Electrochemical Potential and the Thermodynamic Basis of Solute Transport Mechanisms
|
|
|
- Edgar Price
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrochemical Potential and the Thermodynamic Basis of Solute Transport Mechanisms A. Electrochemical Potential The electrochemical potential arising from the distribution of a solute A across a membrane can be considered from the standpoint of an equilibrium which is written for solute uptake into a cell rather than solute loss to the environment. This is a convention that determines the /- sign convention that propagates in the following equations. The free energy change for the movement of A from out to in is given by: G A= G Ain - G Aout = nf ψ 2.3 RT log A Ain out G A : referred to as the Electrochemical Potential R: Gas Law Constant = 8.3 J K -1 mol -1 ( kj K -1 mol -1 l) T: 298 K n: electric charge on A (-1, 0, 2, etc.) F: Faraday Constant = 96 kj V -1 mol -1 ψ: "Membrane Potential" ψ = ψin - ψout ψ is measured experimentally. In metabolically active cells, or mitochondria, carrying out aerobic respiration it often has a value between -0.1 V and -0.2 V (Negative values of ψ mean there is more negative charge inside the cell.) Note that the magnitude of ψ in active cells is comparable in magnitude to the electrical potential used in agarose gel electrophoresis. Ain The RT ln term describes a chemical (mass) gradient, while the A out nf ψ term describes a gradient of electric charge. This is the reason for using the term electrochemical gradient.
2 Do not confuse the equation for electrochemical potential with the Nernst Equation. The intracellular concentration of most solutes is in the neighborhood of 1 mm, often several orders of magnitude higher than the extracellular concentration. Therefore, because [A in ] > [A out ], solute uptake is typically endergonic ( G A < 0). This is the context of the phenomenon you have learned to call active transport.
3 B. Electrochemical Potentail of a Gradient of Protons The foregoing general description of Electrochemical Potential can now be customized to describe an electrochemical gradient based specifically on protons. n = 1: therefore, nf ψ = F ψ H in RT ln H out H in 2.3 RT log H out ( ph = -logh ) ( in out ) ( in out ) 2.3 RT log H -log H -2.3 RT -log H --log H ( in out) -2.3 RT ph - ph G = F ψ RT ( ph - ph ) H in out Typical values in metabolically active bacterial cells, and in mitochondria, (where the proton gradient is maintained by electron transport) are: ψ: -0.1V phin: 7.0 phout: 6.5 You can now calculate the free energy required for transport of a single proton under such typical conditions as follows: kj kj G = V K o V mol K mol kj kj kj G = = mol mol mol o ( ) ( )( )
4 The genome of the bacterium E. coli has at least 427 genes coding for membrane transport proteins. This amounts to a startling 10% of all E. coli genes, and makes this the most frequent type of gene in the genome. By way of comparison, the second most abundant type is biosynthetic genes, at 8% of the total. The large number of transport genes reflects the omnivorous appetite of E. coli for the wide variety of organic substrates it encounters in the complex biochemical stew of the mammalian gut. Another reason there are so many transport genes in E. coli is that there are 2 or more redundant transport mechanisms for many solutes. A good example is transport of the pentose, arabinose, which is transported by the ara F,G,H multicomponent system and, independently, by the arae system. The equation for electrochemical potential, and a basic understanding of biochemical thermodynamics, properly applied, allow you to explain the existence of the two redundant arabinose transport systems.
5 We notice that the two arabinose transport systems are redundant in the sense that they both transport arabinose, but they are not identical. The ara F, G, H multi-component system couples arabinose transport to ATP hydrolysis. The ara E system couples transport to proton transport (i.e. proton symport). Both systems use an exogenous source of free energy to drive endergonic arabinose uptake, therefore both are examples of active transport. Additionally, the binding constants (K m ) of the two systems differ by several orders of magnitude. The ATP-dependent system has high affinity, and the proton symport system low affinity for arabinose. Estimate the free energy change (in kj per mole) for arabinose uptake by these two systems. Assume an intracellular concentration of 1 mm, and extracellular concentrations equal to the respective Km values of the two systems. ABC SYSTEM: kj/mole Simple Proton Symport: kj/mole
Energy and Cells. Appendix 1. The two primary energy transformations in plants are photosynthesis and respiration.
