GG611 Lecture 4 GEOLOGIC MAPS AND CROSS SECTIONS. Maps and Cross Sec6on
|
|
|
- Douglas Cook
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GG611 Lecture 4 Maps and Cross Sec6on GG611 1 I Main Topics A Why make geologic maps? B Construc6on of maps C Contour maps D Introduc6on to geologic map pakerns E Structure contours F Strike of beds on a geologic map G Appearance of planar beds on a geologic map H Appearance of folded beds on a geologic map GG
2 The First Geologic Map of Britain by William Smith, 1815 hkp://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/98/geological_map_britain_william_smith_1815.jpg GG611 3 Por6on of the Geologic Map of the Bright Angel Quadrangle hkp://facweb.northseakle.edu/tbraziunas/geol101tb_par6al/images/bright6a.gif GG
3 Geologic Map of Kauai GG611 5 Geological Map of the Confluence of the Rio Patuca and Rio Wampu, La Mosqui6a, Honduras hkp://geology.csustan.edu/rrogers/honduras/map2v1c.jpg GG
4 II Why make geologic maps? A Documenta6on of structural geometry (and B C D E sequence of events) To force us to look closely; maps act like a tool for observa6on PaKern recogni6on at a useful and appropriate scale. Many structures are too large or outcrop is too poor to see otherwise. To develop conceptual models for kinema6c and mechanical reconstruc6ons of how structures form To help define boundary condi6ons for mechanical models GG611 7 III Construc6on of maps A Establishment of control points on ground and map B Transfer of geometric informa6on at or near control point to map C Linking of informa6on between control points GG
5 IV Contour maps: Maps that represent surfaces in terms of a series of curves A An individual contour represents a part of the surface along which the surface "value" is constant. B Topographic contour map: contour lines represent points of equal eleva6on of the ground surface. 1 Streams flow downhill (contours vee upstream) 2 Contours for a ridge "point" down the ridge GG611 9 C Structure contour map: contour lines represent points of equal eleva6on along a geologic surface (e.g., the top of a geologic unit) that commonly is buried. If the values of a structure contour map are subtracted from the values on a corresponding topographic map, the difference gives the depth from the ground surface to the top of the geologic unit. D Isopach contour map: contour lines represent points of equal thickness of the geologic unit E Given a data set (x, y, z), one can prepare a contour map of z (e.g., concentra6on of contamina6on in ground water) vs. (x, y) - See last page in notes of Lec. 4 - GG
6 4. MAPS V Introduc6on to geologic map pakerns A Geologic maps show the intersec6on (trace) of geologic features with the ground surface, a surface that is generally subhorizontal but irregular (i.e., with 3-D relief). B Geologic maps are not top views of subsurface features as projected into a horizontal plane. hkp://facweb.northseakle.edu/tbraziunas/geol101tb_par6al/images/bright6a.gif GG V Introduc6on to geologic map pakerns C The strike of a geologic surface is obtained by determining the azimuth between two points on the geologic surface that have the same eleva6on (i.e., that lie along the intersec6on of the geologic surface and a horizontal plane). GG
7 V Introduc6on to geologic map pakerns D The contacts of horizontal layers parallel eleva6ons contours. hkp://facweb.northseakle.edu/tbraziunas/geol101tb_par6al/images/bright6a.gif GG V Introduc6on to geologic map pakerns (cont.) E The contacts of ver6cal geologic surfaces appear as straight lines on geologic maps with a topographic base. hkp://facweb.northseakle.edu/tbraziunas/geol101tb_par6al/images/bright6a.gif GG
8 % Matlab script for producing contour map examples x=-2:0.2:2; % Values of x range from 2 to +2; y=-2:0.2:2; % Values of y range from 2 to +2; [X,Y]=meshgrid(x,y); % Makes grid of x and y at each point; Z=(peaks(X,Y)); % Matlab s peaks func6on; clf % Clears any prior plots; subplot(2,2,1) % First plot of 2 rows and 2 columns Surf(X,Y,Z); % 3-D perspec6ve plot; xlabel('x') % Labels the x-axis as 'x'; ylabel('y') % Labels the y-axis as 'y'; 6tle('Surface Plot of the Peaks Func6on') subplot(2,2,2) % Second plot of 2 rows and 2 columns; c= contour(x,y,z); % Calculates the contour line posi6ons; clabel(c) % This plots and labels the contour map; xlabel('x') ylabel('y') 6tle('Contour Plot of the Peaks Func6on') [DX,DY] = gradient(z,.2,.2); subplot(2,2,3) % Third plot of 2 rows and 2 columns; contour(x,y,z) hold on % Allows arrows to plot on contour plot; quiver(x,y,-dx,-dy); the arrows; % This plots colormap hsv % Assigns the hsv color scheme to plot; grid off % Turns off ployng of grid; hold off xlabel('x') ylabel('y') 6tle('Contour Plot Func6on') and Nega6ve Gradient of Peaks subplot(2,2,4) % Fourth plot of 2 rows and 2 columns; contour(x,y,z,[0 0]) % Plots one contour line (here it s 0); xlabel('x') ylabel('y') 6tle('Zero Contour Func6on') of Peaks GG VI Structure contours A A line or curve (contour) that marks the intersec6on of a horizontal plane with some geologic surface; this surface need not be planar. Strike lines are tangent to structure contours (see Fig. 5.1). GG
9 VI Structure contours (cont.) B A geologic map can be thought of as the collec6on of points marking the intersec6ons between structure contours (red) and the corresponding black topographic contours. C A strike view cross sec6on is taken perpendicular to the strike of a geologic unit. It shows the true dip and true thickness of the unit. GG VII Strike of beds on a geologic map A Lines of strike are horizontal (i.e., a series of points of equal eleva6on). For a surface (or layer) of constant strike, a line of strike (i.e., a traverse at equal eleva6on) lies along the surface (or layer) rather than cuyng across the surface (or layer); (see Fig. 5.3). GG
10 VII Strike of beds on a geologic map (cont.) B Lines of strike can be determined by loca6ng where a contact intersects a given contour line in more than one point; these points of intersec6on lie along strike. This is easiest where a contact is steep. GG VIII Appearance of planar beds on a geologic map A Planar beds have a constant strike and a constant dip B Strike lines along structure contours are parallel and straight C Strike lines along structure contours are evenly spaced D Dip direc6on is constant GG
