MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 09; 25 April 2017
|
|
|
- Alisha Montgomery
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SALSA MLPA probemix P143-C2 MFN2-MPZ Lot C As compared to version C1-0813, one reference probe has been removed and two replaced, in addition several probe lengths have been adjusted. This P143 MFN2-MPZ probemix can be used to detect copy number changes in the MFN2 gene resulting in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) type 2A and the MPZ gene resulting in CMT type 1B. Charcot-Marie- Tooth disease constitutes a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies, affecting approximately 1 in every 2500 individuals. On the basis of electrophysiological criteria, CMT is divided into 2 major types. Type 1, the demyelinating form is characterised by a slow motor median nerve conduction velocity. Type 2, the axonal form, has normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocity. The MFN2 gene (19 exons) spans ~33 kb of genomic DNA and is located on 1p36.22, 12 Mb from the p- telomere. Mitofusins, such as MFN2, mediate the fusion of mitochondria and thereby contribute to the dynamic balance between fusion and fission that determines mitochondrial morphology. Mutations in MFN2 have been detected in affected members of several families with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A (CMT2A). The Myelin protein zero (MPZ) gene (6 exons) spans ~5 kb of genomic DNA and is located on 1q23.3, ~161 Mb from the p-telomere. Myelin protein zero is the major structural protein of peripheral myelin. Mutations in the MPZ gene are associated with the autosomal dominant form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1 (CMT1B) which is characterised by progressive slowing of nerve conduction and hypertrophy of Schwann cells. Mutations in MPZ can also produce the more severe polyneuropathies, Dejerine-Sottas syndrome (DSS) and congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy (CHN), as well as several types of axonal CMT2. The P143-C2 probemix contains one probe for each exon of the MFN2 gene and two probes for exon 3. Furthermore it contains one probe for each exon of the MPZ gene and two probes for exon 1. Two probes upstream of MFN2, recognising the PLOD1 gene, are included. Please note that in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome VIA (kyphoscoliotic type) duplications of PLOD1 exons are found (Giunta et al., 2005). In addition, 9 reference probes are included in this probemix, detecting several different autosomal chromosomal locations. This SALSA probemix is designed to detect deletions/duplications of one or more sequences in the aforementioned gene(s) in a DNA sample. Heterozygous deletions of recognition sequences should give a 35-50% reduced relative peak height of the amplification product of that probe. Note that a mutation or polymorphism in the sequence detected by a probe can also cause a reduction in relative peak height, even when not located exactly on the ligation site! In addition, some probe signals are more sensitive to sample purity and small changes in experimental conditions. Therefore, deletions and duplications detected by MLPA should always be confirmed by other methods. Not all deletions and duplications detected by MLPA will be pathogenic; users should always verify the latest scientific literature when interpreting their findings. We have no information on what percentage of defects in these genes is caused by deletions/duplications of complete exons. Finally, note that most defects in this gene are expected to be small (point) mutations which will not be detected by this SALSA test. SALSA probemixes and reagents are sold by for research purposes and to demonstrate the possibilities of the MLPA technique. They are not CE/FDA certified for use in diagnostic procedures. Purchase of the SALSA test probemixes and reagents includes a limited license to use these products for research purposes. The use of this SALSA probemix and reagents requires a thermocycler with heated lid and sequence type electrophoresis equipment. Different fluorescent PCR primers are available. The MLPA technique has been first described in Nucleic Acid Research 30, e57 (2002). More information Website : info@mlpa.com (information & technical questions); order@mlpa.com (for orders) Mail : bv; Willem Schoutenstraat 1, 1057 DL Amsterdam, the Netherlands SALSA P143 MFN2-MPZ probemix Page 1 of 5
2 Related SALSA probemixes P033 CMT1/HNPP region: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease genes included: PMP22, COX, and TEKT3. P129 GJB1: X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease gene included: GJB1. P405 CMT1: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) and hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies (HNPP) genes included: MPZ, GJB1, 17p12 region (including PMP22). References Carr, AS et al., MFN2 deletion of exons 7 and 8: founder mutation in the UK population. J Peripher Nerv Syst 20.2: Høyer, H et al., Copy number variations in a population-based study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. BioMed Res Int Ostern, R et al., Diagnostic laboratory testing for Charcot Marie Tooth disease (CMT): the spectrum of gene defects in Norwegian patients with CMT and its implications for future genetic test strategies. BMC Med Genet. 14:94. Sivera, R et al., Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: Genetic and clinical spectrum in a Spanish clinical series. Neurology 81: Polke, JM et al., Recessive axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease due to compound heterozygous mitofusin 2 mutations. Neurology 77: Data analysis The P143-C2 MFN2-MPZ probemix contains 38 MLPA probes with amplification products between 137 and 427 nt. In addition, it contains 9 control fragments generating an amplification product smaller than 120 nt: four DNA Quantity fragments (Q-fragments) at nt, three DNA denaturation control fragments (D-fragments) at nt, one X-fragment at 100 nt and one Y-fragment at 105 nt. More information on how to interpret observations on these control fragments can be found in the MLPA protocol. Data generated by this probemix can first be normalised intra-sample by dividing the peak height of each probe s amplification product by the total peak height of only the reference probes in this probemix (block normalisation). Secondly, inter-sample normalisation can be achieved by dividing the intra-normalised probe ratio in a sample by the average intra-normalised probe ratio of all reference samples. Please note that this type of normalisation assumes no changes occurred in the genomic regions recognised by the reference probes. Data normalisation should be performed within one experiment. Only samples purified by the same method should be compared. Confirmation of most exons deletions and amplifications can be done by e.g. Southern blotting, long range PCR, qpcr, FISH. Note that Coffalyser, the MLPA analysis tool developed at, can be downloaded free of charge from our website Many copy number alterations in healthy individuals are described in the database of genomic variants: For example, a duplication of a complete gene might not be pathogenic, while a partial duplication or a deletion may result in disease. For some genes, certain in-frame deletions may result in a very mild, or no disease. Copy number changes of reference probes are unlikely to be the cause of the condition tested for. Users should always verify the latest scientific literature when interpreting their findings. This probemix was developed at. Info/remarks/suggestions for improvement: info@mlpa.com. SALSA P143 MFN2-MPZ probemix Page 2 of 5
