Analysis of Relative Importance of Parameters Representing Vegetation, Urbanization and Elevation with Land Surface Temperature using ANN
|
|
|
- Carmella Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Analysis of Relative Importance of Parameters Representing Vegetation, Urbanization and Elevation with Land Surface Temperature using ANN Goyal, Rohit 1, Khandelwal, Sumit 2 and Kaul, Nivedita 2 ABSTRACT Land surface temperature (LST) is a very important physical parameter of the Earth s surface, which depends on a number of parameters including vegetation cover, vegetation type, land use, land cover, percent impervious surface area, elevation, road density (RD) etc. (Yuan & Bauer, 2007; Khandelwal & Goyal, 2010). However the influence of various parameters on LST has not been studied quantatively, which is very important as maximum studies on LST dynamics have compared the relationship of LST with individual parameters and simultaneous effect of number of parameters on LST variations has not been studied. This paper studies the relative importance of parameters representing vegetation (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index, NDVI), urbanization (RD) and surface feature (elevation). Artificial neural network (ANN) technique has been used for the analysis. Analysis has been carried out for three seasons of summer, monsoon and winter seasons for area surrounding Jaipur city study area. Aqua/MODIS and ASTER data for the year 2008 has been used for the study. It is found that of all the parameters studied, NDVI has maximum significance on LST, followed by RD and elevation. 1. Introduction High paced development has taken place during last few decades which has resulted into movement of population from rural to urban areas. This movement has caused large scale urbanization all around the world. Most common visible aspect of urbanization is that the natural landscape having predominantly vegetation cover and pervious areas is converted into built up and impervious area. The impervious area is largely contributed by use of materials like concrete, bricks, tiles etc for buildings and bitumen etc. for roads and parking lots. The introduction of new surface materials coupled with emission of heat, moisture and pollutants change radiative, thermal, moisture, roughness and emission properties of the surface and the atmosphere above (Roth, 2002). In addition, urbanization also causes generation of large amount of heat by vehicular traffic, industries and domestic buildings which also cause increase in local air and surface temperatures. Surface and atmospheric modifications due to urbanization generally lead to a modified thermal climate that causes local air and surface temperatures to rise several degrees higher than the simultaneous temperatures of the surrounding rural areas and this phenomenon is referred as Urban Heat Island, UHI. (Streutker 2003). Heat islands have been * Corresponding author: rgoyal_jp@yahoo.com 1 Professor, Malaviya National Institute of Technology, Jaipur 2 Assistant Professor, Malaviya National Institute of Technology, Jaipur
2 defined as canopy layer urban heat island (CLUHI) when variations in air temperatures are studied and surface urban heat island (SUHI) for variations in surface temperatures (Voogt and Oke, 2003). The study of SUHI has been largely dependent on remote sensing data and land surface temperature (LST) derived from the satellite data is used for that purpose. Satellite derived LST has been used in many studies and one of the important advantages of remote sensing data is higher spatial resolution of such data thus enabling study of very large area (Zhangyan et. al., 2006, Jusuf et. al., 2007, Yuan and Bauer, 2007, Liang and Weng, 2008, Parida et. al., 2008, Cheval and Dumitrescu, 2009). Land surface temperature (LST) is defined as the skin temperature of ground. It indicates soil surface temperature for bare soil. LST can be viewed as the canopy surface temperature of the vegetation for dense vegetated ground and for sparse vegetated ground, it is determined by the temperature of the vegetation canopy, vegetation body and soil surface (Qin and Karnieli, 1999). Due to modifications of the land use and land cover due to urbanization there is change in the surface of ground as well as vegetation which are replaced by buildings of varying heights and surfaces of varying properties and consequently there will be changes in the contributors of the surface temperatures as defined above. A number of studies have been conducted to study the LST dynamics with one or more of the land surface characteristics or parameter measuring extent of urbanization. In various studies vegetation cover has been expressed either as NDVI or as vegetation patches or as vegetation fraction. Similarly parameters such as percent impervious surface area (%ISA) or land use or normalized difference built-up index (NDBI) have been used to quantify the extent of urbanization. In most of the studies negative correlation has been reported between LST and vegetation (Yuan and Bauer, 2007; Liang and Qihao, 2008; Weng at al., 2004; Zhang et al., 2009; Pu et al., 2006). Quality of vegetation cover is dependent on availability of water and the density of vegetation cover is typically found, in increasing order, for agriculture in desert areas, rainfed agriculture, irrigated agriculture and forest. The land surface temperature of these categories of vegetation has been reported to be in falling order from agriculture in desert area to forest (Parida et al., 2008). Khandelwal and Goyal (2010) studied the variations in LST due to the change in elevation derived from ASTER global digital elevation model (GDEM) and concluded inverse relationship between LST and elevation for study area surrounding Jaipur city. The effect of urbanization has long been studied and its effects have been reported on stream habitat, temperature and environment, soils, groundwater and even dietary habits (Wang et al., 2001; Baker et al., 2002; Marcotullio et al., 2008; Naik et al., 2008; Lazarou & Kalavana, 2009). A number of studies have reported positive relationship between LST and indicators representing urbanization such as %ISA, NDBI, land use. While these indicators incorporate the surface property only, Khandelwal and Goyal (2010) suggested road density (RD) as a parameter which incorporates the primary effect of the changes in surface properties as well as the secondary effects due to vehicular, industrial and other pollution and concluded that a strong positive relationship exists between RD and LST for all the study seasons. Most of the studies conducted on LST dynamics have studied the variations in LST over variation of one or other parameters and the correlations thus found have been compared to
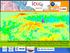
3 suggest the suitability of various indicators. However the relative weightage of these parameters on LST is not reported. The objective of the present research are to analyse the relative weightages of elevation, NDVI and RD for LST variations over study area surrounding Jaipur city. These can be utilized for developing model for predicting the surface temperature of a particular area for given values of other parameters. 2. Methods and Results 2.1 Study Area The study area chosen is Jaipur city, the capital of the state of Rajasthan, India. The city is located on a predominantly flat plain and is surrounded by hills on the north, north-east and east sides. Due to the hills, the development of the city has been more along south and west. The part of city closer to the hills is characterized by mostly built-up and paved areas having very less vegetation cover. Rest of the city has a mixture of barren land, low to medium height vegetation and built-up areas in form of buildings, roads, industries etc. The climate of the city is arid with high temperatures during summers and low temperatures during winter nights. Figure 1 shows the study area for the present study in which MODIS yearly land cover dynamics of 2008 was used to extract the urban boundary of Jaipur city. The Jaipur urban area polygon from land cover dynamics image was automatically converted by using Raster to Polygon conversion tool. A preliminary analysis indicated that a buffer of 12 km is sufficient to include rural belt outside the city area and therefore Buffer tool with 12 km distance outside the urban boundary was used to mark the boundary of study area as shown in fig. 1.
4 Fig. 1: Study Area 2.2 Remote Sensing Data In addition to the land cover dynamics product of MODIS, several other remote sensing data products, as given in table 1, were used. The study area has mainly three seasons and the study has been carried out for all three seasons namely summer, monsoon and winter season.
