r 1 THEGREAT-VOLUMERAINSTORMATELBA,ALABAMA INTRODUCTION
|
|
|
- Oliver Doyle
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JUNE 1964 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW 153 THEGREAT-VOLUMERAINSTORMATELBA,ALABAMA GEORGE A. LOT" Hydrologic Services Mvfsion, U. S. Weather Bureau.1 Washington, D. C. Manuscript received July 7, 1953; revised February INTRODUCTION The depth of rain which fell in the Elba, Ala., storm of March 14, 1929, is the greatest in the United States for most durations from 18 to 48 hours over large areas (from 10,000 to 100,000 square miles) [l]. At Elba alone a rainfd total of21.4 inches was measured in a period of 32 hours ending at 1600 CST, March 14, Observers' notes and indirect evidence seem to indicate that almost all of this rain fell in the final 12 hours of the period. m e 1 is the isohyetal map for the 24-hour period starting at 0300 CST, March 14. Figure 2 shows the depthduration-area curves based on an earlier unpublished Hydrometeorological Section study of this storm. On the basis of the present study it is now considered likely that the 12-hour duration line in the smaller areas shows too little rain. The other lines are substantially correct. The floods resulting from this rain were greater than any recorded before or since on rivers in southeastern Alabama 12, 3, 41. (See[2] for photographs of Elba and Brewton, Ala., at height of flood.) The storm's intensity over so large an area dictated its choice for study. Unfortunately, the Elba storm occurred J In owperation with the Corps of Engineers, Department of the Army. before the present extensive network of upper-air stations, and so most of our knowledge must come from surface observations. There have been somewhat similar storms (synoptically) since the inauguration of widespread upperair observations, but of lesser intensity (e. g., the storm centered in Louisiana on April 29, 1953). A study of the surface maps for the storm period reveals a number of unusual features associated with the occurrence of the phenomenal rainfall. The primary purpose of this paper is to describe these unusual features. Some effort will also be made to offer tentative suggestions concerning the mechanisms involved. 100,000 I0,OOO r 1 n I w 2 1,000 a W Q: 4 IO0 IO IO OEPTH(lnchc8) npmr l.-lsobwtsl ~ S showin D 24hOUr rainfall for period starting auw, CBT. March 14, hawe Z.-Depth-duration- mea for the Elba, Ala., rainstorm, Mhrch 14,1829.
2 154 MONTHLY REVIEW WEATHER JUNE 1954 GENERAL SYNOPTIC SITUATION I I U FIQWE 3.-Surfm map for 0700 CST, March 13, 1929, about 24 hours prior to the stom at Elba. On March 11, 1929, a very deep trough including a cold front extended from about Bismarck, N. Dak., to Phoenix, Me., with mp air behind it. To the east, a large High of Arctic origin was centered near Cape Hatteras, directing a broad southerly current over the central part of the country. By March 12, a warm front had appeared in the Gulf of Mexico, with mt air to the south; rain was falling over a large area north of the front. Meanwhile, the deep mid-continent trough had moved slowly eastward with a well-organized surface Low near North Platte, Nebr., and the eastern High had moved slowly off the coast. Figure 3, the surface weather map about 24 hours prior to the great storm, shows the warm front approaching Pensacola, Fla., from the Gulf. During the afternoon of the 13th the dewpoint at Pensacola rose from 61 to 66O F., while the surface wind shifted from east to south- 0 FIQWE 4.-Surface map for 1900 CST, March 13,1929, about 8 hours prior to the Elba rainstorm.
3 Jdm 1954 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW 155 east. After the frontal passage at Pensacola, no definite position for the warm front could be ascertained. The cold front, which had moved somewhat ahead of the surface mid-continent trough, was oriented north-south near the Mississippi River and extended into the extreme northwestern Gulf. North of Vicksburg, Miss., this frontwas moving slowly eastward, but in the Gulf of Mexico a very weak stable wave had formed about 50 miles east-northeast of Corpus Christi, Tex. The subsequent history of this stable wave was of great importance in the chain of events that led to the major &-burst in the Elba storm. DETAILS OF THE SITUATION A series of hourly surface weather maps was analyzed for the 24-hour period starting at 1800 CST, March 13, The maps cover the States of Alabama, Mississippi, Georgia, and northern Florida in as great detail as possible. Figures 4 and 5 represent two maps from this series, those for 1900 CST, March 13 and 0700 CST, March 14. Cooperative observer synoptic weather data, including current temperature readings, for southern Alabama and northwestern Florida were also plotted on the charts. The rainfall amount, where plotted, is for the hour ending at the time of the map. Rainfall intensity is not merentiated by the weather symbol. Figure 4, illustrating conditions about 8 hours before the deluge, shows a number of interesting features. The stable wave which had formed near Corpus Christi wm centered in northern Mississippi, having averaged about 40 m. p. h. in its sprint from the Gulf. Four to five hours after the time of the map the wave passed Nashville, Tenn., causing a maximum wind of 26 m. p. h. from the southeast before the cold-front passage. A shower area, probably induced by the fast-moving wave, formed over Mississippi during late afternoon of the 13th. The line near Meridian, Miss., shows the approximate eastern boundary of this shower area (the instability line). At about 1930 CST this line passed Meridian, and in the next 14 hours passed, successively, Birmingham, Anniston, and Montgomery, Ala., and Atlanta and Macon, Ga. Every FIQUBE I."surface map for 0700 CST, March 14,1929, the synoptic situation during the heavy rain.