 Energy and Cells Appendix 1 Energy transformations play a key role in all physical and chemical processes that occur in plants. Energy by itself is insufficient to drive plant growth and development. Enzymes
Energy and Cells Appendix 1 Energy transformations play a key role in all physical and chemical processes that occur in plants. Energy by itself is insufficient to drive plant growth and development. Enzymes
Membrane Protein Pumps
 Membrane Protein Pumps Learning objectives You should be able to understand & discuss: Active transport-na + /K + ATPase ABC transporters Metabolite transport by lactose permease 1. Ion pumps: ATP-driven
Membrane Protein Pumps Learning objectives You should be able to understand & discuss: Active transport-na + /K + ATPase ABC transporters Metabolite transport by lactose permease 1. Ion pumps: ATP-driven
Advanced Higher Biology. Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins
 Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANE
 TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANE The plasma membrane functions to isolate the inside of the cell from its environment, but isolation is not complete. A large number of molecules constantly transit between the
TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANE The plasma membrane functions to isolate the inside of the cell from its environment, but isolation is not complete. A large number of molecules constantly transit between the
Importance of solute transport: Nutrition Guard cell control Pulvinus control (sleep movements) Growth
 Solute uptake (I) Importance of solute transport: Nutrition Guard cell control Pulvinus control (sleep movements) Growth The casparian strip enforces membrane control of solute uptake from soil Importance
Solute uptake (I) Importance of solute transport: Nutrition Guard cell control Pulvinus control (sleep movements) Growth The casparian strip enforces membrane control of solute uptake from soil Importance
Chemistry 452/ August 2012
 Chemistry 45/456 7 August 0 End- of-term Examination Professor G. Drobny Enter your answers into a blue or green Composition Book. Perform only the number of problems required. Answers must be given in
Chemistry 45/456 7 August 0 End- of-term Examination Professor G. Drobny Enter your answers into a blue or green Composition Book. Perform only the number of problems required. Answers must be given in
Biochemistry. Biochemistry 9/20/ Bio-Energetics. 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes
 9/20/15 Biochemistry Biochemistry 4. Bio-Energetics 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes Aquaporin, the water channel, consists of four identical transmembrane polypeptides
9/20/15 Biochemistry Biochemistry 4. Bio-Energetics 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes Aquaporin, the water channel, consists of four identical transmembrane polypeptides
Biochemistry. Biochemistry 7/11/ Bio-Energetics. 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes
 Biochemistry Biochemistry 4. Bio-Energetics 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes Aquaporin, the water channel, consists of four identical transmembrane polypeptides Key Energy
Biochemistry Biochemistry 4. Bio-Energetics 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes Aquaporin, the water channel, consists of four identical transmembrane polypeptides Key Energy
The products have more enthalpy and are more ordered than the reactants.
 hapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
hapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
Transporters and Membrane Motors Nov 15, 2007
 BtuB OM vitamin B12 transporter F O F 1 ATP synthase Human multiple drug resistance transporter P-glycoprotein Transporters and Membrane Motors Nov 15, 2007 Transport and membrane motors Concentrations
BtuB OM vitamin B12 transporter F O F 1 ATP synthase Human multiple drug resistance transporter P-glycoprotein Transporters and Membrane Motors Nov 15, 2007 Transport and membrane motors Concentrations
ACTIVE TRANSPORT AND GLUCOSE TRANSPORT. (Chapter 14 and 15, pp and pp )
 ACTIVE TRANSPORT AND GLUCOSE TRANSPORT (Chapter 14 and 15, pp 140-143 and pp 146-151) Overview Active transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane in the direction against their concentration
ACTIVE TRANSPORT AND GLUCOSE TRANSPORT (Chapter 14 and 15, pp 140-143 and pp 146-151) Overview Active transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane in the direction against their concentration
MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics
 MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics MUDr. Jan Pláteník, PhD. Ústav lékařské biochemie 1.LF UK Helpful comments of Prof. MUDr. Jiří Kraml, DrSc., are acknowledged. 1 Respiratory chain and
MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics MUDr. Jan Pláteník, PhD. Ústav lékařské biochemie 1.LF UK Helpful comments of Prof. MUDr. Jiří Kraml, DrSc., are acknowledged. 1 Respiratory chain and
Electrical Properties of the Membrane
 BIOE 2520 Electrical Properties of the Membrane Reading: Chapter 11 of Alberts et al. Stephen Smith, Ph.D. 433 Biotech Center shs46@pitt.edu Permeability of Lipid membrane Lipid bilayer is virtually impermeable
BIOE 2520 Electrical Properties of the Membrane Reading: Chapter 11 of Alberts et al. Stephen Smith, Ph.D. 433 Biotech Center shs46@pitt.edu Permeability of Lipid membrane Lipid bilayer is virtually impermeable
Metabolism. Fermentation vs. Respiration. End products of fermentations are waste products and not fully.
 Outline: Metabolism Part I: Fermentations Part II: Respiration Part III: Metabolic Diversity Learning objectives are: Learn about respiratory metabolism, ATP generation by respiration linked (oxidative)
Outline: Metabolism Part I: Fermentations Part II: Respiration Part III: Metabolic Diversity Learning objectives are: Learn about respiratory metabolism, ATP generation by respiration linked (oxidative)
Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy
 6 Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy Energy is stored in chemical bonds and can be released and transformed by metabolic pathways. Chemical energy available to do work is termed free energy
6 Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy Energy is stored in chemical bonds and can be released and transformed by metabolic pathways. Chemical energy available to do work is termed free energy
Photosynthetic autotrophs use the energy of sunlight to convert low-g CO 2 and H 2 O into energy-rich complex sugar molecules.
 Chapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
Chapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
Cells have an unequal distribution of charge across their membrane: more postiive charges on the outside; more negative charges on the inside.
 Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the cell with a voltmeter. neurons, muscle cells, heart cells, endocrine cells...
Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the cell with a voltmeter. neurons, muscle cells, heart cells, endocrine cells...