5 Table 1: Remote Sensing Data products used for the present study MODIS Product Platform (Sensor) Short Name Cell Size Season Day No. (Period) Land cover Dynamics Combined App. 926 Aqua & Terra MCD12Q2 m (MODIS) All Yearly 001 (00:00:00 hrs on 1 Jan Land Surface Temperature and Emissivity Vegetation Indices Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) Aqua (MODIS) Aqua (MODIS) Terra (ASTER) MYD11A2 MYD13Q1 AST14DEM App. 926 m App. 423 m App. 25 m Winter Summer Monsoon Winter Summer Monsoon to 23:59:59 on 8 Jan) 121 (00:00:00 hrs on 1 May to 23:59:59 on 8 May) 265 (00:00:00 hrs on 22 Sep to 23:59:59 on 29 Sep) 121 (00:00:00 hrs on 1 May to 23:59:59 on 16 May) 265 (00:00:00 hrs on 22 Sep to 23:59:59 on 7 Oct) 361 (00:00:00 hrs on 27 Dec to 23:59:59 on 11 Jan) All - These products were downloaded from Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC) website using NASA Warehouse Inventory Search Tool (WIST). Data for year 2008 has been used for the present study. The data from MODIS sensor is in HDF-EOS format and in Sinusoidal Projection System. MYD11A2 & MYD13Q1 products have 12 Science Data Sets (SDS) layers each and MCD12Q2 has 16 SDS layers. The data was sub-set to the study area and also simultaneously reprojected from Sinusoidal projection to UTM projection system with WGS84 datum (Zone 43N) and was reformatted from HDF-EOS to GeoTiff format using Modis Reprojection Tools (MRT). AST14DEM is available in GeoTIFF format. Single image of ASTER data covers approx. 60km x 60km area and multiple images covering the entire study area were downloaded and mosaic together. The various data layers in GeoTIFF format were then analyzed using ArcGIS software. QC_Night (quality flag for night image) and LST- _Night_1km (Night LST) layers of MYD11A2, 250m_16 days_ndvi and 250m_16_days_VI_Quality (quality flag for vegetation indices) layers of MYD13Q1 and Land_Cover _Type_4_Assesment layer of MCD12Q2 product have been used for the present study. 2.3 Image Processing The MODIS and ASTER products have different spatial resolution and in order to compare them it is necessary to have all of them at same resolution and hence all the products were aggregated to the same resolution as of LST layer. The study area has 1612 pixels of approximately 926 m cell size. The quality flags of MYD11A2 and MYD13Q1 were checked to include only the good quality pixels in the analysis. Those data pixels in which error of the
6 computed LST is less than 1 K have been considered as good quality pixels for LST. Use of quality flag of MYD13Q1 (also known as quality assurance) enables user to remove pixels on the basis of adjacent clouds detected or for which atmosphere bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) correction was not performed, as these may cause error in calculation of NDVI values. The road map of Jaipur city and its surrounding area was prepared by on-screen digitization. The roads were divided into three categories namely, highways and major roads; main roads; secondary roads and streets. These three categories are distinctly visible on Google Earth at different zoom levels. The roads were digitized on screen over the roads visible on Google Earth. The digitized roads were then thoroughly checked for duplication/omission/errors. Total length of roads in the study area is km. The road map has been used to calculate RD value for every cell of the study area. RD has been calculated as line density, which is magnitude per unit area of the road features that fall within a fixed radius around each cell. For the present study this radius has been taken as 655 m, which is the radius of a circle inscribing one complete cell and hence the cell size of RD map has been kept same as that of other parameters. Figure 2 shows the road density map of the study area. The value of RD varies from zero to 27.8 km per square km. 2.4 Artificial Neural Network Fig. 2: Road Density Map of Study Area A neural network, also called a multilayer perceptron, is a simplified model that works by simulating a large number of interconnected neurons. There are typically three parts in a neural network: an input layer, with units representing the input fields; one or more hidden layers; and
7 an output layer, with a unit(s) representing the output field(s). Fig. 3 shows the structure of the neural network. The units are connected with varying connection weights. Input data are presented to the first layer, and values are propagated from each neuron to every neuron in the next layer. Eventually, a result is delivered from the output layer. The network learns by examining individual records, generating a prediction for each record, and making adjustments to the weights whenever it makes an incorrect prediction. This process is repeated many times, and the network continues to improve its predictions until one or more of the stopping criteria have been met. Initially, all weights are random, and the answers that come out of the net are probably nonsensical. The network learns through training. Examples for which the output is known are repeatedly presented to the network, and the answers it gives are compared to the known outcomes. Information from this comparison is passed back through the network, gradually changing the weights. As training progresses, the network becomes increasingly accurate in replicating the known outcomes. Once trained, the network can be applied to future cases where the outcome is unknown. Fig. 3: Structure of Neural Network In the present work a three layered neural network is developed with one input layer containing three neurons, on each for NDVI, road density and elevation values; one hidden layer of three neurons and one output layer of single neuron representing LST. 50% of the sample was used for training of the neuron network, based on which connection weights are determined. The model determines relative importance of the three input parameters and the same has been given in table 2. Table 2: Relative importance of input parameters Input Parameters Relative Importance Value as per ANN Model Remark NDVI 0.49 Highest RD Elevation 0.31 Lowest
8 This can be seen from table 2 that NDVI, which is an indicator of vegetation, is the most significant parameter affecting LST dynamics and as negative relationship exists between LST and NDVI. Though the relative significance of NDVI is high, significance of RD and Elevation is also high. Elevation is slightly less significant as compared to RD. 3. Conclusions This paper studies the relative importance of three different parameters namely NDVI (representing vegetation), RD (representing urbanization) and Elevation (surface physical property) for LST dynamics. NDVI is found to be most significant among the three parameters thus establishing that the variations in LST can be attributed to change in vegetation level. However the significance of other parameters is also comparable thus suggesting that any study of LST dynamics should be carried out using multi parametric approach. 4. References 1. Baker, L. A., Brazel, A. J., Selover, N., Martin, C., McIntyre, N., Steiner, F. R., Nelson, A., & Musacchio, L. (2002). Urbanization and warming of Phoenix (Arizona, USA): Impacts, feedbacks and mitigation. Urban Ecosystems, 6(3), Cheval, S., & Dumitrescu, A. (2009). The July urban heat island of Bucharest as derived from MODIS images. Theoretical and Applied Climatology 96, Jusuf, S.K., Wong, N.H., Hagen, E., Anggoro, R., & Hong, Y. (2007). The influence of land use on the urban heat island in Singapore, Habitat International 31, Khandelwal, S. & Goyal, R. (2010). Assessment of land surface temperature relationship with MODIS vegetation indices and road density for urban heat island analysis, Submitted to Remote Sensing of Environment for publication. 5. Khandelwal, S. & Goyal, R. (2010). Assessment of land surface temperature-elevation relationship using satellite data of area surrounding Jaipur, India, Submitted to International Journal of Remote Sensing for publication. 6. Lazarou, C., & Kalavana, T. (2009). Urbanization influences dietary habits of Cypriot children: the CYKIDS study. International Journal of Public Health, 54(2), Liang, B., & Weng, Q. (2008). Multiscale Analysis of Census-Based Land Surface Temperature Variations and Determinants in Indianapolis, United States. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 134(3), Marcotullio, P. J., Braimoh, A. K., & Onishi, T. (2008). The Impact of Urbanization on Soils. In Braimoh, A. K., Vlek, P. L. G. (Eds.), Land Use and Soil Resources (pp ). Netherlands: Springer. 9. Naik, P. K., Tambe, J. A., Dehury, B. N., & Tiwari, A. N. (2008). Impact of urbanization on the groundwater regime in a fast growing city in central India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 146(1-3),
9 10. Parida, B.R., Oinam, B., Patel, N.R., Sharma, N., Kandwal, R., & Hazarika, M.K., 2008, Land surface temperature variation in relation to vegetation type using MODIS satellite data in Gujarat state of India. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 29, pp Pu, R., Gong, P., Michishita, R., & Sasagawa, T. (2006). Assessment of multi-resolution and multi-sensor data for urban surface temperature retrieval. Remote Sensing of Environment, 104, Qin, Z. & Karnieli, A., 1999, Progress in the remote sensing of land surface temperature and ground emissivity using NOAA-AVHRR data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 20, pp Roth, M. (2002). Effects of cities on local climates. In: Proceedings of Workshop of Institute for Global Environment Studies/ Asia-Pacific Network (IGES/APN) Mega-city Project, January 23-25, Kitakyushu, Japan, 13 pp (invited paper). 14. Streutker, D.R. (2002). A remote sensing study of the urban heat island of Houston, Texas. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 23(13), Voogt, J.A., & Oke, T.R. (2003). Thermal remote sensing of urban climates. Remote Sensing of the Environment, 86, Wang, L., Lyons, J., Kanehl, P., & Bannerman, R. (2001). Impacts of urbanization on stream habitat and fish across multiple spatial scales, Environmental Management, 28(2), Weng, Q., Lu, D., & Schubring, J. (2004). Estimation of land surface temperaturevegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sensing of Environment, 89, Yuan, F., & Bauer, M.E. (2007). Comparison of impervious surface area and normalized difference vegetation index as indicators of surface urban heat island effects in Landsat imagery, Remote Sensing of Environment 106, Zhang, X., Zhong, T., Feng, X., & Wang, K.E. (2009). Estimation of the relationship between vegetation patches and urban land surface temperature with remote sensing. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 30(8), Zhangyan, J., Yunhao, C., & Jing, L. (2006). On urban heat island of Beijing based on Landsat TM data. Geo-spatial Information 9(4),
10 Author s Information Paper Reference No.: PN 368 Title of the paper : Analysis of Relative Importance of Parameters Representing Vegetation, Urbanization and Elevation with Land Surface Temperature using ANN Name of the Presenter : Dr. Rohit Goyal Author (s) Affiliation : Professor, Department of Civil Engg., Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India Mailing Address : Department of Civil Engg., Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur, JLN Marg, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India Address : rgoyal_jp@yahoo.com Telephone number (s) : (O), (M) Fax number (s) : Author(s) Photograph: Brief Biography (100 words): Prof. Goyal completed his Doctoral Research from University of Roorkee, India in He has also done Post Graduate Diploma in Remote Sensing Applications in Water Resources from IIRS, Dehradun. He has undertaken five research projects from MHRD, AICTE and DST. He is member of a number of international and national societies including Indian Society of Geomatics, The Institution of Engineers, Indian Society of Remote Sensing etc. He has published 12 papers in Refereed Journals, about 50 papers in Conferences/Seminars. He has also authored 2 Technical Reports, 1 Edited Book and five Chapter of edited Books. He has organized a number of national conferences, short term training programmes including HYDRO 2008.
