PHOTOVOLTAIC SOLAR ENERGY MODULAR TRAINER DL SOLAR-B Manual
|
|
|
- Tracy Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHOTOVOLTAIC SOLAR ENERGY MODULAR TRAINER DL SOLAR-B Manual
2 DL SOLAR-B Contents 1. Solar energy: our commitment 5 to the environment 1.1. Basic principles and concepts 6 Mechanical work, energy and power: 6 definitions, laws and units Transformation of mechanical energy 7 History of energy-conversion technology 8 Electrical energy and power: definitions 8 and units Heat energy: definitions and units Energy from the Sun Electricity directly from the Sun 15 Photovoltaic effect and photovoltaic cells: 15 history and definitions How does a photovoltaic cell work Solar energy received on land 16 surface Positioning of solar panels 16 Standard Test Conditions (STC) and its 21 aplication 1.5. Characteristics of a solar cell DL SOLAR B Basics of the Solar Trainer Identification of the components of the 26 trainer Current, voltage and power measurements 41 Exercise 1: Measuring the load current, voltage and power 2.2. Irradiation and Temperature Measurements Exercise 1: Setting the solar panel to the most irradiated position Exercise 2: Changing the inclination of the solar panel Exercise 3: Changing the azimuth of the 47 solar panel Exercise 4: Covering the solar panel with 48 different materials 2.3. Solar Irradiation throughout the 49 Day Exercise 1: Obtaining the solar irradiation 49 data 2.4. Solar Panel Voltage-Irradiation 53 Curve, Current-Irradiation Curve and Resistance of the Solar Panel Exercise 1: Obtaining the solar panel 54 voltage-irradiation curve Exercise 2: Calculating the inner 56 resistance of the solar panel 2.5. Current-Voltage Characteristics of 58 the Solar Panel Exercise 1: Obtaining the solar panel 59 current-voltage curve 2.6. Solar Panel Power Measurements 65 Exercise 1: Obtaining the solar panel 67 current-power curve Exercise 2: Overloaded solar panel 70 measurements 2.7. Using Solar Panel to Charge the 72 Battery Exercise 1: Battery charging Using Solar Panel and Battery to 75 Power DC Load Exercise 1: Supplying DC load Using Solar Panel and Battery to 78 Power AC Load Exercise 1: Supplying AC load 79 Appendix 81 Index 83
3 1 to Solar energy: our commitment the environment Basic principles and concepts Energy from the Sun Electricity directly from the Sun Solar energy received on land surface Characteristics of a solar cell
4 Basic principles and concepts Key words Mechanical work, energy and power: definitions, laws and units Mechanical energy is capacity of the body for doing work. E is the symbol used to represent energy. The SI derived unit for energy is the J (joule). 1 J = 1 Nm, where N is the SI unit for the force and m is the SI unit for the distance. Mechanical energy is the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy. E = E k + E p Kinetic energy is a form of energy that an object or a particle has due to its motion. E mv 2 k 2 v R p Gravitational potential energy is an energy that an object possesses because of its reference position (R p ) in a gravitational field. The reference position (R p ) is usually chosen to be the position of zero displacement (Figure 1.1-1). E p = mgh h reference line Mechanical work is a measure of energy transfer that occurs when an object is moved over a distance s [m] by an external force F [N] Airplane taking off from the land W = F s [J] Mechanical power is the time rate of doing mechanical work W or delivering energy E, expressible as the amount of work done W, or energy transferred, divided by the time interval t. P W t Mechanical work The SI derived unit for power is the W (watt). Another unit for measuring power, often used in automobile industry, is horsepower (HP). 1 HP = W function of machines in terms of forces and motions. Because of friction, the work, energy or power output from a machine is always lower than 6 DL SOLAR-B
5 the input energy. For this reason, the, which is the ratio of the two, is always less than 100 percent. Efficiency is the ratio of the work, energy or power output and the work, energy or power input. 1 W o o o = 100 = 100 = 100 [%] W i E E i P P i James Prescott Joule ( ) Conservation law, also called the law of conservation implies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, although it can be changed from one form (mechanical, kinetic, chemical, etc.) into another. Transformation of mechanical energy An ideal system A simple example of a system in which energy is being converted from one form to another is provided in the descending of a wagon with mass m from the top, its speed and thus its kinetic energy E k increases. At the same time gravitational potential energy E p descreses. Total sum of energy has not changed, i.e. it is constant. Applying the law of conservation and conversion of energy and assuming there is no friction in the air, Ek1+ Ep1= Ek2+ Ep2 2 2 mv1 mv2 + mgh1 = + mgh Transformation of potential to kinetic energy E mv 2 k 2 E p = mgh m [kg] - mass v m s g m - gravity acceleration s 2 h [m] - hight from zero point 1 - start 2 - end Solar energy: our commitment to the environment 7
6 1 Key words 1.4. Solar energy received on land surface Positioning of solar panels a) In northern hemisphere, solar panel should be oriented towards the south (S). b) In southern hemisphere, solar panel should be oriented towards the north (N). This is known under name of azimuth. In an ideal case, on the northern hemisphere an azimuth should be changed from south-east in the morning to south-west in the evning tracking the path of the Sun trough the day. includes both, azimuth and angle of inclination, represented by and angle of latitude below. Optimal angle of inclination (α) is equal to latitude Solar panel is positioned in point A oriented to the north on the earth surface under angle of 0, parallel with the earth surface. Sun rays target to point on the panel surface under the angle 120. This is far away from ideal angle of 90. How can we correct this value? Obviously, we have to decrese it, as shown in figure below. = Orientation from north (N) to south (S) in northern hemisphere Orientation from south (S) to north (N) in southern hemisphere Angle of inclination in fact is the latitude of a point A where the solar panel is placed Inclination and azimuth of solar panel in northern hemisphere Inclination and azimuth of solar panel in southern hemisphere. 16 DL SOLAR-B
