Taunton River Salt Marsh Assessment Results from 2014 season
|
|
|
- Andrea Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Taunton River Salt Marsh Assessment Results from 2014 season December, 2014 During the late summer and fall of 2014, Save The Bay evaluated salt marshes in Assonet Bay, Freetown and Broad Cove in Dighton and Somerset, using the Rhode Island Salt Marsh Assessment monitoring protocol. This assessment has been used during the past three years in marshes within Narragansett Bay. The Broad Cove marsh was the northernmost marsh surveyed within the Narragansett Bay watershed to date. We also assessed a section of marsh in Assonet Bay near Payne Cove in the fall of The results of these assessments were compared with the overall data for all Bay marshes. 1
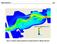
2 Locations of Assonet Marsh Transects, all located around Assonet Bay Shores in Freetown Payne Cove Marsh, completed in 2012 Shepherds Cove 2
3 Wescott Island In general, these areas of salt marsh are isolated within small coves and are bordered by steep uplands surrounded by residential development. It is important to note that Assonet Bay Shores relies on City of Fall River water and septic systems, so residential water is discharged to the ground, resulting in high water tables in the surrounding salt marsh areas. 3
4 Locations of Transects in Broad Cove East side, Dighton East side, Somerset 4
5 West Side, Dighton The marshes around Broad Cove are bordered by gentle uplands that are in use as pasture or residential landscape and open woods. This area is sewered and is served by public water. The marsh on the west side is bordered by Route 138 and on the east side by Pleasant Street and the Taunton River. Marsh Zonation It is generally recognized that the salt marshes in the Taunton River and in the Assonet River in particular are some of the healthiest in Narragansett Bay. The Assonet Bay has the largest areas of contiguous marsh in the Narragansett Bay watershed. In general, the marshes in the Taunton River have a higher elevation in relation to their tidal range. This higher elevation makes these marshes less susceptible to sea level rise as documented by the large percentage of the marsh that is dominated by high marsh vegetation. Other marshes in Narragansett Bay are dominated by Spartina alterniflora and show larger transitional zones and pannes. The tidal range at Fall River is about one foot higher than at Newport. The marshes in Broad Cove in particular have more space to migrate inland across a low coastal plain that is currently in agricultural use. Marsh migration is occurring in a mowed field on the 5
6 eastern side of Broad Cove as documented by Phragmites and upper salt marsh vegetation growing in a field adjacent to the marsh. Many of the marshes in Narragansett Bay have begun to show a change in plant zonation due to frequent flooding and increasingly high tides. Typical marsh zonation outlined below In marshes that are transitioning due to sea level rise and other flooding factors, areas of high marsh shrink to the outer and upper edges of the marsh that are higher elevation and can drain. Short-form Spartina alterniflora (a low marsh grass that can tolerate more frequent flooding and standing water to a degree) becomes dominant in a larger percentage of the marsh due to increased salt water inundation and flooding. In transitional marsh areas, high marsh vegetation and short-form Spartina alterniflora grow together. Over time high marsh vegetation is replaced by short-form Spartina alterniflora or bare areas based upon the amount of flooding or inundation. 6
7 Transitioning marsh outlined below Salt marshes in Assonet and Broad Cove exhibit a more traditional zonation and a higher percentage of high marsh than other Narragansett Bay and coastal Rhode Island marshes. They have a much smaller percentage of short form Spartina alterniflora and transitional marsh where low marsh and high marsh plants grow together. When Broad Cove and Assonet are compared, Broad Cove exhibited a smaller percentage of low marsh because of high rates of erosion along the marsh edge. Large numbers of fiddler crabs were observed during sampling and in some areas low marsh on the edge was almost entirely eroded away with high marsh growing right to the marsh edge. Broad Cove also showed a large terrestrial border when compared to Assonet which is bordered by a steep upland. Broad Cove has large areas of Phragmites that are expanding into what were once active fields. 7
8 Plant species The biggest contrast between Taunton watershed marshes and those in the rest of the study area was shown with percentage cover of Spartina alterniflora. There is less coverage of Spartina alterniflora in the Taunton River marshes, little or no short-form Spartina alterniflora or transitional marsh and no unvegetated areas. In the Taunton, Spartina alterniflora is found on the outer edge of the marsh. There is a greater percentage of high marsh grasses including Spartina patens, Juncus gerardi and Distichlis spicata in marshes of the Taunton River in comparison to marshes in the rest of Narragansett Bay and the south shore of Rhode Island. There is little or no transitional marsh in the Taunton River where high marsh plants and shortform Spartina alterniflora grow together in comparison to the rest of Narragansett Bay. Additionally, there are no bare or die off areas, where no vegetation is growing. These bare areas were documented in most marshes in Narragansett Bay and the coastal ponds. Marshes in the Taunton River, in particular within Broad Cove, are rapidly eroding along their tidal edge, but are retaining their interior elevation. The marsh interior shows higher percentages of salt marsh grasses and rushes such as Juncus (black rush) and Distichlis (spike grass). Tall form Spartina alterniflora along the outer edge of the salt marsh has largely been eroded away, and there are few if any transitional zones. The cause of this marsh edge erosion is unclear and may be related to higher tides that cause erosion of soil particles within the marsh peat or it could be caused by herbivory of the marsh plants due to higher numbers of fiddler crabs and purple marsh crabs. The rapid erosion of the marsh edge and widening of creeks is being observed in marshes throughout the upper Narragansett Bay. 8
9 Plant Species/Cover Type Soil bearing capacity Soil bearing capacity also presented a large contrast between Taunton River marshes and those in the rest of the study area. Soil bearing capacity measures the ability for the soil to support a load applied to the surface. It shows the integrity of the marsh peat which holds plant roots and soil. In the study area, the bare areas and the areas of short-form Spartina alterniflora had low bearing capacity (high penetration depth), which means that their internal structure is weak. Broad Cove exhibited low bearing capacity in the low marsh with rapid erosion and slumping of the marsh edge and more stable high marsh in comparison to all marshes. Assonet Bay showed a very soft high marsh, with a more stable low marsh. The integrity of the high marsh in this area may be compromised by nutrient rich groundwater due to septic system discharges. It has been shown that in eutrophic areas (areas with high human input of nutrients), salt marsh peat tends to be weaker, more decomposed and less resistant to erosion. In addition, increased inundation due to sea level rise causes declines in plant productivity and accumulation of below ground biomass. These results show that these marshes are beginning to show early signs of stress and may begin to experience die back in the future. 9
