7 TRANSPORTATION EQUITY
|
|
|
- Marcia Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 7 TRANSPORTATION EQUITY THE TRANSPORTATION EQUITY PROGRAM The purpose of the MPO s transportation equity (TE) program is to ensure that populations protected under various federal and state civil rights statutes, executive orders, and regulations (TE populations) are provided equal opportunity to participate fully in the MPO s transportation planning and decision-making process. The program also ensures that TE populations share equitably in the benefits and burdens of past, present, and planned future transportation projects, programs, and service. The TE program includes three types of activities: 1) outreach to TE populations; 2) systematic consideration of equity in the planning and programming process; and 3) analyses to identify TE populations and their transportation needs, and to estimate the equity impacts of MPO funding decisions. Environmental Justice (EJ) Executive Order of February 11, 1994 laid the groundwork for the MPO s TE program. This executive order required each federal agency to achieve environmental justice by identifying and addressing any disproportionately high adverse human health or environmental effects including interrelated social and economic effects of its programs, policies, and activities on minority or low-income populations. The EJ executive order was intended not to create new mandates, but to encourage implementation of existing statutes, such as Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which states that, No person in the United States shall, on the ground of race, color, or national origin, be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any program or activity receiving Federal financial assistance. Executive Order of August 11, 2000 extended Title VI national origin protections to individuals with limited English proficiency (LEP). As recipients of federal funding, MPOs are subject to EJ and Title VI requirements. ecause the MPO s TE program grew out of EJ requirements, initially it was designed to serve minority and low-income populations (EJ populations). More recently, in response to Federal Transit Administration (FTA) and Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) LEP requirements and the extension of protections based on age, sex, and disability through the FHWA Title VI/Nondiscrimination program, the MPO is assessing how to expand its TE program to consider systematically the needs of additional protected populations.
2 TRANSPORTATION EQUITY OUTREACH FOR THE LRTP TE outreach is an integral part of the MPO s overall public participation program designed specifically to communicate with low-income and minority residents, the elderly, persons with disabilities, and persons with LEP. The purpose of TE outreach is to identify transportation needs of specific populations served by the TE program and promote their involvement in the planning process. Through this outreach, the MPO hopes to develop relationships that will heighten awareness and sow seeds of mutual understanding, appreciation, and trust to encourage broader participation of TE populations. Outreach targets both individuals and organizations representing the interests of TE populations, such as social-service organizations, community-development corporations, regional employment boards, civic groups, business and labor organizations, transportation advocates, environmental groups, EJ and civil-rights groups, and the state s regional coordinating councils (RCCs) recently formed through the Statewide Mobility Management Program to coordinate human-service transportation services. The MPO maintains an list of TE contacts to provide them general information about the MPO and its planning processes, and give them information about topics and events of specific interest to the communities served by the TE program. During the past year and a half, staff has worked to increase significantly the number of valid contacts on this list. Initial TE outreach for the LRTP began in fall 2014 with a series of public meetings to solicit comments on the MPO s revised Public Participation Plan (P3) and inform members of the public about the MPO s TE program. These meetings were held in areas with high concentrations of minority, low-income, and LEP residents, including Framingham, Lynn, Quincy, and the Fields Corner neighborhood of Dorchester in oston. The focus of these meetings was to provide information about and solicit input on the P3, which describes the public involvement process for the LRTP and other major MPO documents and activities. These meetings set the stage for specific LRTP public engagement, as the P3 provides information about the LRTP development schedule and the types and timing of opportunities for participation. Subsequent notifications to the TE contacts kept them apprised of all public meetings for the LRTP and MPO-sponsored meetings at which the LRTP was discussed. Chapter 2 (Public Participation - Public Outreach Methods section) discusses the public meetings and other outreach opportunities specifically for this LRTP. Notices for all MPO-sponsored public meetings are routinely translated into the three languages, other than English, that are most frequently spoken in the MPO area: Spanish, Portuguese, and Chinese. P3 public meeting notices also were translated into Vietnamese because the Fields Corner meeting was held at the VietAID Center as part of the MPO s effort to forge closer ties with specific organizations as a way of facilitating communication with their constituent populations. Although the TE list is good for reaching many groups quickly, MPO staff sees personal contact as a more effective way to foster meaningful engagement in the future. 7-2 Charting Progress to 2040
3 TRANSPORTATION EQUITY AND THE PLANNING PROCESS The MPO systematically integrates equity concerns into the transportation planning process in a number of ways. At the highest level, equity is part of the MPO s central vision statement, and therefore is reflected in the MPO s goals and objectives. Equity concerns are also integrated by considering feedback from all outreach activities, including TE outreach, and the ongoing public involvement that routinely occurs during development of the LRTP, TIP, UPWP, and other MPO studies. In addition, equity is one of the factors the MPO considers when selecting studies for the UPWP, and it is integrated into the project selection criteria for the LRTP and TIP. Finally, as discussed below, staff performs equity analyses on the recommended projects in the draft LRTP to evaluate the effects on access, mobility, congestion, and air quality for TE populations, and determine whether the recommendations should be changed before a final LRTP is adopted. TRANSPORTATION EQUITY ANALYSES Demographic Analyses The MPO analyzes demographic data to identify the geographic locations and concentration of protected populations. This is done to understand their transportation needs relative to existing and planned infrastructure, and to pinpoint areas where public outreach could be most beneficial and fruitful. For this LRTP, the analysis of benefits and burdens (equity analysis) was based on minority and low-income populations, as defined using federal guidance, census data, and geography. GEOGRAPHIC LEVEL OF ANALYSIS The MPO region is divided into 1,943 Transportation Analysis Zones (TAZs) for the purposes of forecasting travel behavior using the MPO s regional travel demand model set. A TAZ is a unit of geography that is defined based on demographic information population, employment, and housing and the numbers of trips generated in, and attracted to, it. The full geographic area covered by the MPO s travel demand model set, which also includes municipalities adjacent to the MPO s 101 cities and towns, comprises 2,727 TAZs. Using TAZ geography and thresholds established through federal guidance, the MPO has developed demographic profiles that identify areas with concentrations of minority and low-income populations for analyzing benefits and burdens. The MPO has also developed demographic profiles for areas with concentrations of LEP residents, the elderly, and people with disabilities. However, the MPO has yet to develop thresholds for these populations to identify specific areas for the purposes of performing an equity analysis. Transportation Equity 7-3
4 MINORITY AND LOW-INCOME THRESHOLDS Minority s The MPO uses the US Census ureau s racial and ethnic minority group definitions to determine minority status in the region. The census defines non-minority as persons who identify as white and not Hispanic or Latino. Minorities include: American Indian/Alaskan Native Asian/Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander lack/african American Another race or multiple races Hispanic/Latino of any race The FTA Title VI circular (FTA C ) defines a predominantly minority area as one where the proportion of minority persons residing in that area exceeds the average proportion of minority persons in the MPO region. Using this definition, a minority TAZ is one in which the minority population is greater than 27.8 percent. Low-Income s The FTA Title VI circular suggests that a low-income person be defined as one whose median household income is at or below the Department of Health and Human Services poverty guidelines. However, the circular allows MPOs to develop their own definitions of low-income, as long as their thresholds meet or exceed the federal definition of lowincome. The oston Region MPO defines a low-income person as an individual living in a household with a median income that is less than or equal to 60 percent of the median household income in the MPO region. The MPO chose this threshold, which is higher than federal poverty guidelines, because the cost of living in the MPO region is higher than the national average. According to the 2010 census, the median MPO household income was $70,829. Therefore, using the MPO s definition, a low-income TAZ is one in which the average median household income is less than or equal to $42,497. Equity Analysis Zones The MPO uses the above definitions to identify equity analysis zones TAZs that meet the threshold for minority and/or low-income as the basis for its analysis of the benefits and burdens of transportation programs and projects. Figure 7.1 shows the MPO s equity analysis zones, of which 11 percent are low-income TAZs, 33 percent are minority, and 10 percent are both low-income and minority. Also included are the locations of major infrastructure projects recommended in this LRTP. Investments like grounding McGrath 7-4 Charting Progress to 2040