Study of Land Surface Temperature Variations with Distance from Hot Spots for Urban Heat Island Analysis
 Study of Land Surface Temperature Variations with Distance from Hot Spots for Urban Heat Island Analysis Khandelwal, Sumit 1*, Goyal, Rohit 2, Kaul, Nivedita 1 and Singhal, Vijai 3 ABSTRACT Vegetation
Study of Land Surface Temperature Variations with Distance from Hot Spots for Urban Heat Island Analysis Khandelwal, Sumit 1*, Goyal, Rohit 2, Kaul, Nivedita 1 and Singhal, Vijai 3 ABSTRACT Vegetation
Study of Urban heat Island Effect on Ahmedabad City and Its Relationship with Urbanization and Vegetation Parameters
 Study of Urban heat Island Effect on Ahmedabad City and Its Relationship with Urbanization and Vegetation Parameters Aneesh Mathew a,*, Rishabh Chaudhary a, Neha Gupta a, a Research Scholar, Department
Study of Urban heat Island Effect on Ahmedabad City and Its Relationship with Urbanization and Vegetation Parameters Aneesh Mathew a,*, Rishabh Chaudhary a, Neha Gupta a, a Research Scholar, Department
Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island
 Chuanxin Zhu Professor Peter V. August Professor Yeqiao Wang NRS 509 December 15, 2016 Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island Since the last century, the global mean surface
Chuanxin Zhu Professor Peter V. August Professor Yeqiao Wang NRS 509 December 15, 2016 Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island Since the last century, the global mean surface
Mario Flores, Graduate Student Department of Applied Mathematics, UTSA. EES 5053: Remote Sensing
 Mario Flores, Graduate Student Department of Applied Mathematics, UTSA Miguel Balderas, E.I.T., Graduate Student Department of Civil/Environmental Engineering, UTSA EES 5053: Remote Sensing REMOTE SENSING
Mario Flores, Graduate Student Department of Applied Mathematics, UTSA Miguel Balderas, E.I.T., Graduate Student Department of Civil/Environmental Engineering, UTSA EES 5053: Remote Sensing REMOTE SENSING
Critical review of the Climate Change Impact on urban areas by assessment of Heat Island effect
 Critical review of the Climate Change Impact on urban areas by assessment of Heat Island effect Case of Pune, India Town Planning, Civil Department Prof. Omkar Parishwad, ogp.civil@coep.ac.in Climate Change
Critical review of the Climate Change Impact on urban areas by assessment of Heat Island effect Case of Pune, India Town Planning, Civil Department Prof. Omkar Parishwad, ogp.civil@coep.ac.in Climate Change
MODIS-BASED INVESTIGATIONS ON THE URBAN HEAT ISLANDS OF BUCHAREST (ROMANIA) AND PRAGUE (CZECH REPUBLIC)
 MODIS-BASED INVESTIGATIONS ON THE URBAN HEAT ISLANDS OF BUCHAREST (ROMANIA) AND PRAGUE (CZECH REPUBLIC) Sorin Cheval*, Michal Žák***, Alexandru Dumitrescu*, Vít Květoň** *National Meteorological Administration,
MODIS-BASED INVESTIGATIONS ON THE URBAN HEAT ISLANDS OF BUCHAREST (ROMANIA) AND PRAGUE (CZECH REPUBLIC) Sorin Cheval*, Michal Žák***, Alexandru Dumitrescu*, Vít Květoň** *National Meteorological Administration,
Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity
 Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity Isabel C. Perez Hoyos NOAA Crest, City College of New York, CUNY, 160 Convent Avenue,
Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity Isabel C. Perez Hoyos NOAA Crest, City College of New York, CUNY, 160 Convent Avenue,
COMPARASION OF NDBI AND NDVI AS INDICATORS OF SURFACE URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT IN LANDSAT 8 IMAGERY: A CASE STUDY OF IASI
 DOI 10.1515/pesd-2017-0032 PESD, VOL. 11, no. 2, 2017 COMPARASION OF NDBI AND NDVI AS INDICATORS OF SURFACE URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT IN LANDSAT 8 IMAGERY: A CASE STUDY OF IASI Paul Macarof 1, Florian Statescu
DOI 10.1515/pesd-2017-0032 PESD, VOL. 11, no. 2, 2017 COMPARASION OF NDBI AND NDVI AS INDICATORS OF SURFACE URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT IN LANDSAT 8 IMAGERY: A CASE STUDY OF IASI Paul Macarof 1, Florian Statescu
dated : 1 July Introduction
 Analysis of the impact of different temporal aggregation techniques of land surface temperature on SUHI indicators and the relationship of surface temperature with population density and night lighting
Analysis of the impact of different temporal aggregation techniques of land surface temperature on SUHI indicators and the relationship of surface temperature with population density and night lighting
Abstract: Introduction: 10 th ESRI India User Conference 2009 Geography in Action
 Mitigation of Thermal Pollution to enhance urban air quality through Remote Sensing and GIS Anshu Gupta, Lecturer, Centre of Remote Sensing and GIS, MANIT, Bhopal, E- mail: anshugupta20002001@gmail.com
Mitigation of Thermal Pollution to enhance urban air quality through Remote Sensing and GIS Anshu Gupta, Lecturer, Centre of Remote Sensing and GIS, MANIT, Bhopal, E- mail: anshugupta20002001@gmail.com
Remote sensing Based Assessment of Urban Heat Island Phenomenon in Nagpur Metropolitan Area
 International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 11 (2014), pp. 1069-1074 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com Remote sensing
International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 11 (2014), pp. 1069-1074 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com Remote sensing
Lech GAWUC, Joanna STRUZEWSKA. Meteorology Division Faculty of Environmental Engineering Warsaw University of Technology Warsaw, Poland
 Analysis of the impact of different temporal aggregation techniques of land surface temperature on SUHI indicators and the relationship of surface temperature with population density and night lighting
Analysis of the impact of different temporal aggregation techniques of land surface temperature on SUHI indicators and the relationship of surface temperature with population density and night lighting
Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite Multitemporal Data over Abeokuta, Nigeria
 International Atmospheric Sciences Volume 2016, Article ID 3170789, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3170789 Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite
International Atmospheric Sciences Volume 2016, Article ID 3170789, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3170789 Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite
1. Introduction. Chaithanya, V.V. 1, Binoy, B.V. 2, Vinod, T.R. 2. Publication Date: 8 April DOI: https://doi.org/ /cloud.ijarsg.
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2017, Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 2088-2096 ISSN 2320 0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.112 Research Article Open Access Estimation
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2017, Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 2088-2096 ISSN 2320 0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.112 Research Article Open Access Estimation
Remote Sensing Based Inversion of Gap Fraction for Determination of Leaf Area Index. Alemu Gonsamo 1 and Petri Pellikka 1
 Remote Sensing Based Inversion of Gap Fraction for Determination of Leaf Area Index Alemu Gonsamo and Petri Pellikka Department of Geography, University of Helsinki, P.O. Box, FIN- Helsinki, Finland; +-()--;
Remote Sensing Based Inversion of Gap Fraction for Determination of Leaf Area Index Alemu Gonsamo and Petri Pellikka Department of Geography, University of Helsinki, P.O. Box, FIN- Helsinki, Finland; +-()--;
CORRELATION BETWEEN URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT AND THE THERMAL INERTIA USING ASTER DATA IN BEIJING, CHINA
 CORRELATION BETWEEN URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT AND THE THERMAL INERTIA USING ASTER DATA IN BEIJING, CHINA Yurong CHEN a, *, Mingyi DU a, Rentao DONG b a School of Geomatics and Urban Information, Beijing
CORRELATION BETWEEN URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT AND THE THERMAL INERTIA USING ASTER DATA IN BEIJING, CHINA Yurong CHEN a, *, Mingyi DU a, Rentao DONG b a School of Geomatics and Urban Information, Beijing
GIS.
