Study of Urban heat Island Effect on Ahmedabad City and Its Relationship with Urbanization and Vegetation Parameters
|
|
|
- Jocelyn Mason
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Study of Urban heat Island Effect on Ahmedabad City and Its Relationship with Urbanization and Vegetation Parameters Aneesh Mathew a,*, Rishabh Chaudhary a, Neha Gupta a, a Research Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur, JLN Marg, Jaipur (Rajasthan) Sumit Khandelwal b, Nivedita Kaul b b Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur, JLN Marg, Jaipur (Rajasthan) Abstract Rapid urbanization leads to an increase in land surface temperature (LST) which is governed by surface heat fluxes and is an important parameter in global climate change. The objectives of the present study are to analyze the spatial pattern of the night land surface temperature (LST) observed by remote sensing satellites and to analyze the effect of vegetation and urbanization over LST of Ahmedabad city, India. Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and Enhanced vegetation index (EVI) have been used as an indicator for vegetation cover and Normalized difference built-up index () for level of urbanization. Landsat 5 Thematic Mapper (TM) and MODIS data were used for the retrieval of LST and the calculation of normalized difference built-up index (), normalized vegetation index (NDVI) and Enhanced vegetation index (EVI). From the present study, it has been observed that the areas with high LST were located principally in central built-up areas. As per the results of assessment of relationship between LST with NDVI, EVI and shows that LST had the negative correlation with NDVI and EVI and positive correlation with which means that green land can reduce the urban heat island (UHI) effect whereas built-up areas can strengthen the effect of UHI. It has been concluded that NDVI, EVI and can be used to investigate the risk of Urban Heat Island (UHI) and may help city planners better prepare for possible impacts of urban environmental change. Key Words Land Surface Temperature (LST), Urban Heat Island (UHI), NDVI, EVI, MODIS Introduction Urbanization results in global climate change in various ways and across multiple dimensions. Rapid urbanization has led to a significant increase in the number of urban population worldwide. Recent research reported that urban population is expected to reach 65 % by 2025 [1] and in 2008 more than half of the world s population were urban dwellers and 81% of the world population will live in urban areas by 2030 [2]. Natural landscape will transform to an impervious surface due to the significant growth of urban areas that will result in the reduction of green cover [3, 5] and, consequently, an increase in land surface temperature. The degree of Surface Urban Heat Island (SUHI) varies with different impervious surfaces, variation of vegetation cover and climatic conditions like season, wind and rainfall. Formation of the urban heat island (UHI) is one attribute of urban land transformation of the nature lands into impervious built-up lands may have significant impacts on the ecosystem, human health, hydrologic system, biodiversity and local climate. Land 126
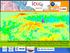
2 surface temperatures can be used as the key parameter for representing Urban Heat Island (UHI) phenomenon. While surface temperatures can be used as both higher and more variable than concurrent air temperatures due to the complexity of the different land surface types in urban environments and variations in urban topography [6, 7]. The primary cause of the urban heat island is the increase of artificial environments which has led to the significant changes of land use and land cover, changes the energy budget at the land surface, produces a great amount of anthropogenic waste heat, and results in a series of changes in the urban environment [8]. These types of changes are usually significant in the urban heat island (UHI), which is the phenomenon where higher atmospheric and surface temperatures occur in urban areas than in the surrounding non-urban areas due to urbanization, particularly at night [9]. Land use and land cover is changed constantly by human activities from the past to the present and is one of the most visible reasons of environmental change [10, 11]. Remotely sensed data of land surface temperature, vegetation indices and other surface characteristics have been widely used to study UHI phenomenon [12-14]. The objectives of the present study are to construct spatial data of land surface temperature (LST), normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), enhanced vegetation index (EVI) and normalized difference built-up index () from satellite imagery and to analyze the relationship between thermal environment and spatial characteristics. 1. Study Area Ahmedabad, located on the bank of river Sabarmati, is the largest city in the Gujarat state of India. Ahmedabad is the fifth largest city and seventh largest metropolitan area of India with a population of 6,352,254 (Census of India 2011). Ahmedabad is situated between WikiMiniAtlas23 02 N E / N E / 23.03; coordinates. Climatic condition of the Ahmedabad is semi-arid and hot. The climate of the Ahmedabad is extremely dry during the summer season from March to mid-june, average recorded maximum temperature of summer is 42 o C and average minimum temperature is 28 o C, maximum average temperature during winter is 30 o C and minimum average temperature is 15 o C. Ahmedabad is situated on dry and sandy soil which absorbs heat during day time. This absorbed heat is than released during the night, thereby making the environment of the city hotter than its surrounding rural areas. This difference in temperature between urban and rural areas is called temperature gradient, making city environment too hostile and difficult to live. This environmental impact created by temperature gradient is called urban heat island (UHI) effect of the city. Thus during summers the temperature of the city go beyond its threshold level creating much warmer area in the city. As UHI phenomenon indicates warmer thermal climate of urban land, compared to non-urbanized area, the study area must include sufficient non-urbanized/sub-urban area outside the urban area for UHI studies. The urban area boundary of Ahmedabad city has been derived by extracting urban area polygon from the MODIS yearly land cover type image (MCD12Q1) of The urban area polygon from this imagery has been converted by using raster to polygon conversion tool in ArcGIS. The length and width of urban area polygon (hereafter referred as urban boundary) is approximately 12 km in North-South direction and 17 km in East-West direction. A buffer of 5 km has been added to the urban boundary avoiding the influence of Gandhinagar to mark the boundary of study area and the study has been carried out for area falling within this boundary. The study area sufficiently includes non-urbanized/sub-urban areas and satellite towns of the city (figure 1). The study area covers approximately 750 square kms. The raster pixel size of LST 127
3 product is m and LST image of the study area has 804 pixels. Figure 1 shows the Google Earth image of the study area and urban area of Ahmedabad city. Figure 1: Google Earth image of the Ahmedabad study area 2. Data and Methodology Eight day, 1 km MYD11A2 and one day, 1 km MYD11A1 land surface temperature and emissivity product [8] and 16 day 1km MYD13Q1, vegetation indices product of MODIS Aqua of overlapping dates have been used for the present study. The study has been undertaken for the year The land surface temperature and emissivity product is available with quality flag which was checked to include only the good quality pixels in the analysis. Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) images from 21 September 2009 have been selected for the present study for their good imaging quality. Table 1: Remote sensing data used for the present work Vegetation Indices MYD13Q1 MODIS Aqua 16 Day m Landsat - TM m The Landsat images have been geometrically rectified to the UTM projection system (datum WGS 84, Zone 43). The ground control points have been carefully selected in order to make sure that the 128 Remote Sensing Product Short Name Sensor Land Cover Type MCD12Q1 MODIS Land Surface Temperature and Emissivity Land Surface Temperature and Emissivity Platform Combined Aqua & Terra Temporal Resolution Yearly Spatial Resolution m MYD11A1 MODIS Aqua Daily m MYD11A2 MODIS Aqua 8 Day m
4 RMS errors lies below pixels. A second-order polynomial and the nearest neighbour resampling method have been employed for implementing the georectification. The digital numbers of the TM images have been converted to the ex-atmospheric reflectance using the methods provided by Chander and Markham and the Landsat 7 Science Data Users Hand book [15, 16]. The downloaded MODIS data is in HDF-EOS format and in Sinusoidal Projection System. The Earth gridded tile area of each MODIS image covers approximately 1100 km x 1100 km. Preprocessing of downloaded MODIS images has been done using MODIS Re-projection Tools (MRT). MRT is used for sub setting of the data to smaller area. The data has also simultaneously been reprojected from Sinusoidal projection to UTM Zone 43N projection system with WGS84 datum and has been reformatted from HDF-EOS to GeoTIFF format. The MODIS product MYD13Q1 gives vegetation indices at approximately m ground resolution, whereas MYD11A2 product for Night LST has a resolution of approximately m. In order to compare EVI with LST it is necessary to have both of them have same resolution so that EVI layers were aggregated to the same resolution as of LST layer and they were also snapped to LST image. Derivation of NDVI and from Landsat 5 TM The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) was used to identify vegetation cover in the study area. The NDVI is a measure of the amount of vegetation at the surface [17, 18]. The value of NDVI varied between -1 and +1. NDVI can be calculated by the following equation [19]. NDVI = NIR RED / NIR +RED Where RED = Red Reflectance; NIR = Near Infrared Reflectance. The normalized difference built-up index () was used to extract built-up areas. The is sensitive to the built-up areas and it can be determined by the following equation [20]. = MIR NIR / MIR + NIR Where NIR = Near Infrared Reflectance; MIR = Mid Infrared Reflectance. 3. Results and Discussions Figure 2: LST images of the study area for 2009, 264 th Day & 2009, Days (September) In the present study, MODIS eight days (2009, ( days)) and one day (2009, 264 th day) night LST data have been used for the retrieval of surface temperatures of the study area and have been shown in figure 2. It has been observed that urban area shows higher LST pixels compared to rural areas and the LST pattern has been found to be well distributed in the high density commercial, residential and industrial areas of Ahmedabad city which shows the clear picture of urban heat island 129
5 effect. The mean LST values of the study area for 2009, days and 2009, 264 th day is observed.659 and.451, respectively and UHI intensities (difference between the maximum and minimum temperature of the study area) values for 2009, days and 2009, 264 th day are 3.62K and 4.1K respectively. Statistical results of land surface temperature values for the two periods of the study area are shown in table 2. Table 2: Statistical Results of LST (K), NDVI, EVI and UHI Parameters Maximum Minimum Mean Standard Deviation LST One Day(K) LST Eight Days(K) NDVI Aggregated NDVI EVI Aggregated EVI Aggregated In the present study, Landsat TM and MODIS data have been used for the derivation of NDVI and EVI, respectively. It has been found that higher values of NDVI and EVI have been observed in agricultural fields in rural areas and comparatively lower values in built-up areas inside the city having less vegetation coverage. Sabarmathi River and lakes in Ahmedabad city have lower values of NDVI and EVI as shown in figures 3 and 4. The statistical results of NDVI and EVI of the study area are shown in table 2. Figure 3: Landsat TM Derived NDVI and Aggregated NDVI images of the study area for 2009, 264 th Day (September) Figure 4: MODIS Derived EVI and Aggregated EVI images of the study area for 2009, Days (September) 130
