Weather Practice. 4. As wind velocity decreases, the distance between isobars on a weather map will A) decrease B) increase C) remain the same
|
|
|
- Ronald Lawrence
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. The chart below shows the air temperature and the dewpoint temperature near the ground at a given location for four consecutive days. All temperatures were recorded at noon. Which statement is best supported by the data? A) Relative humidity was highest on day 1. B) The greatest amount of water vapor was in the atmosphere on day 2. C) The base level for cloud formation was highest on day 3. D) The chance of precipitation was greatest on day As the dewpoint temperature of a sample of air decreases, the amount of moisture in that sample of air A) decreases B) increases C) remains the same 3. The dewpoint changes most directly as a result of changes in the atmosphere's A) pressure B) wind direction C) convection currents D) water vapor content 4. As wind velocity decreases, the distance between isobars on a weather map will A) decrease B) increase C) remain the same
2 5. The map below shows high-pressure and low-pressure weather systems in the United States. Which two lettered positions on the map are most likely receiving precipitation? A) A and B B) B and D C) C and E D) A and D
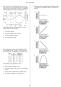
3 6. Which map below shows the most likely storm track for a hurricane in the Atlantic Ocean? A) B) C)
4 D) 7. The diagram below shows the isolines of air pressure around a low-pressure center. On which side of the low-pressure center will the wind speed be greatest? A) north B) south C) east D) west
5 Base your answers to questions 8 and 9 on the weather map below, which shows a low-pressure system over the central United States. Isobars are labeled in millibars. Points A, B, C, and D represent locations on Earth's surface. 8. Which location is most likely experiencing the fastest wind speed? A) A B) B C) C D) D 9. The air pressure at the center of this low is A) 991 mb B) 994 mb C) 997 mb D) 1001 mb 10. How many joules of heat energy must be added to 5 grams of liquid water to change its temperature from 10 C to 30 C? A) 83.6 joules B) 100 joules C) joules D) 418 joules
6 11. The diagram below represents an aneroid barometer that shows the air pressure, in inches of mercury. When converted to millibars, this air pressure is equal to A) mb B) mb C) mb D) mb 12. Which weather condition most directly determines wind speeds at Earth s surface? A) visibility changes B) amount of cloud cover C) air-pressure gradient D) dewpoint differences
7 13. A weather instrument is shown below. Weather Practice Which weather variable is measured by this instrument? A) wind speed B) precipitation C) cloud cover D) air pressure Base your answers to questions 14 through 16 on the graph below which shows variations in Earth's monthly temperatures from normal Earth temperatures between January 1990 and January Earth's average monthly temperature for October 1990 was approximately A) 0.1ºC above normal B) 0.2ºC above normal C) 0.3ºC above normal D) 0.4ºC above normal
8 15. According to the graph, the longest time period that average Earth temperatures were warmer than normal was approximately A) 8 months B) 14 months C) 26 months D) 30 months 16. The greatest temperature variation from normal occurred during A) May 1991 B) August 1992 C) July 1993 D) March 1994 Base your answers to questions 17 and 18 on the weather map below, which shows a low-pressure system over the eastern United States. Letters A through D represent weather stations. 17. Which weather instrument was used to measure wind speed at station D? A) barometer B) thermometer C) psychrometer D) anemometer
9 18. Surface winds within this low-pressure system most likely are flowing A) toward the center in a clockwise pattern B) toward the c enter in a counterclockwise pattern C) away from the center in a clockwise pattern D) away from the center in a counterclockwise pattern
10 19. The weather map below shows the air temperatures recorded at the same time at cities across the United States. Which map correctly shows the locations of the 40 F and 50 F isotherms?
11 A) B) C) D) 20. An air pressure of 1,005 millibars is equivalent to approximately how many inches of mercury? A) B) C) D) 29.72
12 21. Which weather variable is measured by a barometer? A) dewpoint B) wind speed C) air pressure D) visibility Base your answers to questions 22 and 23 on the weather map below, which shows a low-pressure system centered near Poughkeepsie, New York. Isobars shown are measured in millibars. 22. Which city is most likely experiencing winds of the greatest velocity? A) New York City B) Binghamton C) Poughkeepsie D) Scranton 23. Surface winds are most likely blowing from A) Danbury toward New York City B) Poughkeepsie toward Scranton C) Binghamton toward Danbury D) Port Jervis toward Binghamton
13 A) B) Weather Practice 24. Which weather station model for a New York State location indicates that snow may be about to fall? C) D) 25. Wind velocity is most directly dependent on the A) gradient of the air pressure field B) value of the Coriolis effect C) moisture content of the air D) rotational velocity of the Earth 26. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? A) thermometer B) sling psychrometer C) weather satellite D) weather balloon
14 A) B) Weather Practice 27. Which graph best represents the relationship between air temperature and air density in the atmosphere? C) D) 28. Air pressure is usually highest when the air is A) warm and humid B) warm and dry C) cold and humid D) cold and dry 29. Which weather change is most likely indicated by rapidly falling air pressure? A) Humidity is decreasing. B) Temperature is decreasing. C) Skies are clearing. D) A storm is approaching.
15 30. The diagram below represents the path of visible light as it travels from air to water to air through a glass container of water. The light did not travel in a straight line because of A) convection B) scattering C) absorption D) refraction 31. An observer measured the air temperature and the dewpoint and found the difference between them to be 12 C. One hour later, the difference between the air temperature and the dewpoint was found to be 4 C. Which statement best describes the changes that were occurring? A) The relative humidity was decreasing and the chance of precipitation was decreasing. B) The relative humidity was decreasing and the chance of precipitation was increasing. C) The relative humidity was increasing and the chance of precipitation was decreasing. D) The relative humidity was increasing and the chance of precipitation was increasing.
