NANOSCIENCE AND NANOTECHNOLOGY
|
|
|
- Evangeline Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NANOSCIENCE AND NANOTECHNOLOGY Yuehe Lin
2 WHAT IS NANOTECHNOLOGY Nanotechnology is the understanding and control of matter at dimensions of roughly 1 to 100 nanometers, where unique phenomena enable novel applications. Nanoscience and nanotechnology are the study and application of extremely small things and can be used across all the other science fields, such as chemistry, biology, physics, materials science, and engineering. Nanotechnology is distinguished by its interdisciplinary nature. -National Nanotechnology Initiative
3 HOW IT STARTED The ideas and concepts behind nanoscience and nanotechnology started with a talk entitled There s Plenty of Room at the Bottom by physicist Richard Feynman at an American Physical Society meeting at the California Institute of Technology (CalTech) on December 29, 1959, long before the term nanotechnology was used. In his talk, Feynman described a process in which scientists would be able to manipulate and control individual atoms and molecules. Over a decade later, in his explorations of ultraprecision machining in semiconductor processeses, Professor Norio Taniguchi (Tokyo Univ of Science) formulated and used the term nanotechnology. (1974)
4 VIEW AND MANIPULATE NANOSCALE PARTICLES, ATOMS, AND SMALL MOLECULES. Nanoscience and nanotechnology involve the ability to see and to control individual atoms and molecules. Everything on Earth is made up of atoms. But something as small as an atom is impossible to see with the naked eye. The microscopes needed to see things at the nanoscale were invented relatively recently about 30 years ago. Once scientists had the right tools, such as the scanning tunneling microscope (STM) and the atomic force microscope (AFM), the age of nanotechnology was born.
5 HOW SMALL IS NANO? A nanometer (nm) = 1 billionth of a meter; 100,000 x s smaller than the diameter of a human hair. A line of 10 H atoms A strand of DNA has a diameter of 2.5 nm
6 WHY NANOTECHNOLOGY? At the nanoscale, the physical, chemical, and biological properties of materials differ from the bulk matter. Nanotechnology R&D is directed toward understanding and creating improved materials, devices, and systems that exploit these new properties.
7 Unique Property at Nanoscale: I. Optical Properties Of Quantum Dots a) Multiple colors Electronic characteristics of a QD are closely related to its size. The band gap in a QD which determines the frequency range of emitted light is inversely related to its size. Smaller size-> larger band gap. In fluorescent dye applications the frequency of emitted light increases as the size of the QD decreases. Consequently, the color of emitted light shifts from red to blue when the size of the QD is made smaller. This allows the excitation and emission of QDs to be highly tunable.
8 Unique Property at Nanoscale: II. Magnetic properties of nanoparticles Nano particles of magnetic and even non magnetic solids exhibit a totally new class of magnetic properties. Table gives an account of magnetic behavior of very small particles of various metals. Small particles differ from the bulk in that these atoms will have lower co-ordination number. The small particles are more magnetic than the bulk material Metal Bulk Cluster (nm) Na, K Paramagnetic Ferromagnetic Fe, Co, Ni Ferro magnetic Super paramagnetic Gd, Tb Ferromagnetic Super paramagnetic Rh Paramagnetic Ferromagnetic Magnetism in bulk and in nano particles
9 Unique Property at Nanoscale: III. Catalytic activity of nanoparticles Surface atoms are more active for catalysis Pt Nanoparticles have higher catalytic activity for fuel cells Au particles are not good catalyst at micro-scale; but show high catalytic activity at nanoscale Surface atoms [%] (1.2nm, 76%) (5nm, 45%) (7nm, 35%) 20 (63μm, ~0%) d cluster [nm] 10 5 SURFACE TO VOLUME RATIO
10 MANUFACTURING AT NANOSCALE--NANOMANUFACTURING Nanomanufacturing involves scaled-up, reliable, and costeffective manufacturing of nanoscale materials, structures, devices, and systems. Top-down: lithography - Top-down fabrication reduces large pieces of materials all the way down to the nanoscale, like someone carving a model airplane out of a block of wood. - This approach requires larger amounts of materials and can lead to waste if excess material is discarded. The bottom-up: self-assembly, spontaneous growth - This approach creates products by building them up from atomic- and molecular-scale components, which can be timeconsuming. -- Scientists are exploring the concept of placing certain molecular-scale components together that will spontaneously self-assemble, from the bottom up into ordered structures.
11 Nanostructures or nanomaterials Nanoparticles (0 D) Quantum dots; Au nanoparticles Nanorods, nanowires, nanofibers, and nanotubes (1 D) 11 Thin-film, thin-layer (2 D) Graphene Bulk nanomaterials (3 D) Mesoporous materials Also aerogels, zeolites Organic-inorganic hybrids Nanograined bulk materials and nanocomposites
12 Basic building blocks of nanoscale materials
13 Fullerene: 0-D Nanocarbon The most symmetrical large molecule Discovered in Nobel prize Chemistry 1996, Curl, Kroto, and Smalley C 60, also 70, 76 and facets (12 pentagons and 20 hexagons) Epcot center, Paris ~1 nm Architect: R. Buckminster Fuller
14 Carbon nanotube: 1-D Nanocarbon CNT: Rolling-up a graphene sheet to form a tube Schematic of a CNT STM image of CNT 14
15 Carbon nanotube properties: Mechanical Carbon-carbon bonds are one of the strongest bond in nature Carbon nanotube is composed of perfect arrangement of these bonds Extremely high Young s modulus Material Young s modulus (GPa) Steel SWNT 1,000+ Diamond 1,050-1,200 15
16 Synthesis of Carbon Nanotube: Catalytic Chemical Deposition
17 Applications Electrical 1. Field emission in vacuum electronics Energy 1. Lithium ion batteries 2. Fuel cells Biological 1. Bio-sensors 2. Functional AFM tips 3. Drug delivery 17
18 Graphene: 2-D Nanocarbon In late 2004, graphene was discovered by Andre Geim and Kostya Novoselov (Univ. of Manchester) Nobel Prize in Physics Graphene is a one-atom-thick planar sheet of sp 2 -bonded carbon atoms that are densely packed in a honeycomb crystal lattice The name graphene comes from graphite + -ene = graphene Molecular structure of graphene High resolution transmission electron microscope images (TEM) of graphene
19 Properties of Graphene Q1. How thick is it? a million times thinner than paper (The interlayer spacing : 0.33~0.36 nm) Q2. How strong is it? stronger than diamond (Maximum Young's modulus : ~1.3 TPa) Q3. How conductive is it? better than copper (The resistivity : 10 6 Ω cm) (Mobility: 200,000 cm 2 V -1 s -1 ) Q4. Optical Property? -> Monolayer graphene absorbs 2.3% of white light (97.7 % transmittance). 19
20 Preparation of Graphene 1. Mechanical process (Scotch-tape method) In 2004: Andre Geim and Kostya Novoselov at Manchester University managed to extract single-atom-thick crystallites (graphene) from bulk graphite: Pulled out graphene layers from graphite and transferred them onto thin silicon dioxide on a silicon wafer in a process sometimes called micromechanical cleavage or, simply, the Scotch tape technique. Novoselov, K. S.; Geim, A. K.; Morozov, S. V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S. V.; Grigorieva, I. V.; Firsov, A. A. Science 2004, 306, 666.
