Crabtree Publishing Company
|
|
|
- Rosamond Richard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adam McLean Company 1
2 SHAPING MODERN SCIENCE Author: Adam McLean Publishing plan research and development: Sean Charlebois, Reagan Miller Company Editors: Sasha Patton, Adrianna Morganelli Proofreaders: Gina Springer Shirley, Molly Aloian Project coordinator: Kathy Middleton Editorial services: Clarity Content Services Production coordinator and prepress technician: Katherine Berti Print coordinator: Katherine Berti Series consultant: Eric Walters Cover design: Katherine Berti Design: First Image Photo research: Linda Tanaka Illustrations: Adam McLean Photographs: cover left David Parker/Photo Researchers, Inc.; cover top right and bottom right Shutterstock; title page Shutterstock; p4 Andrea Seemann/ Shutterstock; p5 Dariush M/Shutterstock; p6 oriontrail/ Shutterstock; p7 Maximilien Brice/CERN/The Atlas Experiment at CERN p8 AntoinetteW/Shutterstock; p9 frog-traveller/shutterstock; p10 Dmitri Kamenetsky/Shutterstock; p11 David H. Seymour/Shutterstock; p12 Simone Voigt/Shutterstock; p13 Detail of a paintingby Joseph Wright of Derby depicting the discovering of the element Phosphorus. CCL/wiki; p14 Public Domain/wiki; p15 Portrait of Monsieur de Lavoisier and his Wife, chemist Marie-Anne Pierrette Paulze, Metropolitan Museum of Art, N.Y. Public domain/wiki; p16 Frontispiece of John Dalton and the Rise of Modern Chemistry by Henry Roscoe, Public domain/wiki; p17 Magcom/Shutterstock; p21 Jonathunder/Public domain/wiki; p23 Inductiveload/NASA; p24 Michael Faraday in his laboratory at the Royal Institution. From a painting by Harriet Moore. The original is in the Chemical Heritage Foundation Collections, Public domain/wiki; p27 Ron Dale/Shutterstock; p28 Wolfe Larry/Shutterstock; p29 Alhovik/Shutterstock; p30 upper Valentyn Volkov/ Shutterstock; 2009fotofriends/Shutterstock; p33 Ernst Ruska Electron Microscope/Deutsches Museum Munich/J.Brew/Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License; p35 Library of Congress; p37 Public domain/wiki; p38 Public domain/wiki; p39 US Dept of Energy public domain; p40 Andrea Danti/Shutterstock; p41 US Dept of Energy/ Office of Public Affairs public domain; p42 US Dept of Energy public domain; p44 Tyler Boyes/Shutterstock; p45 NASA; p46 Kharkov Institute for Physics and Technology; p47 Moffett Studio/Library and Archives Canada/ C ; p48 US Dept of Energy; p49 Tyler Boyes/Shutterstock; p50 J. Pequenao/ CERN/The AtlasExperiment at CERN p53 Maximilien Brice/CERN/The Atlas Experiment at CERN p55 top Gonul Kokal/Shutterstock, JOANCHANG/Shutterstock; p56 ITER Organization; p57 The TMT Project is a collaboration of Caltech, University of California (UC) and the Association of Canadian Universities for Research in Astronomy (ACURA) Thirty Meter Telescope. Library and Archives Canada Cataloguing in Publication Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data McLean, Adam, What is atomic theory? [electronic resource] / Adam McLean. (Shaping modern science) Includes index. Electronic monograph in PDF format. Issued also in print format. ISBN Atomic theory--juvenile literature. I. Title. II. Series: Shaping modern science (Online) QD461.M a j541'.24 C McLean, Adam. What is atomic theory? / Adam McLean. p. cm. -- (Shaping modern science) Includes index. ISBN (reinforced lib. bdg. : alk. paper) -- ISBN (pbk. : alk. paper) -- ISBN (electronic (PDF) 1. Atomic theory--juvenile literature. 2. Dalton, John, Juvenile literature. I. Title. II. Series. QD461.M dc Company Copyright 2011 CRABTREE PUBLISHING COMPANY. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or be transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of Company. In Canada: We acknowledge the financial support of the Government of Canada through the Canada Book Fund for our publishing activities. Published in Canada 616 Welland Ave. St. Catharines, ON L2M 5V6 Published in the United States PMB Fifth Avenue, 59th Floor New York, New York Published in the United Kingdom Maritime House Basin Road North, Hove BN41 1WR Published in Australia 386 Mt. Alexander Rd. Ascot Vale (Melbourne) VIC 3032
3 Contents Introduction What Is Atomic Theory? Chapter One Early Concepts About the World Chapter Two Atomic Theory Takes Shape Chapter Three Photons, Electrons, and the Nucleus 22 Chapter Four Elements, Properties, and Chemical Reactions Chapter Five Rays and Radiation Chapter Six Nuclear Fission and Fusion Chapter Seven Atomic Theory Today Chapter Eight Cutting-Edge Careers Timeline Glossary For More Information Index
4 INTRODUCTION What Is Atomic Theory? One of the most exciting journeys in all of science has been the quest to imagine, observe, and understand atoms the building blocks of matter within and around us. People have always wanted to see what their eyes cannot see by themselves, to explore what is too small to touch, and to use the energy stored in matter for the benefit of humankind. Scientists have asked questions about matter, made hypotheses about its structure and function, and then tested those hypotheses by doing experiments. As a result, the theory of matter now describes everything from the tiniest amounts of elements and molecules, all the way up to entire planets, stars, and galaxies. Scientific Theory or Law? In science, a theory is a well-tested set of ideas that explains how something occurs. For example, many kinds of evidence together support Atomic Theory. A scientific law describes how something consistently happens under certain conditions. For example, the law of gravity describes how objects fall to Earth s surface. hthis giant statue of atoms joined together is found in Brussels, Belgium, and is called the Atomium. In the current theory of matter, all substances solids, liquids, gases, and other matter at the coldest and hottest temperatures in the universe are made up of parts that are smaller than anyone can imagine. Think about it this way: the human body is made from organs, bones, muscles, and tendons. These are made from many types of cells that contain DNA and chemicals that power life. Similarly, matter is made from smaller and smaller components. These components act together in huge numbers to make materials that people can see, touch, smell, and taste. 4