6 LST(K) MEAN LST(K) International Journal of Computer & Mathematical Sciences In the present study, Landsat TM data has been used for the calculation of. It has been found that higher values of is observed in high density built-up areas which includes commercial, residential and industrial areas within the city and lower values in agricultural fields and water bodies as shown in figure 5. The statistical results of of the study area are shown in table 2. Figure 5: Landsat TM Derived and Aggregated images of the study area for 2009, 264 th Day (September) The scatterplots of LST vs NDVI and LST vs EVI for (2009, 264 th day) and (2009, ( days)) are shown in figure 6 and 7 respectively. Regression analysis has been applied to find a relationship between LST with NDVI and EVI respectively. It has been observed that there is a negative correlation of LST with both NDVI and EVI, which interprets that green spaces can reduce the effect of UHI. Thus vegetation cover is an important parameter which the variations in surface temperature of the study area due to the difference in behaviour of land use/land cover types. Variations in surface temperature is very less in dense vegetated areas. The trend lines of scatter plots show negative relationship between LST and vegetation indices for both periods. From figure 6 and 7, it can be concluded that the relationship of mean LST with EVI and NDVI is linear and shows the negative relationship between mean LST and vegetation indices for both periods. The figures also show the coefficient of correlation (R 2 ) for the linear relationship. 301 LST vs NDVI.5 MEAN LST vs NDVI 30.5 y = x +.47 R² = NDVI - - NDVI Figure 6: LST vs NDVI and Mean LST vs NDVI scatterplots of the study area for 2009, 264 th Day (September).0 131
7 LST(K) MEAN LST(K) LST(K) MEAN LST(K) International Journal of Computer & Mathematical Sciences LST vs EVI MEAN LST vs EVI y = x +.77 R² = EVI EVI Figure 7: LST vs EVI and Mean LST vs EVI scatterplots of the study area for 2009, Days (September) The scatterplots between LST vs relationship for (2009, 264 th day) and (2009, ( days)) are shown in figure 8 and 9 respectively. The same regression analysis which has been used in above two relations is applied to find the relationship between LST and of the study area for the two periods. LST v/s scatterplots show an irregular and compacted pattern and a rising trend can be observed. The analysis in previous case showed negative trend but here it has been found showing a positive correlation between LST and which means that built-up areas can strengthen the effect of UHI. Whereas the higher vegetation covers in rural areas show relatively lower values of. The built up areas like roads, buildings, industries etc. have more imperviousness than the rural areas. Thus it can be deduced that has a direct relationship with the imperviousness of the surface. The trendlines of scatterplots show linear and positive correlation between LST and. Figures 8 and 9 show a linear and positive relationship between mean LST and along with the coefficient of correlation (R 2 ) for the linear relationship. The R 2 value for 2009, 264 th Day (September) is 4 and for 2009, Days (September) is 96, shows that one day analysis gives better result i.e. higher the R 2 value better is the result. The reason behind the better result for one day is over eight day period is that eight day period gives the average effect of land surface temperature over the study area. LST vs MEAN LST vs y = x +.27 R² =
8 NDVI LST(K) MEAN LST(K) International Journal of Computer & Mathematical Sciences Figure 8: LST vs and Mean LST vs scatterplots of the study area for 2009, 264 th Day (September) LST vs MEAN LST vs y = x +.47 R² = Figure 9: LST vs and Mean LST vs scatterplots of the study area for 2009, Days (September) The figures 10 and 11, shows a strong negative relationship between vegetation indices and, which means that higher the vegetation cover, lower will be the value and thus weakens the UHI effect. The figures also show the 3-D scatter plots relationship of LST vs. vs. NDVI and LST vs. vs. NDVI, respectively. NDVI vs LST vs vs NDVI LST(K) NDVI Figure 10: NDVI vs and Mean LST vs vs NDVI scatterplots of the study area for 2009, 264 th Day(September) 133
9 EVI International Journal of Computer & Mathematical Sciences EVI vs LST vs vs EVI LST(K) 0.8 EVI Figure 11: EVI vs and Mean LST vs vs EVI scatterplots of the study area for 2009, Days (September) 4. Conclusion In the present study, Landsat TM and MODIS data have been used for the derivation of four parameters i.e. LST, NDVI, EVI and for Ahmedabad city. The present paper investigated individual relationships of LST with the three parameters NDVI, EVI and. It has been concluded that most of the hotter pixels are located in the built up areas of Ahmedabad city whereas rural areas have lower LST pixels because of the presence of dense vegetation cover. The built-up areas and human activities show high Land Surface Temperature compared to green vegetation cover areas. There is a negative correlation of LST with NDVI and EVI which means that green spaces can reduce the effect of UHI and positive correlation between LST and which means that built-up areas can strengthen the effect of UHI. That is urban areas show smaller NDVI and EVI values and higher values compared to rural areas and there is a strong negative relationship between NDVI and EVI with in the study area. From the results, it has been concluded that rapid urbanization and urban sprawling contributes the major changes in the Land Surface Temperature. Therefore built-up areas like residential, commercial and industrial mainly account for UHI effect. References [1] I Douglas. The case for urban ecology. Urban Nat. Mag. 1992; 1, [2]UNFPA (2007). The state of world population 2007: Unleashing the potential of urban growth. United Nations Population Fund, United Nations Publications 1 pp. [3] HA Choi, WK Lee and WH Byun. Determining the effect of green spaces on urban heat distribution using satellite imagery. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2012; 6, [4] OR García-Cueto, AT Martínez and GB Morales. Urbanization effects upon the air temperature in Mexicali, B.C., México. Atmósfera 2009; 22, [5] KS Kumar, PU Bhaskar and K Padmakumari. Estimation of land surface temperature to study urban heat island effect using landsat ETM+image. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Tech. 2012; 4, [6] Nichol, J. (1996). High-resolution surface temperature patterns related to urban morphology in a tropical city: a satellite-based study. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 35(1), [7] Streutker, D. R. (2002). A remote sensing study of urban heat island of Houston, Texas. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 23(13),
10 [8]Huang, S.; Taniguchi, M.; Yamano, M.; Wang, C. Detecting urbanization effects on surface and subsurface thermal environment A case study of Osaka. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, [9]Voogt, J.A.; Oke, T.R. Thermal remote sensing of urban climates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, [10]Singh, R.B., Global Environmental Change: Perspectives of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System. Balkema Publishers, Rotterdam. [11]Weng, Q., A remote sensing-gis evaluation of urban expansion and its impact on surface temperature in the Zhujiang Delta, China. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22(10), [12]Gallo, K. P., McNab, A. L., Karl, T. R., Brown, J. F., Hood, J. J., & Tarpley, J. D. (1993). The use of NOAA AVHRR data for assessment of the Urban Heat Island effect. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 32(5), [13]Gallo, K. P., & Owen, T. W. (1999). Satellite-based adjustments for the urban heat island temperature bias. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 38, [14] Weng, Q., Dengsheng, L., & Jacquelyn, S. (2004). Estimation of land surface temperature vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sensing of Environment, 89, [15]NASA, Landsat 7 Science Data Users Handbook. (accessed 25 Feb. 2008). [16]Chander, G., & Markham, B. (2003). Revised Landsat-5 TM radiometric calibration procedures and postcalibration dynamic ranges. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 41(11), [17]KS Kumar, PU Bhaskar and K Padmakumari. Estimation of land surface temperature to study urban heat island effect using landsat ETM+image. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Tech. 2012; 4, [18] TS Purevdorj, R Tateishi, T Ishiyama and Y Honda. Relationships between percent vegetation cover and vegetation indices. Int. J. Rem. Sens. 1998; 19, [19] CY Sun, HT Lin and WS Ou. The relationship between urban greening and thermal environment. In: Proceeding of Urban Remote Sensing Joint Event, Paris, France. 2007, p [20] L Liu and Y Zhang. Urban heat island analysis using the landsat TM data and ASTER data: A case study in Hong Kong. Rem. Sens. 2011; 3,
Study of Land Surface Temperature Variations with Distance from Hot Spots for Urban Heat Island Analysis
 Study of Land Surface Temperature Variations with Distance from Hot Spots for Urban Heat Island Analysis Khandelwal, Sumit 1*, Goyal, Rohit 2, Kaul, Nivedita 1 and Singhal, Vijai 3 ABSTRACT Vegetation
Study of Land Surface Temperature Variations with Distance from Hot Spots for Urban Heat Island Analysis Khandelwal, Sumit 1*, Goyal, Rohit 2, Kaul, Nivedita 1 and Singhal, Vijai 3 ABSTRACT Vegetation
Analysis of Relative Importance of Parameters Representing Vegetation, Urbanization and Elevation with Land Surface Temperature using ANN
 Analysis of Relative Importance of Parameters Representing Vegetation, Urbanization and Elevation with Land Surface Temperature using ANN Goyal, Rohit 1, Khandelwal, Sumit 2 and Kaul, Nivedita 2 ABSTRACT
Analysis of Relative Importance of Parameters Representing Vegetation, Urbanization and Elevation with Land Surface Temperature using ANN Goyal, Rohit 1, Khandelwal, Sumit 2 and Kaul, Nivedita 2 ABSTRACT
Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite Multitemporal Data over Abeokuta, Nigeria
 International Atmospheric Sciences Volume 2016, Article ID 3170789, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3170789 Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite
International Atmospheric Sciences Volume 2016, Article ID 3170789, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3170789 Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite
Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island
 Chuanxin Zhu Professor Peter V. August Professor Yeqiao Wang NRS 509 December 15, 2016 Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island Since the last century, the global mean surface
Chuanxin Zhu Professor Peter V. August Professor Yeqiao Wang NRS 509 December 15, 2016 Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island Since the last century, the global mean surface
1. Introduction. Chaithanya, V.V. 1, Binoy, B.V. 2, Vinod, T.R. 2. Publication Date: 8 April DOI: https://doi.org/ /cloud.ijarsg.