10 Penetration Depth by Marsh Zone Conclusions While the Assonet and Broad Cove marshes seem to be healthy by looking at them, they are highly susceptible to erosion and are beginning to show signs of stress related to high nutrient loads, sea level rise and crab predation. Because of their higher elevation, the traditional marsh zonation with large areas of high marsh remains in this area. The marsh surface, however, shows signs of pock marks and hummocks, and bearing capacity shows that the internal marsh structure is failing in the Assonet marshes. A recent study has shown that marshes may be swelling due to being waterlogged. Below ground growth of organic material is the primary way that marshes keep up with sea level rise, because our watersheds are generally sediment poor. Without this growth of marsh peat, continued inundation will cause further marsh subsidence. This is being seen first in marshes throughout Narragansett Bay, and evidence is beginning to show signs of marsh degradation in the Taunton River as well. Continued monitoring and evaluation will need to be conducted to see if this process continues. 10
11 The Taunton River presents an opportunity to support marsh migration through the continued protection of land adjacent to salt marshes. While those marshes that are bordered by steep upland, such as those near Assonet Bay Shores, may not be able to migrate and may drown in place, others that are bordered by low lying agricultural fields may be able to migrate inland. It will also be interesting to look at brackish marshes higher up in the watershed to watch their transition as the salt wedge moves northward with sea level rise. Additionally, there are sites on Broad Cove where creek excavation could occur to drain newly forming impounded water areas. Photos Broad Cove, September Photo shows crab holes and edge erosion. Note the lack of Spartina alterniflora and high marsh extending to marsh edge. 11
12 West Side of Broad Cove, September Large areas of Spartina patens with some standing water in un-vegetated pannes. Assonet, Shepherds Cove, October, This photo shows the pock marked nature of the high marsh where hummocks of Spartina patens grow with areas of bare ground between. These areas of high marsh showed relatively low bearing capacity compared with high marsh in other areas. 12
13 East Side of Broad Cove, October High marsh dominated by Juncus gerardii and Distichlis spicata. This marsh zone was very stable and solid. This zone type is much more dominant in the Taunton River than in other marshes in Narragansett Bay and the Rhode Island south shore where transitional areas dominate. 13
4.2 Tidal Wetlands. Phragmites Australis
 4.2 Tidal Wetlands Few topics elicit such strong emotions in Guilford as the current state of salt marshes. These marshes, more broadly known as tidal wetlands, are undergoing a transformation as sea level
4.2 Tidal Wetlands Few topics elicit such strong emotions in Guilford as the current state of salt marshes. These marshes, more broadly known as tidal wetlands, are undergoing a transformation as sea level
Types of Wetlands. Tidal Systems
 Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems 1 COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands 2 Tidal Estuarine Wetland 3 Definition and Formation of Estuaries Estuary: : partially
Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems 1 COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands 2 Tidal Estuarine Wetland 3 Definition and Formation of Estuaries Estuary: : partially
Subtidal permanently flooded with tidal water. Irregularly exposed surface exposed by tides less often than daily
 Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands Tidal Estuarine Wetland 1 Definition and Formation of Estuaries u Estuary : partially
Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands Tidal Estuarine Wetland 1 Definition and Formation of Estuaries u Estuary : partially
Coastal Tidal Marshes
 Virginia s Wetlands Coastal Tidal Marshes Hydrology driven by lunar tides; Stresses include tidal inundation and/or salts; Found along high latitudes along intertidal coasts; Comprise ~ 70% wetlands of
Virginia s Wetlands Coastal Tidal Marshes Hydrology driven by lunar tides; Stresses include tidal inundation and/or salts; Found along high latitudes along intertidal coasts; Comprise ~ 70% wetlands of
Second Annual Monitoring Report Tidal Wetland Restoration 159 Long Neck Point Road, Darien, CT NAE
 1) Project Overview Second Annual Monitoring Report Tidal Wetland Restoration 159 Long Neck Point Road, Darien, CT NAE-2007-1130 December 13, 2013 This is the second year of a five year monitoring program
1) Project Overview Second Annual Monitoring Report Tidal Wetland Restoration 159 Long Neck Point Road, Darien, CT NAE-2007-1130 December 13, 2013 This is the second year of a five year monitoring program
exposed has to the this soil lowest water salinity. However in the fall, following a lot of Underground
 How deep it collects from Background information for Data Analysis for Mass Audubon s Salt Marsh Science Project* We are measuring salinity at different depths to see what conditions Phragmites, and other
How deep it collects from Background information for Data Analysis for Mass Audubon s Salt Marsh Science Project* We are measuring salinity at different depths to see what conditions Phragmites, and other
Factors Governing Successful Tidal Wetland Mitigation. Walter I. Priest, III Wetland Design and Restoration ASWM Webinar 16 July 2018
 Factors Governing Successful Tidal Wetland Mitigation Walter I. Priest, III Wetland Design and Restoration ASWM Webinar 16 July 2018 Goals and Objectives Successful Tidal Wetland Mitigation Primary production
Factors Governing Successful Tidal Wetland Mitigation Walter I. Priest, III Wetland Design and Restoration ASWM Webinar 16 July 2018 Goals and Objectives Successful Tidal Wetland Mitigation Primary production
Pablo Bay in Sonoma, Solano, and Napa Counties. It is owned and managed by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife
 Appendix L San Pablo Bay Marsh Introduction San Pablo Bay National Wildlife Refuge marsh (hereafter San Pablo) is located on the north shore of San Pablo Bay in Sonoma, Solano, and Napa Counties. It is
Appendix L San Pablo Bay Marsh Introduction San Pablo Bay National Wildlife Refuge marsh (hereafter San Pablo) is located on the north shore of San Pablo Bay in Sonoma, Solano, and Napa Counties. It is
Third Annual Monitoring Report Tidal Wetland Restoration 159 Long Neck Point Road, Darien, CT NAE
 1) Project Overview Third Annual Monitoring Report Tidal Wetland Restoration 159 Long Neck Point Road, Darien, CT NAE-2007-1130 December 15, 2014 This is the third year of a five year monitoring program
1) Project Overview Third Annual Monitoring Report Tidal Wetland Restoration 159 Long Neck Point Road, Darien, CT NAE-2007-1130 December 15, 2014 This is the third year of a five year monitoring program