5 FIGURE 7.1 Equity Analysis Zones Haverhill Groveland Newbury Data Source: CTPS Methuen Georgetown Rowley Pepperell Dunstable Tyngsborough Dracut Lawrence oxford Ipswich Groton Westford Shirley Ayer Littleton Harvard oxborough Acton olton Stow Maynard erlin Hudson Sudbury Marlborough Northborough Framingham Southborough Andover North Andover Lowell Topsfield Hamilton Tewksbury Middleton Wenham Chelmsford NorthReading Danvers everly illerica Wilmington Reading Lynnfield Carlisle Peabody urlington Wakefield Salem Marblehead edford Woburn Saugus Lynn Concord Stoneham Swampscott Winchester Melrose Lexington Lincoln Medford Nahant Arlington Waltham elmont Watertown Winthrop Wayland Weston Newton rookline Wellesley Essex Manchester Gloucester Rockport Miles Westborough Natick Needham Hull Northbridge Uxbridge Upton Millville Hopkinton Milford Hopedale Mendon lackstone Ashland ellingham Holliston Medway Franklin Sherborn Millis Medfield Norfolk Wrentham Plainville Dover Walpole Dedham Westwood Foxborough Norwood Mansfield Sharon Canton Stoughton Easton Quincy Milton raintreeweymouth Randolph Avon Holbrook rockton West ridgewater Abington Whitman Hingham Rockland East ridgewater Hanover Hanson Cohasset Norwell Scituate Pembroke Marshfield Duxbury North Attleborough ridgewater Halifax Plympton Kingston Transportation Analysis Zones (TAZs) That Meet Equity Analysis Zone Criteria* Not minority or low-income Minority zone Low-income zone oth low-income and minority Plan Project *Criteria for Equity Analysis Zones under Title VI (2010 Data) A TAZ in which the median household income in 2010 was equal to or less than 60% of the MPO median of $70,829 ($42,497) or in which the 2010 population was more than 27.8% minority. Transportation Equity 7-5
6 Highway in Somerville, reconstructing Rutherford Avenue in oston, and improving Route 126 and Route 135 in Framingham will address MPO-identified transportation issues for equity populations. Grounding McGrath will help reconnect two transportation equity areas. Reconstructing Rutherford Avenue will improve community access to the Orange Line and bus terminal and will enhance bus operations. Improving Downtown Framingham will enhance MetroWest Regional Transit Authority service for many low-income and minority riders. For the purposes of analyzing the transportation system in 2040, the MPO assumed that the distributions of equity analysis zones would remain unchanged, and that the population growth rate for these zones would be the same as that forecast by MAPC for the overall population of the region. ased on these demographic projections, staff used the regional travel demand model set to forecast the unique distributions of trip flows for the differing transportation networks in the 2040 No- and alternatives. Measuring Impacts To determine whether the benefits and burdens of projects, programs, and service are equitably distributed, the MPO has proposed a policy to measure the following types of disparities, in keeping with federal requirements: Disparate impact: a facially neutral policy or practice that disproportionately affects members of a group identified by race, color, or national origin, where the policy or practice lacks a substantial legitimate justification and where there exists one or more alternatives that would serve the same legitimate objectives, but with less disproportionate effects on the basis, of race, color, or national origin. Disproportionate burden: a neutral policy or practice that disproportionately affects low-income populations more than non-low income populations. A finding of disproportionate burden requires evaluation of alternatives and mitigation of burdens where practicable. The MPO s proposed policy sets thresholds to distinguish an acceptable level of impact from a level of impact that has a meaningful effect for the factors analyzed. For LRTP equity analyses that are completed using the regional travel demand model set, the MPO has proposed the following thresholds: A disparate burden would exist if minority TAZs were projected to sustain more than 20 percent additional burden than nonminority TAZs. Therefore, a projected burden would be found if the analysis results for minority TAZs were more than 1.2 times the projected burden for nonminority TAZs. A disproportionate burden would exist if low-income TAZs were projected to sustain more than 20 percent additional burden than non-low-income TAZs. Therefore, a projected burden would be found if the analysis results for low-income TAZs were more than 1.2 times the projected burden for non-low-income TAZs. 7-6 Charting Progress to 2040
7 A disparate benefit would exist if minority TAZs were projected to receive less than 80 percent of the benefit that nonminority TAZs receive. Therefore, a projected benefit would be found if the analysis results for minority TAZs were more than 0.80 times the projected burden for nonminority TAZs. A disproportionate benefit would exist if low-income TAZs were projected to receive less than 80 percent of the benefits that non-low-income TAZs receive. Therefore, a projected benefit would be found if the analysis results for low-income TAZs were less than 0.80 times the projected burden for nonminority TAZs. Staff proposed a 20 percent threshold based on the belief that a 10 percent differential would be meaningful, plus the model s 10 percent margin of error. The full disparate impact/disproportionate burden policy will undergo public review and comment before it is adopted by the MPO. Equity Analysis Methods MPO staff used the travel demand model to perform two types of equity analyses (discussed below) each of which calculated differences between the No- and 1 alternatives for equity analysis zones (minority TAZs and low-income TAZs) and the difference for non-equity analysis zones (nonminority TAZs and non-low-income TAZs). For each analysis, the rate of change from the No- to the alternatives was compared for minority versus nonminority TAZs to determine whether there was a disparate impact and for low- versus non-low-income TAZs to determine whether there was a disproportionate burden. For the 2040 alternative, only major infrastructure projects (those on the recommended list of projects discussed in Chapter 5 and shown in Figure 7.1) were modeled. Specific projects in the O&M-type investment programs are not identified in the LRTP, as they will be selected through the TIP programming process. ecause most bike and pedestrian improvements will be part of the O&M-type investment programs, they were not captured in the LRTP equity analysis. However, the TIP project-selection process seeks to minimize burdens and maximize benefits for protected populations, and many projects in the TIP go through the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) process, which includes an EJ evaluation. ACCESSIILITY ANALYSIS For the purposes of this analysis, accessibility was based on both the ability to reach desired destinations and the ease of doing so. This analysis investigated the number of employment opportunities, health care facilities, and higher education facilities that could be reached from equity analysis zones and non-equity analysis zones along with average 1 The No- alternative includes projects that are currently under construction, advertised for construction, or programmed in the first year of the TIP. The alternative includes the projects that are recommended in this LRTP. Transportation Equity 7-7
8 transit and highway travel times to these destinations. Analysis of transit travel times included destinations within a 40-minute transit trip, while analysis of highway travel times included destinations within a 20-minute auto trip. Staff used the following factors to examine differences in accessibility between the 2040 No- network and the 2040 network: Average travel time to industrial, retail, and service jobs within a 40-minute transit trip and a 20-minute auto trip Number of industrial, retail, and service jobs within a 40-minute transit trip and a 20-minute auto trip Average travel time to hospitals, weighted by number of beds, within a 40-minute transit trip and a 20-minute auto trip Number of hospitals, weighted by number of beds, within a 40-minute transit trip and a 20-minute auto trip Average travel time to two- and four-year institutions of higher education, weighted by enrollment, within a 40-minute transit trip and a 20-minute auto trip Number of two- and four-year institutions of higher education, weighted by enrollment, within a 40-minute transit trip and a 20-minute auto trip MOILITY, CONGESTION, AND AIR-QUALITY ANALYSIS For the purposes of this analysis, mobility is defined as the ability to move from place to place, and congestion is defined as the level at which transportation system performance becomes unacceptable because of traffic congestion. The MPO s mobility and congestion analysis focused on the average door-to-door travel time and average vehicle-miles traveled (VMT) under congested conditions. The air quality-analysis focused on carbon monoxide, a pollutant that results primarily from incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and accumulates in localized areas creating hot spots that negatively affect human health. Staff used the following mobility, congestion, and air-quality factors in the equity analysis: VMT per square mile number of vehicle-miles traveled (VMT) per square mile of dry land within a TAZ Congested VMT the volume of vehicle-miles traveled within a TAZ on highway links with a volume-to capacity ratio of 0.75 or higher Carbon monoxide (CO) per square mile the number of kilograms of carbon monoxide emitted per square mile of dry land within a TAZ Transit production time 2 average door-to-door travel time for all transit trips produced in the TAZ 2 Productions and attractions are used in transportation modeling to identify types of trip ends and are loosely related to origins and destinations. 7-8 Charting Progress to 2040