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2017, Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 2088-2096 ISSN 2320 0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.112 Research Article Open Access Estimation
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2017, Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 2088-2096 ISSN 2320 0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.112 Research Article Open Access Estimation
GIS GIS ETM+
 GIS 1388 Vol.1, No.1, Spring 2009 39-56 GIS Iranian Remote Sensing & GIS ETM+ *4 3 2 1 GIS -1-2 -3 GIS -4 88/8/9 : 88/4/30 :.. ). (.... ( ). ETM+. (LSU)...V_I_S : Email: soodabeh_namdari@yahoo.com 22431788
GIS 1388 Vol.1, No.1, Spring 2009 39-56 GIS Iranian Remote Sensing & GIS ETM+ *4 3 2 1 GIS -1-2 -3 GIS -4 88/8/9 : 88/4/30 :.. ). (.... ( ). ETM+. (LSU)...V_I_S : Email: soodabeh_namdari@yahoo.com 22431788
COMPARASION OF NDBI AND NDVI AS INDICATORS OF SURFACE URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT IN LANDSAT 8 IMAGERY: A CASE STUDY OF IASI
 DOI 10.1515/pesd-2017-0032 PESD, VOL. 11, no. 2, 2017 COMPARASION OF NDBI AND NDVI AS INDICATORS OF SURFACE URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT IN LANDSAT 8 IMAGERY: A CASE STUDY OF IASI Paul Macarof 1, Florian Statescu
DOI 10.1515/pesd-2017-0032 PESD, VOL. 11, no. 2, 2017 COMPARASION OF NDBI AND NDVI AS INDICATORS OF SURFACE URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT IN LANDSAT 8 IMAGERY: A CASE STUDY OF IASI Paul Macarof 1, Florian Statescu
Spatial Geotechnologies and GIS tools for urban planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115.
 planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115. Fig.1 The city of Caracas, as many others Latin-American cities, has experimented a fast growth in
planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115. Fig.1 The city of Caracas, as many others Latin-American cities, has experimented a fast growth in
Critical review of the Climate Change Impact on urban areas by assessment of Heat Island effect
 Critical review of the Climate Change Impact on urban areas by assessment of Heat Island effect Case of Pune, India Town Planning, Civil Department Prof. Omkar Parishwad, ogp.civil@coep.ac.in Climate Change
Critical review of the Climate Change Impact on urban areas by assessment of Heat Island effect Case of Pune, India Town Planning, Civil Department Prof. Omkar Parishwad, ogp.civil@coep.ac.in Climate Change
Remote sensing Based Assessment of Urban Heat Island Phenomenon in Nagpur Metropolitan Area
 International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 11 (2014), pp. 1069-1074 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com Remote sensing
International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 11 (2014), pp. 1069-1074 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com Remote sensing
Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity
 Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity Isabel C. Perez Hoyos NOAA Crest, City College of New York, CUNY, 160 Convent Avenue,
Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity Isabel C. Perez Hoyos NOAA Crest, City College of New York, CUNY, 160 Convent Avenue,
Mario Flores, Graduate Student Department of Applied Mathematics, UTSA. EES 5053: Remote Sensing
 Mario Flores, Graduate Student Department of Applied Mathematics, UTSA Miguel Balderas, E.I.T., Graduate Student Department of Civil/Environmental Engineering, UTSA EES 5053: Remote Sensing REMOTE SENSING
Mario Flores, Graduate Student Department of Applied Mathematics, UTSA Miguel Balderas, E.I.T., Graduate Student Department of Civil/Environmental Engineering, UTSA EES 5053: Remote Sensing REMOTE SENSING
MAPPING LAND USE/ LAND COVER OF WEST GODAVARI DISTRICT USING NDVI TECHNIQUES AND GIS Anusha. B 1, Sridhar. P 2
 MAPPING LAND USE/ LAND COVER OF WEST GODAVARI DISTRICT USING NDVI TECHNIQUES AND GIS Anusha. B 1, Sridhar. P 2 1 M. Tech. Student, Department of Geoinformatics, SVECW, Bhimavaram, A.P, India 2 Assistant
MAPPING LAND USE/ LAND COVER OF WEST GODAVARI DISTRICT USING NDVI TECHNIQUES AND GIS Anusha. B 1, Sridhar. P 2 1 M. Tech. Student, Department of Geoinformatics, SVECW, Bhimavaram, A.P, India 2 Assistant
Journal of Asian Scientific Research STUDYING OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGES IN MARSH AREA USING LANDSAT SATELLITE IMAGES
 Journal of Asian Scientific Research journal homepage: http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5003 STUDYING OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGES IN MARSH AREA USING LANDSAT SATELLITE IMAGES Salah A. H. Saleh
Journal of Asian Scientific Research journal homepage: http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5003 STUDYING OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGES IN MARSH AREA USING LANDSAT SATELLITE IMAGES Salah A. H. Saleh
DEPENDENCE OF URBAN TEMPERATURE ELEVATION ON LAND COVER TYPES. Ping CHEN, Soo Chin LIEW and Leong Keong KWOH
 DEPENDENCE OF URBAN TEMPERATURE ELEVATION ON LAND COVER TYPES Ping CHEN, Soo Chin LIEW and Leong Keong KWOH Centre for Remote Imaging, Sensing and Processing, National University of Singapore, Lower Kent
DEPENDENCE OF URBAN TEMPERATURE ELEVATION ON LAND COVER TYPES Ping CHEN, Soo Chin LIEW and Leong Keong KWOH Centre for Remote Imaging, Sensing and Processing, National University of Singapore, Lower Kent
Lech GAWUC, Joanna STRUZEWSKA. Meteorology Division Faculty of Environmental Engineering Warsaw University of Technology Warsaw, Poland
 Analysis of the impact of different temporal aggregation techniques of land surface temperature on SUHI indicators and the relationship of surface temperature with population density and night lighting
Analysis of the impact of different temporal aggregation techniques of land surface temperature on SUHI indicators and the relationship of surface temperature with population density and night lighting
VISUALIZATION URBAN SPATIAL GROWTH OF DESERT CITIES FROM SATELLITE IMAGERY: A PRELIMINARY STUDY
 CO-439 VISUALIZATION URBAN SPATIAL GROWTH OF DESERT CITIES FROM SATELLITE IMAGERY: A PRELIMINARY STUDY YANG X. Florida State University, TALLAHASSEE, FLORIDA, UNITED STATES ABSTRACT Desert cities, particularly
CO-439 VISUALIZATION URBAN SPATIAL GROWTH OF DESERT CITIES FROM SATELLITE IMAGERY: A PRELIMINARY STUDY YANG X. Florida State University, TALLAHASSEE, FLORIDA, UNITED STATES ABSTRACT Desert cities, particularly
Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai
 Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai K. Ilayaraja Department of Civil Engineering BIST, Bharath University Selaiyur, Chennai 73 ABSTRACT The synoptic picture
Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai K. Ilayaraja Department of Civil Engineering BIST, Bharath University Selaiyur, Chennai 73 ABSTRACT The synoptic picture
Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach
 Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach Dr.Gowri 1 Dr.Thirumalaivasan 2 1 Associate Professor, Jerusalem College of Engineering, Department of Civil
Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach Dr.Gowri 1 Dr.Thirumalaivasan 2 1 Associate Professor, Jerusalem College of Engineering, Department of Civil
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Spatio-Temporal changes of Land
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Spatio-Temporal changes of Land
dated : 1 July Introduction
 Analysis of the impact of different temporal aggregation techniques of land surface temperature on SUHI indicators and the relationship of surface temperature with population density and night lighting
Analysis of the impact of different temporal aggregation techniques of land surface temperature on SUHI indicators and the relationship of surface temperature with population density and night lighting
Aniekan Eyoh 1* Department of Geoinformatics & Surveying, Faculty of Environmental Studies, University of Uyo, Nigeria
 Available online at http://euroasiapub.org/journals.php, pp. 53~62 Thomson Reuters Researcher ID: L-5236-2015 TEMPORAL APPRAISAL OF LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE DYNAMICS ACROSS THE NINE STATES OF NIGER DELTA
Available online at http://euroasiapub.org/journals.php, pp. 53~62 Thomson Reuters Researcher ID: L-5236-2015 TEMPORAL APPRAISAL OF LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE DYNAMICS ACROSS THE NINE STATES OF NIGER DELTA
EVALUATION OF URBANIZATION INFLUENCES ON URBAN CLIMATE WITH REMOTE SENSING AND CLIMATE OBSERVATIONS. George Xian 1 and Mike Crane 2.