16 Base your answers to questions 32 and 33 on the graph below, which shows the average daily precipitation for Paris, France, during an 8-year period. 32. Which days showed the greatest difference in average precipitation during this 8-year period? A) Mondays and Tuesdays B) Wednesdays and Thursdays C) Thursdays and Fridays D) Fridays and Saturdays 33. The average weekly precipitation total for Paris, France, during the 8-year period was approximately A) 13 mm/week B) 2 mm/week C) 30 mm/week D) 91 mm/week 34. A temperature of 73 Fahrenheit is approximately equal to a temperature of A) 17 Celsius B) 23 Celsius C) 26 Celsius D) 162 Celsius
17 35. Data from two weather instruments have been recorded on the graph below. Line A on the graph represents air-temperature data. Line B was plotted using the scale for variable B. Line B on the graph represents data from which weather instrument? A) thermometer B) barometer C) psychrometer D) anemometer 36. The air-pressure field map below represents a high-pressure system over the central United States. Isobars show the air pressure, in millibars. Letters A through E represent locations on Earth's surface. Between which two locations is the wind speed greatest? A) A and B B) B and C C) C and D D) D and E
18 Base your answers to questions 37 and 38 on the map below, which shows sea-level air pressure, in millibars, for a portion of the eastern coast of North America. Points A, B, C, and D are sea-level locations on Earth s surface. 37. Which weather instrument was used to measure the air pressures? A) thermometer B) wind vane C) sling psychrometer D) barometer 38. The air pressure recorded at point D was most likely A) 1014 mb B) 1012 mb C) 1010 mb D) 1006 mb
19 39. On a July afternoon in Florida, the barometric pressure is inches and falling. This reading most likely indicates A) an approaching storm B) rapidly clearing skies C) continuing fair weather D) gradually improving conditions 40. An air pressure of inches of mercury is equal to A) 996 mb B) 998 mb C) 1,002 mb D) 1,014 mb 41. The highest surface wind speeds occur when there is a A) 4-millibar air-pressure difference between two nearby locations B) 4-millibar air-pressure difference between two distant locations C) 20-millibar air-pressure difference between two nearby locations D) 20-millibar air-pressure difference between two distant locations
20 42. The diagram below shows weather instruments A and B. Which table correctly indicates the name of the weather instrument and the weather variable that it measures? A) B) C) D)
21 43. The weather map below shows isobars labeled in millibars. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. Which location was probably experiencing the highest wind speed? A) A B) B C) C D) D
22 44. The graph below shows the air temperature and dewpoint temperature at one location at four different times during one morning. At what time was the chance of precipitation the greatest? A) 1 a.m. B) 5 a.m. C) 3 a.m. D) 7 a.m. 45. As the temperature of the atmosphere at a given location increases, the air pressure will most likely A) decrease B) increase C) remain the same 46. Which weather variable can be determined by using a psychrometer? A) barometric pressure B) cloud cover C) relative humidity D) wind speed
23 Base your answers to questions 47 and 48 on the data table below, which shows the air temperature, in degrees Fahrenheit, and air pressure, in inches of mercury (Hg), recorded at a weather station in New York State from 11 a.m. to 7 p.m. on a day in September.
24 47. On the grid below, construct a line graph by plotting the data for the air temperature for each time from 11 a.m. to 7 p.m. Connect the plots with a line. The data for air pressure have been plotted. 48. State the relationship between air temperature and air pressure from 11 a.m. to 2 p.m.
25 49. Surface winds on Earth are primarily caused by differences in A) air density due to unequal heating of Earth s surface B) ocean wave heights during the tidal cycle C) rotational speeds of Earth s surface at various latitudes D) distances from the Sun during the year 50. The cartoon below shows a strong wind blowing from right to left. The wind is blowing from right to left because the region to the right has a higher A) air temperature B) air pressure C) relative humidity D) elevation 51. A barometric pressure of millibars is equal to how many inches of mercury? A) B) C) D) 30.50
26 52. In the United States, most tornadoes are classified as intense A) low-pressure funnel clouds that spin clockwise B) low-pressure funnel clouds that spin counterclockwise C) high-pressure funnel clouds that spin clockwise D) high-pressure funnel clouds that spin counterclockwise 53. A map of the United States is shown below. Weather conditions in which location would be of most interest to a person predicting the next day's weather for New York State? A) A B) B C) C D) D 54. Various weather conditions at LAX Airport in Los Angeles are shown on the station model below. What were the barometric pressure and weather conditions at the airport at the time of the observation? A) mb of pressure and smog B) mb of pressure and a clear sky C) mb of pressure and smog D) mb of pressure and a clear sky
27 55. Weather-station measurements indicate that the dewpoint temperature and air temperature are getting farther apart and that air pressure is rising. Which type of weather is most likely arriving at the station? A) a snowstorm B) a warm front C) cool, dry air D) maritime tropical air 56. Which weather variable would most likely decrease ahead of an approaching storm system? A) wind speed B) air pressure C) cloud cover D) relative humidity 57. The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period. Which graph best illustrates the probable change in air pressure during the same time period? A) B) C) D)
28 58. In a certain area the air temperature and the dewpoint temperature are approaching the same value. The air pressure is decreasing and the cloud cover is increasing. What atmospheric change is most likely occurring in this area? A) Warm, moist air is moving into the area. B) Warm, dry air is moving into the area. C) Cold, dry air is moving into the area. D) A cold front has just passed through this area. 59. Base your answer to the following question on the graph below, which shows the average yearly temperature and average yearly precipitation for Earth locations A through E. The climate indicated at location E on the graph would most likely be classified as A) cold and dry B) cold and humid C) warm and dry D) warm and humid
29 60. Which list correctly matches each instrument with the weather variable it measures? A) wind vane wind speed thermometer temperature precipitation gauge relative humidity B) wind vane wind direction thermometer dewpoint psychrometer air pressure C) barometer relative humidity anemometer cloud cover precipitation gauge probability of precipitation D) barometer air pressure anemometer wind speed psychrometer relative humidity 61. Which cross section below best shows the locations of high air pressure and low air pressure near a beach on a hot, sunny, summer afternoon? A) B) C) D)
30 A) B) Weather Practice 62. Which graph best represents the relationship between air temperature and air density in the atmosphere? C) D) 63. Which graph best represents the change in air pressure as air temperature increases at Earth's surface? A) B) C) D)
31 64. The table below shows air-pressure readings taken at two cities, in the same region of the United States, at noon on four different days. The wind speed in the region between cities A and B was probably the greatest at noon on day A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) An instrument used to measure a weather variable is shown below. Which weather variable is measured by this instrument? A) wind direction B) air pressure C) wind speed D) amount of rainfall