9 Highway production time average door-to-door travel time for all highway trips produced in the TAZ Transit attraction time average door-to-door travel time for all transit trips attracted to the TAZ Highway attraction time average door-to-door travel time for all highway trips attracted to the TAZ TRANSPORTATION EQUITY ANALYSIS RESULTS Accessibility Results The accessibility analysis first compared the change in transit and highway travel times to various types of employment between the 2040 No- and alternatives for lowincome, non-low-income, minority, and nonminority TAZs, respectively. The second part of the accessibility analysis compared the ratio of the change from the 2040 No- to the alternative for low-income versus non-low-income TAZs to determine whether there was a disproportionate burden, and for minority versus nonminority TAZs to determine whether there was a disparate impact for each type of employment evaluated. The results of the accessibility analyses are illustrated in the following figures and tables. Figures 7.2 and 7.3 show that average transit travel times to employment destinations are lower for non-low-income and non-minority TAZs than for low-income and minority TAZs, respectively; but the changes for each type of equity analysis zone between the 2040 No- and alternatives are not statistically significant. FIGURE 7.2 Average Transit Travel Times to Destinations for Equity Analysis Zones (Low-Income) in the 2040 No- and 2040 Networks 30.0 Low-Income Non Low-Income N No- Transit Travel Times (minutes) N N N N N Industrial Retail Service Colleges Hospitals Transportation Equity 7-9
10 FIGURE 7.3 Average Transit Travel Times to Destinations for Equity Analysis Zones (Minority) in the 2040 No- and 2040 Networks 30.0 Minority Non Minority N No- Transit Travel Times (minutes) N N N N N Industrial Retail Service Colleges Hospitals Figures 7.4 and 7.5 show that average highway travel times to employment destinations are slightly lower for low-income and minority TAZs than for non-low-income and nonminority TAZs, respectively, but the changes for each type of equity analysis zone between the 2040 No- and alternatives are not statistically significant. FIGURE 7.4 Average Highway Travel Times to Destinations for Equity Analysis Zones (Low-Income) in the 2040 No- and 2040 Networks Low-Income Non Low-Income N No Highway Travel Times (minutes) N N N N N Industrial Retail Service Colleges Hospitals 7-10 Charting Progress to 2040
11 FIGURE 7.5 Average Highway Travel Times to Destinations for Equity Analysis Zones (Minority) in the 2040 No- and 2040 Networks 14.0 Minority Non Minority N No- Highway Travel Times (minutes) N N N N N Industrial Retail Service Colleges Hospitals Tables 7.1 and 7.2 show that there are neither disproportionate burdens nor disparate impacts in average transit and highway travel times to employment destinations, as all differences fall within the MPO s disproportionate burden/disparate impact threshold. TALE 7.1 enefits and urdens Analysis for Average Transit Travel Times to Employment Destination Types No- Pct. Travel- Time Increase No- Pct. Travel- Time Increase No- Industrial Retail Service Pct. Travel- Time Increase a Low-Income % % % Non Low-Income % % % Ratio urden Threshold >1.20 Result: No Disproportionate urden Minority % % % Non-Minority % % % Ratio urden Threshold >1.20 Result: No Disparate Impact a All changes are within the model s margin of error. Transportation Equity 7-11
12 TALE 7.2 enefits and urdens Analysis for Average Highway Travel Times to Employment Destination Types No- Pct. Travel- Time No- Pct. Travel- Time No- Increase Increase Industrial Retail Service Pct. Travel- Time Increase a Low-Income % % % Non Low-Income % % % Ratio urden Threshold >1.20 Result: No Disproportionate urden Minority % % % Non-Minority % % % Ratio urden Threshold >1.20 Result: No Disparate Impact a All changes are within the model s margin of error Mobility and Congestion Results The mobility and congestion analyses first compared the change in average door-to-door travel time, congested VMT, and VMT per square mile for all transit and highway trips produced in, or attracted to, equity analysis zones between the 2040 No- and alternatives for low-income, non-low-income, minority, and nonminority TAZs, respectively. The second part of the mobility and congestion analysis compared the ratio of the change from the 2040 No- to the alternatives for low- versus non-low-income TAZs to determine whether there was a disproportionate burden, and for minority versus nonminority TAZs to determine whether there was a disparate impact for each of the factors evaluated. The results of the mobility and congestion analyses are illustrated in the following figures and tables. Figures 7.6 and 7.7 show that average transit and highway travel times for attractions and productions are shorter for low-income and minority TAZs than for non-low-income and non-minority TAZs, respectively, in both alternatives; but the changes for each type of equity analysis zone between the 2040 No- and alternatives are not statistically significant Charting Progress to 2040
13 FIGURE 7.6 Average Transit Travel Times for Equity Analysis Zones in the 2040 No- and 2040 Networks Low-Income Minority N No- Non Low-Income Non Minority Transit Travel Times (minutes) N N N N Attractions Productions Attractions Productions FIGURE 7.7 Average Highway Travel Times for Equity Analysis Zones in the 2040 No- and 2040 Networks Low-Income Minority N No- Non Low-Income Non Minority Highway Travel Times (minutes) N N N N Attractions Productions Attractions Productions Tables 7.3 and 7.4 show that there are neither disproportionate burdens nor disparate impacts in average transit and highway travel times. Transportation Equity 7-13
14 TALE 7.3 enefits and urdens Analysis for Average Transit Travel Time No- Attractions No- Productions Percentage Travel-Time Increase a Low-Income % Non Low-Income % Ratio 1.14 urden Threshold >1.20 Result: No Disproportionate urden Minority % Non-Minority % Ratio 1.15 urden Threshold >1.20 Result: No Disparate Impact a All changes are within the model s margin of error. TALE 7.4 enefits and urdens Analysis for Average Highway Travel Time No- Attractions Percentage Travel-Time Increase No- Productions Percentage Travel-Time Increase a Low-Income % % Non Low-Income % % Ratio urden Threshold >1.20 Result: No Disproportionate urden Minority % % Non-Minority % % Ratio urden Threshold >1.20 Result: No Disparate Impact a All changes are within the model s margin of error. Figures 7.8 and 7.9 show that average VMT per square mile is greater for low-income and minority TAZs than for non-low-income and non-minority TAZs, respectively, for 7-14 Charting Progress to 2040
15 both alternatives, and that average congested VMT is less for low-income and minority TAZs than for non-low-income and non-minority TAZs, respectively, for both alternatives. However, the changes for each type of equity analysis zone between the 2040 No- and alternatives are not statistically significant. FIGURE 7.8 Average VMT for Equity Analysis Zones in the 2040 No- and 2040 Networks 300,000 Vehichle Miles Travelled (per square mile) 250, , , ,000 50,000 0 Low-Income Non Low-Income Minority Non-Minority No- FIGURE 7.9 Average Congested Vehicle Miles Traveled for Equity Analysis Zones in the 2040 No- and 2040 Networks Congested Vehichle Miles Travelled 35,000 30,000 25,000 20,000 15,000 10,000 5,000 0 No- Low-Income Non Low-Income Minority Non-Minority Transportation Equity 7-15
16 Tables 7.5 and 7.6 show disproportionate burdens and disparate impacts for average VMT, and a disproportionate burden for congested VMT. However, because the changes between the 2040 No- and alternatives for each type of equity/non-equity analysis zone comparison are within the margin of error of the model, it is unlikely that the ratio of the changes is meaningful. The MPO will carefully monitor these possible burdens and impacts over time and, if necessary, address them at the program level through the TIP project selection process and equity analyses. TALE 7.5 Average Vehicle Miles Traveled No- Percentage Increase a Low-Income 261, , % Non Low-Income 146, , % Ratio urden Threshold >1.20 Result: Disproportionate urden b Minority 196, , % Non-Minority 139, , % Ratio urden Threshold >1.20 Result: Disparate Impact b a All changes are within the model s margin of error. b ecause the changes themselves are within the margin of error of the model, this comparison probably does not show a meaningful difference. TALE 7.6 enefits and urdens Analysis for Congested Vehicle Miles Travelled No- Percentage Increase a Low-Income 12,493 12, % Non Low-Income 28,843 29, % Ratio 3.01 urden Threshold >1.20 Result: Disproportionate urden b Minority 18,761 18, % Non-Minority 31,266 31, % Ratio 1.10 urden Threshold >1.20 Result: No Disparate Impact a All changes are within the model s margin of error. b ecause the changes themselves are within the margin of error of the model, this comparison probably does not show a meaningful difference Charting Progress to 2040
17 Air Quality Results Carbon monoxide emissions are essentially the same in the 2040 build network as in the 2040 No- network for all zones. FUTURE TRANSPORTATION EQUITY ANALYSES Although the equity analyses conducted for this LRTP look only at impacts on minority and low-income populations, the MPO plans to increase the number of protected populations covered in the future. The FHWA Title VI/Nondiscrimination Program requires MPOs also to consider and analyze equity impacts based on age, sex, and disability. In the coming year, staff will investigate data sources and analytical techniques to determine the most effective and appropriate ways to incorporate these populations into equity analyses. In addition, the FFY 2016 UPWP will fund a study to evaluate methods for performing more sophisticated equity analyses on the TIP. Such analyses would help to ensure the equitable distribution of benefits and burdens for projects that are not individually listed in the LRTP because they will be funded through O&M-type programs and will be selected through TIP programming. Transportation Equity 7-17
ADDRESSING TITLE VI AND ENVIRONMENTAL JUSTICE IN LONG-RANGE TRANSPORTATION PLANS
 ADDRESSING TITLE VI AND ENVIRONMENTAL JUSTICE IN LONG-RANGE TRANSPORTATION PLANS Activities from the National Capital Region Transportation Planning Board Sergio Ritacco Transportation Planner 2017 Association
ADDRESSING TITLE VI AND ENVIRONMENTAL JUSTICE IN LONG-RANGE TRANSPORTATION PLANS Activities from the National Capital Region Transportation Planning Board Sergio Ritacco Transportation Planner 2017 Association