I. Tidal Salt Marshes (TSMs)
 NREM 665 Salt Marshes 2 I. Tidal Salt Marshes (TSMs) A. Def: halophytic grassland & dwarf brushwood on alluvial sediments bordering saline H 2 O bodies whose H 2 O level fluctuates tidally (Beeftink 1977)
NREM 665 Salt Marshes 2 I. Tidal Salt Marshes (TSMs) A. Def: halophytic grassland & dwarf brushwood on alluvial sediments bordering saline H 2 O bodies whose H 2 O level fluctuates tidally (Beeftink 1977)
The rate and fate of coastal carbon burial
 The rate and fate of coastal carbon burial Matthew L. Kirwan, Virginia Institute of Marine Science Main Points Marsh size Marsh accretion 1. SLR drives wetland carbon burial in vertical and lateral dimensions
The rate and fate of coastal carbon burial Matthew L. Kirwan, Virginia Institute of Marine Science Main Points Marsh size Marsh accretion 1. SLR drives wetland carbon burial in vertical and lateral dimensions
Recent studies indicate that both climate warming (1, 2) and
 Rapid shoreward encroachment of salt marsh cordgrass in response to accelerated sea-level rise Jeffrey P. Donnelly* and Mark D. Bertness Departments of *Geological Sciences and Ecology and Evolutionary
Rapid shoreward encroachment of salt marsh cordgrass in response to accelerated sea-level rise Jeffrey P. Donnelly* and Mark D. Bertness Departments of *Geological Sciences and Ecology and Evolutionary
Section 145 Climate Change and Sea Level Rise
 Section 145 Climate Change and Sea Level Rise A. Definitions Rhode Island Coastal Resources Management Program 1. Climate is the long-term weather average observed within a geographic region, and climate
Section 145 Climate Change and Sea Level Rise A. Definitions Rhode Island Coastal Resources Management Program 1. Climate is the long-term weather average observed within a geographic region, and climate
Changes in Texas Ecoregions
 Comment On Lesson Changes in Texas Ecoregions The state of Texas can be divided into 10 distinct areas based on unique combinations of vegetation, topography, landforms, wildlife, soil, rock, climate,
Comment On Lesson Changes in Texas Ecoregions The state of Texas can be divided into 10 distinct areas based on unique combinations of vegetation, topography, landforms, wildlife, soil, rock, climate,
Effect of wrack accumulation on salt marsh vegetation, Baruch Institute, Georgetown County, South Carolina
 Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions VI 305 Effect of wrack accumulation on salt marsh vegetation, Baruch Institute, Georgetown County, South Carolina R. Stalter 1, A. Jung 1, A. Starosta 1, J. Baden
Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions VI 305 Effect of wrack accumulation on salt marsh vegetation, Baruch Institute, Georgetown County, South Carolina R. Stalter 1, A. Jung 1, A. Starosta 1, J. Baden
Ms. A. Mormando's Class *
 8 th Grade Science Essential Standard: 8.E.1.1 Explain the structure of the hydrosphere including: Water distribution on Earth; Local river basin and water availability Stream - A stream is a body of water
8 th Grade Science Essential Standard: 8.E.1.1 Explain the structure of the hydrosphere including: Water distribution on Earth; Local river basin and water availability Stream - A stream is a body of water
Coastal Oceanography. Coastal Oceanography. Coastal Waters
 Coastal Oceanography Coastal Oceanography 95% of ocean life is in coastal waters (320 km from shore) Estuaries and wetlands are among most productive ecosystems on Earth Major shipping routes, oil and
Coastal Oceanography Coastal Oceanography 95% of ocean life is in coastal waters (320 km from shore) Estuaries and wetlands are among most productive ecosystems on Earth Major shipping routes, oil and
THIN-LAYER PLACEMENT OF DREDGE MATERIAL FOR MARSH NOURISHMENT, RESOTRATION, AND RESPONSE TO SEA LEVEL RISE
 THIN-LAYER PLACEMENT OF DREDGE MATERIAL FOR MARSH NOURISHMENT, RESOTRATION, AND RESPONSE TO SEA LEVEL RISE Case studies and lesson learned regarding thin-layer deposition projects in Delaware, New Jersey,
THIN-LAYER PLACEMENT OF DREDGE MATERIAL FOR MARSH NOURISHMENT, RESOTRATION, AND RESPONSE TO SEA LEVEL RISE Case studies and lesson learned regarding thin-layer deposition projects in Delaware, New Jersey,
Coastal Ecosystems: Salt Marshes and Mangroves. Marine Biology Dr. Ouida Meier
 Coastal Ecosystems: Salt Marshes and Mangroves Marine Biology Dr. Ouida Meier Factors Driving Coastal Ecosystems Latitude temperature light, seasonality Tidal cycles amplitude frequency Wave energy Degree
Coastal Ecosystems: Salt Marshes and Mangroves Marine Biology Dr. Ouida Meier Factors Driving Coastal Ecosystems Latitude temperature light, seasonality Tidal cycles amplitude frequency Wave energy Degree
Year 6. Geography. Revision
 Year 6 Geography Revision November 2017 Rivers and World knowledge How the water cycle works and the meaning of the terms evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration, surface run-off, groundwater
Year 6 Geography Revision November 2017 Rivers and World knowledge How the water cycle works and the meaning of the terms evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration, surface run-off, groundwater
Some Thoughts on the Role of Elevation
 Some Thoughts on the Role of Elevation Data in Sea-level Rise Impact Assessments Rob Thieler* U.S. Geological Survey Coastal and Marine Geology Program Woods Hole, MA *i l d t i l d f D C h D G h *includes
Some Thoughts on the Role of Elevation Data in Sea-level Rise Impact Assessments Rob Thieler* U.S. Geological Survey Coastal and Marine Geology Program Woods Hole, MA *i l d t i l d f D C h D G h *includes
Research Background: Researcher Sam Bond taking Sediment Elevation Table (SET) measurements in the marsh. A view of salt marsh hay growing in a marsh
 Name Keeping up with the sea level Featured scientist: Anne Giblin from the Marine Biological Laboratory and the Plum Island Ecosystems Long-Term Ecological Research site Research Background: Salt marshes
Name Keeping up with the sea level Featured scientist: Anne Giblin from the Marine Biological Laboratory and the Plum Island Ecosystems Long-Term Ecological Research site Research Background: Salt marshes
SOP 1: Vegetation Monitoring in Salt Marshes using Rapid Assessment Method
 SOP 1: Vegetation Monitoring in Salt Marshes using Rapid Assessment Method Adapted from: Rapid Method for Assessing Estuarine (Salt) Marshes in New England Version 1.4 October 2006 by Bruce Carlisle &
SOP 1: Vegetation Monitoring in Salt Marshes using Rapid Assessment Method Adapted from: Rapid Method for Assessing Estuarine (Salt) Marshes in New England Version 1.4 October 2006 by Bruce Carlisle &
Estuarine marshes along the Elbe: past, present and future
 Universität Hamburg Deltas and Climate Change - : past, present and future Kai Jensen & S. Albrecht, Chr. Butzeck, G. Engels, F. Müller, U. Schröder Universität Hamburg kai.jensen@botanik.uni-hamburg.de
Universität Hamburg Deltas and Climate Change - : past, present and future Kai Jensen & S. Albrecht, Chr. Butzeck, G. Engels, F. Müller, U. Schröder Universität Hamburg kai.jensen@botanik.uni-hamburg.de
Mapping of Future Coastal Hazards. for Southern California. January 7th, David Revell, Ph.D. E.
