Unit :- I Chapter-3. Classification of Plant Kingdom
|
|
|
- Alyson Hood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit :- I Chapter-3. Classification of Plant Kingdom IMPORTANT POINTS Five kingdom classification system was given by Whittaker on the basis of following four criteria : (i) Cell structure (ii) Body Structure (iii) Mode of nutrition - Autotrophic and Heterotrophic (iv) Major ecological role. The five kingdoms are Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia. The three-domain system is closely based on five-kingdom system. The Eukarya are then divided into 4 kingdoms : Protistsa, Fungi, plantae and anamalia. Viroids were discovered by Diener from infectious agents which are even smaller than viruses. It consists of a very simple structure and short RNA strand viroids lack protective protein coat known as capsid. Viruses are self reproducing and obligate parasite in living cells : They Viroids remain inactive and behave as non-living things. When they enter inside of the living cells, they are active and behave as living organisms Because of this they are intermediate between living and non-living things. They are also called as living chemical. Algae, Fungi and Lichens are included under thallophyta. The gametophytic plant body is thalloid, without differentiation in to true root, stem and leaves. Zygote does not develop into embryo. Algae have Chlorophylls and they synthesize their one own food so it is Autotrophs, while Fungi are non chlorophylls and they do not Synthesize their own food so it own is called heterotrophs. The lichens, show symbiotic relationship between algae and fungi components. Bryophytes are non vascular plants. After fertilization Zygote undergoes divisions to form embryo. The life cycle of bryophytes has two distinct phases. (1) Gametophytic phases - Haploid, main, autotrophic and gametes formative (2) Sporophytic phase - Diploid, Subsidiary, heterotrophic, spores formative. Pteridophytes have vascular tissues, and develop the embryo. The life cycle of pteridophytes shows alternation of generation. Gemetophytic phase is haploid, subsidiary, short lived and Gametes producing while sporophytic phase is diploid, main long lived and spores producing. Gymnosperm is sporophytic. It is differntiated into root, stem and leaves. Ovules are naked and not enclosed by the ovary therefore recognized as a gymnosperm. The sporophytic and gametophytic phases alternate with each other to complete the life cycle. Gametophytic phase is haploid, subsidiary, short lived and under ground and sporophytic phase is diploid, Main, long and as a whole plant. Endosperm develops before fertilization, ovules are orthotropous and true fruits are lacking because, of the absence of ovary. 15
2 In angiosperms, sporophytic plant body is in the form of herbs, shrubs, trees, climbers or lianas. Ovules are enclosed in the ovary therefore, recognized as angiosperms. Endosperm is developed after fertilization. Members of this group show double fertilization. After fertilization ovules are transformed into seeds and ovary into fruit. The plant life cycle shows alternation of generation. Bentham and Hooker classified the angiosperms into two classes. (1) Dicotyledon and (2) Monocotyledon. From the given options, select the correct option (a, b, c, d) Each carries one mark. 1. Which of the following is included in five kingdom classification. (A) Monera, Protista, Animalia, Plantae, Algae (B) Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia (C) Virus, Prokaryota, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia (D) Algae, Fungi, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Gymnosperm 2. Who is the Father of Taxonomy among the following? (A) Linnaeus (B) Aristotle (C) Maheshwari (D) Birbal Sahani 3. Helophiles is also called... (A) Eubacteria (B) Actinomycetes (C) Cynobacteria (D) Archae bacteria 4. According to Whittaker s classification, prokaryotes are placed in (A) Monera (B) Plantae (C) Protista (D) Animalia 5. Example of blue green algae is in. (A) Fungi (B) Monera (C) Protista (C) Plantae 6. By how many criteria, living organisms have been classified into five kingdom. (A) Two (B) Four (C) Five (D) Three 7. In which of the following kingdoms, bacteria and blue-green algae are included? (A) Monera (B) Plantae (C) Animalia (D) Protista 8. Prokaryotes are included in the kingdom. (A) Monera (B) Protista (C) Protozoa (D) Basidiomycetes 9. Which one of the following is also called halophiles? (A) Eubacteria (B) Actinomyces (C) Cyanobacteria (D) Archaebacteria 10. Match the following. (p) Archaea (i) Cell wall is made up of either cellulose or Fungal-cellulose (q) Bacteria (ii) Cell wall does not contain peptidoglycan (r) Eukarya (iii) Cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan. (A) p - (iii), q - (i), r - (ii) (B) p - (i), q - (ii), r - (iii) (C) p - (ii), q - (i), r - (iii) (D) p - (ii), q - (iii), r - (i) 16