4 156 MONTHLY REVIEW WEATHER
5 Jum 1964 REVIEW WEATHER MONTHLY 157 FIGUBE T.-Upper-level wind, temperature, and humidity data, afternoon, March 14,1929.
6 158 REVIEW WEATHER MONTHLY JUNE 1964 I weather station in the area, without exception, recorded this line passage. Weather changes at each of the stations included: (1) a sharp burst of rain, (2) a wind shift from southeast to northwest, (3) a rise in pressure, (4) a slight lowering of temperature and dewpoint, and (5) a return to a southeast wind, lower pressure, and a diminution of the rain. The temperature and dewpoint remained "permanently" depressed 2' to 6' F., however. Cooling of an air mass in the lower levels by rain is generally attributed to a combination of factors including: (1) cooling due to the melting of sleet and snow at upper levels and the cold rain resulting therefrom at lower levels, (2) cooling of the earth's surface by the cooler rain and its partial vaporization, and (3) cooling by the moist adiabatic descent during the heavy rain [5]. A combination of these factors would be sufficient to lower the temperature by the observed amount (2' to 6' F.) without an air mass change at the surface. Another significant feature pictured in figure 4 is the band of very strong winds between about 86' and 88' W. longitude in Florida and southern Alabama. Within this belt of high winds, moreover, the very strongest appeared to be south of latitude 31' N., probably because of the smaller frictional effect over the water. Although scattered showers and thunderstorms were observed in the high-wind area north of 31' N., rainfall amounts were generally light. Figure 5 is a detailed view of the synoptic situation during the heavy rain. The strong-wind band had remained almost stationary during the 12-hour interval between 1900 CST, March 13 and 0700 CST, March 14, but had increased somewhat in intensity. The northern part of the instability line had reached Macon, Ga., while in the southernmost reaches it had become stationary between Mobile, Ala., and Pensacola, Fla. In this southern part the sequence of weather events at any given point was of the rain-burst lasting an hour or two, very heavy rain continued for many hours. For example, during the 7 hours that the line remained stationary between Mobile and Pensacola, Mobile recorded 6.24 inches of rain, while Pensacola recorded 0.08 inch. About noon (CST) the rain area retreated northward past Mobile. In extreme southeastern Alabama, in the Elba region for example, the rain area remained stationary an even longer time, about 12 hours. Late on the afternoon of the 14th the remnants of the rain area made a general retreat northward. It wil be noted that a warm front could be placed approximately from Mobile to Macon (in fig. 4) on the basis of a weak temperature gradient to the north of this line. This position coincides with the location of the instability line in figure 5, 12 hours later. The difliculties of placing a classical front in this position for 12 hours are that (1) the front would have had to remain Stationary while a strong geostrophic component normal to the front in both warm and cold air was maintained, and (2) no observed data show a cyclonicwind shift. Under these conditions it would seem that ascribing the heavy rainfall to a warm front is to use a deus ex machina. UPPER LEVELS Data for 1929 are insufficient to draw upper-air charta for the southern United States. The available wind, temperature, and humidity observations aloft for March 14 are shown in figures 6 and 7. The upper-wind observation nearest to the Elba center on the morning of March 14 was at Jacksonville, Fla. The southerly wind at that time was a maximum at the 1,000-meter level (fig. 6B). Low-level winds over northwestern Florida were probably much stronger than those over Jacksonville. It may be noted that a very strong southerly wind maximum at the 3,000- to 4,000-ft. level has been observed in several other great storms [6, 71. This lower 3,000 to 4,000 feet is thought by the Hydrometeorological Section to be of great importance in the setup for very heavy rain. In the earlier storms, before the advent of the present dense network of upper-air stations, interaction of the wind and temperature fields aloft must be inferred. A fair approximation to the 3,500-ft. geostrophic wind can be obtained from the surface isobars. The cooling, observed at the earth's surface within the bounds of a rain area and due only to the effect of the rain itself, can be used to outline the area cooled through the lower 3,000 to 4,000 feet of the atmosphere. A sensitive measure of the change in wind speed, and thus of the differential temperature advection, is the 12-hour pressure change. A POSSIBLE MECHANISM On figure 5, 0700 CST, March 14, the axis of the surface cool air associated with the line of showers can be identified by the trough in the isotherms extending from Atlanta, Ga., to near Mobile, Ala. The temperature at Ozark, Ala. (very close to the storm center at Elba) was observed to be 61' F., while at Vernon and Pensacola, Fla., south of the instability line, the temperature was 69' and 68O F., respectively. This temperature gradient was observed during the heavy rainfall of the storm itself, while a slighter temperature gradient had been observed across the instability line earlier, as mentioned above. But, as the line approached the coast, warmer air was encountered, and thus the temperature contrast across the line was increased. Meanwhile, as the temperature contrast increased, a pressure fall area moved in from the west (not shown) and was centered along the Gulf Coast at the longitude of Elba at about 0700 CST, March 14. The effect of this pressure fall was to strengthen further the low-level southerly