7 Solar system. The Earth has third position from the Sun. Notice: all planets rotate around the Sun on the same plane, named plane of the Ecliptic Oscilation Earth axis around the cone. Summer on the north hemisphere. Unfortunatly, the Earth does not rotate around its axis perpendicular to the plane of the Ecliptic. Its axis is incliqhg XQGHU DQJOH RI Ȝ $YHUDJH YDOXH RI WKLV LQFOLQDWLRQ LV Earth axis is inclined under average angle of Changing of sezons through the year is due to oscilatirq RI 1 6 D[LV DURXQG WKH FRQH JXUH DQG,Q JXUH WKH IROORZLQJ VLWXDWLRQ LV REVHUYHG Sun rays target the Arctic area (N) under the angle ȕ. At the same time, the Antarctic area (S) is hiden in the shade.,q JXUH WKH VLWXDWLRQ LV H[DFWO\ WKH RSSRVLWH Sun rays target the Antarctic area (S) under the angle ȕ. At the same time, the Arctic area (N) is hiden in the shade. 7KLV IDFW FRPSOLFDWHV WKH SUHYLRXV H[SODQDWLRQ RI GH ning an optimal angle of solar panel. Fortunately, an answer is very simple. The explanation is provided on the next page. Interesting facts TDJMBUJPO &BSUI BYJT BSPVOE UIF DPOF 8JOUFS PO UIF OPSUI hemisphere. In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees (marked with ). The equator has a latitude of 0, the North pole has a latitude of 90 north (written 90 N), and the South pole has a latitude of 90 south (written 90 S). Solar energy: our commitment to the environment 17
8 1 &RPSDUH JXUHV DQG )LUVWO\ ZH FDQ QRWLFH D VLPSOH IDFW Sun rays target equator (B) under same angles, J Bs and J Bw, during the summer and winter periods. This is the explanation why we have the same weather in equatorial area in all sezons. Compare angles J As and J Aw between Earth surface and sun rays. J As < J Aw This means that the sun rays target point A under angle FORVHU WR LGHDO LQ WKH VXPPHU,Q WKH VDPH WLPH VXQ rays target point A in the winter under angle far from LGHDO Because of that, we have to correct conclusion from previous page Summer on the north hemisphere Optimal angle of inclination (α) is equal to latitude corrected with corrective angle. &RUUHFWLYH DQJOH YDOXHV DUH SURYLGHG LQ WKH WDEOH These values depend on latitude and season. &RUUHFWHG WRWDO RULHQWDWLRQ is represented by the forpxod Į ij FRUUHFWLYH DQJOH D]LPXWK Latitude WR WR WR WR DQG PRUH JOUFS PO UIF OPSUI IFNJTQIFSF Table-3 Corrective angles 18 DL SOLAR-B &RUUHFWLYH DQJOH In Winter In Summer ± ± ± ±
9 1 Example 7 - a) during the winter season Result: b) during the sommer season w corrective angle w w corrective angle s s s Interesting facts Described determination of ideal panel orientation with azimuth 180 strictly to the south on the northern hemisphere and to the north on the southern hemisphere is suitable for the panels installed on the fixed objects, for example roofs, like in example 7. Twice in the year we have to adjust angle of latitude depending on the season using values from the table 3, corrective angles. But can we determinate the orientation of moveble objects? Take a look at the picture right. From our own experience we know: The Sun heats on the best way if we turn strictly against it. Early in the morrning azimuth is less then 180 and panel is oriented almost to the east against the Sun. In the noon azimuth is equal 180 and panel is oriented strictly to the south against the Sun. Finally, in the evning, azimuth is great then 180 and panel is oriented almost to the west against the Sun. Simply, the best orientation of the panel is Solar energy: our commitment to the environment 19
10 1 R h 2 ] R i 2 ] Januar 54 February March 94 April May 158 June July August September 111 October November 54 December Annual sum 1179 Table-4 Monthly iradiation for the panel positioned horizontaly (R h ) and inclinated (R i ) Example 8 Imagine your home somewhere in Central Europe on the latitude 2 a) positioned horizontaly b) positioned under the best angle a 2 R h = 158 kwh/m 2 R i 2 a) E h b) E i c) E i E h Result: a) E h = R h a E h = 158 kwh/m 2 2 E h = 474 kwh b) E i = R i a E i 2 2 E i c) E i E h E i E h = 6 kwh Dailly sum of global irradiation per month R h - horisontaly positined panel (α = 0 ) R i - panel positined optimaly under angle of inclination (α = 36 ) 20 DL SOLAR-B
11 2 DL SOLAR B Basics of the Solar Trainer Irradiation and Temperature Measurements Solar Irradiation throughout the Day Solar Panel Voltage-Irradiation Curve, Current- Irradiation Curve and Resistance of the Solar Panel Current-Voltage Characteristics of the Solar Panel Solar Panel Power Measurements Using Solar Panel to Charge the Battery Using Solar Panel and Battery to Power DC Load Using Solar Panel and Battery to Power AC Load
12 Using Solar Panel and Battery to Power AC Load Objective of the exercise Note The following are the main characteri- Input voltage. Module DL 9013 range is V. Output voltage. Corresponding to the supply network. Power to supply Output waveform. Since DL 9013 plying circuits with inductive characteristics. Efficiency. This characteristic corresponds to the energy transfer factor and is expressed in percentages. The optimum value 100% cannot be achieved. Module DL 9013 has an efficiency close to 90%. Use both solar power and energy stored in the battery to power the AC load. Learn the application of inverters. Required equipment Solar panel, battery, protective module (DL 9014), measurement module (DL 9021), charge regulation module (DL 9012S), inverter (DL 9013), AC load module (DL 9017) Introductory examples 4. Describe the pulse-width modulation basics. 78 DL SOLAR-B