 GIS 389 Vol., No.3, Autumn 00 89-0 GIS Iranian Remote Sensing & GIS ( : ) ETM+ *.. 390/3/7 : 389/5/3 : (LST).. 00 3 ETM+.. MNF NDVI. SEBAL. FVC NDVI... (FVC) SEBAL (LULC) (LST) :. 887708 : : * Email: taleai@kntu.ac.ir
GIS 389 Vol., No.3, Autumn 00 89-0 GIS Iranian Remote Sensing & GIS ( : ) ETM+ *.. 390/3/7 : 389/5/3 : (LST).. 00 3 ETM+.. MNF NDVI. SEBAL. FVC NDVI... (FVC) SEBAL (LULC) (LST) :. 887708 : : * Email: taleai@kntu.ac.ir
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December-2013 ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December-2013 144 Assessment of Seasonal Variation of Land Surface Temperature (LST) in an Urban Area Arun Mondal1, Deepak
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December-2013 144 Assessment of Seasonal Variation of Land Surface Temperature (LST) in an Urban Area Arun Mondal1, Deepak
Comparison of MSG-SEVIRI and SPOT-VEGETATION data for vegetation monitoring over Africa
 Comparison of MSG-SEVIRI and SPOT-VEGETATION data for vegetation monitoring over Africa Bernard LACAZE CNRS UMR 8586 PRODIG Pôle Image et Campus Spatial, Université Paris Diderot Paris 7 Objectives Comparison
Comparison of MSG-SEVIRI and SPOT-VEGETATION data for vegetation monitoring over Africa Bernard LACAZE CNRS UMR 8586 PRODIG Pôle Image et Campus Spatial, Université Paris Diderot Paris 7 Objectives Comparison
ANALYSIS OF VEGETATION DISTRIBUTION IN URBAN AREAS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS APPROACH ON A REGIONAL SCALE
 ANALYSIS OF VEGETATION DISTRIBUTION IN URBAN AREAS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS APPROACH ON A REGIONAL SCALE Kiichiro Kumagai Department of Civil and Environmental System Engineering, Setsunan University 17-8 Ikedanakamachi,
ANALYSIS OF VEGETATION DISTRIBUTION IN URBAN AREAS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS APPROACH ON A REGIONAL SCALE Kiichiro Kumagai Department of Civil and Environmental System Engineering, Setsunan University 17-8 Ikedanakamachi,
Seasonal and interannual relations between precipitation, soil moisture and vegetation in the North American monsoon region
 Seasonal and interannual relations between precipitation, soil moisture and vegetation in the North American monsoon region Luis A. Mendez-Barroso 1, Enrique R. Vivoni 1, Christopher J. Watts 2 and Julio
Seasonal and interannual relations between precipitation, soil moisture and vegetation in the North American monsoon region Luis A. Mendez-Barroso 1, Enrique R. Vivoni 1, Christopher J. Watts 2 and Julio
THE USE OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES FOR URBAN CLIMATE ANALYSIS: A CASE STUDY OF ABU DHABI CITY AREA
 THE USE OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES FOR URBAN CLIMATE ANALYSIS: A CASE STUDY OF ABU DHABI CITY AREA Michele Lazzarini, Jacinto Estima, Prashanth Reddy Marpu, Hosni Ghedira Earth Observation
THE USE OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES FOR URBAN CLIMATE ANALYSIS: A CASE STUDY OF ABU DHABI CITY AREA Michele Lazzarini, Jacinto Estima, Prashanth Reddy Marpu, Hosni Ghedira Earth Observation
Instruction: proposal to class project
 Instruction: proposal to class project (Hongjie Xie, 10/20/2008) A project proposal is the first step to us to get funding from anywhere. You need to write a proposal to your advisor, your university,
Instruction: proposal to class project (Hongjie Xie, 10/20/2008) A project proposal is the first step to us to get funding from anywhere. You need to write a proposal to your advisor, your university,
Observing land from space: Interacting with land data from NASA s LP DAAC
 Observing land from space: Interacting with land data from NASA s LP DAAC Danielle Golon Innovate! Inc., contractor to the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center
Observing land from space: Interacting with land data from NASA s LP DAAC Danielle Golon Innovate! Inc., contractor to the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center
MAPPING LAND USE/ LAND COVER OF WEST GODAVARI DISTRICT USING NDVI TECHNIQUES AND GIS Anusha. B 1, Sridhar. P 2
 MAPPING LAND USE/ LAND COVER OF WEST GODAVARI DISTRICT USING NDVI TECHNIQUES AND GIS Anusha. B 1, Sridhar. P 2 1 M. Tech. Student, Department of Geoinformatics, SVECW, Bhimavaram, A.P, India 2 Assistant
MAPPING LAND USE/ LAND COVER OF WEST GODAVARI DISTRICT USING NDVI TECHNIQUES AND GIS Anusha. B 1, Sridhar. P 2 1 M. Tech. Student, Department of Geoinformatics, SVECW, Bhimavaram, A.P, India 2 Assistant
Greening of Arctic: Knowledge and Uncertainties
 Greening of Arctic: Knowledge and Uncertainties Jiong Jia, Hesong Wang Chinese Academy of Science jiong@tea.ac.cn Howie Epstein Skip Walker Moscow, January 28, 2008 Global Warming and Its Impact IMPACTS
Greening of Arctic: Knowledge and Uncertainties Jiong Jia, Hesong Wang Chinese Academy of Science jiong@tea.ac.cn Howie Epstein Skip Walker Moscow, January 28, 2008 Global Warming and Its Impact IMPACTS
Investigation of the Effect of Transportation Network on Urban Growth by Using Satellite Images and Geographic Information Systems
 Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Investigation of the Effect of Transportation Network on Urban Growth by Using Satellite Images and Geographic Information Systems
Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Investigation of the Effect of Transportation Network on Urban Growth by Using Satellite Images and Geographic Information Systems
AGOG 485/585 /APLN 533 Spring Lecture 5: MODIS land cover product (MCD12Q1). Additional sources of MODIS data
 AGOG 485/585 /APLN 533 Spring 2019 Lecture 5: MODIS land cover product (MCD12Q1). Additional sources of MODIS data Outline Current status of land cover products Overview of the MCD12Q1 algorithm Mapping
AGOG 485/585 /APLN 533 Spring 2019 Lecture 5: MODIS land cover product (MCD12Q1). Additional sources of MODIS data Outline Current status of land cover products Overview of the MCD12Q1 algorithm Mapping
Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl
 Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl Jason Parent jason.parent@uconn.edu Academic Assistant GIS Analyst Daniel Civco Professor of Geomatics Center for Land Use Education
Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl Jason Parent jason.parent@uconn.edu Academic Assistant GIS Analyst Daniel Civco Professor of Geomatics Center for Land Use Education
APPLICATION OF LAND CHANGE MODELER FOR PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER A CASE STUDY OF VIJAYAWADA CITY
 APPLICATION OF LAND CHANGE MODELER FOR PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER A CASE STUDY OF VIJAYAWADA CITY K. Sundara Kumar 1, Dr. P. Udaya Bhaskar 2, Dr. K. Padmakumari 3 1 Research Scholar, 2,3
APPLICATION OF LAND CHANGE MODELER FOR PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER A CASE STUDY OF VIJAYAWADA CITY K. Sundara Kumar 1, Dr. P. Udaya Bhaskar 2, Dr. K. Padmakumari 3 1 Research Scholar, 2,3
Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model
 Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model Gabriella Zsebeházi Gabriella Zsebeházi and Gabriella Szépszó Hungarian Meteorological Service,
Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model Gabriella Zsebeházi Gabriella Zsebeházi and Gabriella Szépszó Hungarian Meteorological Service,
Evaluating Urban Vegetation Cover Using LiDAR and High Resolution Imagery
 Evaluating Urban Vegetation Cover Using LiDAR and High Resolution Imagery Y.A. Ayad and D. C. Mendez Clarion University of Pennsylvania Abstract One of the key planning factors in urban and built up environments
Evaluating Urban Vegetation Cover Using LiDAR and High Resolution Imagery Y.A. Ayad and D. C. Mendez Clarion University of Pennsylvania Abstract One of the key planning factors in urban and built up environments
Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai
 Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai K. Ilayaraja Department of Civil Engineering BIST, Bharath University Selaiyur, Chennai 73 ABSTRACT The synoptic picture
Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai K. Ilayaraja Department of Civil Engineering BIST, Bharath University Selaiyur, Chennai 73 ABSTRACT The synoptic picture
Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens. Title. Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki. Citation Japan.