3 11. Viroids were discovered by... (A) Diener (B) Woese (C) Pasteur (D) Iyengar 12. Viroid consists of... (A) DNA (B) RNA (C) Protein (D) none of above 13. Which of the following diseases is caused by viroid? (A) Polio (B) Diphtheria (C) Alzheimers (D) Typhoid 14. The name virus was given by. (A) Ivanowsky (B) Pasteur (C) Diener (D) Hershey 15. Virus have... (A) DNA core, Lipid coat (B) DNA or RNA core, Protein coat (C) DNA or RNA core, plasma membrane (D) DNA containing nucleus, lipid envelope 16. A virus contains. (A) DNA (B) RNA (C) DNA or RNA (D) DNA and RNA 17. TMV virus was discovered by. (A) Pasteur (B) S. L. Miller (C) Ivanowsky (D) W. M. Stanley 18. The main structural component of virus is. (A) nucleic acid (B) Protein (C) nucleic acid and protein (D) nucleic acid or protein 19. The first existing group of plant is. (A) Fungi (B) Alage (C) Lichens (D) Pteridophytes 20. Match the following : (p) Chlamydomonas (i) Colonial Forms (q) Volvox (ii) Unicellular (r) Ulothrix (iii) Filamentous forms (s) Nostoc (iv) Cyanophyceae (A) p - (i), q - (ii), r - (iii), s-(iv) (B) p - (ii), q - (iii), r - (i), s-(iv) (C) p - (iii), q - (i), r - (iv), s-(ii) (D) p - (ii), q - (i), r - (iii), s-(iv) 21. The study of algae is called. (A) Mycology (B) Algology (C) Taxonomy (D) Lichenology 22. Unicellular eukaryotic microorganisms comprise. (A) Fungi (B) Monera (C) Plants (D) Protista 23. Protista include : (A) Paramecium, Euglena, Dinoflagellates (B) Hydra, Amoeba, Paramoecium (C) Yeast, Euglena, Dinoflagellates (D) Mushroom, Paramoecium, Euglena. 24. The study of fungi is. (A) Cytology (B) Mycology (D) Virology (D) Algology 17
4 25. Fungus cell wall is made up of. (A) Cellulose (B) Protein (C) Chitin (D) Carbohydrates 26. In Fungi reserved food materials are. (A) Glycogen and Lipid droplets (B) Starch (C) Protein (D) Lipid 27. Match the following : (p) Yeast (i) Bread mould (q) Mucor (ii) Mushroom (r) Agaricus (iii) Unicelluar (A) p - (ii), q - (i), r - (iii) (B) p - (i), q - (ii), r - (iii) (C) p - (iii), q - (i), r - (ii) (D) p - (iii), q - (ii), r - (i) 28. Study of lichens is called. (A) Algology (B) Mycology (C) Lichenology (D) Cytology 29. Lichens were first discovered by. (A) Iyengar (B) Tulsane (C) Pasteur (D) Shiv Ram Kashyap 30. In lichens Algal component is known as. (A) mycobiont (B) Phycobiont (C) A & B (D) none of these 31. In lichens fungal component is known as. (A) mycobiont (B) phycobiont (C) A & B (D) none of these 32. The plant cell without chloroplast is. (A) Algue (B) Fungi (C) Bryophytes (D) pteridophytes 33. The shape of Fruting body of lichens is. (A) apothecium - flask shaped (B) perithecium - cup shaped (C) perithecium - flask shaped (D) apothecium - Disc chaped 34. On the basis of external form lichen are. (A) Crustose (B) Foliose (C) Fruticose (D) All of the three 35. Fruting body is characteristic of. (A) Algae (B) Lichens (C) Bryophytes (D) Pteridophytes 36. Symbiotic relationship is found in. (A) Algae (B) Fungi (C) Bryophytes (D) Lichens 37. Plant of this group possess naked seed (A) Pteridophytes (B) Angiosperms (C) Gymnosperms (D) Bryophytes 38. The father of Indian Bryology is. (A) Tulsane (B) Professor Iyengar (C) Ivanowsky (D) Pro. Shiv Ram Kashyap 39. Rothmelur has diveded the Bryophytes into. (A) 3 classes (B) 4 classes (C) 5 classes (D) 6 classes 18
5 40. Which sentence is true for Bryophytes? (A) They are autotropic (B) Vascular tissues are absent (C) Fertilization takes plasce in the presence of water (D) All of the three 41. In which plant, gametophytic phase is main and sporophytic phase is subsidiary. 42. The first land plant on earth was. 43. Match the following : (p) Nephrolepis (i) heterosporous (q) Equisetum (ii) Fossil (r) Selaginella (iii) homosporous (s) Rhynia (iv) Common (A) p - (iv), q - (iii), r - (i), s -(ii) (B) p - (iv), q - (iii), r - (ii), s - (i) (C) p - (iv), q - (ii), r - (iii), s - (i) (D) p - (iv), q - (i), r - (ii), s - (iii) 44. In which plant, the gametophytic phase is main and sporophytic phase is subsidiary. (A) Nephrolepis (B) Selaginella (C) Anthoceros (D) Equisetum 45. The tallest living tree in the world is. (A) Zamia sp. (B) Eucalyptus sp. (C) Wolffia sp. (D) Sequoia sp. 46. The smallest gymnosperm is. (A) Zamia sp. (B) Eucalyptus (C) Wolfia sp. (D) Sequoia sp. 47. Xerophytic Characters are present in. 48. Microsporophyll : Stamen then Megasporophyll :. (A) anther (B) gynoecium (C) Pollen grains (D) ovule 49. Match the following : (p) Microsporophyll (i) Pollen grain (q) Microsporangium (ii) Stemen (r) microspores (iii) anther (s) megasporophyll (iv) gynoecium (A) p - (iv), q - (iii), r - (i), s - (ii) (B) p - (ii), q - (i), r - (iii), s - (iv) (C) p - (iii), q - (ii), r - (i), s - (iv) (D) p - (ii), q - (iii), r - (i), s - (iv) 50. Which is the Fossil member? (A) Cycas (B) Bennettites (C) Thuja (D) Pinus 19