Bio 119 Solute Transport 7/11/2004 SOLUTE TRANSPORT. READING: BOM-10 Sec. 4.7 Membrane Transport Systems p. 71
 SOLUTE TRANSPORT READG: BOM10 Sec. 4.7 Membrane Transport Systems p. 71 DISCUSSION QUESTIONS BOM10: Chapter 4; #6, #8 1. What are the 4 essential features of carrier mediated transport? 2. What does it
SOLUTE TRANSPORT READG: BOM10 Sec. 4.7 Membrane Transport Systems p. 71 DISCUSSION QUESTIONS BOM10: Chapter 4; #6, #8 1. What are the 4 essential features of carrier mediated transport? 2. What does it
Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its effects on matter
 00Note Set 3 1 THE ENERGETICS OF LIFE Thermodynamics and Bioenergetics: Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its effects on matter Bioenergetics is the quantitative analysis of how organisms gain
00Note Set 3 1 THE ENERGETICS OF LIFE Thermodynamics and Bioenergetics: Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its effects on matter Bioenergetics is the quantitative analysis of how organisms gain
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. The Energy of Life
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. The Energy of Life
Lecture 20. Chemical Potential
 Lecture 20 Chemical Potential Reading: Lecture 20, today: Chapter 10, sections A and B Lecture 21, Wednesday: Chapter 10: 10 17 end 3/21/16 1 Pop Question 7 Boltzmann Distribution Two systems with lowest
Lecture 20 Chemical Potential Reading: Lecture 20, today: Chapter 10, sections A and B Lecture 21, Wednesday: Chapter 10: 10 17 end 3/21/16 1 Pop Question 7 Boltzmann Distribution Two systems with lowest
Thermodynamic principles governing metabolic operation : inference, analysis, and prediction Niebel, Bastian
 University of Groningen Thermodynamic principles governing metabolic operation : inference, analysis, and prediction Niebel, Bastian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen Thermodynamic principles governing metabolic operation : inference, analysis, and prediction Niebel, Bastian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
Cell Respiration: Energy for Plant Metabolism
 Cell Respiration: Energy for Plant Metabolism Glucose is the originating molecule for respiration Production and consumption of ATP Coupled reactions: Endergonic reactions are coupled to exergonic ones
Cell Respiration: Energy for Plant Metabolism Glucose is the originating molecule for respiration Production and consumption of ATP Coupled reactions: Endergonic reactions are coupled to exergonic ones
Chem Lecture 9 Pumps and Channels Part 1
 Chem 45 - Lecture 9 Pumps and Channels Part 1 Question of the Day: What two factors about a molecule influence the change in its free energy as it moves across a membrane? Membrane proteins function as
Chem 45 - Lecture 9 Pumps and Channels Part 1 Question of the Day: What two factors about a molecule influence the change in its free energy as it moves across a membrane? Membrane proteins function as
Membranes 2: Transportation
 Membranes 2: Transportation Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Associate Professor Bioinformatics Department of Biology University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Office & Lab: NCN#343B Tel: 787-764-0000 ext. 7798 E-mail:
Membranes 2: Transportation Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Associate Professor Bioinformatics Department of Biology University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Office & Lab: NCN#343B Tel: 787-764-0000 ext. 7798 E-mail:
PNS Chapter 7. Membrane Potential / Neural Signal Processing Spring 2017 Prof. Byron Yu
 PNS Chapter 7 Membrane Potential 18-698 / 42-632 Neural Signal Processing Spring 2017 Prof. Byron Yu Roadmap Introduction to neuroscience Chapter 1 The brain and behavior Chapter 2 Nerve cells and behavior
PNS Chapter 7 Membrane Potential 18-698 / 42-632 Neural Signal Processing Spring 2017 Prof. Byron Yu Roadmap Introduction to neuroscience Chapter 1 The brain and behavior Chapter 2 Nerve cells and behavior
Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 Chapter 10 Chemotrophic Energy Metabolism: Aerobic Respiration Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Figure 10-1 Figure 10-6 Conversion of pyruvate The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl
Chapter 10 Chemotrophic Energy Metabolism: Aerobic Respiration Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Figure 10-1 Figure 10-6 Conversion of pyruvate The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture - 15 Nucleic Acids III
 Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 15 Nucleic Acids III In the last two classes we spoke about lipids and membranes. Now, what we
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 15 Nucleic Acids III In the last two classes we spoke about lipids and membranes. Now, what we
Chapter 6: Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell
 Chapter 6: Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell What is Energy? Answer: The Capacity to do Work Types of Energy: 1) Kinetic Energy = Energy of movement Light (movement of photons) Heat (movement of particles)
Chapter 6: Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell What is Energy? Answer: The Capacity to do Work Types of Energy: 1) Kinetic Energy = Energy of movement Light (movement of photons) Heat (movement of particles)
Supplementary thermodynamics as applied to biosystems
 Supplementary thermodynamics as applied to biosystems Glucose is transferred to glucose-6-phosphate, abbreviated here to G6P. The reaction may be written Glucose + phosphate G6P + H 2 O G o = 13.8kJ/mol
Supplementary thermodynamics as applied to biosystems Glucose is transferred to glucose-6-phosphate, abbreviated here to G6P. The reaction may be written Glucose + phosphate G6P + H 2 O G o = 13.8kJ/mol
BCH 4054 Spring 2001 Chapter 21 Lecture Notes
 BCH 4054 Spring 2001 Chapter 21 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 21 Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation 2 Overview Oxidation of NADH and CoQH 2 produced in TCA cycle by O 2 is very exergonic. Some
BCH 4054 Spring 2001 Chapter 21 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 21 Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation 2 Overview Oxidation of NADH and CoQH 2 produced in TCA cycle by O 2 is very exergonic. Some
Membrane Potential Fox Chapter 6 pt 2
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Membrane Potential Fox Chapter 6 pt 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the
Vert Phys PCB3743 Membrane Potential Fox Chapter 6 pt 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the
Cell membrane resistance and capacitance
 Cell membrane resistance and capacitance 1 Two properties of a cell membrane gives rise to two passive electrical properties: Resistance: Leakage pathways allow inorganic ions to cross the membrane. Capacitance:
Cell membrane resistance and capacitance 1 Two properties of a cell membrane gives rise to two passive electrical properties: Resistance: Leakage pathways allow inorganic ions to cross the membrane. Capacitance:
Neurons and the membrane potential. N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016
 Neurons and the membrane potential N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016 My background, briefly Neurons Structural elements of a typical neuron Figure 1.2 Some nerve cell morphologies found in the human
Neurons and the membrane potential N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016 My background, briefly Neurons Structural elements of a typical neuron Figure 1.2 Some nerve cell morphologies found in the human
Ch/APh2 Bioenergetics Section Lecture of May 14, The thermodynamics of biological energy production.