5 The word atom is derived from the Greek word atomos, meaning indivisible it is the basic unit of matter. There are so many atoms even in tiny objects like grains of sand that they can be counted only in powers of 10. Using powers of 10, the number of zeros in a big number can be shown as a single raised exponent of 10. For example, 100 is shown as 10 2 (10 10), 1,000 is 10 3 ( ), and so on. If the number begins with something other than 1, then the power of 10 is multiplied by that number, so 500,000 would be Using this method makes it easy to write big numbers in a small space. The number of atoms in an average grain of sand, for example, is If that number was written out, it would be 80,000,000,000,000,000,000 (80 billion billion)! How Many Atoms Are in That? Approximately how many atoms are there in some everyday things? Here are some examples: an average-sized ant: a mechanical pencil: a small 8-ounce (227-g) milk carton: an average-sized laptop computer: pounds (50 kg) of gold bars: one 110-pound (50-kg) person: the air inside a school classroom: an average-sized car: hthis picture shows just a few atoms linked together as they would be in a solid material. My goal is simple. It is a complete understanding of the universe, why it is as it is and why it exists at all. Stephen Hawking, English cosmologist and physicist (1942 ) 5
6 Atoms, Atoms Everywhere! Today, the properties of atoms are very well understood. Atomic theory describes the structure and function of matter. For example, it describes why diamond is the hardest material, while mercury a metal unlike all other metals is liquid at room temperature. Atomic theory also explains the nuclear forces that hold atoms together and electric forces that keep atoms apart. Studying these forces helps people understand chemical interactions from those used in hair dye to those used in explosions and the release and storage of energy such as in power plants, photosynthesis, and batteries. From the Smallest to the Largest Scientists who study atomic theory measure the size of atoms in billionths of an inch (which is the same as inches), or billionths of a centimeter ( cm). That s SMALL! At the other extreme, if the entire universe could be measured, including all of the stars in the sky from one side to the other, it would be nearly three billion billion billion feet (one billion billion billion meters) across, or 3 with 27 zeros after it (3,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 feet)! That s HUGE! gthe size of people and objects that people interact with is just about in the middle between the tiny size of atoms, measured in billionths of an inch, and the billions and billions of miles between Earth and the stars in the sky. 6
7 The important thing is not to stop questioning. Curiosity has its own reason for existing. One cannot help but be in awe when contemplating the mysteries of eternity, of life, or the marvelous structure of reality. It is enough if one tries merely to comprehend a little of this mystery every day. Albert Einstein, German theoretical physicist ( ) gthe largest atom smasher in the world is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Europe. In it, particles collide at nearly the speed of light and break apart to reveal the smaller parts that atoms are made of. For over 4,000 years, people from all over the world have made contributions to atomic theory. The earliest ideas about matter were written down in ancient texts of India. From 600 B.C. 300 B.C., Greek philosophers imagined what matter was made of and what atoms might look like. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, scientists experimented in chemistry and chemical interactions, leading to the modern use of cutting-edge technology and studies of nuclear physics. At times, atomic theory developed at a snail s pace even appearing to go backward. At other times, though, especially in recent years, a lot has been learned about matter and energy very quickly. Today, thousands of researchers on every continent study matter and the nature of the universe using atomic theory. For example, they make measurements at scales from the smallest particles to the largest planets, stars, and galaxies. They smash atoms together to probe what the atoms are made from, create new elements that are not found anywhere else in the universe, and use the most powerful computers in the world to learn about how the universe began. 7
Earth s seven continents
 Explore Earth s seven continents Company www.crabtreebooks.com A Book For my Aunt Margaret You taught us how to laugh and love and we sure do love you! Author and Editor-in-Chief Editor Kathy Middleton
Explore Earth s seven continents Company www.crabtreebooks.com A Book For my Aunt Margaret You taught us how to laugh and love and we sure do love you! Author and Editor-in-Chief Editor Kathy Middleton
Crabtree Publishing Company
 Craig Saunders Company www.crabtreebooks.com SHAPING MODERN SCIENCE Author: Craig Saunders Publishing plan research and development: Sean Charlebois, Reagan Miller Company Editors: Renata Brunner Jass,
Craig Saunders Company www.crabtreebooks.com SHAPING MODERN SCIENCE Author: Craig Saunders Publishing plan research and development: Sean Charlebois, Reagan Miller Company Editors: Renata Brunner Jass,
Unsolved! Kathryn Walker. Crabtree Publishing Company. based on original text by Brian Innes.
 Unsolved! Mysteries of Alien Visitors and Abductions Kathryn Walker based on original text by Brian Innes Crabtree Publishing Company www.crabtreebooks.com Crabtree Publishing Company www.crabtreebooks.com
Unsolved! Mysteries of Alien Visitors and Abductions Kathryn Walker based on original text by Brian Innes Crabtree Publishing Company www.crabtreebooks.com Crabtree Publishing Company www.crabtreebooks.com
Crabtree Publishing Company
 Company www.crabtreebooks.com Publishing plan research and development: Sean Charlebois, Reagan Miller Company Developed and Produced by: Plan B Book Packagers Editorial director: Ellen Rodger Art director:
Company www.crabtreebooks.com Publishing plan research and development: Sean Charlebois, Reagan Miller Company Developed and Produced by: Plan B Book Packagers Editorial director: Ellen Rodger Art director:
Unsolved! of UFOs. Kathryn Walker. based on original text by Brian Innes. Crabtree Publishing Company.