11 IX Appearance of folded beds on a geologic map A The strike and/or dip of a folded bed varies with posi:on B Strike lines along structure contours might or might not be parallel; the strike of folded layers does not necessarily change. 1 If strike lines are parallel, then the strike is constant (±180 ) and the axis of the fold is horizontal 2 If strike lines are not parallel, then the strike is not constant and the axis of the fold plunges (e.g., fold with a ver6cal fold Surface curls over fold axis; Fold axis points into page; Structure contours in red Surface curls over fold axis; Fold axis points into page; Structure contours in red GG IX Appearance of folded beds on a geologic map (cont.) C If a folded layer changes dip, then strike lines along structure contours with a uniform contour interval will not be evenly spaced. D Dip direc6on and magnitude may or may not be constant (e.g., fold with a horizontal fold axis). E Cross sec6ons and maps together are powerful 3-D visualiza6on tools, whether on paper or on a computer. GG
The First Geologic Map of Britain by William Smith, 1815
 I Main Topics A Why make geologic maps? B ConstrucDon of maps C Contour maps D IntroducDon to geologic map paherns 8/25/11 GG303 1 The First Geologic Map of Britain by William Smith, 1815 hhp://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/98/geological_map_britain_william_smith_1815.jpg
I Main Topics A Why make geologic maps? B ConstrucDon of maps C Contour maps D IntroducDon to geologic map paherns 8/25/11 GG303 1 The First Geologic Map of Britain by William Smith, 1815 hhp://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/98/geological_map_britain_william_smith_1815.jpg
Lecture Topics. Structural Geology Sec3on Steve Martel POST Introduc3on. 2 Rock structures. 3 Stress and strain 4 Isostacy
 GG611 Structural Geology Sec3on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 1 Philosophy Orienta3on of Lines and Planes in Space 1 1 Introduc3on A. Philosophy Lecture Topics B. Orienta3on of lines
GG611 Structural Geology Sec3on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 1 Philosophy Orienta3on of Lines and Planes in Space 1 1 Introduc3on A. Philosophy Lecture Topics B. Orienta3on of lines
MAPS AND CROSS SECTIONS (I)
 GG303 Lab 3 8/27/09 1 MAPS AND CROSS SECTIONS (I) I Main Topics A Three point problems B Rule of vees C Map interpretation and cross sections II Three point problems (see handout) A Three points define
GG303 Lab 3 8/27/09 1 MAPS AND CROSS SECTIONS (I) I Main Topics A Three point problems B Rule of vees C Map interpretation and cross sections II Three point problems (see handout) A Three points define
A. Refer to Appendix F in back of lab manual for list of commonly used geologic map symbols
 Structural Geology Lab 2: Outcrop Patterns and Structure Contours I. Geologic Map Symbols A. Refer to Appendix F in back of lab manual for list of commonly used geologic map symbols 1. Emphasis: a. strike
Structural Geology Lab 2: Outcrop Patterns and Structure Contours I. Geologic Map Symbols A. Refer to Appendix F in back of lab manual for list of commonly used geologic map symbols 1. Emphasis: a. strike
6. 地質圖 6.1 岩層於地形圖上的分布 6.2 地質剖面圖 6.3 地質圖判識 地調所五萬分之一地質圖台中圖幅
 6. 地質圖 6.1 岩層於地形圖上的分布 6.2 地質剖面圖 6.3 地質圖判識 A geological shows how geological features (rock units, faults, etc.) are distributed across a region. It is a twodimensional representation of part of the Earth
6. 地質圖 6.1 岩層於地形圖上的分布 6.2 地質剖面圖 6.3 地質圖判識 A geological shows how geological features (rock units, faults, etc.) are distributed across a region. It is a twodimensional representation of part of the Earth
LAB 1: ORIENTATION OF LINES AND PLANES
 LAB 1: ORIENTATION OF LINES AND PLANES Read the introductory section, chapter 1, pages 1-3, of the manual by Rowland et al (2007) and make sure you understand the concepts of bearing, strike, dip, trend,
LAB 1: ORIENTATION OF LINES AND PLANES Read the introductory section, chapter 1, pages 1-3, of the manual by Rowland et al (2007) and make sure you understand the concepts of bearing, strike, dip, trend,
GEOL 3700 STRUCTURE AND TECTONICS LABORATORY EXERCISE 3
 GEOL 3700 STRUCTURE AND TECTONICS LABORATORY EXERCISE 3 Goals: 1. Improve your map-reading and map-making skills. 2. Learn to generate and interpret structure contour maps. 3. Learn to generate and interpret
GEOL 3700 STRUCTURE AND TECTONICS LABORATORY EXERCISE 3 Goals: 1. Improve your map-reading and map-making skills. 2. Learn to generate and interpret structure contour maps. 3. Learn to generate and interpret
Team Name. Name(s) SSSS Unome Geologic Mapping Test Packet p1
 Scioly Summer Study Session 2018-2019 Geologic Mapping Test Packet Written by Unome Instructions 1) This test is based on the 2016 rules for Geologic Mapping. 2) This test is out of 115 points. Questions
Scioly Summer Study Session 2018-2019 Geologic Mapping Test Packet Written by Unome Instructions 1) This test is based on the 2016 rules for Geologic Mapping. 2) This test is out of 115 points. Questions
EPS 50 Lab 6: Maps Topography, geologic structures and relative age determinations
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 6: Maps Topography, geologic structures and relative age determinations Introduction: Maps are some of the most interesting and informative printed documents available. We are familiar
Name: EPS 50 Lab 6: Maps Topography, geologic structures and relative age determinations Introduction: Maps are some of the most interesting and informative printed documents available. We are familiar
Topics. GG612 Structural Geology Sec3on Steve Martel POST 805 Lecture 4 Mechanics: Stress and Elas3city Theory
 GG612 Structural Geology Sec3on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 4 Mechanics: Stress and Elas3city Theory 11/6/15 GG611 1 Topics 1. Stress vectors (trac3ons) 2. Stress at a point 3. Cauchy
GG612 Structural Geology Sec3on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 4 Mechanics: Stress and Elas3city Theory 11/6/15 GG611 1 Topics 1. Stress vectors (trac3ons) 2. Stress at a point 3. Cauchy
Interactive 3D Sketchupbook
 THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY - SCHOOL OF GEOSCIENCES Interactive 3D Sketchupbook Patrice F. Rey CHAPTER 1 Orienting Planes and Lines 1 Interactive 1.1 Strike, dip and dip direction In a 3D space, planar surfaces
THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY - SCHOOL OF GEOSCIENCES Interactive 3D Sketchupbook Patrice F. Rey CHAPTER 1 Orienting Planes and Lines 1 Interactive 1.1 Strike, dip and dip direction In a 3D space, planar surfaces
Part I. PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts:
 Student Name: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory #13 Structural Geology II Drawing and Analyzing Folds and Faults Grade: Introduction & Purpose: Structural geology is the study of how geologic rock units
Student Name: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory #13 Structural Geology II Drawing and Analyzing Folds and Faults Grade: Introduction & Purpose: Structural geology is the study of how geologic rock units
Geology 101 Lab Worksheet: Topographic Maps
 Geology 101 Lab Worksheet: Topographic Maps Name: Refer to the Topographic Maps Lab for the information you need to complete this worksheet (http://commons.wvc.edu/rdawes/g101ocl/labs/topomapslab.html).