 Ch/APh2 Bioenergetics Section Lecture of May 14, 2009 Introduction to bioenergetics. The thermodynamics of biological energy production. Kinetic aspects of bioenergetic processes. The molecular and cellular
Ch/APh2 Bioenergetics Section Lecture of May 14, 2009 Introduction to bioenergetics. The thermodynamics of biological energy production. Kinetic aspects of bioenergetic processes. The molecular and cellular
Biochemical Pathways
 Biochemical Pathways Living organisms can be divided into two large groups according to the chemical form in which they obtain carbon from the environment. Autotrophs can use carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
Biochemical Pathways Living organisms can be divided into two large groups according to the chemical form in which they obtain carbon from the environment. Autotrophs can use carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
Free Energy. because H is negative doesn't mean that G will be negative and just because S is positive doesn't mean that G will be negative.
 Biochemistry 462a Bioenergetics Reading - Lehninger Principles, Chapter 14, pp. 485-512 Practice problems - Chapter 14: 2-8, 10, 12, 13; Physical Chemistry extra problems, free energy problems Free Energy
Biochemistry 462a Bioenergetics Reading - Lehninger Principles, Chapter 14, pp. 485-512 Practice problems - Chapter 14: 2-8, 10, 12, 13; Physical Chemistry extra problems, free energy problems Free Energy
CELL SIGNALLING and MEMBRANE TRANSPORT. Mark Louie D. Lopez Department of Biology College of Science Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 CELL SIGNALLING and MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Mark Louie D. Lopez Department of Biology College of Science Polytechnic University of the Philippines GENERIC SIGNALLING PATHWAY CELL RESPONSE TO SIGNALS CELL RESPONSE
CELL SIGNALLING and MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Mark Louie D. Lopez Department of Biology College of Science Polytechnic University of the Philippines GENERIC SIGNALLING PATHWAY CELL RESPONSE TO SIGNALS CELL RESPONSE
Chapter 10. Thermodynamics of Transport. Thermodynamics of Transport, con t. BCH 4053 Summer 2001 Chapter 10 Lecture Notes. Slide 1.
 BCH 4053 Summer 2001 Chapter 10 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 10 Membrane Transport 2 3 Thermodynamics of Transport Free Energy change is given by difference in electrochemical potential and the quantity transported
BCH 4053 Summer 2001 Chapter 10 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 10 Membrane Transport 2 3 Thermodynamics of Transport Free Energy change is given by difference in electrochemical potential and the quantity transported
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 9 - TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
!! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
 Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Essentiality in B. subtilis
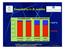 Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Phys498BIO; Prof. Paul Selvin Hw #9 Assigned Wed. 4/18/12: Due 4/25/08
 1. Ionic Movements Across a Permeable Membrane: The Nernst Potential. In class we showed that if a non-permeable membrane separates a solution with high [KCl] from a solution with low [KCl], the net charge
1. Ionic Movements Across a Permeable Membrane: The Nernst Potential. In class we showed that if a non-permeable membrane separates a solution with high [KCl] from a solution with low [KCl], the net charge
Activity: Identifying forms of energy
 Activity: Identifying forms of energy INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Metabolism Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in an organism Metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and ends with
Activity: Identifying forms of energy INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Metabolism Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in an organism Metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and ends with
ΔG o' = ηf ΔΕ o' = (#e ( V mol) ΔΕ acceptor
 Reading: Sec. 19.1 Electron-Transfer Reactions in Mitochondria (listed subsections only) 19.1.1 Electrons are Funneled to Universal Electron Acceptors p. 692/709 19.1.2 Electrons Pass through a Series
Reading: Sec. 19.1 Electron-Transfer Reactions in Mitochondria (listed subsections only) 19.1.1 Electrons are Funneled to Universal Electron Acceptors p. 692/709 19.1.2 Electrons Pass through a Series
CELLS NOT YOUR CELL PHONE HOMEOSTASIS: LESSON 5 OVERVIEW TEKS
 Lesson 5: Active Transport Protein Pumps Objectives: In this lesson the student will: CELLS NOT YOUR CELL PHONE HOMEOSTASIS: LESSON 5 OVERVIEW 1. Identify how the unique structure of the cell membrane
Lesson 5: Active Transport Protein Pumps Objectives: In this lesson the student will: CELLS NOT YOUR CELL PHONE HOMEOSTASIS: LESSON 5 OVERVIEW 1. Identify how the unique structure of the cell membrane
Passive Membrane Properties
 Passive Membrane Properties Communicating through a leaky garden hose... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics
Passive Membrane Properties Communicating through a leaky garden hose... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics
20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
 20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20.1 What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Metabolism? Electron transport - Role of oxygen in metabolism as final acceptor of electrons - In inner
20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20.1 What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Metabolism? Electron transport - Role of oxygen in metabolism as final acceptor of electrons - In inner
b) What is the gradient at room temperature? Du = J/molK * 298 K * ln (1/1000) = kj/mol
 Chem350 Practice Problems Membranes 1. a) What is the chemical potential generated by the movement of glucose by passive diffusion established by a 1000 fold concentration gradient at physiological temperature?
