Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B1: Cell structure and transport. Lesson Keywords I can Before After
|
|
|
- Berniece Cross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B1: Cell structure and transport. microscope Describe how microscopy techniques cells have developed over time eyepiece B1.1 objective lens Calculate the magnification, real size The world of the stage and image size of a specimen microscope focus Explain the differences in magnification magnification and resolution between a light resolving power microscope and electron microscope B1.2 Animal and plant cells nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane mitochondria ribosome algae cell wall cellulose chloroplast chlorophyll vacuole Label the main parts of animal and plant cells Identify the main parts of cells under the microscope Compare animal and plant cells B1.3 Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells eukaryotic cells prokaryotic cells bacteria plasmid Define the terms prokaryotic and eukaryotic Describe similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Compare the size and scale of cells using order of magnitude calculations B1.4 Specialisation in animal cells differentiate specialised cell nerve cell muscle cell sperm cell Define cell differentiation Describe the structure and function of specialised animal cells including nerve cells, muscle cells and sperm cells Explain how the structure of specialised cells relates to their function
2 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B1: Cell structure and transport. B1.5 Specialisation in plant cells root hair cell photosynthetic cell xylem cell phloem cell Describe the structure of specialised plant cells including root hair cells, photosynthetic cells, xylem cells and phloem cells Explain how the structure of specialised plant cells relates to their function Compare xylem cells and phloem cells B1.6 Diffusion diffusion rate concentration temperature surface area net movement concentration gradient Define diffusion Describe what factors affect the rate of diffusion Explain how surface area to volume ratio plays a part in the exchange of substances in single-celled & multicellular organisms B1.7 Osmosis dilute concentrated partially permeable membrane osmosis isotonic hypertonic hypotonic Describe the process of osmosis Describe what happens to an animal cell in different concentrations of water Compare osmosis to diffusion B1.8 Osmosis in plants turgor turgid flaccid plasmolysis Describe what happens to a plant cell in different concentrations of water Investigate the effect of osmosis in plant tissues Evaluate the method used to investigate osmosis in plant cells
3 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B1: Cell structure and transport. Describe the process of active transport B1.9 Active transport active transport Compare active transport and diffusion Explain why active transport is important in animals and plants B1.10 Exchanging materials surface area to volume ratio ventilated alveoli stomata List examples of exchange surfaces Describe how the exchange surfaces are adapted for their role Explain why large multicellular organisms need special systems for exchanging materials with the environment This topic is on pages 11-13, and 39 of your revision guide.
4 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B2: Cell division State why cells need to divide. B2.1 Cell division B2.2 Growth and differentiation B2.3 Stem cells B2.4 Stem cell dilemmas Chromosome Cell cycle Mitosis Differentiate Stem cells Clone Embryo Zygote Embryonic stem cells Adult stem cells Therapeutic cloning Describe how cells divide by mitosis. Explain what happens when mitosis goes wrong. Describe differentiation in animal cells. Describe differentiation in plant cells. Explain why plants can easily clone and animals cannot. State the function of stem cells. Describe how stem cells can be used. Explain why stem cells are useful in cloning plants. State a problem with embryonic stem cells. Describe some problems with embryonic stem cells. Explain the potential uses for stem cells in the future. This topic is on pages 14 to 16 of your revision guide.
5 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B3: Organisation & the digestive system B3.1 Tissues and organs B3.2 The digestive system B3.3a Carbohydrate structure and food test B3.3b Protein structure and food test B3.3c Lipid structure and food test B3.4 Differentiate Tissue Organ Organ system Digestive system Enzymes Mouth Oesophagus (gullet) Stomach Liver Gall bladder Bile duct Pancreas Large intestine Small intestine Rectum anus Carbohydrate Sugar Starch Glucose Benedicts test Iodine test Protein Amino acid Biuret test Lipid Fats and oils Fatty acids Glycerol Ethanol test Cloudy Flammable Catalyst Enzyme Define the terms tissue and organ Describe the role of a variety of tissues in both plants and animals Describe where some organs are found in the human body and their function Identify organs in the digestive system Describe the roles of different organs in the digestive system Explain how each organs structure allows it to carry out its role. Recall what the body needs carbohydrates for Describe the structure of simple sugars and starch Explain the tests we can carry out to tests if foods contain simple sugars or starch Recall why the body requires proteins Describe the structure of proteins Describe how we can test foods to see if they contain proteins Recall what the body needs lipids for Describe the molecular structure of a lipid Describe how we would test foods to see if they contain lipids Describe the role of enzymes in living organisms
6 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B3: Organisation & the digestive system Catalysts and enzymes B3.5 Factors affecting enzyme action B3.6 How the digestive system works B3.7 Making digestion efficient Active site Substrate Enzyme-substrate complex Products Lock and key theory Metabolism Enzyme Temperature ph Active site Denature Optimum Amylase Carbohydrates Sugars (glucose) Protease Proteins Amino acids Lipase Fats and oils Fatty acids Glycerol Digest Enzyme Salivary gland Pancreas Bile Gall bladder Liver Bile duct Emulsion Emulsifier Surface area Alkaline Neutralise Denature Describe the lock and key theory of enzyme action and explain why the shape of the active site is very important Explain why enzymes are important in metabolism Describe the shape of an enzymes active site compared to the substrate that fit into it Describe the effect of changing temperature or ph on the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction Explain the effect of changing temperature or ph on the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction Recall the 3 types of enzymes in the digestive system Describe which food group each enzyme breaks down and what is produced by the reaction Explain where in the digestive system the enzymes that digest carbohydrates, proteins and lipids are made, and where they act Define the term emulsifier Describe the 2 roles bile has in the digestive system Explain how bile ensures enzymes can work efficiently in the digestive system This topic is on pages 24 to 29 of your revision guide.
7 Yr 10 Combined Biology. B4: Organising animals and plants B4.1 The Blood red blood cells white blood cells platelets plasma urea haemoglobin State the main parts of the circulatory system Describe properties and functions of blood Explain adaptations of red and white blood cells B4.2 The blood vessels B4.3 The Heart B4.4 Helping the Heart B4.5 Breathing and gas exchange arteries veins capillaries valves double circulatory system ventricles atrium/atria vena cava pulmonary vein pulmonary artery vena cava aorta coronary arteries pacemaker artificial heart stents statins alveoli diaphragm rib intercostal muscle bronchiole bronchi trachea pressure volume State the 3 main vessels carrying blood around the body Describe the functions of these vessels and describe their structures Explain how the structure of each vessel is linked to its function and the importance of the double circulatory system Label the main structures of the mammalian heart and Explain how the heart beats Explain how the heart can be damaged / diseased and its impact on health Describe ways of solving problems with blood supply to the heart and with valves Describe how an artificial pacemaker, artificial hearts stents and statins can help a heart Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of artificial hearts Label the main structures in the human gas exchange system Describe how gas exchange occurs in the alveoli Explain how the human lungs are adapted for gas exchange
8 Yr 10 Combined Biology. B4: Organising animals and plants B4.6 Tissues and organs in Plants B4.7 Transport Systems in Plants B4.8 Evaporation and transpiration B4.9 Factors Affecting Transpiration root flower leaf stem epidermal tissue palisade mesophyll tissue spongy mesophyll tissue xylem phloem translocation guard cell stoma/stomata transpiration stream photosynthesis evaporation light intensity temperature humidity State examples of plant organs and tissues Describe what substances are required for healthy plant growth and which tissues and organs are involved in their transport Explain what substances are important for respiration and photosynthesis and how plants can obtain and transport these substances State substances that are transported in plants Describe transport systems in plants Compare transport in xylem and phloem tissues Define transpiration Describe the role of stomata and guard cells in controlling gas exchange and water loss Explain how water moves up a plant in a transpiration stream List four factors that affect rate of transpiration Describe conditions that speed up the rate of transpiration Explain how certain factors affect the rate of transpiration and how you could investigate factors affecting water uptake This topic is on pages and of your revision guide.