Geology 101 Lab Worksheet: Topographic Maps Name: Refer to the Topographic Maps Lab for the information you need to complete this worksheet (http://commons.wvc.edu/rdawes/g101ocl/labs/topomapslab.html).
Name. GEOL.5220 Structural Geology Faults, Folds, Outcrop Patterns and Geologic Maps. I. Properties of Earth Materials
 I. Properties of Earth Materials GEOL.5220 Structural Geology Faults, Folds, Outcrop Patterns and Geologic Maps Name When rocks are subjected to differential stress the resulting build-up in strain can
I. Properties of Earth Materials GEOL.5220 Structural Geology Faults, Folds, Outcrop Patterns and Geologic Maps Name When rocks are subjected to differential stress the resulting build-up in strain can
GG303 Lab 5 10/4/17 1
 GG303 Lab 5 10/4/17 1 Lab 5 Spherical Projections Use a separate piece of paper for each exercise, and include printouts of your Matlab work. 103 pts for Ex. 1-4; 124 points for Ex. 1-5. Exercise 1: Plots
GG303 Lab 5 10/4/17 1 Lab 5 Spherical Projections Use a separate piece of paper for each exercise, and include printouts of your Matlab work. 103 pts for Ex. 1-4; 124 points for Ex. 1-5. Exercise 1: Plots
lecture 8 Methods of Structural Geology This lecture Mas Rabassers de Dalt (Spain) Mas Rabassers de Dalt (Spain)
 This lecture Methods of Structural Geology lecture 8 Discuss the plotting exercise on Mas Rabassers de Dalt Look at folding related to shear zones Show an example of the application of new theory: Cap
This lecture Methods of Structural Geology lecture 8 Discuss the plotting exercise on Mas Rabassers de Dalt Look at folding related to shear zones Show an example of the application of new theory: Cap
Chapter 3 SECTION 1 OBJECTIVES
 Chapter 3 SECTION 1 OBJECTIVES Distinguish between latitude and longitude and locate coordinates on maps. Explain how latitude and longitude can be used to locate places on Earth s surface. Explain the
Chapter 3 SECTION 1 OBJECTIVES Distinguish between latitude and longitude and locate coordinates on maps. Explain how latitude and longitude can be used to locate places on Earth s surface. Explain the
Lab 7: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY FOLDS AND FAULTS
 Lab 7: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY FOLDS AND FAULTS This set of labs will focus on the structures that result from deformation in earth s crust, namely folds and faults. By the end of these labs you should be able
Lab 7: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY FOLDS AND FAULTS This set of labs will focus on the structures that result from deformation in earth s crust, namely folds and faults. By the end of these labs you should be able
Geologic Mapping Invitational Trial Event
 Geologic Mapping Invitational Trial Event A TEAM OF UP TO: 2 Team Name AVAILABLE TIME: 50 min Required Materials: Each team MUST have a protractor, ruler, non-programmable calculator, colored pencils,
Geologic Mapping Invitational Trial Event A TEAM OF UP TO: 2 Team Name AVAILABLE TIME: 50 min Required Materials: Each team MUST have a protractor, ruler, non-programmable calculator, colored pencils,
Dip-Sequence Analysis
 Chapter 9 Dip-Sequence Analysis 9.1 Introduction The three-dimensional geometry of a structure can be determined from the bedding attitudes measured in a single well bore or on a traverse through a structure.
Chapter 9 Dip-Sequence Analysis 9.1 Introduction The three-dimensional geometry of a structure can be determined from the bedding attitudes measured in a single well bore or on a traverse through a structure.
Do Now. Copy the ques:on below and write down an. Sketch a profile of the books on the front table.
 Do Now Copy the ques:on below and write down an answer Sketch a profile of the books on the front table. Measurements Contour Lines How do we represent Eleva:on on a flat piece of paper? Eleva?on height
Do Now Copy the ques:on below and write down an answer Sketch a profile of the books on the front table. Measurements Contour Lines How do we represent Eleva:on on a flat piece of paper? Eleva?on height
GG611 Structural Geology Sec1on Steve Martel POST 805
 GG611 Structural Geology Sec1on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 5 Mechanics Stress, Strain, and Rheology 11/6/16 GG611 1 Stresses Control How Rock Fractures hkp://hvo.wr.usgs.gov/kilauea/update/images.html
GG611 Structural Geology Sec1on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 5 Mechanics Stress, Strain, and Rheology 11/6/16 GG611 1 Stresses Control How Rock Fractures hkp://hvo.wr.usgs.gov/kilauea/update/images.html
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille. Chapter Seven. Rota9onal Mo9on and The Law of Gravity
 Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Seven Rota9onal Mo9on and The Law of Gravity Rota9onal Mo9on An important part of everyday life Mo9on of the Earth Rota9ng wheels Angular mo9on Expressed in terms
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Seven Rota9onal Mo9on and The Law of Gravity Rota9onal Mo9on An important part of everyday life Mo9on of the Earth Rota9ng wheels Angular mo9on Expressed in terms
Ge Problem Set 1
 Ge 101 2012 Problem Set 1 This problem set covers basic techniques in structural geology, geomorphology and the construction of cross sections. Questions 2 and 3 are simple exercises; 1 and 4 are reallife
Ge 101 2012 Problem Set 1 This problem set covers basic techniques in structural geology, geomorphology and the construction of cross sections. Questions 2 and 3 are simple exercises; 1 and 4 are reallife
Laboratory Exercise #2 Introduction to Quadrangle Maps
 page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #2 Introduction to Quadrangle Maps A. Introduction to Quadrangle Maps The United States Geological Survey has developed a nationwide series of quadrangle maps that cover small
page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #2 Introduction to Quadrangle Maps A. Introduction to Quadrangle Maps The United States Geological Survey has developed a nationwide series of quadrangle maps that cover small
Laboratory Exercise #2 Introduction to Quadrangle Maps
 page - Laboratory Exercise #2 Introduction to Quadrangle Maps A. Introduction to Quadrangle Maps The United States Geological Survey has developed a nationwide series of quadrangle maps that cover small
page - Laboratory Exercise #2 Introduction to Quadrangle Maps A. Introduction to Quadrangle Maps The United States Geological Survey has developed a nationwide series of quadrangle maps that cover small
Springshed Springshed Management Training Curriculum
 Springshed Springshed Management Training Curriculum Management Training Curriculum Draft Version 2 January 2016 The Springs Initiative 2016 The Springs Initiative SESSION TITLE: Section Mapping SECTION:
Springshed Springshed Management Training Curriculum Management Training Curriculum Draft Version 2 January 2016 The Springs Initiative 2016 The Springs Initiative SESSION TITLE: Section Mapping SECTION:
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI COLLEGE OF EDUCATION AND EXTERNAL STUDIES & SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY SGL 308:
 UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI COLLEGE OF EDUCATION AND EXTERNAL STUDIES & SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY SGL 308: INTRODUCTION TO GEOLOGICAL MAPPING WRITTEN BY Reviewed by: C.M. Nyamai, W.M.