7 JUNE 1954 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW 159 winds in this area. Pensacola reported an extreme wind of 60 m. p. h. from the south at adout 0900 CST, March 14. It can then be inferred that during the morning of March 14 a low-level area of unusually intense temperature advection was set up near the Florida-Alabama line as a result of a combination of these two factors. During the afternoon of the 14th a northward drift of the band of temperature gradient took place, probably occasioned by a shift in upper winds to a more southerly direction. A partial confirmation of this is contained in the Memphis 3,000-meter wind-aloft record (compare figs. 6 and 7). The great rain-burst thus came to an end. SUMMARY It is suggested that an instability line, with its attendant low-level cold air mass, created a concentrated temperature gradient over southern Alabama early on the morning of the 14th. At the same time an increase in the southerly winds took place due to a timely katallobaric area. The result waa a narrow band of strong warm-air advection. This, together with the probably unstable character of the warm air mass, was responsible for the long, heavy rain in southern Alabama, centered at Elba. REFERENCES 1. U. S. Weather Bureau, Hydrometeorological Section, Maximum Observed U. S. Rainfall, rev. Feb (Mimeographed.) 2. A. J. Henry, Weather Abnormalities in the United States. Excessive Rains and Floods in Southeast Alabama, Monthly Weather Review, vol. 57, No. 8, Aug. 1929, pp U. S. Weather Bureau, Daily River Stages, Washington, D. C., (See table River Stations and Miscellaneous Inf~rmation~~.) 4. H. C. Frankenfield, Rivers and Floods, Monthly Weather Review, vol. 57, No. 3, Mar: 1929, pp G. A. Lott, The Unparalled Thrall, Texas Rainstorm, Monthly Weather Review, vol. 81, No. 7, July 1953, pp G. A. Lott, An Extraordinary Rain at Hallett, Oklahoma, Monthly Weather Review, vol. 81, No. 1, Jan. 1953, pp G. A. SuckstorfF, Kaltlufterzeugung durch Niederschlag, Meteorologhche Zeitsch~fl, Bd. 55, Aug. 1938, pp
January 2006 Climate Summary
 Ashley Brooks (765) 494-6574 Feb 9, 2006 http://www.iclimate.org January 1-3 January 2006 Climate Summary Unseasonably warm conditions welcomed in the New Year with highs in the 40s across the northern
Ashley Brooks (765) 494-6574 Feb 9, 2006 http://www.iclimate.org January 1-3 January 2006 Climate Summary Unseasonably warm conditions welcomed in the New Year with highs in the 40s across the northern
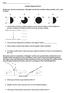
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument.
 1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #2 Page 1 of 8
 1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
Lecture #14 March 29, 2010, Monday. Air Masses & Fronts
 Lecture #14 March 29, 2010, Monday Air Masses & Fronts General definitions air masses source regions fronts Air masses formation types Fronts formation types Air Masses General Definitions a large body
Lecture #14 March 29, 2010, Monday Air Masses & Fronts General definitions air masses source regions fronts Air masses formation types Fronts formation types Air Masses General Definitions a large body
Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class)
 Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class) 1. General Circulation Briefly describe where each of the following features is found in the earth s general
Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class) 1. General Circulation Briefly describe where each of the following features is found in the earth s general
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream
 Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
SEVERE WEATHER AND FRONTS TAKE HOME QUIZ
 1. Most of the hurricanes that affect the east coast of the United States originally form over the A) warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean in summer B) warm land of the southeastern United States in summer
1. Most of the hurricanes that affect the east coast of the United States originally form over the A) warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean in summer B) warm land of the southeastern United States in summer
ANSWER KEY. Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map. Lab 12 Answer Key. Explorations in Meteorology 54
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology. Lecture 8: September 16, AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2)
 MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology Lecture 8: September 16, 2010 AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2) Identifying a cold front on a surface weather map: 1. Surface front is located at the leading edge
MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology Lecture 8: September 16, 2010 AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2) Identifying a cold front on a surface weather map: 1. Surface front is located at the leading edge
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts. Lecture 12 AOS 101
 Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Guided Notes Weather. Part 2: Meteorology Air Masses Fronts Weather Maps Storms Storm Preparation
 Guided Notes Weather Part 2: Meteorology Air Masses Fronts Weather Maps Storms Storm Preparation The map below shows North America and its surrounding bodies of water. Country borders are shown. On the
Guided Notes Weather Part 2: Meteorology Air Masses Fronts Weather Maps Storms Storm Preparation The map below shows North America and its surrounding bodies of water. Country borders are shown. On the
Chapter 12 Fronts & Air Masses
 Chapter overview: Anticyclones or highs Air Masses o Classification o Source regions o Air masses of North America Fronts o Stationary fronts o Cold fronts o Warm fronts o Fronts and the jet stream o Frontogenesis
Chapter overview: Anticyclones or highs Air Masses o Classification o Source regions o Air masses of North America Fronts o Stationary fronts o Cold fronts o Warm fronts o Fronts and the jet stream o Frontogenesis
Fronts. Direction of Front
 Fronts Direction of Front Direction of Front Warm Front A cold air mass meets and displaces a warm air mass. Because the moving cold air is more dense, it moves under the less-dense warm air, pushing it
Fronts Direction of Front Direction of Front Warm Front A cold air mass meets and displaces a warm air mass. Because the moving cold air is more dense, it moves under the less-dense warm air, pushing it
Heavy rains and precipitable water anomalies August 2010 By Richard H. Grumm And Jason Krekeler National Weather Service State College, PA 16803
 Heavy rains and precipitable water anomalies 17-19 August 2010 By Richard H. Grumm And Jason Krekeler National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rain fell over the Gulf States,
Heavy rains and precipitable water anomalies 17-19 August 2010 By Richard H. Grumm And Jason Krekeler National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rain fell over the Gulf States,
True or false: The atmosphere is always in hydrostatic balance. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A complex winter storm brought snow, sleet, and freezing rain to central Pennsylvania.
Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A complex winter storm brought snow, sleet, and freezing rain to central Pennsylvania.
ESCI 1010 Lab 6 Midlatitude Cyclones and Thunderstorms
 ESCI 1010 Lab 6 Midlatitude Cyclones and Thunderstorms Before Lab: Review pages 244-324 in your Weather and Climate textbook. Pay special attention to the sections entitled Fronts, Life Cyclone of a Midlatitude
ESCI 1010 Lab 6 Midlatitude Cyclones and Thunderstorms Before Lab: Review pages 244-324 in your Weather and Climate textbook. Pay special attention to the sections entitled Fronts, Life Cyclone of a Midlatitude
- air masses. Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book. Outline. - air masses of the world and of N. America. - fronts: warm, cold and occluded
 (1 of 10) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - air masses - air masses of the world and of N. America - fronts: warm, cold and occluded (2 of 10) Previously, Introduction We discussed
(1 of 10) Further Reading: Chapter 08 of the text book Outline - air masses - air masses of the world and of N. America - fronts: warm, cold and occluded (2 of 10) Previously, Introduction We discussed
A Cyclogenesis south of the Alps. Manfred Kurz Neustadt/Weinstraße
 A Cyclogenesis south of the Alps Manfred Kurz Neustadt/Weinstraße A cyclogenesis south of the Alps Surface maps 06-11-99, 00 UTC The occluded frontal system of a quasi-stationary low above the North Sea
A Cyclogenesis south of the Alps Manfred Kurz Neustadt/Weinstraße A cyclogenesis south of the Alps Surface maps 06-11-99, 00 UTC The occluded frontal system of a quasi-stationary low above the North Sea
AIR MASSES. Large bodies of air. SOURCE REGIONS areas where air masses originate
 Large bodies of air AIR MASSES SOURCE REGIONS areas where air masses originate Uniform in composition Light surface winds Dominated by high surface pressure The longer the air mass remains over a region,
Large bodies of air AIR MASSES SOURCE REGIONS areas where air masses originate Uniform in composition Light surface winds Dominated by high surface pressure The longer the air mass remains over a region,
4/29/2011. Mid-latitude cyclones form along a
 Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
Weather Related Factors of the Adelaide floods ; 7 th to 8 th November 2005
 Weather Related Factors of the Adelaide floods ; th to th November 2005 Extended Abstract Andrew Watson Regional Director Bureau of Meteorology, South Australian Region 1. Antecedent Weather 1.1 Rainfall
Weather Related Factors of the Adelaide floods ; th to th November 2005 Extended Abstract Andrew Watson Regional Director Bureau of Meteorology, South Australian Region 1. Antecedent Weather 1.1 Rainfall
Fronts in November 1998 Storm
 Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
TROPICAL STORM HARVEY BRIEFING
 TROPICAL STORM HARVEY BRIEFING 10:00 AM CDT Sunday, August 27, 2017 Prepared by: NWS LIX NWSNewOrleans www.weather.gov/neworleans Situation Overview New Information Tropical Storm Winds 40mph Immediate
TROPICAL STORM HARVEY BRIEFING 10:00 AM CDT Sunday, August 27, 2017 Prepared by: NWS LIX NWSNewOrleans www.weather.gov/neworleans Situation Overview New Information Tropical Storm Winds 40mph Immediate
Page 1. Name: 4) State the actual air pressure, in millibars, shown at Miami, Florida on the given weather map.
 Name: Questions 1 and 2 refer to the following: A partial station model and meteorological conditions table, as reported by the weather bureau in the city of Oswego, New York, are shown below. 1) Using
Name: Questions 1 and 2 refer to the following: A partial station model and meteorological conditions table, as reported by the weather bureau in the city of Oswego, New York, are shown below. 1) Using
b. The boundary between two different air masses is called a.
 NAME Earth Science Weather WebQuest Part 1. Air Masses 1. Find out what an air mass is. http://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/airmasses.html a. What is an air mass? An air mass is b. The boundary
NAME Earth Science Weather WebQuest Part 1. Air Masses 1. Find out what an air mass is. http://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/airmasses.html a. What is an air mass? An air mass is b. The boundary
RR#4 - Multiple Choice
 1. The map below shows the amount of snowfall, in inches, produced by a lake-effect snowstorm in central New York State. The wind that produced this snowfall pattern most likely came from the 1) northeast
1. The map below shows the amount of snowfall, in inches, produced by a lake-effect snowstorm in central New York State. The wind that produced this snowfall pattern most likely came from the 1) northeast
THE DEEPENING OF A LOW-LEVEL TROUGH AS INDICATED BY DUST ALOFT IN GOES ' INFRARED PICTURES
 REFERENCES Baughman, R. G., and C. W. Schmid, Jr.: Lightning Storm Characteristics. U.S. Service, Intermountain Forest and Range ment Station, Research Paper in press. Davis, L. S., and R. W. Cooper, 1963:
REFERENCES Baughman, R. G., and C. W. Schmid, Jr.: Lightning Storm Characteristics. U.S. Service, Intermountain Forest and Range ment Station, Research Paper in press. Davis, L. S., and R. W. Cooper, 1963:
TFS WEATHER BRIEF. Monday, March 25
 TFS WEATHER BRIEF Monday, March 25 Review: The leading edge of cooler and drier air was pushing through Central and East TX this morning. A few lingering thunderstorms were in progress south of I-20 in