32 Base your answers to questions 66 and 67 on the diagram below of a weather instrument. 66. In Connecticut, which weather conditions are most likely to exist when the height of the mercury in the tube is much greater than 30 inches? A) cold, dry air with clear skies B) warm, moist air with overcast skies C) strong southerly winds with hail warnings D) a violent storm associated with the autumn season 67. Which weather variable is this instrument designed to measure? A) visibility B) relative humidity C) dewpoint temperature D) air pressure
33 68. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below, which shows the air pressures and air temperatures collected by nine observers at different elevations on the same side of a high mountain. The data were collected at 12:00 noon on a clear, calm day. From sea level to an elevation of 1,200 meters, air pressure decreased at the rate of A) 1.0 mb/m B) 0.1 mb/m C) 10.0 mb/m D) mb/m
34 69. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows the location of fronts and the temperature field on a given day in the United States. Which two cities most likely have an air temperature closest to 75 F? A) Chicago and Detroit B) Los Angeles and Denver C) Oklahoma City and Memphis D) Cincinnati and Kansas City
35 Base your answers to questions 70 and 71 on the weather map below. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 70. The isolines on the map represent values of air A) density B) humidity C) pressure D) temperature 71. The strongest winds are closest to location A) A B) B C) C D) D
36 72. The cross section below shows a sea breeze blowing from the ocean toward the land. The air pressure at the land surface is 1013 millibars. The air pressure at the ocean surface a few miles from the shore is most likely A) 994 mb B) 1005 mb C) 1013 mb D) 1017 mb 73. In the diagram below, points A and B identify two points in the atmosphere above the surface of a body of water. Which graph best represents the vapor pressure (amount of moisture) from point A to point B? A) B) C) D)
37 Base your answers to questions 74 and 75 on the weather map below, which represents a low-pressure system over New York State. The L on the map represents the center of the low-pressure system. Two fronts extend from the center of the low, and are labeled front 1 and front 2. Cloud cover has been omitted from the station models. 74. The arrows on which map best represent the surface wind pattern around this low-pressure center? A) B) C) D)
38 A) B) Weather Practice 75. Which map best represents the type of fronts and direction of movement of these fronts in relation to the low-pressure center? C) D) 76. A temperature of 20 C is equal to a temperature of A) 7 F B) 36 F C) 68 F D) 293 F
39 77. The map below shows two seasonal positions of the polar front jet stream over North America. Which statement best explains why the position of the polar front jet stream varies with the seasons? A) Rising air compresses and cools in winter. B) Water heats and cools more rapidly than land in winter. C) Prevailing winds reverse direction in summer. D) The vertical rays of the Sun shift north of the equator in summer. 78. An air temperature of 30 C is equal to A) 22 F B) 2 F C) 74 F D) 86 F 79. Students wish to study the effect of elevation above sea level on air temperature and air pressure. They plan to hike in the Adirondack Mountains from Heart Lake, elevation 2,179 feet, to the peak of Mt. Marcy, elevation 5,344 feet. Which instruments should they use to collect their data? A) anemometer and psychrometer B) anemometer and barometer C) thermometer and psychrometer D) thermometer and barometer
40 80. The graph below shows the maximum possible amounts of water vapor that air can hold at different temperatures. What is the approximate maximum amount of water vapor that a cubic meter of air can hold at 20 C? A) 15 g B) 20 g C) 25 g D) 30 g 81. At which of these latitudes would average annual precipitation be greatest? A) 0º B) 30º N C) 90º N D) 90º S 82. As warm, moist air moves into a region, barometric pressure readings in the region will generally A) decrease B) increase C) remain the same
41 83. Which weather conditions are most probable when the moisture content of the air increases, resulting in a lower atmospheric pressure? A) sunny and fair B) cold and windy C) partly cloudy, with skies becoming clear D) cloudy, with a chance of precipitation 84. Earth s surface winds generally blow from regions of higher A) air temperature toward regions of lower air temperature B) air pressure toward regions of lower air pressure C) latitudes toward regions of lower latitudes D) elevations toward regions of lower elevations 85. Wind is caused mainly by air-pressure differences that result from A) uneven heating of Earth's atmosphere B) absorption of ultraviolet radiation by Earth's landmasses C) radiation of heat from Earth's landmasses to water bodies D) rotation of Earth on its axis 86. Air pressure is usually highest when the air is A) cool and humid B) cool and dry C) warm and humid D) warm and dry 87. What is the relative humidity when the dry-bulb temperature is 16 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 14 C? A) 90% B) 80% C) 14% D) 13%
42 88. Daily weather forecasts are based primarily on A) ocean currents B) seismic data C) phases of the Moon D) air-mass movements 89. A temperature of 104 F is approximately equal to A) 220 C B) 214 C C) 43 C D) 40 C 90. A weather map of New York State shows isobars that are close together, indicating a steep pressure gradient. Which weather condition is most likely present? A) dry air B) strong winds C) low temperatures D) low visibility 91. Base your answer to the following question on the graph below. The graph shows air temperature and relative humidity at a single location during a 24-hour period. What was the approximate change in relative humidity from 12 noon to 4 p.m.? A) 10% B) 15% C) 20% D) 30%
43 92. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below. The diagram shows the pattern of air movement within a closed room. If the room is considered a model of circulation in the Earth's atmosphere, at which location would air pressure be greatest? A) A B) B C) E D) F 93. Which gas in the atmosphere has the most influence on day-to-day weather changes? A) ozone B) oxygen C) water vapor D) carbon dioxide
44 94. The weather map below shows closely spaced isobars in the region of Albany, New York. At the time that the weather data were collected, Albany was most probably experiencing A) a high wind velocity B) a high temperature C) the passage of a dry air mass D) the passage of a warm air mass
45 95. The map below shows a weather variable recorded at noon on a certain day. Isolines show values from 20 to 70. Which atmospheric variable is most likely represented by the isolines on this map? A) snowfall in inches B) wind speed in knots C) barometric pressure in millibars D) air temperature in degrees Fahrenheit
46 96. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a storm system centered near the Great Lakes. Letters A through D represent weather stations shown on the map. What weather conditions are shown at location D? A) cloudy skies with light snow B) cloudy skies with freezing rain C) saturated air with no precipitation D) partly cloudy skies with rain showers 97. Which factor most directly affects the wind speed between two locations? A) air pressure B) Coriolis force C) dewpoint temperature D) cloud cover
47 98. The graph below shows the surface air pressure at a certain city during a five-day period. On which day was the warmest airmass probably over the city for the entire day? A) Monday B) Tuesday C) Wednesday D) Friday 99. Adjacent water and landmasses are heated by the morning Sun on a clear, calm day. After a few hours, a surface wind develops. Which map best represents this wind's direction? A) B) C) D)
48 A) B) Weather Practice 100. Which graph best shows the general relationship between altitude and temperature in the troposphere? C) D) 101. A high-pressure center is generally characterized by A) cool, wet weather B) cool, dry weather C) warm, wet weather D) warm, dry weather
4. Which map best represents the type of fronts and direction of movement of these fronts in relation to the low-pressure center?