21 Graphene Preparation: 2. Chemical Method Graphene Oxide Production with Hummers Method Graphite Graphite oxide Exfoliated graphene oxide 1. Pre-oxidation with H 2 SO 4, K 2 S 2 O 8, and P 2 O 5 2. Secondary Oxidation with H2SO4 + KMnO 4 3. Sonication for splitting 4. Using chemical reduction to convert Graphene oxide to graphene
22 Graphene Applications OLED Techonologies Body Armour Lightweight Aircraft/vehicles Photovoltaics Superconductor/battery Filtration
23 Biomedical Applications of Nanotechnology
24 Nanotechnology Applications: Biosensors Based On Carbon Nanotube Arrays Tu, Lin, Ren, Nano Lett. 3, , 2003 Lin, Lu, Ru, Ren, Nano Lett. 4, , 2004
25 Fabrication of CNT Nanoelectrode Array Aligned CNT by PECVD (A) Deposition of Ni Catalysts (EC or E-beam lithography) PECVD (B) Spin-coating of epoxy resin Cr Si Epoxy passivation layer (C) Exposed CNT tip Polishing to expose the tip of CNTs Electric connection Tu, Lin, Ren, Nano Lett. 2003, 3,
26 CONTROL DENSITY OF CARBON NANOTUBES BY CONTROLLING DENSITY OF CATALYST NANOPARTICLES Electron beam lithography Ni dots Precisely control the density of Ni dots with regular arrays High S/N ratio Cr Si Insulation Layer Unique properties of CNT-Tip nanoeletrode array: Only sensitive part, CNT-tip is exposed to solution for sensing, side-wall are insulted to reduce capacitance background current High sensitivity 1-2 millions vs. single CNT 26
27 Nanotechnology Applications: Biosensors Based On Carbon Nanotube Arrays Enzymes Enzyme-based Biosensors Antibody Immunosensors Cr Si Insulation Layer DNA DNA Sensors US Patent issued 2008
28 NANOPROBES FOR IMAGING Quantum Dots Gold Nanoparticles Carbon materials functionalized to achieve biocompatibility and cell targeting Magnetic nanoparticles Liposomes Polymeric Nanoparticles
29 A Quantum Dot Nanoparticle The quantum dot itself (the semiconductor nanoparticle) is toxic. Therefore some typical modifications has to be made for it to become biocompatible. 1) The core consist of the semiconductor material that emits lights ) The shell consist of an insulator material that protects the light emitting properties of the QD in the upcoming functionalization 3) The shell is functionalized with a biocompatible material such as PEG or a lipid layer 4) Additional functionalization can be done with several purposes (e.g. embed a drug for drug delivery, or assemble an antibody to become the QD target-specific) Source: The scientist (2005), Vol. 19, p. 35
30 Nanotechnology Applications: In Vivo Cell Imaging Y QD + Organelle QD-Antibody conjugates Antigen Y QD Organelle 3T3 cell nucleus stained with red QDs and microtubules with green QDs - Multiple Color Imaging - Stronger Signals Wu et al. Nature Biotech
31 Nanotechnology Applications: In Vivo Tumor Imaging Quantum Dot Injection 10um Red Quantum Dot locating a tumor in a live mouse
32 Protein-Cage Based Platform for Drug Delivery and Release Approach The drug molecules will be trapped in the cavity Apoferritin Surface channels become wider and drug molecule can easily diffuse into the cavity Poly aspartic acid (PLAA) Daunomycin (DN) J. Mater. Chem. 2011
33 Biosensing and Bioimaging Based on Protein-Cage Nanoparticles Ligand peptide Protein cage surface can be easily modified with biomolecules Antibody
34 Schematic illustration of the synthesis of the hyaluronic acid apoferritin daunomycin poly-l-aspartic acid (HA Apo DN PLAA) drug delivery system. DOI: /C5BM00067J (Paper) Biomater. Sci., 2015, 3,
35 Protein Cage for Drug Delivery 1 1) Apoferritin is a naturally derived protein cage and it is composed of 24 subunits. We have used apoferritin s ability to disassemble and reassemble under ph control to load the therapeutic compound. 2) HA has been used as a targeting moiety to recognize overexpression CD44 in A549 lung cells. 3) Endosomes break and drug release. 3 2 Biomater. Sci., 2015, 3,
36 DOI: /C5BM00067J (Paper) Biomater. Sci., 2015, 3,
37 Environmental Applications of Nanotechnology 1. Functionalized Mesoporous Silica for Water Treatment High capacity due to high surface area (1000 m2/g) and high-density of functional groups a. Toxic heavy metals: Hg, Cd, Pb, As Cr b. Radioisotopes: Cs-137; U, Pu 2. Sensors Based on Functionalized Mesoporous Silica for Environmental Monitoring Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39,
38 SAMMS: Self-Assembled Monolayer on Mesoporous Silica For Environmental Applications 38
39 Synthesis of SAMMS A. Ordered mesoporous silica C. Self-assembled monolayers on mesoporous supports (SAMMS) + B. Self-assembled monolayers Pore size ~4 nm One end group of the functionalized monolayers is covalently bonded to the silica surface and the other end group can be used to bind metal ions 39
40 Nanotechnology Application: Nanocatalysts for Fuel Cells Supercritical fluid deposition and wet chemical methods to prepare well-dispersed Pt, Pt-Ru, Pt-Au, Au, on nanocarbon supports (CNTs, mesoporous C, graphene) CNTs Graphene
In the name of Allah
 In the name of Allah Nano chemistry- 4 th stage Lecture No. 1 History of nanotechnology 16-10-2016 Assistance prof. Dr. Luma Majeed Ahmed lumamajeed2013@gmail.com, luma.ahmed@uokerbala.edu.iq Nano chemistry-4
In the name of Allah Nano chemistry- 4 th stage Lecture No. 1 History of nanotechnology 16-10-2016 Assistance prof. Dr. Luma Majeed Ahmed lumamajeed2013@gmail.com, luma.ahmed@uokerbala.edu.iq Nano chemistry-4
Carbon nanomaterials. Gavin Lawes Wayne State University.
 Carbon nanomaterials Gavin Lawes Wayne State University glawes@wayne.edu Outline 1. Carbon structures 2. Carbon nanostructures 3. Potential applications for Carbon nanostructures Periodic table from bpc.edu
Carbon nanomaterials Gavin Lawes Wayne State University glawes@wayne.edu Outline 1. Carbon structures 2. Carbon nanostructures 3. Potential applications for Carbon nanostructures Periodic table from bpc.edu
Materials. Definitions of nanotechnology. The term nanotechnology was invented by Professor Norio Taniguchi at the University of Tokyo in 1971.