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI COLLEGE OF EDUCATION AND EXTERNAL STUDIES & SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY SGL 308: INTRODUCTION TO GEOLOGICAL MAPPING WRITTEN BY Reviewed by: C.M. Nyamai, W.M.
In this lab, we will study and analyze geologic maps from a few regions, including the Grand Canyon, western Wyoming, and coastal California.
 Name: Lab Section: work in groups, but each person turns in his/her own GEOSCIENCE 001 LAB UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC MAPS Geologic maps are colorful and even beautiful, but they also contain an amazing amount
Name: Lab Section: work in groups, but each person turns in his/her own GEOSCIENCE 001 LAB UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC MAPS Geologic maps are colorful and even beautiful, but they also contain an amazing amount
Answer sheet for question 1 Answer question 1 as soon as the sample arrives at your desk.
 EAS 233 Geologic structures. Final test. April 2012. 3 hours. Answer question 1 and 2 and three other questions. If you start more than the required number of questions, clearly delete the answers you
EAS 233 Geologic structures. Final test. April 2012. 3 hours. Answer question 1 and 2 and three other questions. If you start more than the required number of questions, clearly delete the answers you
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab
 Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
Structural Geology and Geology Maps Lab
 Structural Geology and Geology Maps Lab Mesa College Geology 101 Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Structural Geology Lab Pre-Lab Resources Pre-Lab Internet Links 1) Fundamentals of Structural Geology 2) Visualizing
Structural Geology and Geology Maps Lab Mesa College Geology 101 Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Structural Geology Lab Pre-Lab Resources Pre-Lab Internet Links 1) Fundamentals of Structural Geology 2) Visualizing
Geological mapwork from scratch 2: valley with simple geology Draw your own cross sections and 3D geological model
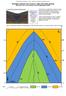 Geological mapwork scratch 2: valley with simple geology Draw your own cross sections and 3D geological model A valley with a stream looks like this: Modified the Geograph project collection. Copyright
Geological mapwork scratch 2: valley with simple geology Draw your own cross sections and 3D geological model A valley with a stream looks like this: Modified the Geograph project collection. Copyright
Image Processing 1 (IP1) Bildverarbeitung 1
 MIN-Fakultät Fachbereich Informatik Arbeitsbereich SAV/BV (KOGS) Image Processing 1 (IP1) Bildverarbeitung 1 Lecture 18 Mo
MIN-Fakultät Fachbereich Informatik Arbeitsbereich SAV/BV (KOGS) Image Processing 1 (IP1) Bildverarbeitung 1 Lecture 18 Mo
UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC M APS
 Name: Lab Section: work in groups, but each person turns in his/her own GEOSCIENCE 001 L AB UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC M APS Geologic maps are colorful and even beautiful, but they also contain an amazing
Name: Lab Section: work in groups, but each person turns in his/her own GEOSCIENCE 001 L AB UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC M APS Geologic maps are colorful and even beautiful, but they also contain an amazing
Structural Geology Lab. The Objectives are to gain experience
 Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
1. Introduc9on 2. Bivariate Data 3. Linear Analysis of Data
 Lecture 3: Bivariate Data & Linear Regression 1. Introduc9on 2. Bivariate Data 3. Linear Analysis of Data a) Freehand Linear Fit b) Least Squares Fit c) Interpola9on/Extrapola9on 4. Correla9on 1. Introduc9on
Lecture 3: Bivariate Data & Linear Regression 1. Introduc9on 2. Bivariate Data 3. Linear Analysis of Data a) Freehand Linear Fit b) Least Squares Fit c) Interpola9on/Extrapola9on 4. Correla9on 1. Introduc9on
Derivative and Integral: Some Concepts for Geodesy
 Derivative and Integral: Some Concepts for Geodesy James R. Clynch, 2003 I. Rates of Change (Derivatives) and Integrals There are many places in physics where the rates of change occur. This is the derivative
Derivative and Integral: Some Concepts for Geodesy James R. Clynch, 2003 I. Rates of Change (Derivatives) and Integrals There are many places in physics where the rates of change occur. This is the derivative
SSSS Unome Geologic Mapping Answer Key p1
 Scioly Summer Study Session 2018-2019 Geologic Mapping Answer Key Written by Unome Instructions Because this test is written for SSSS, the answer key includes explanations for most questions. It is also
Scioly Summer Study Session 2018-2019 Geologic Mapping Answer Key Written by Unome Instructions Because this test is written for SSSS, the answer key includes explanations for most questions. It is also
GEOL 02: Historical Geology Lab 14: Topographic Maps. Name: Date:
 GEOL 02: Historical Geology Lab 14: Topographic Maps Name: Date: A topographic map is a two dimensional (flat) representation (model) of a three dimensional land surface (landscape). It shows landforms
GEOL 02: Historical Geology Lab 14: Topographic Maps Name: Date: A topographic map is a two dimensional (flat) representation (model) of a three dimensional land surface (landscape). It shows landforms
Field Trip to Tempe Butte
 Synopsis Field Trip to Tempe Butte So far you have been identifying rocks and mapping their locations without actually going there. Now it is your chance to put it all together and see real rocks out in
Synopsis Field Trip to Tempe Butte So far you have been identifying rocks and mapping their locations without actually going there. Now it is your chance to put it all together and see real rocks out in
Geo 303 Lab 6 9/8/09 1 LAB 6 - ROTATIONS
 Geo 303 Lab 6 9/8/09 1 LAB 6 - ROTATIONS Exercise 1: Apparent dip problem (28 points total) 1a) An apparent dip of 52 to the southwest is measured for a bedding plane in a vertical cross section that strikes
Geo 303 Lab 6 9/8/09 1 LAB 6 - ROTATIONS Exercise 1: Apparent dip problem (28 points total) 1a) An apparent dip of 52 to the southwest is measured for a bedding plane in a vertical cross section that strikes
GEOLOGIC MAPS PART II
 EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT THROUGH TIME LABORATORY - EES 1005 LABORATORY FIVE GEOLOGIC MAPS PART II Introduction Geologic maps of orogenic belts are much more complex than maps of the stable interior. Just
EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT THROUGH TIME LABORATORY - EES 1005 LABORATORY FIVE GEOLOGIC MAPS PART II Introduction Geologic maps of orogenic belts are much more complex than maps of the stable interior. Just
MAPPING THE EARTH HOW DO YOU FIND A LOCATION ON THE EARTH?