 Mapping of Future Coastal Hazards for Southern California January 7th, 2014 David Revell, Ph.D. drevell@esassoc.com E. Vandebroek, 2012 Outline Coastal erosion hazard zones Flood hazard zones: Coastal
Mapping of Future Coastal Hazards for Southern California January 7th, 2014 David Revell, Ph.D. drevell@esassoc.com E. Vandebroek, 2012 Outline Coastal erosion hazard zones Flood hazard zones: Coastal
Implementing the NERR Sentinel Sites Program at the Narragansett Bay Research Reserve to Track Salt Marsh Responses to Climate Change Stessors
 Narragansett Bay Research Reserve Implementing the NERR Sentinel Sites Program at the Narragansett Bay Research Reserve to Track Salt Marsh Responses to Climate Change Stessors Technical Report 1 2013:1
Narragansett Bay Research Reserve Implementing the NERR Sentinel Sites Program at the Narragansett Bay Research Reserve to Track Salt Marsh Responses to Climate Change Stessors Technical Report 1 2013:1
ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN
 ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN Conor Shea - Hydrologist U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Conservation Partnerships Program Arcata, CA Learning Objectives Examine
ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN Conor Shea - Hydrologist U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Conservation Partnerships Program Arcata, CA Learning Objectives Examine
9 th INTECOL Orlando, Florida June 7, 2012
 Restoration of the Everglades Saline Wetlands and Florida Bay: Responses Driven from Land and Sea David Rudnick 1, Colin Saunders 2, Carlos Coronado 2, Fred Sklar 2 Erik Stabenau 1, Vic Engel 1, Rene Price
Restoration of the Everglades Saline Wetlands and Florida Bay: Responses Driven from Land and Sea David Rudnick 1, Colin Saunders 2, Carlos Coronado 2, Fred Sklar 2 Erik Stabenau 1, Vic Engel 1, Rene Price
MEMORANDUM FOR SWG
 MEMORANDUM FOR SWG-2007-1623 Subject: Jurisdictional Determination (JD) for SWG-2007-1623 on Interdunal Wetlands Adjacent to Traditional Navigable Waters (TNWs) Summary The U.S. Environmental Protection
MEMORANDUM FOR SWG-2007-1623 Subject: Jurisdictional Determination (JD) for SWG-2007-1623 on Interdunal Wetlands Adjacent to Traditional Navigable Waters (TNWs) Summary The U.S. Environmental Protection
Spatial Distribution of Salt Marsh Vegetation Cover and Salinity Regimes in Response to Mosquito Ditching
 Spatial Distribution of Salt Marsh Vegetation Cover and Salinity Regimes in Response to Mosquito Ditching Andrew J. Paolucci University of Rhode Island Department of Natural Resources Science NRS 533 Final
Spatial Distribution of Salt Marsh Vegetation Cover and Salinity Regimes in Response to Mosquito Ditching Andrew J. Paolucci University of Rhode Island Department of Natural Resources Science NRS 533 Final
Stream Geomorphology. Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012
 Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
GIS and Coastal Nutrients Luke Cole
 GIS and Coastal Nutrients Luke Cole Human population density has been widely utilized as a valid predictor of terrestrial nitrogen loads into marine systems. As 50% of the world s population lives within
GIS and Coastal Nutrients Luke Cole Human population density has been widely utilized as a valid predictor of terrestrial nitrogen loads into marine systems. As 50% of the world s population lives within
Tidal Wetlands & Climate Change
 Tidal Wetlands & Climate Change Tom Parker (SF State) John Callaway (Univ SF) Lisa Schile (UCB); Ellen Herbert (Indiana U); Evyan Borgnis (USF, SFSU) Jessica Vandenberg (SFSU) Vance Vredenburg (SF State)
Tidal Wetlands & Climate Change Tom Parker (SF State) John Callaway (Univ SF) Lisa Schile (UCB); Ellen Herbert (Indiana U); Evyan Borgnis (USF, SFSU) Jessica Vandenberg (SFSU) Vance Vredenburg (SF State)
Wetland Sediment Dynamics at Crissy Field Marsh Annual Report
 Wetland Sediment Dynamics at Crissy Field Marsh 27 Annual Report John Callaway Department of Environmental Science University of San Francisco 217 Fulton St. San Francisco, CA 94117 (415) 422-572 callaway@usfca.edu
Wetland Sediment Dynamics at Crissy Field Marsh 27 Annual Report John Callaway Department of Environmental Science University of San Francisco 217 Fulton St. San Francisco, CA 94117 (415) 422-572 callaway@usfca.edu
5. MANY COASTAL COMMUNITIES AND FACILITIES WILL FACE INCREASING EXPOSURE TO STORMS.
 5. MANY COASTAL COMMUNITIES AND FACILITIES WILL FACE INCREASING EXPOSURE TO STORMS. Climate change is altering the Arctic coastline and much greater changes are projected for the future as a result of
5. MANY COASTAL COMMUNITIES AND FACILITIES WILL FACE INCREASING EXPOSURE TO STORMS. Climate change is altering the Arctic coastline and much greater changes are projected for the future as a result of
Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road
 Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
Modeling Sea-Level Rise in Coastal Wetlands: Understanding Potential Impacts and Their Implications for Management on Cape Cod
 Modeling Sea-Level Rise in Coastal Wetlands: Understanding Potential Impacts and Their Implications for Management on Cape Cod C a p e C o a s t a l C o n f e r e n c e H y a n n i s R e s o r t a n d
Modeling Sea-Level Rise in Coastal Wetlands: Understanding Potential Impacts and Their Implications for Management on Cape Cod C a p e C o a s t a l C o n f e r e n c e H y a n n i s R e s o r t a n d
Erosion Surface Water. moving, transporting, and depositing sediment.
 + Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
+ Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage
 Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
PLANT COMMUNITY COMPOSITION OF THE BUCKTOWN CREATED MARSH:
 PLANT COMMUNITY COMPOSITION OF THE BUCKTOWN CREATED MARSH: A PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT Prepared for: John Lopez, Director Coastal Sustainability Program Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation Prepared by: Mark
PLANT COMMUNITY COMPOSITION OF THE BUCKTOWN CREATED MARSH: A PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT Prepared for: John Lopez, Director Coastal Sustainability Program Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation Prepared by: Mark
Technical Report: Rhode Island Salt Marsh Habitat Mapping Project
 Technical Report: Rhode Island Salt Marsh Habitat Mapping Project Introduction This project was designed to build on prior efforts within the State of Rhode Island (RI) to gauge the health and resilience
Technical Report: Rhode Island Salt Marsh Habitat Mapping Project Introduction This project was designed to build on prior efforts within the State of Rhode Island (RI) to gauge the health and resilience
Design of Levee Breaches in Sheltered Water for Flood Risk Reduction & Marsh Restoration ASFMP; June 5, 2014 Presented By:
 Design of Levee Breaches in Sheltered Water for Flood Risk Reduction & Marsh Restoration ASFMP; June 5, 2014 Presented By: Rohin Saleh Alameda County Flood Control District Matt Powers, P.E. GEI Consultants
Design of Levee Breaches in Sheltered Water for Flood Risk Reduction & Marsh Restoration ASFMP; June 5, 2014 Presented By: Rohin Saleh Alameda County Flood Control District Matt Powers, P.E. GEI Consultants
STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. Surface Water Movement
 Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
Descriptions and Performance
 LSU AgCenter Coastal Plants Program Smooth Cordgrass Varieties: Descriptions and Performance Smooth cordgrass (Spartina alterniflora Loisel.) is a perennial grass native to intertidal saline marshes along
LSU AgCenter Coastal Plants Program Smooth Cordgrass Varieties: Descriptions and Performance Smooth cordgrass (Spartina alterniflora Loisel.) is a perennial grass native to intertidal saline marshes along
Environmental Science
 Environmental Science A Study of Interrelationships Cui Jiansheng Hebei University of Science and Technology CH06 Kinds of Ecosystems and Communities Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you
Environmental Science A Study of Interrelationships Cui Jiansheng Hebei University of Science and Technology CH06 Kinds of Ecosystems and Communities Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you
Permafrost-influenced Geomorphic Processes
 Section 4 Permafrost-influenced Geomorphic Processes Geomorphic processes vary greatly among ecoregions in northern Alaska, extending from the Beaufort Sea coast to the Brooks Range (Figure 4.1). Regional
Section 4 Permafrost-influenced Geomorphic Processes Geomorphic processes vary greatly among ecoregions in northern Alaska, extending from the Beaufort Sea coast to the Brooks Range (Figure 4.1). Regional
Supplemental Slides. Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Junction of Land & Water. Sea Level Variations. Shore vs. Coast. Sea Level Variations
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Ecological Society of America is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Ecology.
 Competition and Salt-Marsh Plant Zonation: Stress Tolerators May Be Dominant Competitors Author(s): Nancy C. Emery, Patrick J. Ewanchuk, Mark D. Bertness Source: Ecology, Vol. 82, No. 9 (Sep., 2001), pp.
Competition and Salt-Marsh Plant Zonation: Stress Tolerators May Be Dominant Competitors Author(s): Nancy C. Emery, Patrick J. Ewanchuk, Mark D. Bertness Source: Ecology, Vol. 82, No. 9 (Sep., 2001), pp.
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES WEATHERING 1 1998 Q 7 (a) (i) What is the difference between weathering and mass wasting (ii) List five processes involved in chemical weathering
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES WEATHERING 1 1998 Q 7 (a) (i) What is the difference between weathering and mass wasting (ii) List five processes involved in chemical weathering
Beneficial Reuse of Dredge Material for Salt Marsh Restoration: Early Recovery of Vegetation and Epifaunal Macroinvertebrate
 Metthea Yepsen myepsen@tnc.org Adrianna Zito-Livingston Jessie Buckner Projects funded by New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection and Department of Transportation, The National Fish and Wildlife
Metthea Yepsen myepsen@tnc.org Adrianna Zito-Livingston Jessie Buckner Projects funded by New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection and Department of Transportation, The National Fish and Wildlife
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10
 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
2.2.7 Backbarrier flats
 FIGURE 24. VERTICAL PHOTOGRAPH SHOWING THE DEVELOPMENT OF SMALL PARABOLIC DUNES FROM BLOWOUTS IN A LARGE RELICT FOREDUNE NORTHWEST OF HUNTER'S CREEK. PHOTOGRAPH COURTESY OF CAR'T'ER HOLT HARVEY FORESTS
FIGURE 24. VERTICAL PHOTOGRAPH SHOWING THE DEVELOPMENT OF SMALL PARABOLIC DUNES FROM BLOWOUTS IN A LARGE RELICT FOREDUNE NORTHWEST OF HUNTER'S CREEK. PHOTOGRAPH COURTESY OF CAR'T'ER HOLT HARVEY FORESTS
Ground Water Control of Tree Island Origin, Genesis and Destruction. By John F. Meeder and Peter W. Harlem SERC,FIU
 Ground Water Control of Tree Island Origin, Genesis and Destruction By John F. Meeder and Peter W. Harlem SERC,FIU Functional Definition Our functional definition of a Tree Island is; an isolated scrub
Ground Water Control of Tree Island Origin, Genesis and Destruction By John F. Meeder and Peter W. Harlem SERC,FIU Functional Definition Our functional definition of a Tree Island is; an isolated scrub
netw rks Guided Reading Activity Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? Earth's Physical Geography
 Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Earth and the Sun Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? Looking at Earth Directions: What are the layers that make up Earth? Use your textbook
Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Earth and the Sun Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? Looking at Earth Directions: What are the layers that make up Earth? Use your textbook
Chapter 2. Regional Landscapes and the Hydrologic Cycle
 Chapter 2. Regional Landscapes and the Hydrologic Cycle W. Lee Daniels Department of Crop and Soil Environmental Sciences, Virginia Tech Table of Contents Introduction... 23 Soils and landscapes of the
Chapter 2. Regional Landscapes and the Hydrologic Cycle W. Lee Daniels Department of Crop and Soil Environmental Sciences, Virginia Tech Table of Contents Introduction... 23 Soils and landscapes of the
3.7 VISUAL RESOURCES Environmental Setting
 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 20 2 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 3 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 4 3.7 VISUAL RESOURCES This section assesses the effects of the treatment techniques on views from public
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 20 2 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 3 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 4 3.7 VISUAL RESOURCES This section assesses the effects of the treatment techniques on views from public
Phillip Island Nature Parks Coastal Process Study 8 October 2014
 Phillip Island Nature Parks Coastal Process Study 8 October 2014 Project Overview Coastal Geology Basaltic and fragmented lavas, granite at Pyramid Rock and Cape Woolamai Weathered basalt (>10m thick)
Phillip Island Nature Parks Coastal Process Study 8 October 2014 Project Overview Coastal Geology Basaltic and fragmented lavas, granite at Pyramid Rock and Cape Woolamai Weathered basalt (>10m thick)
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin?