13 2 Exercise 1: Supplying AC load Connection scheme of exercise 1 1. Find the position in which the solar panel provides highest irradiation (read the azimuth using compass and inclination using the angle-me- the circuit. Using the charge regulation module DL 9012S read the voltage of the battery. Using the charge regulation module DL 9012S read the load current 6. Calculate the DC power. DL SOLAR B 79
14 2 8. Knowing input and output power to the inverter, calculate the inverter 9. Switch off the halogen lamp and switch on the LED lamp. 11. Switch on the halogen lamp. 12. Repeat points 4-8. from the circuit. Voltage (V) Load current (A) DC power (W) AC power (W) Questions for evaluation 1. Which element limits the load power that can be supplied in this exer- 80 DL SOLAR-B
15 DE LORENZO S.p.A. V. le Romagna, Rozzano (MI) Italy Tel Fax
PHOTOVOLTAIC SOLAR ENERGY TRAINER DL SOLAR-D1 Manual
 PHOTOVOLTAIC SOLAR ENERGY TRAINER DL SOLAR-D1 Manual DL SOLAR-D1 Contents 1. Solar energy: our commitment 5 to the environment 1.1. Basic principles and concepts 6 Mechanical work, energy and power: 6
PHOTOVOLTAIC SOLAR ENERGY TRAINER DL SOLAR-D1 Manual DL SOLAR-D1 Contents 1. Solar energy: our commitment 5 to the environment 1.1. Basic principles and concepts 6 Mechanical work, energy and power: 6
Exercise 6. Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE. Introduction to the importance of solar panel orientation DISCUSSION
 Exercise 6 Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will understand how the solar illumination at any location on Earth varies over the course of a year. You
Exercise 6 Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will understand how the solar illumination at any location on Earth varies over the course of a year. You
NABCEP Entry Level Exam Review Solfest practice test by Sean White
 1. A fall protection system must be in place for all work done at heights in excess of a. 4 feet b. 6 feet c. 8 feet d. 10 feet 2. A circuit breaker performs the same function a. as a fuse b. as a switch
1. A fall protection system must be in place for all work done at heights in excess of a. 4 feet b. 6 feet c. 8 feet d. 10 feet 2. A circuit breaker performs the same function a. as a fuse b. as a switch
Solar photovoltaic energy production comparison of east, west, south-facing and tracked arrays
 The Canadian Society for Bioengineering The Canadian society for engineering in agricultural, food, environmental, and biological systems. La Société Canadienne de Génie Agroalimentaire et de Bioingénierie
The Canadian Society for Bioengineering The Canadian society for engineering in agricultural, food, environmental, and biological systems. La Société Canadienne de Génie Agroalimentaire et de Bioingénierie
Practice Questions: Seasons #1
 1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
UNITED KINGDOM FOREIGN AND COMMONWEALTH OFFICE, DRAGON CAPITAL GROUP
 UNITED KINGDOM FOREIGN AND COMMONWEALTH OFFICE, DRAGON CAPITAL GROUP SOLAR OUTPUT AT PEAK TARIFF FOR DIFFERENT SLOPE AND ORIENTATION IN HOCHIMINH CITY ARTELIA Vietnam Ho Chi Minh City Office 6 Phung Khac
UNITED KINGDOM FOREIGN AND COMMONWEALTH OFFICE, DRAGON CAPITAL GROUP SOLAR OUTPUT AT PEAK TARIFF FOR DIFFERENT SLOPE AND ORIENTATION IN HOCHIMINH CITY ARTELIA Vietnam Ho Chi Minh City Office 6 Phung Khac
Earth s Orbit. Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology
 1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere 23.5 tilts away from sun) 2 Solar radiation
1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere 23.5 tilts away from sun) 2 Solar radiation
Basic information about developed Calculator for solar / wind hybrid power supply
 Basic information about developed Calculator for solar / wind hybrid power supply It simulates behavior of the system for off grid power supply (components: solar panels, wind generator, batteries and
Basic information about developed Calculator for solar / wind hybrid power supply It simulates behavior of the system for off grid power supply (components: solar panels, wind generator, batteries and
Practice Seasons Moon Quiz
 1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
Geography Class 6 Chapters 3 and
 CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
LESSON PLAN - Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels Using Soltrex Data
 LESSON PLAN - Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels Using Soltrex Data Title of Lesson: Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels Using Soltrex Data Description of class: High School physics, astronomy, or environmental
LESSON PLAN - Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels Using Soltrex Data Title of Lesson: Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels Using Soltrex Data Description of class: High School physics, astronomy, or environmental
Work and Energy. Intext Exercise 2
 Intext Exercise 1 Question 1: A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (Fig. 11.3). Let us take it that the force acts on the object through the displacement.
Intext Exercise 1 Question 1: A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (Fig. 11.3). Let us take it that the force acts on the object through the displacement.
Section 1: Overhang. Sizing an Overhang
 Section 1: Overhang A horizontal overhang is a straightforward method for shading solar glazing in summer. Passive heating strategies call for major glazed areas (solar glazing) in a building to be oriented
Section 1: Overhang A horizontal overhang is a straightforward method for shading solar glazing in summer. Passive heating strategies call for major glazed areas (solar glazing) in a building to be oriented
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER)
 L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
Exploration Phase What are the differences between these pictures?