 Unsolved! Mysteries of UFOs Kathryn Walker based on original text by Brian Innes www.crabtreebooks.com www.crabtreebooks.com Author: Kathryn Walker based on original text by Brian Innes Project editor:
Unsolved! Mysteries of UFOs Kathryn Walker based on original text by Brian Innes www.crabtreebooks.com www.crabtreebooks.com Author: Kathryn Walker based on original text by Brian Innes Project editor:
A c l A s s O f t h e i R O w n. Protists. Algae, Amoebas, Plankton, and Other Protists. By Rona Arato
 A c l A s s O f t h e i R O w n Protists Algae, Amoebas, Plankton, and Other Protists By Rona Arato Company www.crabtreebooks.com Company www.crabtreebooks.com Author: Rona Arato Series consultant: Sally
A c l A s s O f t h e i R O w n Protists Algae, Amoebas, Plankton, and Other Protists By Rona Arato Company www.crabtreebooks.com Company www.crabtreebooks.com Author: Rona Arato Series consultant: Sally
Copyright Crabtree Publishing. All rights reserved. May not be reproduced in any form without permission from the publisher, except fair uses
 Author Kelley MacAulay Publishing plan research and development Reagan Miller Notes to adults Reagan Miller Editor Crystal Sikkens Proofreader Wendy Scavuzzo Design Tammy McGarr Library and Archives Canada
Author Kelley MacAulay Publishing plan research and development Reagan Miller Notes to adults Reagan Miller Editor Crystal Sikkens Proofreader Wendy Scavuzzo Design Tammy McGarr Library and Archives Canada
Bobbie Kalman. Crabtree Publishing Company.
 Bobbie Kalman Company www.crabtreebooks.com Created by Bobbie Kalman For Magdalena and Otto, our favorite migrating couple, with love from Peter and Bobbie Author and Editor-in-Chief Bobbie Kalman Research
Bobbie Kalman Company www.crabtreebooks.com Created by Bobbie Kalman For Magdalena and Otto, our favorite migrating couple, with love from Peter and Bobbie Author and Editor-in-Chief Bobbie Kalman Research
Crabtree Publishing Company
 Company www.crabtreebooks.com Publishing plan research and development: Sean Charlebois, Reagan Miller Company Developed and Produced by: Plan B Book Packagers Editorial director: Ellen Rodger Art director:
Company www.crabtreebooks.com Publishing plan research and development: Sean Charlebois, Reagan Miller Company Developed and Produced by: Plan B Book Packagers Editorial director: Ellen Rodger Art director:
Crabtree Publishing Company
 Company www.crabtreebooks.com Publishing plan research and development: Sean Charlebois, Reagan Miller Company Developed and Produced by: Plan B Book Packagers Editorial director: Ellen Rodger Art director:
Company www.crabtreebooks.com Publishing plan research and development: Sean Charlebois, Reagan Miller Company Developed and Produced by: Plan B Book Packagers Editorial director: Ellen Rodger Art director:
Revised and Updated Edition Paul Challen
 Revised and Updated Edition Paul Challen For Sam, Evelina, and Henry Researcher and editor: Adrianna Morganelli Proofreader: Emily McMullen Photo research: Crystal Sikkens Cover design: Ken Wright Editorial
Revised and Updated Edition Paul Challen For Sam, Evelina, and Henry Researcher and editor: Adrianna Morganelli Proofreader: Emily McMullen Photo research: Crystal Sikkens Cover design: Ken Wright Editorial
A C L A S S O F T H E I R O W N. Fungi. Mushrooms, Toadstools, Molds, Yeasts, and Other Fungi. By Judy Wearing
 A C L A S S O F T H E I R O W N Fungi Mushrooms, Toadstools, Molds, Yeasts, and Other Fungi By Judy Wearing Company www.crabtreebooks.com Company www.crabtreebooks.com Author: Judy Wearing Series consultant:
A C L A S S O F T H E I R O W N Fungi Mushrooms, Toadstools, Molds, Yeasts, and Other Fungi By Judy Wearing Company www.crabtreebooks.com Company www.crabtreebooks.com Author: Judy Wearing Series consultant:
Carol Alexander. Crabtree Publishing Company.
 Carol Alexander Company www.crabtreebooks.com Author: Carol Alexander Coordinating editor: Reagan Miller Publishing plan research and development: Sean Charlebois, Reagan Miller Company Editorial director:
Carol Alexander Company www.crabtreebooks.com Author: Carol Alexander Coordinating editor: Reagan Miller Publishing plan research and development: Sean Charlebois, Reagan Miller Company Editorial director:
Crabtree Publishing Company
 Natalie Hyde Company www.crabtreebooks.com Company www.crabtreebooks.com Author: Natalie Hyde Coordinating editor: Chester Fisher Series editor: Jessica Cohn Editorial director: Kathy Middleton Editor:
Natalie Hyde Company www.crabtreebooks.com Company www.crabtreebooks.com Author: Natalie Hyde Coordinating editor: Chester Fisher Series editor: Jessica Cohn Editorial director: Kathy Middleton Editor:
Activity 12 Isotopes and Radioactivity
 OUR LEARNING FIRST ABOUT IDEAS OTHER IDEAS Activity 12 Isotopes and Radioactivity Part of painting by Joseph Wright of Derby, 1734-1797: The Alchemist in Search of the Philosopher s Stone Discovers Phosphorus.
OUR LEARNING FIRST ABOUT IDEAS OTHER IDEAS Activity 12 Isotopes and Radioactivity Part of painting by Joseph Wright of Derby, 1734-1797: The Alchemist in Search of the Philosopher s Stone Discovers Phosphorus.
Learning About Our Solar System
 Learning About Our Solar System By debbie Routh COPYRIGHT 2004 Mark Twain Media, Inc. ISBN 978-1-58037-876-5 Printing No. 404007-EB Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers Distributed by Carson-Dellosa Publishing
Learning About Our Solar System By debbie Routh COPYRIGHT 2004 Mark Twain Media, Inc. ISBN 978-1-58037-876-5 Printing No. 404007-EB Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers Distributed by Carson-Dellosa Publishing
Vocabulary atom atomos Dalton's atomic theory law of constant composition law of definite proportions law of multiple proportions matter.
 1.3 Early Atomic Theory Lesson Objectives The student will: define matter and explain how it is composed of building blocks known as atoms. give a short history of how the concept of the atom developed.
1.3 Early Atomic Theory Lesson Objectives The student will: define matter and explain how it is composed of building blocks known as atoms. give a short history of how the concept of the atom developed.