 Title Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki International Symposium on "The Imp Citation Region Specific Systems". 6 Nove Japan.
Title Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki International Symposium on "The Imp Citation Region Specific Systems". 6 Nove Japan.
Software requirements * : Part III: 2 hrs.
 Title: Product Type: Developer: Target audience: Format: Software requirements * : Data: Estimated time to complete: Mapping snow cover using MODIS Part I: The MODIS Instrument Part II: Normalized Difference
Title: Product Type: Developer: Target audience: Format: Software requirements * : Data: Estimated time to complete: Mapping snow cover using MODIS Part I: The MODIS Instrument Part II: Normalized Difference
EFFECT OF ANCILLARY DATA ON THE PERFORMANCE OF LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION USING A NEURAL NETWORK MODEL. Duong Dang KHOI.
 EFFECT OF ANCILLARY DATA ON THE PERFORMANCE OF LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION USING A NEURAL NETWORK MODEL Duong Dang KHOI 1 10 Feb, 2011 Presentation contents 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Results 4. Discussion
EFFECT OF ANCILLARY DATA ON THE PERFORMANCE OF LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION USING A NEURAL NETWORK MODEL Duong Dang KHOI 1 10 Feb, 2011 Presentation contents 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Results 4. Discussion
International Journal on Emerging Technologies 8(1): (2017) ISSN No. (Print) : ISSN No. (Online) :
 e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 8(1): 553-559(2017) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 Critical Review of the Climate Change Impact on Urban Areas by Assessment
e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 8(1): 553-559(2017) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 Critical Review of the Climate Change Impact on Urban Areas by Assessment
This is trial version
 Journal of Rangeland Science, 2012, Vol. 2, No. 2 J. Barkhordari and T. Vardanian/ 459 Contents available at ISC and SID Journal homepage: www.rangeland.ir Full Paper Article: Using Post-Classification
Journal of Rangeland Science, 2012, Vol. 2, No. 2 J. Barkhordari and T. Vardanian/ 459 Contents available at ISC and SID Journal homepage: www.rangeland.ir Full Paper Article: Using Post-Classification
Remote Sensing of Urban Surface Temperatures
 Remote Sensing of Urban Surface Temperatures James Voogt University of Western Ontario London, Ontario, Canada This work is supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Remote Sensing of Urban Surface Temperatures James Voogt University of Western Ontario London, Ontario, Canada This work is supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Projecting Urban Land Cover on the basis of Population
 Projecting Urban Land Cover on the basis of Population Dan Miller Runfola Postdoctoral Researcher National Center for Atmospheric Research CGD & RAL CU:Boulder Institute of Behavioral Science 1 The Challenge
Projecting Urban Land Cover on the basis of Population Dan Miller Runfola Postdoctoral Researcher National Center for Atmospheric Research CGD & RAL CU:Boulder Institute of Behavioral Science 1 The Challenge
Seasonal Variations of the Urban Heat Island Effect:
 Seasonal Variations of the Urban Heat Island Effect: Examining the Differences in Temperature Between the City of Philadelphia and its Outlying Suburbs By: Frank Vecchio 1 P a g e We re calling for a high
Seasonal Variations of the Urban Heat Island Effect: Examining the Differences in Temperature Between the City of Philadelphia and its Outlying Suburbs By: Frank Vecchio 1 P a g e We re calling for a high
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. Ecological restoration and its effects on the
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Ecological restoration and its effects on the regional climate: the case in the source region of the Yellow River, China Zhouyuan Li, Xuehua Liu,* Tianlin Niu, De Kejia, Qingping
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Ecological restoration and its effects on the regional climate: the case in the source region of the Yellow River, China Zhouyuan Li, Xuehua Liu,* Tianlin Niu, De Kejia, Qingping
Spatial Geotechnologies and GIS tools for urban planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115.
 planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115. Fig.1 The city of Caracas, as many others Latin-American cities, has experimented a fast growth in
planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115. Fig.1 The city of Caracas, as many others Latin-American cities, has experimented a fast growth in
MONITORING THE SURFACE HEAT ISLAND (SHI) EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES
 MONITORING THE SURFACE HEAT ISLAND (SHI) EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES A. Şekertekin a, *, Ş. H. Kutoglu a, S. Kaya b, A. M. Marangoz a a BEU, Engineering Faculty, Geomatics Engineering Department
MONITORING THE SURFACE HEAT ISLAND (SHI) EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES A. Şekertekin a, *, Ş. H. Kutoglu a, S. Kaya b, A. M. Marangoz a a BEU, Engineering Faculty, Geomatics Engineering Department
DEPENDENCE OF URBAN TEMPERATURE ELEVATION ON LAND COVER TYPES. Ping CHEN, Soo Chin LIEW and Leong Keong KWOH
 DEPENDENCE OF URBAN TEMPERATURE ELEVATION ON LAND COVER TYPES Ping CHEN, Soo Chin LIEW and Leong Keong KWOH Centre for Remote Imaging, Sensing and Processing, National University of Singapore, Lower Kent
DEPENDENCE OF URBAN TEMPERATURE ELEVATION ON LAND COVER TYPES Ping CHEN, Soo Chin LIEW and Leong Keong KWOH Centre for Remote Imaging, Sensing and Processing, National University of Singapore, Lower Kent
Land Surface Remote Sensing II
 PROCEEDINGS OFSPIE Land Surface Remote Sensing II Thomas J. Jackson Jing Ming Chen Peng Gong Shunlin Liang Editors 13-16 October 2014 Beijing, China Sponsored by SPIE Cosponsored by State Key Laboratory
PROCEEDINGS OFSPIE Land Surface Remote Sensing II Thomas J. Jackson Jing Ming Chen Peng Gong Shunlin Liang Editors 13-16 October 2014 Beijing, China Sponsored by SPIE Cosponsored by State Key Laboratory
Urban remote sensing: from local to global and back
 Urban remote sensing: from local to global and back Paolo Gamba University of Pavia, Italy A few words about Pavia Historical University (1361) in a nice town slide 3 Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society
Urban remote sensing: from local to global and back Paolo Gamba University of Pavia, Italy A few words about Pavia Historical University (1361) in a nice town slide 3 Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society
How Researchers Measure Urban Heat Islands. James Voogt Department of Geography, University of Western Ontario London ON Canada
 How Researchers Measure Urban Heat Islands James Voogt Department of Geography, University of Western Ontario London ON Canada Outline What is the urban heat island? What types of urban heat islands exist?
How Researchers Measure Urban Heat Islands James Voogt Department of Geography, University of Western Ontario London ON Canada Outline What is the urban heat island? What types of urban heat islands exist?