 Light Power and seasons Exploration Phase What are the differences between these pictures? 1 Lab Activity: Lab Activity Obtain a Styrofoam ball. This will represent the earth. Stick a push pin into the
Light Power and seasons Exploration Phase What are the differences between these pictures? 1 Lab Activity: Lab Activity Obtain a Styrofoam ball. This will represent the earth. Stick a push pin into the
Daylight Data: Days and Nights Around the World
 Days & Nights 1 Name Daylight Data: Days and Nights Around the World Purpose: To investigate the number of hours of daylight received by countries at different latitudes. Materials: Daylight data sheet
Days & Nights 1 Name Daylight Data: Days and Nights Around the World Purpose: To investigate the number of hours of daylight received by countries at different latitudes. Materials: Daylight data sheet
Which Earth latitude receives the greatest intensity of insolation when Earth is at the position shown in the diagram? A) 0 B) 23 N C) 55 N D) 90 N
 1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
1. In which list are the forms of electromagnetic energy arranged in order from longest to shortest wavelengths? A) gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light B) radio waves, infrared rays, visible
Lab Activity: Climate Variables
 Name: Date: Period: Water and Climate The Physical Setting: Earth Science Lab Activity: Climate Variables INTRODUCTION:! The state of the atmosphere continually changes over time in response to the uneven
Name: Date: Period: Water and Climate The Physical Setting: Earth Science Lab Activity: Climate Variables INTRODUCTION:! The state of the atmosphere continually changes over time in response to the uneven
Seasons. What causes the seasons?
 Questions: Seasons What causes the seasons? How do we mark the progression of the seasons? What is the seasonal motion of the sun in the sky? What could cause the seasonal motion of the sun to change over
Questions: Seasons What causes the seasons? How do we mark the progression of the seasons? What is the seasonal motion of the sun in the sky? What could cause the seasonal motion of the sun to change over
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
Class IX Chapter 11 Work and Energy Science
 Class IX Chapter 11 Work and Energy Science Question 1: A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (Fig. 11.3). Let us take it that the force acts on
Class IX Chapter 11 Work and Energy Science Question 1: A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (Fig. 11.3). Let us take it that the force acts on
AME LEX-4 Solar Panels Week 2-3
 AME 20213 LEX-4 Solar Panels Week 2-3 TA: Dustin Coleman Email: dcolema4@nd.edu LEX-4 website : www.nd.edu/ dcolema4/homepage/ame 20213.html Report Due: May 3, 2011 Last Revised: April 18, 2011 Overview
AME 20213 LEX-4 Solar Panels Week 2-3 TA: Dustin Coleman Email: dcolema4@nd.edu LEX-4 website : www.nd.edu/ dcolema4/homepage/ame 20213.html Report Due: May 3, 2011 Last Revised: April 18, 2011 Overview
b. So at 12:00 p.m., are the shadows pointing in the direction you predicted? If they are not, you must explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Northern Alberta Institute of Technology
 Northern Alberta Institute of Technology Alternative Energy Program Solar Photovoltaic Reference Array Report March 31, 2016 Goals Provide solar energy system educators, installers and adopters with real
Northern Alberta Institute of Technology Alternative Energy Program Solar Photovoltaic Reference Array Report March 31, 2016 Goals Provide solar energy system educators, installers and adopters with real
PV 2012/2013. Radiation from the Sun Atmospheric effects Insolation maps Tracking the Sun PV in urban environment
 SOLAR RESOURCE Radiation from the Sun Atmospheric effects Insolation maps Tracking the Sun PV in urban environment 1 is immense Human energy use: 4.0x10 14 kwh/year on Earth s surface: 5.5x10 17 kwh/year
SOLAR RESOURCE Radiation from the Sun Atmospheric effects Insolation maps Tracking the Sun PV in urban environment 1 is immense Human energy use: 4.0x10 14 kwh/year on Earth s surface: 5.5x10 17 kwh/year
Solar resource. Radiation from the Sun Atmospheric effects Insolation maps Tracking the Sun PV in urban environment
 SOLAR RESOURCE 1 Solar resource Radiation from the Sun Atmospheric effects Insolation maps Tracking the Sun PV in urban environment 2 Solar resource Solar resource is immense Human energy use: 4.0x10 14
SOLAR RESOURCE 1 Solar resource Radiation from the Sun Atmospheric effects Insolation maps Tracking the Sun PV in urban environment 2 Solar resource Solar resource is immense Human energy use: 4.0x10 14
NCERT solution for Work and energy
 1 NCERT solution for Work and energy Question 1 A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (See below figure). Let us take it that the force acts on the
1 NCERT solution for Work and energy Question 1 A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (See below figure). Let us take it that the force acts on the
Daily Motions. Daily Motions. Solar and Sidereal Days. Annual Motions of the Sun. Coordinate system on Earth. Annual Motion of the Stars.