Environmental Analysis, Chapter 4 Consequences, and Mitigation
 Environmental Analysis, Chapter 4 4.17 Environmental Justice This section summarizes the potential impacts described in Chapter 3, Transportation Impacts and Mitigation, and other sections of Chapter 4,
Environmental Analysis, Chapter 4 4.17 Environmental Justice This section summarizes the potential impacts described in Chapter 3, Transportation Impacts and Mitigation, and other sections of Chapter 4,
Massachusetts Department of Revenue
 Massachusetts Department of Revenue Division of Local Services Communities with s for FY 2013 as of 3/4/2013 Report Last Updated at 7:11:58PM Total Number of Communities 342 Out of 353 Approval 1 2 3 4
Massachusetts Department of Revenue Division of Local Services Communities with s for FY 2013 as of 3/4/2013 Report Last Updated at 7:11:58PM Total Number of Communities 342 Out of 353 Approval 1 2 3 4
APPENDIX C-3 Equitable Target Areas (ETA) Technical Analysis Methodology
 APPENDIX C-3 Equitable Target Areas (ETA) Technical Analysis Methodology Contents Introduction... 1 ETA Index Methodology... 1 ETA Index Development... 1 Other EJ Measures... 4 The Limited English Proficiency
APPENDIX C-3 Equitable Target Areas (ETA) Technical Analysis Methodology Contents Introduction... 1 ETA Index Methodology... 1 ETA Index Development... 1 Other EJ Measures... 4 The Limited English Proficiency
Environmental Justice Analysis
 Environmental Justice Analysis October 2013 Transportation Department Environmental Justice Analysis Background The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines environmental justice as the fair
Environmental Justice Analysis October 2013 Transportation Department Environmental Justice Analysis Background The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines environmental justice as the fair
Map of Middlesex County, MA 1856
 Map of Middlesex County, MA 1856 To find your town, click on the name in the list below (See also the detailed Table of Contents inside) ACTON ASHBY ASHLAND BEDFORD BILLERICA BOXBOROUGH BRIGHTON BURLINGTON
Map of Middlesex County, MA 1856 To find your town, click on the name in the list below (See also the detailed Table of Contents inside) ACTON ASHBY ASHLAND BEDFORD BILLERICA BOXBOROUGH BRIGHTON BURLINGTON
Environmental Justice Analysis FOR THE MINNESOTA STATEWIDE FREIGHT SYSTEM PLAN
 Environmental Justice Analysis FOR THE MINNESOTA STATEWIDE FREIGHT SYSTEM PLAN Presentation Overview Minnesota Freight Plan Summary Environmental Justice (EJ) Background Freight Plan EJ Analysis Methodology
Environmental Justice Analysis FOR THE MINNESOTA STATEWIDE FREIGHT SYSTEM PLAN Presentation Overview Minnesota Freight Plan Summary Environmental Justice (EJ) Background Freight Plan EJ Analysis Methodology
NEW YORK AND CONNECTICUT SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITIES. Fair Housing & Equity Assessment & Regional Planning Enhancement
 NEW YORK AND CONNECTICUT SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITIES Fair Housing & Equity Assessment & Regional Planning Enhancement November 19, 2013 White Plains Public Library Federal grant to improve regional planning
NEW YORK AND CONNECTICUT SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITIES Fair Housing & Equity Assessment & Regional Planning Enhancement November 19, 2013 White Plains Public Library Federal grant to improve regional planning
Study Overview. the nassau hub study. The Nassau Hub
 Livable Communities through Sustainable Transportation the nassau hub study AlternativeS analysis / environmental impact statement The Nassau Hub Study Overview Nassau County has initiated the preparation
Livable Communities through Sustainable Transportation the nassau hub study AlternativeS analysis / environmental impact statement The Nassau Hub Study Overview Nassau County has initiated the preparation
NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF SANITATION. Spatial Analysis of Complaints
 NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF SANITATION Spatial Analysis of Complaints Spatial Information Design Lab Columbia University Graduate School of Architecture, Planning and Preservation November 2007 Title New York
NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF SANITATION Spatial Analysis of Complaints Spatial Information Design Lab Columbia University Graduate School of Architecture, Planning and Preservation November 2007 Title New York
Regional Performance Measures
 G Performance Measures Regional Performance Measures Introduction This appendix highlights the performance of the MTP/SCS for 2035. The performance of the Revenue Constrained network also is compared to
G Performance Measures Regional Performance Measures Introduction This appendix highlights the performance of the MTP/SCS for 2035. The performance of the Revenue Constrained network also is compared to
MPOs SB 375 LAFCOs SCAG Practices/Experiences And Future Collaborations with LAFCOs
 Connecting LAFCOs and COGs for Mutual Benefits MPOs SB 375 LAFCOs SCAG Practices/Experiences And Future Collaborations with LAFCOs Frank Wen, Manager Research & Analysis Land Use & Environmental Planning
Connecting LAFCOs and COGs for Mutual Benefits MPOs SB 375 LAFCOs SCAG Practices/Experiences And Future Collaborations with LAFCOs Frank Wen, Manager Research & Analysis Land Use & Environmental Planning
Regional Snapshot Series: Transportation and Transit. Commuting and Places of Work in the Fraser Valley Regional District
 Regional Snapshot Series: Transportation and Transit Commuting and Places of Work in the Fraser Valley Regional District TABLE OF CONTENTS Complete Communities Daily Trips Live/Work Ratio Commuting Local
Regional Snapshot Series: Transportation and Transit Commuting and Places of Work in the Fraser Valley Regional District TABLE OF CONTENTS Complete Communities Daily Trips Live/Work Ratio Commuting Local
BOSTON REGION METROPOLITAN PLANNING ORGANIZATION
 PLANNING ORGANIZATIO BOSTON REGION MPO NMETROPOLITAN BOSTON REGION METROPOLITAN PLANNING ORGANIZATION Richard A. Davey, MassDOT Secretary and CEO and MPO Chairman Karl H. Quackenbush, Executive Director,
PLANNING ORGANIZATIO BOSTON REGION MPO NMETROPOLITAN BOSTON REGION METROPOLITAN PLANNING ORGANIZATION Richard A. Davey, MassDOT Secretary and CEO and MPO Chairman Karl H. Quackenbush, Executive Director,
NEW YORK AND CONNECTICUT SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITIES. Fair Housing & Equity Assessment & Regional Planning Enhancement
 NEW YORK AND CONNECTICUT SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITIES Fair Housing & Equity Assessment & Regional Planning Enhancement November 18, 2013 Fordham University Bronx, NY Federal grant to improve regional planning
NEW YORK AND CONNECTICUT SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITIES Fair Housing & Equity Assessment & Regional Planning Enhancement November 18, 2013 Fordham University Bronx, NY Federal grant to improve regional planning
Regional Performance Measures
 G Performance Measures Regional Performance Measures Introduction This appendix highlights the performance of the MTP/SCS for 2035. The performance of the Revenue Constrained network also is compared to
G Performance Measures Regional Performance Measures Introduction This appendix highlights the performance of the MTP/SCS for 2035. The performance of the Revenue Constrained network also is compared to
Evaluating the Distributional Effects of Regional Transportation Plans and Projects
 Portland State University PDXScholar TREC Final Reports Transportation Research and Education Center (TREC) 5-2017 Evaluating the Distributional Effects of Regional Transportation Plans and Projects Kristine
Portland State University PDXScholar TREC Final Reports Transportation Research and Education Center (TREC) 5-2017 Evaluating the Distributional Effects of Regional Transportation Plans and Projects Kristine
Proposed Scope of Work Village of Farmingdale Downtown Farmingdale BOA Step 2 BOA Nomination Study / Draft Generic Environmental Impact Statement
 Proposed Scope of Work Village of Farmingdale Downtown Farmingdale BOA Step 2 BOA Nomination Study / Draft Generic Environmental Impact Statement The scope of work that follows incorporates and covers
Proposed Scope of Work Village of Farmingdale Downtown Farmingdale BOA Step 2 BOA Nomination Study / Draft Generic Environmental Impact Statement The scope of work that follows incorporates and covers
Geospatial Analysis of Job-Housing Mismatch Using ArcGIS and Python
 Geospatial Analysis of Job-Housing Mismatch Using ArcGIS and Python 2016 ESRI User Conference June 29, 2016 San Diego, CA Jung Seo, Frank Wen, Simon Choi and Tom Vo, Research & Analysis Southern California
Geospatial Analysis of Job-Housing Mismatch Using ArcGIS and Python 2016 ESRI User Conference June 29, 2016 San Diego, CA Jung Seo, Frank Wen, Simon Choi and Tom Vo, Research & Analysis Southern California
Metrolinx Transit Accessibility/Connectivity Toolkit
 Metrolinx Transit Accessibility/Connectivity Toolkit Christopher Livett, MSc Transportation Planning Analyst Research and Planning Analytics Tweet about this presentation #TransitGIS OUTLINE 1. Who is
Metrolinx Transit Accessibility/Connectivity Toolkit Christopher Livett, MSc Transportation Planning Analyst Research and Planning Analytics Tweet about this presentation #TransitGIS OUTLINE 1. Who is
PENINSULA. POWERS BOARD 1250 San
 PENINSULA CORRIDOR JOINT POWERS BOARD TITLE VI COMPLIANCE PROGRAM OCTOBER 2013 PENINSULA CORRIDOR JOINT POWERS BOARD 1250 San Carlos Avenue San Carlos, CA 94070 1306 650.508.6200 PENINSULA CORRIDOR JOINT
PENINSULA CORRIDOR JOINT POWERS BOARD TITLE VI COMPLIANCE PROGRAM OCTOBER 2013 PENINSULA CORRIDOR JOINT POWERS BOARD 1250 San Carlos Avenue San Carlos, CA 94070 1306 650.508.6200 PENINSULA CORRIDOR JOINT
Economic and Social Urban Indicators: A Spatial Decision Support System for Chicago Area Transportation Planning
 Economic and Social Urban Indicators: A Spatial Decision Support System for Chicago Area Transportation Planning Piyushimita Thakuriah (Vonu), P.S. Sriraj, Paul Metaxatos, Inshu Minocha & Tanushri Swarup
Economic and Social Urban Indicators: A Spatial Decision Support System for Chicago Area Transportation Planning Piyushimita Thakuriah (Vonu), P.S. Sriraj, Paul Metaxatos, Inshu Minocha & Tanushri Swarup
Local Economic Activity Around Rapid Transit Stations