6 51. The biggest and dominant group is. 52. Match the following : (p) Wolffia globosa (i) largest plant (q) Eucalyptus sp (ii) largest flower (r) Rafflesia arnoldii (iii) smallest plant (s) Agave sp. (iv) largest infloresence (A) p - (i), q - (ii), r - (iii), s - (iv) (B) p - (iii), q - (ii), r - (i), s - (iv) (C) p - (iii), q - (i), r - (iv), s - (ii) (D) p - (iii), q - (i), r - (ii), s - (iv) 53. Pre-fertilized endosperm is characteristic of. (A) Pteridophytes (B) Angiosperms (C) Gymnosperms (D) Bryophytes 54. Class dicotyledon is dived into. (A) 7 sub classes (B) 5 sub classes (C) 3 sub classes (D) 2 sub classes. 55. Who classified the Angiosperms into two classes? (A) Theophratus (B) Bentham and Hooker (C) Aristotle (D) Linnaeus 56. Presence of rigid cell wall is characterized by kingdom. (A) Protista (B) Plantae (C) Monera (D) Animalia 57. The tallest living tree of a Angioperm is. (A) Wolffia sp. (B) Zamia sp. (C) Eucalyptus sp. (D) Sequoia sp. 58. If the seeds are formed from the megasporophylls and not enclosed in a fruits the plant belongs to. (A) Pteridophytes (B) Bryophytes (C) Angiosperms (D) Gymnosperms 59. Embryo is not formed in. (A) Bryophytes (B) Algae (C) Gymnosperms (D) Pteriodophytes 60. Which classification system had been given by Whittaker? (A) Three domain classification (B) Binomial classification (C) Five kingdom classification (D) Artificial classification 61. A = Lichens show symbiotic relationship between algae and fungi. R = Algae absorb water and mineral nutrients from environment and provides to fungi. While fungi synthesize food by the process of photo synthesis and provide to algae. (A) Both (A) and (R) true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A) (B) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A) (C) (A) is true statement but (R) is false (D) A is false and R is true. 20
7 ANSWER KEY 1. (B) 2. (A) 3. (D) 4. (A) 5. (B) 6. (B) 7. (A) 8. (A) 9. (D) 10. (D) 11. (A) 12. (B) 13. (C) 14. (B) 15. (B) 16. (C) 17. (C) 18. (C) 19. (B) 20. (D) 21. (B) 22. (C) 23. (A) 24. (B) 25. (C) 26. (A) 27. (C) 28. (C) 29. (B) 30. (B) 31. (A) 32. (B) 33. (C) 34. (D) 35. (B) 36. (D) 37. (C) 38. (D) 39. (A) 40. (D) 41. (A) 42. (B) 43. (A) 44. (C) 45. (D) 46. (A) 47. (C) 48. (B) 49. (D) 50. (B) 51. (D) 52. (D) 53. (C) 54. (C) 55. (B) 56. (C) 57. (D) 58. (D) 59. (B) 60. (C) 61. (C) 21
The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains.
 Section 3: The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the major characteristics
Section 3: The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the major characteristics
Multiple Choice Write the letter on the line provided that best answers the question or completes the statement.
 Chapter 18 Classification Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter on the line provided that best answers the question or completes the statement. 1. Scientists assign each kind of organism a universally
Chapter 18 Classification Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter on the line provided that best answers the question or completes the statement. 1. Scientists assign each kind of organism a universally
Biology 2201 Unit Test Holy Spirit High Mr. Pretty Name: ANSWER KEY
 Biology 2201 Unit Test Holy Spirit High Mr. Pretty Name: ANSWER KEY 1.) Which of the following increases as you proceed down classification levels from kingdom to species? A) Activity B) Diversity among
Biology 2201 Unit Test Holy Spirit High Mr. Pretty Name: ANSWER KEY 1.) Which of the following increases as you proceed down classification levels from kingdom to species? A) Activity B) Diversity among
CHAPTERS 16 & 17: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 2012 PROKARYOTES PROKARYOTES. Fig Lived alone on Earth for over 1 billion years
 CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
Building the Tree of Life
 18.3 Building the Tree of Life Changing Ideas About Kingdoms This diagram shows some of the ways in which organisms have been classified into kingdoms since the 1700s. Three Domains Genetic analysis has
18.3 Building the Tree of Life Changing Ideas About Kingdoms This diagram shows some of the ways in which organisms have been classified into kingdoms since the 1700s. Three Domains Genetic analysis has
Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups. Mrs. Hilliard
 Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups Mrs. Hilliard Communication in Science Choose one of the three topics to write a detailed procedure for. 1. How to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. 2. How to brush your
Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups Mrs. Hilliard Communication in Science Choose one of the three topics to write a detailed procedure for. 1. How to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. 2. How to brush your
Organizing Life s Diversity
 17 Organizing Life s Diversity section 3 Domains and Kingdoms The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. What You ll Learn major characteristics of the
17 Organizing Life s Diversity section 3 Domains and Kingdoms The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. What You ll Learn major characteristics of the
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter in class follow along lecture notes
 Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM. Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna
 KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
SG 9.2 notes Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants
 Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Downloaded from
 3. Plant Kingdom POINTS TO REMEMBER : CLASSIFICATION : Artificial System of Classification : Used superficial morphological characters. Based on a few characteristics like habit, colors, number and shape
3. Plant Kingdom POINTS TO REMEMBER : CLASSIFICATION : Artificial System of Classification : Used superficial morphological characters. Based on a few characteristics like habit, colors, number and shape
Classification. One Big Mess!