 How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
HURRICANE IRENE. CONFERENCE CALL BRIEFING SLIDES Saturday August 27, :30 AM
 HURRICANE IRENE CONFERENCE CALL BRIEFING SLIDES Saturday August 27, 2011 8:30 AM NHC TRACK AND CONE HURRICANE IRENE WATCHES/WARNINGS Hurricane Warning along south coast including all of Cape Cod and Islands
HURRICANE IRENE CONFERENCE CALL BRIEFING SLIDES Saturday August 27, 2011 8:30 AM NHC TRACK AND CONE HURRICANE IRENE WATCHES/WARNINGS Hurricane Warning along south coast including all of Cape Cod and Islands
Sediment Management in the Coastal Bays
 Sediment Management in the Coastal Bays Introduction Need for ecosystem view of sediment management in Coastal Bays Island loss and restoration Navigation needs Habitat Trade offs Living Shoreline Requirements
Sediment Management in the Coastal Bays Introduction Need for ecosystem view of sediment management in Coastal Bays Island loss and restoration Navigation needs Habitat Trade offs Living Shoreline Requirements
Kakagon Sloughs, Bad River Reservation 1980s Jim Meeker, Northland College
 Natural history of coastal wetlands in the greater Chequamegon Bay region Kakagon Sloughs, Bad River Reservation 1980s Jim Meeker, Northland College small large northern Great Lake wetlands are dominated
Natural history of coastal wetlands in the greater Chequamegon Bay region Kakagon Sloughs, Bad River Reservation 1980s Jim Meeker, Northland College small large northern Great Lake wetlands are dominated
Erosion and Deposition
 CHAPTER 3 LESSON 2 Erosion and Deposition Landforms Shaped by Water and Wind Key Concepts What are the stages of stream development? How do water erosion and deposition change Earth s surface? How do wind
CHAPTER 3 LESSON 2 Erosion and Deposition Landforms Shaped by Water and Wind Key Concepts What are the stages of stream development? How do water erosion and deposition change Earth s surface? How do wind
IS THERE ENOUGH SEDIMENT? Presentation at the State of the Estuary Conference San Francisco, CA, October 9-10, By Philip B.
 IS THERE ENOUGH SEDIMENT? Presentation at the State of the Estuary Conference San Francisco, CA, October 9-10, 2001 By Philip B. Williams 1. INTRO I AM TEMPTED TO MAKE THIS THE SHORTEST TALK OF THE CONFERENCE:
IS THERE ENOUGH SEDIMENT? Presentation at the State of the Estuary Conference San Francisco, CA, October 9-10, 2001 By Philip B. Williams 1. INTRO I AM TEMPTED TO MAKE THIS THE SHORTEST TALK OF THE CONFERENCE:
Zonation of shrubs in western Atlantic salt marshes
 Oecologia (2001) 126:587 594 DOI 10.1007/s004420000548 Steven C. Pennings Darrin J. Moore Zonation of shrubs in western Atlantic salt marshes Received: 29 February 2000 / Accepted: 14 September 2000 /
Oecologia (2001) 126:587 594 DOI 10.1007/s004420000548 Steven C. Pennings Darrin J. Moore Zonation of shrubs in western Atlantic salt marshes Received: 29 February 2000 / Accepted: 14 September 2000 /
Evaluating Wildlife Habitats
 Lesson C5 4 Evaluating Wildlife Habitats Unit C. Animal Wildlife Management Problem Area 5. Game Animals Management Lesson 4. Evaluating Wildlife Habitats New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway Strand: Natural
Lesson C5 4 Evaluating Wildlife Habitats Unit C. Animal Wildlife Management Problem Area 5. Game Animals Management Lesson 4. Evaluating Wildlife Habitats New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway Strand: Natural
Shoreline Mapping & Erosion Patterns. Julia Knisel Julia Knisel Coastal Shoreline & Floodplain Manager
 Shoreline Mapping & Erosion Patterns Along the Massachusetts Coast Julia Knisel Julia Knisel Coastal Shoreline & Floodplain Manager CZM Shoreline Change Project Timeline 1989: produced coast wide maps
Shoreline Mapping & Erosion Patterns Along the Massachusetts Coast Julia Knisel Julia Knisel Coastal Shoreline & Floodplain Manager CZM Shoreline Change Project Timeline 1989: produced coast wide maps
Surface Water Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Surface Water Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The three ways in which a stream carries
Name: Class: Date: Surface Water Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The three ways in which a stream carries
Opportunities to Improve Ecological Functions of Floodplains and Reduce Flood Risk along Major Rivers in the Puget Sound Basin
 Opportunities to Improve Ecological Functions of Floodplains and Reduce Flood Risk along Major Rivers in the Puget Sound Basin Christopher Konrad, US Geological Survey Tim Beechie, NOAA Fisheries Managing
Opportunities to Improve Ecological Functions of Floodplains and Reduce Flood Risk along Major Rivers in the Puget Sound Basin Christopher Konrad, US Geological Survey Tim Beechie, NOAA Fisheries Managing
Abiotic Dominant Dominant Factors Plants Animals
 TERRESTRIAL BIOMES Abiotic Dominant Dominant Factors Plants Animals Tropical Rain Forest Hot & wet year round Ferns Woody vines Broad leaved evergreen trees Sloths Jaguars Monkeys Toucans Tropical Dry
TERRESTRIAL BIOMES Abiotic Dominant Dominant Factors Plants Animals Tropical Rain Forest Hot & wet year round Ferns Woody vines Broad leaved evergreen trees Sloths Jaguars Monkeys Toucans Tropical Dry
Module 3. Basic Ecological Principles
 Module 3. Basic Ecological Principles Ecosystem Components Abiotic Biotic Species & Habitat The Biomes of North America Communities Energy & Matter Cycles in Ecosystems Primary Productivity Simple Ecosystem
Module 3. Basic Ecological Principles Ecosystem Components Abiotic Biotic Species & Habitat The Biomes of North America Communities Energy & Matter Cycles in Ecosystems Primary Productivity Simple Ecosystem
The Heat Budget for Mt. Hope Bay
 The School for Marine Science and Technology The Heat Budget for Mt. Hope Bay Y. Fan and W. Brown SMAST, UMassD SMAST Technical Report No. SMAST-03-0801 The School for Marine Science and Technology University
The School for Marine Science and Technology The Heat Budget for Mt. Hope Bay Y. Fan and W. Brown SMAST, UMassD SMAST Technical Report No. SMAST-03-0801 The School for Marine Science and Technology University
SAN FRANCISCO DISTRICT INFORMATION REQUESTED FOR VERIFICATION OF CORPS JURISDICTION
 DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY SAN FRANCISCO DISTRICT, U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS 1455 MARKET STREET SAN FRANCISCO, CALIFORNIA 94103-1398 SAN FRANCISCO DISTRICT INFORMATION REQUESTED FOR VERIFICATION OF CORPS
DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY SAN FRANCISCO DISTRICT, U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS 1455 MARKET STREET SAN FRANCISCO, CALIFORNIA 94103-1398 SAN FRANCISCO DISTRICT INFORMATION REQUESTED FOR VERIFICATION OF CORPS
EROSIONAL RATES IN THE POINT AUX CHENES BAY AREA, MISSISSIPPI: Kathleen P. Wacker G. Alan Criss INTRODUCTION
 Summary of a Paper Presented at the: Sixtieth Annual Meeting of the Mississippi Academy of Sciences in Jackson, Mississippi February 22, 1996 ===============================================================
Summary of a Paper Presented at the: Sixtieth Annual Meeting of the Mississippi Academy of Sciences in Jackson, Mississippi February 22, 1996 ===============================================================
Smooth Cordgrass Varieties. Description and Performance
 Smooth Cordgrass Varieties Description and Performance Smooth cordgrass (Spartina alterniflora Loisel.) is a perennial grass native to intertidal saline marshes along the Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic coasts.