TFS WEATHER BRIEF Monday, March 25 Review: The leading edge of cooler and drier air was pushing through Central and East TX this morning. A few lingering thunderstorms were in progress south of I-20 in
Observation Homework Due 11/24. Previous Lecture. Midlatitude Cyclones
 Lecture 21 Midlatitude Cyclones Observation Homework Due 11/24 1 2 Midlatitude Cyclones Midlatitude Cyclone or Winter Storm Cyclogenesis Energy Source Life Cycle Air Streams Vertical Structure Storm Hazards
Lecture 21 Midlatitude Cyclones Observation Homework Due 11/24 1 2 Midlatitude Cyclones Midlatitude Cyclone or Winter Storm Cyclogenesis Energy Source Life Cycle Air Streams Vertical Structure Storm Hazards
Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns. Meteorology
 Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns Meteorology Weather is what conditions of the atmosphere are over a short period of time. Climate is how the atmosphere "behaves" over long periods
Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns Meteorology Weather is what conditions of the atmosphere are over a short period of time. Climate is how the atmosphere "behaves" over long periods
and 24 mm, hPa lapse rates between 3 and 4 K km 1, lifted index values
 3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
air masses and Fronts 2013.notebook January 29, 2013
 1/4/12 Notes 1 Weather Data Log.docx 2 Air Masses Uniform bodies of air An air mass is a large body of air that has similar temperature and moisture throughout. How to name an air mass: first write the
1/4/12 Notes 1 Weather Data Log.docx 2 Air Masses Uniform bodies of air An air mass is a large body of air that has similar temperature and moisture throughout. How to name an air mass: first write the
L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment
 Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 18, 2017 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP,
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 18, 2017 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sroot@weatherbank.com MARCH 2017 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average contiguous
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 18, 2017 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sroot@weatherbank.com MARCH 2017 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average contiguous
September 2005 Climate Summary
 Ashley Brooks (765) 494-6574 Oct 5, 2005 http://iclimate.org September 2005 Climate Summary September 1-7 A cold front came through on the 1 st of the month, however little moisture was associated with
Ashley Brooks (765) 494-6574 Oct 5, 2005 http://iclimate.org September 2005 Climate Summary September 1-7 A cold front came through on the 1 st of the month, however little moisture was associated with
Refer to Figure 1 and what you have learned so far in this course when responding to the following:
 Refer to Figure 1 and what you have learned so far in this course when responding to the following: 1.Looking down on a Northern Hemisphere extratropical cyclone, surface winds blow [(clockwise and outward)(counterclockwise
Refer to Figure 1 and what you have learned so far in this course when responding to the following: 1.Looking down on a Northern Hemisphere extratropical cyclone, surface winds blow [(clockwise and outward)(counterclockwise
Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses
 Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
What a Hurricane Needs to Develop
 Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
5. Which type of front is represented by letter X?
 Name Weather Regents Review ased your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the four weather station models,,,, and D, below. D 82 012 56 999 78 978 32 002 62 75 24 1. List the letters of the four station
Name Weather Regents Review ased your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the four weather station models,,,, and D, below. D 82 012 56 999 78 978 32 002 62 75 24 1. List the letters of the four station
2011 Year in Review TORNADOES
 2011 Year in Review The year 2011 had weather events that will be remembered for a long time. Two significant tornado outbreaks in April, widespread damage and power outages from Hurricane Irene in August
2011 Year in Review The year 2011 had weather events that will be remembered for a long time. Two significant tornado outbreaks in April, widespread damage and power outages from Hurricane Irene in August
May 2005 Climate Summary
 Ashley Brooks (765) 494-6574 Jun 7, 2005 http://iclimate.org May 2005 Climate Summary May 1-5 Early May was characterized by an upper-level trough that was in place over Indiana that brought in very cool
Ashley Brooks (765) 494-6574 Jun 7, 2005 http://iclimate.org May 2005 Climate Summary May 1-5 Early May was characterized by an upper-level trough that was in place over Indiana that brought in very cool
ERTH 365 Homework #2: Hurricane Harvey. 100 points
 ERTH 365 Homework #2: Hurricane Harvey 100 points Due by 6pm, Tuesday 30 October 2018, ELECTRONIC SUBMISSON BY EMAIL ONLY BY 6PM (send to klevey@sfsu.edu) (acceptable formats: MS Word, Google Doc, plain
ERTH 365 Homework #2: Hurricane Harvey 100 points Due by 6pm, Tuesday 30 October 2018, ELECTRONIC SUBMISSON BY EMAIL ONLY BY 6PM (send to klevey@sfsu.edu) (acceptable formats: MS Word, Google Doc, plain
Hurricanes. Hurricanes are large, tropical storm systems that form and develop over the warm waters near the equator.