 MAPPING THE EARTH HOW DO YOU FIND A LOCATION ON THE EARTH? UNIT TOPICS TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE TOPIC 2: FIELD MAPS TOPIC 3: TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS TOPIC 4: NYS LANDSCAPES TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE
MAPPING THE EARTH HOW DO YOU FIND A LOCATION ON THE EARTH? UNIT TOPICS TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE TOPIC 2: FIELD MAPS TOPIC 3: TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS TOPIC 4: NYS LANDSCAPES TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE
Chapter 6 Mapping and Online Tools
 Chapter 6 Mapping and Online Tools The stream site you monitor is just part of a much larger system. When analyzing stream health, it is important to take a holistic view by considering the entire watershed.
Chapter 6 Mapping and Online Tools The stream site you monitor is just part of a much larger system. When analyzing stream health, it is important to take a holistic view by considering the entire watershed.
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth. 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth. 3.1 Objectives
 Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
PHYS1121 and MECHANICS
 PHYS1121 and 1131 - MECHANICS Lecturer weeks 1-6: John Webb, Dept of Astrophysics, School of Physics Multimedia tutorials www.physclips.unsw.edu.au Where can I find the lecture slides? There will be a
PHYS1121 and 1131 - MECHANICS Lecturer weeks 1-6: John Webb, Dept of Astrophysics, School of Physics Multimedia tutorials www.physclips.unsw.edu.au Where can I find the lecture slides? There will be a
27. Folds (I) I Main Topics A What is a fold? B Curvature of a plane curve C Curvature of a surface 10/10/18 GG303 1
 I Main Topics A What is a fold? B Curvature of a plane curve C Curvature of a surface 10/10/18 GG303 1 http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/ae/caledonian_orogeny_fold_in_king_oscar_fjord.jpg
I Main Topics A What is a fold? B Curvature of a plane curve C Curvature of a surface 10/10/18 GG303 1 http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/ae/caledonian_orogeny_fold_in_king_oscar_fjord.jpg
Enhanced Subsurface Interpolation by Geological Cross-Sections by SangGi Hwang, PaiChai University, Korea
 Enhanced Subsurface Interpolation by Geological Cross-Sections by SangGi Hwang, PaiChai University, Korea Abstract Subsurface geological structures, such as bedding, fault planes and ore body, are disturbed
Enhanced Subsurface Interpolation by Geological Cross-Sections by SangGi Hwang, PaiChai University, Korea Abstract Subsurface geological structures, such as bedding, fault planes and ore body, are disturbed
N30 E-45 SE S25 E-10 SW N85 W-80 NE
 Geologic aps and tructures Name Geology 100 Harbor section Read h. 7 before you begin. The objectives of this lab are for you to learn the basic geologic structures in 3- and to develop some facility in
Geologic aps and tructures Name Geology 100 Harbor section Read h. 7 before you begin. The objectives of this lab are for you to learn the basic geologic structures in 3- and to develop some facility in
23. Disloca0ons. 23. Disloca0ons. I Main Topics
 I Main Topics A Disloca0ons and other defects in solids B Significance of disloca0ons C Planar disloca0ons D Displacement and stress fields for a screw disloca0on (mode III) 11/10/16 GG303 1 hhp://volcanoes.usgs.gov/imgs/jpg/photoglossary/fissure4_large.jpg
I Main Topics A Disloca0ons and other defects in solids B Significance of disloca0ons C Planar disloca0ons D Displacement and stress fields for a screw disloca0on (mode III) 11/10/16 GG303 1 hhp://volcanoes.usgs.gov/imgs/jpg/photoglossary/fissure4_large.jpg
Using An Introduction to Structural Methods - An Interactive CD-ROM - In and Out of the Classroom
 Using An to Structural Methods - An Interactive CD-ROM - In and Out of the Classroom Tekla A. Harms, Amherst College taharms@amherst.edu H. Robert Burger, Smith College rburger@email.smith.edu TYPE OF
Using An to Structural Methods - An Interactive CD-ROM - In and Out of the Classroom Tekla A. Harms, Amherst College taharms@amherst.edu H. Robert Burger, Smith College rburger@email.smith.edu TYPE OF
EOSC 110 Reading Week Activity, February Visible Geology: Building structural geology skills by exploring 3D models online
 EOSC 110 Reading Week Activity, February 2015. Visible Geology: Building structural geology skills by exploring 3D models online Geological maps show where rocks of different ages occur on the Earth s
EOSC 110 Reading Week Activity, February 2015. Visible Geology: Building structural geology skills by exploring 3D models online Geological maps show where rocks of different ages occur on the Earth s
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy Mechanics Lecture 7, Slide 1 Notices Midterm Exam Friday Feb 8 will cover stuff we do un6l today. 10 mul6ple choice + 2 problems, 2
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy Mechanics Lecture 7, Slide 1 Notices Midterm Exam Friday Feb 8 will cover stuff we do un6l today. 10 mul6ple choice + 2 problems, 2
11. ALPINE GLACIAL LANDFORMS
 Geomorphology 11. Alpine Glacial Landforms 11. ALPINE GLACIAL LANDFORMS 40 Points One objective of this exercise is for you be able to identify alpine glacial landforms and measure their characteristics.
Geomorphology 11. Alpine Glacial Landforms 11. ALPINE GLACIAL LANDFORMS 40 Points One objective of this exercise is for you be able to identify alpine glacial landforms and measure their characteristics.