 Materials Definitions of nanotechnology The term nanotechnology was invented by Professor Norio Taniguchi at the University of Tokyo in 1971. The original definition, translated into English Nano-technology'
Materials Definitions of nanotechnology The term nanotechnology was invented by Professor Norio Taniguchi at the University of Tokyo in 1971. The original definition, translated into English Nano-technology'
Seminars in Nanosystems - I
 Seminars in Nanosystems - I Winter Semester 2011/2012 Dr. Emanuela Margapoti Emanuela.Margapoti@wsi.tum.de Dr. Gregor Koblmüller Gregor.Koblmueller@wsi.tum.de Seminar Room at ZNN 1 floor Topics of the
Seminars in Nanosystems - I Winter Semester 2011/2012 Dr. Emanuela Margapoti Emanuela.Margapoti@wsi.tum.de Dr. Gregor Koblmüller Gregor.Koblmueller@wsi.tum.de Seminar Room at ZNN 1 floor Topics of the
Nanotechnology. Yung Liou P601 Institute of Physics Academia Sinica
 Nanotechnology Yung Liou P601 yung@phys.sinica.edu.tw Institute of Physics Academia Sinica 1 1st week Definition of Nanotechnology The Interagency Subcommittee on Nanoscale Science, Engineering and Technology
Nanotechnology Yung Liou P601 yung@phys.sinica.edu.tw Institute of Physics Academia Sinica 1 1st week Definition of Nanotechnology The Interagency Subcommittee on Nanoscale Science, Engineering and Technology
In today s lecture, we will cover:
 In today s lecture, we will cover: Metal and Metal oxide Nanoparticles Semiconductor Nanocrystals Carbon Nanotubes 1 Week 2: Nanoparticles Goals for this section Develop an understanding of the physical
In today s lecture, we will cover: Metal and Metal oxide Nanoparticles Semiconductor Nanocrystals Carbon Nanotubes 1 Week 2: Nanoparticles Goals for this section Develop an understanding of the physical
29: Nanotechnology. What is Nanotechnology? Properties Control and Understanding. Nanomaterials
 29: Nanotechnology What is Nanotechnology? Properties Control and Understanding Nanomaterials Making nanomaterials Seeing at the nanoscale Quantum Dots Carbon Nanotubes Biology at the Nanoscale Some Applications
29: Nanotechnology What is Nanotechnology? Properties Control and Understanding Nanomaterials Making nanomaterials Seeing at the nanoscale Quantum Dots Carbon Nanotubes Biology at the Nanoscale Some Applications
Carbon Nanomaterials: Nanotubes and Nanobuds and Graphene towards new products 2030
 Carbon Nanomaterials: Nanotubes and Nanobuds and Graphene towards new products 2030 Prof. Dr. Esko I. Kauppinen Helsinki University of Technology (TKK) Espoo, Finland Forecast Seminar February 13, 2009
Carbon Nanomaterials: Nanotubes and Nanobuds and Graphene towards new products 2030 Prof. Dr. Esko I. Kauppinen Helsinki University of Technology (TKK) Espoo, Finland Forecast Seminar February 13, 2009
Nanotechnology. Gavin Lawes Department of Physics and Astronomy
 Nanotechnology Gavin Lawes Department of Physics and Astronomy Earth-Moon distance 4x10 8 m (courtesy NASA) Length scales (Part I) Person 2m Magnetic nanoparticle 5x10-9 m 10 10 m 10 5 m 1 m 10-5 m 10-10
Nanotechnology Gavin Lawes Department of Physics and Astronomy Earth-Moon distance 4x10 8 m (courtesy NASA) Length scales (Part I) Person 2m Magnetic nanoparticle 5x10-9 m 10 10 m 10 5 m 1 m 10-5 m 10-10
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A nanometer (nm) is one billionth (10-9 ) of a meter. Nanoscience can be defined as the science of objects and phenomena occurring at the scale of 1 to 100 nm. The range of 1 100
Chapter 1 Introduction A nanometer (nm) is one billionth (10-9 ) of a meter. Nanoscience can be defined as the science of objects and phenomena occurring at the scale of 1 to 100 nm. The range of 1 100
Nanotechnology in Consumer Products
 Nanotechnology in Consumer Products June 17, 2015 October 31, 2014 The webinar will begin at 1pm Eastern Time Perform an audio check by going to Tools > Audio > Audio Setup Wizard Chat Box Chat Box Send
Nanotechnology in Consumer Products June 17, 2015 October 31, 2014 The webinar will begin at 1pm Eastern Time Perform an audio check by going to Tools > Audio > Audio Setup Wizard Chat Box Chat Box Send
NANOMEDICINE. WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication DESIGN AND APPLICATIONS OF MAGNETIC NANOMATERIALS, NANOSENSORS AND NANOSYSTEMS
 NANOMEDICINE DESIGN AND APPLICATIONS OF MAGNETIC NANOMATERIALS, NANOSENSORS AND NANOSYSTEMS Vijay K. Varadan Linfeng Chen Jining Xie WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication Preface About the Authors
NANOMEDICINE DESIGN AND APPLICATIONS OF MAGNETIC NANOMATERIALS, NANOSENSORS AND NANOSYSTEMS Vijay K. Varadan Linfeng Chen Jining Xie WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication Preface About the Authors
Graphene films on silicon carbide (SiC) wafers supplied by Nitride Crystals, Inc.
 9702 Gayton Road, Suite 320, Richmond, VA 23238, USA Phone: +1 (804) 709-6696 info@nitride-crystals.com www.nitride-crystals.com Graphene films on silicon carbide (SiC) wafers supplied by Nitride Crystals,
9702 Gayton Road, Suite 320, Richmond, VA 23238, USA Phone: +1 (804) 709-6696 info@nitride-crystals.com www.nitride-crystals.com Graphene films on silicon carbide (SiC) wafers supplied by Nitride Crystals,
Wafer-scale fabrication of graphene
 Wafer-scale fabrication of graphene Sten Vollebregt, MSc Delft University of Technology, Delft Institute of Mircosystems and Nanotechnology Delft University of Technology Challenge the future Delft University
Wafer-scale fabrication of graphene Sten Vollebregt, MSc Delft University of Technology, Delft Institute of Mircosystems and Nanotechnology Delft University of Technology Challenge the future Delft University
The many forms of carbon
 The many forms of carbon Carbon is not only the basis of life, it also provides an enormous variety of structures for nanotechnology. This versatility is connected to the ability of carbon to form two
The many forms of carbon Carbon is not only the basis of life, it also provides an enormous variety of structures for nanotechnology. This versatility is connected to the ability of carbon to form two
Like space travel and the Internet before it, the possibilities of the nano world catches the imagination of school children and scientists alike.
 The Nano World Preface Nano is the cool thing and it s the buzzword Like space travel and the Internet before it, the possibilities of the nano world catches the imagination of school children and scientists
The Nano World Preface Nano is the cool thing and it s the buzzword Like space travel and the Internet before it, the possibilities of the nano world catches the imagination of school children and scientists
Nanotechnology Fabrication Methods.