3 Table 1. SALSA MLPA P143-C2 MFN2-MPZ probemix Chromosomal position SALSA MLPA probe Reference MFN2 MPZ Q-fragments: DNA quantity; only visible with less than 100 ng sample DNA D-fragments: Low signal of 88 or 96 nt fragment indicates incomplete denaturation 100 X-fragment: Specific for the X chromosome 105 Y-fragment: Specific for the Y chromosome 137 Reference probe L p Reference probe L q «MFN2 probe L05353 Exon MPZ probe L04279 Exon * Reference probe L p MFN2 probe L04261 Exon «MFN2 probe L04271 Exon MPZ probe L04280 Exon MFN2 probe L29924 Exon MFN2 probe L05581 Exon «MFN2 probe L04272 Exon MPZ probe L04281 Exon * Reference probe L q MFN2 probe L04263 Exon «MFN2 probe L29925 Exon MPZ probe L29923 Exon MPZ probe L08284 Exon MFN2 probe L29700 Exon Reference probe L q «MFN2 probe L05354 Exon MPZ probe L04283 Exon Reference probe L q MFN2 probe L04265 Exon «MFN2 probe L04275 Exon MPZ probe L04284 Exon PLOD1 probe L kb upstream of MFN2 320 MFN2 probe L04266 Exon «MFN2 probe L04276 Exon PLOD1 probe L kb upstream of MFN2 346 MFN2 probe L04267 Exon «MFN2 probe L04277 Exon Reference probe L q MFN2 probe L04268 Exon «MFN2 probe L04278 Exon Reference probe L p «MFN2 probe L24212 Exon MFN2 probe L29926 Exon Reference probe L p14 * New in version C2 (from lot C onwards). Changed in version C2 (from lot C onwards). Small change in length, no change in sequence detected. «This probe is located within, or close to, a very strong CpG island. A low signal of this probe can be due to incomplete sample DNA denaturation, e.g. due to the presence of salt in the sample DNA. Flanking probe. Included to facilitate the determination of the extent of a deletion/duplication. Copy number alterations of flanking and reference probes are unlikely to be related to the condition tested. Note: Exon numbering used here may differ from literature! Please notify us of any mistakes. The identity of the genes detected by the reference probes is available on request: info@mlpa.com. SALSA P143 MFN2-MPZ probemix Page 3 of 5
4 Table 2. P143 probes arranged according to chromosomal location Table 2a. MFN2 probes SALSA MLPA probe L L04064 MFN2 Exon PLOD1 gene Exon 10 PLOD1 gene Exon 16 Ligation site in NM_ NM_ NM_ Partial sequence (24 nt adjacent to ligation site) GCATGGCAGCGA-GTACCAGTCTGT CCATCTTCACGG-AGGTGGCCTGTG Distance to next probe 6.3 kb 13.2 kb start codon (exon 3) L29700 Exon GAGTCCGAGCCT-CTGCGTCGTCCG 1.8 kb L04261 Exon CAGTCAATCAAT-AGCCAACCTCAA 7.2 kb L29924 Exon TCTCTCGATGCA-ACTCTATCGTCA 0.1 kb L29926 Exon reverse GGTGGCGCTCTC-CTGGATGTAGGC 3.3 kb L04263 Exon GACGTCAAAGGT-TACCTATCCAAA 3.6 kb L05581 Exon GCACCGTGATCA-ATGCCATGCTCT 1.2 kb L04265 Exon GCCCAACTCTAA-GTGCCCACTTCT 1.4 kb L04266 Exon ACAGAGCTGGAC-AGCTGGATTGAC 0.3 kb L04267 Exon ACAACCGCTGGG-ATGCATCTGCCT 2.4 kb L04268 Exon TTCTTTGTGTCT-GCTAAGGAGGTG 0.3 kb 410 «20882-L24212 Exon CGCAGAAGGCTT-TCAAGTGAGGAT 0.3 kb 148 «04886-L05353 Exon GAGGCGGTTCGA-CTCATCATGGAC 2.0 kb 172 «04887-L04271 Exon GCTCAAGACTAT-AAGCTGCGAATT 0.5 kb 196 «04888-L04272 Exon CTGGTGGACGAT-TACCAGATGGAC 0.3 kb 220 «04889-L29925 Exon CACATAGAGGAA-GGACTGGGTCGA 1.0 kb 256 «04890-L05354 Exon ATGCTGGTGAAT-AGGTTCCTGGGC 0.7 kb 292 «04891-L04275 Exon CAGGGCTCGCTC-ACCCAGGAGGAG 0.6 kb 328 «04892-L04276 Exon AGCTTGTCATCA-GCTACACTGGCT 2.5 kb 355 «04893-L04277 Exon GGAGCAGGAAAT-TGCCGCCATGAA 1.9 kb 382 «04894-L04278 Exon AGCTCAACATGT-TCACACACCAGT stop codon (exon 19) «This probe is located within, or close to, a very strong CpG island. A low signal of this probe can be due to incomplete sample DNA denaturation, e.g. due to the presence of salt in the sample DNA. Flanking probe. Included to facilitate the determination of the extent of a deletion/duplication. Copy number alterations of flanking probes are unlikely to be related to the condition tested. The NM_ sequence (MFN2) represents transcript variant 1 and is a reference standard in the NCBI RefSeqGene project. The NM_ sequence (PLOD1) is a reference standard in the NCBI RefSeqGene project. Table 2b. MPZ probes SALSA MLPA probe MPZ Exon Ligation site in NM_ Partial sequence (24 nt adjacent to ligation site) Distance to next probe start codon (exon 1) L29923 Exon 1 81 nt before exon 1 CTGCACATGCCA-GGCTGCAATTGG 0.2 kb L04279 Exon CTCCCTCATCCA-GCCCCAGCCCTA 2.6 kb L04280 Exon TGCACTGCTCCT-TCTGGTCCAGTG 0.5 kb L04281 Exon CCCTCGCTGGAA-GGATGGCTCCAT 0.4 kb L08284 Exon CGGGGTCGTTCT-GGGAGCTGTGAT 0.3 kb L04283 Exon TTGCACAAGCCA-GGAAAGGACGCG 0.2 kb L04284 Exon ATGCAATGCTGG-ACCACAGCAGAA stop codon (exon 6) The NM_ sequence represents transcript variant 1. Note: Exon numbering used here may differ from literature! Complete probe sequences are available on request: info@mlpa.com. Please notify us of any mistakes: info@mlpa.com. SALSA P143 MFN2-MPZ probemix Page 4 of 5
5 SALSA MLPA probemix P143-C2 MFN2-MPZ sample picture Figure 1. Capillary electrophoresis pattern from a sample of approximately 50 ng human male control DNA analysed with SALSA MLPA probemix P143-C2 MFN2-MPZ (lot C2-0317). Implemented Changes compared to the previous product description version(s). Version April 2017 (55) - Various minor textual changes on pages 1 and 2. - New references added on page 1. - Small changes of probe lengths in Table 1 and 2 in order to better reflect the true lengths of the amplification products. Version 08 (52) Version 07 (48) - Electropherogram pictures using the new MLPA buffer (introduced in December 2012) added. Version 6 (47) - Ligation sites of the probes targeting the MPZ gene updated according to new version of the NM_reference sequence. - New reference added on page 1. - Various minor textual changes. - Various minor layout changes. - Remark on RefSeqGene standard and transcript variant added below Table 2. Version 5 (45) - Product name changed from CMT2A/1B to MFN2-MPZ - Ligation sites updated according to new version of the NM_reference sequence. - Small changes of probe lengths in Table 1 and 2 in order to better reflect the true lengths of the amplification products; tables have been numbered. - Data analysis section modified. Sentence when only small numbers of samples are tested, visual comparison of peak profiles should be sufficient removed from data analysis section SALSA P143 MFN2-MPZ probemix Page 5 of 5
