Scan the adjacent QR code or visit to download Hints for relevant questions and Evaluation Test in PDF format.
|
|
|
- Lucinda Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Written in accordance with the latest MHT-CET Paper Pattern which includes topics based on Std. XII Sc. and relevant chapters of Std. XI Sc. (Maharashtra State Board) MHT-CET TRIUMPH BIOLOGY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Salient Features Includes chapters of Std. XII and relevant chapters of Std. XI as per latest MHT-CET Paper Pattern. Exhaustive subtopic wise coverage of MCQs. Quick review provided for each chapter. Various competitive exam questions updated till the latest year. Includes solved MCQs upto MHT-CET Includes solved MCQs from NEET 2016, 2017 and Evaluation test provided at the end of each chapter. Scan the adjacent QR code or visit to download Hints for relevant questions and Evaluation Test in PDF format. Printed at: Print Vision, Navi Mumbai Target Publications Pvt. Ltd. No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, C.D. ROM/Audio Video Cassettes or electronic, mechanical including photocopying; recording or by any information storage and retrieval system without permission in writing from the Publisher. TEID: 12741_JUP P.O. No
2 CONTENT Sr. No. Textbook Chapter Chapter Name Page No. No. Std. XI 1 1 Diversity in Organisms Biochemistry of Cell Plant Water Relations and Mineral Nutrition Plant Growth and Development Organization of Cell Study of Animal Tissues Human Nutrition Human Respiration 132 Std. XII 9 1 Genetic Basis of Inheritance Gene: Its Nature, Expression and Regulation Biotechnology: Process and Application Enhancement in Food Production Microbes in Human Welfare Photosynthesis Respiration Reproduction in Plants Organisms and Environment I Origin and Evolution of Life Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Genetic Engineering and Genomics Human Health and Diseases Animal Husbandry Circulation Excretion and Osmoregulation Control and Co-ordination Human Reproduction Organisms and Environment II 544 Model Question Paper - I 565 Model Question Paper - II 571 Note: Questions of standard XI are indicated by * in each Model Question Paper.
3 Textbook Chapter No. 01 Diversity in Organisms Syllabus 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Diversity in Living Organisms 1.2 Systematics: Taxonomy, Taxonomic Hierarchy and Binomial Nomenclature 1.3 Five Kingdom System of Classification 1.4 Lichens 1.5 Viruses and Viroids Carolus Linnaeus ( ) Carolus Linnaeus proposed the Binomial nomenclature system in 1758 which is a significant contribution to plant taxonomy and is widely accepted throughout the world. Quick Review Taxonomic hierarchy Kingdom Division / Phylum Class Sub-class Series Order Family Genus Species Five kingdom classification Kingdom Monera e.g. Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Cyanobacteria, Actinomycetes Kingdom Protista Kingdom Fungi e.g. Mucor, Rhizopus, Penicillium Kingdom Plantae Algae Bryophytes Pteridophytes Gymnosperms Kingdom Animalia Angiosperms Plant like Protists e.g. Dinoflagellates, Diatoms Animal like Protists e.g. Amoeba, Paramoecium Fungi like Protists e.g. Slime moulds Euglenoids e.g. Euglena 1
4 MHT-CET Triumph Biology (MCQs) Lichens Fungal components External form Ascolichens Basidio-lichens Deutero-lichens Crustose-lichens Foliose-lichens Fruticose-lichens Viruses Plant virus e.g. Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) Animal virus e.g. Influenza virus, HIV Bacteriophage e.g. phage Classical Thinking 1.0 Introduction 1. Sum total of all the reactions occurring in the body of an organism is called (A) bioreaction (B) metabolism (C) expansion (D) regeneration 2. is the defining property of living organisms. (A) Reproduction (B) Growth (C) Consciousness (D) Increase in weight 3. Living organisms are (A) self replicating (B) capable of responding to external stimuli (C) self regulating interactive systems (D) all of above 1.1 Diversity in Living Organisms 4. What is the approximate number of plants and animal species present on earth? (A) 2 10 million (B) 3 20 million (C) 4 30 million (D) 5 30 million 1.2 Systematics: Taxonomy, Taxonomic Hierarchy and Binomial Nomenclature 5. The study of diversity of organism is called as (A) taxonomy (B) systematics (C) classification (D) nomenclature 6. Who among the following is associated with systematics? (A) Watson (B) Robert Hooke (C) Linnaeus (D) Dixon 7. The term classification was coined by (A) Linnaeus (B) A. P. de Candolle (C) Darwin (D) R.H. Whittaker 8. Branch of biology dealing with identification, nomenclature, description and classification is (A) biogeography (B) eugenics (C) ecology (D) taxonomy 9. Three domain system was introduced by (A) Carl Woese (B) Hackel (C) Whittaker (D) H.J. Lam 10. Three domain system includes (A) Plantae, Animalia, Prokaryotes (B) Monera, Protista, Eukaryotes (C) Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya (D) Bacteria, Plantae and Animalia 11. Kingdom animalia is included under domain (A) Archaebacteria (B) Bacteria (C) Eukarya (D) None of these 12. The taxonomic hierarchy was established by (A) John Ray (B) Lamarck (C) Aristotle (D) Carolus Linnaeus 13. Descending arrangement of categories is known as (A) classification (B) taxonomy (C) systematics (D) hierarchy 14. The term taxon was coined by (A) Lamarck (B) H. J. Lam (C) Linnaeus (D) John Ray 15. A group of organisms used to represent a concrete unit of classification is (A) rank (B) order (C) taxon (D) genus 2
5 Chapter 01 : Diversity in Organisms 16. Which is the CORRECT sequence in taxonomic hierarchy? (A) Class species order family division (B) Division order class family genus species (C) Division class order family genus species (D) Species class order division family 17. In biological terminology, a group of similar organisms which are capable of inter-breeding and forming fertile offspring is called (A) species (B) tribe (C) genus (D) family 18. The basic unit upon which the system of classification is constructed is the (A) species (B) order (C) family (D) class 19. The species refers to a group of (A) individuals with some similarity (B) similar individuals with common ancestry (C) interbreeding members (D) both (B) and (C) 20. Concept of species was remodified as closely resembling interbreeding population by (A) Theophrastus (B) Darwin (C) Linnaeus (D) Ernst Mayr 21. Mayr s biological concept of species is mainly based on (A) morphological traits (B) reproductive isolation (C) modes of reproduction (D) morphology and reproduction 22. Morphological concept of species was given by (A) H.J. Lam (B) Charles Darwin (C) Carolus Linnaeus (D) A. P. de Candolle 23. A group of organisms that can interbreed under natural conditions is called (A) morphospecies (B) biospecies (C) polyspecies (D) indica 24. Which of the following