9 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B5: communicable diseases Define communicable and noncommunicable B5.1 Communicable disease Describe factors which affect Health and Non-communicable disease health disease Pathogens Explain how different types of diseases interact B5.2 Pathogens and disease B5.5 Preventing infections B5.6 Viral diseases B5.7 Bacterial diseases Vaccine Hygiene Vector Pathogen Communicable disease Microorganism Virus Fungi Bacterium/bacteria Health Ignaz Semmelweis Louis Pasteur Joseph Lister Vaccines Hygiene Vectors Measles HIV/AIDS Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) Virus Salmonella Gonorrhoea Sexually transmitted disease (STD) Define the terms health and pathogen Describe how pathogens can cause disease, and how they are spread Explain how the spread of disease can be reduced or prevented Describe the work of Semmelweis, Pasteur and Lister Describe how hygiene measures prevent the spread of pathogens Explain how the spread of disease can be prevented by isolating infecting individuals, destroying vectors and vaccination State the symptoms and causes of measles, HIV & TMV Describe how these diseases are spread Explain treatments or preventative methods for these viral diseases State the symptoms and causes of salmonella & gonorrhoea Describe how these diseases are spread Explain how these can be treated or preventative methods
10 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B5: communicable diseases B5.8 Fungi and protist diseases B5.9 Human body defences Fungi Protist Rose black spot Malaria White blood cell Antibody Antitoxin Phagocytosis Microorganism Mucus Cilia Platelets Pathogen Immune system State the symptoms and causes of rose black spot in plants and malaria in humans Describe how these diseases are spread Explain how the spread of these diseases can be reduced or prevented Describe the non-specific defence systems of the human body Explain the role of the immune system in defence against disease Use the following key terms in your explanations; white blood cell, antibody, antitoxin, phagocytosis. This topic is on pages 36 and 43 to 46 of your revision guide.
11 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B6: Preventing and treating disease B6.1 Vaccination B6.2 Antibiotics & painkillers Vaccine Herd immunity Antibodies Pathogen White blood cell Symptoms Antibiotics Bacterial Virus Define vaccine and immunisation. Explain how vaccines work. Analyse graphs to explain the importance of vaccinating an entire population. Recall what medicines are and how some of them work e.g painkillers. Explain how antibiotics work and why they don t kill viruses. Explain antibiotic resistance. B6.3 Discovery of drugs Microorganisms Penicillin Antibiotic resistance Preclinical testing Clinical trials Placebo Double blind trial Recall how drugs are discovered. Explain examples of discoveries. Explain the role of laboratories and any difficulties they face. B6.4 Developing drugs Pre-clinical testing Clinical trials Placebo State features of a good medicine Describe how drugs are tested Explain the importance of double blind trials and placebos This topic is on pages 47 to 49 of your revision guide.
12 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B7: Non-communicable diseases Classify diseases as communicable B7.1 and non-communicable. Non-communicable Noncommunicable that increase the rate of disease Identify risk factors (lifestyle factor Risk factor Correlation diseases occurring) from data. Causal mechanism Explain why a correlation does not prove a causal mechanism. B7.2 Cancer B7.3 Smoking and the risk of disease B7.4 Diet, exercise and disease 7.5 Alcohol and other carcinogens Tumour Benign Malignant Mutations Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Nicotine Carbon monoxide Cardiovascular disease COPD Type 2 diabetes Cardiovascular disease Obesity BMI Ethanol Addiction Cirrhosis Placenta Carcinogens Ionising radiation Describe what a tumour is. Describe the difference between benign and malignant tumours. Discuss causes and treatments of cancer. Describe how smoking affects the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Describe how smoking affects the risk of developing lung disease and lung cancer. Evaluate the effect of smoking during pregnancy. Identify correlations between diet, exercise and disease. Explain how diet and lack of exercise cause heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Link risk factors together to identify how they interact to cause disease. Describe some effects of drinking alcohol and the carcinogenic effects of ionising radiation. Explain how alcohol causes these effects. Evaluate evidence on the effects of alcohol on developing babies. This topic is on pages 37 to 38 of your revision guide.
13 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B8: Photosynthesis Know that photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction. B8.1 Photosynthesis photosynthesis chlorophyll chloroplast stoma stomata guard cell Describe the reaction that summarises photosynthesis. Evaluate how a leaf is adapted for photosynthesis B8.2 Rate of photosynthesis B8.3 How plants use glucose B8.4 Making the most of photosynthesis carbon dioxide light intensity temperature limiting factor inverse square law glucose protein starch respiration cellulose limiting factors polytunnel greenhouse environment hydroponics Name the factors which limit the rate of photosynthesis. Explain the effects of temperature, light, carbon dioxide and chlorophyll on rate of photosynthesis. Interpret graphs showing rate of photosynthesis Name some substances that plants make from glucose and recall how to test for the presence of these in the lab. Describe the uses of these substances. Explain how proteins are made by plants. State the different factors which affect the rate of photosynthesis. Describe how the different factors interact. Explain how humans can manipulate the environment in which plants grow This topic is on pages 50 to 53 of your revision guide.
14 Yr 10 Combined Biology. Chapter B9: Respiration 9.1 Aerobic respiration Mitochondria Calories Oxygen Glucose Water Carbon dioxide Exothermic Enzymes Recall the equation for aerobic respiration Explain why cellular respiration is so important Explain how the body facilitates respiration by making connections between your knowledge of the respiratory, cardiovascular and digestive systems. 9.2 Response to exercise Heart rate Glycogen Breathing rate Carbohydrate Muscle Describe how our body responds to exercise. Explain why heart rate and breathing rate are affected by exercise. Evaluate the effect of exercise on glycogen stores Recall the equation for anaerobic respiration. 9.3 Anaerobic respiration Anaerobic Aerobic Oxygen debt Lactic acid Compare aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Describe anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast. Explain how the oxygen debt is paid off. 9.4 Metabolism and the liver Metabolism Liver Hydrogen peroxide enzymes Define metabolism. Give examples of reactions that happen in living organisms. Explain how the liver performs metabolic functions in paying back the oxygen debt. This topic is on pages 54 to 56 of your revision guide.
15 Yr 10 Combined Chemistry. Chapter C1: Atomic Structure C1.1 Atoms atoms elements periodic table groups compounds nucleus electrons Describe or explain the difference between an atom, an element and a compound Use chemical formulae and the periodic table to name elements in a compound Use chemical symbols and keywords (atom, element and compound) to explain combustion reactions in simple terms C1.2 Chemical equations C1.3 Separating Mixtures C1.4 Fractional distillation and paper chromatography reactants products balanced state symbols separation distillation filtration crystallisation fractional distillation paper chromatography biofuel dyes State what happens to atoms in a chemical reaction Decide if chemical equations are balanced and balance them. Explain why you can t change a formula when balancing chemical equations. Describe 4 different methods by which mixtures can be separated Explain 4 different methods by which mixtures can be separated Plan a sequence of steps to separate a mixture of given substances Separate a mixture using a given method and describe what happened in each step Separate a mixture using a method of your own devising and explain what happened in each step Evaluate the success of a separation method
16 Yr 10 Combined Chemistry. Chapter C1: Atomic Structure C1.5 History of the atom C1.6 Structure of the atom C1.7 Ions, atoms and isotopes C1.8 Electronic Structure electron neutron nucleus proton shell protons neutrons electrons atomic number proton number atomic mass mass number subatomic ions nanometres standard form isotopes electronic structure electron shells noble gases State how the plum pudding model of the atom differs from the nuclear model. Describe the changes in the theories about the model of the atom. Explain evidence for the nuclear model of the atom. Recall the components of an atom Describe where in the atom each component is found Apply your knowledge of the atom to explain how the atomic number and atomic mass number can be calculated Describe what an isotope is Use symbol forms of isotopes to compare the atomic structure of different isotopes Explain what an ion is, and why ions of isotopes form in the same way Describe the rules for drawing electronic structures Draw the electronic structure for the first 20 elements Explain how electronic structures relate to groups in the periodic table with examples This topic is on pages 96 to 104 of your revision guide.