 Sun: rises in the east sets in the west travels on an arc across the sky 24 hours Daily Motions Solar Day = 24 hours Stars: stars travel on arcs in the sky moving from east to west. some stars rise and
Sun: rises in the east sets in the west travels on an arc across the sky 24 hours Daily Motions Solar Day = 24 hours Stars: stars travel on arcs in the sky moving from east to west. some stars rise and
March 21. Observer located at 42 N. Horizon
 March 21 Sun Observer located at 42 N Horizon 48 June 21 March 21 A 48 90 S 23.5 S 0 23.5 N 42 N 90 N Equator (June 21) C (March 21) B A 71.5 48 Horizon 24.5 Observer Sun 40 Observer Sun 22 Observer Sun
March 21 Sun Observer located at 42 N Horizon 48 June 21 March 21 A 48 90 S 23.5 S 0 23.5 N 42 N 90 N Equator (June 21) C (March 21) B A 71.5 48 Horizon 24.5 Observer Sun 40 Observer Sun 22 Observer Sun
Optimizing the Photovoltaic Solar Energy Capture on Sunny and Cloudy Days Using a Solar Tracking System
 Optimizing the Photovoltaic Solar Energy Capture on Sunny and Cloudy Days Using a Solar Tracking System Nelson A. Kelly and Thomas L. Gibson Chemical Sciences and Material Systems Laboratory General Motors
Optimizing the Photovoltaic Solar Energy Capture on Sunny and Cloudy Days Using a Solar Tracking System Nelson A. Kelly and Thomas L. Gibson Chemical Sciences and Material Systems Laboratory General Motors
Bi-annual Sun Tracking for Solar PV Module Support Structure: Study and Implementation
 16th NATIONAL POWER SYSTEMS CONFERENCE, 15th-17th DECEMBER, 2010 56 Bi-annual Sun Tracking for Solar PV Module Support Structure: Study and Implementation Prabodh Bajpai, Member IEEE, Vaishalee Dash, N.K.
16th NATIONAL POWER SYSTEMS CONFERENCE, 15th-17th DECEMBER, 2010 56 Bi-annual Sun Tracking for Solar PV Module Support Structure: Study and Implementation Prabodh Bajpai, Member IEEE, Vaishalee Dash, N.K.
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION
 ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION Unit Outline 2 What is the sun? Radiation from the sun Factors affecting solar radiation Atmospheric effects Solar radiation intensity Air mass Seasonal variations
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION Unit Outline 2 What is the sun? Radiation from the sun Factors affecting solar radiation Atmospheric effects Solar radiation intensity Air mass Seasonal variations
Name Date. What s the weather like today? Watch the beginning of the video Basics of geography- climate.
 FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE CLIMATE worksheet 1 STARTER Look at the weather symbols and answer: What s the weather like today? WHAT S CLIMATE? Watch the beginning of the video Basics of geography- climate.
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE CLIMATE worksheet 1 STARTER Look at the weather symbols and answer: What s the weather like today? WHAT S CLIMATE? Watch the beginning of the video Basics of geography- climate.
The following terms are some of the vocabulary that students should be familiar with in order to fully master this lesson.
 Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
Sunlight and its Properties Part I. EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz
 Sunlight and its Properties Part I EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz The Sun a Thermonuclear Furnace The sun is a hot sphere of gas whose internal temperatures reach over 20 million deg. K. Nuclear fusion reaction
Sunlight and its Properties Part I EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz The Sun a Thermonuclear Furnace The sun is a hot sphere of gas whose internal temperatures reach over 20 million deg. K. Nuclear fusion reaction
Physics Curriculum Map - Norwell High School SUBJECT: Physics Grade Level: 11 or 12. Month or Unit: September
 SUBJECT: Physics Grade Level: 11 or 12 Month or Unit: September Scientific Inquiry Skills Scientific literacy can be achieved as students inquire about chemical phenomena. The curriculum should include
SUBJECT: Physics Grade Level: 11 or 12 Month or Unit: September Scientific Inquiry Skills Scientific literacy can be achieved as students inquire about chemical phenomena. The curriculum should include
Experimental and Theoretical Study on the Optimal Tilt Angle of Photovoltaic Panels
 Experimental and Theoretical Study on the Optimal Tilt Angle of Photovoltaic Panels Naihong Shu* 1, Nobuhiro Kameda 2, Yasumitsu Kishida 2 and Hirotora Sonoda 3 1 Graduate School, Kyushu Kyoritsu University,
Experimental and Theoretical Study on the Optimal Tilt Angle of Photovoltaic Panels Naihong Shu* 1, Nobuhiro Kameda 2, Yasumitsu Kishida 2 and Hirotora Sonoda 3 1 Graduate School, Kyushu Kyoritsu University,
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
Seasons Quiz Please Do Not Write on this Paper Obrigado
 Seasons Quiz Please Do Not Write on this Paper Obrigado Use this diagram of the sun and Earth's path around the sun to answer the next two questions. The N indicates North and Earth is traveling from A
Seasons Quiz Please Do Not Write on this Paper Obrigado Use this diagram of the sun and Earth's path around the sun to answer the next two questions. The N indicates North and Earth is traveling from A
HEATING THE ATMOSPHERE
 HEATING THE ATMOSPHERE Earth and Sun 99.9% of Earth s heat comes from Sun But
HEATING THE ATMOSPHERE Earth and Sun 99.9% of Earth s heat comes from Sun But
Discovering the Universe for Yourself (Chapter 2) Years, Seasons, and Months: The Motions of Sun, Earth, and Moon
 Discovering the Universe for Yourself (Chapter 2) Years, Seasons, and Months: The Motions of Sun, Earth, and Moon Based on Chapter 2 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 3 and 4 on The
Discovering the Universe for Yourself (Chapter 2) Years, Seasons, and Months: The Motions of Sun, Earth, and Moon Based on Chapter 2 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 3 and 4 on The
The Celestial Sphere. Chapter 1. Constellations. Models and Science. Constellations. Diurnal vs. Annular Motion 9/16/2010
 The Celestial Sphere Chapter 1 Cycles of the Sky Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
The Celestial Sphere Chapter 1 Cycles of the Sky Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
Part I: What Time Is It? A Model of Day and Night
 Part I: What Time Is It? A Model of Day and Night Find a place in a circle around the lamp where no one is between you and the lamp. Once you face the lamp, answer questions 1-3 below. 1. If the sticker
Part I: What Time Is It? A Model of Day and Night Find a place in a circle around the lamp where no one is between you and the lamp. Once you face the lamp, answer questions 1-3 below. 1. If the sticker
What Is the Relationship Between Earth s Tilt and the Seasons?