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 14; 21 January 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P229-B2 OPA1 Lot B2-0412. As compared to version B1-0809, two reference probes and the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). The OPA1 gene product is a nuclear-encoded
SALSA MLPA probemix P229-B2 OPA1 Lot B2-0412. As compared to version B1-0809, two reference probes and the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). The OPA1 gene product is a nuclear-encoded
Product Description SALSA MLPA Probemix P229-B4 OPA1 To be used with the MLPA General Protocol.
 Product Description SALSA Probemix P229-B4 OPA1 To be used with the MLPA General Protocol. Version B4. As compared to version B3, three reference probes have been replaced. For complete product history
Product Description SALSA Probemix P229-B4 OPA1 To be used with the MLPA General Protocol. Version B4. As compared to version B3, three reference probes have been replaced. For complete product history
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 8: , 2013
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 8: 1779-1784, 2013 Spectrum and frequencies of mutations in the MFN2 gene and its phenotypical expression in Czech hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type II patients DANA
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 8: 1779-1784, 2013 Spectrum and frequencies of mutations in the MFN2 gene and its phenotypical expression in Czech hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type II patients DANA
Mitochondria associate with the cytoskeleton. Figure 14-5 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
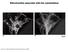 Mitochondria associate with the cytoskeleton Figure 14-5 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Special arrangements of mitochondria Figure 14-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science
Mitochondria associate with the cytoskeleton Figure 14-5 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Special arrangements of mitochondria Figure 14-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science
Review Article Diagnosis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology Volume 2009, Article ID 985415, 10 pages doi:10.1155/2009/985415 Review Article Diagnosis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Isabel Banchs,
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology Volume 2009, Article ID 985415, 10 pages doi:10.1155/2009/985415 Review Article Diagnosis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Isabel Banchs,
mrna Codon Table Mutant Dinosaur Name: Period:
 Mutant Dinosaur Name: Period: Intro Your dinosaur is born with a new genetic mutation. Your job is to map out the genes that are influenced by the mutation and to discover how the new dinosaurs interact
Mutant Dinosaur Name: Period: Intro Your dinosaur is born with a new genetic mutation. Your job is to map out the genes that are influenced by the mutation and to discover how the new dinosaurs interact
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2 Caused by Mitofusin 2 Mutations
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2 Caused by Mitofusin 2 Mutations Judith Calvo, MD; Benoît Funalot, MD, PhD; Robert A. Ouvrier, MD; Leila Lazaro,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2 Caused by Mitofusin 2 Mutations Judith Calvo, MD; Benoît Funalot, MD, PhD; Robert A. Ouvrier, MD; Leila Lazaro,
Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis)
 Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis) DNA Structure o Discovered by Watson and Crick o Double-stranded o Shape is a double helix (twisted ladder) o Made of chains of nucleotides: o Has four types
Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis) DNA Structure o Discovered by Watson and Crick o Double-stranded o Shape is a double helix (twisted ladder) o Made of chains of nucleotides: o Has four types
Evaluation of the performance of Amersham HyPer5 dye in comparative genomic hybridization microarray applications
 GE Healthcare Application note 28-9304-76 AA Nucleic acid labeling and detection Evaluation of the performance of Amersham HyPer5 dye in comparative genomic hybridization microarray applications Key words:
GE Healthcare Application note 28-9304-76 AA Nucleic acid labeling and detection Evaluation of the performance of Amersham HyPer5 dye in comparative genomic hybridization microarray applications Key words:
allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand dominant constitutive mutation coordinate regulation of genes denatured
 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z AA BB CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PP QQ RR SS TT UU VV allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand codominant constitutive mutation coordinate
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z AA BB CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PP QQ RR SS TT UU VV allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand codominant constitutive mutation coordinate
Curriculum Links. AQA GCE Biology. AS level
 Curriculum Links AQA GCE Biology Unit 2 BIOL2 The variety of living organisms 3.2.1 Living organisms vary and this variation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors Causes of variation 3.2.2
Curriculum Links AQA GCE Biology Unit 2 BIOL2 The variety of living organisms 3.2.1 Living organisms vary and this variation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors Causes of variation 3.2.2
Genomes and Their Evolution
 Chapter 21 Genomes and Their Evolution PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 21 Genomes and Their Evolution PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
M i t o c h o n d r i a
 M i t o c h o n d r i a Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Mitochondria Function: generation of metabolic energy in eukaryotic cells Generation of ATP from the breakdown of
M i t o c h o n d r i a Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Mitochondria Function: generation of metabolic energy in eukaryotic cells Generation of ATP from the breakdown of
Analysis of Y-STR Profiles in Mixed DNA using Next Generation Sequencing
 Analysis of Y-STR Profiles in Mixed DNA using Next Generation Sequencing So Yeun Kwon, Hwan Young Lee, and Kyoung-Jin Shin Department of Forensic Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul,
Analysis of Y-STR Profiles in Mixed DNA using Next Generation Sequencing So Yeun Kwon, Hwan Young Lee, and Kyoung-Jin Shin Department of Forensic Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul,
What is the structure of DNA?