Atomic Theory Timeline Project
 Atomic Theory Timeline Project MAKE AN ATOMIC THEORY TIMELINE! Directions: 1) Read the information about the scientists and theories that have developed over time about matter and the atom in the Atomic
Atomic Theory Timeline Project MAKE AN ATOMIC THEORY TIMELINE! Directions: 1) Read the information about the scientists and theories that have developed over time about matter and the atom in the Atomic
t h e s c i e n c e o f C A T A S T R O P H E N A T U R A L D I S A S T E R S V I O L E N T W E A T H E R Crabtree Publishing Company
 t h e s c i e n c e o f C A T A S T R O P H E N A T U R A L D I S A S T E R S V I O L E N T W E A T H E R S T E v E P A R k E R & D A v i D W E S T Company www.crabtreebooks.com Company www.crabtreebooks.com
t h e s c i e n c e o f C A T A S T R O P H E N A T U R A L D I S A S T E R S V I O L E N T W E A T H E R S T E v E P A R k E R & D A v i D W E S T Company www.crabtreebooks.com Company www.crabtreebooks.com
SU230R Grades 4-8. Hayes FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM
 Hayes SU230R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM Fast Facts & Dazzling Data Our Solar System This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc.,
Hayes SU230R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM Fast Facts & Dazzling Data Our Solar System This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc.,
 Physics The study of the energy, matter, and forces in the Universe Why do stars move in the sky? How can heat be changed into electricity? What is the difference between an atom of one substance and an
Physics The study of the energy, matter, and forces in the Universe Why do stars move in the sky? How can heat be changed into electricity? What is the difference between an atom of one substance and an
1 The Development of Atomic Theory
 CHAPTER 4 1 The Development of Atomic Theory SECTION Atoms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What scientists helped to develop atomic theory? What part of atoms did Thomson
CHAPTER 4 1 The Development of Atomic Theory SECTION Atoms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What scientists helped to develop atomic theory? What part of atoms did Thomson
Atomic Theory. The History of Atomic Theory
 Atomic Theory The History of Atomic Theory This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels.
Atomic Theory The History of Atomic Theory This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels.
History of the Atom. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 History of the Atom Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
History of the Atom Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
The History of Atomic Theory Chapter 3--Chemistry
 The History of Atomic Theory Chapter 3--Chemistry In this lesson, we ll learn about the men whose quests for knowledge about the fundamental nature of the universe helped define our views. The atomic model
The History of Atomic Theory Chapter 3--Chemistry In this lesson, we ll learn about the men whose quests for knowledge about the fundamental nature of the universe helped define our views. The atomic model
4.1 Defining the Atom > Chapter 4 Atomic Structure. 4.1 Defining the Atom. 4.2 Structure of the Nuclear Atom. 4.3 Distinguishing Among Atoms
 Chapter 4 Atomic Structure 4.1 Defining the Atom 4.2 Structure of the Nuclear Atom 4.3 Distinguishing Among Atoms 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure 4.1 Defining the Atom 4.2 Structure of the Nuclear Atom 4.3 Distinguishing Among Atoms 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY
ACTIVITY SHEETS PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY 2 nd ESO) NAME:
 ACTIVITY SHEETS PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY 2 nd ESO) NAME:. READING 1 The atom Lesson 4. JOURNEY TO THE INTERIOR OF MATTER Wise men and women of the great ancient civilisations thought a long time ago about
ACTIVITY SHEETS PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY 2 nd ESO) NAME:. READING 1 The atom Lesson 4. JOURNEY TO THE INTERIOR OF MATTER Wise men and women of the great ancient civilisations thought a long time ago about
The origins of atomic theory
 Models of the atom It is important to realise that a lot of what we know about the structure of atoms has been developed over a long period of time. This is often how scientific knowledge develops, with
Models of the atom It is important to realise that a lot of what we know about the structure of atoms has been developed over a long period of time. This is often how scientific knowledge develops, with
MOR TIME TEACHERS. ONCE UPON A TIME Activity Overview BIG IDEA
 MOR TIME 04 Activity Overview BIG IDEA OBJECTIVE BACKGROUND The geologic time scale can be challenging for students to understand. This activity explores how scientists divide the Earth s long history
MOR TIME 04 Activity Overview BIG IDEA OBJECTIVE BACKGROUND The geologic time scale can be challenging for students to understand. This activity explores how scientists divide the Earth s long history
The Story of the Atom. A history of atomic theory over many years
 The Story of the Atom A history of atomic theory over many years Democritus Many years ago, between 460BC and 370BC the Greek philosophers wondered what we were made of. Leucippus and Democritus came up
The Story of the Atom A history of atomic theory over many years Democritus Many years ago, between 460BC and 370BC the Greek philosophers wondered what we were made of. Leucippus and Democritus came up
What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory?
 Gents of Texas A&M What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy March 2018 Prologue We live
Gents of Texas A&M What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy March 2018 Prologue We live
Understanding the Atom 1.3
 Understanding the Atom 1.3 Introduction to Atoms 1.What are some ways that scientists have described the atom? 2.What are the parts of the atom, and how are they arranged? 3.How are atoms of all elements
Understanding the Atom 1.3 Introduction to Atoms 1.What are some ways that scientists have described the atom? 2.What are the parts of the atom, and how are they arranged? 3.How are atoms of all elements
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
 Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory Students should be able to: Describe the particle theory of matter. PS.2a Use the Bohr model to differentiate among the three basic particles in the atom (proton,
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory Students should be able to: Describe the particle theory of matter. PS.2a Use the Bohr model to differentiate among the three basic particles in the atom (proton,
Atomic Models. A model uses familiar ideas to explain unfamiliar facts observed in nature. A model can be changed as new information is collected.
 This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels. Atomic Models A model uses familiar ideas
This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels. Atomic Models A model uses familiar ideas
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table
 chapter 00 3 3 Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table section 1 Structure of Matter Before You Read Take a deep breath. What fills your lungs? Can you see it or hold it in your hand? What You ll Learn
chapter 00 3 3 Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table section 1 Structure of Matter Before You Read Take a deep breath. What fills your lungs? Can you see it or hold it in your hand? What You ll Learn
What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory?
 MSC Bethancourt Lecture What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy Prologue We live in a
MSC Bethancourt Lecture What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy Prologue We live in a
Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D.