 Learning Set 2 Why Are There Differences in Temperature? Review Images and Graphics While reading about Earth s tilt and the seasons, pay particular attention to the graphics included. How do they help
Learning Set 2 Why Are There Differences in Temperature? Review Images and Graphics While reading about Earth s tilt and the seasons, pay particular attention to the graphics included. How do they help
Gay E. Canough Solar Math. PV Installer s Class: Units and Math
 Gay E. Canough 1.1--Solar Math October 2012 PV Installer s Class: Units and Math 1 Units Electricity Fluid KW, a unit of power Horsepower, a unit of power KWh, a unit of energy BTU, a unit of energy Voltage
Gay E. Canough 1.1--Solar Math October 2012 PV Installer s Class: Units and Math 1 Units Electricity Fluid KW, a unit of power Horsepower, a unit of power KWh, a unit of energy BTU, a unit of energy Voltage
b. Assuming that the sundial is set up correctly, explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increase.
 1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
The Earth, Moon, and Sky. Lecture 5 1/31/2017
 The Earth, Moon, and Sky Lecture 5 1/31/2017 From Last Time: Stable Orbits The type of orbit depends on the initial speed of the object Stable orbits are either circular or elliptical. Too slow and gravity
The Earth, Moon, and Sky Lecture 5 1/31/2017 From Last Time: Stable Orbits The type of orbit depends on the initial speed of the object Stable orbits are either circular or elliptical. Too slow and gravity
This equation is only used when the velocity is constant, or for an average velocity.
 1 2 The speed distance - time equation. d = distance travelled, in metres (m) v = average velocity, in metres per second (m/s) t = time taken for trip, in seconds (s) This equation is only used when the
1 2 The speed distance - time equation. d = distance travelled, in metres (m) v = average velocity, in metres per second (m/s) t = time taken for trip, in seconds (s) This equation is only used when the
Motion of the Sun. View Comments
 Login 2017 Survey to Improve Photovoltaic Education Christiana Honsberg and Stuart Bowden View Comments Instructions 1. Introduction 2. Properties of Sunlight 2.1. Basics of Light Properties of Light Energy
Login 2017 Survey to Improve Photovoltaic Education Christiana Honsberg and Stuart Bowden View Comments Instructions 1. Introduction 2. Properties of Sunlight 2.1. Basics of Light Properties of Light Energy
1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude
 1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude There are many opportunities for making observations of shadows cast with a vertical stick and the Sun. Observations
1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude There are many opportunities for making observations of shadows cast with a vertical stick and the Sun. Observations
Meteorology. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Chapter 3 Worksheet 1 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, the daily
Chapter 3 Worksheet 1 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, the daily
Energy. E d. Energy Power = time. E t P = E t = P
 Energy Forms of energy Energy can never be created or destroyed. It can only be transformed from one type to another (or other types). here are many different forms of energy: Kinetic (movement) Energy
Energy Forms of energy Energy can never be created or destroyed. It can only be transformed from one type to another (or other types). here are many different forms of energy: Kinetic (movement) Energy
Admin. 8/29/17. If you re at North Pole, you ll NEVER see stars that are below your horizon. Key Concepts: Lecture 4
 Admin. 8/29/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections (start Aug. 30th) (see me at end of lecture if you can t make one of these times)! Tuesday
Admin. 8/29/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections (start Aug. 30th) (see me at end of lecture if you can t make one of these times)! Tuesday
Solar System Test - Grade 5
 Solar System Test - Grade 5 Multiple Choice Directions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write this answer on your answer document. 1. The tilt of Earth s
Solar System Test - Grade 5 Multiple Choice Directions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write this answer on your answer document. 1. The tilt of Earth s
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest).
 Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
XI PHYSICS. M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K. https://promotephysics.wordpress.com
 XI PHYSICS M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [WORK, POWER AND ENERGY] CHAPTER NO. 7 A little concept of vector mathematics is applied here
XI PHYSICS M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [WORK, POWER AND ENERGY] CHAPTER NO. 7 A little concept of vector mathematics is applied here
Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky 107
 Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky 107 planetariums around the world. Figure 4.4 Foucault s Pendulum. As Earth turns, the plane of oscillation of the Foucault pendulum shifts gradually so that over the course
Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky 107 planetariums around the world. Figure 4.4 Foucault s Pendulum. As Earth turns, the plane of oscillation of the Foucault pendulum shifts gradually so that over the course
Planet Earth. Part 2
 Planet Earth Part 2 Sun, Earth and Moon Motions The Solar System revolves around the Milky Way galaxy center. The Sun rotates on its own axis. Earth revolves around the Sun (1 year) and rotates on its
Planet Earth Part 2 Sun, Earth and Moon Motions The Solar System revolves around the Milky Way galaxy center. The Sun rotates on its own axis. Earth revolves around the Sun (1 year) and rotates on its
01) The Sun s rays strike the surface of the Earth at 90 degrees at the on December 22.