 NAME Biology Final Review Sem. II Genetics 1. Define: a. allele b. phenotype c. genotype d. recessive e. dominant f. heterozygous g. homozygous h. autosomes i. sex chromosomes j. Punnett square k. pedigree
NAME Biology Final Review Sem. II Genetics 1. Define: a. allele b. phenotype c. genotype d. recessive e. dominant f. heterozygous g. homozygous h. autosomes i. sex chromosomes j. Punnett square k. pedigree
(Lys), resulting in translation of a polypeptide without the Lys amino acid. resulting in translation of a polypeptide without the Lys amino acid.
 1. A change that makes a polypeptide defective has been discovered in its amino acid sequence. The normal and defective amino acid sequences are shown below. Researchers are attempting to reproduce the
1. A change that makes a polypeptide defective has been discovered in its amino acid sequence. The normal and defective amino acid sequences are shown below. Researchers are attempting to reproduce the
Mole_Oce Lecture # 24: Introduction to genomics
 Mole_Oce Lecture # 24: Introduction to genomics DEFINITION: Genomics: the study of genomes or he study of genes and their function. Genomics (1980s):The systematic generation of information about genes
Mole_Oce Lecture # 24: Introduction to genomics DEFINITION: Genomics: the study of genomes or he study of genes and their function. Genomics (1980s):The systematic generation of information about genes
BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Chapters 10-15, 17-30
 Name Hour Due Date: BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Chapters 10-15, 17-30 The exam was prepared by the Biology teachers in the science departments of CVHS and DHS. 1. What is a Punnett Square? 2. Cross
Name Hour Due Date: BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Chapters 10-15, 17-30 The exam was prepared by the Biology teachers in the science departments of CVHS and DHS. 1. What is a Punnett Square? 2. Cross
 www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Dinosaur Evolution Project Summary: Students pretend to evolve two dinosaurs using genetics and watch how the dinosaurs adapt to an environmental change. This is a very comprehensive
www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Dinosaur Evolution Project Summary: Students pretend to evolve two dinosaurs using genetics and watch how the dinosaurs adapt to an environmental change. This is a very comprehensive
Patterns of inheritance
 Patterns of inheritance Learning goals By the end of this material you would have learnt about: How traits and characteristics are passed on from one generation to another The different patterns of inheritance
Patterns of inheritance Learning goals By the end of this material you would have learnt about: How traits and characteristics are passed on from one generation to another The different patterns of inheritance
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7): /ISSN: /IJCEM
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):10730-10735 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0050950 Original Article Heterogeneous phenotype detection in a Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A family with Mitofusin 2
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):10730-10735 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0050950 Original Article Heterogeneous phenotype detection in a Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A family with Mitofusin 2
The Complete Set Of Genetic Instructions In An Organism's Chromosomes Is Called The
 The Complete Set Of Genetic Instructions In An Organism's Chromosomes Is Called The What is a genome? A genome is an organism's complete set of genetic instructions. Single strands of DNA are coiled up
The Complete Set Of Genetic Instructions In An Organism's Chromosomes Is Called The What is a genome? A genome is an organism's complete set of genetic instructions. Single strands of DNA are coiled up
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A versatile genome-scale PCR-based pipeline for high-definition DNA FISH Magda Bienko,, Nicola Crosetto,, Leonid Teytelman, Sandy Klemm, Shalev Itzkovitz & Alexander van Oudenaarden,,
Supplementary Information A versatile genome-scale PCR-based pipeline for high-definition DNA FISH Magda Bienko,, Nicola Crosetto,, Leonid Teytelman, Sandy Klemm, Shalev Itzkovitz & Alexander van Oudenaarden,,
NETWORK BIOLOGY AND COMPLEX DISEASES. Ahto Salumets
 NETWORK BIOLOGY AND COMPLEX DISEASES Ahto Salumets CENTRAL DOGMA OF BIOLOGY https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/central_dogma_of_molecular_biology http://www.qaraqalpaq.com/genetics.html CHROMOSOMES SINGLE-NUCLEOTIDE
NETWORK BIOLOGY AND COMPLEX DISEASES Ahto Salumets CENTRAL DOGMA OF BIOLOGY https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/central_dogma_of_molecular_biology http://www.qaraqalpaq.com/genetics.html CHROMOSOMES SINGLE-NUCLEOTIDE
Sperm & Eggs & Variation..OH MY!
 Sperm & Eggs & Variation..OH MY! 1 What if a new individual was formed through mitosis? 2 allele amniocentesis asexual reproduction autosome binary fission chorionic villi sampling crossing over diploid
Sperm & Eggs & Variation..OH MY! 1 What if a new individual was formed through mitosis? 2 allele amniocentesis asexual reproduction autosome binary fission chorionic villi sampling crossing over diploid
Cells. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Quiz Section 4 Molecular analysis of inheritance: An amphibian puzzle
 Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 4 Molecular analysis of inheritance: An amphibian puzzle Goals: To illustrate how molecular tools can be used to track inheritance. In this particular example, we will
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 4 Molecular analysis of inheritance: An amphibian puzzle Goals: To illustrate how molecular tools can be used to track inheritance. In this particular example, we will
Name Date Period Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life?
 Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life? Eukaryotic cell parts you should be able a. to identify and label: Nucleus b. Nucleolus c. Rough/smooth ER Ribosomes d. Golgi
Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life? Eukaryotic cell parts you should be able a. to identify and label: Nucleus b. Nucleolus c. Rough/smooth ER Ribosomes d. Golgi
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review
 Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Graduate Funding Information Center
 Graduate Funding Information Center UNC-Chapel Hill, The Graduate School Graduate Student Proposal Sponsor: Program Title: NESCent Graduate Fellowship Department: Biology Funding Type: Fellowship Year:
Graduate Funding Information Center UNC-Chapel Hill, The Graduate School Graduate Student Proposal Sponsor: Program Title: NESCent Graduate Fellowship Department: Biology Funding Type: Fellowship Year:
 www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Dinosaur Evolution Project Summary: Students pretend to evolve two dinosaurs using genetics and watch how the dinosaurs adapt to an environmental change. This is a very comprehensive
www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Dinosaur Evolution Project Summary: Students pretend to evolve two dinosaurs using genetics and watch how the dinosaurs adapt to an environmental change. This is a very comprehensive
UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148
 UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148 CP: CHAPTER 6, Sections 1-6; CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-4; HN: CHAPTER 11, Section 1-5 Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular
UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148 CP: CHAPTER 6, Sections 1-6; CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-4; HN: CHAPTER 11, Section 1-5 Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular
Exome sequencing reveals a novel MFN2 missense mutation in a Chinese family with Charcot Marie Tooth type 2A
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 16: 2281-2286, 2018 Exome sequencing reveals a novel MFN2 missense mutation in a Chinese family with Charcot Marie Tooth type 2A YI YOU 1*, XIAODONG WANG 2*, SHAN
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 16: 2281-2286, 2018 Exome sequencing reveals a novel MFN2 missense mutation in a Chinese family with Charcot Marie Tooth type 2A YI YOU 1*, XIAODONG WANG 2*, SHAN
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline
 Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: Seventeen Causative Genes
 Journal of Clinical Neurology / Volume 2 / June, 2006 Review Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: Seventeen Causative Genes Jung-Hwa Lee, M.D., Byung-Ok Choi, M.D. Department of Neurology and Ewha Medical Research
Journal of Clinical Neurology / Volume 2 / June, 2006 Review Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: Seventeen Causative Genes Jung-Hwa Lee, M.D., Byung-Ok Choi, M.D. Department of Neurology and Ewha Medical Research
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 26. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 26 Fruit fly chromosome 12-5 Gene Regulation Mouse chromosomes Fruit fly embryo Mouse embryo Adult fruit fly Adult mouse 2 of 26 Gene Regulation: An Example Gene Regulation: An Example
Biology Biology 1 of 26 Fruit fly chromosome 12-5 Gene Regulation Mouse chromosomes Fruit fly embryo Mouse embryo Adult fruit fly Adult mouse 2 of 26 Gene Regulation: An Example Gene Regulation: An Example
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division
 Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in. A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in. A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Use of Agilent Feature Extraction Software (v8.1) QC Report to Evaluate Microarray Performance
 Use of Agilent Feature Extraction Software (v8.1) QC Report to Evaluate Microarray Performance Anthea Dokidis Glenda Delenstarr Abstract The performance of the Agilent microarray system can now be evaluated
Use of Agilent Feature Extraction Software (v8.1) QC Report to Evaluate Microarray Performance Anthea Dokidis Glenda Delenstarr Abstract The performance of the Agilent microarray system can now be evaluated
Ch 11.4, 11.5, and 14.1 Review. Game
 Ch 11.4, 11.5, and 14.1 Review Game What happens to the chromosome number during meiosis? A It doubles B It stays the same C It halves D It becomes diploid Ans: C Gametes are A Sex cells B Sperm and eggs
Ch 11.4, 11.5, and 14.1 Review Game What happens to the chromosome number during meiosis? A It doubles B It stays the same C It halves D It becomes diploid Ans: C Gametes are A Sex cells B Sperm and eggs
Understanding Charcot-Marie-Tooth Pathogenesis Using in vivo and Gene Networking Studies
 University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Dissertations Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2015-04-29 Understanding Charcot-Marie-Tooth Pathogenesis Using in vivo and Gene Networking Studies
University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Dissertations Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2015-04-29 Understanding Charcot-Marie-Tooth Pathogenesis Using in vivo and Gene Networking Studies
Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics
 Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics 1 Terms Alleles Chromosome Co dominance Crossover Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA Dominant Genetic code Genome Genotype Heredity Heritability Heritability estimate Heterozygous
Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics 1 Terms Alleles Chromosome Co dominance Crossover Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA Dominant Genetic code Genome Genotype Heredity Heritability Heritability estimate Heterozygous
Chromosomes and Inheritance
 Chromosomes and Inheritance Overview Number of instructional days: 14 (1 day = 50 minutes) Content to be learned Describe the structure of DNA as a way to demonstrate an understanding of the molecular
Chromosomes and Inheritance Overview Number of instructional days: 14 (1 day = 50 minutes) Content to be learned Describe the structure of DNA as a way to demonstrate an understanding of the molecular
CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing Technique for Salmonella Subtyping
 Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Midterm Review Guide. Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer.
 Midterm Review Guide Name: Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer. 4. Fill in the Organic Compounds chart : Elements Monomer
Midterm Review Guide Name: Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer. 4. Fill in the Organic Compounds chart : Elements Monomer
Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy
 Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Dear Editor: It is well known that the majority of Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) cases was caused by 3 mtdna primary mutations (m.3460g A, m.11778g A, and
Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Dear Editor: It is well known that the majority of Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) cases was caused by 3 mtdna primary mutations (m.3460g A, m.11778g A, and
Miller & Levine Biology
 A Correlation of To the Science Biology A Correlation of, 2014 to the, Table of Contents From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes... 3 Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics... 4 Heredity:
A Correlation of To the Science Biology A Correlation of, 2014 to the, Table of Contents From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes... 3 Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics... 4 Heredity:
TE content correlates positively with genome size
 TE content correlates positively with genome size Mb 3000 Genomic DNA 2500 2000 1500 1000 TE DNA Protein-coding DNA 500 0 Feschotte & Pritham 2006 Transposable elements. Variation in gene numbers cannot
TE content correlates positively with genome size Mb 3000 Genomic DNA 2500 2000 1500 1000 TE DNA Protein-coding DNA 500 0 Feschotte & Pritham 2006 Transposable elements. Variation in gene numbers cannot
Campbell Biology Concepts & Connections 2015
 A Correlation of Concepts & Connections 2015 To the Science, , Science - Table of Contents From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes... 3 Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics... 5
A Correlation of Concepts & Connections 2015 To the Science, , Science - Table of Contents From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes... 3 Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics... 5
Bio/Life: Cell Biology
 Bio/Life: Cell Biology 1a The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding
Bio/Life: Cell Biology 1a The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding
Lecture 7 Mutation and genetic variation
 Lecture 7 Mutation and genetic variation Thymidine dimer Natural selection at a single locus 2. Purifying selection a form of selection acting to eliminate harmful (deleterious) alleles from natural populations.