 EVALUATION OF URBANIZATION INFLUENCES ON URBAN CLIMATE WITH REMOTE SENSING AND CLIMATE OBSERVATIONS George Xian 1 and Mike Crane 2 1 SAIC/ 2 USGS National Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science,
EVALUATION OF URBANIZATION INFLUENCES ON URBAN CLIMATE WITH REMOTE SENSING AND CLIMATE OBSERVATIONS George Xian 1 and Mike Crane 2 1 SAIC/ 2 USGS National Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science,
Evaluation of Land Surface Temperature and Vegetation Relation Based on Landsat TM5 Data
 SCIREA Journal of Geosciences http://www.scirea.org/journal/geosciences October 15, 2016 Volume 1, Issue1, October 2016 Evaluation of Land Surface Temperature and Vegetation Relation Based on Landsat TM5
SCIREA Journal of Geosciences http://www.scirea.org/journal/geosciences October 15, 2016 Volume 1, Issue1, October 2016 Evaluation of Land Surface Temperature and Vegetation Relation Based on Landsat TM5
The footprint of urban heat island effect in China
 A discussion on the paper The footprint of urban heat island effect in China By Decheng Zhou, Shuqing Zhao, Liangxia Zhang, Ge Sun & Yongqiang Liu Published in SCIENCE REPORRTS Reporter: Mu Qingchen 2015.10.23
A discussion on the paper The footprint of urban heat island effect in China By Decheng Zhou, Shuqing Zhao, Liangxia Zhang, Ge Sun & Yongqiang Liu Published in SCIENCE REPORRTS Reporter: Mu Qingchen 2015.10.23
Influence of Micro-Climate Parameters on Natural Vegetation A Study on Orkhon and Selenge Basins, Mongolia, Using Landsat-TM and NOAA-AVHRR Data
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2013, Volume 2, Issue 1, pp. 160-172, Article ID Tech-102 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access Influence of Micro-Climate
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2013, Volume 2, Issue 1, pp. 160-172, Article ID Tech-102 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access Influence of Micro-Climate
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December-2013 ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December-2013 144 Assessment of Seasonal Variation of Land Surface Temperature (LST) in an Urban Area Arun Mondal1, Deepak
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December-2013 144 Assessment of Seasonal Variation of Land Surface Temperature (LST) in an Urban Area Arun Mondal1, Deepak
Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction in Tabriz
 Int. J. Environ. Res. 1 (1): 35-41, Winter 2007 ISSN:1735-6865 Graduate Faculty of Environment University of Tehran Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction
Int. J. Environ. Res. 1 (1): 35-41, Winter 2007 ISSN:1735-6865 Graduate Faculty of Environment University of Tehran Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction
THE USE OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES FOR URBAN CLIMATE ANALYSIS: A CASE STUDY OF ABU DHABI CITY AREA
 THE USE OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES FOR URBAN CLIMATE ANALYSIS: A CASE STUDY OF ABU DHABI CITY AREA Michele Lazzarini, Jacinto Estima, Prashanth Reddy Marpu, Hosni Ghedira Earth Observation
THE USE OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES FOR URBAN CLIMATE ANALYSIS: A CASE STUDY OF ABU DHABI CITY AREA Michele Lazzarini, Jacinto Estima, Prashanth Reddy Marpu, Hosni Ghedira Earth Observation
URBAN SPRAWL AND SPATIO TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF HISAR CITY IN HARYANA USING REMOTE SENSING & GIS TECNOLOGY
 URBAN SPRAWL AND SPATIO TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF HISAR CITY IN HARYANA USING REMOTE SENSING & GIS TECNOLOGY Shashikant 1, Pallavi Singh 2, R. D. Doi 3, Ankur Sharma 4, Ravinder Kumar 5, Parveen Bhatti 6 Abstract
URBAN SPRAWL AND SPATIO TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF HISAR CITY IN HARYANA USING REMOTE SENSING & GIS TECNOLOGY Shashikant 1, Pallavi Singh 2, R. D. Doi 3, Ankur Sharma 4, Ravinder Kumar 5, Parveen Bhatti 6 Abstract
Defining microclimates on Long Island using interannual surface temperature records from satellite imagery
 Defining microclimates on Long Island using interannual surface temperature records from satellite imagery Deanne Rogers*, Katherine Schwarting, and Gilbert Hanson Dept. of Geosciences, Stony Brook University,
Defining microclimates on Long Island using interannual surface temperature records from satellite imagery Deanne Rogers*, Katherine Schwarting, and Gilbert Hanson Dept. of Geosciences, Stony Brook University,
COMPARISON OF NOAA/AVHRR AND LANDSAT/TM DATA IN TERMS OF RESEARCH APPLICATIONS ON THERMAL CONDITIONS IN URBAN AREAS
 COMPARISON OF NOAA/AVHRR AND LANDSAT/TM DATA IN TERMS OF RESEARCH APPLICATIONS ON THERMAL CONDITIONS IN URBAN AREAS Monika J. Hajto 1 *, Jakub P. Walawender 2,3 and Piotr Struzik 2 1 Department of Air
COMPARISON OF NOAA/AVHRR AND LANDSAT/TM DATA IN TERMS OF RESEARCH APPLICATIONS ON THERMAL CONDITIONS IN URBAN AREAS Monika J. Hajto 1 *, Jakub P. Walawender 2,3 and Piotr Struzik 2 1 Department of Air
Monitoring Vegetation Growth of Spectrally Landsat Satellite Imagery ETM+ 7 & TM 5 for Western Region of Iraq by Using Remote Sensing Techniques.