is NOT a taxon but category? (A) Division (B) Dicotyledons (C) Angiosperms (D) Polypetalae 25. Basic unit of classification is (A) genus (B) class (C) species (D) order 26. In classification, the category present below family is (A) genus (B) species (C) order (D) class 27. Which one of the following covers a greater number of organisms? (A) Species (B) Family (C) Class (D) Kingdom 28. Dicotyledonae is a (A) category (B) class (C) order (D) kingdom 29. Taxonomic category order comes in between (A) genus and species (B) genus and family (C) family and series (D) division and class 30. The smallest taxon is (A) class (B) order (C) species (D) genus 31. A group of closely related families which resemble in major characters are included under one (A) class (B) genus (C) order (D) division 32. A group of plants or animals with similar characters of any rank is (A) species (B) genus (C) order (D) taxon 33. Taxon Mangifera denotes (A) genus (B) species (C) division (D) class 34. Angiospermae and Gymnospermae are (A) kingdom (B) order (C) division (D) family 35. In Solanum tuberosum, tuberosum denotes (A) genus (B) species (C) family (D) tuber 36. Binomial nomenclature is published in (A) Philosophia Botanica (B) Species Plantarum (C) Systema Naturae (D) Historia Naturalis 3
6 MHT-CET Triumph Biology (MCQs) 37. Binomial nomemclature systems follows rules such as the (A) specific name should begin with a capital letter. (B) scientific names must be printed in italics. (C) name of the author cannot be written in abbreviated form. (D) name of the species cannot be repeated even if the genera are different. 38. Mention of author s name after the species name is called (A) citation (B) translation (C) recognization (D) publication 39. Which name is written correctly? (A) Apis indica (B) hibiscus esculentus (C) Mangifera indica (D) benghalensis Ficus 40. Botanical name of potato is (A) Ipomea batatas (B) Solanum tuberosum (C) Mangifera indica (D) Azadirachta indica 41. The scientific name of sunflower is (A) Hibiscus rosa-sinensis (B) Mangifera indica (C) Helianthus annuus (D) Sida acuta 42. When a single species is described under different names by different authors, then these names are called as (A) antonyms (B) synonyms (C) holotype (D) variety 43. Which of the following is a wrong statement? (A) Vernacular names may be misleading. (B) Vernacular names are not universal. (C) Vernacular names are short and easy to follow. (D) Vernacular names indicate phylogeny, i.e. evolutionary history of organisms. 44. Which of the following is a heterogeneous group? (A) Family, Genus, Order (B) Division, Class, Species (C) Hibiscus, Genus, Species (D) Hibiscus, Sorghum, Cycas 45. International code of binomial nomenclature applies to (A) viruses (B) plants (C) animals (D) both (B) and (C) Prior to the proposal of binomial, the plant names were (A) Polynomials (B) Mononomials (C) Trinomial (D) Tetranomials 1.3 Five Kingdom System of Classification 47. Haeckel classified the organisms into kingdoms. (A) two (B) three (C) four (D) five 48. Two kingdom classification system was given by (A) Carl Linnaeus (B) Huxley (C) Whittaker (D) John Ray 49. Whittaker proposed the system of classification. (A) two kingdom (B) three kingdom (C) four kingdom (D) five kingdom 50. Whittaker could not give place to one of the following in five kingdom classification. (A) Cyanobacteria (B) Slime moulds (C) Virus (D) Amoeba 51. In the five kingdom classification, the members in Kingdom Animalia are eukaryotic, heterotrophic and (A) unicellular (B) multicellular (C) photobiont (D) non motile 52. Out of the following, which system shows the phylogenetic relationship between organisms? (A) Two kingdom classification (B) Five kingdom classification (C) Three kingdom classification (D) All of these 53. The five kingdom classification is based on (A) complexity in cell structure (B) mode of nutrition (C) complexity of organism s body (D) all of these 54. Primitive nucleus, DNA without histone proteins, absence of membrane bound cell organelles are the characters of Kingdom (A) Protista (B) Monera (C) Fungi (D) Plantae 55. Blue green algae belong to kingdom (A) Plantae (B) Protista (C) Fungi (D) Monera 56. Thiobacillus is a (A) Photoautotroph (B) Chemoautotroph (C) Protist (D) Heterotroph
7 Chapter 01 : Diversity in Organisms 57. Organisms of kingdom Monera shows (A) Chloroplasts (B) Mitochondria (C) Rigid cell wall (D) All of these 58. In five kingdom classification, protista comprises of (A) both uni and multicellular microscopic eukaryotes (B) unicellular eukaryotes (C) all prokaryotes (D) multicellular eukaryotes 59. In kingdom Protista, the locomotory organs are (A) cilia (B) flagella (C) pseudopodia (D) all of these 60. Protists obtain their food as (A) photosynthesizers only (B) chemosynthesizers (C) heterotrophs only (D) both (A) and (C) 61. Which one of the following is a member of protista? (A) Nostoc (B) Frog (C) Slime moulds (D) Mushroom 62. Desmids are also called as (A) Red algae (B) Golden algae (C) Ascocarps (D) Euglenoids 63. Chrysophytes include (A) diatoms (B) desmids (C) dinoflagellates (D) all of these 64. Amoeba and Paramoecium are included in kingdom (A) Animalia (B) Protista (C) Monera (D) Fungi 65. The Kingdom which is a link between prokaryotes and multicellular eukaryotes is (A) Protista (B) Monera (C) Plantae (D) Animalia 66. Which of the following is CORRECT regarding protists? (A) They reproduce by asexual or sexual method. (B) Amoeba and Paramoecium are autotrophic. (C) They are multicellular, prokaryotic and mostly aquatic. (D) Trichophyton, slime moulds, Euglena are some protists. 67. Some fungi have no cross walls in their hyphae. These hyphae are called (A) septate (B) non-septate (C) septum (D) all of these 68. Which cell organelle is absent in Kingdom fungi? (A) Chloroplast (B) Ribosome (C) Nucleus (D) Golgi body 69. Multicellular eukaryotic decomposers belong to kingdom (A) Animalia (B) Fungi (C) Plantae (D) Monera 70. are also called as Sac fungi. (A) Ascomycetes (B) Basidiomycetes (C) Phycomycetes (D) Deuteromycetes 71. Deuteromycetes are also called as. (A) bracket fungi (B) algal fungi (C) ascocarps (D) imperfect fungi 72. Multicellular eukaryotic consumers belong to Kingdom (A) Fungi (B) Protista (C) Plantae (D) Animalia 73. The kingdom of true multicellular producers is (A) Animalia (B) Plantae (C) Monera (D) Protista 74. Plants are (A) unicellular, eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms (B) multicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms (C) multicellular, eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms (D) unicellular prokaryotic organisms 75. Vascular tissues are absent in (A) algae and bryophyta (B) bryophyta and pteridophyta (C) algae and gymnosperm (D) bryophyta and gymnosperm 76. Which is NOT a correct match? (A) Fungi Penicillium (B) Monera bacteria (C) Protista yeast (D) Plantae moss 1.4 Lichens 77. was first to use the word lichen. (A) Theodor Diener (B) Theodor Schwann (C) Linnaeus (D) Theophrastus 5