17 Yr 10 Combined Chemistry. Chapter C2: The Periodic Table C2.1 Development of the Periodic Table elements periodic table Mendeleev Describe how the periodic table is structured Explain how the periodic table was developed by Mendeleev Predict the properties of elements using ideas about periodicity C2.2 Electronic Structures and the Periodic Table C2.3 Group 1 The Alkali Metals C2.4 Group 7 The Halogens C2.5 Explaining Trends metals non-metals electron group shell alkali metal property reactive halogen reaction trend pattern effect State how atomic structure is linked to the periodic table Describe how metals and nonmetals differ Explain why noble gases are so unreactive Describe some physical and chemical properties of Group 1 elements Analyse data to observe patterns Explain the trends in Group 1 elements State some physical and chemical properties of Group 7 elements Analyse data to observe patterns Explain the trends in Group 7 elements State the trends in reactivity in Group 1 and 7 Describe how electronic structure is linked to trends in reactivity Explain how electronic structure is linked to trends in reactivity This topic is on pages 105 to 111 of your revision guide.
18 Yr 10 Combined Chemistry. Chapter C3: Structure and Bonding solid Describe the properties and particle liquid arrangements of 3 states of matter C3.1 gas States of Matter particle model heating curve melting point boiling point Predict states of matter of substances given data Explain the limitations of particle theory C3.2 Atoms into ions C3.3 Ionic bonding C3.4 Giant ionic structures C3.5 Covalent bonding C3.6 Structure of simple molecules ion electron shell charge electrostatic giant structure lattice conductivity molten fixed melting point electron pair full outer shell molecule intermolecular forces boiling point State what is meant by a compound Describe how atoms form negative or positive ions using dot-cross diagrams Explain how a group 1 element will react with a group 7 element State what kinds of elements form ionic compounds Draw dot and cross diagrams to show ionic bonding Predict the formula of ionic compounds State some properties of ionic compounds Describe the structure of an ionic lattice Use the structure to explain the properties of ionic compounds Draw dot and cross diagrams for simple covalent bonds Draw dot and cross diagrams for more complex covalent substances Compare and contrast covalent and ionic bonding Recognise simple molecules represented by different models. Draw dot and cross diagrams and write the displayed formulae of simple molecules. Draw dot and cross diagrams and write the displayed formulae of simple molecules. Evaluate the models used to represent simple covalent molecules.
19 Yr 10 Combined Chemistry. Chapter C3: Structure and Bonding C3.7 Giant covalent structures C3.8 Fullerenes and Graphene C3.9 Bonding in metals C3.10 Giant metallic structures diamond graphite lattice covalent delocalised layers fullerene graphene delocalised buckyball delocalised conductivity alloy ductile malleable lattice State the general properties of giant covalent molecules Describe the chemical structures of diamond, graphite and silica Explain how chemical structure influences chemical and physical properties. State the general properties of giant covalent molecules Describe the chemical structures of diamond, graphite and silica Explain how chemical structure influences chemical and physical properties. Name some general properties of metals Describe the arrangement of particles in metals Explain how the arrangement of atoms influences some of the properties of metals. Recall why metals are ductile and malleable Describe the difference in structure of alloys and pure metals. Explain the difference in properties between pure metals and alloys. This topic is on pages 112 to 122 of your revision guide.
20 Yr 10 Combined Chemistry. Chapter C4: Chemical calculations Identify relative atomic mass of an element and relative relative atomic mass (A C4.1 r ) formula mass of a compound relative formula mass (M Relative r ) Apply the equation n= m M r mole to find the number of moles of masses and Avogadro constant a substance moles standard form Rearrange the above equation to find moles, mass or M r of a substance C4.2 Equations and calculations C4.3 From masses to balanced equations C4.4 Expressing concentrations equation balanced unbalanced ratio mass balanced equation reactant limiting reactant concentration volume g/dm 3 Balance basic chemical equations Identify mole ratios from a balanced equation Calculate the amount of product formed in a reaction using the balanced equation Balance equations from mass of reactants and mass of products Explain why limiting a quantity of reacts affects the amount of product it is possible to obtain Balance and find the limiting factor of complex chemical equations Recall what is meant by the term concentration Calculate concentration from number of moles and volume using correct units Convert units in order to calculate concentrations This topic is on pages 123 to 128 of your revision guide.
21 Yr 10 Chemistry. Chapter C5: Chemical changes Lesson keywords I can Before After C5.1 The reactivity series C5.2 Displacement reactions C5.3 Extracting metals C5.4 Salts from metals ore reactivity series oxidised reduced metal acid water displacement reactions positive ions electrons oxidation reduction O.I.L. R.I.G. word equations symbol equations ionic equations half-equations metal ore carbon hydrogen oxidation reduction metal hydrochloric acid sulfuric acid salt hydrogen electrons redox Define ore. Explain reduction and oxidation in terms of loss or gain of oxygen. Predict and then describe reactions of metals using the reactivity series. Describe displacement reactions using the reactivity table and represent as word and symbol equations. Explain how the reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive ions. Represent displacement reactions as ionic equations half equations Describe factors which should be considered selecting an ore to extract a metal from. Describe how metals can be extracted from their ore using displacement reactions. Explain the extraction in terms of oxidation and reduction. Write word and symbol equations to show how salts are formed from metals and acids. Correctly name the salt. Describe how salts can be made and collected and the how to test the gas. Explain the reaction in terms of oxidation and reduction. Explain redox reactions in terms of loss and gain of electrons.
22 Yr 10 Chemistry. Chapter C5: Chemical changes C5.6 Salts from insoluble bases C5.7 Making more salts C5.8 Neutralisation and the ph scale base alkali hydrochloric acid sulfuric acid salt water acid alkali carbonate neutralisation salt water carbon dioxide indicator acid alkali base neutral ph universal indicator ph probe/sensor ph curve H + OH - Define the terms base and alkali. Write word and symbol equations to show how salts are formed from metals and bases. Correctly name the salt. Describe how salts can be made and collected Write word and symbol equations to show how salts are formed from acids and alkalis. Correctly name the salt. Write word and symbol equations to show how salts are formed from acids and carbonates. Correctly name the salt. Describe how salts can be made and collected. Describe what the ph scale shows. Describe how we can measure the ph of a solution. Explain why solutions are acidic or alkaline. C5.9 Strong and weak acids dilute concentrated weak strong H + equilibrium ph Define the terms dilute / concentrated. Describe the terms strong acid / weak acid. Explain how the H + concentration of a solution affects the ph value. This topic is on pages 129 to 134 of your revision guide.
23 Yr 10 Combined Chemistry. Chapter C6: Electrolysis Lesson keywords I can Before After anode Define electrolysis, electrode and cathode electrolyte electrode C6.1 electrolysis Describe what electrolysis is used Introduction electrolyte for to Electrolysis inert Use the charges on ions to predict negative what will form at each electrode positive C6.2 Changes at the Electrodes C6.3 Extracting Aluminium Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions C6.4 Electrolysis of Brine attract repel half equation oxidation oxidised reduced reduction bauxite cryolite decompose impurity molten oxidised alkali chlorine gas gases hydrogen hydroxide indicator bleach brine chlorine hydrogen sodium chloride sodium hydroxide Describe what happens to ions during electrolysis Describe the effect of water on the products of electrolysis Write half-equations to represent a reaction at an electrode Describe the process of aluminium extraction Write the half-equation for the reactions at each electrode Explain why the carbon electrodes need to be replaced periodically Set up the circuit required for electrolysis Identify the gases collected at an electrode Explain why a certain gas is produced at an electrode State the products from electrolysis of brine and their uses Explain how each product is formed during electrolysis Write a half equation for the process at each electrode This topic is on pages 135 to 137 of your revision guide.