 Nanotechnology Fabrication Methods. 10 / 05 / 2016 1 Summary: 1.Introduction to Nanotechnology:...3 2.Nanotechnology Fabrication Methods:...5 2.1.Top-down Methods:...7 2.2.Bottom-up Methods:...16 3.Conclusions:...19
Nanotechnology Fabrication Methods. 10 / 05 / 2016 1 Summary: 1.Introduction to Nanotechnology:...3 2.Nanotechnology Fabrication Methods:...5 2.1.Top-down Methods:...7 2.2.Bottom-up Methods:...16 3.Conclusions:...19
Nanotechnology? Source: National Science Foundation (NSF), USA
 2 2 Nanotechnology? Ability to work at the atomic, molecular and even sub-molecular levels in order to create and use material structures, devices and systems with new properties and functions Source:
2 2 Nanotechnology? Ability to work at the atomic, molecular and even sub-molecular levels in order to create and use material structures, devices and systems with new properties and functions Source:
Overview. Carbon in all its forms. Background & Discovery Fabrication. Important properties. Summary & References. Overview of current research
 Graphene Prepared for Solid State Physics II Pr Dagotto Spring 2009 Laurene Tetard 03/23/09 Overview Carbon in all its forms Background & Discovery Fabrication Important properties Overview of current
Graphene Prepared for Solid State Physics II Pr Dagotto Spring 2009 Laurene Tetard 03/23/09 Overview Carbon in all its forms Background & Discovery Fabrication Important properties Overview of current
Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics)
 Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de Office: Unterpoerlitzer
Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de Office: Unterpoerlitzer
Ciência (Bio)nanosystems based on quantum dots, plasmonic or magnetic nanoparticles
 Ciência 216 (Bio)nanosystems based on quantum dots, plasmonic or magnetic nanoparticles Paulo J. G. Coutinho Departamento/Centro de Física Escola de Ciências Universidade do Minho 4 Julho 216 OVERVIEW
Ciência 216 (Bio)nanosystems based on quantum dots, plasmonic or magnetic nanoparticles Paulo J. G. Coutinho Departamento/Centro de Física Escola de Ciências Universidade do Minho 4 Julho 216 OVERVIEW
Electrochemically Synthesized Multi-block
 Electrochemically Synthesized Multi-block Nanorods Sungho Park SungKyunKwan University, Department of Chemistry & SKKU Advanced Institute of Nanotechnology (SAINT) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2282-2290
Electrochemically Synthesized Multi-block Nanorods Sungho Park SungKyunKwan University, Department of Chemistry & SKKU Advanced Institute of Nanotechnology (SAINT) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2282-2290
Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics)
 Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de Office: Unterpoerlitzer
Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de Office: Unterpoerlitzer
1.1. Introduction to Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
 1.1. Introduction to Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 1.1.1. A Brief Historical Overview Before trying to understand and discuss about synthesis, characterization and application of nanomaterials, it is
1.1. Introduction to Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 1.1.1. A Brief Historical Overview Before trying to understand and discuss about synthesis, characterization and application of nanomaterials, it is
Graphene Fundamentals and Emergent Applications
 Graphene Fundamentals and Emergent Applications Jamie H. Warner Department of Materials University of Oxford Oxford, UK Franziska Schaffel Department of Materials University of Oxford Oxford, UK Alicja
Graphene Fundamentals and Emergent Applications Jamie H. Warner Department of Materials University of Oxford Oxford, UK Franziska Schaffel Department of Materials University of Oxford Oxford, UK Alicja
State of São Paulo. Brasil. Localization. Santo André
 Brasil State of São Paulo Localization Santo André The Group www.crespilho.com Frank N. Crespilho Pablo R. S. Abdias Group Leader Synthesis of nanostructured materials using polyelectrolytes Andressa R.
Brasil State of São Paulo Localization Santo André The Group www.crespilho.com Frank N. Crespilho Pablo R. S. Abdias Group Leader Synthesis of nanostructured materials using polyelectrolytes Andressa R.
Graphene The Search For Two Dimensions. Christopher Scott Friedline Arizona State University
 Graphene The Search For Two Dimensions Christopher Scott Friedline Arizona State University What Is Graphene? Single atomic layer of graphite arranged in a honeycomb crystal lattice Consists of sp 2 -bonded
Graphene The Search For Two Dimensions Christopher Scott Friedline Arizona State University What Is Graphene? Single atomic layer of graphite arranged in a honeycomb crystal lattice Consists of sp 2 -bonded
Chemistry 1000 Lecture 22: Group 14 and Boron. Marc R. Roussel
 Chemistry 1000 Lecture 22: Group 14 and Boron Marc R. Roussel Group 14 In this group again, we see a full range of nonmetallic to metallic behavior: C is a nonmetal. Si and Ge are metalloids. Sn and Pb
Chemistry 1000 Lecture 22: Group 14 and Boron Marc R. Roussel Group 14 In this group again, we see a full range of nonmetallic to metallic behavior: C is a nonmetal. Si and Ge are metalloids. Sn and Pb
Nanotechnology 5 th lecture
 Nanotechnology 5 th lecture (c) http://www.nccr-nano.org/nccr_data/ gallery/gallery_01/gallery_01_03/pics_06/ internet/nanotube_spiral.jpg Plan for today: http://www.nccr-nano.org/nccr_data/gallery/ gallery_01/gallery_01_03/pics_04/internet/
Nanotechnology 5 th lecture (c) http://www.nccr-nano.org/nccr_data/ gallery/gallery_01/gallery_01_03/pics_06/ internet/nanotube_spiral.jpg Plan for today: http://www.nccr-nano.org/nccr_data/gallery/ gallery_01/gallery_01_03/pics_04/internet/
Nanostructures. Lecture 13 OUTLINE
 Nanostructures MTX9100 Nanomaterials Lecture 13 OUTLINE -What is quantum confinement? - How can zero-dimensional materials be used? -What are one dimensional structures? -Why does graphene attract so much
Nanostructures MTX9100 Nanomaterials Lecture 13 OUTLINE -What is quantum confinement? - How can zero-dimensional materials be used? -What are one dimensional structures? -Why does graphene attract so much
Nano Materials and Devices
 Nano Materials and Devices Professor Michael Austin Platform Technologies Research Institute Nano Materials and Devices Program Aim: to develop an integrated capability in nanotechnology Design and modelling
Nano Materials and Devices Professor Michael Austin Platform Technologies Research Institute Nano Materials and Devices Program Aim: to develop an integrated capability in nanotechnology Design and modelling
Graphene. Tianyu Ye November 30th, 2011
 Graphene Tianyu Ye November 30th, 2011 Outline What is graphene? How to make graphene? (Exfoliation, Epitaxial, CVD) Is it graphene? (Identification methods) Transport properties; Other properties; Applications;
Graphene Tianyu Ye November 30th, 2011 Outline What is graphene? How to make graphene? (Exfoliation, Epitaxial, CVD) Is it graphene? (Identification methods) Transport properties; Other properties; Applications;
Final Reading Assignment: Travels to the Nanoworld: pages pages pages
 Final Reading Assignment: Travels to the Nanoworld: pages 152-164 pages 201-214 pages 219-227 Bottom-up nanofabrication Can we assemble nanomachines manually? What are the components (parts)? nanoparticles
Final Reading Assignment: Travels to the Nanoworld: pages 152-164 pages 201-214 pages 219-227 Bottom-up nanofabrication Can we assemble nanomachines manually? What are the components (parts)? nanoparticles
There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom
 There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom 12/29/1959 Feynman asked why not put the entire Encyclopedia Britannica (24 volumes) on a pin head (requires atomic scale recording). He proposed to use electron microscope
There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom 12/29/1959 Feynman asked why not put the entire Encyclopedia Britannica (24 volumes) on a pin head (requires atomic scale recording). He proposed to use electron microscope
Techniken der Oberflächenphysik (Technique of Surface Physics)
 Techniken der Oberflächenphysik (Technique of Surface Physics) Yong Lei & Fabian Grote Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; fabian.grote@tu-ilmenau.de
Techniken der Oberflächenphysik (Technique of Surface Physics) Yong Lei & Fabian Grote Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; fabian.grote@tu-ilmenau.de
ESH Benign Processes for he Integration of Quantum Dots (QDs)
 ESH Benign Processes for he Integration of Quantum Dots (QDs) PIs: Karen K. Gleason, Department of Chemical Engineering, MIT Graduate Students: Chia-Hua Lee: PhD Candidate, Department of Material Science
ESH Benign Processes for he Integration of Quantum Dots (QDs) PIs: Karen K. Gleason, Department of Chemical Engineering, MIT Graduate Students: Chia-Hua Lee: PhD Candidate, Department of Material Science
TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE
 International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
Chapter 10. Nanometrology. Oxford University Press All rights reserved.
 Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1
 Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Carbon contains 6 electrons: (1s) 2,
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Carbon contains 6 electrons: (1s) 2,
Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics
 Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics 09 02 200802 2008 ME class Outline driving force for the carbon nanomaterial electronic properties of fullerene exploration of electronic carbon nanotube gold rush of
Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics 09 02 200802 2008 ME class Outline driving force for the carbon nanomaterial electronic properties of fullerene exploration of electronic carbon nanotube gold rush of
Nanobiotechnology. Place: IOP 1 st Meeting Room Time: 9:30-12:00. Reference: Review Papers. Grade: 40% midterm, 60% final report (oral + written)
 Nanobiotechnology Place: IOP 1 st Meeting Room Time: 9:30-12:00 Reference: Review Papers Grade: 40% midterm, 60% final report (oral + written) Midterm: 5/18 Oral Presentation 1. 20 minutes each person
Nanobiotechnology Place: IOP 1 st Meeting Room Time: 9:30-12:00 Reference: Review Papers Grade: 40% midterm, 60% final report (oral + written) Midterm: 5/18 Oral Presentation 1. 20 minutes each person
Initial Stages of Growth of Organic Semiconductors on Graphene
 Initial Stages of Growth of Organic Semiconductors on Graphene Presented by: Manisha Chhikara Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Gvido Bratina University of Nova Gorica Outline Introduction to Graphene Fabrication
Initial Stages of Growth of Organic Semiconductors on Graphene Presented by: Manisha Chhikara Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Gvido Bratina University of Nova Gorica Outline Introduction to Graphene Fabrication
Monolayer Semiconductors
 Monolayer Semiconductors Gilbert Arias California State University San Bernardino University of Washington INT REU, 2013 Advisor: Xiaodong Xu (Dated: August 24, 2013) Abstract Silicon may be unable to
Monolayer Semiconductors Gilbert Arias California State University San Bernardino University of Washington INT REU, 2013 Advisor: Xiaodong Xu (Dated: August 24, 2013) Abstract Silicon may be unable to
Chemistry 1000 Lecture 24: Group 14 and Boron
 Chemistry 1000 Lecture 24: Group 14 and Boron Marc R. Roussel November 2, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Group 14 and Boron November 2, 2018 1 / 17 Group 14 In this group again, we see a full range of nonmetallic
Chemistry 1000 Lecture 24: Group 14 and Boron Marc R. Roussel November 2, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Group 14 and Boron November 2, 2018 1 / 17 Group 14 In this group again, we see a full range of nonmetallic
SPECIFIC USES OR APPLICATIONS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MEASUREMENT OR ANALYSIS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF NANOSTRUCTURES
 CPC - B82Y - 2017.08 B82Y SPECIFIC USES OR APPLICATIONS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MEASUREMENT OR ANALYSIS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF NANOSTRUCTURES Definition statement This place covers:
CPC - B82Y - 2017.08 B82Y SPECIFIC USES OR APPLICATIONS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MEASUREMENT OR ANALYSIS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF NANOSTRUCTURES Definition statement This place covers:
STM and graphene. W. W. Larry Pai ( 白偉武 ) Center for condensed matter sciences, National Taiwan University NTHU, 2013/05/23
 STM and graphene W. W. Larry Pai ( 白偉武 ) Center for condensed matter sciences, National Taiwan University NTHU, 2013/05/23 Why graphene is important: It is a new form of material (two dimensional, single
STM and graphene W. W. Larry Pai ( 白偉武 ) Center for condensed matter sciences, National Taiwan University NTHU, 2013/05/23 Why graphene is important: It is a new form of material (two dimensional, single
Lectures Graphene and
 Lectures 15-16 Graphene and carbon nanotubes Graphene is atomically thin crystal of carbon which is stronger than steel but flexible, is transparent for light, and conducts electricity (gapless semiconductor).
Lectures 15-16 Graphene and carbon nanotubes Graphene is atomically thin crystal of carbon which is stronger than steel but flexible, is transparent for light, and conducts electricity (gapless semiconductor).