STD. XI Sci. Precise Biology
 Written as per the revised syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, Pune. STD. XI Sci. Precise Biology Salient Features Concise coverage of syllabus
Written as per the revised syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, Pune. STD. XI Sci. Precise Biology Salient Features Concise coverage of syllabus
Taxonomy and Biodiversity
 Chapter 25/26 Taxonomy and Biodiversity Evolutionary biology The major goal of evolutionary biology is to reconstruct the history of life on earth Process: a- natural selection b- mechanisms that change
Chapter 25/26 Taxonomy and Biodiversity Evolutionary biology The major goal of evolutionary biology is to reconstruct the history of life on earth Process: a- natural selection b- mechanisms that change
1A Review Questions. Matching 6. Class 7. Order 8. Binomial nomenclature 9. Phylum 10. Species
 1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM. Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna
 KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
An Introduction to the Science of Botany. Chapter 1
 An Introduction to the Science of Botany Chapter 1 TTU MS 43131 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Briefly describe the field of botany, and give short definitions of at least five subdisciplines of plant biology Summarize
An Introduction to the Science of Botany Chapter 1 TTU MS 43131 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Briefly describe the field of botany, and give short definitions of at least five subdisciplines of plant biology Summarize
Fig. 26.7a. Biodiversity. 1. Course Outline Outcomes Instructors Text Grading. 2. Course Syllabus. Fig. 26.7b Table
 Fig. 26.7a Biodiversity 1. Course Outline Outcomes Instructors Text Grading 2. Course Syllabus Fig. 26.7b Table 26.2-1 1 Table 26.2-2 Outline: Systematics and the Phylogenetic Revolution I. Naming and
Fig. 26.7a Biodiversity 1. Course Outline Outcomes Instructors Text Grading 2. Course Syllabus Fig. 26.7b Table 26.2-1 1 Table 26.2-2 Outline: Systematics and the Phylogenetic Revolution I. Naming and
SECTION 17-1 REVIEW BIODIVERSITY. VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms.
 SECTION 17-1 REVIEW BIODIVERSITY VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. taxonomy, taxon 2. kingdom, species 3. phylum, division 4. species name, species
SECTION 17-1 REVIEW BIODIVERSITY VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. taxonomy, taxon 2. kingdom, species 3. phylum, division 4. species name, species
Section 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
 Name Class Date Section 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity (pages 447-450) Key Concepts How are living things organized for study? What is binomial nomenclature? What is Linnaeus s system of classification?
Name Class Date Section 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity (pages 447-450) Key Concepts How are living things organized for study? What is binomial nomenclature? What is Linnaeus s system of classification?
Outline. Classification of Living Things
 Outline Classification of Living Things Chapter 20 Mader: Biology 8th Ed. Taxonomy Binomial System Species Identification Classification Categories Phylogenetic Trees Tracing Phylogeny Cladistic Systematics
Outline Classification of Living Things Chapter 20 Mader: Biology 8th Ed. Taxonomy Binomial System Species Identification Classification Categories Phylogenetic Trees Tracing Phylogeny Cladistic Systematics
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: _ Date: _ Ch 17 Practice test 1. A segment of DNA that stores genetic information is called a(n) a. amino acid. b. gene. c. protein. d. intron. 2. In which of the following processes does change
Class: _ Date: _ Ch 17 Practice test 1. A segment of DNA that stores genetic information is called a(n) a. amino acid. b. gene. c. protein. d. intron. 2. In which of the following processes does change
STD. VIII General Science
 Written as per the latest syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. STD. VIII General Science Salient Features Written as per the new textbook.
Written as per the latest syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. STD. VIII General Science Salient Features Written as per the new textbook.
A. Correct! Taxonomy is the science of classification. B. Incorrect! Taxonomy is the science of classification.
 DAT - Problem Drill 07: Diversity of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What is taxonomy? Question #01 (A) Taxonomy
DAT - Problem Drill 07: Diversity of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What is taxonomy? Question #01 (A) Taxonomy
Carolus Linnaeus System for Classifying Organisms. Unit 3 Lesson 2
 Carolus Linnaeus System for Classifying Organisms Unit 3 Lesson 2 Students will be able to: Conclude some of the classification benefits and importance. Define what is meant by species. Describe the binomial
Carolus Linnaeus System for Classifying Organisms Unit 3 Lesson 2 Students will be able to: Conclude some of the classification benefits and importance. Define what is meant by species. Describe the binomial
Chapter 17. Organizing Life's Diversity
 Chapter 17 Organizing Life's Diversity Key Concepts: Chapter 17 1. List the 3 domains and the 6 kingdoms. 2. Our current system of classification was originally based on structures; scientists now base
Chapter 17 Organizing Life's Diversity Key Concepts: Chapter 17 1. List the 3 domains and the 6 kingdoms. 2. Our current system of classification was originally based on structures; scientists now base
Learning Outcome B1 13/10/2012. Student Achievement Indicators. Taxonomy: Scientific Classification. Student Achievement Indicators
 Classification of Living Organisms Learning Outcome B1 Learning Outcome B1 Apply the Kingdom System of classification to study the diversity of organisms. Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
Classification of Living Organisms Learning Outcome B1 Learning Outcome B1 Apply the Kingdom System of classification to study the diversity of organisms. Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
The Tree of Life. Chapter 17
 The Tree of Life Chapter 17 1 17.1 Taxonomy The science of naming and classifying organisms 2000 years ago Aristotle Grouped plants and animals Based on structural similarities Greeks and Romans included
The Tree of Life Chapter 17 1 17.1 Taxonomy The science of naming and classifying organisms 2000 years ago Aristotle Grouped plants and animals Based on structural similarities Greeks and Romans included
CLASSIFICATION. Why Classify? 2/18/2013. History of Taxonomy Biodiversity: variety of organisms at all levels from populations to ecosystems.