[Sakthivel *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor
![[Sakthivel *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor [Sakthivel *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor](/thumbs/91/106248739.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES URBAN HEAT ISLAND (UHI) ANALYSIS USING GEO-SPATIAL TECHNOLOGY IN PUNE CITY, MAHARASHTRA Dr. M. Sakthivel* 1, Dr. M. H. Kalubarme 2, Gaikwad Vishal Vilas
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES URBAN HEAT ISLAND (UHI) ANALYSIS USING GEO-SPATIAL TECHNOLOGY IN PUNE CITY, MAHARASHTRA Dr. M. Sakthivel* 1, Dr. M. H. Kalubarme 2, Gaikwad Vishal Vilas
Comparison of NASA AIRS and MODIS Land Surface Temperature and Infrared Emissivity Measurements from the EOS AQUA platform
 Comparison of NASA AIRS and MODIS Land Surface Temperature and Infrared Emissivity Measurements from the EOS AQUA platform Robert Knuteson, Steve Ackerman, Hank Revercomb, Dave Tobin University of Wisconsin-Madison
Comparison of NASA AIRS and MODIS Land Surface Temperature and Infrared Emissivity Measurements from the EOS AQUA platform Robert Knuteson, Steve Ackerman, Hank Revercomb, Dave Tobin University of Wisconsin-Madison
Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach
 Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach Dr.Gowri 1 Dr.Thirumalaivasan 2 1 Associate Professor, Jerusalem College of Engineering, Department of Civil
Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach Dr.Gowri 1 Dr.Thirumalaivasan 2 1 Associate Professor, Jerusalem College of Engineering, Department of Civil
Results of the ESA-DUE UHI project
 13/12/2011 Results of the ESA-DUE UHI project Bino Maiheu (bino.maiheu@vito.be), on behalf of the UHI project Outline» Urban heat island problem» The ESA-DUE urban heat island project» UHI air temperature
13/12/2011 Results of the ESA-DUE UHI project Bino Maiheu (bino.maiheu@vito.be), on behalf of the UHI project Outline» Urban heat island problem» The ESA-DUE urban heat island project» UHI air temperature
Spatio-Temporal Trends of Urban Heat Island and Surface Temperature in Izmir, Turkey
 American Journal of Remote Sensing 2017; 5(3): 24-29 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajrs doi: 0.11648/j.ajrs.20170503.11 ISSN: 2328-5788 (Print); ISSN: 2328-580X (Online) Spatio-Temporal Trends
American Journal of Remote Sensing 2017; 5(3): 24-29 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajrs doi: 0.11648/j.ajrs.20170503.11 ISSN: 2328-5788 (Print); ISSN: 2328-580X (Online) Spatio-Temporal Trends
Abstract. TECHNOFAME- A Journal of Multidisciplinary Advance Research. Vol.2 No. 2, (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct.
 Vol.2 No. 2, 83-87 (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct. 2013 Landuse Pattern Analysis Using Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Morar Block, of Gwalior District, M.P. Subhash Thakur 1 Akhilesh Singh 2
Vol.2 No. 2, 83-87 (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct. 2013 Landuse Pattern Analysis Using Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Morar Block, of Gwalior District, M.P. Subhash Thakur 1 Akhilesh Singh 2
GIS GIS ETM+
 GIS 1388 Vol.1, No.1, Spring 2009 39-56 GIS Iranian Remote Sensing & GIS ETM+ *4 3 2 1 GIS -1-2 -3 GIS -4 88/8/9 : 88/4/30 :.. ). (.... ( ). ETM+. (LSU)...V_I_S : Email: soodabeh_namdari@yahoo.com 22431788
GIS 1388 Vol.1, No.1, Spring 2009 39-56 GIS Iranian Remote Sensing & GIS ETM+ *4 3 2 1 GIS -1-2 -3 GIS -4 88/8/9 : 88/4/30 :.. ). (.... ( ). ETM+. (LSU)...V_I_S : Email: soodabeh_namdari@yahoo.com 22431788
The footprint of urban heat island effect in China
 A discussion on the paper The footprint of urban heat island effect in China By Decheng Zhou, Shuqing Zhao, Liangxia Zhang, Ge Sun & Yongqiang Liu Published in SCIENCE REPORRTS Reporter: Mu Qingchen 2015.10.23
A discussion on the paper The footprint of urban heat island effect in China By Decheng Zhou, Shuqing Zhao, Liangxia Zhang, Ge Sun & Yongqiang Liu Published in SCIENCE REPORRTS Reporter: Mu Qingchen 2015.10.23
New Opportunities in Urban Remote Sensing. Philip Christensen Arizona State University
 New Opportunities in Urban Remote Sensing Philip Christensen Arizona State University Advantages: Uniform, global data Role of Remote Sensing Repeatable at regular intervals over long periods of time Broad
New Opportunities in Urban Remote Sensing Philip Christensen Arizona State University Advantages: Uniform, global data Role of Remote Sensing Repeatable at regular intervals over long periods of time Broad
Urban Area Delineation Using Pattern Recognition Technique
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2018, Volume 7, Issue 1, pp. 2466-2470 ISSN 2320 0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.333 Methodology Article Urban Area Delineation
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2018, Volume 7, Issue 1, pp. 2466-2470 ISSN 2320 0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.333 Methodology Article Urban Area Delineation
METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION DATA FOR ASSESSMENT OF SURFACE MOISTURE STATUS
 METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION DATA FOR ASSESSMENT OF SURFACE MOISTURE STATUS Simon Stisen (1), Inge Sandholt (1), Rasmus Fensholt (1) (1) Institute of Geography, University of Copenhagen, Oestervoldgade 10,
METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION DATA FOR ASSESSMENT OF SURFACE MOISTURE STATUS Simon Stisen (1), Inge Sandholt (1), Rasmus Fensholt (1) (1) Institute of Geography, University of Copenhagen, Oestervoldgade 10,
A Facility for Producing Consistent Remotely Sensed Biophysical Data Products of Australia
 TERRESTRIAL ECOSYSTEM RESEARCH NETWORK - AusCover - A Facility for Producing Consistent Remotely Sensed Biophysical Data Products of Australia June, 2011 Mervyn Lynch Professor of Remote Sensing Curtin
TERRESTRIAL ECOSYSTEM RESEARCH NETWORK - AusCover - A Facility for Producing Consistent Remotely Sensed Biophysical Data Products of Australia June, 2011 Mervyn Lynch Professor of Remote Sensing Curtin
VISUALIZATION URBAN SPATIAL GROWTH OF DESERT CITIES FROM SATELLITE IMAGERY: A PRELIMINARY STUDY
 CO-439 VISUALIZATION URBAN SPATIAL GROWTH OF DESERT CITIES FROM SATELLITE IMAGERY: A PRELIMINARY STUDY YANG X. Florida State University, TALLAHASSEE, FLORIDA, UNITED STATES ABSTRACT Desert cities, particularly
CO-439 VISUALIZATION URBAN SPATIAL GROWTH OF DESERT CITIES FROM SATELLITE IMAGERY: A PRELIMINARY STUDY YANG X. Florida State University, TALLAHASSEE, FLORIDA, UNITED STATES ABSTRACT Desert cities, particularly
Comparison of MLC and FCM Techniques with Satellite Imagery in A Part of Narmada River Basin of Madhya Pradesh, India
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 013, Volume, Issue 1, pp. 130-137, Article ID Tech-96 ISS 30-043 Research Article Open Access Comparison of MLC and FCM Techniques
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 013, Volume, Issue 1, pp. 130-137, Article ID Tech-96 ISS 30-043 Research Article Open Access Comparison of MLC and FCM Techniques
Enhancement of the U.S. Drought Monitor Through the Integration of NASA Vegetation Index Imagery
 Enhancement of the U.S. Drought Monitor Through the Integration of NASA Vegetation Index Imagery Project and Related Activities at USGS/EROS Jim Verdin, Jesslyn Brown, Yingxin Gu, Gail Schmidt, Troy McVay
Enhancement of the U.S. Drought Monitor Through the Integration of NASA Vegetation Index Imagery Project and Related Activities at USGS/EROS Jim Verdin, Jesslyn Brown, Yingxin Gu, Gail Schmidt, Troy McVay
An Analysis of Urban Cooling Island (UCI) Effects by Water Spaces Applying UCI Indices
 An Analysis of Urban Cooling Island (UCI) Effects by Water Spaces Applying UCI Indices D. Lee, K. Oh, and J. Seo Abstract An urban cooling island (UCI) involves an area that has a lower temperature compared
An Analysis of Urban Cooling Island (UCI) Effects by Water Spaces Applying UCI Indices D. Lee, K. Oh, and J. Seo Abstract An urban cooling island (UCI) involves an area that has a lower temperature compared
Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT
 Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT Technical briefs are short summaries of the models used in the project aimed at nontechnical readers. The aim of the PES India
Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT Technical briefs are short summaries of the models used in the project aimed at nontechnical readers. The aim of the PES India
PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER CHANGES OF VIJAYAWADA CITY USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS
 PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER CHANGES OF VIJAYAWADA CITY USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS K. Sundara Kumar 1 *, N V A Sai Sankar Valasala 2, J V Subrahmanyam V 3, Mounika Mallampati 4 Kowsharajaha
PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER CHANGES OF VIJAYAWADA CITY USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS K. Sundara Kumar 1 *, N V A Sai Sankar Valasala 2, J V Subrahmanyam V 3, Mounika Mallampati 4 Kowsharajaha
ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF A METHODOLOGY TO EVALUATE LAND COVER CHANGE IN THE MEDITERRANEAN BASIN USING MULTITEMPORAL MODIS DATA
 PRESENT ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT, NR. 4, 2010 ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF A METHODOLOGY TO EVALUATE LAND COVER CHANGE IN THE MEDITERRANEAN BASIN USING MULTITEMPORAL MODIS DATA Mara Pilloni
PRESENT ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT, NR. 4, 2010 ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF A METHODOLOGY TO EVALUATE LAND COVER CHANGE IN THE MEDITERRANEAN BASIN USING MULTITEMPORAL MODIS DATA Mara Pilloni