Graphene Novel Material for Nanoelectronics
 Graphene Novel Material for Nanoelectronics Shintaro Sato Naoki Harada Daiyu Kondo Mari Ohfuchi (Manuscript received May 12, 2009) Graphene is a flat monolayer of carbon atoms with a two-dimensional honeycomb
Graphene Novel Material for Nanoelectronics Shintaro Sato Naoki Harada Daiyu Kondo Mari Ohfuchi (Manuscript received May 12, 2009) Graphene is a flat monolayer of carbon atoms with a two-dimensional honeycomb
Intrinsic Electronic Transport Properties of High. Information
 Intrinsic Electronic Transport Properties of High Quality and MoS 2 : Supporting Information Britton W. H. Baugher, Hugh O. H. Churchill, Yafang Yang, and Pablo Jarillo-Herrero Department of Physics, Massachusetts
Intrinsic Electronic Transport Properties of High Quality and MoS 2 : Supporting Information Britton W. H. Baugher, Hugh O. H. Churchill, Yafang Yang, and Pablo Jarillo-Herrero Department of Physics, Massachusetts
Energy Storage. Light-emitting. Nano-Carbons. H 2 Energy. CNT synthesis. Graphene synthesis Top-down. Solar H 2 generation
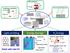 Nano-Carbon battery Graphene synthesis Top-down CNT synthesis CVD reactor hydrocarbon gas Catalyst CNTs Chemical Modification COO O NO 2 COO COO COO Bottom-up O O NO NO 2 2 COO COO Nano-Carbons 20 nm Light-emitting
Nano-Carbon battery Graphene synthesis Top-down CNT synthesis CVD reactor hydrocarbon gas Catalyst CNTs Chemical Modification COO O NO 2 COO COO COO Bottom-up O O NO NO 2 2 COO COO Nano-Carbons 20 nm Light-emitting
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction In our planet carbon forms the basis of all organic molecules which makes it the most important element of life. It is present in over 95% of the known chemical compounds overall
Chapter 1 Introduction In our planet carbon forms the basis of all organic molecules which makes it the most important element of life. It is present in over 95% of the known chemical compounds overall
CHAPTER 11 Semiconductor Theory and Devices
 CHAPTER 11 Semiconductor Theory and Devices 11.1 Band Theory of Solids 11.2 Semiconductor Theory 11.3 Semiconductor Devices 11.4 Nanotechnology It is evident that many years of research by a great many
CHAPTER 11 Semiconductor Theory and Devices 11.1 Band Theory of Solids 11.2 Semiconductor Theory 11.3 Semiconductor Devices 11.4 Nanotechnology It is evident that many years of research by a great many
Nanostrukturphysik Übung 2 (Class 3&4)
 Nanostrukturphysik Übung 2 (Class 3&4) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu 2017.05.03 Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de (3748), yang.xu@tuilmenau.de (4902)
Nanostrukturphysik Übung 2 (Class 3&4) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu 2017.05.03 Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de (3748), yang.xu@tuilmenau.de (4902)
Halbleiter Prof. Yong Lei Prof. Thomas Hannappel
 Halbleiter Prof. Yong Lei Prof. Thomas Hannappel yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de thomas.hannappel@tu-ilmenau.de http:///nanostruk/ Organic semiconductors Small-molecular materials Rubrene Pentacene Polymers PEDOT:PSS
Halbleiter Prof. Yong Lei Prof. Thomas Hannappel yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de thomas.hannappel@tu-ilmenau.de http:///nanostruk/ Organic semiconductors Small-molecular materials Rubrene Pentacene Polymers PEDOT:PSS
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes
 Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
EN2912C: Future Directions in Computing Lecture 08: Overview of Near-Term Emerging Computing Technologies
 EN2912C: Future Directions in Computing Lecture 08: Overview of Near-Term Emerging Computing Technologies Prof. Sherief Reda Division of Engineering Brown University Fall 2008 1 Near-term emerging computing
EN2912C: Future Directions in Computing Lecture 08: Overview of Near-Term Emerging Computing Technologies Prof. Sherief Reda Division of Engineering Brown University Fall 2008 1 Near-term emerging computing
Chapter 12. Nanometrology. Oxford University Press All rights reserved.
 Chapter 12 Nanometrology Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands in relation to a meter and sub divisions of meter. Nanometrology
Chapter 12 Nanometrology Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands in relation to a meter and sub divisions of meter. Nanometrology
Conference Return Seminar- NANO2014,Moscow State University,Moscow,Russia Date: th July 2014
 Conference Return Seminar- NANO2014,Moscow State University,Moscow,Russia Date:13-1818 th July 2014 An electrochemical method for the synthesis of single and few layers graphene sheets for high temperature
Conference Return Seminar- NANO2014,Moscow State University,Moscow,Russia Date:13-1818 th July 2014 An electrochemical method for the synthesis of single and few layers graphene sheets for high temperature
Lecture 4. Conductance sensors. ChemFET. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. py Practical consideration for electrochemical biosensors.
 Lecture 4 Conductance sensors. ChemFET. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. py Practical consideration for electrochemical biosensors. Conductivity I V = I R=, L - conductance L= κa/, l Λ= κ /[ C]
Lecture 4 Conductance sensors. ChemFET. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. py Practical consideration for electrochemical biosensors. Conductivity I V = I R=, L - conductance L= κa/, l Λ= κ /[ C]
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Facile Synthesis of High Quality Graphene Nanoribbons Liying Jiao, Xinran Wang, Georgi Diankov, Hailiang Wang & Hongjie Dai* Supplementary Information 1. Photograph of graphene
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Facile Synthesis of High Quality Graphene Nanoribbons Liying Jiao, Xinran Wang, Georgi Diankov, Hailiang Wang & Hongjie Dai* Supplementary Information 1. Photograph of graphene
M.J. Buehler, Strength in numbers, Nature Nanotechnology, Vol. 5, pp ,
 1 M.J. Buehler, Strength in numbers, Nature Nanotechnology, Vol. 5, pp. 172-174, 2010 NANOMATERIALS Strength in numbers Self-assembly of proteins commonly associated with neurodegenerative diseases can
1 M.J. Buehler, Strength in numbers, Nature Nanotechnology, Vol. 5, pp. 172-174, 2010 NANOMATERIALS Strength in numbers Self-assembly of proteins commonly associated with neurodegenerative diseases can
RAJASTHAN TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, KOTA
 RAJASTHAN TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, KOTA (Electronics & Communication) Submitted By: LAKSHIKA SOMANI E&C II yr, IV sem. Session: 2007-08 Department of Electronics & Communication Geetanjali Institute of Technical
RAJASTHAN TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, KOTA (Electronics & Communication) Submitted By: LAKSHIKA SOMANI E&C II yr, IV sem. Session: 2007-08 Department of Electronics & Communication Geetanjali Institute of Technical
Nano-mechatronics. Presented by: György BudaváriSzabó (X0LY4M)
 Nano-mechatronics Presented by: György BudaváriSzabó (X0LY4M) Nano-mechatronics Nano-mechatronics is currently used in broader spectra, ranging from basic applications in robotics, actuators, sensors,
Nano-mechatronics Presented by: György BudaváriSzabó (X0LY4M) Nano-mechatronics Nano-mechatronics is currently used in broader spectra, ranging from basic applications in robotics, actuators, sensors,
Carbon Nanotubes in Interconnect Applications
 Carbon Nanotubes in Interconnect Applications Page 1 What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? Comparison of electrical properties
Carbon Nanotubes in Interconnect Applications Page 1 What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? Comparison of electrical properties
Scalable Nanomaterials and Nanostructures for Energy and Flexible Electronics
 Scalable Nanomaterials and Nanostructures for Energy and Flexible Electronics Liangbing (Bing) Hu MSE & Energy Center University of Maryland College Park Email: binghu@umd.edu 1 Transparent Paper from
Scalable Nanomaterials and Nanostructures for Energy and Flexible Electronics Liangbing (Bing) Hu MSE & Energy Center University of Maryland College Park Email: binghu@umd.edu 1 Transparent Paper from
Special Properties of Au Nanoparticles
 Special Properties of Au Nanoparticles Maryam Ebrahimi Chem 7500/750 March 28 th, 2007 1 Outline Introduction The importance of unexpected electronic, geometric, and chemical properties of nanoparticles
Special Properties of Au Nanoparticles Maryam Ebrahimi Chem 7500/750 March 28 th, 2007 1 Outline Introduction The importance of unexpected electronic, geometric, and chemical properties of nanoparticles
Chapter 12 - Modern Materials
 Chapter 12 - Modern Materials 12.1 Semiconductors Inorganic compounds that semiconduct tend to have chemical formulas related to Si and Ge valence electron count of four. Semiconductor conductivity can
Chapter 12 - Modern Materials 12.1 Semiconductors Inorganic compounds that semiconduct tend to have chemical formulas related to Si and Ge valence electron count of four. Semiconductor conductivity can
What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them?