 Why Classify? Classification has been around ever since people paid attention to organisms. CLASSIFICATION One primeval system was based on harmful and non-harmful organisms. Life is easier when we organize
Why Classify? Classification has been around ever since people paid attention to organisms. CLASSIFICATION One primeval system was based on harmful and non-harmful organisms. Life is easier when we organize
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
 CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS 1. Taxonomy The branch of biology that deals with the classification of living organisms About 1.8 million species of plants and animals have been identified. Some scientists
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS 1. Taxonomy The branch of biology that deals with the classification of living organisms About 1.8 million species of plants and animals have been identified. Some scientists
The Living Environment Unit 4 History of Biological Diversity Unit 17: Organizing the Diversity of Life-class key.
 Name: Period: Chapter 17 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Topic: The Tree of Life Objective: How may we organize so many different organisms? The Tree of Life o organize organisms by structure
Name: Period: Chapter 17 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Topic: The Tree of Life Objective: How may we organize so many different organisms? The Tree of Life o organize organisms by structure
9/19/2012. Chapter 17 Organizing Life s Diversity. Early Systems of Classification
 Section 1: The History of Classification Section 2: Modern Classification Section 3: Domains and Kingdoms Click on a lesson name to select. Early Systems of Classification Biologists use a system of classification
Section 1: The History of Classification Section 2: Modern Classification Section 3: Domains and Kingdoms Click on a lesson name to select. Early Systems of Classification Biologists use a system of classification
Study Guide. Biology 2101B. Science. Biodiversity. Adult Basic Education. Biology 2101A. Prerequisite: Credit Value: 1
 Adult Basic Education Science Biodiversity Prerequisite: Biology 2101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003. Biology Concentration Biology 1101 Biology 2101A
Adult Basic Education Science Biodiversity Prerequisite: Biology 2101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003. Biology Concentration Biology 1101 Biology 2101A
Chapter 18: Classification Structured Notes
 Chapter 18: Classification Structured Notes Why Classify? 1) ) Taxon = Taxonomy = Field of biology that deals with classifying and naming organisms Taxonomist = is a scientists who determines relationships
Chapter 18: Classification Structured Notes Why Classify? 1) ) Taxon = Taxonomy = Field of biology that deals with classifying and naming organisms Taxonomist = is a scientists who determines relationships
STD. XI Sci. Perfect Biology
 Written as per the revised syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, Pune. STD. XI Sci. Perfect Biology Salient Features Exhaustive coverage of syllabus
Written as per the revised syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, Pune. STD. XI Sci. Perfect Biology Salient Features Exhaustive coverage of syllabus
CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION. K C Meena PGT Biology KVS
 CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION K C Meena PGT Biology KVS Biological classification The process of grouping living organisms into convenient categories based on simple characters is known as Biological
CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION K C Meena PGT Biology KVS Biological classification The process of grouping living organisms into convenient categories based on simple characters is known as Biological
AP Biology Exam #7 (PRACTICE) Subunit #7: Diversity of Life
 AP Biology Exam #7 (PRACTICE) Subunit #7: Diversity of Life Multiple Choice Questions: Choose the best answer then bubble your answer on your scantron sheet. 1. Armadillos and spiny anteaters are not related.
AP Biology Exam #7 (PRACTICE) Subunit #7: Diversity of Life Multiple Choice Questions: Choose the best answer then bubble your answer on your scantron sheet. 1. Armadillos and spiny anteaters are not related.
Biology Test Review: Classification/Taxonomy
 Name: Period: Biology Test Review: Classification/Taxonomy MAKE SURE YOUR BOOKLET IS COMPLETELY FINISHED! If you are missing information, it can be found on your teacher s webpage. I. Definitions Try to
Name: Period: Biology Test Review: Classification/Taxonomy MAKE SURE YOUR BOOKLET IS COMPLETELY FINISHED! If you are missing information, it can be found on your teacher s webpage. I. Definitions Try to
Classification. One Big Mess!
 Classification One Big Mess! Three domains, 5 (or 6) Kingdoms Let s make a big chart. Cell type? Chromosomes? Ribosomes? Cell wall or not? Made of what? Unicellular or multicellular? Autotroph or heterotroph?
Classification One Big Mess! Three domains, 5 (or 6) Kingdoms Let s make a big chart. Cell type? Chromosomes? Ribosomes? Cell wall or not? Made of what? Unicellular or multicellular? Autotroph or heterotroph?
3) What are the names of the SIX kingdoms? Next to each one, write whether it is prokaryotic or Eukaryotic
 Topic #1: Taxonomy 1) What is taxonomy? system of naming and classifying organisms 2) Name the eight levels of taxonomic categories, starting with the most general and ending with the most specific. Domain,
Topic #1: Taxonomy 1) What is taxonomy? system of naming and classifying organisms 2) Name the eight levels of taxonomic categories, starting with the most general and ending with the most specific. Domain,
Building the Tree of Life
 18.3 Building the Tree of Life Changing Ideas About Kingdoms This diagram shows some of the ways in which organisms have been classified into kingdoms since the 1700s. Three Domains Genetic analysis has
18.3 Building the Tree of Life Changing Ideas About Kingdoms This diagram shows some of the ways in which organisms have been classified into kingdoms since the 1700s. Three Domains Genetic analysis has
Classification Systems. - Taxonomy
 Classification Systems - Taxonomy Why Classify? 2.5 million kinds of organisms Not complete- 20 million organisms estimated Must divide into manageable groups To work with the diversity of life we need
Classification Systems - Taxonomy Why Classify? 2.5 million kinds of organisms Not complete- 20 million organisms estimated Must divide into manageable groups To work with the diversity of life we need
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/37 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/37 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Zoology. Classification
 Zoology Zoology involves studying all aspects of organisms belonging to the animal kingdom taxonomy, animal physiology, comparative anatomy, and ecology. Our study of Zoology will be focused on the different
Zoology Zoology involves studying all aspects of organisms belonging to the animal kingdom taxonomy, animal physiology, comparative anatomy, and ecology. Our study of Zoology will be focused on the different
The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains.