 Monitoring Vegetation Growth of Spectrally Landsat Satellite Imagery ETM+ 7 & TM 5 for Western Region of Iraq by Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Fouad K. Mashee, Ahmed A. Zaeen & Gheidaa S. Hadi Remote
Monitoring Vegetation Growth of Spectrally Landsat Satellite Imagery ETM+ 7 & TM 5 for Western Region of Iraq by Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Fouad K. Mashee, Ahmed A. Zaeen & Gheidaa S. Hadi Remote
Spatial Drought Assessment Using Remote Sensing and GIS techniques in Northwest region of Liaoning, China
 Spatial Drought Assessment Using Remote Sensing and GIS techniques in Northwest region of Liaoning, China FUJUN SUN, MENG-LUNG LIN, CHENG-HWANG PERNG, QIUBING WANG, YI-CHIANG SHIU & CHIUNG-HSU LIU Department
Spatial Drought Assessment Using Remote Sensing and GIS techniques in Northwest region of Liaoning, China FUJUN SUN, MENG-LUNG LIN, CHENG-HWANG PERNG, QIUBING WANG, YI-CHIANG SHIU & CHIUNG-HSU LIU Department
[Sakthivel *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor
![[Sakthivel *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor [Sakthivel *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor](/thumbs/91/106248739.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES URBAN HEAT ISLAND (UHI) ANALYSIS USING GEO-SPATIAL TECHNOLOGY IN PUNE CITY, MAHARASHTRA Dr. M. Sakthivel* 1, Dr. M. H. Kalubarme 2, Gaikwad Vishal Vilas
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES URBAN HEAT ISLAND (UHI) ANALYSIS USING GEO-SPATIAL TECHNOLOGY IN PUNE CITY, MAHARASHTRA Dr. M. Sakthivel* 1, Dr. M. H. Kalubarme 2, Gaikwad Vishal Vilas
ISO MODIS NDVI Weekly Composites for Canada South of 60 N Data Product Specification
 ISO 19131 MODIS NDVI Weekly Composites for South of 60 N Data Product Specification Revision: A Data specification: MODIS NDVI Composites for South of 60 N - Table of Contents - 1. OVERVIEW... 3 1.1. Informal
ISO 19131 MODIS NDVI Weekly Composites for South of 60 N Data Product Specification Revision: A Data specification: MODIS NDVI Composites for South of 60 N - Table of Contents - 1. OVERVIEW... 3 1.1. Informal
MONITORING THE SURFACE HEAT ISLAND (SHI) EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES
 MONITORING THE SURFACE HEAT ISLAND (SHI) EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES A. Şekertekin a, *, Ş. H. Kutoglu a, S. Kaya b, A. M. Marangoz a a BEU, Engineering Faculty, Geomatics Engineering Department
MONITORING THE SURFACE HEAT ISLAND (SHI) EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES A. Şekertekin a, *, Ş. H. Kutoglu a, S. Kaya b, A. M. Marangoz a a BEU, Engineering Faculty, Geomatics Engineering Department
Abstract: Introduction: 10 th ESRI India User Conference 2009 Geography in Action
 Mitigation of Thermal Pollution to enhance urban air quality through Remote Sensing and GIS Anshu Gupta, Lecturer, Centre of Remote Sensing and GIS, MANIT, Bhopal, E- mail: anshugupta20002001@gmail.com
Mitigation of Thermal Pollution to enhance urban air quality through Remote Sensing and GIS Anshu Gupta, Lecturer, Centre of Remote Sensing and GIS, MANIT, Bhopal, E- mail: anshugupta20002001@gmail.com
Investigation of the Effect of Transportation Network on Urban Growth by Using Satellite Images and Geographic Information Systems
 Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Investigation of the Effect of Transportation Network on Urban Growth by Using Satellite Images and Geographic Information Systems
Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Investigation of the Effect of Transportation Network on Urban Growth by Using Satellite Images and Geographic Information Systems
Results of the ESA-DUE UHI project
 13/12/2011 Results of the ESA-DUE UHI project Bino Maiheu (bino.maiheu@vito.be), on behalf of the UHI project Outline» Urban heat island problem» The ESA-DUE urban heat island project» UHI air temperature
13/12/2011 Results of the ESA-DUE UHI project Bino Maiheu (bino.maiheu@vito.be), on behalf of the UHI project Outline» Urban heat island problem» The ESA-DUE urban heat island project» UHI air temperature
AssessmentofUrbanHeatIslandUHIusingRemoteSensingandGIS
 Global Journal of HUMANSOCIAL SCIENCE: B Geography, GeoSciences, Environmental Science & Disaster Management Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal
Global Journal of HUMANSOCIAL SCIENCE: B Geography, GeoSciences, Environmental Science & Disaster Management Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. Ecological restoration and its effects on the
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Ecological restoration and its effects on the regional climate: the case in the source region of the Yellow River, China Zhouyuan Li, Xuehua Liu,* Tianlin Niu, De Kejia, Qingping
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Ecological restoration and its effects on the regional climate: the case in the source region of the Yellow River, China Zhouyuan Li, Xuehua Liu,* Tianlin Niu, De Kejia, Qingping
APPLICATION OF LAND CHANGE MODELER FOR PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER A CASE STUDY OF VIJAYAWADA CITY
 APPLICATION OF LAND CHANGE MODELER FOR PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER A CASE STUDY OF VIJAYAWADA CITY K. Sundara Kumar 1, Dr. P. Udaya Bhaskar 2, Dr. K. Padmakumari 3 1 Research Scholar, 2,3
APPLICATION OF LAND CHANGE MODELER FOR PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER A CASE STUDY OF VIJAYAWADA CITY K. Sundara Kumar 1, Dr. P. Udaya Bhaskar 2, Dr. K. Padmakumari 3 1 Research Scholar, 2,3
GIS.
 GIS 389 Vol., No.3, Autumn 00 89-0 GIS Iranian Remote Sensing & GIS ( : ) ETM+ *.. 390/3/7 : 389/5/3 : (LST).. 00 3 ETM+.. MNF NDVI. SEBAL. FVC NDVI... (FVC) SEBAL (LULC) (LST) :. 887708 : : * Email: taleai@kntu.ac.ir
GIS 389 Vol., No.3, Autumn 00 89-0 GIS Iranian Remote Sensing & GIS ( : ) ETM+ *.. 390/3/7 : 389/5/3 : (LST).. 00 3 ETM+.. MNF NDVI. SEBAL. FVC NDVI... (FVC) SEBAL (LULC) (LST) :. 887708 : : * Email: taleai@kntu.ac.ir
PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER CHANGES OF VIJAYAWADA CITY USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS
 PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER CHANGES OF VIJAYAWADA CITY USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS K. Sundara Kumar 1 *, N V A Sai Sankar Valasala 2, J V Subrahmanyam V 3, Mounika Mallampati 4 Kowsharajaha
PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER CHANGES OF VIJAYAWADA CITY USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS K. Sundara Kumar 1 *, N V A Sai Sankar Valasala 2, J V Subrahmanyam V 3, Mounika Mallampati 4 Kowsharajaha
Greening of Arctic: Knowledge and Uncertainties
 Greening of Arctic: Knowledge and Uncertainties Jiong Jia, Hesong Wang Chinese Academy of Science jiong@tea.ac.cn Howie Epstein Skip Walker Moscow, January 28, 2008 Global Warming and Its Impact IMPACTS
Greening of Arctic: Knowledge and Uncertainties Jiong Jia, Hesong Wang Chinese Academy of Science jiong@tea.ac.cn Howie Epstein Skip Walker Moscow, January 28, 2008 Global Warming and Its Impact IMPACTS
Evaluation of SEBAL Model for Evapotranspiration Mapping in Iraq Using Remote Sensing and GIS
 Evaluation of SEBAL Model for Evapotranspiration Mapping in Iraq Using Remote Sensing and GIS Hussein Sabah Jaber* Department of Civil Engineering, University Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor,
Evaluation of SEBAL Model for Evapotranspiration Mapping in Iraq Using Remote Sensing and GIS Hussein Sabah Jaber* Department of Civil Engineering, University Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor,
CORRELATION BETWEEN URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT AND THE THERMAL INERTIA USING ASTER DATA IN BEIJING, CHINA
 CORRELATION BETWEEN URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT AND THE THERMAL INERTIA USING ASTER DATA IN BEIJING, CHINA Yurong CHEN a, *, Mingyi DU a, Rentao DONG b a School of Geomatics and Urban Information, Beijing
CORRELATION BETWEEN URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT AND THE THERMAL INERTIA USING ASTER DATA IN BEIJING, CHINA Yurong CHEN a, *, Mingyi DU a, Rentao DONG b a School of Geomatics and Urban Information, Beijing