 Growth and Properties of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? - our vision Where do we stand - our
Growth and Properties of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? - our vision Where do we stand - our
Nanotechnology where size matters
 Nanotechnology where size matters J Emyr Macdonald Overview Ways of seeing very small things What is nanotechnology and why is it important? Building nanostructures What we can do with nanotechnology?
Nanotechnology where size matters J Emyr Macdonald Overview Ways of seeing very small things What is nanotechnology and why is it important? Building nanostructures What we can do with nanotechnology?
Top down and bottom up fabrication
 Lecture 24 Top down and bottom up fabrication Lithography ( lithos stone / graphein to write) City of words lithograph h (Vito Acconci, 1999) 1930 s lithography press Photolithography d 2( NA) NA=numerical
Lecture 24 Top down and bottom up fabrication Lithography ( lithos stone / graphein to write) City of words lithograph h (Vito Acconci, 1999) 1930 s lithography press Photolithography d 2( NA) NA=numerical
CSCI 2570 Introduction to Nanocomputing
 CSCI 2570 Introduction to Nanocomputing The Emergence of Nanotechnology John E Savage Purpose of the Course The end of Moore s Law is in sight. Researchers are now exploring replacements for standard methods
CSCI 2570 Introduction to Nanocomputing The Emergence of Nanotechnology John E Savage Purpose of the Course The end of Moore s Law is in sight. Researchers are now exploring replacements for standard methods
The Program Committee of the 2013 Annual Joint Symposium of the Florida Chapter of the American Vacuum Society, and Florida Society for Microscopy
 Florida Chapter American Vacuum Society, Grand Prize in Computational and Experimental Materials Science Alamgir Kabir MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF Fe AND Fe-Pt NANOPARTICLES: APPLICATION OF THE DFT- INHOMOGENEOUS-DMFT
Florida Chapter American Vacuum Society, Grand Prize in Computational and Experimental Materials Science Alamgir Kabir MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF Fe AND Fe-Pt NANOPARTICLES: APPLICATION OF THE DFT- INHOMOGENEOUS-DMFT
Fabrication at the nanoscale for nanophotonics
 Fabrication at the nanoscale for nanophotonics Ilya Sychugov, KTH Materials Physics, Kista silicon nanocrystal by electron beam induced deposition lithography Outline of basic nanofabrication methods Devices
Fabrication at the nanoscale for nanophotonics Ilya Sychugov, KTH Materials Physics, Kista silicon nanocrystal by electron beam induced deposition lithography Outline of basic nanofabrication methods Devices
PV Tutorial Allen Hermann, Ph. D. Professor of Physics Emeritus, and Professor of Music Adjunct, University of Colorado, Boulder, Colorado, USA and
 PV Tutorial Allen Hermann, Ph. D. Professor of Physics Emeritus, and Professor of Music Adjunct, University of Colorado, Boulder, Colorado, USA and Vice-president, NanoTech Inc. Lexington, Kentucky, USA
PV Tutorial Allen Hermann, Ph. D. Professor of Physics Emeritus, and Professor of Music Adjunct, University of Colorado, Boulder, Colorado, USA and Vice-president, NanoTech Inc. Lexington, Kentucky, USA
SELF-ASSEMBLY AND NANOTECHNOLOGY A Force Balance Approach
 SELF-ASSEMBLY AND NANOTECHNOLOGY A Force Balance Approach Yoon S. Lee Scientific Information Analyst Chemical Abstracts Service A Division of the American Chemical Society Columbus, Ohio WILEY A JOHN WILEY
SELF-ASSEMBLY AND NANOTECHNOLOGY A Force Balance Approach Yoon S. Lee Scientific Information Analyst Chemical Abstracts Service A Division of the American Chemical Society Columbus, Ohio WILEY A JOHN WILEY
A BIT OF MATERIALS SCIENCE THEN PHYSICS
 GRAPHENE AND OTHER D ATOMIC CRYSTALS Andre Geim with many thanks to K. Novoselov, S. Morozov, D. Jiang, F. Schedin, I. Grigorieva, J. Meyer, M. Katsnelson A BIT OF MATERIALS SCIENCE THEN PHYSICS CARBON
GRAPHENE AND OTHER D ATOMIC CRYSTALS Andre Geim with many thanks to K. Novoselov, S. Morozov, D. Jiang, F. Schedin, I. Grigorieva, J. Meyer, M. Katsnelson A BIT OF MATERIALS SCIENCE THEN PHYSICS CARBON
3-month progress Report
 3-month progress Report Graphene Devices and Circuits Supervisor Dr. P.A Childs Table of Content Abstract... 1 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Graphene gold rush... 1 1.2 Properties of graphene... 3 1.3 Semiconductor
3-month progress Report Graphene Devices and Circuits Supervisor Dr. P.A Childs Table of Content Abstract... 1 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Graphene gold rush... 1 1.2 Properties of graphene... 3 1.3 Semiconductor
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices
 Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
Raman Imaging and Electronic Properties of Graphene
 Raman Imaging and Electronic Properties of Graphene F. Molitor, D. Graf, C. Stampfer, T. Ihn, and K. Ensslin Laboratory for Solid State Physics, ETH Zurich, 8093 Zurich, Switzerland ensslin@phys.ethz.ch
Raman Imaging and Electronic Properties of Graphene F. Molitor, D. Graf, C. Stampfer, T. Ihn, and K. Ensslin Laboratory for Solid State Physics, ETH Zurich, 8093 Zurich, Switzerland ensslin@phys.ethz.ch
Nanoparticles, nanorods, nanowires
 Nanoparticles, nanorods, nanowires Nanoparticles, nanocrystals, nanospheres, quantum dots, etc. Drugs, proteins, etc. Nanorods, nanowires. Optical and electronic properties. Organization using biomolecules.
Nanoparticles, nanorods, nanowires Nanoparticles, nanocrystals, nanospheres, quantum dots, etc. Drugs, proteins, etc. Nanorods, nanowires. Optical and electronic properties. Organization using biomolecules.