 Section 3: The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the major characteristics
Section 3: The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the major characteristics
Chapter 1. How Do Biologists Study Life?
 Chapter 1 How Do Biologists Study Life? Biology is the study of life Biologists ask questions about all aspects of living organisms Bios logos means a discourse on life in Greek Biology has many sub-disciplines
Chapter 1 How Do Biologists Study Life? Biology is the study of life Biologists ask questions about all aspects of living organisms Bios logos means a discourse on life in Greek Biology has many sub-disciplines
Biology 2201 Unit Test Holy Spirit High Mr. Pretty Name: ANSWER KEY
 Biology 2201 Unit Test Holy Spirit High Mr. Pretty Name: ANSWER KEY 1.) Which of the following increases as you proceed down classification levels from kingdom to species? A) Activity B) Diversity among
Biology 2201 Unit Test Holy Spirit High Mr. Pretty Name: ANSWER KEY 1.) Which of the following increases as you proceed down classification levels from kingdom to species? A) Activity B) Diversity among
Biodiversity and Classification
 Biodiversity and Classification BIODIVERSITY AND CLASSIFICATION Biodiversity of life on earth There are a great variety of organisms (plants and animals) which co-inhabit the earth. These organisms occur
Biodiversity and Classification BIODIVERSITY AND CLASSIFICATION Biodiversity of life on earth There are a great variety of organisms (plants and animals) which co-inhabit the earth. These organisms occur
Multiple Choice Write the letter on the line provided that best answers the question or completes the statement.
 Chapter 18 Classification Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter on the line provided that best answers the question or completes the statement. 1. Scientists assign each kind of organism a universally
Chapter 18 Classification Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter on the line provided that best answers the question or completes the statement. 1. Scientists assign each kind of organism a universally
6 Kingdoms of Life. What is life? How are all living things organized?
 6 Kingdoms of Life What is life? How are all living things organized? Engage List reasons to support why this man is living. List reasons to support why this car is not living. Characteristics of Life
6 Kingdoms of Life What is life? How are all living things organized? Engage List reasons to support why this man is living. List reasons to support why this car is not living. Characteristics of Life
Taxonomy. Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms. It has two main purposes: to identify organisms to represent relationships among organisms
 Taxonomy Taxonomy Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms. It has two main purposes: to identify organisms to represent relationships among organisms Binomial Nomenclature Our present biological
Taxonomy Taxonomy Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms. It has two main purposes: to identify organisms to represent relationships among organisms Binomial Nomenclature Our present biological
CLASSIFICATION NOTES
 CLASSIFICATION NOTES Classification Classification = arrangement of living things into groups according to their observed similarities. Important because it allows us to be able to study life easier Living
CLASSIFICATION NOTES Classification Classification = arrangement of living things into groups according to their observed similarities. Important because it allows us to be able to study life easier Living
Unit Two: Biodiversity. Chapter 4
 Unit Two: Biodiversity Chapter 4 A. Classifying Living Things (Ch.4 - page 100) Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving ( changing ): new evidence is discovered laws and theories are tested and possibly
Unit Two: Biodiversity Chapter 4 A. Classifying Living Things (Ch.4 - page 100) Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving ( changing ): new evidence is discovered laws and theories are tested and possibly
Biological Kingdoms. An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things
 Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
What are living things, and how can they be classified?
 Classifying Organisms What are living things, and how can they be classified? binomial nomenclature species genus dichotomous key cladogram Classifying Living Things Classification: organizing information
Classifying Organisms What are living things, and how can they be classified? binomial nomenclature species genus dichotomous key cladogram Classifying Living Things Classification: organizing information
Classification Systems. Classification is just a fancy word for organization. So this chapter is equivalent to Biology cleaning its room!
 Classification Systems Classification is just a fancy word for organization. So this chapter is equivalent to Biology cleaning its room! A Vast Science Biology, the study of life, is no simple science.
Classification Systems Classification is just a fancy word for organization. So this chapter is equivalent to Biology cleaning its room! A Vast Science Biology, the study of life, is no simple science.
Unit 9: Taxonomy (Classification) Notes
 Name Exam Date Class Unit 9: Taxonomy (Classification) Notes What is Classification? is when we place organisms into based on their. Classification is also known as. Taxonomists are scientists that & organisms
Name Exam Date Class Unit 9: Taxonomy (Classification) Notes What is Classification? is when we place organisms into based on their. Classification is also known as. Taxonomists are scientists that & organisms
Summary Finding Order in Diversity Modern Evolutionary Classification
 ( Is (.'I.isiifiuilimi Summary 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity There are millions of different species on Earth. To study this great diversity of organisms, biologists must give each organ ism a name.
( Is (.'I.isiifiuilimi Summary 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity There are millions of different species on Earth. To study this great diversity of organisms, biologists must give each organ ism a name.
Chapter 18: Classification
 Chapter 18: Classification Dichotomous Key A way to identify unknown organisms Contains major characteristics of groups of organisms Pairs of CONTRASTING descriptions 4. After each description key either
Chapter 18: Classification Dichotomous Key A way to identify unknown organisms Contains major characteristics of groups of organisms Pairs of CONTRASTING descriptions 4. After each description key either
For all Medical Entrance Examinations held across India.