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: Introducing Physical Geography 6e Chapter Number: 01 Question Type: Multiple Choice 01) The Sun s rays strike the surface of the Earth at 90 degrees at the on December
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: Introducing Physical Geography 6e Chapter Number: 01 Question Type: Multiple Choice 01) The Sun s rays strike the surface of the Earth at 90 degrees at the on December
The Sky Perceptions of the Sky
 The Sky Perceptions of the Sky An Observer-Centered Hemisphere Night & Day - Black & Blue - Stars & Sun Atmospheric & Astronomical Phenomena Weather, Clouds, Rainbows,... versus Sun, Moon, Stars, Planets,...
The Sky Perceptions of the Sky An Observer-Centered Hemisphere Night & Day - Black & Blue - Stars & Sun Atmospheric & Astronomical Phenomena Weather, Clouds, Rainbows,... versus Sun, Moon, Stars, Planets,...
LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations
 LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations Name School The amount of solar energy striking the Earth s atmosphere is not uniform; distances, angles and seasons play a dominant role on this distribution of radiation. Needless
LAB 2: Earth Sun Relations Name School The amount of solar energy striking the Earth s atmosphere is not uniform; distances, angles and seasons play a dominant role on this distribution of radiation. Needless
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere
 The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
GLOSSARY OF PHYSICS TERMS. v-u t. a =
 GLOSSARY OF PHYSICS TERMS Scalar: A quantity that has magnitude only. Vector: A quantity that has magnitude and direction. Speed is the distance travelled per unit time. OR the rate of change of distance.
GLOSSARY OF PHYSICS TERMS Scalar: A quantity that has magnitude only. Vector: A quantity that has magnitude and direction. Speed is the distance travelled per unit time. OR the rate of change of distance.
(1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why?
 (1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why? (Note: Although all responses below are true statements, only one of them actually explains the observation!) (A)The sun
(1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why? (Note: Although all responses below are true statements, only one of them actually explains the observation!) (A)The sun
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4)
 Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, Anne Green / Richard Thompson
 Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, 2006 Anne Green / Richard Thompson http://www.physics.usyd.edu.au/ag/agschome.htm Course Coordinator: Mike Wheatland Course Goals Evaluate & interpret information,
Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, 2006 Anne Green / Richard Thompson http://www.physics.usyd.edu.au/ag/agschome.htm Course Coordinator: Mike Wheatland Course Goals Evaluate & interpret information,
EARTH MOON SUN REVIEW
 1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
A User s Guide to the Sky
 A User s Guide to the Sky Constellations Betelgeuse Rigel Stars are named by a Greek letter ( ) according to their relative brightness within a given constellation plus the possessive form of the name
A User s Guide to the Sky Constellations Betelgeuse Rigel Stars are named by a Greek letter ( ) according to their relative brightness within a given constellation plus the possessive form of the name
[04] Seasons, Phases, and Eclipses (9/7/17)
![[04] Seasons, Phases, and Eclipses (9/7/17) [04] Seasons, Phases, and Eclipses (9/7/17)](/thumbs/79/80259995.jpg) 1 [04] Seasons, Phases, and Eclipses (9/7/17) Upcoming Items Homework #2 due next lecture. Read Ch. 3.3 and do the self-study quizzes for next lecture, and skim 2.4, 3.1, 3.2, & 3.4. https://pbs.twimg.com/media/dh69il_u0aenivq.jpg:large
1 [04] Seasons, Phases, and Eclipses (9/7/17) Upcoming Items Homework #2 due next lecture. Read Ch. 3.3 and do the self-study quizzes for next lecture, and skim 2.4, 3.1, 3.2, & 3.4. https://pbs.twimg.com/media/dh69il_u0aenivq.jpg:large
World Geography Chapter 3
 World Geography Chapter 3 Section 1 A. Introduction a. Weather b. Climate c. Both weather and climate are influenced by i. direct sunlight. ii. iii. iv. the features of the earth s surface. B. The Greenhouse
World Geography Chapter 3 Section 1 A. Introduction a. Weather b. Climate c. Both weather and climate are influenced by i. direct sunlight. ii. iii. iv. the features of the earth s surface. B. The Greenhouse
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics
 AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
UNIT 1: THE PLANET EARTH
 UNIT 1: THE PLANET EARTH How many planets are there in our Solar System? What is the Equator? Why does life exist in our planet? Does The Earth move? What is a map? 1. Planet Earth TOPICS 2. Movements
UNIT 1: THE PLANET EARTH How many planets are there in our Solar System? What is the Equator? Why does life exist in our planet? Does The Earth move? What is a map? 1. Planet Earth TOPICS 2. Movements
Which graph best shows the relationship between intensity of insolation and position on the Earth's surface? A) B) C) D)
 1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
Earth is tilted (oblique) on its Axis!
 MONDAY AM Radiation, Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Earth's orbit around the Sun is slightly elliptical (not circular) Seasons & Days Why do we have seasons? Why aren't seasonal temperatures highest at
MONDAY AM Radiation, Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Earth's orbit around the Sun is slightly elliptical (not circular) Seasons & Days Why do we have seasons? Why aren't seasonal temperatures highest at
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations
 Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky. The sky is divided into 88 unequal areas that we call constellations.
 Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
3. a. In the figure below, indicate the direction of the Sun with an arrow.