Jeopardy Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
 Jeopardy Size and Scale Nano Products Tools Structure Of Matter Science and Society Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300
Jeopardy Size and Scale Nano Products Tools Structure Of Matter Science and Society Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300
PHYS-E0424 Nanophysics Lecture 5: Fullerenes, Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene
 PHYS-E0424 Nanophysics Lecture 5: Fullerenes, Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene PHYS-E0424 Nanophysics Lecture 5: Carbon Nanostructures Sebastiaan van Dijken 1 SEM/TEM Recently I was operating SEM for a first
PHYS-E0424 Nanophysics Lecture 5: Fullerenes, Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene PHYS-E0424 Nanophysics Lecture 5: Carbon Nanostructures Sebastiaan van Dijken 1 SEM/TEM Recently I was operating SEM for a first
Lesson 4: Tools of the Nanosciences. Student Materials
 Lesson 4: Tools of the Nanosciences Student Materials Contents Black Box Lab Activity: Student Instructions and Worksheet Seeing and Building Small Things: Student Reading Seeing and Building Small Things:
Lesson 4: Tools of the Nanosciences Student Materials Contents Black Box Lab Activity: Student Instructions and Worksheet Seeing and Building Small Things: Student Reading Seeing and Building Small Things:
Contents. Foreword by Darrell H. Reneker
 Table of Foreword by Darrell H. Reneker Preface page xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 How big is a nanometer? 1 1.2 What is nanotechnology? 1 1.3 Historical development of nanotechnology 2 1.4 Classification
Table of Foreword by Darrell H. Reneker Preface page xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 How big is a nanometer? 1 1.2 What is nanotechnology? 1 1.3 Historical development of nanotechnology 2 1.4 Classification
master thesis STM studies of molecules for molecular electronics
 STM studies of molecules for molecular electronics Experimental study of single organic molecules by Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) and spectroscopy at low temperature Experimental STM images of Aza-BODIPY
STM studies of molecules for molecular electronics Experimental study of single organic molecules by Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) and spectroscopy at low temperature Experimental STM images of Aza-BODIPY
MSN551 LITHOGRAPHY II
 MSN551 Introduction to Micro and Nano Fabrication LITHOGRAPHY II E-Beam, Focused Ion Beam and Soft Lithography Why need electron beam lithography? Smaller features are required By electronics industry:
MSN551 Introduction to Micro and Nano Fabrication LITHOGRAPHY II E-Beam, Focused Ion Beam and Soft Lithography Why need electron beam lithography? Smaller features are required By electronics industry:
Electrically pulsatile responsive drug delivery platform for treatment of Alzheimer s disease
 Electronic Supplementary Material Electrically pulsatile responsive drug delivery platform for treatment of Alzheimer s disease Li Wu 1,2, Jiasi Wang 1,2, Nan Gao 1, Jinsong Ren 1, Andong Zhao 1,2, and
Electronic Supplementary Material Electrically pulsatile responsive drug delivery platform for treatment of Alzheimer s disease Li Wu 1,2, Jiasi Wang 1,2, Nan Gao 1, Jinsong Ren 1, Andong Zhao 1,2, and
Calculating Electronic Structure of Different Carbon Nanotubes and its Affect on Band Gap
 Calculating Electronic Structure of Different Carbon Nanotubes and its Affect on Band Gap 1 Rashid Nizam, 2 S. Mahdi A. Rizvi, 3 Ameer Azam 1 Centre of Excellence in Material Science, Applied Physics AMU,
Calculating Electronic Structure of Different Carbon Nanotubes and its Affect on Band Gap 1 Rashid Nizam, 2 S. Mahdi A. Rizvi, 3 Ameer Azam 1 Centre of Excellence in Material Science, Applied Physics AMU,
Novel Dispersion and Self-Assembly
 Novel Dispersion and Self-Assembly of Carbon Nanotubes Mohammad F. Islam 100g Department of Chemical Engineering and Department of Materials Science & Engineering Funding Agencies http://islamgroup.cheme.cmu.edu
Novel Dispersion and Self-Assembly of Carbon Nanotubes Mohammad F. Islam 100g Department of Chemical Engineering and Department of Materials Science & Engineering Funding Agencies http://islamgroup.cheme.cmu.edu
Techniken der Oberflächenphysik (Techniques of Surface Physics)
 Techniken der Oberflächenphysik (Techniques of Surface Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu, Dr. Huaping Zhao Fachgebiet Angewante Nanophysik, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de
Techniken der Oberflächenphysik (Techniques of Surface Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu, Dr. Huaping Zhao Fachgebiet Angewante Nanophysik, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Graphene transfer method 1 : Monolayer graphene was pre-deposited on both
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Graphene transfer method 1 : Monolayer graphene was pre-deposited on both
II.1.4 Nanoengineering of Hybrid Carbon Nanotube-Metal Nanocluster Composite Materials for Hydrogen Storage
 II.1.4 Nanoengineering of Hybrid Carbon Nanotube-Metal Nanocluster Composite Materials for Hydrogen Storage Investigators Kyeongjae (KJ) Cho, Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering; Bruce Clemens,
II.1.4 Nanoengineering of Hybrid Carbon Nanotube-Metal Nanocluster Composite Materials for Hydrogen Storage Investigators Kyeongjae (KJ) Cho, Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering; Bruce Clemens,
Kavli Workshop for Journalists. June 13th, CNF Cleanroom Activities
 Kavli Workshop for Journalists June 13th, 2007 CNF Cleanroom Activities Seeing nm-sized Objects with an SEM Lab experience: Scanning Electron Microscopy Equipment: Zeiss Supra 55VP Scanning electron microscopes
Kavli Workshop for Journalists June 13th, 2007 CNF Cleanroom Activities Seeing nm-sized Objects with an SEM Lab experience: Scanning Electron Microscopy Equipment: Zeiss Supra 55VP Scanning electron microscopes
High-resolution Characterization of Organic Ultrathin Films Using Atomic Force Microscopy
 High-resolution Characterization of Organic Ultrathin Films Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jing-jiang Yu Nanotechnology Measurements Division Agilent Technologies, Inc. Atomic Force Microscopy High-Resolution
High-resolution Characterization of Organic Ultrathin Films Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jing-jiang Yu Nanotechnology Measurements Division Agilent Technologies, Inc. Atomic Force Microscopy High-Resolution
1. Introduction : 1.2 New properties:
 Nanodevices In Electronics Rakesh Kasaraneni(PID : 4672248) Department of Electrical Engineering EEL 5425 Introduction to Nanotechnology Florida International University Abstract : This paper describes
Nanodevices In Electronics Rakesh Kasaraneni(PID : 4672248) Department of Electrical Engineering EEL 5425 Introduction to Nanotechnology Florida International University Abstract : This paper describes
Solutions for Assignment-8
 Solutions for Assignment-8 Q1. The process of adding impurities to a pure semiconductor is called: [1] (a) Mixing (b) Doping (c) Diffusing (d) None of the above In semiconductor production, doping intentionally
Solutions for Assignment-8 Q1. The process of adding impurities to a pure semiconductor is called: [1] (a) Mixing (b) Doping (c) Diffusing (d) None of the above In semiconductor production, doping intentionally
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1
 Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Section 5.2.1 Nature of the Carbon Bond
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Section 5.2.1 Nature of the Carbon Bond
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications
 Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2012 Lecture 06 Tentative version of November 13, 2012 Check for the definitive version after the lecture rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2012 Lecture 06 Tentative version of November 13, 2012 Check for the definitive version after the lecture rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton
Applications of Quantum Dots to Biosensing
 Applications of Quantum Dots to Biosensing CHEM 681 Student Seminar Series March 17 th, 2003 Heechang Ye Advisor : Dr. Richard M. Crooks Introduction Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductor particles that
Applications of Quantum Dots to Biosensing CHEM 681 Student Seminar Series March 17 th, 2003 Heechang Ye Advisor : Dr. Richard M. Crooks Introduction Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductor particles that
what happens if we make materials smaller?
 what happens if we make materials smaller? IAP VI/10 ummer chool 2007 Couvin Prof. ns outline Introduction making materials smaller? ynthesis how do you make nanomaterials? Properties why would you make
what happens if we make materials smaller? IAP VI/10 ummer chool 2007 Couvin Prof. ns outline Introduction making materials smaller? ynthesis how do you make nanomaterials? Properties why would you make