 Hurricanes Hurricanes are large, tropical storm systems that form and develop over the warm waters near the equator. They are responsible for weather that can devastate entire communities: Heavy rain --
Hurricanes Hurricanes are large, tropical storm systems that form and develop over the warm waters near the equator. They are responsible for weather that can devastate entire communities: Heavy rain --
Weather Unit Part 2: Meteorology
 Name: Earth Science Date: Period: Weather Unit Part 2: Meteorology 1 The map below shows North America and its surrounding bodies of water. Country borders are shown. On the map, label the following locations:
Name: Earth Science Date: Period: Weather Unit Part 2: Meteorology 1 The map below shows North America and its surrounding bodies of water. Country borders are shown. On the map, label the following locations:
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
 http://www.ssec.wisc.edu/data/composites.html Red curve: Incoming solar radiation Blue curve: Outgoing infrared radiation. Three-cell model of general circulation Mid-latitudes: 30 to 60 latitude MID-LATITUDES
http://www.ssec.wisc.edu/data/composites.html Red curve: Incoming solar radiation Blue curve: Outgoing infrared radiation. Three-cell model of general circulation Mid-latitudes: 30 to 60 latitude MID-LATITUDES
Air Masses and Fronts II
 Air Masses and Fronts II Brief review An air mass is a large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are fairly similar in any horizontal direction Source regions for air masses tend to
Air Masses and Fronts II Brief review An air mass is a large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are fairly similar in any horizontal direction Source regions for air masses tend to
Summary of November Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge
 Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 19 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 19 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 19 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Earth Science, 11e. Weather Patterns and Severe Storms Chapter 19. Air masses. A cold Canadian air mass Figure Air masses. Air masses 9/5/2012
 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 19 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 19 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox
 Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Transient and Eddy. Transient/Eddy Flux. Flux Components. Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance. Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean
 Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Weather and Climate of the Rogue Valley By Gregory V. Jones, Ph.D., Southern Oregon University
 Weather and Climate of the Rogue Valley By Gregory V. Jones, Ph.D., Southern Oregon University The Rogue Valley region is one of many intermountain valley areas along the west coast of the United States.
Weather and Climate of the Rogue Valley By Gregory V. Jones, Ph.D., Southern Oregon University The Rogue Valley region is one of many intermountain valley areas along the west coast of the United States.
Middle-Latitude Cyclone
 Middle-Latitude Cyclone What is a mid-latitude cyclone? - The mid-latitude cyclone is a synoptic scale low pressure system that has cyclonic (counter-clockwise in northern hemisphere) flow that is found
Middle-Latitude Cyclone What is a mid-latitude cyclone? - The mid-latitude cyclone is a synoptic scale low pressure system that has cyclonic (counter-clockwise in northern hemisphere) flow that is found
Lecture 14. Extratropical Cyclones extratropical cyclone
 Lecture 14. Extratropical Cyclones In mid-latitudes, much of our weather is associated with a particular kind of storm, the extratropical cyclone Cyclone: circulation around low pressure center Some midwesterners
Lecture 14. Extratropical Cyclones In mid-latitudes, much of our weather is associated with a particular kind of storm, the extratropical cyclone Cyclone: circulation around low pressure center Some midwesterners
Air Masses of North America cp and ca air masses Air mass characterized by very cold and dry conditions
 Chapter 8: Air Masses, Fronts, and Middle-Latitude Cyclones Air masses Fronts Middle-latitude cyclones Air Masses Air mass an extremely large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are
Chapter 8: Air Masses, Fronts, and Middle-Latitude Cyclones Air masses Fronts Middle-latitude cyclones Air Masses Air mass an extremely large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are
Thanksgiving Snow and Arctic Front 25 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16801
 Thanksgiving Snow and Arctic Front 25 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION An approaching arctic front brought light snow to most of western
Thanksgiving Snow and Arctic Front 25 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION An approaching arctic front brought light snow to most of western
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains
 Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Snapshot of Seeding Operations. Number of Flares (total) 2 August 1.0 2H, 0G Rio Grande de Loiza 13:07 2 August 0.6 0H, 0G Reconnaissance 16:10
 9..25 Monthly Report August 25 Project Puerto Rico Cloud Seeding Program Project Manager Gary L. Walker 9 missions this month 8:48 flight time this month 6 this month this month Snapshot of Seeding Operations
9..25 Monthly Report August 25 Project Puerto Rico Cloud Seeding Program Project Manager Gary L. Walker 9 missions this month 8:48 flight time this month 6 this month this month Snapshot of Seeding Operations
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017)
 UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for November 2017 1.1 In November 2017, Southeast Asia experienced inter-monsoon conditions in the first
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for November 2017 1.1 In November 2017, Southeast Asia experienced inter-monsoon conditions in the first
Warm Up Vocabulary Check
 Warm Up Vocabulary Check Surface current Coriolis Effect global winds upwelling Gulf Stream deep current climate El Nino convection current continental deflection 1.The apparent curving of the path of
Warm Up Vocabulary Check Surface current Coriolis Effect global winds upwelling Gulf Stream deep current climate El Nino convection current continental deflection 1.The apparent curving of the path of
National Meteorological Library and Archive
 National Meteorological Library and Archive Fact sheet No. 4 Climate of the United Kingdom Causes of the weather in the United Kingdom The United Kingdom lies in the latitude of predominately westerly
National Meteorological Library and Archive Fact sheet No. 4 Climate of the United Kingdom Causes of the weather in the United Kingdom The United Kingdom lies in the latitude of predominately westerly
January 2008 Climate Summary
 Joseph Mays (765) 494-6574 Feb 5, 2008 http://www.iclimate.org Summary January 2008 Climate Summary January was a mix bag of conditions, with an oscillatory pattern developing. We experienced phases of
Joseph Mays (765) 494-6574 Feb 5, 2008 http://www.iclimate.org Summary January 2008 Climate Summary January was a mix bag of conditions, with an oscillatory pattern developing. We experienced phases of
Current Weather Studies 4 TEMPERATURE AND AIR MASS ADVECTION
 CWS 4-1 SP19 Current Weather Studies 4 TEMPERATURE AND AIR MASS ADVECTION Reference: Chapter 4 in the Weather Studies textbook. Complete the introductory and other appropriate sections of Investigations
CWS 4-1 SP19 Current Weather Studies 4 TEMPERATURE AND AIR MASS ADVECTION Reference: Chapter 4 in the Weather Studies textbook. Complete the introductory and other appropriate sections of Investigations
Weather Practice. 4. As wind velocity decreases, the distance between isobars on a weather map will A) decrease B) increase C) remain the same
 1. The chart below shows the air temperature and the dewpoint temperature near the ground at a given location for four consecutive days. All temperatures were recorded at noon. Which statement is best
1. The chart below shows the air temperature and the dewpoint temperature near the ground at a given location for four consecutive days. All temperatures were recorded at noon. Which statement is best
The Pennsylvania Observer
 The Pennsylvania Observer April 2, 2009 March 2009 Pennsylvania Weather Recap Prepared by Curt Harpster For the month of March the saying, In like a lion and out like a lamb really fit the pattern quite
The Pennsylvania Observer April 2, 2009 March 2009 Pennsylvania Weather Recap Prepared by Curt Harpster For the month of March the saying, In like a lion and out like a lamb really fit the pattern quite
4. Which map best represents the type of fronts and direction of movement of these fronts in relation to the low-pressure center?