 Astronomy 100, Fall 2005 Name(s): Exercise 2: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 100, Fall 2005 Name(s): Exercise 2: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Reasons for the seasons - Rebecca Kaplan
 Reasons for the seasons - Rebecca Kaplan https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dd_8jm5ptlk https://www.timeanddate.com/worldclock/sunearth.html https://www.time.gov/ https://www.space.com/33790-harvest-moon-guide.html
Reasons for the seasons - Rebecca Kaplan https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dd_8jm5ptlk https://www.timeanddate.com/worldclock/sunearth.html https://www.time.gov/ https://www.space.com/33790-harvest-moon-guide.html
EELE408 Photovoltaics Lecture 04: Apparent Motion of the Sum
 EELE408 Photovoltaics Lecture 04: Apparent Motion of the um Dr. Todd J. Kaiser tjkaiser@ece.montana.edu Apparent motion of the sun EAT Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Montana tate University
EELE408 Photovoltaics Lecture 04: Apparent Motion of the um Dr. Todd J. Kaiser tjkaiser@ece.montana.edu Apparent motion of the sun EAT Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Montana tate University
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
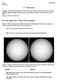 Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Earth s Motion. Lesson Outline LESSON 1. A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than
 Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Chapter 4. Energy. Work Power Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy. W = Fs Work = (force)(distance)
 Chapter 4 Energy In This Chapter: Work Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Work Work is a measure of the amount of change (in a general sense) that a force produces when it acts on a
Chapter 4 Energy In This Chapter: Work Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Work Work is a measure of the amount of change (in a general sense) that a force produces when it acts on a
Solutions Manual to Exercises for Weather & Climate, 8th ed. Appendix A Dimensions and Units 60 Appendix B Earth Measures 62 Appendix C GeoClock 63
 Solutions Manual to Exercises for Weather & Climate, 8th ed. 1 Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere 1 2 Earth Sun Geometry 4 3 The Surface Energy Budget 8 4 The Global Energy Budget 10 5 Atmospheric Moisture
Solutions Manual to Exercises for Weather & Climate, 8th ed. 1 Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere 1 2 Earth Sun Geometry 4 3 The Surface Energy Budget 8 4 The Global Energy Budget 10 5 Atmospheric Moisture
SUBJECT : GEOGRAPHY ROTATION AND REVOLUTION This paper consists of 5 printed pages.
 SUBJECT : GEOGRAPHY ROTATION AND REVOLUTION 2017-2018 This paper consists of 5 printed pages. 1. Name the motions of the earth. A. They are Rotation and Revolution. 2. What is Rotation? A. Rotation is
SUBJECT : GEOGRAPHY ROTATION AND REVOLUTION 2017-2018 This paper consists of 5 printed pages. 1. Name the motions of the earth. A. They are Rotation and Revolution. 2. What is Rotation? A. Rotation is
The content contained in all sections of chapter 6 of the textbook is included on the AP Physics B exam.
 WORK AND ENERGY PREVIEW Work is the scalar product of the force acting on an object and the displacement through which it acts. When work is done on or by a system, the energy of that system is always
WORK AND ENERGY PREVIEW Work is the scalar product of the force acting on an object and the displacement through which it acts. When work is done on or by a system, the energy of that system is always
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon. Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017
 Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
5. In which diagram is the observer experiencing the greatest intensity of insolation? A) B)
 1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
What causes the seasons? 2/11/09
 2/11/09 We can recognize solstices and equinoxes by Sun s path across sky: Summer solstice: Highest path, rise and set at most extreme north of due east. Winter solstice: Lowest path, rise and set at most
2/11/09 We can recognize solstices and equinoxes by Sun s path across sky: Summer solstice: Highest path, rise and set at most extreme north of due east. Winter solstice: Lowest path, rise and set at most
Work Done by a Constant Force
 Work and Energy Work Done by a Constant Force In physics, work is described by what is accomplished when a force acts on an object, and the object moves through a distance. The work done by a constant
Work and Energy Work Done by a Constant Force In physics, work is described by what is accomplished when a force acts on an object, and the object moves through a distance. The work done by a constant
DIRECTING SUN PANELS
 sunpan, April 9, 2015 1 DIRECTING SUN PANELS GERRIT DRAISMA 1. Introduction The quantity of sun light captured by sun panels depends on intensity and direction of solar radiation, area of the panels, and
sunpan, April 9, 2015 1 DIRECTING SUN PANELS GERRIT DRAISMA 1. Introduction The quantity of sun light captured by sun panels depends on intensity and direction of solar radiation, area of the panels, and
Discovering the Night Sky
 Discovering the Night Sky Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Discovering the Night Sky Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Discovering the Night Sky
 Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Cartesian Coordinates Need two dimensional system 2 number lines perpendicular to each other X-axis is horizontal Y-axis is vertical Position relative
 General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
Knowing the Heavens. Chapter Two. Guiding Questions. Naked-eye (unaided-eye) astronomy had an important place in ancient civilizations
 Knowing the Heavens Chapter Two Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same
Knowing the Heavens Chapter Two Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Physics 3.1 & 3.3 & 3.4 - Energy, Work, and Power Energy, Work, and Power You need to know what energy, work, and power is, and the units for energy and
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Physics 3.1 & 3.3 & 3.4 - Energy, Work, and Power Energy, Work, and Power You need to know what energy, work, and power is, and the units for energy and
Laboratory Exercise #7 - Introduction to Atmospheric Science: The Seasons
 Laboratory Exercise #7 - Introduction to Atmospheric Science: The Seasons page - 1 Section A - Introduction: This lab consists of both computer-based and noncomputer-based questions dealing with atmospheric
Laboratory Exercise #7 - Introduction to Atmospheric Science: The Seasons page - 1 Section A - Introduction: This lab consists of both computer-based and noncomputer-based questions dealing with atmospheric
Heat Transfer. Energy from the Sun. Introduction
 Heat Transfer Energy from the Sun Introduction The sun rises in the east and sets in the west, but its exact path changes over the course of the year, which causes the seasons. In order to use the sun
Heat Transfer Energy from the Sun Introduction The sun rises in the east and sets in the west, but its exact path changes over the course of the year, which causes the seasons. In order to use the sun