 Classification One Big Mess! Three domains, 5 (or 6) Kingdoms Let s make a big chart. Cell type? Chromosomes? Ribosomes? Cell wall or not? Made of what? Unicellular or multicellular? Autotroph or heterotroph?
Classification One Big Mess! Three domains, 5 (or 6) Kingdoms Let s make a big chart. Cell type? Chromosomes? Ribosomes? Cell wall or not? Made of what? Unicellular or multicellular? Autotroph or heterotroph?
A. Correct! Taxonomy is the science of classification. B. Incorrect! Taxonomy is the science of classification.
 DAT - Problem Drill 07: Diversity of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What is taxonomy? Question #01 (A) Taxonomy
DAT - Problem Drill 07: Diversity of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What is taxonomy? Question #01 (A) Taxonomy
Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms
 Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms Why do we need it? problems with different languages common names can be confusing examples: woodchuck, groundhog crayfish,
Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms Why do we need it? problems with different languages common names can be confusing examples: woodchuck, groundhog crayfish,
Major Events in the History of Earth
 Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Kingdom Plantae. Biology : A Brief Survey of Plants. Jun 22 7:09 PM
 Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review! Chapter 31!
 Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review Chapter 31 Origin of Land Plants: 1. Fill in the correct amount of years ago the following events occurred. years ago there was a thin coating of cyanobacteri b. years ago
Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review Chapter 31 Origin of Land Plants: 1. Fill in the correct amount of years ago the following events occurred. years ago there was a thin coating of cyanobacteri b. years ago
CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION. K C Meena PGT Biology KVS
 CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION K C Meena PGT Biology KVS Biological classification The process of grouping living organisms into convenient categories based on simple characters is known as Biological
CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION K C Meena PGT Biology KVS Biological classification The process of grouping living organisms into convenient categories based on simple characters is known as Biological
CHAPTER 3 : PLANT KINGDOM. K C Meena PGT Biology KVS
 CHAPTER 3 : PLANT KINGDOM K C Meena PGT Biology KVS Classification System Artificial classification oldest classification and it is based on few vegetative and sexual characters. Natural classification
CHAPTER 3 : PLANT KINGDOM K C Meena PGT Biology KVS Classification System Artificial classification oldest classification and it is based on few vegetative and sexual characters. Natural classification
Biological Kingdoms. An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things
 Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
3) What are the names of the SIX kingdoms? Next to each one, write whether it is prokaryotic or Eukaryotic
 Topic #1: Taxonomy 1) What is taxonomy? system of naming and classifying organisms 2) Name the eight levels of taxonomic categories, starting with the most general and ending with the most specific. Domain,
Topic #1: Taxonomy 1) What is taxonomy? system of naming and classifying organisms 2) Name the eight levels of taxonomic categories, starting with the most general and ending with the most specific. Domain,
copyright cmassengale Kingdoms and Classification
 1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline)
 Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Resources. Visual Concepts. Chapter Presentation. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
Kingdom: Plantae. Domain Archaea. Domain Eukarya. Domain Bacteria. Common ancestor
 Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Diversity in Living Organisms
 Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years ago. The
Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years ago. The
Domains and Kingdoms. Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria
 Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
Biodiversity and Classification
 Biodiversity and Classification BIODIVERSITY AND CLASSIFICATION Biodiversity of life on earth There are a great variety of organisms (plants and animals) which co-inhabit the earth. These organisms occur
Biodiversity and Classification BIODIVERSITY AND CLASSIFICATION Biodiversity of life on earth There are a great variety of organisms (plants and animals) which co-inhabit the earth. These organisms occur
Class IX Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms Science
 Question 1: Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years
Question 1: Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years
What is a Plant? Plant Life Cycle. What did they evolve from? Original Habitat 1/15/2018. Plant Life Cycle Alternation of Generations
 What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
Chapter 17B. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains. Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
 Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
Plants and Fungi. Bryophytes Bryophytes, most commonly mosses Sprawl as low mats over acres of land
 Plants and Fungi Terrestrial Adaptations of Plants Structural Adaptations A plant is a multicellular eukaryote and a photoautotroph, making organic molecules by photosynthesis In terrestrial habitats,
Plants and Fungi Terrestrial Adaptations of Plants Structural Adaptations A plant is a multicellular eukaryote and a photoautotroph, making organic molecules by photosynthesis In terrestrial habitats,
TEST on PLANT TAXONOMY for NEET 2017
 TEST on PLANT TAXONOMY for NEET 2017 1. Which one of the following shows isogamy with non-flagellated gametes? a) Sargassum b) Ectocarpus c) Ulothrix d) Spirogyra 2. Which of the following is responsible
TEST on PLANT TAXONOMY for NEET 2017 1. Which one of the following shows isogamy with non-flagellated gametes? a) Sargassum b) Ectocarpus c) Ulothrix d) Spirogyra 2. Which of the following is responsible
Plants. SC.912.L.14.7 Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes.
 Plants SC.912.L.14.7 Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes. 1. Students will explain how the structures of plant tissues and organs are directly
Plants SC.912.L.14.7 Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes. 1. Students will explain how the structures of plant tissues and organs are directly
Classification. Classifying Organisms. * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics
 Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Section 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
 Name Class Date Section 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity (pages 447-450) Key Concepts How are living things organized for study? What is binomial nomenclature? What is Linnaeus s system of classification?
Name Class Date Section 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity (pages 447-450) Key Concepts How are living things organized for study? What is binomial nomenclature? What is Linnaeus s system of classification?