24 Yr 10 Combined Chemistry. Chapter C7: Energy changes Lesson keywords I can Before After C7.1 Exothermic and Endothermic reactions C7.2 Using energy transfers from reactions C7.3 Reaction profiles C7.4 Bond energy calculation exothermic endothermic energy transfer Exothermic Endothermic Energy transfer Activation energy Released absorbed Bond energy Exothermic endothermic State the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions Describe exothermic and endothermic reactions in terms of energy transfer Evaluate uses and applications of exothermic and endothermic reactions Measure the temperature change of a chemical reaction Investigate how the quantities of reactants affect temperature change Evaluate and improve the accuracy of an experiment Draw and label the reaction profiles for exothermic and endothermic reaction Use reaction profiles to identify reactions as exothermic and endothermic Explain overall energy change in terms of bond making and bond breaking Describe reactions in terms of the energy involved in bond breaking and bond formation List the number and types of bonds broken and formed in a reaction Use bond energies to calculate the energy change in chemical reactions This topic is on pages 138 to 141 of your revision guide.
25 Yr 10 Combined Physics. Chapter P1: Energy and Energy Resources P1.1 Changes in energy stores Energy Store Transferred Thermal Chemical Kinetic Elastic Gravitational Potential Recall ways in which energy can be stored Describe the energy changes in a falling object Explain why an object that bounces will not bounce back to the height it was dropped from P 1.2 Conservation of energy P 1.3 Energy and work P1.4 Gravitational Potential Energy Stores P 1.5 Kinetic Energy and Elastic Stores P 1.6 Energy dissipation Created Destroyed Closed System Conservation Work Done Line of Action Friction Thermal Joules Gravitational Potential Weight Mass Kinetic Elastic Potential Speed Spring Constant Useful Wasted Surroundings Dissipates Define a closed system Explain the meaning of conservation of energy Apply the principle of conservation of energy to specific situations Recall the equation and units for work done Calculate work done Explain where work done to overcome friction is stored Recall the equation for gravitational potential energy Describe changes in gravitational potential energy for an object being raised or lowered Calculate a change in gravitational potential energy Recall the equations for kinetic energy and elastic potential energy Calculate kinetic and elastic potential energy Calculate the speed of an object with known kinetic energy Define useful and waste energy State where waste energy is eventually transferred to Describe the energy transfers in an object, identifying useful and waste energy
26 Yr 10 Combined Physics. Chapter P1: Energy and Energy Resources P 1.7 Energy and efficiency P 1.8 Electrical Appliances P 1.9 Energy and Power Efficiency Air Resistance Electrical Resistance Noise Lubrication Fossil Fuel Appliance Power Watts Rate Efficiency Recall the equation for efficiency Calculate the efficiency of an object Explain how to maximise the efficiency of a machine State examples of electrical appliances in the home Recall the source of most energy supplied to our homes Describe the useful and waste energy for specific electrical appliances Recall the equation and unit for power Calculate power Calculate efficiency using the useful power output and total power input This topic is on pages 167 to 170 and 172 of your revision guide.
27 Yr 10 Combined Physics. Chapter P2: Energy Transfer P2.1 Energy Transfer by Conduction Conductor Insulator Thermal Conductivity Define thermal conductivity Give examples of materials with high and low thermal conductivity, and where they may be used. P2.2 Specific Heat Capacity P2.3 Heating and Insulating Buildings Specific Heat Capacity Storage Heaters Thermal Insulators Thermal Conductivity Vacuum Rate Predict whether specific objects will make good insulation. Define specific heat capacity. Calculate the energy change when an object changes temperature. Explain how to measure the specific heat capacity of a substance Describe examples where it is useful to reduce the rate of energy transfer Describe how the rate of cooling of a building is affected by the thickness and thermal conductivity of its walls. Explain how double glazing, aluminium foil and loft insulation reduce energy transfer This topic is on page 171 of your revision guide.
28 Yr 10 Combined Physics. Chapter P3: Energy resources Fossil fuel Name some energy resources Biofuel Classify energy resources into Energy Renewable renewable and non-renewable Demands Carbon neutral Nuclear power Hydroelectricity Compare different types of nonrenewable power Energy from wind and water Power from the Sun and the Earth Energy and the environment Big Energy issues Wind power Wave power Hydroelectric power Tidal power Solar water heating Solar cells Geothermal power Greenhouse gas Carbon dioxide Acid rain Nuclear waste Reliable Supply and demand Start-up time Base load Describe how power can be generated from wind and water Explain the advantages and disadvantages of each power station Explain how hydroelectricity can be used to store energy Describe how power can be generated from the Sun and the Earth Explain the advantages of disadvantages of each power station Compare solar water heating and solar cells State some problems with fossil fuels and renewable Explain how problems with power generation can be overcome Evaluate different sources of power in terms of reliability, pollution and waste. State which power sources have long and short start-up times Explain why energy demand varies during the day Evaluate which energy resources can help meet power demand This topic is on pages 173 to 178 of your revision guide.
29 Yr 10 Combined Physics. Chapter P4: Electric Circuits P4.1 Current and charge P4.2 Potential difference and resistance P4.3 Component characteristics P4.4 Series Circuits P4.5 Parallel Circuits Cell, Switch, Bulb, Diode LED, Ammeter Voltmeter, Resistor Variable resistor Heater, Fuse, Charge, LDR, Current, Time Potential difference Parallel, Series Resistance Electrons Charge, Current Diode LED Thermistor LDR Bulb Series Total resistance Parallel Current Voltage Resistance Branch/loop Draw an accurate diagram of a circuit. Calculate an electric current. Explain what causes the current in a circuit to vary Define potential difference Calculate resistance in a circuit. Explain how resistance varies with length of a wire. Describe what happened to resistance of a filament bulb as temperature increases Explain what happens to resistance of a filament as current increases Explain the shape of characteristic graphs for Diodes and thermistors Calculate the total resistance in a series circuit given resistance of resistors Calculate total resistance given current and supply voltage Explain current, p.d and resistance values in series circuits State the potential difference across each parallel component Describe the current in each branch of a parallel circuit Explain parallel circuit rules for current, potential difference and resistance This topic is on pages 179 to 185 of your revision guide.
30 Yr 10 Combined Physics. Chapter P5: Electricity in the home P5.1 Alternating current P5.2 Cables and plugs P5.3Electrical power and potential difference P5.4 Electrical currents and energy transfer P5.5 Appliances and efficiency Direct current Alternating current Live wire Neutral wire Frequency oscilloscope Earth wire Live wire Neutral wire Cable grip Fuse Power Energy transferred Time Resistance Fuse Potential difference Heating effect Charge Coulomb Potential difference current Output\input Power Appliance energy Compare Direct current and alternating current Describe the national grid and its use Calculate voltage and frequency from an oscilloscope display Describe the main parts of a plug Explain material choice for different parts of a plug Explain the safety features of a three-pin plug Calculate power given energy transferred and time Calculate power given current and potential difference Calculate the power of an appliance due to the heating effect of current. Recall the relationship between charge, current and time Calculate energy transferred to a component due to charge flow. Explain energy transfer from the battery to the components using conservation Recall calculations of energy involving energy and power Describe the terms useful energy and wasted energy Compare the efficiency of different electrical components This topic is on pages 186 to 190 of your revision guide.