 Real Science-4-Kids Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Cover design: David Keller Opening page: David Keller Illustrations: Janet Moneymaker, Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Copyright 2004, 2005, 2007, 2008, 2010 Gravitas
Real Science-4-Kids Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Cover design: David Keller Opening page: David Keller Illustrations: Janet Moneymaker, Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Copyright 2004, 2005, 2007, 2008, 2010 Gravitas
Resources for Treasure Hunt In Earth s Attic Try This!
 Try This! Work in groups or as a family to determine the order of events that in the history of the Earth and Moon. More information and graphics are available at http://www.lpi.usra.edu/education/timeline/introduction.shtml
Try This! Work in groups or as a family to determine the order of events that in the history of the Earth and Moon. More information and graphics are available at http://www.lpi.usra.edu/education/timeline/introduction.shtml
What are atoms? -:-.L'::'
 What are atoms? -:-.L'::' What is the smallest particle of dust? thing you can think of? A single grain of sand? A Now try to imagine something so small that you would need millions of them to make one
What are atoms? -:-.L'::' What is the smallest particle of dust? thing you can think of? A single grain of sand? A Now try to imagine something so small that you would need millions of them to make one
Plants Biological Sciences Written for the Australian Curriculum: Science
 Plants Biological Sciences Written for the Australian Curriculum: Science Sienna Osborne Randall Hall Richard John AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM: SCIENCE Strand: Sub-strand: Descriptor: SCIENCE WORDS Science Understanding
Plants Biological Sciences Written for the Australian Curriculum: Science Sienna Osborne Randall Hall Richard John AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM: SCIENCE Strand: Sub-strand: Descriptor: SCIENCE WORDS Science Understanding
ì<(sk$m)=bdcdhj< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Space and Technology Explore the Galaxy Genre Expository nonfiction Comprehension
Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Space and Technology Explore the Galaxy Genre Expository nonfiction Comprehension
CLIL Content Language Integrated Learning
 Atomos CLIL Content Language Integrated Learning PET - Preliminary English Test Teacher: Mr Pierluigi Stroppa Tutor: Mrs Angela Valentini 1 Investigating atoms You should be able to: Describe the particle
Atomos CLIL Content Language Integrated Learning PET - Preliminary English Test Teacher: Mr Pierluigi Stroppa Tutor: Mrs Angela Valentini 1 Investigating atoms You should be able to: Describe the particle
Scott Foresman Science 4.17
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Cause and Effect Captions Labels Diagrams Glossary Earth Cycles Scott Foresman Science 4.17 ISBN-13: 978-0-328-34240-2 ISBN-10: 0-328-34240-8
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Cause and Effect Captions Labels Diagrams Glossary Earth Cycles Scott Foresman Science 4.17 ISBN-13: 978-0-328-34240-2 ISBN-10: 0-328-34240-8
Matter and Energy: What are atoms?
 Matter and Energy: What are atoms? By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.31.17 Word Count 546 Level 820L An illustration of an atom. The nucleus, containing neutrons and protons,
Matter and Energy: What are atoms? By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.31.17 Word Count 546 Level 820L An illustration of an atom. The nucleus, containing neutrons and protons,
Atomic Structure. For thousands of years, people had many ideas about matter Ancient Greeks believed that everything was made up of the four elements
 An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. Although early philosophers and scientists could not observe individual atoms, they were still able to propose
An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. Although early philosophers and scientists could not observe individual atoms, they were still able to propose
Particle Theory of Matter. By the late 1700s, scientists had adopted the Particle Theory of Matter. This theory states that:
 Particle Theory of Matter By the late 1700s, scientists had adopted the Particle Theory of Matter. This theory states that: all matter is made up of very tiny particles each pure substance has its own
Particle Theory of Matter By the late 1700s, scientists had adopted the Particle Theory of Matter. This theory states that: all matter is made up of very tiny particles each pure substance has its own
meteorologist By Geoffrey M. Horn Reading Consultant: Susan Nations, M.Ed., author/literacy coach/consultant in literacy development
 meteorologist By Geoffrey M. Horn Reading Consultant: Susan Nations, M.Ed., author/literacy coach/consultant in literacy development Please visit our web site at www.garethstevens.com. For a free catalog
meteorologist By Geoffrey M. Horn Reading Consultant: Susan Nations, M.Ed., author/literacy coach/consultant in literacy development Please visit our web site at www.garethstevens.com. For a free catalog
Atomic Structure. A model uses familiar ideas to explain unfamiliar facts observed in nature.
 Atomic Structure 1 2 This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels. A model uses familiar
Atomic Structure 1 2 This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels. A model uses familiar
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
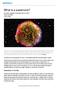 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
The Start of the LHC Era. Peter Wittich Laboratory of Elementary Particle Physics Cornell University
 The Start of the LHC Era Peter Wittich Laboratory of Elementary Particle Physics Cornell University Big Bang - where it all began 3 4 13 billion years ago 4 13 billion years ago hot, highly energetic
The Start of the LHC Era Peter Wittich Laboratory of Elementary Particle Physics Cornell University Big Bang - where it all began 3 4 13 billion years ago 4 13 billion years ago hot, highly energetic
Understanding Main Idea and Details
 C Understanding Main Idea and Details To the Student In this book, you will learn how to use the reading strategy called Understanding Main Idea and Details. With your teacher s help, you will practice
C Understanding Main Idea and Details To the Student In this book, you will learn how to use the reading strategy called Understanding Main Idea and Details. With your teacher s help, you will practice
Real Science-4-Kids. Level I. Dr. R. W. Keller
 Real Science-4-Kids Level I Dr. R. W. Keller Cover design: David Keller Opening page: David Keller Illustrations: Janet Moneymaker, Rebecca Keller Copyright 2004 Gravitas Publications, Inc. All rights
Real Science-4-Kids Level I Dr. R. W. Keller Cover design: David Keller Opening page: David Keller Illustrations: Janet Moneymaker, Rebecca Keller Copyright 2004 Gravitas Publications, Inc. All rights
OUTSIDE THE SOLAR SYSTEM Outside the Solar System
 Written by Patricia Walsh and Ron Fridell INTRODUCTION Outside the Solar System This book is available at three reading levels, as indicated by the one, two, or three dots beside the Science A Z logo on
Written by Patricia Walsh and Ron Fridell INTRODUCTION Outside the Solar System This book is available at three reading levels, as indicated by the one, two, or three dots beside the Science A Z logo on
What is matter? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Matter is made up of atoms.