Mapping forests in monsoon Asia with ALOS PALSAR 50-m mosaic images and MODIS
 1 Supplementary Information 2 3 Mapping forests in monsoon Asia with ALOS PALSAR 50-m mosaic images and MODIS imagery in 2010 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Yuanwei Qin, Xiangming Xiao, Jinwei Dong, Geli Zhang, Partha
1 Supplementary Information 2 3 Mapping forests in monsoon Asia with ALOS PALSAR 50-m mosaic images and MODIS imagery in 2010 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Yuanwei Qin, Xiangming Xiao, Jinwei Dong, Geli Zhang, Partha
Assessment of Urban Heat Island through Remote Sensing in Nagpur Urban Area Using Landsat 7 ETM+ Satellite Images
 Assessment of Urban Heat Island through Remote Sensing in Nagpur Urban Area Using Landsat 7 ETM+ Satellite Images Meenal Surawar, Rajashree Kotharkar 1 Abstract Urban Heat Island (UHI) is found more pronounced
Assessment of Urban Heat Island through Remote Sensing in Nagpur Urban Area Using Landsat 7 ETM+ Satellite Images Meenal Surawar, Rajashree Kotharkar 1 Abstract Urban Heat Island (UHI) is found more pronounced
Comparing the diurnal and seasonal variabilities of atmospheric and surface urban heat islands based on the Beijing urban meteorological network
 Comparing the diurnal and seasonal variabilities of atmospheric and surface urban heat islands based on the Beijing urban meteorological network Kaicun Wang, Shaojing Jiang, Jiankai Wang, Chunlüe Zhou,
Comparing the diurnal and seasonal variabilities of atmospheric and surface urban heat islands based on the Beijing urban meteorological network Kaicun Wang, Shaojing Jiang, Jiankai Wang, Chunlüe Zhou,
Urban Mapping. Sebastian van der Linden, Akpona Okujeni, Franz Schug 11/09/2018
 Urban Mapping Sebastian van der Linden, Akpona Okujeni, Franz Schug 11/09/2018 Introduction to urban remote sensing Introduction The urban millennium Source: United Nations, 2014 Urban areas mark extremes
Urban Mapping Sebastian van der Linden, Akpona Okujeni, Franz Schug 11/09/2018 Introduction to urban remote sensing Introduction The urban millennium Source: United Nations, 2014 Urban areas mark extremes
Sources of Imagery and GIS Data Layers (Last updated October 2005)
 Sources of Imagery and GIS Data Layers (Last updated October 2005) The question of where to find data is one often asked by beginners in precision agriculture and other geospatial projects. The following
Sources of Imagery and GIS Data Layers (Last updated October 2005) The question of where to find data is one often asked by beginners in precision agriculture and other geospatial projects. The following
GLOBAL/CONTINENTAL LAND COVER MAPPING AND MONITORING
 GLOBAL/CONTINENTAL LAND COVER MAPPING AND MONITORING Ryutaro Tateishi, Cheng Gang Wen, and Jong-Geol Park Center for Environmental Remote Sensing (CEReS), Chiba University 1-33 Yayoi-cho Inage-ku Chiba
GLOBAL/CONTINENTAL LAND COVER MAPPING AND MONITORING Ryutaro Tateishi, Cheng Gang Wen, and Jong-Geol Park Center for Environmental Remote Sensing (CEReS), Chiba University 1-33 Yayoi-cho Inage-ku Chiba
Global Broadband IR Surface Emissivity Computed from Combined ASTER and MODIS Emissivity over Land (CAMEL)
 P76 Global Broadband IR Surface Emissivity Computed from Combined ASTER and MODIS Emissivity over Land (CAMEL) Michelle Feltz, Eva Borbas, Robert Knuteson, Glynn Hulley*, Simon Hook* University of Wisconsin-Madison
P76 Global Broadband IR Surface Emissivity Computed from Combined ASTER and MODIS Emissivity over Land (CAMEL) Michelle Feltz, Eva Borbas, Robert Knuteson, Glynn Hulley*, Simon Hook* University of Wisconsin-Madison
SYNERGY OF SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING AND SENSOR NETWORKS ON GEO GRID
 SYNERGY OF SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING AND SENSOR NETWORKS ON GEO GRID National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Japan Yoshio Tanaka (on behalf of AIST GEO Grid team) Contents Brief
SYNERGY OF SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING AND SENSOR NETWORKS ON GEO GRID National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Japan Yoshio Tanaka (on behalf of AIST GEO Grid team) Contents Brief
Documentation for the Global Urban Heat Island (UHI) Data Set, 2013
 Documentation for the Global Urban Heat Island (UHI) Data Set, 2013 September 2016 Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN) Columbia University Abstract This document presents
Documentation for the Global Urban Heat Island (UHI) Data Set, 2013 September 2016 Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN) Columbia University Abstract This document presents
International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations
 ISSN:2348-2079 Volume-5 Issue-2 International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations Agricultural land investigation and change detection in Coimbatore district by
ISSN:2348-2079 Volume-5 Issue-2 International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations Agricultural land investigation and change detection in Coimbatore district by
URBAN SPRAWL AND SPATIO TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF HISAR CITY IN HARYANA USING REMOTE SENSING & GIS TECNOLOGY
 URBAN SPRAWL AND SPATIO TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF HISAR CITY IN HARYANA USING REMOTE SENSING & GIS TECNOLOGY Shashikant 1, Pallavi Singh 2, R. D. Doi 3, Ankur Sharma 4, Ravinder Kumar 5, Parveen Bhatti 6 Abstract
URBAN SPRAWL AND SPATIO TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF HISAR CITY IN HARYANA USING REMOTE SENSING & GIS TECNOLOGY Shashikant 1, Pallavi Singh 2, R. D. Doi 3, Ankur Sharma 4, Ravinder Kumar 5, Parveen Bhatti 6 Abstract
ISO MODIS NDVI Weekly Composites for Canada South of 60 N Data Product Specification
 ISO 19131 MODIS NDVI Weekly Composites for South of 60 N Data Product Specification Revision: A Data specification: MODIS NDVI Composites for South of 60 N - Table of Contents - 1. OVERVIEW... 3 1.1. Informal
ISO 19131 MODIS NDVI Weekly Composites for South of 60 N Data Product Specification Revision: A Data specification: MODIS NDVI Composites for South of 60 N - Table of Contents - 1. OVERVIEW... 3 1.1. Informal
Remote Sensing products and global datasets. Joint Research Centre, European Commission
 Remote Sensing products and global datasets Joint Research Centre, European Commission Setting the stage. Needs and requirements for integrated approach(es) for land degradation assessment. in Special
Remote Sensing products and global datasets Joint Research Centre, European Commission Setting the stage. Needs and requirements for integrated approach(es) for land degradation assessment. in Special
Defining microclimates on Long Island using interannual surface temperature records from satellite imagery
 Defining microclimates on Long Island using interannual surface temperature records from satellite imagery Deanne Rogers*, Katherine Schwarting, and Gilbert Hanson Dept. of Geosciences, Stony Brook University,
Defining microclimates on Long Island using interannual surface temperature records from satellite imagery Deanne Rogers*, Katherine Schwarting, and Gilbert Hanson Dept. of Geosciences, Stony Brook University,
CHAPTER 2 REMOTE SENSING IN URBAN SPRAWL ANALYSIS
 9 CHAPTER 2 REMOTE SENSING IN URBAN SPRAWL ANALYSIS 2.1. REMOTE SENSING Remote sensing is the science of acquiring information about the Earth's surface without actually being in contact with it. This
9 CHAPTER 2 REMOTE SENSING IN URBAN SPRAWL ANALYSIS 2.1. REMOTE SENSING Remote sensing is the science of acquiring information about the Earth's surface without actually being in contact with it. This
The relationship between land cover changes and spatial-temporal dynamics of land surface temperature
 76 The relationship between land cover changes and spatial-temporal dynamics of land surface temperature Samereh Falahatkar 1, Seyed Mohsen Hosseini 2 and Ali Reza Soffianian 3 1 Academic center for education,
76 The relationship between land cover changes and spatial-temporal dynamics of land surface temperature Samereh Falahatkar 1, Seyed Mohsen Hosseini 2 and Ali Reza Soffianian 3 1 Academic center for education,
Estimation of Land Surface Temperature of Kumta Taluk Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques
 Estimation of Land Surface Temperature of Kumta Taluk Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques Dr. A.G Koppad 1 and Malini P.J 2 Research Associate, NISAR Project (NRM) COF SIRSI, UAS Dharwad Professor
Estimation of Land Surface Temperature of Kumta Taluk Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques Dr. A.G Koppad 1 and Malini P.J 2 Research Associate, NISAR Project (NRM) COF SIRSI, UAS Dharwad Professor
DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION
 DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION Researcher: Saad-ul-Haque Supervisor: Dr. Badar Ghauri Department of RS & GISc Institute of Space Technology
DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION Researcher: Saad-ul-Haque Supervisor: Dr. Badar Ghauri Department of RS & GISc Institute of Space Technology
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 7, July ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 7, July-2015 1428 Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover /Land Use Mapping Using Medium Resolution Satellite Imagery Paliwal M.C &.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 7, July-2015 1428 Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover /Land Use Mapping Using Medium Resolution Satellite Imagery Paliwal M.C &.