Chem350 Practice Problems Membranes 1. a) What is the chemical potential generated by the movement of glucose by passive diffusion established by a 1000 fold concentration gradient at physiological temperature?
Outline. Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes. Forms of Energy. Chapter 6
 Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Chapter 6 Forms of Energy Outline Laws of Thermodynamics Metabolic Reactions ATP Metabolic Pathways Energy of Activation Enzymes Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration 1 2 Forms
Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Chapter 6 Forms of Energy Outline Laws of Thermodynamics Metabolic Reactions ATP Metabolic Pathways Energy of Activation Enzymes Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration 1 2 Forms
Main idea of this lecture:
 Ac#ve Transport Main idea of this lecture: How do molecules, big and small, get in OR out of a cell? 2 Main ways: Passive Transport (Does not require energy) Lecture 1 Ac=ve Transport (Requires energy)
Ac#ve Transport Main idea of this lecture: How do molecules, big and small, get in OR out of a cell? 2 Main ways: Passive Transport (Does not require energy) Lecture 1 Ac=ve Transport (Requires energy)
BIOCHEMISTRY. František Vácha. JKU, Linz.
 BIOCHEMISTRY František Vácha http://www.prf.jcu.cz/~vacha/ JKU, Linz Recommended reading: D.L. Nelson, M.M. Cox Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry D.J. Voet, J.G. Voet, C.W. Pratt Principles of Biochemistry
BIOCHEMISTRY František Vácha http://www.prf.jcu.cz/~vacha/ JKU, Linz Recommended reading: D.L. Nelson, M.M. Cox Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry D.J. Voet, J.G. Voet, C.W. Pratt Principles of Biochemistry
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism. 1. Energy & Chemical Reactions 2. ATP 3. Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways
 Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism 1. Energy & Chemical Reactions 2. ATP 3. Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways 1. Energy & Chemical Reactions 2 Basic Forms of Energy Kinetic Energy (KE) energy in motion
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism 1. Energy & Chemical Reactions 2. ATP 3. Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways 1. Energy & Chemical Reactions 2 Basic Forms of Energy Kinetic Energy (KE) energy in motion
CHAPTER 8. An Introduction to Metabolism
 CHAPTER 8 An Introduction to Metabolism WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: Examples of endergonic and exergonic reactions. The key role of ATP in energy coupling. That enzymes work by lowering the energy of activation.
CHAPTER 8 An Introduction to Metabolism WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: Examples of endergonic and exergonic reactions. The key role of ATP in energy coupling. That enzymes work by lowering the energy of activation.
Chapter 6: Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell
 Chapter 6: Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell What is Energy? Answer: The capacity to do work Types of Energy: 1) Potential Energy = Stored energy Positional (stored in location of object) Chemical (stored
Chapter 6: Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell What is Energy? Answer: The capacity to do work Types of Energy: 1) Potential Energy = Stored energy Positional (stored in location of object) Chemical (stored
Title: Nutrient Movement Towards and Into Plant Roots Speaker: Bill Pan. online.wsu.edu
 Title: Nutrient Movement Towards and Into Plant Roots Speaker: Bill Pan online.wsu.edu Unit 1, Lesson 4 Nutrient Movement Towards and Into Plant Roots http://soils.usda.gov/education/resources/k_12/lessons/profile/
Title: Nutrient Movement Towards and Into Plant Roots Speaker: Bill Pan online.wsu.edu Unit 1, Lesson 4 Nutrient Movement Towards and Into Plant Roots http://soils.usda.gov/education/resources/k_12/lessons/profile/
Chapter Cells and the Flow of Energy A. Forms of Energy 1. Energy is capacity to do work; cells continually use energy to develop, grow,
 Chapter 6 6.1 Cells and the Flow of Energy A. Forms of Energy 1. Energy is capacity to do work; cells continually use energy to develop, grow, repair, reproduce, etc. 2. Kinetic energy is energy of motion;
Chapter 6 6.1 Cells and the Flow of Energy A. Forms of Energy 1. Energy is capacity to do work; cells continually use energy to develop, grow, repair, reproduce, etc. 2. Kinetic energy is energy of motion;
Scale in the biological world
 Scale in the biological world 2 A cell seen by TEM 3 4 From living cells to atoms 5 Compartmentalisation in the cell: internal membranes and the cytosol 6 The Origin of mitochondria: The endosymbion hypothesis