 1. Adjacent water and landmasses are heated by the morning Sun on a clear, calm day. After a few hours, a surface wind develops. Which map best represents this wind's direction? 2. An air pressure of 29.47
1. Adjacent water and landmasses are heated by the morning Sun on a clear, calm day. After a few hours, a surface wind develops. Which map best represents this wind's direction? 2. An air pressure of 29.47
A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time
 WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
Global Wind Patterns
 Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
CASE STUDY OF THE NOVEMBER WINDSTORM IN SOUTH CENTRAL COLORADO
 32 CASE STUDY OF THE 12-13 NOVEMBER WINDSTORM IN SOUTH CENTRAL COLORADO Paul Wolyn * NOAA/NWS Pueblo, CO 1. INTRODUCTION During the evening and early morning of 12-13 November 2011, a damaging downslope
32 CASE STUDY OF THE 12-13 NOVEMBER WINDSTORM IN SOUTH CENTRAL COLORADO Paul Wolyn * NOAA/NWS Pueblo, CO 1. INTRODUCTION During the evening and early morning of 12-13 November 2011, a damaging downslope
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #1 Page 1 of 7
 1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY. Metr Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts. Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation.
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 356.01 Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Figure 1. Surface Chart for 1500Z 7 September 2007 1 1. Pressure
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 356.01 Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Figure 1. Surface Chart for 1500Z 7 September 2007 1 1. Pressure
3A.4 AN ANALYSIS OF THE ELEVATED MIXED LAYER DURING THE SUPER TUESDAY OUTBREAK
 3A.4 AN ANALYSIS OF THE ELEVATED MIXED LAYER DURING THE SUPER TUESDAY OUTBREAK Christina C. Crowe* & John R. Mecikalski University of Alabama - Huntsville, Huntsville, Alabama 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Elevated
3A.4 AN ANALYSIS OF THE ELEVATED MIXED LAYER DURING THE SUPER TUESDAY OUTBREAK Christina C. Crowe* & John R. Mecikalski University of Alabama - Huntsville, Huntsville, Alabama 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Elevated
Meteorology 311. General Circulation/Fronts Fall 2017
 Meteorology 311 General Circulation/Fronts Fall 2017 Precipitation Types Rain Snow growth of ice crystals through deposition, accretion, and aggregation. Freezing Rain Rain freezes when it hits the surface.
Meteorology 311 General Circulation/Fronts Fall 2017 Precipitation Types Rain Snow growth of ice crystals through deposition, accretion, and aggregation. Freezing Rain Rain freezes when it hits the surface.
Weather Systems Study Guide:
 Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
also known as barometric pressure; weight of the air above the surface of the earth; measured by a barometer air pressure, high
 Weather Vocabulary Vocabulary Term Meaning/Definition air mass * large bodies of air that have the similar properties throughout such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure; causes most of the weather
Weather Vocabulary Vocabulary Term Meaning/Definition air mass * large bodies of air that have the similar properties throughout such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure; causes most of the weather
National Meteorological Library and Archive
 National Meteorological Library and Archive Fact sheet No. 4 Climate of the United Kingdom Causes of the weather in the United Kingdom The United Kingdom lies in the latitude of predominately westerly
National Meteorological Library and Archive Fact sheet No. 4 Climate of the United Kingdom Causes of the weather in the United Kingdom The United Kingdom lies in the latitude of predominately westerly
July 2007 Climate Summary
 Dan Bowman (765) 494-6574 Sep 3, 2007 http://www.iclimate.org Summary July 2007 Climate Summary The month of July ended as a very unusual month. Many events occurred during the month of July that is not
Dan Bowman (765) 494-6574 Sep 3, 2007 http://www.iclimate.org Summary July 2007 Climate Summary The month of July ended as a very unusual month. Many events occurred during the month of July that is not
Background: What is Weather?