 Local Economic Activity Around Rapid Transit Stations The Case of Chicago s Orange Line Julie Cooper, MPP 2014 Harris School of Public Policy Transport Chicago June 6, 2014 Motivation Impacts of transit
Local Economic Activity Around Rapid Transit Stations The Case of Chicago s Orange Line Julie Cooper, MPP 2014 Harris School of Public Policy Transport Chicago June 6, 2014 Motivation Impacts of transit
HORIZON 2030: Land Use & Transportation November 2005
 PROJECTS Land Use An important component of the Horizon transportation planning process involved reviewing the area s comprehensive land use plans to ensure consistency between them and the longrange transportation
PROJECTS Land Use An important component of the Horizon transportation planning process involved reviewing the area s comprehensive land use plans to ensure consistency between them and the longrange transportation
StanCOG Transportation Model Program. General Summary
 StanCOG Transportation Model Program Adopted By the StanCOG Policy Board March 17, 2010 What are Transportation Models? General Summary Transportation Models are technical planning and decision support
StanCOG Transportation Model Program Adopted By the StanCOG Policy Board March 17, 2010 What are Transportation Models? General Summary Transportation Models are technical planning and decision support
Mapping and Health Equity Advocacy
 Mapping and Health Equity Advocacy Sarah Treuhaft PolicyLink November 7, 2008 About us PolicyLink National research and action institute that advances policies to achieve economic and social equity Center
Mapping and Health Equity Advocacy Sarah Treuhaft PolicyLink November 7, 2008 About us PolicyLink National research and action institute that advances policies to achieve economic and social equity Center
Council Workshop on Neighbourhoods Thursday, October 4 th, :00 to 4:00 p.m. Burlington Performing Arts Centre
 Council Workshop on Neighbourhoods Thursday, October 4 th, 2012 1:00 to 4:00 p.m. Burlington Performing Arts Centre Agenda Introductions Warm-Up Exercise Presentation Exercise Neighbourhood Planning Break
Council Workshop on Neighbourhoods Thursday, October 4 th, 2012 1:00 to 4:00 p.m. Burlington Performing Arts Centre Agenda Introductions Warm-Up Exercise Presentation Exercise Neighbourhood Planning Break
ITEM 11 Information June 20, Visualize 2045: Update to the Equity Emphasis Areas. None
 ITEM 11 Information June 20, 2018 Visualize 2045: Update to the Equity Emphasis Areas Staff Recommendation: Issues: Background: Briefing on the TPB-approved methodology to update the Equity Emphasis Areas
ITEM 11 Information June 20, 2018 Visualize 2045: Update to the Equity Emphasis Areas Staff Recommendation: Issues: Background: Briefing on the TPB-approved methodology to update the Equity Emphasis Areas
Technical Methods to Support Analysis of Environmental Justice Issues
 final report Technical Methods to Support Analysis of prepared for National Cooperative Highway Research Program Project 8-36 (11), Support to the Standing Committee on Planning of the American Association
final report Technical Methods to Support Analysis of prepared for National Cooperative Highway Research Program Project 8-36 (11), Support to the Standing Committee on Planning of the American Association
THE FUTURE OF FORECASTING AT METROPOLITAN COUNCIL. CTS Research Conference May 23, 2012
 THE FUTURE OF FORECASTING AT METROPOLITAN COUNCIL CTS Research Conference May 23, 2012 Metropolitan Council forecasts Regional planning agency and MPO for Twin Cities metropolitan area Operates regional
THE FUTURE OF FORECASTING AT METROPOLITAN COUNCIL CTS Research Conference May 23, 2012 Metropolitan Council forecasts Regional planning agency and MPO for Twin Cities metropolitan area Operates regional
Frequently Asked Questions
 What is the Regional Transit Engagement Series? As one of the fastest growing regions in the country, there is recognition that long-term transit planning efforts should be accelerated if we are to remain
What is the Regional Transit Engagement Series? As one of the fastest growing regions in the country, there is recognition that long-term transit planning efforts should be accelerated if we are to remain
Initial Findings from Regional Initiatives Planning Enhancement Fair Housing & Equity Assessment
 NEW YORK AND CONNECTICUT SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITIES Initial Findings from Regional Initiatives Planning Enhancement Fair Housing & Equity Assessment July 30, 2013 White Plains Library Federal grant to improve
NEW YORK AND CONNECTICUT SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITIES Initial Findings from Regional Initiatives Planning Enhancement Fair Housing & Equity Assessment July 30, 2013 White Plains Library Federal grant to improve
Volume Title: Evaluation of Econometric Models. Volume Author/Editor: Jan Kmenta and James B. Ramsey, eds.
 This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Evaluation of Econometric Models Volume Author/Editor: Jan Kmenta and James B. Ramsey, eds.
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Evaluation of Econometric Models Volume Author/Editor: Jan Kmenta and James B. Ramsey, eds.
2040 MTP and CTP Socioeconomic Data
 SE Data 6-1 24 MTP and CTP Socioeconomic Data Purpose of Socioeconomic Data The socioeconomic data (SE Data) shows the location of the population and employment, median household income and other demographic
SE Data 6-1 24 MTP and CTP Socioeconomic Data Purpose of Socioeconomic Data The socioeconomic data (SE Data) shows the location of the population and employment, median household income and other demographic
Regional Transit Development Plan Strategic Corridors Analysis. Employment Access and Commuting Patterns Analysis. (Draft)
 Regional Transit Development Plan Strategic Corridors Analysis Employment Access and Commuting Patterns Analysis (Draft) April 2010 Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 4 1.1 Overview and Data Sources... 4 1.2
Regional Transit Development Plan Strategic Corridors Analysis Employment Access and Commuting Patterns Analysis (Draft) April 2010 Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 4 1.1 Overview and Data Sources... 4 1.2
CRP 608 Winter 10 Class presentation February 04, Senior Research Associate Kirwan Institute for the Study of Race and Ethnicity
 CRP 608 Winter 10 Class presentation February 04, 2010 SAMIR GAMBHIR SAMIR GAMBHIR Senior Research Associate Kirwan Institute for the Study of Race and Ethnicity Background Kirwan Institute Our work Using
CRP 608 Winter 10 Class presentation February 04, 2010 SAMIR GAMBHIR SAMIR GAMBHIR Senior Research Associate Kirwan Institute for the Study of Race and Ethnicity Background Kirwan Institute Our work Using
The CRP stresses a number of factors that point to both our changing demographics and our future opportunities with recommendations for:
 Plan Overview The CRP represents the first broad planning initiative covering Lake, Porter and LaPorte counties. Unlike previous plans released by NIRPC, which focused primarily on transportation, the
Plan Overview The CRP represents the first broad planning initiative covering Lake, Porter and LaPorte counties. Unlike previous plans released by NIRPC, which focused primarily on transportation, the
3.0 ANALYSIS OF FUTURE TRANSPORTATION NEEDS
 3.0 ANALYSIS OF FUTURE TRANSPORTATION NEEDS In order to better determine future roadway expansion and connectivity needs, future population growth and land development patterns were analyzed as part of
3.0 ANALYSIS OF FUTURE TRANSPORTATION NEEDS In order to better determine future roadway expansion and connectivity needs, future population growth and land development patterns were analyzed as part of
Appendixx C Travel Demand Model Development and Forecasting Lubbock Outer Route Study June 2014
 Appendix C Travel Demand Model Development and Forecasting Lubbock Outer Route Study June 2014 CONTENTS List of Figures-... 3 List of Tables... 4 Introduction... 1 Application of the Lubbock Travel Demand
Appendix C Travel Demand Model Development and Forecasting Lubbock Outer Route Study June 2014 CONTENTS List of Figures-... 3 List of Tables... 4 Introduction... 1 Application of the Lubbock Travel Demand
Improving the Model s Sensitivity to Land Use Policies and Nonmotorized Travel
 Improving the Model s Sensitivity to Land Use Policies and Nonmotorized Travel presented to MWCOG/NCRTPB Travel Forecasting Subcommittee presented by John (Jay) Evans, P.E., AICP Cambridge Systematics,
Improving the Model s Sensitivity to Land Use Policies and Nonmotorized Travel presented to MWCOG/NCRTPB Travel Forecasting Subcommittee presented by John (Jay) Evans, P.E., AICP Cambridge Systematics,
BROOKINGS May
 Appendix 1. Technical Methodology This study combines detailed data on transit systems, demographics, and employment to determine the accessibility of jobs via transit within and across the country s 100
Appendix 1. Technical Methodology This study combines detailed data on transit systems, demographics, and employment to determine the accessibility of jobs via transit within and across the country s 100
California Urban Infill Trip Generation Study. Jim Daisa, P.E.
 California Urban Infill Trip Generation Study Jim Daisa, P.E. What We Did in the Study Develop trip generation rates for land uses in urban areas of California Establish a California urban land use trip
California Urban Infill Trip Generation Study Jim Daisa, P.E. What We Did in the Study Develop trip generation rates for land uses in urban areas of California Establish a California urban land use trip
East Bay BRT. Planning for Bus Rapid Transit
 East Bay BRT Planning for Bus Rapid Transit Regional Vision Draper Prison The Bottleneck is a State-Level issue, Salt Lake County 2050 Population: 1.5M Draper Prison hopefully with some State-Level funding!
East Bay BRT Planning for Bus Rapid Transit Regional Vision Draper Prison The Bottleneck is a State-Level issue, Salt Lake County 2050 Population: 1.5M Draper Prison hopefully with some State-Level funding!
Data Collection. Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering. Prof. Tom V. Mathew. 1 Overview 1
 Data Collection Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Survey design 2 2.1 Information needed................................. 2 2.2 Study area.....................................
Data Collection Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Survey design 2 2.1 Information needed................................. 2 2.2 Study area.....................................