Comparison of MSG-SEVIRI and SPOT-VEGETATION data for vegetation monitoring over Africa
 Comparison of MSG-SEVIRI and SPOT-VEGETATION data for vegetation monitoring over Africa Bernard LACAZE CNRS UMR 8586 PRODIG Pôle Image et Campus Spatial, Université Paris Diderot Paris 7 Objectives Comparison
Comparison of MSG-SEVIRI and SPOT-VEGETATION data for vegetation monitoring over Africa Bernard LACAZE CNRS UMR 8586 PRODIG Pôle Image et Campus Spatial, Université Paris Diderot Paris 7 Objectives Comparison
Spatio-Temporal Trends of Urban Heat Island and Surface Temperature in Izmir, Turkey
 American Journal of Remote Sensing 2017; 5(3): 24-29 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajrs doi: 0.11648/j.ajrs.20170503.11 ISSN: 2328-5788 (Print); ISSN: 2328-580X (Online) Spatio-Temporal Trends
American Journal of Remote Sensing 2017; 5(3): 24-29 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajrs doi: 0.11648/j.ajrs.20170503.11 ISSN: 2328-5788 (Print); ISSN: 2328-580X (Online) Spatio-Temporal Trends
Seasonal and interannual relations between precipitation, soil moisture and vegetation in the North American monsoon region
 Seasonal and interannual relations between precipitation, soil moisture and vegetation in the North American monsoon region Luis A. Mendez-Barroso 1, Enrique R. Vivoni 1, Christopher J. Watts 2 and Julio
Seasonal and interannual relations between precipitation, soil moisture and vegetation in the North American monsoon region Luis A. Mendez-Barroso 1, Enrique R. Vivoni 1, Christopher J. Watts 2 and Julio
Coastal Water Quality Monitoring in Cyprus using Satellite Remote Sensing
 Coastal Water Quality Monitoring in Cyprus using Satellite Remote Sensing D. G. Hadjimitsis 1*, M.G. Hadjimitsis 1, 2, A. Agapiou 1, G. Papadavid 1 and K. Themistocleous 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering
Coastal Water Quality Monitoring in Cyprus using Satellite Remote Sensing D. G. Hadjimitsis 1*, M.G. Hadjimitsis 1, 2, A. Agapiou 1, G. Papadavid 1 and K. Themistocleous 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering
Evaluation of a MODIS Triangle-based Algorithm for Improving ET Estimates in the Northern Sierra Nevada Mountain Range
 Evaluation of a MODIS Triangle-based Algorithm for Improving ET Estimates in the Northern Sierra Nevada Mountain Range Kyle R. Knipper 1, Alicia M. Kinoshita 2, and Terri S. Hogue 1 January 5 th, 2015
Evaluation of a MODIS Triangle-based Algorithm for Improving ET Estimates in the Northern Sierra Nevada Mountain Range Kyle R. Knipper 1, Alicia M. Kinoshita 2, and Terri S. Hogue 1 January 5 th, 2015
ESTIMATING TEMPORAL LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE USING REMOTE SENSING: A STUDY OF VADODARA URBAN AREA, GUJARAT
 ESTIMATING TEMPORAL LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE USING REMOTE SENSING: A STUDY OF VADODARA URBAN AREA, GUJARAT Janak P. Joshi and *Bindu Bhatt Department of Geography, Faculty of Science, the Maharaja Sayajirao
ESTIMATING TEMPORAL LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE USING REMOTE SENSING: A STUDY OF VADODARA URBAN AREA, GUJARAT Janak P. Joshi and *Bindu Bhatt Department of Geography, Faculty of Science, the Maharaja Sayajirao
Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl
 Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl Jason Parent jason.parent@uconn.edu Academic Assistant GIS Analyst Daniel Civco Professor of Geomatics Center for Land Use Education
Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl Jason Parent jason.parent@uconn.edu Academic Assistant GIS Analyst Daniel Civco Professor of Geomatics Center for Land Use Education
Spatio-temporal dynamics of the urban fringe landscapes
 Spatio-temporal dynamics of the urban fringe landscapes Yulia Grinblat 1, 2 1 The Porter School of Environmental Studies, Tel Aviv University 2 Department of Geography and Human Environment, Tel Aviv University
Spatio-temporal dynamics of the urban fringe landscapes Yulia Grinblat 1, 2 1 The Porter School of Environmental Studies, Tel Aviv University 2 Department of Geography and Human Environment, Tel Aviv University
Comparison of MLC and FCM Techniques with Satellite Imagery in A Part of Narmada River Basin of Madhya Pradesh, India
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 013, Volume, Issue 1, pp. 130-137, Article ID Tech-96 ISS 30-043 Research Article Open Access Comparison of MLC and FCM Techniques
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 013, Volume, Issue 1, pp. 130-137, Article ID Tech-96 ISS 30-043 Research Article Open Access Comparison of MLC and FCM Techniques
Projecting Urban Land Cover on the basis of Population
 Projecting Urban Land Cover on the basis of Population Dan Miller Runfola Postdoctoral Researcher National Center for Atmospheric Research CGD & RAL CU:Boulder Institute of Behavioral Science 1 The Challenge
Projecting Urban Land Cover on the basis of Population Dan Miller Runfola Postdoctoral Researcher National Center for Atmospheric Research CGD & RAL CU:Boulder Institute of Behavioral Science 1 The Challenge
Dynamical Monitoring and Evaluation Methods to Urban Heat Island Effects Based on RS&GIS
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 10 (2011 ) 1228 1237 Procedia 2011 Environmental 3rd International Sciences 00 Conference (2011) 000 000 on Environmental Science
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 10 (2011 ) 1228 1237 Procedia 2011 Environmental 3rd International Sciences 00 Conference (2011) 000 000 on Environmental Science
MODIS-BASED INVESTIGATIONS ON THE URBAN HEAT ISLANDS OF BUCHAREST (ROMANIA) AND PRAGUE (CZECH REPUBLIC)
 MODIS-BASED INVESTIGATIONS ON THE URBAN HEAT ISLANDS OF BUCHAREST (ROMANIA) AND PRAGUE (CZECH REPUBLIC) Sorin Cheval*, Michal Žák***, Alexandru Dumitrescu*, Vít Květoň** *National Meteorological Administration,
MODIS-BASED INVESTIGATIONS ON THE URBAN HEAT ISLANDS OF BUCHAREST (ROMANIA) AND PRAGUE (CZECH REPUBLIC) Sorin Cheval*, Michal Žák***, Alexandru Dumitrescu*, Vít Květoň** *National Meteorological Administration,
Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region
 Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region ZhangZhen 2015.07.10 1 Outline Introduction Data
Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment Interannual variation of MODIS NDVI in Lake Taihu and its relation to climate in submerged macrophyte region ZhangZhen 2015.07.10 1 Outline Introduction Data
Instruction: proposal to class project
 Instruction: proposal to class project (Hongjie Xie, 10/20/2008) A project proposal is the first step to us to get funding from anywhere. You need to write a proposal to your advisor, your university,
Instruction: proposal to class project (Hongjie Xie, 10/20/2008) A project proposal is the first step to us to get funding from anywhere. You need to write a proposal to your advisor, your university,
Assessing Drought in Agricultural Area of central U.S. with the MODIS sensor
 Assessing Drought in Agricultural Area of central U.S. with the MODIS sensor Di Wu George Mason University Oct 17 th, 2012 Introduction: Drought is one of the major natural hazards which has devastating
Assessing Drought in Agricultural Area of central U.S. with the MODIS sensor Di Wu George Mason University Oct 17 th, 2012 Introduction: Drought is one of the major natural hazards which has devastating
Study of Land Use and Land Cover of Chaksu block, Jaipur through Remote Sensing and GIS
 Study of Land Use and Land Cover of Chaksu block, Jaipur through Remote Sensing and GIS Ruchi Middha *, Sonal Jain* and Shelja K.Juneja ** *RESEARCH SCHOLAR, ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE, THE IIS UNIVERSITY,
Study of Land Use and Land Cover of Chaksu block, Jaipur through Remote Sensing and GIS Ruchi Middha *, Sonal Jain* and Shelja K.Juneja ** *RESEARCH SCHOLAR, ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE, THE IIS UNIVERSITY,
An Assessment of Urban Heat Island of Lokoja Town and Surroundings Using Landsat ETM data.