Lecture 7 Mutation and genetic variation Thymidine dimer Natural selection at a single locus 2. Purifying selection a form of selection acting to eliminate harmful (deleterious) alleles from natural populations.
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS. Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent.
 THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.1 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HISTORY OF GENETICS The earliest use of genetics was through of plants and animals (8000-1000 B.C.) Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process of breeding organisms
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HISTORY OF GENETICS The earliest use of genetics was through of plants and animals (8000-1000 B.C.) Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process of breeding organisms
1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine.
 Protein Synthesis & Mutations RNA 1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine. RNA Contains: 1. Adenine 2.
Protein Synthesis & Mutations RNA 1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine. RNA Contains: 1. Adenine 2.
Junctophilin-1 is a modifier gene of GDAP1-related Charcot-Marie-
 Junctophilin-1 is a modifier gene of GDAP1-related Charcot-Marie- Tooth disease David Pla-Martín 1,2#, Eduardo Calpena 1,2#, Vincenzo Lupo 1,2, Celedonio Márquez 3, Eloy Rivas 4, Rafael Sivera 5,6, Teresa
Junctophilin-1 is a modifier gene of GDAP1-related Charcot-Marie- Tooth disease David Pla-Martín 1,2#, Eduardo Calpena 1,2#, Vincenzo Lupo 1,2, Celedonio Márquez 3, Eloy Rivas 4, Rafael Sivera 5,6, Teresa
Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology
 Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the molecular basis of disease? What
Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the molecular basis of disease? What
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
HORIZONTAL TRANSFER IN EUKARYOTES KIMBERLEY MC GRAIL FERNÁNDEZ GENOMICS
 HORIZONTAL TRANSFER IN EUKARYOTES KIMBERLEY MC GRAIL FERNÁNDEZ GENOMICS OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION MECHANISMS OF HGT IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES EXAMPLES - Wolbachia pipientis - Fungus - Plants - Drosophila ananassae
HORIZONTAL TRANSFER IN EUKARYOTES KIMBERLEY MC GRAIL FERNÁNDEZ GENOMICS OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION MECHANISMS OF HGT IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES EXAMPLES - Wolbachia pipientis - Fungus - Plants - Drosophila ananassae
Going Beyond SNPs with Next Genera5on Sequencing Technology Personalized Medicine: Understanding Your Own Genome Fall 2014
 Going Beyond SNPs with Next Genera5on Sequencing Technology 02-223 Personalized Medicine: Understanding Your Own Genome Fall 2014 Next Genera5on Sequencing Technology (NGS) NGS technology Discover more
Going Beyond SNPs with Next Genera5on Sequencing Technology 02-223 Personalized Medicine: Understanding Your Own Genome Fall 2014 Next Genera5on Sequencing Technology (NGS) NGS technology Discover more
GEP Annotation Report
 GEP Annotation Report Note: For each gene described in this annotation report, you should also prepare the corresponding GFF, transcript and peptide sequence files as part of your submission. Student name:
GEP Annotation Report Note: For each gene described in this annotation report, you should also prepare the corresponding GFF, transcript and peptide sequence files as part of your submission. Student name:
Experimental Neurology
 Experimental Neurology 246 (2013) 14 25 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Experimental Neurology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yexnr Review Overlapping molecular pathological
Experimental Neurology 246 (2013) 14 25 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Experimental Neurology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yexnr Review Overlapping molecular pathological
2012 Univ Aguilera Lecture. Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology
 2012 Univ. 1301 Aguilera Lecture Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the
2012 Univ. 1301 Aguilera Lecture Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the
Chromosomal rearrangements in mammalian genomes : characterising the breakpoints. Claire Lemaitre
 PhD defense Chromosomal rearrangements in mammalian genomes : characterising the breakpoints Claire Lemaitre Laboratoire de Biométrie et Biologie Évolutive Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1 6 novembre 2008
PhD defense Chromosomal rearrangements in mammalian genomes : characterising the breakpoints Claire Lemaitre Laboratoire de Biométrie et Biologie Évolutive Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1 6 novembre 2008
Q2 (4.6) Put the following in order from biggest to smallest: Gene DNA Cell Chromosome Nucleus. Q8 (Biology) (4.6)
 Q1 (4.6) What is variation? Q2 (4.6) Put the following in order from biggest to smallest: Gene DNA Cell Chromosome Nucleus Q3 (4.6) What are genes? Q4 (4.6) What sort of reproduction produces genetically
Q1 (4.6) What is variation? Q2 (4.6) Put the following in order from biggest to smallest: Gene DNA Cell Chromosome Nucleus Q3 (4.6) What are genes? Q4 (4.6) What sort of reproduction produces genetically
Designer Genes C Test
 Northern Regional: January 19 th, 2019 Designer Genes C Test Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Rank: Score: Directions: You will have 50 minutes to complete the test. You may not write on the
Northern Regional: January 19 th, 2019 Designer Genes C Test Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Rank: Score: Directions: You will have 50 minutes to complete the test. You may not write on the
BIO GENETICS CHROMOSOME MUTATIONS
 BIO 390 - GENETICS CHROMOSOME MUTATIONS OVERVIEW - Multiples of complete sets of chromosomes are called polyploidy. Even numbers are usually fertile. Odd numbers are usually sterile. - Aneuploidy refers
BIO 390 - GENETICS CHROMOSOME MUTATIONS OVERVIEW - Multiples of complete sets of chromosomes are called polyploidy. Even numbers are usually fertile. Odd numbers are usually sterile. - Aneuploidy refers
Biology regimented study plan
 For each topic, write down notes, make it organized, always have a pencil and paper while studying. At the end of each section, test yourself (Answer past exam questions, practice Quizlet, watch Crash
For each topic, write down notes, make it organized, always have a pencil and paper while studying. At the end of each section, test yourself (Answer past exam questions, practice Quizlet, watch Crash
Teachers Guide. Overview
 Teachers Guide Overview BioLogica is multilevel courseware for genetics. All the levels are linked so that changes in one level are reflected in all the other levels. The BioLogica activities guide learners
Teachers Guide Overview BioLogica is multilevel courseware for genetics. All the levels are linked so that changes in one level are reflected in all the other levels. The BioLogica activities guide learners
Recessive Genetic Disorders: a recessive trait is expressed when the individual is homozygous recessive for the trait.