Changes in the Spatial Distribution of Mobile Source Emissions due to the Interactions between Land-use and Regional Transportation Systems
 Changes in the Spatial Distribution of Mobile Source Emissions due to the Interactions between Land-use and Regional Transportation Systems A Framework for Analysis Urban Transportation Center University
Changes in the Spatial Distribution of Mobile Source Emissions due to the Interactions between Land-use and Regional Transportation Systems A Framework for Analysis Urban Transportation Center University
CLAREMONT MASTER PLAN 2017: LAND USE COMMUNITY INPUT
 Planning and Development Department 14 North Street Claremont, New Hampshire 03743 Ph: (603) 542-7008 Fax: (603) 542-7033 Email: cityplanner@claremontnh.com www.claremontnh.com CLAREMONT MASTER PLAN 2017:
Planning and Development Department 14 North Street Claremont, New Hampshire 03743 Ph: (603) 542-7008 Fax: (603) 542-7033 Email: cityplanner@claremontnh.com www.claremontnh.com CLAREMONT MASTER PLAN 2017:
CHAPTER 4: REGIONAL PROFILE AND DEMOGRAPHICS
 CHAPTER 4: REGIONAL PROFILE AND DEMOGRAPHICS The Greater Lowell region consists of the City of Lowell and its eight suburbs Billerica, Chelmsford, Dracut, Dunstable, Pepperell, Tewksbury, Tyngsborough
CHAPTER 4: REGIONAL PROFILE AND DEMOGRAPHICS The Greater Lowell region consists of the City of Lowell and its eight suburbs Billerica, Chelmsford, Dracut, Dunstable, Pepperell, Tewksbury, Tyngsborough
Impact of Metropolitan-level Built Environment on Travel Behavior
 Impact of Metropolitan-level Built Environment on Travel Behavior Arefeh Nasri 1 and Lei Zhang 2,* 1. Graduate Research Assistant; 2. Assistant Professor (*Corresponding Author) Department of Civil and
Impact of Metropolitan-level Built Environment on Travel Behavior Arefeh Nasri 1 and Lei Zhang 2,* 1. Graduate Research Assistant; 2. Assistant Professor (*Corresponding Author) Department of Civil and
GUIDE FOR ENVIRONMENTAL JUSTICE ANALYSIS WITH THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS PROCESS (EIAP) Department of the Air Force
 GUIDE FOR ENVIRONMENTAL JUSTICE ANALYSIS WITH THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS PROCESS (EIAP) Department of the Air Force November 1997 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION............... 1 FLOWCHART STEP 1:
GUIDE FOR ENVIRONMENTAL JUSTICE ANALYSIS WITH THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS PROCESS (EIAP) Department of the Air Force November 1997 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION............... 1 FLOWCHART STEP 1:
Mapping Accessibility Over Time
 Journal of Maps, 2006, 76-87 Mapping Accessibility Over Time AHMED EL-GENEIDY and DAVID LEVINSON University of Minnesota, 500 Pillsbury Drive S.E., Minneapolis, MN 55455, USA; geneidy@umn.edu (Received
Journal of Maps, 2006, 76-87 Mapping Accessibility Over Time AHMED EL-GENEIDY and DAVID LEVINSON University of Minnesota, 500 Pillsbury Drive S.E., Minneapolis, MN 55455, USA; geneidy@umn.edu (Received
INCORPORATING ACCESSIBILITY INTO ENVIRONMENTAL JUSTICE ASSESSMENT: APPLICATIONS IN THE ATLANTA METROPOLITAN REGION
 INCORPORATING ACCESSIBILITY INTO ENVIRONMENTAL JUSTICE ASSESSMENT: APPLICATIONS IN THE ATLANTA METROPOLITAN REGION A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Stefanie R. Brodie In Partial Fulfillment
INCORPORATING ACCESSIBILITY INTO ENVIRONMENTAL JUSTICE ASSESSMENT: APPLICATIONS IN THE ATLANTA METROPOLITAN REGION A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Stefanie R. Brodie In Partial Fulfillment
Economic Activity Economic A ctivity
 5 Economic Economic Activity Activity ECONOMIC ACTIVITY 5.1 EMPLOYMENT... 5-7 5.1.1 OBJECTIVE... 5-7 5.1.2 POLICIES... 5-7 5.2 PROTECTING THE AREA OF EMPLOYMENT... 5-9 5.2.1 OBJECTIVE... 5-9 5.2.2 POLICIES...
5 Economic Economic Activity Activity ECONOMIC ACTIVITY 5.1 EMPLOYMENT... 5-7 5.1.1 OBJECTIVE... 5-7 5.1.2 POLICIES... 5-7 5.2 PROTECTING THE AREA OF EMPLOYMENT... 5-9 5.2.1 OBJECTIVE... 5-9 5.2.2 POLICIES...
Urbanization and Sustainable Development of Cities: A Ready Engine to Promote Economic Growth and Cooperation
 Urbanization and Sustainable Development of Cities: A Ready Engine to Promote Economic Growth and Cooperation Wan Portia Hamzah Institute of Strategic and International Studies (ISIS) Malaysia 10 September
Urbanization and Sustainable Development of Cities: A Ready Engine to Promote Economic Growth and Cooperation Wan Portia Hamzah Institute of Strategic and International Studies (ISIS) Malaysia 10 September
Foreword. Vision and Strategy
 GREATER MANCHESTER SPATIAL FRAMEWORK Friends of Walkden Station Consultation Response January 2017 Foreword Friends of Walkden Station are a group of dedicated volunteers seeking to raise the status and
GREATER MANCHESTER SPATIAL FRAMEWORK Friends of Walkden Station Consultation Response January 2017 Foreword Friends of Walkden Station are a group of dedicated volunteers seeking to raise the status and
Regional Growth Strategy Regional Staff Committee
 Regional Growth Strategy Regional Staff Committee June 21, 2018 1 Overview Summary of June Growth Management Policy Board Regional Growth Strategy Objectives Regional Geographies Regional Growth Strategy
Regional Growth Strategy Regional Staff Committee June 21, 2018 1 Overview Summary of June Growth Management Policy Board Regional Growth Strategy Objectives Regional Geographies Regional Growth Strategy
Environmental Justice Areas with 2040 Roads
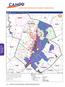 CAPITAL AREA METROPOLITAN PLANNING ORGANIZATION CAMPO Region Date: 2/23/15 Environmental Justice Areas with 40 Roads Map : EJ Areas with 40 Road Types BRNET I BELL 138 WILLIAMSON 1 MILAM LLANO 9 281 TRAIS
CAPITAL AREA METROPOLITAN PLANNING ORGANIZATION CAMPO Region Date: 2/23/15 Environmental Justice Areas with 40 Roads Map : EJ Areas with 40 Road Types BRNET I BELL 138 WILLIAMSON 1 MILAM LLANO 9 281 TRAIS
The 3V Approach. Transforming the Urban Space through Transit Oriented Development. Gerald Ollivier Transport Cluster Leader World Bank Hub Singapore
 Transforming the Urban Space through Transit Oriented Development The 3V Approach Gerald Ollivier Transport Cluster Leader World Bank Hub Singapore MDTF on Sustainable Urbanization The China-World Bank
Transforming the Urban Space through Transit Oriented Development The 3V Approach Gerald Ollivier Transport Cluster Leader World Bank Hub Singapore MDTF on Sustainable Urbanization The China-World Bank
User Guide. Affirmatively Furthering Fair Housing Data and Mapping Tool. U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development
 User Guide Affirmatively Furthering Fair Housing Data and Mapping Tool U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development December, 2015 1 Table of Contents 1. Getting Started... 5 1.1 Software Version...
User Guide Affirmatively Furthering Fair Housing Data and Mapping Tool U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development December, 2015 1 Table of Contents 1. Getting Started... 5 1.1 Software Version...