31 Yr 10 Combined Physics. Chapter P6: Molecules and matter P6.1 Density P6.2 States of matter P6.3 Changes of state P6.4 Internal energy P6.5 Specific latent heat P6.6 Gas Pressure and temperature Density Mass, Volume Kilograms Irregular Regular Physical Change Gas, Solid Liquid Vaporisation Boiling Sublimation Melting Freezing Melting point Freezing point Boiling point Latent heat Internal energy Pressure Forces Bonds Specific latent heat of fusion Specific latent heat of vaporisation Energy Joules Pressure Temperature Kinetic theory Calculate density using an equation Calculate the density of a regular object experimentally Calculate the density of an irregular object experimentally Describe the properties of solids, liquids and gasses Draw the arrangement of particles and explain the behaviour of particles in solids, liquids and gasses Explain mass of a material as it changes state. Define melting point and boiling point Determine meting and boiling point from temperature time graphs Explain the difference between boiling and evaporation Describe the relationship between temperature and internal energy Explain the properties of solids liquids and gasses refereeing to internal energy Explain why gasses exert pressure Describe the difference between Specific latent heat of fusion and the Specific latent heat of vaporisation Calculate the specific latent heat of a material using an equation Describe an experiment to determine the specific latent heat of a substance Describe how gas exerts pressure on a surface Explain gas pressure in terms of temperature, speed, force and number of impacts Use experimental findings to describe the random motion of gas particles This topic is on pages 191 to 194 of your revision guide.
32 Yr 10 Combined Physics. Chapter P7: Radioactivity P7.1 Atoms and Radiation P7.2 Discovery of the Nucleus P7.3 Changes in the Nucleus P7.4 More about Alpha, Beta and Gamma Geiger counter Alpaha radiation Beta radiation Gamma radiation Nuclei Radioactive decay Random Plum pudding Atom Alpha Charge Mass number Atomic number Emission Proton neutron Isotope Ionisation Irradiated Radioactive contamination lead State three types of radiation Describe the type of nuclei that can decay Explain what is meant by a random event Draw and label a diagram of the atom Describe the Rutherford experiment Explain how the Rutherford experiment provides evidence against the plum pudding model. Define an isotope Describe how the nucleus changes in alpha, beta and gamma decay Write and interpret equations for nuclear decays Define ionisation State the materials required to block alpha, beta and gamma. Compare the ionising power of alpha, beta and gamma. Define half-life P7.5 Activity and half life Activity Count rate Describe how to measure the count-rate from a source Determine the half-life of a source from a graph of countrate Calculate the count rate from a source after n half-lives This topic is on pages 195 to 200 of your revision guide.
Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined. Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours
 Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours Half Term.7.. Communities Competition Ecosystems Interdependence ASSESSED HOMEWORK (Communities).7.. Abiotic
Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours Half Term.7.. Communities Competition Ecosystems Interdependence ASSESSED HOMEWORK (Communities).7.. Abiotic
Cecil Jones Academy Science Fundamentals Map
 Fundamentals: Year 9 Biology Knowledge Unit 1 Skills B1 Cell Structure and Transport Unit 2 Use the terms 'eukaryotic' and 'prokaryotic' to describe types of cells Describe the features of bacterial (prokaryotic)
Fundamentals: Year 9 Biology Knowledge Unit 1 Skills B1 Cell Structure and Transport Unit 2 Use the terms 'eukaryotic' and 'prokaryotic' to describe types of cells Describe the features of bacterial (prokaryotic)
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
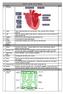 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Lymm High School- KS3 Life after levels - Science Y9
 Biology BRONZE SILVER GOLD PLATINUM D and below= GCSE 1,2,3 C= GCSE 4 C/B= GCSE 5,6 A/A*= GCSE 7,8,9 Explain that cells are very Demonstrate an small and a microscope is understanding of the scale needed
Biology BRONZE SILVER GOLD PLATINUM D and below= GCSE 1,2,3 C= GCSE 4 C/B= GCSE 5,6 A/A*= GCSE 7,8,9 Explain that cells are very Demonstrate an small and a microscope is understanding of the scale needed
PLC Booklet for. Paper 1
 PLC Booklet for Combined Science Paper 1 This personalised learning checklist (PLC) booklet has been put together to support your preparation for Biology Paper 1, Chemistry Paper 1 and Physics Paper1.
PLC Booklet for Combined Science Paper 1 This personalised learning checklist (PLC) booklet has been put together to support your preparation for Biology Paper 1, Chemistry Paper 1 and Physics Paper1.
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
YEAR 9 - AQA GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE (9-1) Cell Biology
 YEAR 9 - AQA GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE (9-1) Cell Biology Cell structure Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in
YEAR 9 - AQA GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE (9-1) Cell Biology Cell structure Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Y9 3Y Combined BIOLOGY POS
 Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 4... 4... 4... 4... Animal and Plant Cells - Eukaryotes Structure Organelle function Bacterial cells - Prokaryotes Structure Organelle function Term (7w) 4... Cell
Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 4... 4... 4... 4... Animal and Plant Cells - Eukaryotes Structure Organelle function Bacterial cells - Prokaryotes Structure Organelle function Term (7w) 4... Cell
YEAR 7. St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map New AQA Course Started November 2016
 YEAR 7 St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map 201-2017 New AQA Course Started November 2016 05/09/2016 12/09/2016 19/09/2016 26/09/2016 03/10/2016 10/10/2016 17/10/2016 24/10/2016
YEAR 7 St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map 201-2017 New AQA Course Started November 2016 05/09/2016 12/09/2016 19/09/2016 26/09/2016 03/10/2016 10/10/2016 17/10/2016 24/10/2016
PLC Booklet for. Separate Science. Paper
 PLC Booklet for Separate Science Paper 1 This personalised learning checklist (PLC) booklet has been put together to support your preparation for Biology Paper 1, Chemistry Paper 1 and Physics Paper 1.
PLC Booklet for Separate Science Paper 1 This personalised learning checklist (PLC) booklet has been put together to support your preparation for Biology Paper 1, Chemistry Paper 1 and Physics Paper 1.
Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE)
 Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE) This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our legacy Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology (8401) to
Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE) This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our legacy Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology (8401) to
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Level 789 Pathway: Combined Science Double Award
 Level 789 Pathway: Combined Science Double Award Yr Combined Science Targets: Pathway 8 11 Biology a) Explain in detail the role of the hormone ADH on the nephron b) Explain in detail the process by which
Level 789 Pathway: Combined Science Double Award Yr Combined Science Targets: Pathway 8 11 Biology a) Explain in detail the role of the hormone ADH on the nephron b) Explain in detail the process by which
Main Topic Sub-topics Students should be able to R O G
 Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks
 Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks Cell Biology (Yr9) Cell Organisation (Yr9) Infection and Response (Yr10) Bioenergetics (Yr10) Cells Cell Organisation Competition Photosynthesis Microscopy Enzymes Abiotic
Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks Cell Biology (Yr9) Cell Organisation (Yr9) Infection and Response (Yr10) Bioenergetics (Yr10) Cells Cell Organisation Competition Photosynthesis Microscopy Enzymes Abiotic
Review Chemistry Paper 1
 Atomic Structure Topic Define an atom and element. Use scientific conventions to identify chemical symbols Identify elements by chemical symbols Define compound Use chemical formulae to show different
Atomic Structure Topic Define an atom and element. Use scientific conventions to identify chemical symbols Identify elements by chemical symbols Define compound Use chemical formulae to show different
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of the cell wall. membrane?
 Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Chemistry Paper 1
 AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State that elements
AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State that elements
AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists. Name: Teacher:
 AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists Name: Teacher: Paper 1-4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic
AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists Name: Teacher: Paper 1-4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic
Chemistry (separate) for November PPE
 1.1 Elements and 1.2 Atoms, formulae and Chapter 1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table Recognise the properties of elements and. Identify the elements
1.1 Elements and 1.2 Atoms, formulae and Chapter 1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table Recognise the properties of elements and. Identify the elements
Combined GCSE OCR Revision Science magnification tur tur magnification ell Struc ell Struc ells ells Combined GCSE OCR Revision Science
 Cell Structures How is the magnification of a light microscope calculated? Cell Structures Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of
Cell Structures How is the magnification of a light microscope calculated? Cell Structures Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of
Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and recall names used for these inter-conversions
 Understand the arrangements, movements and energy of the particle in each of the 3 states of matter : solid, liquid and gas Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and
Understand the arrangements, movements and energy of the particle in each of the 3 states of matter : solid, liquid and gas Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and
AQA Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell biology Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Distinguish between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Compare animal and plant cells. Relate cell structures to their functions. Video: Specialised
Topic 1. Cell biology Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Distinguish between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Compare animal and plant cells. Relate cell structures to their functions. Video: Specialised
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Trilogy Chemistry Paper 1
 AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State
AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State
How many lessons is it?
 Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview
 Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 Hypothesis
Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 Hypothesis
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview
 Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) To pic. Student Checklist
 Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 s T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are 5.1.1 A simple
Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 s T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are 5.1.1 A simple
Cell Structure. Cell Structure. Investigating Cells. Investigating Cells. Cell Division. Cell Division. Transport In and Out of Cells
 Cell Structure What are the two main types of cell? Cell Structure The two main types of cell are prokaryotic and eukaryotic. 1 1 Investigating Cells How is magnification calculated? 2 Investigating Cells
Cell Structure What are the two main types of cell? Cell Structure The two main types of cell are prokaryotic and eukaryotic. 1 1 Investigating Cells How is magnification calculated? 2 Investigating Cells
Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8. atom.
 Student checklist C1 Atomic structure Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8 C1.1 Atoms I can define the word element. I can classify familiar substances as elements or compounds. I can use the periodic table
Student checklist C1 Atomic structure Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8 C1.1 Atoms I can define the word element. I can classify familiar substances as elements or compounds. I can use the periodic table
Paget High School. Preparing for A level Biology
 Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
2012 SECONDARY 1 SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK
 2012 SECONDARY 1 SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK Term 1 1 Orientation 2 Introduction to Science Lab Safety 3 Physical Quantities and Units 1. All physical quantities consist of a numerical magnitude and a unit
2012 SECONDARY 1 SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK Term 1 1 Orientation 2 Introduction to Science Lab Safety 3 Physical Quantities and Units 1. All physical quantities consist of a numerical magnitude and a unit
Year 8 Tracking Document. Year 8 Science National Curriculum. Health and Lifestyle
 Health and Lifestyle Describe the components of a healthy diet Explain the role of each food group in the body Describe the test for starch, lipids, sugar and proteins Describe the positive test for each
Health and Lifestyle Describe the components of a healthy diet Explain the role of each food group in the body Describe the test for starch, lipids, sugar and proteins Describe the positive test for each
Foundation Cell Biology
 Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
HASTINGS HIGH SCHOOL
 Subject ASTINGS IG SCOOL YEAR 11 EXAMINATION GUIDE 2017-19 COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY- BIOLOGY Course code AQA GCSE BIOLOGY 8464 Website address Provisional examination dates http://www.aqa.org.uk/subjects/science/gcse/combined-science-trilogy-
Subject ASTINGS IG SCOOL YEAR 11 EXAMINATION GUIDE 2017-19 COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY- BIOLOGY Course code AQA GCSE BIOLOGY 8464 Website address Provisional examination dates http://www.aqa.org.uk/subjects/science/gcse/combined-science-trilogy-
Science 9-1 Grades Guidance
 U1 U2 U3 Science 9-1 Grades Guidance This guide is designed to help explain the level that a student is working at using examples of the curriculum that a student should be able to access. This is not
U1 U2 U3 Science 9-1 Grades Guidance This guide is designed to help explain the level that a student is working at using examples of the curriculum that a student should be able to access. This is not
KS3 Science Levelness Posters
 KS Science Levelness Posters Contents Year Year 8 Year 9 A. Cells 8A. Food and digestion 9A. Inheritance and selection B. Reproduction 8B. Respiration 9B. Fit and healthy C. Environment and feeding 8C.
KS Science Levelness Posters Contents Year Year 8 Year 9 A. Cells 8A. Food and digestion 9A. Inheritance and selection B. Reproduction 8B. Respiration 9B. Fit and healthy C. Environment and feeding 8C.
Paper Atomic structure and the periodic table
 Paper 1 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in
Paper 1 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in
Semester 1 Study Guide Name Period
 2017-2018 Semester 1 Study Guide Name Period Chapter 1: Scientific Method and Microscopes (p. 2-31 and A-1 through A-17) Vocab: experiment, hypothesis, scientific theory, scientific law, controlled experiment,
2017-2018 Semester 1 Study Guide Name Period Chapter 1: Scientific Method and Microscopes (p. 2-31 and A-1 through A-17) Vocab: experiment, hypothesis, scientific theory, scientific law, controlled experiment,
Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 5 Overview
 e Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 5 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology How do we keep your body healthy L01 4.3.1.1 Communicable (infectious) disease L02 4.3.1.2 Viral diseases L03 4.3.1.3 Bacterial
e Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 5 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology How do we keep your body healthy L01 4.3.1.1 Communicable (infectious) disease L02 4.3.1.2 Viral diseases L03 4.3.1.3 Bacterial
- know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues can be massed together to form organs
 Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
Personalised Learning Checklist
 Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.1 Cell biology (Bio Paper 1) 4.1.1 Cell structure 4.1.2 Cell division Use the terms 'eukaryotic' and 'prokaryotic' to describe
Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.1 Cell biology (Bio Paper 1) 4.1.1 Cell structure 4.1.2 Cell division Use the terms 'eukaryotic' and 'prokaryotic' to describe
Animal Cell Organelles. Plant Cell. Organelle. Cell Wall. Chloroplasts. Vacuole
 Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
Time (s) Velocity (m/s)
 29.01.18 22.01.18 15.01.18 w/c Weekly Combined Science revision countdown plan (revision guide / workbook page numbers) *content across both paper 1 and paper 2 15 14 13 Revise *Key concepts in biology
29.01.18 22.01.18 15.01.18 w/c Weekly Combined Science revision countdown plan (revision guide / workbook page numbers) *content across both paper 1 and paper 2 15 14 13 Revise *Key concepts in biology
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST
 GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Atomic Structure Recall the different charges of the particles that make up an atom. Describe why atoms have no overall charge. Use the periodic table to identify
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Atomic Structure Recall the different charges of the particles that make up an atom. Describe why atoms have no overall charge. Use the periodic table to identify
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Combined GCSE OCR Revision Science magnification tur tur magnification ell Struc ell Struc ells ells Combined GCSE OCR Revision Science
 Cell Structures How is the magnification of a light microscope calculated? Cell Structures Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of
Cell Structures How is the magnification of a light microscope calculated? Cell Structures Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of
The Science Department Academic Year Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview
 The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview Subject: Biology Term 1 Year Level: 10 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview Subject: Biology Term 1 Year Level: 10 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
Ark Elvin Academy Year 10 Science Study Pack Spring assessment 2018 Cumulative content part 1
 Ark Elvin Academy Year 10 Science Study Pack Spring assessment 2018 Cumulative content part 1 Name Biology Cell Biology: structure and transport Part 1: Glossary 1. active transport the movement of substances
Ark Elvin Academy Year 10 Science Study Pack Spring assessment 2018 Cumulative content part 1 Name Biology Cell Biology: structure and transport Part 1: Glossary 1. active transport the movement of substances
GCSE Biology B2 Revision Questions. 1. Draw and label the parts of these different types of cell, explaining what the role of each part is -
 B2.1 Cells and Simple Cell Transport GCSE Biology B2 Revision Questions 1. Draw and label the parts of these different types of cell, explaining what the role of each part is - a) Animal cell b) Plant
B2.1 Cells and Simple Cell Transport GCSE Biology B2 Revision Questions 1. Draw and label the parts of these different types of cell, explaining what the role of each part is - a) Animal cell b) Plant
AQA GCSE CHEMISTRY (9-1) Topic 1: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
 AQA GCSE CHEMISTRY (9-1) Topic 1: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table 4.1.1 Atoms, elements and compounds 4.1.1.1 Atoms, elements and compounds All substances are made of atoms. An atom is the smallest
AQA GCSE CHEMISTRY (9-1) Topic 1: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table 4.1.1 Atoms, elements and compounds 4.1.1.1 Atoms, elements and compounds All substances are made of atoms. An atom is the smallest
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan
 YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
Science. Biology Year 7. Chemistry Year 7. Physics Year 7
 Science Biology Year 7 Chemistry Year 7 Physics Year 7 Using a microscope Slide Preparation o Prepare specimens of plant cells and animal cells o Describe the role of stain in specimen preparation o Draw
Science Biology Year 7 Chemistry Year 7 Physics Year 7 Using a microscope Slide Preparation o Prepare specimens of plant cells and animal cells o Describe the role of stain in specimen preparation o Draw
Same theme covered in Combined but extra content Extra parts atomic symbols (first 20, Group 1 and Group 7)
 Co-teaching document new ELC Science 5960 and Foundation Level GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy (8464) Chemistry: Component 3 Elements, mixtures and compounds ELC Outcomes Summary of content covered in ELC
Co-teaching document new ELC Science 5960 and Foundation Level GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy (8464) Chemistry: Component 3 Elements, mixtures and compounds ELC Outcomes Summary of content covered in ELC
Personalised Learning Checklists Edexcel Combined: Chemistry Paper 1
 Edexcel (combined) Chemistry Topics (1SC0) from 2016 - Paper 1 (Topic 1 parts a&b) Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe how the Dalton model of an atom has changed over time because of the discovery
Edexcel (combined) Chemistry Topics (1SC0) from 2016 - Paper 1 (Topic 1 parts a&b) Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe how the Dalton model of an atom has changed over time because of the discovery
Fill in the gaps: You would write this as: we can use for living processes.