Domains and Kingdoms
 Domains and Kingdoms Archaea Ancient Bacteria Bacteria Regular Bacteria Eukaryota Organisms with a nucleus DOMAIN: Archaea KINGDOM: Archaebacteria Cell Type Structural Organization Cell Wall Mode of Nutrition
Domains and Kingdoms Archaea Ancient Bacteria Bacteria Regular Bacteria Eukaryota Organisms with a nucleus DOMAIN: Archaea KINGDOM: Archaebacteria Cell Type Structural Organization Cell Wall Mode of Nutrition
BOT 161 Notes Syllabus Theme B B1: NAMING AND CLASSIFICATION OF ORGANISMS
 BOT 161 Notes Syllabus Theme B (Copyright reserved) Dr TE Tshikalange Natural Sciences II Building Room 3-30 Tel: 420 2008 Very important: These notes are only a summary and not complete. The prescribed
BOT 161 Notes Syllabus Theme B (Copyright reserved) Dr TE Tshikalange Natural Sciences II Building Room 3-30 Tel: 420 2008 Very important: These notes are only a summary and not complete. The prescribed
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-03 PLANT KINGDOM
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-03 PLANT KINGDOM Eukaryotic, multicellular, chlorophyll containing and having cell wall, are grouped the kingdom Plantae, popularly known as plant kingdom.
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-03 PLANT KINGDOM Eukaryotic, multicellular, chlorophyll containing and having cell wall, are grouped the kingdom Plantae, popularly known as plant kingdom.
1A Review Questions. Matching 6. Class 7. Order 8. Binomial nomenclature 9. Phylum 10. Species
 1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
Kingdoms of organisms. Presented by Dr. Jeya Kennedy 2014
 Kingdoms of organisms Presented by Dr. Jeya Kennedy 2014 Learning Objectives: At the end you should be able to: Define biology and distinguish between living and nonliving things by describing the features
Kingdoms of organisms Presented by Dr. Jeya Kennedy 2014 Learning Objectives: At the end you should be able to: Define biology and distinguish between living and nonliving things by describing the features
Plants. and their classi.ication
 + Plants and their classi.ication +Why are plants important? n Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water + energy à sugar + oxygen 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O à C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 n Food (green tea, fruits, seeds, roots,
+ Plants and their classi.ication +Why are plants important? n Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water + energy à sugar + oxygen 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O à C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 n Food (green tea, fruits, seeds, roots,
Bacillus anthracis. Causes Anthrax Especially deadly when inhaled
 Eubacteria Bacteria are the most abundant organisms on earth. An estimated 5 X 1030individuals. One bacterium can give rise to 10 million in 24 hours. Both aerobic (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without
Eubacteria Bacteria are the most abundant organisms on earth. An estimated 5 X 1030individuals. One bacterium can give rise to 10 million in 24 hours. Both aerobic (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without
Plant Evolution & Diversity
 Plant Evolution & Diversity Ancestors of plants were probably charophytes (green algae) Chlorophyll a and b, beta carotene Similar thylakoid arrangements Identical cell walls Starch as a storage carbohydrate
Plant Evolution & Diversity Ancestors of plants were probably charophytes (green algae) Chlorophyll a and b, beta carotene Similar thylakoid arrangements Identical cell walls Starch as a storage carbohydrate
CLASSIFICATION. Why Classify? 2/18/2013. History of Taxonomy Biodiversity: variety of organisms at all levels from populations to ecosystems.
 Why Classify? Classification has been around ever since people paid attention to organisms. CLASSIFICATION One primeval system was based on harmful and non-harmful organisms. Life is easier when we organize
Why Classify? Classification has been around ever since people paid attention to organisms. CLASSIFICATION One primeval system was based on harmful and non-harmful organisms. Life is easier when we organize
06/09/05. A survey of the plant kingdom based on a detailed study of the morphology, anatomy and physiology of selected representative specimens.
 06/09/05 Common Course Number: BOT -1010 Course Title: General Botany Catalog Course Description: A survey of the plant kingdom based on a detailed study of the morphology, anatomy and physiology of selected
06/09/05 Common Course Number: BOT -1010 Course Title: General Botany Catalog Course Description: A survey of the plant kingdom based on a detailed study of the morphology, anatomy and physiology of selected
AP: CHAPTER 18: the Genetics of VIRUSES p What makes microbes good models to study molecular mechanisms? 4. What is a bacteriophage?