Committee Meeting November 6, 2018
 Committee Meeting November 6, 2018 Agenda Where we are in the process Land Use Plan Transportation Element Housing & Neighborhoods Elements Next Steps Schedule November 6: Plan Elements December: Plan
Committee Meeting November 6, 2018 Agenda Where we are in the process Land Use Plan Transportation Element Housing & Neighborhoods Elements Next Steps Schedule November 6: Plan Elements December: Plan
Date: June 19, 2013 Meeting Date: July 5, Consideration of the City of Vancouver s Regional Context Statement
 Section E 1.5 To: From: Regional Planning and Agriculture Committee Lee-Ann Garnett, Senior Regional Planner Planning, Policy and Environment Department Date: June 19, 2013 Meeting Date: July 5, 2013 Subject:
Section E 1.5 To: From: Regional Planning and Agriculture Committee Lee-Ann Garnett, Senior Regional Planner Planning, Policy and Environment Department Date: June 19, 2013 Meeting Date: July 5, 2013 Subject:
Understanding Land Use and Walk Behavior in Utah
 Understanding Land Use and Walk Behavior in Utah 15 th TRB National Transportation Planning Applications Conference Callie New GIS Analyst + Planner STUDY AREA STUDY AREA 11 statistical areas (2010 census)
Understanding Land Use and Walk Behavior in Utah 15 th TRB National Transportation Planning Applications Conference Callie New GIS Analyst + Planner STUDY AREA STUDY AREA 11 statistical areas (2010 census)
GIS Analysis of Crenshaw/LAX Line
 PDD 631 Geographic Information Systems for Public Policy, Planning & Development GIS Analysis of Crenshaw/LAX Line Biying Zhao 6679361256 Professor Barry Waite and Bonnie Shrewsbury May 12 th, 2015 Introduction
PDD 631 Geographic Information Systems for Public Policy, Planning & Development GIS Analysis of Crenshaw/LAX Line Biying Zhao 6679361256 Professor Barry Waite and Bonnie Shrewsbury May 12 th, 2015 Introduction
NSHE DIVERSITY REPORT
 University of Nevada, Las Vegas University of Nevada, Reno NSHE DIVERSITY REPORT 2006-07 Nevada State College at Henderson College of Southern Nevada December 2007 Prepared by the Office of Academic and
University of Nevada, Las Vegas University of Nevada, Reno NSHE DIVERSITY REPORT 2006-07 Nevada State College at Henderson College of Southern Nevada December 2007 Prepared by the Office of Academic and
WICHITA FALLS METROPOLITAN PLANNING ORGANIZATION
 WICHITA FALLS METROPOLITAN PLANNING ORGANIZATION Urban Transportation Study ANNUAL PERFORMANCE and EXPENDITURE REPORT Fiscal Year 2014 October 1, 2013 to September 30, 2014 Prepared by the Wichita Falls
WICHITA FALLS METROPOLITAN PLANNING ORGANIZATION Urban Transportation Study ANNUAL PERFORMANCE and EXPENDITURE REPORT Fiscal Year 2014 October 1, 2013 to September 30, 2014 Prepared by the Wichita Falls
Spatiotemporal Analysis of Commuting Patterns: Using ArcGIS and Big Data
 Spatiotemporal Analysis of Commuting Patterns: Using ArcGIS and Big Data 2017 ESRI User Conference July 13, 2017 San Diego, VA Jung Seo, Tom Vo, Frank Wen and Simon Choi Research & Analysis Southern California
Spatiotemporal Analysis of Commuting Patterns: Using ArcGIS and Big Data 2017 ESRI User Conference July 13, 2017 San Diego, VA Jung Seo, Tom Vo, Frank Wen and Simon Choi Research & Analysis Southern California
Measuring Performance:
 Accessibility Metrics in Metropolitan Regions around the World Geneviève Boisjoly and Ahmed El-Geneidy August 2017 Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 1 Introduction...4 2 Theoretical Background...4
Accessibility Metrics in Metropolitan Regions around the World Geneviève Boisjoly and Ahmed El-Geneidy August 2017 Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 1 Introduction...4 2 Theoretical Background...4
CERTIFIED RESOLUTION. introduction: and dated May 29, 2017, as attached, as appropriate
 15322 Buena Vista Avenue, White Rock BC, Canada V4B 1Y6 www.whiterockcity.ca City of White Rock P: 604.541.22121 F: 604.541.9348 /2tC% City Clerk s Office IT E ROC K June 13,2017 Stephanie Lam, Deputy
15322 Buena Vista Avenue, White Rock BC, Canada V4B 1Y6 www.whiterockcity.ca City of White Rock P: 604.541.22121 F: 604.541.9348 /2tC% City Clerk s Office IT E ROC K June 13,2017 Stephanie Lam, Deputy
Regional Growth Strategy Work Session Growth Management Policy Board
 Regional Growth Strategy Work Session Growth Management Policy Board September 6, 2018 1 Overview Recap June GMPB work session Objectives and outcomes Regional geographies Growth scenarios Breakout Discussion:
Regional Growth Strategy Work Session Growth Management Policy Board September 6, 2018 1 Overview Recap June GMPB work session Objectives and outcomes Regional geographies Growth scenarios Breakout Discussion:
MANAGING TRANSPORTATION & LAND USE INTERACTIONS (PL-58)
 MANAGING TRANSPORTATION & LAND USE INTERACTIONS (PL-58) COURSE OUTLINE DAY ONE 1:30 2:00 p.m. MODULE 1: History and Context Understand history and foundation for transportation and land use planning today
MANAGING TRANSPORTATION & LAND USE INTERACTIONS (PL-58) COURSE OUTLINE DAY ONE 1:30 2:00 p.m. MODULE 1: History and Context Understand history and foundation for transportation and land use planning today
Planning for Economic and Job Growth
 Planning for Economic and Job Growth Mayors Innovation Project Winter 2012 Meeting January 21, 2012 Mary Kay Leonard Initiative for a Competitive Inner City AGENDA The Evolving Model for Urban Economic
Planning for Economic and Job Growth Mayors Innovation Project Winter 2012 Meeting January 21, 2012 Mary Kay Leonard Initiative for a Competitive Inner City AGENDA The Evolving Model for Urban Economic
Typical information required from the data collection can be grouped into four categories, enumerated as below.
 Chapter 6 Data Collection 6.1 Overview The four-stage modeling, an important tool for forecasting future demand and performance of a transportation system, was developed for evaluating large-scale infrastructure
Chapter 6 Data Collection 6.1 Overview The four-stage modeling, an important tool for forecasting future demand and performance of a transportation system, was developed for evaluating large-scale infrastructure
Transportation Statistical Data Development Report OKALOOSA-WALTON OUTLOOK 2035 LONG RANGE TRANSPORTATION PLAN
 Transportation Statistical Data Development Report OKALOOSA-WALTON OUTLOOK 2035 LONG RANGE TRANSPORTATION PLAN Prepared for the Okaloosa-Walton Transportation Planning Organization and The Florida Department
Transportation Statistical Data Development Report OKALOOSA-WALTON OUTLOOK 2035 LONG RANGE TRANSPORTATION PLAN Prepared for the Okaloosa-Walton Transportation Planning Organization and The Florida Department
Managing Growth: Integrating Land Use & Transportation Planning
 Managing Growth: Integrating Land Use & Transportation Planning Metro Vancouver Sustainability Community Breakfast Andrew Curran Manager, Strategy June 12, 2013 2 Integrating Land Use & Transportation
Managing Growth: Integrating Land Use & Transportation Planning Metro Vancouver Sustainability Community Breakfast Andrew Curran Manager, Strategy June 12, 2013 2 Integrating Land Use & Transportation
Spatial and Socioeconomic Analysis of Commuting Patterns in Southern California Using LODES, CTPP, and ACS PUMS
 Spatial and Socioeconomic Analysis of Commuting Patterns in Southern California Using LODES, CTPP, and ACS PUMS Census for Transportation Planning Subcommittee meeting TRB 95th Annual Meeting January 11,
Spatial and Socioeconomic Analysis of Commuting Patterns in Southern California Using LODES, CTPP, and ACS PUMS Census for Transportation Planning Subcommittee meeting TRB 95th Annual Meeting January 11,
FHWA GIS Outreach Activities. Loveland, Colorado April 17, 2012
 FHWA GIS Outreach Activities Loveland, Colorado April 17, 2012 GIS for Improved Decision Making FHWA believes that geographic information systems and other geospatial technologies (remote sensing and GPS)
FHWA GIS Outreach Activities Loveland, Colorado April 17, 2012 GIS for Improved Decision Making FHWA believes that geographic information systems and other geospatial technologies (remote sensing and GPS)
Forecasts from the Strategy Planning Model
 Forecasts from the Strategy Planning Model Appendix A A12.1 As reported in Chapter 4, we used the Greater Manchester Strategy Planning Model (SPM) to test our long-term transport strategy. A12.2 The origins
Forecasts from the Strategy Planning Model Appendix A A12.1 As reported in Chapter 4, we used the Greater Manchester Strategy Planning Model (SPM) to test our long-term transport strategy. A12.2 The origins
An online data and consulting resource of THE UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO THE JACK FORD URBAN AFFAIRS CENTER
 An online data and consulting resource of THE JACK FORD URBAN AFFAIRS CENTER THE CENTER FOR GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SCIENCE AND APPLIED GEOGRAPHICS DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY AND PLANNING THE UNIVERSITY OF
An online data and consulting resource of THE JACK FORD URBAN AFFAIRS CENTER THE CENTER FOR GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SCIENCE AND APPLIED GEOGRAPHICS DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY AND PLANNING THE UNIVERSITY OF
A Micro-Analysis of Accessibility and Travel Behavior of a Small Sized Indian City: A Case Study of Agartala
 A Micro-Analysis of Accessibility and Travel Behavior of a Small Sized Indian City: A Case Study of Agartala Moumita Saha #1, ParthaPratim Sarkar #2,Joyanta Pal #3 #1 Ex-Post graduate student, Department
A Micro-Analysis of Accessibility and Travel Behavior of a Small Sized Indian City: A Case Study of Agartala Moumita Saha #1, ParthaPratim Sarkar #2,Joyanta Pal #3 #1 Ex-Post graduate student, Department
We Can Get There From Here: New Perspectives on Transportation Equity
 We Can Get There From Here: New Perspectives on Transportation Equity SEPTEMBER 2016 A White Paper from the National Center for Sustainable Transportation Alex Karner, Georgia Institute of Technology Dana