 AQA Trilogy Biology Unit 4.4: Bioenergetics Complete the word equation for + + Write the name of each chemical next to its formula. Which elements make up each chemical? How does the rate of photosynthesis
AQA Trilogy Biology Unit 4.4: Bioenergetics Complete the word equation for + + Write the name of each chemical next to its formula. Which elements make up each chemical? How does the rate of photosynthesis
AQA Trilogy Science. Knowledge Organisers for All Topics
 AQA Trilogy Science s for All Topics The information on each page is a summary of key information needed for each topic. It does not cover all content and is not intended as a replacement to other study
AQA Trilogy Science s for All Topics The information on each page is a summary of key information needed for each topic. It does not cover all content and is not intended as a replacement to other study
Lesson title Lesson objectives AQA specification reference 1.1 Elements and compounds
 1.1 Elements and compounds 1.2 Atoms, formulae and equations Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table Recognise the properties of elements and compounds. Identify the elements in a compound
1.1 Elements and compounds 1.2 Atoms, formulae and equations Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table Recognise the properties of elements and compounds. Identify the elements in a compound
Military High School AL- Ain. Grade 10 &11. Biology Sample Questions. Student Name: Computer #:
 Military High School AL- Ain Grade 10 &11 Biology Sample Questions Student Name: Computer #: Chapter 1: Cells In all multiple choice questions, more than answer could be correct Section : 1 What Is a Cell?
Military High School AL- Ain Grade 10 &11 Biology Sample Questions Student Name: Computer #: Chapter 1: Cells In all multiple choice questions, more than answer could be correct Section : 1 What Is a Cell?
Year 8 Biology Knowledge Organiser Topic 1: Health and Lifestyle
 Year 8 Biology Knowledge Organiser Topic 1: Health and Lifestyle KPI 1: Describe the requirements for a healthy human diet. Kilojoules (kj) Deficiency Disease A unit used to measure energy in foods A disease
Year 8 Biology Knowledge Organiser Topic 1: Health and Lifestyle KPI 1: Describe the requirements for a healthy human diet. Kilojoules (kj) Deficiency Disease A unit used to measure energy in foods A disease
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
for sodium ion (Na + )
 3.4 Unit 2 Chemistry 2 Throughout this unit candidates will be expected to write word equations for reactions specified. Higher tier candidates will also be expected to write and balance symbol equations
3.4 Unit 2 Chemistry 2 Throughout this unit candidates will be expected to write word equations for reactions specified. Higher tier candidates will also be expected to write and balance symbol equations
Additional Science. Important exam information and revision booklet
 Additional Science Important exam information and revision booklet CONTENTS PAGE Page Introduction 3 Section One When are my exams? What will they test 4 Useful places to help you to revise Additional
Additional Science Important exam information and revision booklet CONTENTS PAGE Page Introduction 3 Section One When are my exams? What will they test 4 Useful places to help you to revise Additional
GCSE Combined Science
 AQA GCSE Combined Science Grades 9-1 Chace Community School Combined Science Grade 9-1 GCSE This course will give you two GCSE Science qualifications. You will cover Biology, Chemistry and Physics. During
AQA GCSE Combined Science Grades 9-1 Chace Community School Combined Science Grade 9-1 GCSE This course will give you two GCSE Science qualifications. You will cover Biology, Chemistry and Physics. During
Cell Biology. AQA Biology topic 1
 Cell Biology AQA Biology topic 1 1.1 Cell Structure Plant and Animal cells (eukaryotic cells) Eukaryotic cells have these features: 1) Cytoplasm 2) Genetic material within a nucleus 3) Cell Membrane Typical
Cell Biology AQA Biology topic 1 1.1 Cell Structure Plant and Animal cells (eukaryotic cells) Eukaryotic cells have these features: 1) Cytoplasm 2) Genetic material within a nucleus 3) Cell Membrane Typical
Queen s Park High School Key Stage 3 Assessment Science - Earth IA6 target.
 Year 7 Enquiry Skills Queen s Park High School Key Stage 3 Assessment Science - Earth IA6 target. EARTH STRUCTURE AND UNIVERSE Draw simple graphs outlining information about planets Construct models of
Year 7 Enquiry Skills Queen s Park High School Key Stage 3 Assessment Science - Earth IA6 target. EARTH STRUCTURE AND UNIVERSE Draw simple graphs outlining information about planets Construct models of
This unit will help you define health, learn about some pathogens and the diseases they cause, medicines and about the immune system.