 1. Adjacent water and landmasses are heated by the morning Sun on a clear, calm day. After a few hours, a surface wind develops. Which map best represents this wind's direction? 2. An air pressure of 29.47
1. Adjacent water and landmasses are heated by the morning Sun on a clear, calm day. After a few hours, a surface wind develops. Which map best represents this wind's direction? 2. An air pressure of 29.47
RR#4 - Multiple Choice
 1. The map below shows the amount of snowfall, in inches, produced by a lake-effect snowstorm in central New York State. The wind that produced this snowfall pattern most likely came from the 1) northeast
1. The map below shows the amount of snowfall, in inches, produced by a lake-effect snowstorm in central New York State. The wind that produced this snowfall pattern most likely came from the 1) northeast
Mr. Lanik Practice Test Name:
 Mr. Lanik Practice Test Name: 1. New York State s Catskills are classified as which type of landscape region? mountain plateau Adirondacks Catskills lowland plain 2. In which New York State landscape region
Mr. Lanik Practice Test Name: 1. New York State s Catskills are classified as which type of landscape region? mountain plateau Adirondacks Catskills lowland plain 2. In which New York State landscape region
ALL PRESSURE VARIABLES AND STATION MODELS MEGA PACKET
 NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A change in the type and location of large high-pressure systems (H) and large low-pressure systems ( L) over Asia creates shifts in prevailing winds that cause a rainy summer season
NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A change in the type and location of large high-pressure systems (H) and large low-pressure systems ( L) over Asia creates shifts in prevailing winds that cause a rainy summer season
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
MOISTURE IN THE ATMOSPHERE MEGA PACKET
 NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A psychrometer is used to determine which weather variables? A) wind speed and wind direction B) percentage of cloud cover and cloud height C) air pressure and air temperature D) relative
NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A psychrometer is used to determine which weather variables? A) wind speed and wind direction B) percentage of cloud cover and cloud height C) air pressure and air temperature D) relative
Name: Regents Earth Science. Weather and Climate - Review Questions
 Name: Regents Earth Science Weather and Climate - Review Questions Date: Thayer - 279 1. People sometimes release substances into the atmosphere to increase the probability of rain by A) raising the air
Name: Regents Earth Science Weather and Climate - Review Questions Date: Thayer - 279 1. People sometimes release substances into the atmosphere to increase the probability of rain by A) raising the air
Weather and Climate A B1
 Weather and Climate A B1 1. What causes the Coriolis effect? (1) Earth s tilt on its axis (2) the spin of Earth on its axis (3) the orbital motion of the Moon around Earth (4) the orbital motion of Earth
Weather and Climate A B1 1. What causes the Coriolis effect? (1) Earth s tilt on its axis (2) the spin of Earth on its axis (3) the orbital motion of the Moon around Earth (4) the orbital motion of Earth
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument.
 1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
Weather Practice Test
 Name: Weather Practice Test 1. The diagram below shows weather instruments A and B. Which table correctly indicates the name of the weather instrument and the weather variable that it measures? A) B) C)
Name: Weather Practice Test 1. The diagram below shows weather instruments A and B. Which table correctly indicates the name of the weather instrument and the weather variable that it measures? A) B) C)
Ch 7 Weather Practice Questions
 Practice Questions 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows two weather fronts moving across New York State. Lines X and Y represent frontal boundaries. The
Practice Questions 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows two weather fronts moving across New York State. Lines X and Y represent frontal boundaries. The
Weather and Energy Review
 Weather and Energy Review Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents the greenhouse effect in which heat energy is trapped in Earth's atmosphere Which type
Weather and Energy Review Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents the greenhouse effect in which heat energy is trapped in Earth's atmosphere Which type
L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment
 Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Page 1. Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period.
 Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period. Which graph best illustrates the probable change in air pressure during the same time period?
Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period. Which graph best illustrates the probable change in air pressure during the same time period?
Class Notes: Weather
 Name: Date: Period: Weather The Physical Setting: Earth Science I. Cyclonic Weather Hurricane - Hurricane Statistics Largest of all the storms Approximately per year Nearly deaths per year Saffir-Simpson
Name: Date: Period: Weather The Physical Setting: Earth Science I. Cyclonic Weather Hurricane - Hurricane Statistics Largest of all the storms Approximately per year Nearly deaths per year Saffir-Simpson
Name Period Date L.O: students will be able to describe air temperature and air pressure
 Name Period Date L.O: students will be able to describe air temperature and air pressure 1. As the altitude increases within Earth s stratosphere, air temperature generally A) decreases, only B) increases,
Name Period Date L.O: students will be able to describe air temperature and air pressure 1. As the altitude increases within Earth s stratosphere, air temperature generally A) decreases, only B) increases,
SEVERE WEATHER AND FRONTS TAKE HOME QUIZ
 1. Most of the hurricanes that affect the east coast of the United States originally form over the A) warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean in summer B) warm land of the southeastern United States in summer
1. Most of the hurricanes that affect the east coast of the United States originally form over the A) warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean in summer B) warm land of the southeastern United States in summer
7. The weather instrument below can be used to determine relative humidity.
 1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel.
 NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel. REFERENCE TABLES (Videos 8.1 & 8.2 ESRT 12, 13a, 14b) 1. Use the temperature scales on page 13. (notes-air temperature conversions) a. 80 C to F
NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel. REFERENCE TABLES (Videos 8.1 & 8.2 ESRT 12, 13a, 14b) 1. Use the temperature scales on page 13. (notes-air temperature conversions) a. 80 C to F
latent heat/humidity
 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables
 Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
also known as barometric pressure; weight of the air above the surface of the earth; measured by a barometer air pressure, high
 Weather Vocabulary Vocabulary Term Meaning/Definition air mass * large bodies of air that have the similar properties throughout such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure; causes most of the weather
Weather Vocabulary Vocabulary Term Meaning/Definition air mass * large bodies of air that have the similar properties throughout such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure; causes most of the weather
Page 1. Name: 4) State the actual air pressure, in millibars, shown at Miami, Florida on the given weather map.
 Name: Questions 1 and 2 refer to the following: A partial station model and meteorological conditions table, as reported by the weather bureau in the city of Oswego, New York, are shown below. 1) Using
Name: Questions 1 and 2 refer to the following: A partial station model and meteorological conditions table, as reported by the weather bureau in the city of Oswego, New York, are shown below. 1) Using
Atmospheric Layers. Earth s atmosphere is divided into several different atmospheric layers extending from Earth s surface outward.
 6-4.1 Compare the composition and structure of Earth s atmospheric layers (including the gases and differences in temperature and pressure within the layers). Taxonomy level: 2.6-B Understand Conceptual
6-4.1 Compare the composition and structure of Earth s atmospheric layers (including the gases and differences in temperature and pressure within the layers). Taxonomy level: 2.6-B Understand Conceptual
Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17. Weather and Climate
 Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17 Weather and Climate Prediction Old way Groundhog Color of the sky Modern way satellites instruments computers Goal Weather Factors Studied by meteorologists Several factors
Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17 Weather and Climate Prediction Old way Groundhog Color of the sky Modern way satellites instruments computers Goal Weather Factors Studied by meteorologists Several factors
3. As warm, moist air moves into a region, barometric pressure readings in the region will generally 1. decrease 2. increase 3.
 Teacher: Mr. Prizzi Castle Learning Review 1 1. Which process most directly results in cloud formation? 1. condensation 3. precipitation 2. transpiration 4. radiation 2. An air mass originating over north
Teacher: Mr. Prizzi Castle Learning Review 1 1. Which process most directly results in cloud formation? 1. condensation 3. precipitation 2. transpiration 4. radiation 2. An air mass originating over north
WEATHER. Review Note Cards
 WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
3. This room is located in a building in New York State. On which side of the building is the window located? (1) north (3) east (2) south (4) west
 1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
1. The planetary winds in Earth s Northern Hemisphere generally curve to the right due to Earth s (1) orbit around the Sun (2) spin on its axis (3) magnetic field (4) force of gravity Base your answers
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review
 Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at different times in August.
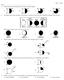 Name: 1) Which weather station model indicates the highest relative humidity? 8605-1 - Page 1 A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at
Name: 1) Which weather station model indicates the highest relative humidity? 8605-1 - Page 1 A) B) C) D) 2) The diagrams below show the phases of the Moon as viewed by an observer in New York State at
Weather Systems Study Guide:
 Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
Weather Final Review Page 1
 Weather Final Review Name 1. Which change would cause a decrease in the amount of insolation absorbed at Earths surface? A) a decrease in cloud cover B) a decrease in atmospheric transparency C) an increase
Weather Final Review Name 1. Which change would cause a decrease in the amount of insolation absorbed at Earths surface? A) a decrease in cloud cover B) a decrease in atmospheric transparency C) an increase
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars
 Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
UNIT 13: WEATHER AND CLIMATE
 UNIT 13: WEATHER AND CLIMATE After Unit 13 you should be able to: o Be able to use Selected Properties of Earth s Atmosphere, Planetary Wind and Moisture Belts in the Troposphere, Temperature, Pressure,
UNIT 13: WEATHER AND CLIMATE After Unit 13 you should be able to: o Be able to use Selected Properties of Earth s Atmosphere, Planetary Wind and Moisture Belts in the Troposphere, Temperature, Pressure,
Unit 8: Meteorology. How is Earth s weather influenced by different atmospheric variables? How can we predict weather?