 For all Medical Entrance Examinations held across India. Absolute NEET UG / AIPMT Biology Vol. I Salient Features Precise theory for every topic. Exhaustive subtopic wise coverage of MCQs. Neat, labelled
For all Medical Entrance Examinations held across India. Absolute NEET UG / AIPMT Biology Vol. I Salient Features Precise theory for every topic. Exhaustive subtopic wise coverage of MCQs. Neat, labelled
Domains and Kingdoms
 Domains and Kingdoms Archaea Ancient Bacteria Bacteria Regular Bacteria Eukaryota Organisms with a nucleus DOMAIN: Archaea KINGDOM: Archaebacteria Cell Type Structural Organization Cell Wall Mode of Nutrition
Domains and Kingdoms Archaea Ancient Bacteria Bacteria Regular Bacteria Eukaryota Organisms with a nucleus DOMAIN: Archaea KINGDOM: Archaebacteria Cell Type Structural Organization Cell Wall Mode of Nutrition
Study of Biology. copyright cmassengale
 Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Chapter 18 Systematics: Seeking Order Amidst Diversity
 Chapter 18 Systematics: Seeking Order Amidst Diversity Bird Diversity in Indonesia Chapter 18 At a Glance 18.1 How Are Organisms Named and Classified? 18.2 What Are the Domains of Life? 18.1 How Are Organisms
Chapter 18 Systematics: Seeking Order Amidst Diversity Bird Diversity in Indonesia Chapter 18 At a Glance 18.1 How Are Organisms Named and Classified? 18.2 What Are the Domains of Life? 18.1 How Are Organisms
Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort
 Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort All of these terms are characteristics of organisms that allow scientists to classify (organize) them into groups. Chapter 9 in your text covers the characteristics
Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort All of these terms are characteristics of organisms that allow scientists to classify (organize) them into groups. Chapter 9 in your text covers the characteristics
Kingdoms in Eukarya: Protista, Fungi, Plantae, & Animalia Each Eukarya kingdom has distinguishing characteristics:
 NAME pg. 1 Classification Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species Eukarya Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primate Hominidae Homo sapiens Mnemonic: DUMB KING PHILIP CAME OVER FOR GOOD SOUP Domain
NAME pg. 1 Classification Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species Eukarya Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primate Hominidae Homo sapiens Mnemonic: DUMB KING PHILIP CAME OVER FOR GOOD SOUP Domain
Classification Cladistics & The Three Domains of Life. Biology Mrs. Flannery
 Classification Cladistics & The Three Domains of Life Biology Mrs. Flannery Finding Order in Diversity Earth is over 4.5 billion years old. Life on Earth appeared approximately 3.5 billion years ago and
Classification Cladistics & The Three Domains of Life Biology Mrs. Flannery Finding Order in Diversity Earth is over 4.5 billion years old. Life on Earth appeared approximately 3.5 billion years ago and
Shree Krishna Pranami Public School,Siwani Mandi. Class XI (Biology) Summar Assignment June- 2018
 Shree Krishna Pranami Public School,Siwani Mandi Class XI (Biology) Summar Assignment June- 2018 Subjective Questions CHAPTER-1 THE LIVING WORLD VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS 1. Linnaeus is considered
Shree Krishna Pranami Public School,Siwani Mandi Class XI (Biology) Summar Assignment June- 2018 Subjective Questions CHAPTER-1 THE LIVING WORLD VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS 1. Linnaeus is considered
Unit 2 Biodiversity Ch. 4 Patterns of Life
 Unit 2 Biodiversity Ch. 4 Patterns of Life Name: 4.1 Characteristics of Life In order to be considered living, an organism must possess the following Six (6) characteristics: 1. Living things are organized
Unit 2 Biodiversity Ch. 4 Patterns of Life Name: 4.1 Characteristics of Life In order to be considered living, an organism must possess the following Six (6) characteristics: 1. Living things are organized
DO NOW (On notecard):
 Learner Profile: Communicators Monday, September 28 AGENDA 15 min Enter the classroom silently and find your seat. 1. Take out pencils, HAWK card, agenda, and classification notes 2. Everything else gets
Learner Profile: Communicators Monday, September 28 AGENDA 15 min Enter the classroom silently and find your seat. 1. Take out pencils, HAWK card, agenda, and classification notes 2. Everything else gets
Background: Why Is Taxonomy Important?
 Background: Why Is Taxonomy Important? Taxonomy is the system of classifying, or organizing, living organisms into a system based on their similarities and differences. Imagine you are a scientist who
Background: Why Is Taxonomy Important? Taxonomy is the system of classifying, or organizing, living organisms into a system based on their similarities and differences. Imagine you are a scientist who
Characteristics of Life
 UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY Chapter 4- Patterns of Life Biology 2201 Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1) living things are organized systems made up of one or more cells
UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY Chapter 4- Patterns of Life Biology 2201 Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1) living things are organized systems made up of one or more cells
XI CLASS BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION
 XI CLASS BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION The process of grouping living organisms into convenient categories based on simple characters is known as Biological classification. Importance
XI CLASS BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION The process of grouping living organisms into convenient categories based on simple characters is known as Biological classification. Importance
Classification Practice Test
 Classification Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. An organism may have different
Classification Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. An organism may have different
Biology Classification Unit 11. CLASSIFICATION: process of dividing organisms into groups with similar characteristics
 Biology Classification Unit 11 11:1 Classification and Taxonomy CLASSIFICATION: process of dividing organisms into groups with similar characteristics TAXONOMY: the science of classifying living things
Biology Classification Unit 11 11:1 Classification and Taxonomy CLASSIFICATION: process of dividing organisms into groups with similar characteristics TAXONOMY: the science of classifying living things
Chapter 17A. Table of Contents. Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification. Section 2 How Biologists Classify Organisms
 Classification of Organisms Table of Contents Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification
Classification of Organisms Table of Contents Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification
Vocabulary Classification the process of arranging organisms into groups based on similarities Taxonomy the science of naming and classifying
 Classification.. Vocabulary Classification the process of arranging organisms into groups based on similarities Taxonomy the science of naming and classifying organisms trait a characteristic or behavior
Classification.. Vocabulary Classification the process of arranging organisms into groups based on similarities Taxonomy the science of naming and classifying organisms trait a characteristic or behavior
Classification. copyright cmassengale
 Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are 13 billion known species of organisms This is only 5% of all organisms that ever lived!!!!! New organisms are still being found and identified 2 What is
Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are 13 billion known species of organisms This is only 5% of all organisms that ever lived!!!!! New organisms are still being found and identified 2 What is
Finding Order in Diversity
