene reltion on Z Let f: R R e defined if f if Is f one-one nd onto if If f, g : R
HOMEWORK FOR CLASS XII 8-9 Show tht the reltion R on the set Z of ll integers defined R,, Z,, is, divisile,, is n equivlene reltion on Z Let f: R R e defined if f if Is f one-one nd onto if If f, g : R
3 Angle Geometry. 3.1 Measuring Angles. 1. Using a protractor, measure the marked angles.
 3 ngle Geometry MEP Prtie ook S3 3.1 Mesuring ngles 1. Using protrtor, mesure the mrked ngles. () () (d) (e) (f) 2. Drw ngles with the following sizes. () 22 () 75 120 (d) 90 (e) 153 (f) 45 (g) 180 (h)
3 ngle Geometry MEP Prtie ook S3 3.1 Mesuring ngles 1. Using protrtor, mesure the mrked ngles. () () (d) (e) (f) 2. Drw ngles with the following sizes. () 22 () 75 120 (d) 90 (e) 153 (f) 45 (g) 180 (h)
Dorf, R.C., Wan, Z. T- Equivalent Networks The Electrical Engineering Handbook Ed. Richard C. Dorf Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 2000
 orf, R.C., Wn,. T- Equivlent Networks The Eletril Engineering Hndook Ed. Rihrd C. orf Bo Rton: CRC Press LLC, 000 9 T P Equivlent Networks hen Wn University of Cliforni, vis Rihrd C. orf University of
orf, R.C., Wn,. T- Equivlent Networks The Eletril Engineering Hndook Ed. Rihrd C. orf Bo Rton: CRC Press LLC, 000 9 T P Equivlent Networks hen Wn University of Cliforni, vis Rihrd C. orf University of
Engr354: Digital Logic Circuits
 Engr354: Digitl Logi Ciruits Chpter 4: Logi Optimiztion Curtis Nelson Logi Optimiztion In hpter 4 you will lern out: Synthesis of logi funtions; Anlysis of logi iruits; Tehniques for deriving minimum-ost
Engr354: Digitl Logi Ciruits Chpter 4: Logi Optimiztion Curtis Nelson Logi Optimiztion In hpter 4 you will lern out: Synthesis of logi funtions; Anlysis of logi iruits; Tehniques for deriving minimum-ost
LINEAR ALGEBRA APPLIED
 5.5 Applictions of Inner Product Spces 5.5 Applictions of Inner Product Spces 7 Find the cross product of two vectors in R. Find the liner or qudrtic lest squres pproimtion of function. Find the nth-order
5.5 Applictions of Inner Product Spces 5.5 Applictions of Inner Product Spces 7 Find the cross product of two vectors in R. Find the liner or qudrtic lest squres pproimtion of function. Find the nth-order
8.6 The Hyperbola. and F 2. is a constant. P F 2. P =k The two fixed points, F 1. , are called the foci of the hyperbola. The line segments F 1
 8. The Hperol Some ships nvigte using rdio nvigtion sstem clled LORAN, which is n cronm for LOng RAnge Nvigtion. A ship receives rdio signls from pirs of trnsmitting sttions tht send signls t the sme time.
8. The Hperol Some ships nvigte using rdio nvigtion sstem clled LORAN, which is n cronm for LOng RAnge Nvigtion. A ship receives rdio signls from pirs of trnsmitting sttions tht send signls t the sme time.
Review Topic 14: Relationships between two numerical variables
 Review Topi 14: Reltionships etween two numeril vriles Multiple hoie 1. Whih of the following stterplots est demonstrtes line of est fit? A B C D E 2. The regression line eqution for the following grph
Review Topi 14: Reltionships etween two numeril vriles Multiple hoie 1. Whih of the following stterplots est demonstrtes line of est fit? A B C D E 2. The regression line eqution for the following grph
Before we can begin Ch. 3 on Radicals, we need to be familiar with perfect squares, cubes, etc. Try and do as many as you can without a calculator!!!
 Nme: Algebr II Honors Pre-Chpter Homework Before we cn begin Ch on Rdicls, we need to be fmilir with perfect squres, cubes, etc Try nd do s mny s you cn without clcultor!!! n The nth root of n n Be ble
Nme: Algebr II Honors Pre-Chpter Homework Before we cn begin Ch on Rdicls, we need to be fmilir with perfect squres, cubes, etc Try nd do s mny s you cn without clcultor!!! n The nth root of n n Be ble
MCR 3U Exam Review. 1. Determine which of the following equations represent functions. Explain. Include a graph. 2. y x
 MCR U MCR U Em Review Introduction to Functions. Determine which of the following equtions represent functions. Eplin. Include grph. ) b) c) d) 0. Stte the domin nd rnge for ech reltion in question.. If
MCR U MCR U Em Review Introduction to Functions. Determine which of the following equtions represent functions. Eplin. Include grph. ) b) c) d) 0. Stte the domin nd rnge for ech reltion in question.. If
Running an NFA & the subset algorithm (NFA->DFA) CS 350 Fall 2018 gilray.org/classes/fall2018/cs350/
 Running n NFA & the suset lgorithm (NFA->DFA) CS 350 Fll 2018 gilry.org/lsses/fll2018/s350/ 1 NFAs operte y simultneously exploring ll pths nd epting if ny pth termintes t n ept stte.!2 Try n exmple: L
Running n NFA & the suset lgorithm (NFA->DFA) CS 350 Fll 2018 gilry.org/lsses/fll2018/s350/ 1 NFAs operte y simultneously exploring ll pths nd epting if ny pth termintes t n ept stte.!2 Try n exmple: L
The Trapezoidal Rule
 _.qd // : PM Pge 9 SECTION. Numericl Integrtion 9 f Section. The re of the region cn e pproimted using four trpezoids. Figure. = f( ) f( ) n The re of the first trpezoid is f f n. Figure. = Numericl Integrtion
_.qd // : PM Pge 9 SECTION. Numericl Integrtion 9 f Section. The re of the region cn e pproimted using four trpezoids. Figure. = f( ) f( ) n The re of the first trpezoid is f f n. Figure. = Numericl Integrtion