 Unit 8: Meteorology How is Earth s weather influenced by different atmospheric variables? How can we predict weather? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Weather Structure of Earth s atmosphere Air Temperature
Unit 8: Meteorology How is Earth s weather influenced by different atmospheric variables? How can we predict weather? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Weather Structure of Earth s atmosphere Air Temperature
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Weather Packet 10. Your Name Group Members. Score. Minutes
 Weather Packet 10 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key idea 2 Performance Indicator: 2.1 Use the concepts of density and heat energy to explain observations of weather patterns, seasonal
Weather Packet 10 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key idea 2 Performance Indicator: 2.1 Use the concepts of density and heat energy to explain observations of weather patterns, seasonal
Weather Notes. Chapter 16, 17, & 18
 Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Solar Energy. Convection Zones. Weather Observations and Measurements
 Atmospheric Layers Atmospheric Gases Atmospheric Temperatures Atmospheric Pressure Water Cycle Precipitation Clouds Air Masses Fronts High & Low Pressure Solar Energy Convection Zones Weather Observations
Atmospheric Layers Atmospheric Gases Atmospheric Temperatures Atmospheric Pressure Water Cycle Precipitation Clouds Air Masses Fronts High & Low Pressure Solar Energy Convection Zones Weather Observations
Unit 9: Climate & Meteorology. Vocabulary
 Unit 9: Climate & Meteorology Vocabulary Weather Temperature Dew Point Relative Humidity Psychrometer Air Pressure Barometer Isobars Wind Anemometer condensation Sea Breeze Land Breeze Coriolis Effect
Unit 9: Climate & Meteorology Vocabulary Weather Temperature Dew Point Relative Humidity Psychrometer Air Pressure Barometer Isobars Wind Anemometer condensation Sea Breeze Land Breeze Coriolis Effect
Space Atmospheric Gases. the two most common gases; found throughout all the layers a form of oxygen found in the stratosphere
 Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Unit 5. Seasons and Atmosphere
 Unit 5 Seasons and Atmosphere Standard 1: Revolution Motion of a body along a path around some point in space. Earth s orbit is elliptical Earth s distance from the sun varies Perihelion Earth is closest
Unit 5 Seasons and Atmosphere Standard 1: Revolution Motion of a body along a path around some point in space. Earth s orbit is elliptical Earth s distance from the sun varies Perihelion Earth is closest
25.1 Air Masses. Section 25.1 Objectives
 Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
above the land to be warmer, causing convection currents because of the difference in air pressure.
 Name Date Period Earth Science Unit Test Review Sheet Directions: Use my web site and/or your lab book to help to answer the following questions. 1. What type of weather does a low pressure system bring?
Name Date Period Earth Science Unit Test Review Sheet Directions: Use my web site and/or your lab book to help to answer the following questions. 1. What type of weather does a low pressure system bring?
COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE
 Name Air COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE 1. What are the two most abundant gases in the atmospherere? 2. Why do you think the percentage of water vapor in the air varies? 3. Would you classify carbon dioxide
Name Air COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE 1. What are the two most abundant gases in the atmospherere? 2. Why do you think the percentage of water vapor in the air varies? 3. Would you classify carbon dioxide
Forecasts include: Temperature. Barometric (air) Pressure. Wind direction/speed Humidity
 Meteorology I Intro. to Weather 1. What is Weather? A) Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a given time and place. B) Weather changes on a regular basis. C) Meteorologists forecast weather conditions
Meteorology I Intro. to Weather 1. What is Weather? A) Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a given time and place. B) Weather changes on a regular basis. C) Meteorologists forecast weather conditions
according to and water. High atmospheric pressure - Cold dry air is other air so it remains close to the earth, giving weather.
 EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Composition of the atmosphere - Earth's atmosphere consists of nitrogen ( %), oxygen ( %), small amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, argon, krypton, ozone, neon and other gases such
EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Composition of the atmosphere - Earth's atmosphere consists of nitrogen ( %), oxygen ( %), small amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, argon, krypton, ozone, neon and other gases such
Key. Name: OBJECTIVES
 Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated,
Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated,
Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time. It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the
 Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Introduction. Sunny Partly Cloudy Cloudy. Flurries Snow Ice. Showers Thunderstorms Rain. High Pressure Low Pressure FRONTS. Cold Warm Stationary
 Introduction Weather can change from minute to minute, hour to hour, day to day, or season to season. Meteorologists are scientists who study Earth s atmosphere in order to predict these changes. Meteorologists
Introduction Weather can change from minute to minute, hour to hour, day to day, or season to season. Meteorologists are scientists who study Earth s atmosphere in order to predict these changes. Meteorologists
Weather. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left.
 Weather Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. The most dangerous aspect of a snowstorm is often the a. high winds. b. depth of snow. c. brightness.
Weather Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. The most dangerous aspect of a snowstorm is often the a. high winds. b. depth of snow. c. brightness.
Atmosphere and Weather Revision Notes
 Atmosphere and Weather Revision Notes Atmosphere The blanket of gases that surrounds the Earth is called the atmosphere. The main gases are nitrogen (78 %), oxygen (21 %), water vapour, ozone and carbon
Atmosphere and Weather Revision Notes Atmosphere The blanket of gases that surrounds the Earth is called the atmosphere. The main gases are nitrogen (78 %), oxygen (21 %), water vapour, ozone and carbon
Final Weather Unit Study Guide
 Name: Atmospheric Composition and Layers Altitude Atmosphere Composition Troposphere Air Pressure Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere Ionosphere Sample Questions: Final Weather Unit Study Guide
Name: Atmospheric Composition and Layers Altitude Atmosphere Composition Troposphere Air Pressure Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere Ionosphere Sample Questions: Final Weather Unit Study Guide
A) its rotation D) Sun, the Moon, and some stars C) an oblate sphere D) troposphere B) hydrosphere and troposphere B) less dense and more felsic
 1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its molten core 2. The Earth's actual shape
1. The Earth is slightly flattened from a perfect spherical shape because of A) its rotation B) the pull of the sun and moon C) storms on the sun's surface D) its molten core 2. The Earth's actual shape
Page 1. C) reducing the gradient of a steep hill D) planting grasses and shrubs on a hillside
 Name: 1) One result of a large volcanic eruption is that surface air temperatures decrease over a sizable region of Earth. This phenomenon occurs because volcanic eruptions usually decrease the number
Name: 1) One result of a large volcanic eruption is that surface air temperatures decrease over a sizable region of Earth. This phenomenon occurs because volcanic eruptions usually decrease the number
Tuesday, September 13, 16
 Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A.
 Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A. COLUMN A 1. a unit of atmospheric pressure 2. a line joining points of equal air pressure
Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A. COLUMN A 1. a unit of atmospheric pressure 2. a line joining points of equal air pressure
Predicting Weather Conditions. Do you have a career as a meteorologist?
 Predicting Weather Conditions Do you have a career as a meteorologist? It is essential for students for know 1. Weather conditions and patterns can be based on weather data collected from various sources.
Predicting Weather Conditions Do you have a career as a meteorologist? It is essential for students for know 1. Weather conditions and patterns can be based on weather data collected from various sources.