Smooth Cordgrass Varieties Description and Performance Smooth cordgrass (Spartina alterniflora Loisel.) is a perennial grass native to intertidal saline marshes along the Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic coasts.
Elkhorn Slough Marsh Stratigraphy
 Elkhorn Slough Marsh Stratigraphy Prehistoric marsh extent & recent sediment accretion Elizabeth Burke Watson, Ph.D. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Narragansett, RI Paleoecology: Reconstruction of
Elkhorn Slough Marsh Stratigraphy Prehistoric marsh extent & recent sediment accretion Elizabeth Burke Watson, Ph.D. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Narragansett, RI Paleoecology: Reconstruction of
Sea Level Rise in Miami-Dade County Florida Implications for Management of Coastal Wetlands and the Everglades
 Sea Level Rise in Miami-Dade County Florida Implications for Management of Coastal Wetlands and the Everglades Peter W. Harlem Dr. John F. Meeder Florida International University Southeast Environmental
Sea Level Rise in Miami-Dade County Florida Implications for Management of Coastal Wetlands and the Everglades Peter W. Harlem Dr. John F. Meeder Florida International University Southeast Environmental
Coastal Vulnerability Assessment in Semarang City, Indonesia Based on Sea Level Rise and Land Subsidence Scenarios
 Coastal Vulnerability Assessment in Semarang City, Indonesia Based on Sea Level Rise and Land Subsidence Scenarios I. M. Radjawane, D. Hartadi and W. R. Lusano Oceanography Research Division Fac. of Earth
Coastal Vulnerability Assessment in Semarang City, Indonesia Based on Sea Level Rise and Land Subsidence Scenarios I. M. Radjawane, D. Hartadi and W. R. Lusano Oceanography Research Division Fac. of Earth
The combination of factors required for the accumulation of sulphides occurs in three distinct environments (Pons and van Breemen 1982):
 6 Soil patterns 6.1 Potential acid sulphate environments Soil variation is always a problem for land-use planning and management. Acid sulphate soils are notoriously localised. Even within a single area
6 Soil patterns 6.1 Potential acid sulphate environments Soil variation is always a problem for land-use planning and management. Acid sulphate soils are notoriously localised. Even within a single area
STRUCTURAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT
 STRUCTURAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT CFR 257.73(d) Bottom Ash Pond Complex Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio October, 2016 Prepared for: Cardinal Operating Company Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio Prepared by: Geotechnical
STRUCTURAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT CFR 257.73(d) Bottom Ash Pond Complex Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio October, 2016 Prepared for: Cardinal Operating Company Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio Prepared by: Geotechnical
UPDATE ON THE TAMPA BAY CRITICAL COASTAL HABITAT ASSESSMENT
 UPDATE ON THE TAMPA BAY CRITICAL COASTAL HABITAT ASSESSMENT CHIMMP Meeting September 15, 2015 Lindsay Cross, Ed Sherwood Tampa Bay Estuary Program PURPOSE OF PROJECT Develop a long term monitoring program
UPDATE ON THE TAMPA BAY CRITICAL COASTAL HABITAT ASSESSMENT CHIMMP Meeting September 15, 2015 Lindsay Cross, Ed Sherwood Tampa Bay Estuary Program PURPOSE OF PROJECT Develop a long term monitoring program
Sedimentation Rate Change in the Winooski River Delta
 Sedimentation Rate Change in the Winooski River Delta Chris Ricker and Brian Connelly Abstract Historical air photographs, from 1937 show the Winooski River Delta extended much farther into Lake Champlain
Sedimentation Rate Change in the Winooski River Delta Chris Ricker and Brian Connelly Abstract Historical air photographs, from 1937 show the Winooski River Delta extended much farther into Lake Champlain
The Use of Geographic Information Systems to Assess Change in Salt Marsh Ecosystems Under Rising Sea Level Scenarios.