 Complex Inhertiance Recessive Genetic Disorders: a recessive trait is expressed when the individual is homozygous recessive for the trait. This is true for other species besides humans Carriers: Individuals
Complex Inhertiance Recessive Genetic Disorders: a recessive trait is expressed when the individual is homozygous recessive for the trait. This is true for other species besides humans Carriers: Individuals
Solutions to Problem Set 4
 Question 1 Solutions to 7.014 Problem Set 4 Because you have not read much scientific literature, you decide to study the genetics of garden peas. You have two pure breeding pea strains. One that is tall
Question 1 Solutions to 7.014 Problem Set 4 Because you have not read much scientific literature, you decide to study the genetics of garden peas. You have two pure breeding pea strains. One that is tall
Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation
 Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation What Is Molecular Evolution? Molecular evolution differs from phenotypic evolution in that mutations and genetic drift are much more important determinants
Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation What Is Molecular Evolution? Molecular evolution differs from phenotypic evolution in that mutations and genetic drift are much more important determinants
Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation
 Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation What Is Molecular Evolution? Molecular evolution differs from phenotypic evolution in that mutations and genetic drift are much more important determinants
Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation What Is Molecular Evolution? Molecular evolution differs from phenotypic evolution in that mutations and genetic drift are much more important determinants
Outline. Genome Evolution. Genome. Genome Architecture. Constraints on Genome Evolution. New Evolutionary Synthesis 11/8/16
 Genome Evolution Outline 1. What: Patterns of Genome Evolution Carol Eunmi Lee Evolution 410 University of Wisconsin 2. Why? Evolution of Genome Complexity and the interaction between Natural Selection
Genome Evolution Outline 1. What: Patterns of Genome Evolution Carol Eunmi Lee Evolution 410 University of Wisconsin 2. Why? Evolution of Genome Complexity and the interaction between Natural Selection
Genetics 275 Notes Week 7
 Cytoplasmic Inheritance Genetics 275 Notes Week 7 Criteriafor recognition of cytoplasmic inheritance: 1. Reciprocal crosses give different results -mainly due to the fact that the female parent contributes
Cytoplasmic Inheritance Genetics 275 Notes Week 7 Criteriafor recognition of cytoplasmic inheritance: 1. Reciprocal crosses give different results -mainly due to the fact that the female parent contributes
Functions and dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics
 Functions and dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics Scott A. Detmer and David C. Chan Abstract Recent findings have sparked renewed appreciation for the remarkably dynamic nature of mitochondria. These
Functions and dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics Scott A. Detmer and David C. Chan Abstract Recent findings have sparked renewed appreciation for the remarkably dynamic nature of mitochondria. These
The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression. The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression. A. The Eukaryotic Genome. Lecture Series 11
 The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression Lecture Series 11 The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression A. The Eukaryotic Genome B. Repetitive Sequences (rem: teleomeres) C. The Structures of Protein-Coding
The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression Lecture Series 11 The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression A. The Eukaryotic Genome B. Repetitive Sequences (rem: teleomeres) C. The Structures of Protein-Coding
Name: Date: Chromosome Webquest (35 points)
 Name: Date: Chromosome Webquest (35 points) This is due by 11:59pm Monday January 9th on google classroom. This is an individual assignment. If you have questions, please email me and I will try to answer
Name: Date: Chromosome Webquest (35 points) This is due by 11:59pm Monday January 9th on google classroom. This is an individual assignment. If you have questions, please email me and I will try to answer
- mutations can occur at different levels from single nucleotide positions in DNA to entire genomes.
 February 8, 2005 Bio 107/207 Winter 2005 Lecture 11 Mutation and transposable elements - the term mutation has an interesting history. - as far back as the 17th century, it was used to describe any drastic
February 8, 2005 Bio 107/207 Winter 2005 Lecture 11 Mutation and transposable elements - the term mutation has an interesting history. - as far back as the 17th century, it was used to describe any drastic
1 Introduction. Abstract
 CBS 530 Assignment No 2 SHUBHRA GUPTA shubhg@asu.edu 993755974 Review of the papers: Construction and Analysis of a Human-Chimpanzee Comparative Clone Map and Intra- and Interspecific Variation in Primate
CBS 530 Assignment No 2 SHUBHRA GUPTA shubhg@asu.edu 993755974 Review of the papers: Construction and Analysis of a Human-Chimpanzee Comparative Clone Map and Intra- and Interspecific Variation in Primate
2. Draw two water molecules. Using a dotted line, show a hydrogen bond that could form between them.
 Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
Molecular evolution - Part 1. Pawan Dhar BII
 Molecular evolution - Part 1 Pawan Dhar BII Theodosius Dobzhansky Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution Age of life on earth: 3.85 billion years Formation of planet: 4.5 billion
Molecular evolution - Part 1 Pawan Dhar BII Theodosius Dobzhansky Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution Age of life on earth: 3.85 billion years Formation of planet: 4.5 billion
Cell Structure and Function
 Quarter 2 Review Biology Cell Structure and Function Identify the organelles AND give function of each. 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. Looking at the above diagram, what does the structure labeled 1 do? Why
Quarter 2 Review Biology Cell Structure and Function Identify the organelles AND give function of each. 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. Looking at the above diagram, what does the structure labeled 1 do? Why
The Research Plan. Functional Genomics Research Stream. Transcription Factors. Tuning In Is A Good Idea
 Functional Genomics Research Stream The Research Plan Tuning In Is A Good Idea Research Meeting: March 23, 2010 The Road to Publication Transcription Factors Protein that binds specific DNA sequences controlling
Functional Genomics Research Stream The Research Plan Tuning In Is A Good Idea Research Meeting: March 23, 2010 The Road to Publication Transcription Factors Protein that binds specific DNA sequences controlling
Introduction. Gene expression is the combined process of :
 1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
Introduction to analyzing NanoString ncounter data using the NanoStringNormCNV package
 Introduction to analyzing NanoString ncounter data using the NanoStringNormCNV package Dorota Sendorek May 25, 2017 Contents 1 Getting started 2 2 Setting Up Data 2 3 Quality Control Metrics 3 3.1 Positive
Introduction to analyzing NanoString ncounter data using the NanoStringNormCNV package Dorota Sendorek May 25, 2017 Contents 1 Getting started 2 2 Setting Up Data 2 3 Quality Control Metrics 3 3.1 Positive
Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis
 Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis IN: How is transcription like making a jello mold? (be specific) What process does this diagram represent? A. Mutation B. Replication C.Transcription D.Translation
Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis IN: How is transcription like making a jello mold? (be specific) What process does this diagram represent? A. Mutation B. Replication C.Transcription D.Translation
4) Please cite Dagda et al J Biol Chem 284: , for any publications or presentations resulting from use or modification of the macro.
 Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Protocol S1. Replicate Evolution Experiment
 Protocol S Replicate Evolution Experiment 30 lines were initiated from the same ancestral stock (BMN, BMN, BM4N) and were evolved for 58 asexual generations using the same batch culture evolution methodology
Protocol S Replicate Evolution Experiment 30 lines were initiated from the same ancestral stock (BMN, BMN, BM4N) and were evolved for 58 asexual generations using the same batch culture evolution methodology
Constructing a Pedigree
 Constructing a Pedigree Use the appropriate symbols: Unaffected Male Unaffected Female Affected Male Affected Female Male carrier of trait Mating of Offspring 2. Label each generation down the left hand
Constructing a Pedigree Use the appropriate symbols: Unaffected Male Unaffected Female Affected Male Affected Female Male carrier of trait Mating of Offspring 2. Label each generation down the left hand
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein. Biology Kevin Dees
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein DNA The information molecule Sequences of bases is a code DNA organized in to chromosomes Chromosomes are organized into genes What do the genes actually say??? Reflecting
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein DNA The information molecule Sequences of bases is a code DNA organized in to chromosomes Chromosomes are organized into genes What do the genes actually say??? Reflecting
Science Unit Learning Summary
 Learning Summary Inheritance, variation and evolution Content Sexual and asexual reproduction. Meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed. In
Learning Summary Inheritance, variation and evolution Content Sexual and asexual reproduction. Meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed. In
Genetically Engineering Yeast to Understand Molecular Modes of Speciation
 Genetically Engineering Yeast to Understand Molecular Modes of Speciation Mark Umbarger Biophysics 242 May 6, 2004 Abstract: An understanding of the molecular mechanisms of speciation (reproductive isolation)
Genetically Engineering Yeast to Understand Molecular Modes of Speciation Mark Umbarger Biophysics 242 May 6, 2004 Abstract: An understanding of the molecular mechanisms of speciation (reproductive isolation)
J. MITCHELL MCGRATH, LESLIE G. HICKOK, and ERAN PICHERSKY
 P1. Syst. Evol. 189:203-210 (1994) --Plant Systematics and Evolution Springer-Verlag 1994 Printed in Austria Assessment of gene copy number in the homosporous ferns Ceratopteris thalictroides and C. richardii
P1. Syst. Evol. 189:203-210 (1994) --Plant Systematics and Evolution Springer-Verlag 1994 Printed in Austria Assessment of gene copy number in the homosporous ferns Ceratopteris thalictroides and C. richardii
Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans, two fruit fly species that are nearly
 Comparative Genomics: Human versus chimpanzee 1. Introduction The chimpanzee is the closest living relative to humans. The two species are nearly identical in DNA sequence (>98% identity), yet vastly different
Comparative Genomics: Human versus chimpanzee 1. Introduction The chimpanzee is the closest living relative to humans. The two species are nearly identical in DNA sequence (>98% identity), yet vastly different
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems
 Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Practice Test on Cell Biology (the REAL test is on Friday the 17th) KEY LO: Describe and explain the Central Dogma. SLE: Meet NGSS.
 Practice Test on Cell Biology (the REAL test is on Friday the 17th) KEY LO: Describe and explain the Central Dogma. SLE: Meet NGSS. On the real test, you will be given this chart of the genetic code (from
Practice Test on Cell Biology (the REAL test is on Friday the 17th) KEY LO: Describe and explain the Central Dogma. SLE: Meet NGSS. On the real test, you will be given this chart of the genetic code (from
EVOLUTION ALGEBRA Hartl-Clark and Ayala-Kiger
 EVOLUTION ALGEBRA Hartl-Clark and Ayala-Kiger Freshman Seminar University of California, Irvine Bernard Russo University of California, Irvine Winter 2015 Bernard Russo (UCI) EVOLUTION ALGEBRA 1 / 10 Hartl
EVOLUTION ALGEBRA Hartl-Clark and Ayala-Kiger Freshman Seminar University of California, Irvine Bernard Russo University of California, Irvine Winter 2015 Bernard Russo (UCI) EVOLUTION ALGEBRA 1 / 10 Hartl
Philipsburg-Osceola Area School District Science Department. Standard(s )
 Philipsburg-Osceola Area School District Science Department Course Name: Biology Grade Level: 10 Timelin e Big Ideas Essential Questions Content/ Concepts Skills/ Competencies Standard(s ) Eligible Content
Philipsburg-Osceola Area School District Science Department Course Name: Biology Grade Level: 10 Timelin e Big Ideas Essential Questions Content/ Concepts Skills/ Competencies Standard(s ) Eligible Content
Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic genes
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 18: Eukaryotic genes http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic genes Like in prokaryotes,
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 18: Eukaryotic genes http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic genes Like in prokaryotes,
METHODS FOR DETERMINING PHYLOGENY. In Chapter 11, we discovered that classifying organisms into groups was, and still is, a difficult task.
 Chapter 12 (Strikberger) Molecular Phylogenies and Evolution METHODS FOR DETERMINING PHYLOGENY In Chapter 11, we discovered that classifying organisms into groups was, and still is, a difficult task. Modern
Chapter 12 (Strikberger) Molecular Phylogenies and Evolution METHODS FOR DETERMINING PHYLOGENY In Chapter 11, we discovered that classifying organisms into groups was, and still is, a difficult task. Modern