Soil Erosion Calculation using Remote Sensing and GIS in Río Grande de Arecibo Watershed, Puerto Rico
 Soil Erosion Calculation using Remote Sensing and GIS in Río Grande de Arecibo Watershed, Puerto Rico Alejandra M. Rojas González Department of Civil Engineering University of Puerto Rico at Mayaguez.
Soil Erosion Calculation using Remote Sensing and GIS in Río Grande de Arecibo Watershed, Puerto Rico Alejandra M. Rojas González Department of Civil Engineering University of Puerto Rico at Mayaguez.
Cross-Sensor Continuity Science Algorithm
 Cross-Sensor Continuity Science Algorithm - Long Term Vegetation Index and Phenology Workshop - Javzan Tsend-Ayush and Tomoaki Miura Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Management University
Cross-Sensor Continuity Science Algorithm - Long Term Vegetation Index and Phenology Workshop - Javzan Tsend-Ayush and Tomoaki Miura Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Management University
Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction in Tabriz
 Int. J. Environ. Res. 1 (1): 35-41, Winter 2007 ISSN:1735-6865 Graduate Faculty of Environment University of Tehran Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction
Int. J. Environ. Res. 1 (1): 35-41, Winter 2007 ISSN:1735-6865 Graduate Faculty of Environment University of Tehran Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction
Permanent Ice and Snow
 Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Ancillary Data Report Permanent Ice and Snow Preliminary, v.1 SMAP Science Document no. 048 Kyle McDonald, E. Podest, E. Njoku Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute
Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Ancillary Data Report Permanent Ice and Snow Preliminary, v.1 SMAP Science Document no. 048 Kyle McDonald, E. Podest, E. Njoku Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute
Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region
 Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region ZhangZhen 2015.07.10 1 Outline Introduction Data
Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region ZhangZhen 2015.07.10 1 Outline Introduction Data
Percentage of Vegetation Cover Change Monitoring in Wuhan Region Based on Remote Sensing
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 10 (2011 ) 1466 1472 2011 3rd International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Conference Application Title Technology
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 10 (2011 ) 1466 1472 2011 3rd International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Conference Application Title Technology
METRIC tm. Mapping Evapotranspiration at high Resolution with Internalized Calibration. Shifa Dinesh
 METRIC tm Mapping Evapotranspiration at high Resolution with Internalized Calibration Shifa Dinesh Outline Introduction Background of METRIC tm Surface Energy Balance Image Processing Estimation of Energy
METRIC tm Mapping Evapotranspiration at high Resolution with Internalized Calibration Shifa Dinesh Outline Introduction Background of METRIC tm Surface Energy Balance Image Processing Estimation of Energy
COMPARISON OF NOAA/AVHRR AND LANDSAT/TM DATA IN TERMS OF RESEARCH APPLICATIONS ON THERMAL CONDITIONS IN URBAN AREAS
 COMPARISON OF NOAA/AVHRR AND LANDSAT/TM DATA IN TERMS OF RESEARCH APPLICATIONS ON THERMAL CONDITIONS IN URBAN AREAS Monika J. Hajto 1 *, Jakub P. Walawender 2,3 and Piotr Struzik 2 1 Department of Air
COMPARISON OF NOAA/AVHRR AND LANDSAT/TM DATA IN TERMS OF RESEARCH APPLICATIONS ON THERMAL CONDITIONS IN URBAN AREAS Monika J. Hajto 1 *, Jakub P. Walawender 2,3 and Piotr Struzik 2 1 Department of Air
Development of a Regional Land Cover Monitoring System In the Lower Mekong Region a Joint Effort Between SERVIR-Mekong and Partners -
 Mekong Development of a Regional Land Cover Monitoring System In the Lower Mekong Region a Joint Effort Between SERVIR-Mekong and Partners - Aekkapol Aekakkararungroj SERVIR-Mekong Asian Disaster Preparedness
Mekong Development of a Regional Land Cover Monitoring System In the Lower Mekong Region a Joint Effort Between SERVIR-Mekong and Partners - Aekkapol Aekakkararungroj SERVIR-Mekong Asian Disaster Preparedness
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
 III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 3.1 Time and Location This research has been conducted in period March until October 2010. Location of research is over Sumatra terrain. Figure 3.1 show the area of interest of
III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 3.1 Time and Location This research has been conducted in period March until October 2010. Location of research is over Sumatra terrain. Figure 3.1 show the area of interest of
An Internet-based Agricultural Land Use Trends Visualization System (AgLuT)
 An Internet-based Agricultural Land Use Trends Visualization System (AgLuT) Second half yearly report 01-01-2001-06-30-2001 Prepared for Missouri Department of Natural Resources Missouri Department of
An Internet-based Agricultural Land Use Trends Visualization System (AgLuT) Second half yearly report 01-01-2001-06-30-2001 Prepared for Missouri Department of Natural Resources Missouri Department of
EVALUATION OF URBANIZATION INFLUENCES ON URBAN CLIMATE WITH REMOTE SENSING AND CLIMATE OBSERVATIONS. George Xian 1 and Mike Crane 2.
 EVALUATION OF URBANIZATION INFLUENCES ON URBAN CLIMATE WITH REMOTE SENSING AND CLIMATE OBSERVATIONS George Xian 1 and Mike Crane 2 1 SAIC/ 2 USGS National Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science,
EVALUATION OF URBANIZATION INFLUENCES ON URBAN CLIMATE WITH REMOTE SENSING AND CLIMATE OBSERVATIONS George Xian 1 and Mike Crane 2 1 SAIC/ 2 USGS National Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science,
SWAMP GIS: A spatial decision support system for predicting and treating stormwater runoff. Michael G. Wing 1 * and Derek Godwin
 Journal of Spatial Hydrology Vol. 11, No. 2 Fall 2011 SWAMP GIS: A spatial decision support system for predicting and treating stormwater runoff Michael G. Wing 1 * and Derek Godwin Abstract SWAMP GIS
Journal of Spatial Hydrology Vol. 11, No. 2 Fall 2011 SWAMP GIS: A spatial decision support system for predicting and treating stormwater runoff Michael G. Wing 1 * and Derek Godwin Abstract SWAMP GIS
Lancaster Environment Centre, Lancaster University, Lancaster, LA1 4YQ, UK;
 Title Page Dynamics and controls of urban heat sink and island phenomena in a desert city: development of a local climate zone scheme using remotely-sensed inputs Ahmed K. NASSAR (corresponding author)
Title Page Dynamics and controls of urban heat sink and island phenomena in a desert city: development of a local climate zone scheme using remotely-sensed inputs Ahmed K. NASSAR (corresponding author)