Name Date Hour Table. Chapter 12-AP Lesson One
 Name Date Hour Table 1. Chapter 12-AP Lesson One 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. Name Date Hour Table Directions: Answer each question to create your word bank.
Name Date Hour Table 1. Chapter 12-AP Lesson One 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. Name Date Hour Table Directions: Answer each question to create your word bank.
Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere
 14. Day Breezes H L Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere Questions Pages 177 179 1. (3) 2. (4) 3. (4) 4. (3) 5. (2) 6. (3) 7. (2) 8. (2) 9. (3) 10. (1) 11. (4) 12. (2) Questions Pages 186 188 13. (3)
14. Day Breezes H L Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere Questions Pages 177 179 1. (3) 2. (4) 3. (4) 4. (3) 5. (2) 6. (3) 7. (2) 8. (2) 9. (3) 10. (1) 11. (4) 12. (2) Questions Pages 186 188 13. (3)
The Atmosphere. All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere
 The Atmosphere Structure/Layers Contains 4 major layers See E.S.R.T pg 14 o Troposphere All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere o Stratosphere Contains
The Atmosphere Structure/Layers Contains 4 major layers See E.S.R.T pg 14 o Troposphere All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere o Stratosphere Contains
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather
 Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream
 Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Global Wind Patterns
 Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Name 28-MAY-08. FA RP 1 Mr. Chase. 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of millibars?
 FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. WOW (Weather on Wheels)
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Highlights Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Highlights Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
Name: C) wind speed D) visibility 3) The diagram below represents a weather instrument.
 Name: 1) An increase in the transparency of Earth's atmosphere is often caused by A) a decrease in solar radiation B) an increase in airborne dust particles C) an increase in the duration of insolation
Name: 1) An increase in the transparency of Earth's atmosphere is often caused by A) a decrease in solar radiation B) an increase in airborne dust particles C) an increase in the duration of insolation
Week: Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: EVEN Period: Week: 28 30 Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2 O 3 E *Vocabulary *Water in the Atmosphere and Clouds Notes *Cloud Drawings
clementaged.weebly.com Name: EVEN Period: Week: 28 30 Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2 O 3 E *Vocabulary *Water in the Atmosphere and Clouds Notes *Cloud Drawings
Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period.
 Topic 8: WEATHER Workbook chapter 7 Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period. Differences in how Earth s surfaces absorb and reradiate energy from
Topic 8: WEATHER Workbook chapter 7 Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period. Differences in how Earth s surfaces absorb and reradiate energy from
In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. as waves. thermosphere
 Skills Worksheet Concept Review In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. layers of the atmosphere 2. radiation 3. conduction 4. convection 5.
Skills Worksheet Concept Review In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. layers of the atmosphere 2. radiation 3. conduction 4. convection 5.
Background: What is Weather?
 Weather Maps Background: What is Weather? Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere. The interaction of three important factors result in weather systems: air temperature, air pressure, and the
Weather Maps Background: What is Weather? Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere. The interaction of three important factors result in weather systems: air temperature, air pressure, and the
The Atmosphere. Characteristics of the Atmosphere. Section 23.1 Objectives. Chapter 23. Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science. Section 1
 The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
Chapter 18/19. Ch 18
 Chapter 18/19 Ch 18 Pressure Force of the weight of the air above At sea level: 14.7 lbs/in2 Decreases with altitude Inches of mercury (29.92 @ sea level) Barometer - instrument used to measure air pressure
Chapter 18/19 Ch 18 Pressure Force of the weight of the air above At sea level: 14.7 lbs/in2 Decreases with altitude Inches of mercury (29.92 @ sea level) Barometer - instrument used to measure air pressure
Clever Catch Weather Ball Question and Answer Sheets
 Clever Catch Weather Ball Question and Answer Sheets 1. Too much exposure to can cause skin cancer. B. Ultraviolet radiation 2. The layer of the atmosphere closest to the Earth s surface is the 3. Some
Clever Catch Weather Ball Question and Answer Sheets 1. Too much exposure to can cause skin cancer. B. Ultraviolet radiation 2. The layer of the atmosphere closest to the Earth s surface is the 3. Some
Weather Maps. The Sun s radiation produces weather on Earth.
 Sunny days give way to rainy days. Storms appear, then fade away. Howling winds become gentle breezes. At one o clock on an autumn afternoon, an outdoor thermometer reads 20 C. An hour later, the temperature
Sunny days give way to rainy days. Storms appear, then fade away. Howling winds become gentle breezes. At one o clock on an autumn afternoon, an outdoor thermometer reads 20 C. An hour later, the temperature
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns
 Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 4: Weather forecasters use advanced technologies Ch. 3 Weather Fronts and Storms Objective(s) 7.E.1.3
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 4: Weather forecasters use advanced technologies Ch. 3 Weather Fronts and Storms Objective(s) 7.E.1.3
Weather Part I- Weather Variables
 Weather Part I- Weather Variables 3-1-19 Definitions Meteorology- is the study of the atmosphere- including weather. Weather-the daily conditions of the atmosphere. It can change from time to time and
Weather Part I- Weather Variables 3-1-19 Definitions Meteorology- is the study of the atmosphere- including weather. Weather-the daily conditions of the atmosphere. It can change from time to time and
3. The map below shows an eastern portion of North America. Points A and B represent locations on the eastern shoreline.
 1. Most tornadoes in the Northern Hemisphere are best described as violently rotating columns of air surrounded by A) clockwise surface winds moving toward the columns B) clockwise surface winds moving
1. Most tornadoes in the Northern Hemisphere are best described as violently rotating columns of air surrounded by A) clockwise surface winds moving toward the columns B) clockwise surface winds moving
Chapter 12: Meteorology
 Chapter 12: Meteorology Section 1: The Causes of Weather 1. Compare and contrast weather and climate. 2. Analyze how imbalances in the heating of Earth s surface create weather. 3. Describe how and where
Chapter 12: Meteorology Section 1: The Causes of Weather 1. Compare and contrast weather and climate. 2. Analyze how imbalances in the heating of Earth s surface create weather. 3. Describe how and where
Mr. P s Science Test!