Scale in the biological world 2 A cell seen by TEM 3 4 From living cells to atoms 5 Compartmentalisation in the cell: internal membranes and the cytosol 6 The Origin of mitochondria: The endosymbion hypothesis
ph calculations
 Medical hemistry. Department of uman Physiology and Biochemistry p calculations http://aris.gusc.lv/biothermodynamics/paprekiniuzdld.pdf Universal gas constant R=8.3144 J/(mol K); Faraday s constant F=96485
Medical hemistry. Department of uman Physiology and Biochemistry p calculations http://aris.gusc.lv/biothermodynamics/paprekiniuzdld.pdf Universal gas constant R=8.3144 J/(mol K); Faraday s constant F=96485
An Introduction to Metabolism
 An Introduction to Metabolism I. All of an organism=s chemical reactions taken together is called metabolism. A. Metabolic pathways begin with a specific molecule, which is then altered in a series of
An Introduction to Metabolism I. All of an organism=s chemical reactions taken together is called metabolism. A. Metabolic pathways begin with a specific molecule, which is then altered in a series of
CELL BIOLOGY. by the numbers. Ron Milo. Rob Phillips. illustrated by. Nigel Orme
 CELL BIOLOGY by the numbers Ron Milo Rob Phillips illustrated by Nigel Orme viii Detailed Table of Contents List of Estimates xii Preface xv Acknowledgments xiii The Path to Biological Numeracy Why We
CELL BIOLOGY by the numbers Ron Milo Rob Phillips illustrated by Nigel Orme viii Detailed Table of Contents List of Estimates xii Preface xv Acknowledgments xiii The Path to Biological Numeracy Why We
Lecture 10. Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis. Oxidative. Photo-Phosphorylation
 Lecture 10 Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation Photo-Phosphorylation Model of the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Glycerol-3-P Shuttle Outer Mitochondrial Membrane G3P DHAP
Lecture 10 Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation Photo-Phosphorylation Model of the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Glycerol-3-P Shuttle Outer Mitochondrial Membrane G3P DHAP
Introduction to Metabolism (Or Energy Management) Chapter 8
 Introduction to Metabolism (Or Energy Management) Chapter 8 Metabolism of the chemical reactions in the organism Building up molecules Breaking down molecules Managing energy and materials Route to end-product
Introduction to Metabolism (Or Energy Management) Chapter 8 Metabolism of the chemical reactions in the organism Building up molecules Breaking down molecules Managing energy and materials Route to end-product
Metabolism and Energy. Mrs. Stahl AP Biology
 Metabolism and Energy Mrs. Stahl AP Biology The Energy of Life The living cell is a miniature chemical factory where thousands of reactions occur The cell extracts energy stored in sugars and other fuels
Metabolism and Energy Mrs. Stahl AP Biology The Energy of Life The living cell is a miniature chemical factory where thousands of reactions occur The cell extracts energy stored in sugars and other fuels
Be sure to understand:
 Learning Targets & Focus Questions for Unit 6: Bioenergetics Chapter 8: Thermodynamics Chapter 9: Cell Resp Focus Q Ch. 10: Photosynthesis Chapter 8 (141-150) 1. I can explain how living systems adhere
Learning Targets & Focus Questions for Unit 6: Bioenergetics Chapter 8: Thermodynamics Chapter 9: Cell Resp Focus Q Ch. 10: Photosynthesis Chapter 8 (141-150) 1. I can explain how living systems adhere
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism
 Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism Name Period Concept 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 1. Define metabolism. 2. There are two types
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism Name Period Concept 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 1. Define metabolism. 2. There are two types
2. In regards to the fluid mosaic model, which of the following is TRUE?
 General Biology: Exam I Sample Questions 1. How many electrons are required to fill the valence shell of a neutral atom with an atomic number of 24? a. 0 the atom is inert b. 1 c. 2 d. 4 e. 6 2. In regards
General Biology: Exam I Sample Questions 1. How many electrons are required to fill the valence shell of a neutral atom with an atomic number of 24? a. 0 the atom is inert b. 1 c. 2 d. 4 e. 6 2. In regards
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism
 AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism Concept 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 1. Define metabolism. 2.
AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism Concept 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 1. Define metabolism. 2.