 Finding Order in Diversity Videos Scishow Taxonomy: https://youtu.be/f38bmgpcz_i Bozeman Taxonomy: https://youtu.be/tyl_8gv7rie Terms to Know 1. Radiometric Dating 12. Miller and Urey s 2. Geologic Time
Finding Order in Diversity Videos Scishow Taxonomy: https://youtu.be/f38bmgpcz_i Bozeman Taxonomy: https://youtu.be/tyl_8gv7rie Terms to Know 1. Radiometric Dating 12. Miller and Urey s 2. Geologic Time
Origins of Life. Fundamental Properties of Life. Conditions on Early Earth. Evolution of Cells. The Tree of Life
 The Tree of Life Chapter 26 Origins of Life The Earth formed as a hot mass of molten rock about 4.5 billion years ago (BYA) -As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were formed from water condensation Life
The Tree of Life Chapter 26 Origins of Life The Earth formed as a hot mass of molten rock about 4.5 billion years ago (BYA) -As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were formed from water condensation Life
UNIT 4 TAXONOMY AND CLASSIFICATION
 UNIT 4 TAXONOMY AND CLASSIFICATION CHAPTER 13 IN TEXT READ P. 4.0 CLASSIFICATION AND TAXONOMY 4.1 Define taxonomy 4.2 Discuss the reasons for classifying organisms 4.3 Define species and binomial nomenclature
UNIT 4 TAXONOMY AND CLASSIFICATION CHAPTER 13 IN TEXT READ P. 4.0 CLASSIFICATION AND TAXONOMY 4.1 Define taxonomy 4.2 Discuss the reasons for classifying organisms 4.3 Define species and binomial nomenclature
A.P. Biology Lecture Notes Unit 1A - Themes of Life
 A.P. Biology Lecture Notes Unit 1A - Themes of Life I. Why study biology? A. Life is attractive, diverse, and interesting. B. The study of biology is enormous in scope C. Organisms span size scales from
A.P. Biology Lecture Notes Unit 1A - Themes of Life I. Why study biology? A. Life is attractive, diverse, and interesting. B. The study of biology is enormous in scope C. Organisms span size scales from
Introduction. Recall: 1) Life is both similar and diverse 2) Evolution helps us understand who is related to who
 Biology 11 Taxonomy Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the levels of classification and the man who created the classification system Describe the 3 domains and the 4 kingdoms
Biology 11 Taxonomy Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the levels of classification and the man who created the classification system Describe the 3 domains and the 4 kingdoms
The Classification of Plants and Other Organisms. Chapter 18
 The Classification of Plants and Other Organisms Chapter 18 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1 Define taxonomy Explain why the assignment of a scientific name to each species is important for biologists KEY TERMS TAXONOMY
The Classification of Plants and Other Organisms Chapter 18 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1 Define taxonomy Explain why the assignment of a scientific name to each species is important for biologists KEY TERMS TAXONOMY
CLASS XI BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 1: LIVING WORLD
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 1: LIVING WORLD Biology is the science of life forms and non-living processes. The living world comprises an amazing diversity of living organisms. In order to facilitate
CLASS XI BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 1: LIVING WORLD Biology is the science of life forms and non-living processes. The living world comprises an amazing diversity of living organisms. In order to facilitate
1B Review Questions (54)
 1) Taxing is the science of a) Finding animals b) Involving naming and categorizing species 1B Review Questions (54) c) Microorganisms d) Discovery on protists 2) What is the order of classification from
1) Taxing is the science of a) Finding animals b) Involving naming and categorizing species 1B Review Questions (54) c) Microorganisms d) Discovery on protists 2) What is the order of classification from
Microbiology / Active Lecture Questions Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms 1 Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms
 1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
Classification Highlight Packet
 Name: Period: Date: 1. Which kingdom is NOT prokaryotic? A. Eubacteria B. Archaeabacteria C. Protists 2. Which kingdom contains "extremophiles"? A. eubacteria B. archaebacteria C. fungi 3. Which example
Name: Period: Date: 1. Which kingdom is NOT prokaryotic? A. Eubacteria B. Archaeabacteria C. Protists 2. Which kingdom contains "extremophiles"? A. eubacteria B. archaebacteria C. fungi 3. Which example
Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food.
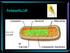 Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food. Heterotrophs must get energy by eating autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food. Heterotrophs must get energy by eating autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
6 Kingdoms 1.Eubacteria 2.Archaebacteria 3.Protista 4.Fungi 5.Plantae 6.Animalia "Dear King Phillip Came Over From Greece Saturday"
 Unit 7 Classification & Plants What you Need to Know: Classification: Classification, Taxonomy, Binomial Nomenclature + Scientific Names, Kingdoms, Cladograms, Kingdoms and Domains // Characteristics of
Unit 7 Classification & Plants What you Need to Know: Classification: Classification, Taxonomy, Binomial Nomenclature + Scientific Names, Kingdoms, Cladograms, Kingdoms and Domains // Characteristics of
Classification of Living Things
 Classification of Living Things Heather Spalding: University of Hawaii-Manoa GK-12 program VOCABULARY Write the term next to the definition. You will need to know these terms to understand the classification
Classification of Living Things Heather Spalding: University of Hawaii-Manoa GK-12 program VOCABULARY Write the term next to the definition. You will need to know these terms to understand the classification
Organizing Life s Diversity
 17 Organizing Life s Diversity section 3 Domains and Kingdoms The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. What You ll Learn major characteristics of the
17 Organizing Life s Diversity section 3 Domains and Kingdoms The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. What You ll Learn major characteristics of the
STD. XI Sci. Perfect Biology
 Written according to the Text book (2012-2013) published by the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, Pune. STD. XI Sci. Perfect Biology Fifth Edition: February 2015 Salient
Written according to the Text book (2012-2013) published by the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, Pune. STD. XI Sci. Perfect Biology Fifth Edition: February 2015 Salient
S T U D E N T G U I D E
 How do scientists organize organisms? Part IA: In what domain do I belong? Scientists sort life forms into categories based on their characteristics. First, scientists look at the types of cells an organism
How do scientists organize organisms? Part IA: In what domain do I belong? Scientists sort life forms into categories based on their characteristics. First, scientists look at the types of cells an organism
Biology Unit 02 Biodiversity Section 01 Test Taxonomy/Classification
 Biology 2201(A) Unit 02 Biodiversity Page 1 of 12 Biology 2201 Unit 02 Biodiversity Section 01 Test Taxonomy/Classification Instructions for Students: 1. This test is composed of two parts. Part 1 consists
Biology 2201(A) Unit 02 Biodiversity Page 1 of 12 Biology 2201 Unit 02 Biodiversity Section 01 Test Taxonomy/Classification Instructions for Students: 1. This test is composed of two parts. Part 1 consists
Classification of Living Things. Unit II pp 98
 Classification of Living Things Unit II pp 98 Why There is a Need for Classifying There are over 2 million different types of organisms known. biologists can organize living things into groups. Taxonomy
Classification of Living Things Unit II pp 98 Why There is a Need for Classifying There are over 2 million different types of organisms known. biologists can organize living things into groups. Taxonomy
Classification. Essential Question Why is it important to place living things into categories?