 WEATHER- 2017 Mr. P s Science Test! # Name Date 1. Draw and label a weather station model. (10 pts) 2. The is the layer of the atmosphere with our weather. 3. Meteorologists classify clouds in about different
WEATHER- 2017 Mr. P s Science Test! # Name Date 1. Draw and label a weather station model. (10 pts) 2. The is the layer of the atmosphere with our weather. 3. Meteorologists classify clouds in about different
CURRICULUM OUTLINE. DEPARTMENT: Science DATE: January, 2004
 PARAMUS ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PARAMUS, NEW JERSEY CURRICULUM OUTLINE DEPARTMENT: Science DATE: January, 2004 COURSE: The Earth s Atmosphere GRADE LEVEL: Grade 6 I. COURSE DESCRIPTION: The student will explore
PARAMUS ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PARAMUS, NEW JERSEY CURRICULUM OUTLINE DEPARTMENT: Science DATE: January, 2004 COURSE: The Earth s Atmosphere GRADE LEVEL: Grade 6 I. COURSE DESCRIPTION: The student will explore
Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12)
 Name Class Period Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12) 1. When hot and cold air meet, the hot air rises to the top. Which process causes
Name Class Period Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12) 1. When hot and cold air meet, the hot air rises to the top. Which process causes
Atmospheric Conditions Geography Notes JC-Learn. JC-Learn. Geography Notes Atmospheric Conditions. 1 P a g e
 JC-Learn Geography Notes Atmospheric Conditions 1 P a g e Atmospheric Conditions The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases surrounding the earth. It is usually referred to as air and it is constantly changing.
JC-Learn Geography Notes Atmospheric Conditions 1 P a g e Atmospheric Conditions The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases surrounding the earth. It is usually referred to as air and it is constantly changing.
Deliverable 4-2: Assessment items. Activity-oriented Quiz for Weather or Not? Investigation in Exploring the Environment
 Deliverable 4-2: Assessment items Activity-oriented Quiz for Weather or Not? Investigation in Exploring the Environment In Weather or Not? you predicted the weather using satellite images and other kinds
Deliverable 4-2: Assessment items Activity-oriented Quiz for Weather or Not? Investigation in Exploring the Environment In Weather or Not? you predicted the weather using satellite images and other kinds
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. WOW (Weather on Wheels)
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) Teacher Instructions / Answer Keys MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) Teacher Instructions / Answer Keys MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
The Atmosphere - Chapter Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Weather and Climate Review
 Weather and Climate Review STUFF YOU NEED TO KNOW and to UNDERSTAND! 1) Because water has a higher specific heat than land, water will warm and cool more slowly than the land will. Because of this: a)
Weather and Climate Review STUFF YOU NEED TO KNOW and to UNDERSTAND! 1) Because water has a higher specific heat than land, water will warm and cool more slowly than the land will. Because of this: a)
3) What is the difference between latitude and longitude and what is their affect on local and world weather and climate?
 www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
MASTERY ASSIGNMENT 2015
 Climate & Meteorology MASTERY ASSIGNMENT 2015 Directions: You must submit this document via Google Docs to lzimmerman@wcpss.net. The document must include the questions and pictures must be hand drawn
Climate & Meteorology MASTERY ASSIGNMENT 2015 Directions: You must submit this document via Google Docs to lzimmerman@wcpss.net. The document must include the questions and pictures must be hand drawn
WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program
 WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH On-Site Packet Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH WEATHER ON WHEELS ELEMENTARY ON-SITE HIGHLIGHTS PACKET
WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH On-Site Packet Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH WEATHER ON WHEELS ELEMENTARY ON-SITE HIGHLIGHTS PACKET
Science 1206 SAMPLE Test ( Weather Dynamics)
 Science 1206 SAMPLE Test ( Weather Dynamics) Name:. Part A: Multiple Choice (60%) Shade the letter of the best answer on the Scantron sheet provided. 1. Which term refers to the current atmospheric conditions?
Science 1206 SAMPLE Test ( Weather Dynamics) Name:. Part A: Multiple Choice (60%) Shade the letter of the best answer on the Scantron sheet provided. 1. Which term refers to the current atmospheric conditions?
The Causes of Weather
 Meteorology The Causes of Weather Where does the weather in our country come from? * Which air masses determine the weather in our country? * Weather or Climate? *The current state of the atmosphere *
Meteorology The Causes of Weather Where does the weather in our country come from? * Which air masses determine the weather in our country? * Weather or Climate? *The current state of the atmosphere *
Unit Three Worksheet Meteorology/Oceanography 2 WS GE U3 2
 Unit Three Worksheet Meteorology/Oceanography 2 WS GE U3 2 Name Period Section 17.3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Of the following, which is NOT a factor that controls temperature? (C) latitude (D) longitude
Unit Three Worksheet Meteorology/Oceanography 2 WS GE U3 2 Name Period Section 17.3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Of the following, which is NOT a factor that controls temperature? (C) latitude (D) longitude
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. WOW (Weather on Wheels)
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami,
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami,
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns. Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather
 Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
2. What causes these weather changes?
 Weather Table of Contents Essential Questions... 1 Vocabulary... 2 Weather Symbols... 5 Bringing the Rain to Kapiti Plain... 7 Weather Instruments... 8 Weather Forecasting... 13 Essential Questions 1.
Weather Table of Contents Essential Questions... 1 Vocabulary... 2 Weather Symbols... 5 Bringing the Rain to Kapiti Plain... 7 Weather Instruments... 8 Weather Forecasting... 13 Essential Questions 1.
Probabilistic Decision-Making and Weather Assessment
 5 Student Packet Probabilistic Decision-Making and Weather Assessment Use contents of this packet as you feel appropriate. You are free to copy and use any of the material in this lesson plan. Packet Contents
5 Student Packet Probabilistic Decision-Making and Weather Assessment Use contents of this packet as you feel appropriate. You are free to copy and use any of the material in this lesson plan. Packet Contents