 The Use of Geographic Information Systems to Assess Change in Salt Marsh Ecosystems Under Rising Sea Level Scenarios Robert Hancock The ecological challenges presented by global climate change are vast,
The Use of Geographic Information Systems to Assess Change in Salt Marsh Ecosystems Under Rising Sea Level Scenarios Robert Hancock The ecological challenges presented by global climate change are vast,
Extreme Weather Events: Infrastructure Damage and Impact on Vulnerable Populations
 Extreme Weather Events: Infrastructure Damage and Impact on Vulnerable Populations Cindy L. Parker MD, MPH Physicians for Social Responsibility Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health 1 Climate
Extreme Weather Events: Infrastructure Damage and Impact on Vulnerable Populations Cindy L. Parker MD, MPH Physicians for Social Responsibility Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health 1 Climate
Nutrient and Carbon Sequestration by Salt Marsh Plants in the Face of Eutrophication and Sea Level Rise
 Nutrient and Carbon Sequestration by Salt Marsh Plants in the Face of Eutrophication and Sea Level Rise Tracy Elsey, Jack Gallagher, and Denise Seliskar Halophyte Biotechnology Center College of Marine
Nutrient and Carbon Sequestration by Salt Marsh Plants in the Face of Eutrophication and Sea Level Rise Tracy Elsey, Jack Gallagher, and Denise Seliskar Halophyte Biotechnology Center College of Marine
Vetiver System for Stream Bank Stabilisation. Paul Truong
 Vetiver System for Stream Bank Stabilisation (With special references to the river and canal bank stabilisation in Australia and Vietnam) Paul Truong Director, The Vetiver Network International, Veticon
Vetiver System for Stream Bank Stabilisation (With special references to the river and canal bank stabilisation in Australia and Vietnam) Paul Truong Director, The Vetiver Network International, Veticon
GLOBAL WARMING: GLOBAL WARMING. landscape implications. Andrew Goudie St Cross College Oxford
 GLOBAL WARMING: GLOBAL WARMING landscape implications Andrew Goudie St Cross College Oxford THE PROCESS OF CHANGE HAS STARTED IPCC 2007 Increased Glacier retreat since the early 1990s Area of seasonally
GLOBAL WARMING: GLOBAL WARMING landscape implications Andrew Goudie St Cross College Oxford THE PROCESS OF CHANGE HAS STARTED IPCC 2007 Increased Glacier retreat since the early 1990s Area of seasonally
Chapter 2. Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice. Physical Weathering
 Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
Chapter 3 - White Oak River Subbasin Includes Bogue Sound and the Newport River
 Chapter 3 - White Oak River Subbasin 03-05-03 Includes Bogue Sound and the Newport River 3.1 Water Quality Overview Subbasin 03-05-03 at a Glance Land and Water Area (sq. mi.) Total area: 228 Land area:
Chapter 3 - White Oak River Subbasin 03-05-03 Includes Bogue Sound and the Newport River 3.1 Water Quality Overview Subbasin 03-05-03 at a Glance Land and Water Area (sq. mi.) Total area: 228 Land area:
Soil Formation. Lesson Plan: NRES B2-4
 Soil Formation Lesson Plan: NRES B2-4 1 Anticipated Problems 1. What are five different factors that affect soil formation? 2. What are some different types of parent material that affect soils? 3. What
Soil Formation Lesson Plan: NRES B2-4 1 Anticipated Problems 1. What are five different factors that affect soil formation? 2. What are some different types of parent material that affect soils? 3. What
SEARCHING FOR SEDIMENT SOURCES IN SPRING CREEK
 SEARCHING FOR SEDIMENT SOURCES IN SPRING CREEK Christopher Frederick, Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL 36688. E-mail: cjf702@jaguar1.usouthal.edu. Sediment deposition
SEARCHING FOR SEDIMENT SOURCES IN SPRING CREEK Christopher Frederick, Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL 36688. E-mail: cjf702@jaguar1.usouthal.edu. Sediment deposition
CHAPTER FIVE 5.0 STABILITY OF CUT SLOPES IN THE STUDY AREA. them limited by a thick canopy of vegetation and steep slope angles.
 CHAPTER FIVE 5.0 STABILITY OF CUT SLOPES IN THE STUDY AREA 5.1. Introduction Ukay Perdana area is a developing community with continuous building activities and road construction. There are thus only left
CHAPTER FIVE 5.0 STABILITY OF CUT SLOPES IN THE STUDY AREA 5.1. Introduction Ukay Perdana area is a developing community with continuous building activities and road construction. There are thus only left
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100. Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event
 ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
Shoreline and Climate Change Adaptation Alternatives for The Letter Parcel, Bolinas Lagoon
 Shoreline and Climate Change Adaptation Alternatives for The Letter Parcel, Bolinas Lagoon Scenic shoreline vista of Bolinas Lagoon and ridges, from Letter Parcel, March 2016 Peter Baye, Coastal Ecologist
Shoreline and Climate Change Adaptation Alternatives for The Letter Parcel, Bolinas Lagoon Scenic shoreline vista of Bolinas Lagoon and ridges, from Letter Parcel, March 2016 Peter Baye, Coastal Ecologist
Coastal issues: Beaches and Estuaries
 Coastal issues: Beaches and Estuaries Definitions: Coast = broad zone where both marine & terrestrial processes act It includes the beach, lagoons, marshes, bars etc. Coastal processes act to shape the
Coastal issues: Beaches and Estuaries Definitions: Coast = broad zone where both marine & terrestrial processes act It includes the beach, lagoons, marshes, bars etc. Coastal processes act to shape the
Sediment Transport and Strata Formation in the Adriatic Sea
 Sediment Transport and Strata Formation in the Adriatic Sea Wayne R. Geyer James D. Irish Peter A. Traykovski Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 Tel. (508) 289-2868, Fax: (508) 457-2194,
Sediment Transport and Strata Formation in the Adriatic Sea Wayne R. Geyer James D. Irish Peter A. Traykovski Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 Tel. (508) 289-2868, Fax: (508) 457-2194,
Observations on Surface Water in the Seminary Fen in Spring, Prepared 6/4/13 by Sam Wetterlin; updated 7/28/13
 Observations on Surface Water in the Seminary Fen in Spring, 2013 Prepared 6/4/13 by Sam Wetterlin; updated 7/28/13 Ordinarily, a calcareous fen is primarily dependent on upwelling mineral-rich, oxygen-poor
Observations on Surface Water in the Seminary Fen in Spring, 2013 Prepared 6/4/13 by Sam Wetterlin; updated 7/28/13 Ordinarily, a calcareous fen is primarily dependent on upwelling mineral-rich, oxygen-poor
27. Running Water I (p ; )
 27. Running Water I (p. 424-436; 440-444) Hydrosphere How much of the Earth s surface is covered by water? Earth's water is collectively called the and is stored in a number of so-called as follows: 1.
27. Running Water I (p. 424-436; 440-444) Hydrosphere How much of the Earth s surface is covered by water? Earth's water is collectively called the and is stored in a number of so-called as follows: 1.
Whiskey Island Marsh Creation Rolling with the Punches
 Whiskey Island Marsh Creation Rolling with the Punches Santiago Alfageme, M&N Jerry Carroll, LADNR Brad Miller, LADNR Project Location Historic Island Retreat Previous Restoration Project Whiskey Island
Whiskey Island Marsh Creation Rolling with the Punches Santiago Alfageme, M&N Jerry Carroll, LADNR Brad Miller, LADNR Project Location Historic Island Retreat Previous Restoration Project Whiskey Island