We Can Get There From Here: New Perspectives on Transportation Equity SEPTEMBER 2016 A White Paper from the National Center for Sustainable Transportation Alex Karner, Georgia Institute of Technology Dana
Applying Health Outcome Data to Improve Health Equity
 Applying Health Outcome Data to Improve Health Equity Devon Williford, MPH, Health GIS Specialist Lorraine Dixon-Jones, Policy Analyst CDPHE Health Equity and Environmental Justice Collaborative Mile High
Applying Health Outcome Data to Improve Health Equity Devon Williford, MPH, Health GIS Specialist Lorraine Dixon-Jones, Policy Analyst CDPHE Health Equity and Environmental Justice Collaborative Mile High
Alternatives Analysis
 Alternatives Analysis Prepared for: Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority Prepared by: AECOM/Jacobs-JJG Joint Venture Atlanta, GA November 2012 Page Left Intentionally Blank ii TABLE OF CONTENTS
Alternatives Analysis Prepared for: Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority Prepared by: AECOM/Jacobs-JJG Joint Venture Atlanta, GA November 2012 Page Left Intentionally Blank ii TABLE OF CONTENTS
OREGON POPULATION FORECAST PROGRAM
 OREGON POPULATION FORECAST PROGRAM PROGRAM OVERVIEW BACKGROUND Beginning in 1973 with the passage of Senate Bill (SB) 100, Oregon s growth management system has relied on population forecasts as the primary
OREGON POPULATION FORECAST PROGRAM PROGRAM OVERVIEW BACKGROUND Beginning in 1973 with the passage of Senate Bill (SB) 100, Oregon s growth management system has relied on population forecasts as the primary
November 29, World Urban Forum 6. Prosperity of Cities: Balancing Ecology, Economy and Equity. Concept Note
 November 29, 2010 World Urban Forum 6 Prosperity of Cities: Balancing Ecology, Economy and Equity Concept Note 1 CONTENT Thematic Continuity Conceptualizing the Theme The 6 Domains of Prosperity The WUF
November 29, 2010 World Urban Forum 6 Prosperity of Cities: Balancing Ecology, Economy and Equity Concept Note 1 CONTENT Thematic Continuity Conceptualizing the Theme The 6 Domains of Prosperity The WUF
Rural Pennsylvania: Where Is It Anyway? A Compendium of the Definitions of Rural and Rationale for Their Use
 Rural Pennsylvania: Where Is It Anyway? A Compendium of the Definitions of Rural and Rationale for Their Use Pennsylvania Office of Rural Health 310 Nursing Sciences Building University Park, PA 16802
Rural Pennsylvania: Where Is It Anyway? A Compendium of the Definitions of Rural and Rationale for Their Use Pennsylvania Office of Rural Health 310 Nursing Sciences Building University Park, PA 16802
Measuring Disaster Risk for Urban areas in Asia-Pacific
 Measuring Disaster Risk for Urban areas in Asia-Pacific Acknowledgement: Trevor Clifford, Intl Consultant 1 SDG 11 Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable 11.1: By
Measuring Disaster Risk for Urban areas in Asia-Pacific Acknowledgement: Trevor Clifford, Intl Consultant 1 SDG 11 Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable 11.1: By
Cipra D. Revised Submittal 1
 Cipra D. Revised Submittal 1 Enhancing MPO Travel Models with Statewide Model Inputs: An Application from Wisconsin David Cipra, PhD * Wisconsin Department of Transportation PO Box 7913 Madison, Wisconsin
Cipra D. Revised Submittal 1 Enhancing MPO Travel Models with Statewide Model Inputs: An Application from Wisconsin David Cipra, PhD * Wisconsin Department of Transportation PO Box 7913 Madison, Wisconsin
Sustainable tourism in for Sustaibale Danang
 Sustainable tourism in for Sustaibale Danang A case study of Balearic Ecotax in Spain toward Sustainable tourism Miki Yoshizumi Associate Professor College of Gastronomy Management Ritsumeikan University
Sustainable tourism in for Sustaibale Danang A case study of Balearic Ecotax in Spain toward Sustainable tourism Miki Yoshizumi Associate Professor College of Gastronomy Management Ritsumeikan University
How GIS based Visualizations Support Land Use and Transportation Modeling
 How GIS based Visualizations Support Land Use and Transportation Modeling ESRI International Users Conference San Diego, CA - July 23, 2015 Prepared by: Troy Hightower Introduction This presentation will
How GIS based Visualizations Support Land Use and Transportation Modeling ESRI International Users Conference San Diego, CA - July 23, 2015 Prepared by: Troy Hightower Introduction This presentation will
Spatiotemporal Analysis of Commuting Patterns in Southern California Using ACS PUMS, CTPP and LODES
 Spatiotemporal Analysis of Commuting Patterns in Southern California Using ACS PUMS, CTPP and LODES 2017 ACS Data Users Conference May 11-12, 2017 Alexandria, VA Jung Seo, Tom Vo, Frank Wen and Simon Choi
Spatiotemporal Analysis of Commuting Patterns in Southern California Using ACS PUMS, CTPP and LODES 2017 ACS Data Users Conference May 11-12, 2017 Alexandria, VA Jung Seo, Tom Vo, Frank Wen and Simon Choi
Cultural Data in Planning and Economic Development. Chris Dwyer, RMC Research Sponsor: Rockefeller Foundation
 Cultural Data in Planning and Economic Development Chris Dwyer, RMC Research Sponsor: Rockefeller Foundation A Decade of Attempts to Quantify Arts and Culture Economic impact studies Community indicators
Cultural Data in Planning and Economic Development Chris Dwyer, RMC Research Sponsor: Rockefeller Foundation A Decade of Attempts to Quantify Arts and Culture Economic impact studies Community indicators
Figure 8.2a Variation of suburban character, transit access and pedestrian accessibility by TAZ label in the study area
 Figure 8.2a Variation of suburban character, transit access and pedestrian accessibility by TAZ label in the study area Figure 8.2b Variation of suburban character, commercial residential balance and mix
Figure 8.2a Variation of suburban character, transit access and pedestrian accessibility by TAZ label in the study area Figure 8.2b Variation of suburban character, commercial residential balance and mix
Transit Time Shed Analyzing Accessibility to Employment and Services
 Transit Time Shed Analyzing Accessibility to Employment and Services presented by Ammar Naji, Liz Thompson and Abdulnaser Arafat Shimberg Center for Housing Studies at the University of Florida www.shimberg.ufl.edu
Transit Time Shed Analyzing Accessibility to Employment and Services presented by Ammar Naji, Liz Thompson and Abdulnaser Arafat Shimberg Center for Housing Studies at the University of Florida www.shimberg.ufl.edu
J^tatldhcA. (Hnmmnnw?aii1j of ilaaaarijubrtta PAUL GUZZI COMPILED IN THE OFFICE OF (TERCENTENARY EDITION) CHAPTER 54, SECTION 133 GOVERNMENT DOCUMENTS
 Public Document No 3 C^lecLion GOVERNMENT DOCUMENTS DEPARTMENT PUBLIC LIBRARY J^tatldhcA (Hnmmnnw?aii1j of ilaaaarijubrtta 19 IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE PROVISIONS OF GENERAL LAWS (TERCENTENARY EDITION) CHAPTER,
Public Document No 3 C^lecLion GOVERNMENT DOCUMENTS DEPARTMENT PUBLIC LIBRARY J^tatldhcA (Hnmmnnw?aii1j of ilaaaarijubrtta 19 IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE PROVISIONS OF GENERAL LAWS (TERCENTENARY EDITION) CHAPTER,
Transforming Geospatial Data for Visualization with D3
 Transforming Geospatial Data for Visualization with D3 FOSS4G Boston August 17, 2017 Beatrice Jin and Benjamin Krepp Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization Agenda Who we are Project context Implementation
Transforming Geospatial Data for Visualization with D3 FOSS4G Boston August 17, 2017 Beatrice Jin and Benjamin Krepp Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization Agenda Who we are Project context Implementation
BIG IDEAS. Area of Learning: SOCIAL STUDIES Urban Studies Grade 12. Learning Standards. Curricular Competencies
 Area of Learning: SOCIAL STUDIES Urban Studies Grade 12 BIG IDEAS Urbanization is a critical force that shapes both human life and the planet. The historical development of cities has been shaped by geographic,
Area of Learning: SOCIAL STUDIES Urban Studies Grade 12 BIG IDEAS Urbanization is a critical force that shapes both human life and the planet. The historical development of cities has been shaped by geographic,
Advancing Urban Models in the 21 st Century. Jeff Tayman Lecturer, Dept. of Economics University of California, San Diego
 Advancing Urban Models in the 21 st Century Jeff Tayman Lecturer, Dept. of Economics University of California, San Diego 1 Regional Decision System Better tools Better data Better access Better Decisions
Advancing Urban Models in the 21 st Century Jeff Tayman Lecturer, Dept. of Economics University of California, San Diego 1 Regional Decision System Better tools Better data Better access Better Decisions
April 18, Accessibility and Smart Scale: Using Access Scores to Prioritize Projects
 Accessibility and Smart Scale: Using Access Scores to Prioritize Projects April 18, 2017 Accessibility and Smart Scale: Using Access Scores to Prioritize Projects State Smart Transportation Initiative
Accessibility and Smart Scale: Using Access Scores to Prioritize Projects April 18, 2017 Accessibility and Smart Scale: Using Access Scores to Prioritize Projects State Smart Transportation Initiative
Local Area Key Issues Paper No. 13: Southern Hinterland townships growth opportunities
 Draft Sunshine Coast Planning Scheme Review of Submissions Local Area Key Issues Paper No. 13: Southern Hinterland townships growth opportunities Key Issue: Growth opportunities for Southern Hinterland
Draft Sunshine Coast Planning Scheme Review of Submissions Local Area Key Issues Paper No. 13: Southern Hinterland townships growth opportunities Key Issue: Growth opportunities for Southern Hinterland
PlaceTypes. How the built environment is measured. Variables Measures Levels. AREA TYPE + DEVELOPMENT TYPE = PlaceType
 PlaceTypes In order to better understand land use and transportation interactions and to make more informed policy decisions, neighborhood characteristics can be analyzed by the role that they play in
PlaceTypes In order to better understand land use and transportation interactions and to make more informed policy decisions, neighborhood characteristics can be analyzed by the role that they play in