 Matter What is matter? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Matter is made up of atoms. Is it matter? Can you measure the object? Does it take up space? Does the object have a mass? Come
Matter What is matter? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Matter is made up of atoms. Is it matter? Can you measure the object? Does it take up space? Does the object have a mass? Come
Atomic Theory. Introducing the Atomic Theory:
 Atomic Theory Chemistry is the science of matter. Matter is made up of things called atoms, elements, and molecules. But have you ever wondered if atoms and molecules are real? Would you be surprised to
Atomic Theory Chemistry is the science of matter. Matter is made up of things called atoms, elements, and molecules. But have you ever wondered if atoms and molecules are real? Would you be surprised to
Chapter 2 Energy, Force, and Motion Lesson 6 Describing Motion C, D; 8.2C, D; 8.4A; 8.6B
 Table of Contents Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills Correlation Chart....... 7 Chapter 1 Matter..................................... 11 Lesson 1 Atoms and Elements.......................... 12 6.5A*,
Table of Contents Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills Correlation Chart....... 7 Chapter 1 Matter..................................... 11 Lesson 1 Atoms and Elements.......................... 12 6.5A*,
4.2 A Scientific View of Energy Kinetic Energy
 4. A Universe of Matter and Energy 4.1 Matter and Energy in Everyday Life The eternal mystery of the world is its comprehensibility. The fact that it is comprehensible is a miracle. Albert Einstein (1879
4. A Universe of Matter and Energy 4.1 Matter and Energy in Everyday Life The eternal mystery of the world is its comprehensibility. The fact that it is comprehensible is a miracle. Albert Einstein (1879
ì<(sk$m)=beabid< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Physical Science by Lillian Duggan Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Captions Charts Diagrams Glossary Forms of Energy Scott Foresman Science 6.17 ì
Physical Science by Lillian Duggan Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Captions Charts Diagrams Glossary Forms of Energy Scott Foresman Science 6.17 ì
A brief history of Chemistry. Science 9- Mr. Klasz
 A brief history of Chemistry Science 9- Mr. Klasz What is a pure substance? An element is a pure substance. A compound is made up of two or more elements which have been chemically compounded together.
A brief history of Chemistry Science 9- Mr. Klasz What is a pure substance? An element is a pure substance. A compound is made up of two or more elements which have been chemically compounded together.
ì<(sk$m)=bdidjf< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Cause and Effect Captions Labels Glossary Changes in Matter Scott Foresman Science 3.11 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Cause and Effect Captions Labels Glossary Changes in Matter Scott Foresman Science 3.11 ì
ì<(sk$m)=bdhded< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Feature Science Content Nonfiction Alike and Different Glossary Living and Nonliving Things Scott Foresman Science 1.1 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Feature Science Content Nonfiction Alike and Different Glossary Living and Nonliving Things Scott Foresman Science 1.1 ì
Sample file. Solar System. Author: Tina Griep. Understanding Science Series
 Author: Tina Griep Understanding Science Series Our Copyright 2007 New Learning Publishing All rights reserved. Except as permitted under the United States Copyright Act, no portion of this publication
Author: Tina Griep Understanding Science Series Our Copyright 2007 New Learning Publishing All rights reserved. Except as permitted under the United States Copyright Act, no portion of this publication
Space. Earth. EARTH and EARTH and SPACE SPACE. Earth. William B. Rice
 Space Earth rth EARTH and EARTH and SPACE SPACE SCIENCE Earth is covered with mountains, canyons, and oceans. These landforms change over time. Mountains are made. Valleys may become deeper. Earth s landforms
Space Earth rth EARTH and EARTH and SPACE SPACE SCIENCE Earth is covered with mountains, canyons, and oceans. These landforms change over time. Mountains are made. Valleys may become deeper. Earth s landforms
RealScience-4-Kids. LaboratoryWorkbook. RebeccaW.Keler,Ph.D.
 RealScience-4-Kids LaboratoryWorkbook RebeccaW.Keler,Ph.D. Real Science-4-Kids Level I Laboratory Workbook Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Illustrations: Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Copyright 2011 Gravitas Publications,
RealScience-4-Kids LaboratoryWorkbook RebeccaW.Keler,Ph.D. Real Science-4-Kids Level I Laboratory Workbook Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Illustrations: Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Copyright 2011 Gravitas Publications,
UNIT 2 The Particulate Nature of Matter
 UNIT 2 The Particulate Nature of Matter Take a moment to think about all of the different properties which can be exhibited by matter. The list seems endless. Matter can be found in a variety of forms,
UNIT 2 The Particulate Nature of Matter Take a moment to think about all of the different properties which can be exhibited by matter. The list seems endless. Matter can be found in a variety of forms,
The Practice Book for Conceptual Physics. Paul G. Hewitt Eleventh Edition
 The Practice Book for Conceptual Physics Paul G. Hewitt Eleventh Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on
The Practice Book for Conceptual Physics Paul G. Hewitt Eleventh Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on
Matter: Properties and Change
 Matter: Properties and Change 6.P.2 Understand the structure, classifications and physical properties of matter. 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are
Matter: Properties and Change 6.P.2 Understand the structure, classifications and physical properties of matter. 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are
Development of Atomic Theory Elements of chemistry- Atoms, the building blocks of matter Video
 Development of Atomic Theory Elements of chemistry- Atoms, the building blocks of matter Video 2 CH 4- Atoms 1 Discovering the Atom In this lesson we will take a look at the scientists who explored the
Development of Atomic Theory Elements of chemistry- Atoms, the building blocks of matter Video 2 CH 4- Atoms 1 Discovering the Atom In this lesson we will take a look at the scientists who explored the
Scientists stunned to learn universe may be accelerating
 Scientists stunned to learn universe may be accelerating In this story: Finding may prove Einstein's blunder Tracking the debris of exploded stars Parallel study confirms finding A fifth force at work?
Scientists stunned to learn universe may be accelerating In this story: Finding may prove Einstein's blunder Tracking the debris of exploded stars Parallel study confirms finding A fifth force at work?