An Introduction to Metabolism
 An Introduction to Metabolism Chapter 8 Objectives Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: catabolic and anabolic pathways; kinetic and potential energy; open and closed systems; exergonic and
An Introduction to Metabolism Chapter 8 Objectives Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: catabolic and anabolic pathways; kinetic and potential energy; open and closed systems; exergonic and
Energy Transformation and Metabolism (Outline)
 Energy Transformation and Metabolism (Outline) - Definitions & Laws of Thermodynamics - Overview of energy flow ecosystem - Biochemical processes: Anabolic/endergonic & Catabolic/exergonic - Chemical reactions
Energy Transformation and Metabolism (Outline) - Definitions & Laws of Thermodynamics - Overview of energy flow ecosystem - Biochemical processes: Anabolic/endergonic & Catabolic/exergonic - Chemical reactions
Chapter 8 Notes. An Introduction to Metabolism
 Chapter 8 Notes An Introduction to Metabolism Describe how allosteric regulators may inhibit or stimulate the activity of an enzyme. Objectives Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: catabolic
Chapter 8 Notes An Introduction to Metabolism Describe how allosteric regulators may inhibit or stimulate the activity of an enzyme. Objectives Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: catabolic
Membrane transport 1. Summary
 Membrane transport 1. Summary A. Simple diffusion 1) Diffusion by electrochemical gradient no energy required 2) No channel or carrier (or transporter protein) is needed B. Passive transport (= Facilitated
Membrane transport 1. Summary A. Simple diffusion 1) Diffusion by electrochemical gradient no energy required 2) No channel or carrier (or transporter protein) is needed B. Passive transport (= Facilitated
Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease
 Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease Lecture 4: Membrane Transport Proteins Kiaran Kirk Research School of Biology Learning objectives To understand: The need for membrane transport proteins in
Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease Lecture 4: Membrane Transport Proteins Kiaran Kirk Research School of Biology Learning objectives To understand: The need for membrane transport proteins in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013
 Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013 Lecture 10. Biochemical Transformations II. Phosphoryl transfer and the kinetics and thermodynamics of energy currency in the cell: ATP and GTP.
Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013 Lecture 10. Biochemical Transformations II. Phosphoryl transfer and the kinetics and thermodynamics of energy currency in the cell: ATP and GTP.
Biochemical bases for energy transformations. Biochemical bases for energy transformations. Nutrition 202 Animal Energetics R. D.
 Biochemical bases for energy transformations Biochemical bases for energy transformations Nutrition 202 Animal Energetics R. D. Sainz Lecture 02 Energy originally from radiant sun energy Captured in chemical
Biochemical bases for energy transformations Biochemical bases for energy transformations Nutrition 202 Animal Energetics R. D. Sainz Lecture 02 Energy originally from radiant sun energy Captured in chemical
= 16! = 16! W A = 3 = 3 N = = W B 3!3!10! = ΔS = nrln V. = ln ( 3 ) V 1 = 27.4 J.
 Answer key: Q1A Both configurations are equally likely because the particles are non-interacting (i.e., the energy does not favor one configuration over another). For A M = 16 N = 6 W A = 16! 0.9 101 =
Answer key: Q1A Both configurations are equally likely because the particles are non-interacting (i.e., the energy does not favor one configuration over another). For A M = 16 N = 6 W A = 16! 0.9 101 =
Resting membrane potential,
 Resting membrane potential Inside of each cell is negative as compared with outer surface: negative resting membrane potential (between -30 and -90 mv) Examination with microelectrode (Filled with KCl
Resting membrane potential Inside of each cell is negative as compared with outer surface: negative resting membrane potential (between -30 and -90 mv) Examination with microelectrode (Filled with KCl
Principles of Bioenergetics. Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 14
 1 Principles of Bioenergetics Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 14 2 Metabolism A highly coordinated cellular activity aimed at achieving the following goals: Obtain chemical energy. Convert nutrient molecules
1 Principles of Bioenergetics Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 14 2 Metabolism A highly coordinated cellular activity aimed at achieving the following goals: Obtain chemical energy. Convert nutrient molecules
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34
 NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism
 Name Period Concept 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 1. Define metabolism. 2. There are two types of reactions in metabolic pathways: anabolic
Name Period Concept 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 1. Define metabolism. 2. There are two types of reactions in metabolic pathways: anabolic
Lecture 2: Biological Thermodynamics [PDF] Key Concepts
![Lecture 2: Biological Thermodynamics [PDF] Key Concepts Lecture 2: Biological Thermodynamics [PDF] Key Concepts](/thumbs/76/73872045.jpg) Lecture 2: Biological Thermodynamics [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer: pp. 11-14; pp. 208-210 problems in textbook: chapter 1, pp. 23-24, #4; and thermodynamics practice problems [PDF] Updated on:
Lecture 2: Biological Thermodynamics [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer: pp. 11-14; pp. 208-210 problems in textbook: chapter 1, pp. 23-24, #4; and thermodynamics practice problems [PDF] Updated on:
An Introduction to Metabolism
 An Introduction to Metabolism The living cell is a microscopic factory where life s giant processes can be performed: -sugars to amino acids to proteins and vise versa -reactions to dismantle polymers
An Introduction to Metabolism The living cell is a microscopic factory where life s giant processes can be performed: -sugars to amino acids to proteins and vise versa -reactions to dismantle polymers
Chapter 15 part 2. Biochemistry I Introduction to Metabolism Bioenergetics: Thermodynamics in Biochemistry. ATP 4- + H 2 O ADP 3- + P i + H +
 Biochemistry I Introduction to Metabolism Bioenergetics: Thermodynamics in Biochemistry ATP 4- + 2 ADP 3- + P i 2- + + Chapter 15 part 2 Dr. Ray 1 Energy flow in biological systems: Energy Transformations
Biochemistry I Introduction to Metabolism Bioenergetics: Thermodynamics in Biochemistry ATP 4- + 2 ADP 3- + P i 2- + + Chapter 15 part 2 Dr. Ray 1 Energy flow in biological systems: Energy Transformations