 Weather Maps Background: What is Weather? Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere. The interaction of three important factors result in weather systems: air temperature, air pressure, and the
Weather Maps Background: What is Weather? Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere. The interaction of three important factors result in weather systems: air temperature, air pressure, and the
Hurricanes. April 14, 2009
 Tropical Weather & Hurricanes Chapter 15 April 14, 2009 Tropical meteorology Tropics characterized by seasonal wet and drier periods- wet when sun is nearly overhead at noon and inter-tropical convergence
Tropical Weather & Hurricanes Chapter 15 April 14, 2009 Tropical meteorology Tropics characterized by seasonal wet and drier periods- wet when sun is nearly overhead at noon and inter-tropical convergence
Type of storm viewed by Spotter A Ordinary, multi-cell thunderstorm. Type of storm viewed by Spotter B Supecell thunderstorm
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
NWS FORM E-5 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE HSA OFFICE:
 NWS FORM E-5 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE HSA OFFICE: NOAA, NATIONAL WEATHER SERVICE MONTHLY REPORT OF RIVER AND FLOOD CONDITIONS DATE: TO: North Webster, IN REPORT FOR (MONTH &YEAR): July 1998 August 5,
NWS FORM E-5 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE HSA OFFICE: NOAA, NATIONAL WEATHER SERVICE MONTHLY REPORT OF RIVER AND FLOOD CONDITIONS DATE: TO: North Webster, IN REPORT FOR (MONTH &YEAR): July 1998 August 5,
Investigation 11.3 Weather Maps
 Name: Date: Investigation 11.3 Weather Maps What can you identify weather patterns based on information read on a weather map? There have been some amazing technological advancements in the gathering and
Name: Date: Investigation 11.3 Weather Maps What can you identify weather patterns based on information read on a weather map? There have been some amazing technological advancements in the gathering and
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
August 2006 Summary. August 1-5
 Ashley Brooks (765) 494-6574 Sep 8, 2006 http://www.iclimate.org August 1-5 August 2006 Summary The heat wave that started during the end of July continued into the beginning parts of August with temperatures
Ashley Brooks (765) 494-6574 Sep 8, 2006 http://www.iclimate.org August 1-5 August 2006 Summary The heat wave that started during the end of July continued into the beginning parts of August with temperatures
Minor Winter Flooding Event in northwestern Pennsylvania January 2017
 1. Overview Minor Winter Flooding Event in northwestern Pennsylvania 12-13 January 2017 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A combination of snow melt, frozen ground, and areas
1. Overview Minor Winter Flooding Event in northwestern Pennsylvania 12-13 January 2017 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A combination of snow melt, frozen ground, and areas
HEAVY THUNDERSTORMS OVER SOUTH AND CENTRAL MISSISSIPPI, Monday, July 7, 1980
 Volume 7 Number 2 Severe Weather HEAVY THUNDERSTORMS OVER SOUTH AND CENTRAL MISSISSIPPI, Monday, July 7, 1980 Russell L. Pfost (1) Weather Service Forecast Office Jackson, Mississippi 39208 ABSTRACT An
Volume 7 Number 2 Severe Weather HEAVY THUNDERSTORMS OVER SOUTH AND CENTRAL MISSISSIPPI, Monday, July 7, 1980 Russell L. Pfost (1) Weather Service Forecast Office Jackson, Mississippi 39208 ABSTRACT An
THREE LATE SPRING FRONTS IN THE CARIBBEAN by W. K. Henry Texas A&M University College Station, TX
 NATONAL WEATHER DGEST THREE LATE SPRNG FRONTS N THE CARBBEAN by W. K. Henry Texas A&M University College Station, TX ABSTRACT The analysis and weather of three late-spring fronts in the western Caribbean
NATONAL WEATHER DGEST THREE LATE SPRNG FRONTS N THE CARBBEAN by W. K. Henry Texas A&M University College Station, TX ABSTRACT The analysis and weather of three late-spring fronts in the western Caribbean
Bill Kappel. Doug Hultstrand. Applied Weather Associates
 Cool-Season PMP/PMF Meteorological Time Series for Snow Melt Calculations Bill Kappel Senior Meteorologist/Vice President Doug Hultstrand Hydrometeorologist Applied Weather Associates www.appliedweatherassociates.com
Cool-Season PMP/PMF Meteorological Time Series for Snow Melt Calculations Bill Kappel Senior Meteorologist/Vice President Doug Hultstrand Hydrometeorologist Applied Weather Associates www.appliedweatherassociates.com
The Spring Storm of April 2007 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College PA 16803
 The Spring Storm of 13-16 April 2007 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A major spring storm struck the eastern United States from 13 through 16
The Spring Storm of 13-16 April 2007 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A major spring storm struck the eastern United States from 13 through 16
A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at different times in August.
 Name: 1) Which weather station model indicates the highest relative humidity? 8605-1 - Page 1 A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at
Name: 1) Which weather station model indicates the highest relative humidity? 8605-1 - Page 1 A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at
Key. Name: OBJECTIVES
 Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated,
Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated,
Divergence, Spin, and Tilt. Convergence and Divergence. Midlatitude Cyclones. Large-Scale Setting
 Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
WEATHER. rain. thunder. The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning.
 WEATHER rain thunder The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning. rainbow lightning hurricane They are intense storms with swirling winds up to 150 miles per hour. tornado cold front warm front
WEATHER rain thunder The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning. rainbow lightning hurricane They are intense storms with swirling winds up to 150 miles per hour. tornado cold front warm front
THE type of sounding that is characteristic
 VOL. 39, No. 4, APRIL, 1958 195 Tornado Proximity Soundings ROBERT G. BEEBE U. S. Weather Bureau, Kansas City, Missouri (Manuscript received 12 March 1957) ABSTRACT Soundings near the time and site of
VOL. 39, No. 4, APRIL, 1958 195 Tornado Proximity Soundings ROBERT G. BEEBE U. S. Weather Bureau, Kansas City, Missouri (Manuscript received 12 March 1957) ABSTRACT Soundings near the time and site of