 Classification Essential Question Why is it important to place living things into categories? Compare and contrast Taxonomy comparison 18.1 History of Taxonomy Objectives Describe Aristotle s classification
Classification Essential Question Why is it important to place living things into categories? Compare and contrast Taxonomy comparison 18.1 History of Taxonomy Objectives Describe Aristotle s classification
Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms
 Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms Why do we need it? problems with different languages common names can be confusing examples: woodchuck, groundhog crayfish,
Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms Why do we need it? problems with different languages common names can be confusing examples: woodchuck, groundhog crayfish,
Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups. Mrs. Hilliard
 Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups Mrs. Hilliard Communication in Science Choose one of the three topics to write a detailed procedure for. 1. How to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. 2. How to brush your
Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups Mrs. Hilliard Communication in Science Choose one of the three topics to write a detailed procedure for. 1. How to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. 2. How to brush your
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter focus Shifting from the process of how evolution works to the pattern evolution produces over time. Phylogeny Phylon = tribe, geny = genesis or origin
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter focus Shifting from the process of how evolution works to the pattern evolution produces over time. Phylogeny Phylon = tribe, geny = genesis or origin
Resources. Visual Concepts. Chapter Presentation. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
Chapter 17B. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains. Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
 Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
All cells have a CELL MEMBRANE. What is a cell membrane? Functions of cell membrane: 1)
 Name: Pd: ORGANISMS & ENVIRONMENTS STUDY GUIDE KE EY 9 Weeks Test Date: Parent Signature (BONUS!): 6.12A+B CELLS (cells, cells they re made of organelles!) All living things have CELLS ELLS. Cell - The
Name: Pd: ORGANISMS & ENVIRONMENTS STUDY GUIDE KE EY 9 Weeks Test Date: Parent Signature (BONUS!): 6.12A+B CELLS (cells, cells they re made of organelles!) All living things have CELLS ELLS. Cell - The
Head Office : B-32, Shivalik Main Road, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi Sales Office : B-48, Shivalik Main Road, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi
 Head Office : B-32, Shivalik Main Road, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi-110017 Sales Office : B-48, Shivalik Main Road, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi-110017 Tel. : 011-26691021 / 26691713 Price : ` 125 Typeset by
Head Office : B-32, Shivalik Main Road, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi-110017 Sales Office : B-48, Shivalik Main Road, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi-110017 Tel. : 011-26691021 / 26691713 Price : ` 125 Typeset by
Unit :- I Chapter-3. Classification of Plant Kingdom
 Unit :- I Chapter-3. Classification of Plant Kingdom IMPORTANT POINTS Five kingdom classification system was given by Whittaker on the basis of following four criteria : (i) Cell structure (ii) Body Structure
Unit :- I Chapter-3. Classification of Plant Kingdom IMPORTANT POINTS Five kingdom classification system was given by Whittaker on the basis of following four criteria : (i) Cell structure (ii) Body Structure
and just what is science? how about this biology stuff?
 Welcome to Life on Earth! Rob Lewis 512.775.6940 rlewis3@austincc.edu 1 The Science of Biology Themes and just what is science? how about this biology stuff? 2 1 The Process Of Science No absolute truths
Welcome to Life on Earth! Rob Lewis 512.775.6940 rlewis3@austincc.edu 1 The Science of Biology Themes and just what is science? how about this biology stuff? 2 1 The Process Of Science No absolute truths
Creating a Dichotomous Key
 Dichotomous Keys A tool used that allows users to determine the identity of unknown species Keys consist of a series of choices, where the user selects from a series of connected pairs Each pair of choices
Dichotomous Keys A tool used that allows users to determine the identity of unknown species Keys consist of a series of choices, where the user selects from a series of connected pairs Each pair of choices
Station A: #3. If two organisms belong to the same order, they must also belong to the same
 Station A: #1. Write your mnemonic for remembering the order of the taxa (from the broadest, most generic taxon to the most specific). Out to the side of each, write the name of each taxon the mnemonic
Station A: #1. Write your mnemonic for remembering the order of the taxa (from the broadest, most generic taxon to the most specific). Out to the side of each, write the name of each taxon the mnemonic
DO NOW: Four Square Do Now
 Learner Profile: Communicators Thursday, September 24 AGENDA 15 min Enter the classroom silently and find your seat. 1. Take out pencils, HAWK card, agenda, and cells guided notes 2. Everything else gets
Learner Profile: Communicators Thursday, September 24 AGENDA 15 min Enter the classroom silently and find your seat. 1. Take out pencils, HAWK card, agenda, and cells guided notes 2. Everything else gets
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase.
 Assessment Chapter Test B Classification of Organisms In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. Archaea 2. Bacteria a. kingdom; includes Euglena
Assessment Chapter Test B Classification of Organisms In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. Archaea 2. Bacteria a. kingdom; includes Euglena
There are two commonly accepted theories for how eukaryotic cells evolved: infolding and endosymbiosis. Infolding
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
What is classification? Basically classification is a fancy word for organization.
 Classification What is classification? Basically classification is a fancy word for organization. Some Scientists believe there are as many as 200 million different kinds of living things on our planet.
Classification What is classification? Basically classification is a fancy word for organization. Some Scientists believe there are as many as 200 million different kinds of living things on our planet.
The Classification of Organisms
 Biology Chapter 8 The Classification of Organisms 8A - The Necessity of Classifying People group things together for convenience. (spices, pans, tools, instruments in orchestra) Taxonomy (or systematics)
Biology Chapter 8 The Classification of Organisms 8A - The Necessity of Classifying People group things together for convenience. (spices, pans, tools, instruments in orchestra) Taxonomy (or systematics)