L A N D F O R M S W E D N E S D A Y
 E P S C 2 4 0 : G E O L O G Y I N T H E F I E L D L A N D F O R M S W E D N E S D A Y Google Earth/Mars lab Laptops Install Google Earth Pro Île Sainte Hélène report due Return mineral ID kits (for non-mineralogy
E P S C 2 4 0 : G E O L O G Y I N T H E F I E L D L A N D F O R M S W E D N E S D A Y Google Earth/Mars lab Laptops Install Google Earth Pro Île Sainte Hélène report due Return mineral ID kits (for non-mineralogy
Structural Geology, GEOL 330 Fold mapping lab: Even folds get parasites Spring, 2012
 Structural Geology, GEOL 330 Name: Fold mapping lab: Even folds get parasites Spring, 2012 This exercise is meant to mimic a field experience in which you, the student, will measure beddingcleavage relationships
Structural Geology, GEOL 330 Name: Fold mapping lab: Even folds get parasites Spring, 2012 This exercise is meant to mimic a field experience in which you, the student, will measure beddingcleavage relationships
Stress and Strain. Stress is a force per unit area. Strain is a change in size or shape in response to stress
 Geologic Structures Geologic structures are dynamically-produced patterns or arrangements of rock or sediment that result from, and give information about, forces within the Earth Produced as rocks change
Geologic Structures Geologic structures are dynamically-produced patterns or arrangements of rock or sediment that result from, and give information about, forces within the Earth Produced as rocks change
Lecture 1: Systems of linear equations and their solutions
 Lecture 1: Systems of linear equations and their solutions Course overview Topics to be covered this semester: Systems of linear equations and Gaussian elimination: Solving linear equations and applications
Lecture 1: Systems of linear equations and their solutions Course overview Topics to be covered this semester: Systems of linear equations and Gaussian elimination: Solving linear equations and applications
14. HOMOGENEOUS FINITE STRAIN
 I Main Topics A vectors B vectors C Infinitesimal differences in posi>on D Infinitesimal differences in displacement E Chain rule for a func>on of mul>ple variables F Gradient tensors and matri representa>on
I Main Topics A vectors B vectors C Infinitesimal differences in posi>on D Infinitesimal differences in displacement E Chain rule for a func>on of mul>ple variables F Gradient tensors and matri representa>on
You must take the exam in the lecture section for which you are registered. Any exceptions must be cleared with the instructor in advance.
 Geo 101, Fall 2000 Review Questions for Final Exam GEOLOGIC TIME AND FOLDING AND FAULTING THE FINAL EXAM FOR MWF CLASS WILL BE TUESDAY 1400 THE FINAL EXAM FOR TR CLASS WILL BE FRIDAY 930 These questions
Geo 101, Fall 2000 Review Questions for Final Exam GEOLOGIC TIME AND FOLDING AND FAULTING THE FINAL EXAM FOR MWF CLASS WILL BE TUESDAY 1400 THE FINAL EXAM FOR TR CLASS WILL BE FRIDAY 930 These questions
The University of Jordan. Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center. Course Name: Structural Geology COURSE Syllabus
 The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus Course Name: Structural Geology 0305341 1 Course title Structural Geology 2 Course number 0305341 3 Credit hours (theory,
The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus Course Name: Structural Geology 0305341 1 Course title Structural Geology 2 Course number 0305341 3 Credit hours (theory,
Stratigraphic Cross-Section
 Stratigraphic cross-sections are used to show stratigraphic relationships of strata along some path. They differ from structural cross-sections in three ways. First, their goals differ. Stratigraphic cross-sections
Stratigraphic cross-sections are used to show stratigraphic relationships of strata along some path. They differ from structural cross-sections in three ways. First, their goals differ. Stratigraphic cross-sections
Latitude and Longitude
 U n i t 3 M a p p i n g P a g e 1 Latitude and Longitude Note: These coordinates are always expressed LATITUDE/LONGITUDE!!! Coordinate System: Using and to find your position on Earth. LATITUDE LATITUDE
U n i t 3 M a p p i n g P a g e 1 Latitude and Longitude Note: These coordinates are always expressed LATITUDE/LONGITUDE!!! Coordinate System: Using and to find your position on Earth. LATITUDE LATITUDE
Edge Detection in Computer Vision Systems
 1 CS332 Visual Processing in Computer and Biological Vision Systems Edge Detection in Computer Vision Systems This handout summarizes much of the material on the detection and description of intensity
1 CS332 Visual Processing in Computer and Biological Vision Systems Edge Detection in Computer Vision Systems This handout summarizes much of the material on the detection and description of intensity
Compass Basics. Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use
 Compass Basics Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use A topographic map tells you where things are and how to get to them, whether you're hiking, biking, hunting, fishing, or just interested in the world
Compass Basics Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use A topographic map tells you where things are and how to get to them, whether you're hiking, biking, hunting, fishing, or just interested in the world
Lecture 17: Face Recogni2on
 Lecture 17: Face Recogni2on Dr. Juan Carlos Niebles Stanford AI Lab Professor Fei-Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab Lecture 17-1! What we will learn today Introduc2on to face recogni2on Principal Component Analysis
Lecture 17: Face Recogni2on Dr. Juan Carlos Niebles Stanford AI Lab Professor Fei-Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab Lecture 17-1! What we will learn today Introduc2on to face recogni2on Principal Component Analysis
EPSS 15. Spring Introduction to Oceanography. Laboratory #1 Maps, Cross-sections, Vertical Exaggeration, Graphs, and Contour Skills 4/7/17
 EPSS 15 Spring 2017 Introduction to Oceanography Laboratory #1 Maps, Cross-sections, Vertical Exaggeration, Graphs, and Contour Skills MAPS Provide valuable interface to explore the geography of the world
EPSS 15 Spring 2017 Introduction to Oceanography Laboratory #1 Maps, Cross-sections, Vertical Exaggeration, Graphs, and Contour Skills MAPS Provide valuable interface to explore the geography of the world
Eleva&on vs. Wind Streaks
 Eleva&on vs. Wind Streaks Scien&fic Ques&on Are wind streaks more common in higher or lower eleva&ons on the Southern Hemisphere of Mars? Why This Is Important o Answering this ques&on may help give us
Eleva&on vs. Wind Streaks Scien&fic Ques&on Are wind streaks more common in higher or lower eleva&ons on the Southern Hemisphere of Mars? Why This Is Important o Answering this ques&on may help give us
Map Reading & Compass Use
 Spring 2013 Kestrel Land Trust Page 2 / 10 Contents Map Basics... 3 Map Types... 3 Terrain Association... 4 Estimating Distance: Pacing... 4 Contour Lines... 5 Navigating with a Compass... 6 Compass Types...
Spring 2013 Kestrel Land Trust Page 2 / 10 Contents Map Basics... 3 Map Types... 3 Terrain Association... 4 Estimating Distance: Pacing... 4 Contour Lines... 5 Navigating with a Compass... 6 Compass Types...
Cecilia first drops off the edge mostly moving parallel the x coordinate. As she gets near bottom of the parabola, she starts moving turning toward
 Cecilia first drops off the edge mostly moving parallel the x coordinate. As she gets near bottom of the parabola, she starts moving turning toward walking nearly parallel to the y-axis Electric Dipole
Cecilia first drops off the edge mostly moving parallel the x coordinate. As she gets near bottom of the parabola, she starts moving turning toward walking nearly parallel to the y-axis Electric Dipole
Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems
 To locate a point in a plane, two numbers are necessary. We know that any point in the plane can be represented as an ordered pair (a, b) of real numbers, where a is the x-coordinate and b is the y-coordinate.