Discover The Life Of An Inventor. Albert Einstein
 Discover The Life Of An Inventor Albert Einstein ALBERT EINSTEIN DISCOVER THE LIFE OF AN INVENTOR Don McLeese Rourke Publishing LLC Vero Beach, Florida 32964 2006 Rourke Publishing LLC All rights reserved.
Discover The Life Of An Inventor Albert Einstein ALBERT EINSTEIN DISCOVER THE LIFE OF AN INVENTOR Don McLeese Rourke Publishing LLC Vero Beach, Florida 32964 2006 Rourke Publishing LLC All rights reserved.
Length, mass, and time
 Length, mass, and time Objectives Record data using scientific notation. Record data using International System (SI) units. 1. Express the following numbers in scientific notation: a. 275 b..173 c. 93,422
Length, mass, and time Objectives Record data using scientific notation. Record data using International System (SI) units. 1. Express the following numbers in scientific notation: a. 275 b..173 c. 93,422
Space Exploration. Before You Read LESSON 6
 LESSON 6 Before You Read Space Exploration Since ancient times, people have dreamed of leaving their home planet and exploring other worlds. In the later half of the 20th century, that dream became a reality.
LESSON 6 Before You Read Space Exploration Since ancient times, people have dreamed of leaving their home planet and exploring other worlds. In the later half of the 20th century, that dream became a reality.
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES
 THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
The Big Bang Theory. Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra
 The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory?
 Lunar Society What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy Prologue We live in a time of remarkable
Lunar Society What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy Prologue We live in a time of remarkable
The Nature of Science
 chapter 1 The Nature of Science section 2 Standards of Measurement Before You Read If someone asked you how wide your desk is, how would you measure it? Would you measure using inches, centimeters, feet,
chapter 1 The Nature of Science section 2 Standards of Measurement Before You Read If someone asked you how wide your desk is, how would you measure it? Would you measure using inches, centimeters, feet,
STATES OF MATTER NOTES..
 STATES OF MATTER NOTES.. While you are reading, answer the following which will help you with the States of Matter Project. What is matter (definition): What are the states of matter and what are the characteristics/properties
STATES OF MATTER NOTES.. While you are reading, answer the following which will help you with the States of Matter Project. What is matter (definition): What are the states of matter and what are the characteristics/properties
Courtesy of NASA nasaimages.org
 Illustrations: Photographs: Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Courtesy of NASA nasaimages.org Copyright 2011 Gravitas Publications, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
Illustrations: Photographs: Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Courtesy of NASA nasaimages.org Copyright 2011 Gravitas Publications, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
Name Chemistry-PAP Per. Notes: Atomic Structure
 Name Chemistry-PAP Per. I. Historical Development of the Atomic Model Ancient Greek Model Notes: Atomic Structure Democritus (460-370 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher credited with the first particle
Name Chemistry-PAP Per. I. Historical Development of the Atomic Model Ancient Greek Model Notes: Atomic Structure Democritus (460-370 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher credited with the first particle
The Electromagnetic Spectrum. 7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay. Isotopes. 19K, 19K, 19K Representing Isotopes
 7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay Natural background radiation exists all around us. Radioactivity is the release of high energy particles or waves When atoms lose high energy particles and waves,
7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay Natural background radiation exists all around us. Radioactivity is the release of high energy particles or waves When atoms lose high energy particles and waves,
Chemistry and Atoms! 8 th grade history information to help you understand the background of how our knowledge grew through the years.
 Chemistry and Atoms! 8 th grade history information to help you understand the background of how our knowledge grew through the years. Chemistry lies at the roots of civilization! Chemical reactions are
Chemistry and Atoms! 8 th grade history information to help you understand the background of how our knowledge grew through the years. Chemistry lies at the roots of civilization! Chemical reactions are
Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book You have learned that a nebula can turn into a star, and that the star can turn into a new nebula. Now design a comic, timeline, flowchart, or cycle diagram to explain this process. Include
FOCUS Book You have learned that a nebula can turn into a star, and that the star can turn into a new nebula. Now design a comic, timeline, flowchart, or cycle diagram to explain this process. Include
CAVES CAVES BAYS BEACHES CANYONS ISLANDS LAKES MOUNTAINS PENINSULAS PLAINS VALLEYS GLACIERS HILLS. Titles in This Series. Exploring.
 Caves Titles in This Series E M PL Melody S. Mis SA ROSEN / PowerKids Press ISBN 978-1-4358-2713-4 Geographical CAVES Melody S. Mis ISLANDS LAKES MOUNTAINS PENINSULAS PLAINS VALLEYS Exploring Exploring
Caves Titles in This Series E M PL Melody S. Mis SA ROSEN / PowerKids Press ISBN 978-1-4358-2713-4 Geographical CAVES Melody S. Mis ISLANDS LAKES MOUNTAINS PENINSULAS PLAINS VALLEYS Exploring Exploring
Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table. Unit 3
 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Unit 3 Lesson 1: Atoms Unit 5: Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table Atoms How small can things get? If you break a stone wall into smaller and smaller pieces, you
Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Unit 3 Lesson 1: Atoms Unit 5: Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table Atoms How small can things get? If you break a stone wall into smaller and smaller pieces, you
v = H o d Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d):
 Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d): v = H o d The Hubble Constant was measured after decades of observation: H 0 = 70 km/s/mpc Velocity (km/s)
Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d): v = H o d The Hubble Constant was measured after decades of observation: H 0 = 70 km/s/mpc Velocity (km/s)
o Terms to know o Big Bang Theory o Doppler Effect o Redshift o Universe
 Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Major upsetting discoveries: Today s Objectives/Agenda. Notice: New Unit: with Ms. V. after school Before Friday 9/22.
 Bellwork Monday 9 18 17 Tuesday 9 19 17 *This should be the last box on bellwork: 1. What are some major points in history where common knowledge was upset by a new discovery? 2. Draw what you think an
Bellwork Monday 9 18 17 Tuesday 9 19 17 *This should be the last box on bellwork: 1. What are some major points in history where common knowledge was upset by a new discovery? 2. Draw what you think an
Pre-Level I. Teacher s Manual. Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D.