 Kogi State University, Anyigba From the SelectedWorks of Olarewaju Oluseyi Ifatimehin July, 2007 An Assessment of Urban Heat Island of Lokoja Town and Surroundings Using Landsat ETM data. Olarewaju Oluseyi
Kogi State University, Anyigba From the SelectedWorks of Olarewaju Oluseyi Ifatimehin July, 2007 An Assessment of Urban Heat Island of Lokoja Town and Surroundings Using Landsat ETM data. Olarewaju Oluseyi
SPATIO-TEMPORAL ASSESSMENT OF LAND USE/ LAND COVER DYNAMICS AND URBAN HEAT ISLAND OF JAIPUR CITY USING SATELLITE DATA
 SPATIO-TEMPORAL ASSESSMENT OF LAND USE/ LAND COVER DYNAMICS AND URBAN HEAT ISLAND OF JAIPUR CITY USING SATELLITE DATA Seema Jalan a, Kavita Sharma b, * a Department of Geography, Mohanlal Sukhadia University,
SPATIO-TEMPORAL ASSESSMENT OF LAND USE/ LAND COVER DYNAMICS AND URBAN HEAT ISLAND OF JAIPUR CITY USING SATELLITE DATA Seema Jalan a, Kavita Sharma b, * a Department of Geography, Mohanlal Sukhadia University,
GLOBAL/CONTINENTAL LAND COVER MAPPING AND MONITORING
 GLOBAL/CONTINENTAL LAND COVER MAPPING AND MONITORING Ryutaro Tateishi, Cheng Gang Wen, and Jong-Geol Park Center for Environmental Remote Sensing (CEReS), Chiba University 1-33 Yayoi-cho Inage-ku Chiba
GLOBAL/CONTINENTAL LAND COVER MAPPING AND MONITORING Ryutaro Tateishi, Cheng Gang Wen, and Jong-Geol Park Center for Environmental Remote Sensing (CEReS), Chiba University 1-33 Yayoi-cho Inage-ku Chiba
An Approach to analyse Drought occurrences using Geospatial Techniques
 An Approach to analyse Drought occurrences using Geospatial Techniques Shuchi Mala 1, Mahesh Kumar Jat 2, Parul Pradhan 3 1 Research Scholar, Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur 2 Associate
An Approach to analyse Drought occurrences using Geospatial Techniques Shuchi Mala 1, Mahesh Kumar Jat 2, Parul Pradhan 3 1 Research Scholar, Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur 2 Associate
METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION DATA FOR ASSESSMENT OF SURFACE MOISTURE STATUS
 METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION DATA FOR ASSESSMENT OF SURFACE MOISTURE STATUS Simon Stisen (1), Inge Sandholt (1), Rasmus Fensholt (1) (1) Institute of Geography, University of Copenhagen, Oestervoldgade 10,
METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION DATA FOR ASSESSMENT OF SURFACE MOISTURE STATUS Simon Stisen (1), Inge Sandholt (1), Rasmus Fensholt (1) (1) Institute of Geography, University of Copenhagen, Oestervoldgade 10,
Remote Sensing Based Inversion of Gap Fraction for Determination of Leaf Area Index. Alemu Gonsamo 1 and Petri Pellikka 1
 Remote Sensing Based Inversion of Gap Fraction for Determination of Leaf Area Index Alemu Gonsamo and Petri Pellikka Department of Geography, University of Helsinki, P.O. Box, FIN- Helsinki, Finland; +-()--;
Remote Sensing Based Inversion of Gap Fraction for Determination of Leaf Area Index Alemu Gonsamo and Petri Pellikka Department of Geography, University of Helsinki, P.O. Box, FIN- Helsinki, Finland; +-()--;
RESEARCHER ESTIMATION OF EVAPORATION LOSSES FROM LAKE NASSER USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS RASTER CALCULATOR MODEL
 RESEARCHER ESTIMATION OF EVAPORATION LOSSES FROM LAKE NASSER USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS RASTER CALCULATOR MODEL Hala M. Ebaid Researcher, Survey Research Institute, National Water Research Center, E-Mail:hala_sri@yahoo.com
RESEARCHER ESTIMATION OF EVAPORATION LOSSES FROM LAKE NASSER USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS RASTER CALCULATOR MODEL Hala M. Ebaid Researcher, Survey Research Institute, National Water Research Center, E-Mail:hala_sri@yahoo.com
ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data -
 ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data - Shoichi NAKAI 1 and Jaegyu BAE 2 1 Professor, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan.
ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data - Shoichi NAKAI 1 and Jaegyu BAE 2 1 Professor, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan.
ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF A METHODOLOGY TO EVALUATE LAND COVER CHANGE IN THE MEDITERRANEAN BASIN USING MULTITEMPORAL MODIS DATA
 PRESENT ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT, NR. 4, 2010 ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF A METHODOLOGY TO EVALUATE LAND COVER CHANGE IN THE MEDITERRANEAN BASIN USING MULTITEMPORAL MODIS DATA Mara Pilloni
PRESENT ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT, NR. 4, 2010 ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF A METHODOLOGY TO EVALUATE LAND COVER CHANGE IN THE MEDITERRANEAN BASIN USING MULTITEMPORAL MODIS DATA Mara Pilloni
Analysis of Land Use Zoning Regulations and Green Coverage Ratio
 Analysis of Land Use Zoning Regulations and Green Coverage Ratio Masahiro Sotoma* 1, Hiroshi Miyazaki 2, Takashi Kyakuno 3 and Masakazu Moriyama 4 1 Graduate Student, Graduate School of Science and Technology,
Analysis of Land Use Zoning Regulations and Green Coverage Ratio Masahiro Sotoma* 1, Hiroshi Miyazaki 2, Takashi Kyakuno 3 and Masakazu Moriyama 4 1 Graduate Student, Graduate School of Science and Technology,
EXTRACTION OF REMOTE SENSING INFORMATION OF BANANA UNDER SUPPORT OF 3S TECHNOLOGY IN GUANGXI PROVINCE
 EXTRACTION OF REMOTE SENSING INFORMATION OF BANANA UNDER SUPPORT OF 3S TECHNOLOGY IN GUANGXI PROVINCE Xin Yang 1,2,*, Han Sun 1, 2, Zongkun Tan 1, 2, Meihua Ding 1, 2 1 Remote Sensing Application and Test
EXTRACTION OF REMOTE SENSING INFORMATION OF BANANA UNDER SUPPORT OF 3S TECHNOLOGY IN GUANGXI PROVINCE Xin Yang 1,2,*, Han Sun 1, 2, Zongkun Tan 1, 2, Meihua Ding 1, 2 1 Remote Sensing Application and Test
Drought and its effect on vegetation, comparison of NDVI for drought and non-drought years related to Land use classifications
 Drought and its effect on vegetation, comparison of NDVI for drought and non-drought years related to Land use classifications Jabbari *, S., Khajeddin, S. J. Jafari, R, Soltani, S and Riahi, F s.jabbari_62@yahoo.com
Drought and its effect on vegetation, comparison of NDVI for drought and non-drought years related to Land use classifications Jabbari *, S., Khajeddin, S. J. Jafari, R, Soltani, S and Riahi, F s.jabbari_62@yahoo.com
URBAN CHANGE DETECTION OF LAHORE (PAKISTAN) USING A TIME SERIES OF SATELLITE IMAGES SINCE 1972
 URBAN CHANGE DETECTION OF LAHORE (PAKISTAN) USING A TIME SERIES OF SATELLITE IMAGES SINCE 1972 Omar Riaz Department of Earth Sciences, University of Sargodha, Sargodha, PAKISTAN. omarriazpk@gmail.com ABSTRACT
URBAN CHANGE DETECTION OF LAHORE (PAKISTAN) USING A TIME SERIES OF SATELLITE IMAGES SINCE 1972 Omar Riaz Department of Earth Sciences, University of Sargodha, Sargodha, PAKISTAN. omarriazpk@gmail.com ABSTRACT
International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Modern Education (IJMRME) ISSN (Online): ( Volume I, Issue
 ESTIMATE THE TEMPERATURE OF AN-NAJAF CITY BY USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES AND SATELLITE IMAGES Watheq F Shneen Remote Sensing Centre, University of Kufa, Iraq Abstract: The temperature is of high importance
ESTIMATE THE TEMPERATURE OF AN-NAJAF CITY BY USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES AND SATELLITE IMAGES Watheq F Shneen Remote Sensing Centre, University of Kufa, Iraq Abstract: The temperature is of high importance
DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION
 DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION Researcher: Saad-ul-Haque Supervisor: Dr. Badar Ghauri Department of RS & GISc Institute of Space Technology
DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION Researcher: Saad-ul-Haque Supervisor: Dr. Badar Ghauri Department of RS & GISc Institute of Space Technology
Spatial variability of building frontal area index and its relationship with urban heat island intensity
 Spatial variability of building frontal area index and its relationship with urban heat island intensity Man Sing WONG, Janet NICHOL Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatic, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
Spatial variability of building frontal area index and its relationship with urban heat island intensity Man Sing WONG, Janet NICHOL Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatic, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
ANALYSIS OF VEGETATION DISTRIBUTION IN URBAN AREAS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS APPROACH ON A REGIONAL SCALE
 ANALYSIS OF VEGETATION DISTRIBUTION IN URBAN AREAS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS APPROACH ON A REGIONAL SCALE Kiichiro Kumagai Department of Civil and Environmental System Engineering, Setsunan University 17-8 Ikedanakamachi,
ANALYSIS OF VEGETATION DISTRIBUTION IN URBAN AREAS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS APPROACH ON A REGIONAL SCALE Kiichiro Kumagai Department of Civil and Environmental System Engineering, Setsunan University 17-8 Ikedanakamachi,
IMPACT OF URBAN EVOLUTION ON LAND-USE CHANGE OF SARGODHA CITY, PAKISTAN
 Impact of Urban Evolution on Land-Use Change of Sargodha City in Pakistan J. Sc. & Tech. Univ. Peshawar, 2015, 39 (2), 29-36. IMPACT OF URBAN EVOLUTION ON LAND-USE CHANGE OF SARGODHA CITY, PAKISTAN SAJJAD
Impact of Urban Evolution on Land-Use Change of Sargodha City in Pakistan J. Sc. & Tech. Univ. Peshawar, 2015, 39 (2), 29-36. IMPACT OF URBAN EVOLUTION ON LAND-USE CHANGE OF SARGODHA CITY, PAKISTAN SAJJAD
Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens. Title. Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki. Citation Japan.
 Title Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki International Symposium on "The Imp Citation Region Specific Systems". 6 Nove Japan.
Title Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki International Symposium on "The Imp Citation Region Specific Systems". 6 Nove Japan.