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE. Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge. FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison
 BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison 8 Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge Roadmap 8 In this chapter you will learn how Enzymes use
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison 8 Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge Roadmap 8 In this chapter you will learn how Enzymes use
Review Questions - Lecture 5: Metabolism, Part 1
 Review Questions - Lecture 5: Metabolism, Part 1 Questions: 1. What is metabolism? 2. What does it mean to say that a cell has emergent properties? 3. Define metabolic pathway. 4. What is the difference
Review Questions - Lecture 5: Metabolism, Part 1 Questions: 1. What is metabolism? 2. What does it mean to say that a cell has emergent properties? 3. Define metabolic pathway. 4. What is the difference
2.6 The Membrane Potential
 2.6: The Membrane Potential 51 tracellular potassium, so that the energy stored in the electrochemical gradients can be extracted. Indeed, when this is the case experimentally, ATP is synthesized from
2.6: The Membrane Potential 51 tracellular potassium, so that the energy stored in the electrochemical gradients can be extracted. Indeed, when this is the case experimentally, ATP is synthesized from
2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chemical Reactions
 Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction occurs when chemical bonds are broken and reformed. Rust forms very slowly, while rocket fuel combustion is explosive! The significance of this comparison is that
Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction occurs when chemical bonds are broken and reformed. Rust forms very slowly, while rocket fuel combustion is explosive! The significance of this comparison is that
AP Biology Thermodyamics
 AP Biology Thermodyamics Introduction to Thermodynamics The living cell is a chemical industry in miniature The totality of an organism s chemical reaction is called metabolism Metabolism involves managing
AP Biology Thermodyamics Introduction to Thermodynamics The living cell is a chemical industry in miniature The totality of an organism s chemical reaction is called metabolism Metabolism involves managing
Electrochemistry objectives
 Electrochemistry objectives 1) Understand how a voltaic and electrolytic cell work 2) Be able to tell which substance is being oxidized and reduced and where it is occuring the anode or cathode 3) Students
Electrochemistry objectives 1) Understand how a voltaic and electrolytic cell work 2) Be able to tell which substance is being oxidized and reduced and where it is occuring the anode or cathode 3) Students
7.014 Quiz I Handout
 7.014 Quiz I andout Quiz I announcements: Quiz I: Friday, February 27 12:05 12:55 Walker Gym, rd floor (room 5040) **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Wednesday, February 25 7:00 9:00
7.014 Quiz I andout Quiz I announcements: Quiz I: Friday, February 27 12:05 12:55 Walker Gym, rd floor (room 5040) **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Wednesday, February 25 7:00 9:00
Electrochemical Cells at Non-Standard Conditions
 Electrochemical Cells at Non-Standard Conditions Oxidation-reduction reactions in the real world rarely occur under standard conditions. Even if the cell started out with all dissolved species at 1M concentration,
Electrochemical Cells at Non-Standard Conditions Oxidation-reduction reactions in the real world rarely occur under standard conditions. Even if the cell started out with all dissolved species at 1M concentration,
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 Transmembrane Transport of Ions and Small Molecules Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 Transmembrane Transport of Ions and Small Molecules Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name
 AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the image below. 7. Base your answer to the following question on Which of the following choices correctly
AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the image below. 7. Base your answer to the following question on Which of the following choices correctly
Enzymes: Basic Principles
 Enzymes: Basic Principles BIO161 Basic Biochemistry Dr John Puddefoot J.R.Puddefoot@qmul.ac.uk Objectives: To introduce the basic concepts and definitions of enzymology You should be able to able to define
Enzymes: Basic Principles BIO161 Basic Biochemistry Dr John Puddefoot J.R.Puddefoot@qmul.ac.uk Objectives: To introduce the basic concepts and definitions of enzymology You should be able to able to define
9/25/2011. Outline. Overview: The Energy of Life. I. Forms of Energy II. Laws of Thermodynamics III. Energy and metabolism IV. ATP V.
 Chapter 8 Introduction to Metabolism Outline I. Forms of Energy II. Laws of Thermodynamics III. Energy and metabolism IV. ATP V. Enzymes Overview: The Energy of Life Figure 8.1 The living cell is a miniature
Chapter 8 Introduction to Metabolism Outline I. Forms of Energy II. Laws of Thermodynamics III. Energy and metabolism IV. ATP V. Enzymes Overview: The Energy of Life Figure 8.1 The living cell is a miniature
State state describe
 Warm-Up State the products of the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis, state which product has chemical energy, and describe how that product is made. KREBS ETC FADH 2 Glucose Pyruvate H 2 O NADH
Warm-Up State the products of the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis, state which product has chemical energy, and describe how that product is made. KREBS ETC FADH 2 Glucose Pyruvate H 2 O NADH
C. Incorrect! Catalysts themselves are not altered or consumed during the reaction.
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 04: Enzymes and Energy Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed, (3) Pick the answer,
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 04: Enzymes and Energy Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed, (3) Pick the answer,
Channels can be activated by ligand-binding (chemical), voltage change, or mechanical changes such as stretch.
 1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
Chemistry August Useful Constants and Conversions
 Chemistry 45 August 8 End- of-term Examination Key rofessor G. Drobny Useful Constants and Conversions Universal Gas Constant= R = 8.3 J / mole K =.8 L atm / mole K Faraday s Constant= I= 96,458 Coulombs
Chemistry 45 August 8 End- of-term Examination Key rofessor G. Drobny Useful Constants and Conversions Universal Gas Constant= R = 8.3 J / mole K =.8 L atm / mole K Faraday s Constant= I= 96,458 Coulombs