 YEAR 10 Biology Units 1-5 Biology Unit CB1 Key biological concepts [Paper 1 & CB2 Cells and Control CB3 Genetics CB4 Natural Selection and Genetic Modification CB5 Health, Disease and the Development of
YEAR 10 Biology Units 1-5 Biology Unit CB1 Key biological concepts [Paper 1 & CB2 Cells and Control CB3 Genetics CB4 Natural Selection and Genetic Modification CB5 Health, Disease and the Development of
IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences Chemistry Glossary
 IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences Chemistry Glossary acid = any substance that produces hydrogen ions, H+, when dissolved in water acidic solution = a solution with a ph less than 7 acid rain = rain with a ph
IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences Chemistry Glossary acid = any substance that produces hydrogen ions, H+, when dissolved in water acidic solution = a solution with a ph less than 7 acid rain = rain with a ph
Separate Science: Chemistry Paper 1. Knowledge Organisers. Chemistry Paper 1 17 th May AM 1h 45min. Atomic Structure The Periodic Table
 Separate Science: Chemistry Paper 1 Chemistry Paper 1 17 th May AM 1h 45min Topics in the Paper: C1 C2 Atomic Structure The Periodic Table Knowledge Organisers C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 Structure and Bonding Chemical
Separate Science: Chemistry Paper 1 Chemistry Paper 1 17 th May AM 1h 45min Topics in the Paper: C1 C2 Atomic Structure The Periodic Table Knowledge Organisers C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 Structure and Bonding Chemical
4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes. Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3. C2.1.1a Structure and bonding
 Summary of changes This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our previous GCSE Chemistry (4402) to the new specification (8462). Our new specifications
Summary of changes This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our previous GCSE Chemistry (4402) to the new specification (8462). Our new specifications
Combined Science: Physics Paper 1 Higher. Knowledge Organisers. Physics Paper 1 23 rd May PM 1h 15min. Conservation and Dissipation of Energy P2
 Combined Science: Physics Paper 1 Higher Knowledge Organisers Physics Paper 1 23 rd May PM 1h 15min Topics in the Paper: P1 Conservation and Dissipation of Energy P2 Energy Transfer By Heating P3 P4 P5
Combined Science: Physics Paper 1 Higher Knowledge Organisers Physics Paper 1 23 rd May PM 1h 15min Topics in the Paper: P1 Conservation and Dissipation of Energy P2 Energy Transfer By Heating P3 P4 P5
YEAR 7- Science Term 1 plan
 Week Topic YEAR 7- Science Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Learning outcomes 1 Cells the building blocks of life Develop models to explain the differences between animal cells and plant cells. Record evidence using
Week Topic YEAR 7- Science Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Learning outcomes 1 Cells the building blocks of life Develop models to explain the differences between animal cells and plant cells. Record evidence using
Science Years 9 to 10
 Boardworks Contents Guide Boardworks Presentations: Acids and metal oxides 10 slides Reactions of metal oxides with acids. Adapting to changes 9 slides Ways that animals adapt to their habitats. Air pollution
Boardworks Contents Guide Boardworks Presentations: Acids and metal oxides 10 slides Reactions of metal oxides with acids. Adapting to changes 9 slides Ways that animals adapt to their habitats. Air pollution
KS3 Science PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST. YEAR 7 CONTENT Use this document to monitor your revision and target specific areas.
 KS3 Science PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST YEAR 7 CONTENT Use this document to monitor your revision and target specific areas. Topic Name BIOLOGY Historical ideas about living things Content Cells as the
KS3 Science PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST YEAR 7 CONTENT Use this document to monitor your revision and target specific areas. Topic Name BIOLOGY Historical ideas about living things Content Cells as the
CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010
 CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010 The following concepts and terms will be covered by all BIO 120 lecture instructors. Presentation of additional concepts is left to the discretion of the individual
CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010 The following concepts and terms will be covered by all BIO 120 lecture instructors. Presentation of additional concepts is left to the discretion of the individual
AQA GCSE (9-1) Combined Chemistry Three Year Scheme of Work
 Year 9 Term 1 1/2 1.1 Elements and compounds Year 9 Term 1 1/2 1.2 Atoms, formulae and equations Chapter 1: Atomic structure and the periodic table Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table
Year 9 Term 1 1/2 1.1 Elements and compounds Year 9 Term 1 1/2 1.2 Atoms, formulae and equations Chapter 1: Atomic structure and the periodic table Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2016 Science I & II Duration: 3 Hours Index No:- 1) The most essential organelle that should be present in a typical cell
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2016 Science I & II Duration: 3 Hours Index No:- 1) The most essential organelle that should be present in a typical cell
C1 REVISION 5.1 Atomic Structure
 C1 REVISION 5.1 Atomic Structure Draw the symbol for sodium include its mass number and atomic number (what do they tell us) Complete the table Relative Charge Relative Mass Balance the following equation:
C1 REVISION 5.1 Atomic Structure Draw the symbol for sodium include its mass number and atomic number (what do they tell us) Complete the table Relative Charge Relative Mass Balance the following equation:
Chapter 2 1. Using an annotated diagram, describe the structure of a plant cell. (12 marks)
 Essays Chapter 2 1. Using an annotated diagram, describe the structure of a plant cell. 2. Compare and contrast the structure of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. 3. Describe the correct procedures
Essays Chapter 2 1. Using an annotated diagram, describe the structure of a plant cell. 2. Compare and contrast the structure of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. 3. Describe the correct procedures
B4 Organising animals and plants. Student Book answers. B4.1 The blood. Question Answer Marks Guidance
 B4. The blood Any three from: 3 transport of blood cells, transport of dissolved gases, transport of food, transport of hormones, removal of waste products, defence against infection, preventing blood
B4. The blood Any three from: 3 transport of blood cells, transport of dissolved gases, transport of food, transport of hormones, removal of waste products, defence against infection, preventing blood
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)
 PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
Science Home Learning Task. Year 9. GCSE Cell structure and transport
 Science Home Learning Task Year 9 GCSE Cell structure and transport Name Tutor Group Teacher Given out: Monday 23 April Hand in: Monday 30 April Parent/Carer Comment Staff Comment GCSE level Target Investigating
Science Home Learning Task Year 9 GCSE Cell structure and transport Name Tutor Group Teacher Given out: Monday 23 April Hand in: Monday 30 April Parent/Carer Comment Staff Comment GCSE level Target Investigating
0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers
Trilogy - Science Revision
 Trilogy - Science Revision Sept 2015- June 2018 Year 11 Subject Unit Date AM/PM Name: Biology Paper 1 Biology Paper 2 Chemistry Paper 1 Chemistry Paper 2 Physics Paper 1 Physics Paper 2 Target: Tuesday
Trilogy - Science Revision Sept 2015- June 2018 Year 11 Subject Unit Date AM/PM Name: Biology Paper 1 Biology Paper 2 Chemistry Paper 1 Chemistry Paper 2 Physics Paper 1 Physics Paper 2 Target: Tuesday
0653 COMBINED SCIENCE
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0653 COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/31 Paper 3 (Extended
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0653 COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/31 Paper 3 (Extended
3 Movement of substances in living organisms
 Mark schemes Movement of substances in living organisms Using and interpreting data a) (0 to 0 minutes) () decrease (in CO ) () carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis (0 to 0 minutes) () (steep) rise then
Mark schemes Movement of substances in living organisms Using and interpreting data a) (0 to 0 minutes) () decrease (in CO ) () carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis (0 to 0 minutes) () (steep) rise then
Additional Science Chemistry
 Additional Science Chemistry C2 Core Questions and Keywords and Definitions Question How did Mendeleev arrange the elements known at the time into a periodic table? How did Mendeleev use his table? Where
Additional Science Chemistry C2 Core Questions and Keywords and Definitions Question How did Mendeleev arrange the elements known at the time into a periodic table? How did Mendeleev use his table? Where
Science. synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis Using physics to make things work 3 Magnetic fields to keep things moving Energy calculations 4 Energy
 Year 11 (Triple science) 2016-17 Half-term Topic Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 1 Exchange of materials Keeping internal conditions constant Analysis and synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis
Year 11 (Triple science) 2016-17 Half-term Topic Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 1 Exchange of materials Keeping internal conditions constant Analysis and synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis
Science A. B2.1.1a, c Cells and cell structure
 Summary of changes This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our current A (4405), (4408) and (4410) specifications to the new : Trilogy specification.
Summary of changes This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our current A (4405), (4408) and (4410) specifications to the new : Trilogy specification.
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Combined Science Trilogy) 15 Week Revision Timetable
 Exam advice o READ THE WHOLE QUESTION CAREFULLY before starting to write an answer. o Make sure you have all the necessary equipment o It s ok to draw diagrams even if there are lines for writing. Don
Exam advice o READ THE WHOLE QUESTION CAREFULLY before starting to write an answer. o Make sure you have all the necessary equipment o It s ok to draw diagrams even if there are lines for writing. Don
0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-DINATED SCIENCES 0654/32 Paper 3 (Extended Theory), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-DINATED SCIENCES 0654/32 Paper 3 (Extended Theory), maximum
active transport active transport support
 1 Which row matches the cell membrane and cell wall of a palisade cell to their functions? cell membrane active transport active transport support support cell wall active transport support active transport
1 Which row matches the cell membrane and cell wall of a palisade cell to their functions? cell membrane active transport active transport support support cell wall active transport support active transport