An Analysis of Temperature Variations Using Remote Sensing Approach in Lokoja Area
 Nigeria Infrastructure Advisory Facility From the SelectedWorks of Dr. Fanan Ujoh 2010 An Analysis of Temperature Variations Using Remote Sensing Approach in Lokoja Area Fanan Ujoh, Mr Olarewaju O Ifatimehin,
Nigeria Infrastructure Advisory Facility From the SelectedWorks of Dr. Fanan Ujoh 2010 An Analysis of Temperature Variations Using Remote Sensing Approach in Lokoja Area Fanan Ujoh, Mr Olarewaju O Ifatimehin,
CALIBRATION INFRASTRUCTURE AND TYPICAL APPLICATIONS OF CHINA LAND OBSERVATION SATELLITES. Li Liu. Executive summary (corresponding to ca ½ a page)
 Prepared by CNSA Agenda Item: WG.3 CALIBRATION INFRASTRUCTURE AND TYPICAL APPLICATIONS OF CHINA LAND OBSERVATION SATELLITES Li Liu Executive summary (corresponding to ca ½ a page) This report introduces
Prepared by CNSA Agenda Item: WG.3 CALIBRATION INFRASTRUCTURE AND TYPICAL APPLICATIONS OF CHINA LAND OBSERVATION SATELLITES Li Liu Executive summary (corresponding to ca ½ a page) This report introduces
LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE CHANGE AFTER CONSTRUCTION OF THE KOZJAK DAM BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA
 LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE CHANGE AFTER CONSTRUCTION OF THE KOZJAK DAM BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18509/gbp.2016.02 UDC: 627.82:551.525.2]:528.85(497.782) MSc. Gordana JOVANOVSKA
LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE CHANGE AFTER CONSTRUCTION OF THE KOZJAK DAM BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18509/gbp.2016.02 UDC: 627.82:551.525.2]:528.85(497.782) MSc. Gordana JOVANOVSKA
Drought Estimation Maps by Means of Multidate Landsat Fused Images
 Remote Sensing for Science, Education, Rainer Reuter (Editor) and Natural and Cultural Heritage EARSeL, 2010 Drought Estimation Maps by Means of Multidate Landsat Fused Images Diego RENZA, Estíbaliz MARTINEZ,
Remote Sensing for Science, Education, Rainer Reuter (Editor) and Natural and Cultural Heritage EARSeL, 2010 Drought Estimation Maps by Means of Multidate Landsat Fused Images Diego RENZA, Estíbaliz MARTINEZ,
Assessment of Urban Heat Island through Remote Sensing in Nagpur Urban Area Using Landsat 7 ETM+ Satellite Images
 Assessment of Urban Heat Island through Remote Sensing in Nagpur Urban Area Using Landsat 7 ETM+ Satellite Images Meenal Surawar, Rajashree Kotharkar 1 Abstract Urban Heat Island (UHI) is found more pronounced
Assessment of Urban Heat Island through Remote Sensing in Nagpur Urban Area Using Landsat 7 ETM+ Satellite Images Meenal Surawar, Rajashree Kotharkar 1 Abstract Urban Heat Island (UHI) is found more pronounced
Evaluation of land surface temperature (LST) patterns in the urban agglomeration of Krakow using different satellite data and GIS
 Evaluation of land surface temperature (LST) patterns in the urban agglomeration of Krakow using different satellite data and GIS Jakub P. Walawender 1,2 1 Satellite Remote Sensing Centre, Institute of
Evaluation of land surface temperature (LST) patterns in the urban agglomeration of Krakow using different satellite data and GIS Jakub P. Walawender 1,2 1 Satellite Remote Sensing Centre, Institute of
Progress Report Year 2, NAG5-6003: The Dynamics of a Semi-Arid Region in Response to Climate and Water-Use Policy
 Progress Report Year 2, NAG5-6003: The Dynamics of a Semi-Arid Region in Response to Climate and Water-Use Policy Principal Investigator: Dr. John F. Mustard Department of Geological Sciences Brown University
Progress Report Year 2, NAG5-6003: The Dynamics of a Semi-Arid Region in Response to Climate and Water-Use Policy Principal Investigator: Dr. John F. Mustard Department of Geological Sciences Brown University
Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping
 Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping What is remote sensing? Why remote sensing? Examples of remote sensing in natural resources mapping Class goals What is Remote Sensing A remote sensing
Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping What is remote sensing? Why remote sensing? Examples of remote sensing in natural resources mapping Class goals What is Remote Sensing A remote sensing
Abstract: About the Author:
 REMOTE SENSING AND GIS IN LAND USE PLANNING Sathees kumar P 1, Nisha Radhakrishnan 2 1 1 Ph.D Research Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli- 620015,
REMOTE SENSING AND GIS IN LAND USE PLANNING Sathees kumar P 1, Nisha Radhakrishnan 2 1 1 Ph.D Research Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli- 620015,
Spati-temporal Changes of NDVI and Their Relations with Precipitation and Temperature in Yangtze River Catchment from 1992 to 2001
 Spati-temporal Changes of NDVI and Their Relations with Precipitation and Temperature in Yangtze River Catchment from 1992 to 2001 ZHANG Li 1, CHEN Xiao-Ling 1, 2 1State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering
Spati-temporal Changes of NDVI and Their Relations with Precipitation and Temperature in Yangtze River Catchment from 1992 to 2001 ZHANG Li 1, CHEN Xiao-Ling 1, 2 1State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering
The Study of Impact of Urbanization on Urban Heat Island with Temperature Variation Analysis of MODIS Data Using Remote Sensing and GIS Technology
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2015, Volume 4, Issue 1, pp. 944-952, Article ID Tech-269 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access The Study of Impact of
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2015, Volume 4, Issue 1, pp. 944-952, Article ID Tech-269 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access The Study of Impact of
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
 III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 3.1 Time and Location This research has been conducted in period March until October 2010. Location of research is over Sumatra terrain. Figure 3.1 show the area of interest of
III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 3.1 Time and Location This research has been conducted in period March until October 2010. Location of research is over Sumatra terrain. Figure 3.1 show the area of interest of
AGRICULTURE DROUGHT AND FOREST FIRE MONITORING IN CHONGQING CITY WITH MODIS AND METEOROLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS *
 AGRICULTURE DROUGHT AND FOREST FIRE MONITORING IN CHONGQING CITY WITH MODIS AND METEOROLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS * HONGRUI ZHAO a ZHONGSHI TANG a, BIN YANG b AND MING ZHAO a a 3S Centre, Tsinghua University,
AGRICULTURE DROUGHT AND FOREST FIRE MONITORING IN CHONGQING CITY WITH MODIS AND METEOROLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS * HONGRUI ZHAO a ZHONGSHI TANG a, BIN YANG b AND MING ZHAO a a 3S Centre, Tsinghua University,
Civil Engineering Journal
 Available online at www.civilejournal.org Civil Engineering Journal Vol. 1, No. 2, December, 2015 Comparative Study of Landsat and Aster Data by Morphometric Analysis Sujit Kumar a*, Tapasi Bhandary b
Available online at www.civilejournal.org Civil Engineering Journal Vol. 1, No. 2, December, 2015 Comparative Study of Landsat and Aster Data by Morphometric Analysis Sujit Kumar a*, Tapasi Bhandary b
Kimberly J. Mueller Risk Management Solutions, Newark, CA. Dr. Auguste Boissonade Risk Management Solutions, Newark, CA
 1.3 The Utility of Surface Roughness Datasets in the Modeling of United States Hurricane Property Losses Kimberly J. Mueller Risk Management Solutions, Newark, CA Dr. Auguste Boissonade Risk Management
1.3 The Utility of Surface Roughness Datasets in the Modeling of United States Hurricane Property Losses Kimberly J. Mueller Risk Management Solutions, Newark, CA Dr. Auguste Boissonade Risk Management
GNR401 Principles of Satellite Image Processing
 Principles of Satellite Image Processing Instructor: Prof. CSRE, IIT Bombay bkmohan@csre.iitb.ac.in Slot 5 Guest Lecture PCT and Band Arithmetic November 07, 2012 9.30 AM 10.55 AM IIT Bombay Slide 1 November
Principles of Satellite Image Processing Instructor: Prof. CSRE, IIT Bombay bkmohan@csre.iitb.ac.in Slot 5 Guest Lecture PCT and Band Arithmetic November 07, 2012 9.30 AM 10.55 AM IIT Bombay Slide 1 November
Vegetation Change Detection of Central part of Nepal using Landsat TM
 Vegetation Change Detection of Central part of Nepal using Landsat TM Kalpana G. Bastakoti Department of Geography, University of Calgary, kalpanagb@gmail.com Abstract This paper presents a study of detecting
Vegetation Change Detection of Central part of Nepal using Landsat TM Kalpana G. Bastakoti Department of Geography, University of Calgary, kalpanagb@gmail.com Abstract This paper presents a study of detecting