 Pre-Level I Teacher s Manual Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Illustrations: Janet Moneymaker Marjie Bassler Copyright 2011 Gravitas Publications, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
Pre-Level I Teacher s Manual Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Illustrations: Janet Moneymaker Marjie Bassler Copyright 2011 Gravitas Publications, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
Changes in the sky Earth and Space Sciences Written for the Australian Curriculum: Science
 Changes in the sky Earth and Space Sciences Written for the Australian Curriculum: Science Sienna Osborne Randall Hall Richard John AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM: SCIENCE Strand: Sub-strand: Descriptor: Science
Changes in the sky Earth and Space Sciences Written for the Australian Curriculum: Science Sienna Osborne Randall Hall Richard John AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM: SCIENCE Strand: Sub-strand: Descriptor: Science
Atom s Structure. Chemistry is the study of the structure, characteristics and behavior of matter. The basic
 AlMarzooqi 1 Hamad AlMarzooqi Professor Kafle ESL 015 26 February 2013 Atom s Structure Chemistry is the study of the structure, characteristics and behavior of matter. The basic unit of matter is an atom,
AlMarzooqi 1 Hamad AlMarzooqi Professor Kafle ESL 015 26 February 2013 Atom s Structure Chemistry is the study of the structure, characteristics and behavior of matter. The basic unit of matter is an atom,
ì<(sk$m)=bdhgea< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Important Details Call Outs Captions Diagrams Glossary Day and Night Sky Scott Foresman Science 1.11 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Important Details Call Outs Captions Diagrams Glossary Day and Night Sky Scott Foresman Science 1.11 ì
by Gloria Jasperse HOUGHTON MIFFLIN
 by Gloria Jasperse HOUGHTON MIFFLIN by Gloria Jasperse PHOTOGRAPHY CREDITS: Cover NASA David Scott. 1 NASA Marshall Space Flight Center. 2 Tiziou Jacques/CORBIS SYGMA. 33 (l) NASA, (r) NASA. 4 NASA Marshall
by Gloria Jasperse HOUGHTON MIFFLIN by Gloria Jasperse PHOTOGRAPHY CREDITS: Cover NASA David Scott. 1 NASA Marshall Space Flight Center. 2 Tiziou Jacques/CORBIS SYGMA. 33 (l) NASA, (r) NASA. 4 NASA Marshall
Photo Credits: All images Harcourt
 CXEGA09ALR1X_OL16.indd 2 3/2/07 6:19:50 PM Photo Credits: All images Harcourt If you have received these materials as examination copies free of charge, Harcourt School Publishers retains title to the
CXEGA09ALR1X_OL16.indd 2 3/2/07 6:19:50 PM Photo Credits: All images Harcourt If you have received these materials as examination copies free of charge, Harcourt School Publishers retains title to the
Alive! ì<(sk$m)=bdcibc< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U. It s. by Linda Yoshizawa. Life Science. Scott Foresman Reading Street 2.4.2
 Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Life Science It s Alive! Genre Comprehension Skills and Strategy Text Features
Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Life Science It s Alive! Genre Comprehension Skills and Strategy Text Features
Exploring North America
 Exploring North America Continents of the World Geography Series Author: Michael Kramme, Ph.D. Consultants: Schyrlet Cameron and Carolyn Craig Editors: Mary Dieterich and Sarah M. Anderson COPYRIGHT 2012
Exploring North America Continents of the World Geography Series Author: Michael Kramme, Ph.D. Consultants: Schyrlet Cameron and Carolyn Craig Editors: Mary Dieterich and Sarah M. Anderson COPYRIGHT 2012
Properties of Matter BEFORE READING BUILD BACKGROUND PREVIEW TEXT AND GRAPHICS
 READING FOCUS SKILLS: Main Idea and Details, Cause and Effect VOCABULARY: density, gas, liquid, mass, matter, mixture, solid, solubility, solution, state of matter, suspension, volume EXTENSIONS: Writing,
READING FOCUS SKILLS: Main Idea and Details, Cause and Effect VOCABULARY: density, gas, liquid, mass, matter, mixture, solid, solubility, solution, state of matter, suspension, volume EXTENSIONS: Writing,
Exploring Europe. Continents of the World Geography Series
 Exploring Europe Continents of the World Geography Series Author: Michael Kramme, Ph.D. Consultants: Schyrlet Cameron and Carolyn Craig Editors: Mary Dieterich and Sarah M. Anderson COPYRIGHT 2012 Mark
Exploring Europe Continents of the World Geography Series Author: Michael Kramme, Ph.D. Consultants: Schyrlet Cameron and Carolyn Craig Editors: Mary Dieterich and Sarah M. Anderson COPYRIGHT 2012 Mark
Year 7 Science. 7C1: The Particle Model. PPA Challenge
 Year 7 Science 7C1: The Particle Model PPA Challenge Name: Form: Task Sheet 1 (Bronze Challenge): The Particle Model Use the words in the box to label the diagram below. This particle diagram shows the
Year 7 Science 7C1: The Particle Model PPA Challenge Name: Form: Task Sheet 1 (Bronze Challenge): The Particle Model Use the words in the box to label the diagram below. This particle diagram shows the
1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? WHY DO WE LOOK AT THINGS FROM FAR AWAY AND CLOSE UP?
 1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? WHY DO WE LOOK AT THINGS FROM FAR AWAY AND CLOSE UP? UNIT 1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? CONTENTS UNIT 1 BASICS 3 Unit 1 Overview 4 Unit 1 Learning Outcomes 5 Unit 1 Lessons 7 Unit 1 Key
1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? WHY DO WE LOOK AT THINGS FROM FAR AWAY AND CLOSE UP? UNIT 1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? CONTENTS UNIT 1 BASICS 3 Unit 1 Overview 4 Unit 1 Learning Outcomes 5 Unit 1 Lessons 7 Unit 1 Key
Courtesy of NASA nasaimages.org. Copyright 2011, 2013 Gravitas Publications, Inc.
 Illustrations: Photographs: Rebecca W. Keller, PhD Courtesy of NASA nasaimages.org Copyright 2011, 2013 Gravitas Publications, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
Illustrations: Photographs: Rebecca W. Keller, PhD Courtesy of NASA nasaimages.org Copyright 2011, 2013 Gravitas Publications, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