 AP: CHAPTER 18: the Genetics of VIRUSES p328-340 1. What makes microbes good models to study molecular mechanisms? Name Per 2. How were viruses first discovered? 3. What are the two basic components of
AP: CHAPTER 18: the Genetics of VIRUSES p328-340 1. What makes microbes good models to study molecular mechanisms? Name Per 2. How were viruses first discovered? 3. What are the two basic components of
CLASSIFICATION NOTES
 CLASSIFICATION NOTES Classification Classification = arrangement of living things into groups according to their observed similarities. Important because it allows us to be able to study life easier Living
CLASSIFICATION NOTES Classification Classification = arrangement of living things into groups according to their observed similarities. Important because it allows us to be able to study life easier Living
Kingdoms and Domains. Lisa Michalek
 Kingdoms and Domains Lisa Michalek The Kingdoms of Life Biologists have organized living things into large groups called Kingdoms. Biologists group organisms into six Kingdoms based on RNA and DNA sequencing
Kingdoms and Domains Lisa Michalek The Kingdoms of Life Biologists have organized living things into large groups called Kingdoms. Biologists group organisms into six Kingdoms based on RNA and DNA sequencing
6 Kingdoms 1.Eubacteria 2.Archaebacteria 3.Protista 4.Fungi 5.Plantae 6.Animalia "Dear King Phillip Came Over From Greece Saturday"
 Unit 7 Classification & Plants What you Need to Know: Classification: Classification, Taxonomy, Binomial Nomenclature + Scientific Names, Kingdoms, Cladograms, Kingdoms and Domains // Characteristics of
Unit 7 Classification & Plants What you Need to Know: Classification: Classification, Taxonomy, Binomial Nomenclature + Scientific Names, Kingdoms, Cladograms, Kingdoms and Domains // Characteristics of
Unit 10: The simplest living beings
 Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Lesson 23 Taxonomy GUIDED INSTRUCTION DIRECTIONS. Guided Questions
 Lesson 23 Taxonomy You will learn how scientists have developed a branch of biology known as taxonomy, the goal of which is to organize the great diversity of life. You will also learn why this organization
Lesson 23 Taxonomy You will learn how scientists have developed a branch of biology known as taxonomy, the goal of which is to organize the great diversity of life. You will also learn why this organization
Classification Systems. - Taxonomy
 Classification Systems - Taxonomy Why Classify? 2.5 million kinds of organisms Not complete- 20 million organisms estimated Must divide into manageable groups To work with the diversity of life we need
Classification Systems - Taxonomy Why Classify? 2.5 million kinds of organisms Not complete- 20 million organisms estimated Must divide into manageable groups To work with the diversity of life we need
Biology EOCT Review. Milton High School
 Biology EOCT Review Milton High School Cell Organelles Nucleus holds DNA Cell membrane what comes in and goes out Mitochondria powerhouse of the cell Ribosomes protein synthesis Lysosomes digestion Cell
Biology EOCT Review Milton High School Cell Organelles Nucleus holds DNA Cell membrane what comes in and goes out Mitochondria powerhouse of the cell Ribosomes protein synthesis Lysosomes digestion Cell
What is classification?
 Classification Table of Contents Objectives Explain why and how organisms are classified. List the eight levels of classification. Explain scientific names. Describe how dichotomous keys help in identifying
Classification Table of Contents Objectives Explain why and how organisms are classified. List the eight levels of classification. Explain scientific names. Describe how dichotomous keys help in identifying
SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT
 SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY B1: Naming and classification of organisms Biology of Plants - Raven et al. 2005 pp. 219-237 INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY Taxonomy Naming Describing Classifying
SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY B1: Naming and classification of organisms Biology of Plants - Raven et al. 2005 pp. 219-237 INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY Taxonomy Naming Describing Classifying
Six Kingdoms By Cindy Grigg. 1 The first scientist to try to classify organisms was the
 Six Kingdoms By Cindy Grigg 1 The first scientist to try to classify organisms was the Greek scholar Aristotle. He classified living things as either plants or animals. Then he divided each of these large
Six Kingdoms By Cindy Grigg 1 The first scientist to try to classify organisms was the Greek scholar Aristotle. He classified living things as either plants or animals. Then he divided each of these large
SAFE HANDS NEET -IB PT 1 Date : 21/12/2017 TEST ID: 1 Time : 01:30:00 Marks : 360 PCB
 SAFE HANDS NEET -IB PT 1 Date : 21/12/2017 TEST ID: 1 Time : 01:30:00 Marks : 360 PCB PHYSICS 1) c 2) a 3) b 4) a 5) d 6) a 7) a 8) a 9) d 10) b 11) c 12) a 13) b 14) c 15) d CHEMISTRY 16) d 17) d 18)
SAFE HANDS NEET -IB PT 1 Date : 21/12/2017 TEST ID: 1 Time : 01:30:00 Marks : 360 PCB PHYSICS 1) c 2) a 3) b 4) a 5) d 6) a 7) a 8) a 9) d 10) b 11) c 12) a 13) b 14) c 15) d CHEMISTRY 16) d 17) d 18)
An Introduction to the Science of Botany. Chapter 1
 An Introduction to the Science of Botany Chapter 1 TTU MS 43131 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Briefly describe the field of botany, and give short definitions of at least five subdisciplines of plant biology Summarize
An Introduction to the Science of Botany Chapter 1 TTU MS 43131 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Briefly describe the field of botany, and give short definitions of at least five subdisciplines of plant biology Summarize
Prokaryotes. Prokaryotes. Chapter 15: Prokaryotes and Protists. Major episodes in the history of life. Major episodes in the history of life
 Chapter 15: Prokaryotes and Protists The book lumps these VERY DIFFERENT organsims together, simply because they are small, or microscopic Bacteria Archae Protista Major episodes in the history of life
Chapter 15: Prokaryotes and Protists The book lumps these VERY DIFFERENT organsims together, simply because they are small, or microscopic Bacteria Archae Protista Major episodes in the history of life
BRYOPHYTA, PTERIDOPHYTA
 Botany Rexine Charts CYTOLOGY (ELB.106.125).01 Cell Membrane showing structure & functions.02 Cell Wall, showing structure & functions.03 Endoplasmic Reticulum showing structure & functions.04 Mitochondrion
Botany Rexine Charts CYTOLOGY (ELB.106.125).01 Cell Membrane showing structure & functions.02 Cell Wall, showing structure & functions.03 Endoplasmic Reticulum showing structure & functions.04 Mitochondrion
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28
 Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land
 Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land for a plant? 4. What are the 3 main groups of plants?
Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land for a plant? 4. What are the 3 main groups of plants?
Classification of Plants
 Classification of Plants Plants Aquatic Plants Ex. green algae Similarities between green algae and land plants: A) have chlorophylls a and b B) cellulose cell walls C) store food energy in the form of
Classification of Plants Plants Aquatic Plants Ex. green algae Similarities between green algae and land plants: A) have chlorophylls a and b B) cellulose cell walls C) store food energy in the form of
XI CLASS BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION
 XI CLASS BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION The process of grouping living organisms into convenient categories based on simple characters is known as Biological classification. Importance
XI CLASS BIOLOGY NOTES CHAPTER 2 - BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION The process of grouping living organisms into convenient categories based on simple characters is known as Biological classification. Importance
22 1 Introduction to Plants Slide 2 of 33
 2 of 33 What Is a Plant? What is a plant? 3 of 33 What Is a Plant? What Is a Plant? Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. Plants develop from multicellular embryos
2 of 33 What Is a Plant? What is a plant? 3 of 33 What Is a Plant? What Is a Plant? Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. Plants develop from multicellular embryos
STD. VIII General Science
 Written as per the latest syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. STD. VIII General Science Salient Features Written as per the new textbook.
Written as per the latest syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. STD. VIII General Science Salient Features Written as per the new textbook.
BIODIVERSITY OF PLANTS 12 FEBRUARY 2014
 BIODIVERSITY OF PLANTS 12 FEBRUARY 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at how plants are classified Define Alternation of generations Summarise the main characteristics of four groupings of
BIODIVERSITY OF PLANTS 12 FEBRUARY 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at how plants are classified Define Alternation of generations Summarise the main characteristics of four groupings of
There are 5 kingdoms: Animalia multicellular animals, heterotrophic (eat other things), evolved 700,000,000 years ago (1,000,000 2,000,000 species)
 Classification The modern system of naming gives each living thing 7 names. Each name is a little more specific than the one before it. The categories are (in order from least to most specific): Kingdom
Classification The modern system of naming gives each living thing 7 names. Each name is a little more specific than the one before it. The categories are (in order from least to most specific): Kingdom
-Producers & Cellular Energy Notes-
 -Producers & Cellular Energy Notes- Part 1 Plants LT 5.1 - I can describe basic information about plants, including the ways they move materials, are classified, reproduce, and evolved. What are plants?
-Producers & Cellular Energy Notes- Part 1 Plants LT 5.1 - I can describe basic information about plants, including the ways they move materials, are classified, reproduce, and evolved. What are plants?
Scan the adjacent QR code or visit to download Hints for relevant questions and Evaluation Test in PDF format.
 Written in accordance with the latest MHT-CET Paper Pattern which includes topics based on Std. XII Sc. and relevant chapters of Std. XI Sc. (Maharashtra State Board) MHT-CET TRIUMPH BIOLOGY MULTIPLE CHOICE
Written in accordance with the latest MHT-CET Paper Pattern which includes topics based on Std. XII Sc. and relevant chapters of Std. XI Sc. (Maharashtra State Board) MHT-CET TRIUMPH BIOLOGY MULTIPLE CHOICE
3/22/2011. Review. Review. Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell
 Review Review Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell Meiosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with one-half
Review Review Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell Meiosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with one-half
Zoology. Classification
 Zoology Zoology involves studying all aspects of organisms belonging to the animal kingdom taxonomy, animal physiology, comparative anatomy, and ecology. Our study of Zoology will be focused on the different
Zoology Zoology involves studying all aspects of organisms belonging to the animal kingdom taxonomy, animal physiology, comparative anatomy, and ecology. Our study of Zoology will be focused on the different
1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT
 Page 1 1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT A haploid spores. B specialized cells and tissues. C vascular tissue for
Page 1 1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT A haploid spores. B specialized cells and tissues. C vascular tissue for
Kingdom Plantae. A Brief Survey of Plants
 Kingdom Plantae A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as follows: 1. Common cellular
Kingdom Plantae A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as follows: 1. Common cellular
es tion Nota Classific
 Classification Notes Fractions Nouns and verbs Circumference of a circle Prepositions World War II The 60s Cells Mark Twain Iliad Periodic table Paragraph structure Genetics Square root What do McDonald
Classification Notes Fractions Nouns and verbs Circumference of a circle Prepositions World War II The 60s Cells Mark Twain Iliad Periodic table Paragraph structure Genetics Square root What do McDonald
copyright cmassengale Unit 12 Classification & Taxonomy Ch. 17 Test 3-18/19
 copyright cmassengale 1 Unit 12 Classification & Taxonomy Ch. 17 Test 3-18/19 copyright cmassengale 2 BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION(pp. 447-450) I. Early Systems of CLASSIFICATION Classification is the grouping
copyright cmassengale 1 Unit 12 Classification & Taxonomy Ch. 17 Test 3-18/19 copyright cmassengale 2 BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION(pp. 447-450) I. Early Systems of CLASSIFICATION Classification is the grouping
Six Kingdoms By Cindy Grigg
 Six Kingdoms By Cindy Grigg Trevor 1 The first scientist to try to classify organisms was the Greek scholar Aristotle. He classified living things as either plants or animals. Then he divided each of these
Six Kingdoms By Cindy Grigg Trevor 1 The first scientist to try to classify organisms was the Greek scholar Aristotle. He classified living things as either plants or animals. Then he divided each of these
Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land
 Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Name Period Concept 29.1 Land plants evolved from green algae 1. Plants colonized land about
Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Name Period Concept 29.1 Land plants evolved from green algae 1. Plants colonized land about
Plants Notes. Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light
 Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom
 Class XI Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom Biology Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions
Class XI Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom Biology Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions
AP Biology. Evolution of Land Plants. Kingdom: Plants. Plant Diversity. Animal vs. Plant life cycle. Bryophytes: mosses & liverworts
 Kingdom: Plants Domain Eukarya Domain Domain Domain Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya 2007-2008 Common ancestor Evolution of Land Plants 500 mya land plants evolved special adaptations for life on dry land protection
Kingdom: Plants Domain Eukarya Domain Domain Domain Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya 2007-2008 Common ancestor Evolution of Land Plants 500 mya land plants evolved special adaptations for life on dry land protection
Bell Work. identify the phylum that each character belongs to. Tuesday, February 19, 13
 Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera
Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: _ Date: _ Ch 17 Practice test 1. A segment of DNA that stores genetic information is called a(n) a. amino acid. b. gene. c. protein. d. intron. 2. In which of the following processes does change
Class: _ Date: _ Ch 17 Practice test 1. A segment of DNA that stores genetic information is called a(n) a. amino acid. b. gene. c. protein. d. intron. 2. In which of the following processes does change
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites
 Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites Date: Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are made up of one or many cells, each of which has
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites Date: Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are made up of one or many cells, each of which has
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites. 8th grade
 Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites 8th grade Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. What is a prokaryote? Eukaryotes are made up of one or many
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites 8th grade Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. What is a prokaryote? Eukaryotes are made up of one or many
Classification and Viruses Practice Test
 Classification and Viruses Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Biologists use a classification system to group organisms in part
Classification and Viruses Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Biologists use a classification system to group organisms in part
Taxonomy. Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms. It has two main purposes: to identify organisms to represent relationships among organisms
 Taxonomy Taxonomy Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms. It has two main purposes: to identify organisms to represent relationships among organisms Binomial Nomenclature Our present biological
Taxonomy Taxonomy Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms. It has two main purposes: to identify organisms to represent relationships among organisms Binomial Nomenclature Our present biological
Unit 2B- The Plants. Plants can be classified according to the presence or absence of vascular tissue.
 Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
9/19/2012. Chapter 17 Organizing Life s Diversity. Early Systems of Classification
 Section 1: The History of Classification Section 2: Modern Classification Section 3: Domains and Kingdoms Click on a lesson name to select. Early Systems of Classification Biologists use a system of classification
Section 1: The History of Classification Section 2: Modern Classification Section 3: Domains and Kingdoms Click on a lesson name to select. Early Systems of Classification Biologists use a system of classification
Comparing Kingdoms Lab
 Comparing Kingdoms Lab Name: Introduction: Living things are all around us. In der to identify ganisms effectively, scientists have developed methods of classifying ganisms into six maj groups called Kingdoms.
Comparing Kingdoms Lab Name: Introduction: Living things are all around us. In der to identify ganisms effectively, scientists have developed methods of classifying ganisms into six maj groups called Kingdoms.
6 Kingdoms of Life. What is life? How are all living things organized?
 6 Kingdoms of Life What is life? How are all living things organized? Engage List reasons to support why this man is living. List reasons to support why this car is not living. Characteristics of Life
6 Kingdoms of Life What is life? How are all living things organized? Engage List reasons to support why this man is living. List reasons to support why this car is not living. Characteristics of Life
2 Domains and Kingdoms
 CHAPTER 11 2 s and Kingdoms SECTION Classification 7.1.a, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Which domains are
CHAPTER 11 2 s and Kingdoms SECTION Classification 7.1.a, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Which domains are
Building the Tree of Life
 Building the Tree of Life THINK ABOUT IT The process of identifying and naming all known organisms, living and extinct, is a huge first step toward the goal of systematics. Yet naming organisms is only
Building the Tree of Life THINK ABOUT IT The process of identifying and naming all known organisms, living and extinct, is a huge first step toward the goal of systematics. Yet naming organisms is only
Class XI Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom Biology
 Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions are based on the following factors:
Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions are based on the following factors:
Plants -- autotrophs (they make their own. Animals -- heterotrophs (they can t make. Once upon a time, Linnaeus determined there were two kingdoms
 PLANTS Once upon a time, Linnaeus determined there were two kingdoms Plants -- autotrophs (they make their own food) Animals -- heterotrophs (they can t make their own food, so they eat other living things)
PLANTS Once upon a time, Linnaeus determined there were two kingdoms Plants -- autotrophs (they make their own food) Animals -- heterotrophs (they can t make their own food, so they eat other living things)
Have cell walls Made of
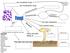 _ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
_ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
Name: Date: Period: Forms a spore producing structure called an ascus Morals Truffles Yeast
 Name: Date: Period: Fungi and Plant Unit Review Worksheet Part I (KEY) Directions: Treat this like an assessment and answer as much as you can without ANY help. See how much you actually know by highlighting/starring
Name: Date: Period: Fungi and Plant Unit Review Worksheet Part I (KEY) Directions: Treat this like an assessment and answer as much as you can without ANY help. See how much you actually know by highlighting/starring
Importance of Protists
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants. Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR
 Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