To locate a point in a plane, two numbers are necessary. We know that any point in the plane can be represented as an ordered pair (a, b) of real numbers, where a is the x-coordinate and b is the y-coordinate.
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 UNIT 10: WORK AND ENERGY Approximate Classroom Time: Three 100 minute sessions Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy ES "Knowing is not enough; we must apply. Willing is
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 UNIT 10: WORK AND ENERGY Approximate Classroom Time: Three 100 minute sessions Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy ES "Knowing is not enough; we must apply. Willing is
Final Project Teaching Quantitative Skills in Geoscience Context Carleton College: July 24 July 27, 2002
 Final Project Teaching Quantitative Skills in Geoscience Context Carleton College: July 24 July 27, 2002 Albert T. Hsui, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Ping Wang, University of South Florida
Final Project Teaching Quantitative Skills in Geoscience Context Carleton College: July 24 July 27, 2002 Albert T. Hsui, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Ping Wang, University of South Florida
AU-5029 GURU GHASIDAS VISHWAVIDYALAYA, BILASPUR (C.G.) INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING B.TECH
 AU-5029 GURU GHASIDAS VISHWAVIDYALAYA, BILASPUR (C.G.) INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING B.TECH 2 nd YEAR, III rd SEMESTER SUBJECT: SURVEYING-I COURSE CODE: 21CE02T Max Marks: 60
AU-5029 GURU GHASIDAS VISHWAVIDYALAYA, BILASPUR (C.G.) INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING B.TECH 2 nd YEAR, III rd SEMESTER SUBJECT: SURVEYING-I COURSE CODE: 21CE02T Max Marks: 60
Lecture 17: Face Recogni2on
 Lecture 17: Face Recogni2on Dr. Juan Carlos Niebles Stanford AI Lab Professor Fei-Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab Lecture 17-1! What we will learn today Introduc2on to face recogni2on Principal Component Analysis
Lecture 17: Face Recogni2on Dr. Juan Carlos Niebles Stanford AI Lab Professor Fei-Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab Lecture 17-1! What we will learn today Introduc2on to face recogni2on Principal Component Analysis
Examples: u = is a vector in 2. is a vector in 5.
 3 Vectors and vector equations We'll carefully define vectors, algebraic operations on vectors and geometric interpretations of these operations, in terms of displacements These ideas will eventually give
3 Vectors and vector equations We'll carefully define vectors, algebraic operations on vectors and geometric interpretations of these operations, in terms of displacements These ideas will eventually give
B. Topographic maps are also called. contour maps
 Topographic Maps Introduction A. Topographic maps are essential tools in geologic and engineering studies because they show the configuration of Earth's surface in remarkable detail and permit one to measure
Topographic Maps Introduction A. Topographic maps are essential tools in geologic and engineering studies because they show the configuration of Earth's surface in remarkable detail and permit one to measure
Earth Science Regents Reading Topographic Maps
 Earth Science Regents Reading Topographic Maps Name Period Quick Tutorial on Degrees, Minutes, and Seconds of Latitude and Longitude A degree of latitude on the surface of the earth is about 70 miles long.
Earth Science Regents Reading Topographic Maps Name Period Quick Tutorial on Degrees, Minutes, and Seconds of Latitude and Longitude A degree of latitude on the surface of the earth is about 70 miles long.
CSCI1950 Z Computa4onal Methods for Biology Lecture 4. Ben Raphael February 2, hhp://cs.brown.edu/courses/csci1950 z/ Algorithm Summary
 CSCI1950 Z Computa4onal Methods for Biology Lecture 4 Ben Raphael February 2, 2009 hhp://cs.brown.edu/courses/csci1950 z/ Algorithm Summary Parsimony Probabilis4c Method Input Output Sankoff s & Fitch
CSCI1950 Z Computa4onal Methods for Biology Lecture 4 Ben Raphael February 2, 2009 hhp://cs.brown.edu/courses/csci1950 z/ Algorithm Summary Parsimony Probabilis4c Method Input Output Sankoff s & Fitch
ENGRG Introduction to GIS
 ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki March 17, 2014 Lecture 08: Terrain Analysis Outline: Terrain Analysis Earth Surface Representation Contour TIN Mass Points Digital Elevation Models Slope
ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki March 17, 2014 Lecture 08: Terrain Analysis Outline: Terrain Analysis Earth Surface Representation Contour TIN Mass Points Digital Elevation Models Slope
Problem Set #4: Folds and Folding Stereonet Analysis Due Tuesday, Nov. 22
 Geol 360 PS #4 Name Problem Set #4: Folds and Folding Stereonet Analysis Due Tuesday, Nov. 22 Supplies: a. Data: i. Compilation of bedding attitudes at Mt Baldy; BaldyBedding.txt ii. Compilation of bedding
Geol 360 PS #4 Name Problem Set #4: Folds and Folding Stereonet Analysis Due Tuesday, Nov. 22 Supplies: a. Data: i. Compilation of bedding attitudes at Mt Baldy; BaldyBedding.txt ii. Compilation of bedding
Smith Chart The quarter-wave transformer
 Smith Chart The quarter-wave transformer We will cover these topics The Smith Chart The Quarter-Wave Transformer Watcharapan Suwansan8suk #3 EIE/ENE 450 Applied Communica8ons and Transmission Lines King
Smith Chart The quarter-wave transformer We will cover these topics The Smith Chart The Quarter-Wave Transformer Watcharapan Suwansan8suk #3 EIE/ENE 450 Applied Communica8ons and Transmission Lines King
Topographic Map Series:
 DEFINITION OF A MAP A MAP IS A GEOGRAPHIC PREPRESENTATION OF A PORTION OF THE EARTH S SURFACE DRAWN TO SCALE, AS SEEN FROM ABOVE. IT S USES COLORS, SYMBOLS AND LABELS TO REPRESENT FEATURES FOUND ON THE
DEFINITION OF A MAP A MAP IS A GEOGRAPHIC PREPRESENTATION OF A PORTION OF THE EARTH S SURFACE DRAWN TO SCALE, AS SEEN FROM ABOVE. IT S USES COLORS, SYMBOLS AND LABELS TO REPRESENT FEATURES FOUND ON THE
Electricity & Magnetism Lecture 10: Kirchhoff s Rules
 Electricity & Magnetism Lecture 10: Kirchhoff s Rules Today s Concept: Kirchhoff s Rules Electricity & Magne/sm Lecture 10, Slide 1 Deadline for Unit 23 Ac>vity guide and WriBen Homework is pushed to Friday
Electricity & Magnetism Lecture 10: Kirchhoff s Rules Today s Concept: Kirchhoff s Rules Electricity & Magne/sm Lecture 10, Slide 1 Deadline for Unit 23 Ac>vity guide and WriBen Homework is pushed to Friday
Modeling Pinch-Outs and Steep Topography in RockWorks
 Modeling Pinch-Outs and Steep Topography in RockWorks Table of Contents Table of Figures... 1 Summary... 1 Introduction... 1 Stratigraphy Model Generation The Borehole Manager... 2 Step 1: Create Top &
Modeling Pinch-Outs and Steep Topography in RockWorks Table of Contents Table of Figures... 1 Summary... 1 Introduction... 1 Stratigraphy Model Generation The Borehole Manager... 2 Step 1: Create Top &
Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM
 Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM http://www.tasagraphicarts.com/progstruct.html AN INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL METHODS - DETAILED CONTENTS: (Navigate
Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM http://www.tasagraphicarts.com/progstruct.html AN INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL METHODS - DETAILED CONTENTS: (Navigate
GLY-5828 Calculus Review/Assignment 1
 Rise GLY-5828 Calculus Review/Assignment 1 Slope y 2 y 1 Run x 1 x 2 Slope is defined as the rise over the run: Slope = rise/run. The rise is the change in the y value and the run is the change in the
Rise GLY-5828 Calculus Review/Assignment 1 Slope y 2 y 1 Run x 1 x 2 Slope is defined as the rise over the run: Slope = rise/run. The rise is the change in the y value and the run is the change in the
ENGRG Introduction to GIS
 ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki November 17, 2017 Lecture 11: Terrain Analysis Outline: Terrain Analysis Earth Surface Representation Contour TIN Mass Points Digital Elevation Models Slope
ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki November 17, 2017 Lecture 11: Terrain Analysis Outline: Terrain Analysis Earth Surface Representation Contour TIN Mass Points Digital Elevation Models Slope
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy Mechanics Lecture 7, Slide 1 Karate Will not do Session 3 of Unit 8. It is a Karate thing. We will only mark Session 2 of unit 8. You
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy Mechanics Lecture 7, Slide 1 Karate Will not do Session 3 of Unit 8. It is a Karate thing. We will only mark Session 2 of unit 8. You
Subsurface Mapping 1 TYPES OF SUBSURFACE MAPS:- 1.1 Structural Maps and Sections: -
 Subsurface Mapping The purpose of subsurface mapping in the geology of petroleum Is to find traps that contain oil and gas pools and the information obtained from wells forms the heart of the data upon
Subsurface Mapping The purpose of subsurface mapping in the geology of petroleum Is to find traps that contain oil and gas pools and the information obtained from wells forms the heart of the data upon
In order to be adequately prepared for a test on this topic you should be able to:-
 Topic 2: MAPPING In order to be adequately prepared for a test on this topic you should be able to:- 1. Find and also provide both FOUR and SIX figure Area and Grid References 2. Calculate distances both
Topic 2: MAPPING In order to be adequately prepared for a test on this topic you should be able to:- 1. Find and also provide both FOUR and SIX figure Area and Grid References 2. Calculate distances both
Using Map and Compass Together
 Using Map and Compass Together In situations where you foresee a potential evacuation on foot, where there are no roads, and no indication as to the direction of travel (i.e., road signs), it is recommended
Using Map and Compass Together In situations where you foresee a potential evacuation on foot, where there are no roads, and no indication as to the direction of travel (i.e., road signs), it is recommended
Algorithms, Lecture 3 on NP : Nondeterminis7c Polynomial Time
 Algorithms, Lecture 3 on NP : Nondeterminis7c Polynomial Time Last week: Defined Polynomial Time Reduc7ons: Problem X is poly 7me reducible to Y X P Y if can solve X using poly computa7on and a poly number
Algorithms, Lecture 3 on NP : Nondeterminis7c Polynomial Time Last week: Defined Polynomial Time Reduc7ons: Problem X is poly 7me reducible to Y X P Y if can solve X using poly computa7on and a poly number
Borehole Problems. Horizontal Level Ground. Boreholes Sunk on Horizontal Ground. Depth Diagram (Not to Scale)
 Borehole roblems 43 4 Borehole roblems Horizontal Level Ground In order to determine the subsurface geology of an area, boreholes are sunk at convenient places in areas such as cultivated lands, forests
Borehole roblems 43 4 Borehole roblems Horizontal Level Ground In order to determine the subsurface geology of an area, boreholes are sunk at convenient places in areas such as cultivated lands, forests
Structural Geology Lab. The Objectives are to gain experience
 Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
FLUIDS Problem Set #3 SOLUTIONS 10/27/ v y = A A = 0. + w z. Y = C / x
 FLUIDS 2009 Problem Set #3 SOLUTIONS 10/27/2009 1.i. The flow is clearly incompressible because iu = u x + v y + w z = A A = 0 1.ii. The equation for a streamline is dy dx = Y. Guessing a solution of the
FLUIDS 2009 Problem Set #3 SOLUTIONS 10/27/2009 1.i. The flow is clearly incompressible because iu = u x + v y + w z = A A = 0 1.ii. The equation for a streamline is dy dx = Y. Guessing a solution of the
Matrices. A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. Cells in a matrix can be referenced in the form.
 Matrices A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 7 2 5 4 2 0 5 10 12 8 4 9 25 30 1 1 Reading Information from a Matrix Cells in a matrix can be referenced
Matrices A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 7 2 5 4 2 0 5 10 12 8 4 9 25 30 1 1 Reading Information from a Matrix Cells in a matrix can be referenced
EAS 233 Geologic Structures and Maps Winter Miscellaneous practice map exercises. 1. Fault and separation:
 Miscellaneous practice map exercises 1. Fault and separation: With respect to Map 1, what are (a) the orientation of the fault, and (b) the orientation of bedding in the units cut by the fault. (c) Mark
Miscellaneous practice map exercises 1. Fault and separation: With respect to Map 1, what are (a) the orientation of the fault, and (b) the orientation of bedding in the units cut by the fault. (c) Mark
How quickly can you stop a car?
 How quickly can you stop a car? You are driving along a road at a constant speed V 0. You see a stop sign, you step on the breaks, and the car slows down with constant decelera;on a. 1. How much ;me does
How quickly can you stop a car? You are driving along a road at a constant speed V 0. You see a stop sign, you step on the breaks, and the car slows down with constant decelera;on a. 1. How much ;me does
