Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
|
|
|
- Shana Booth
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate Q.2 The passengers were angry the airline staff about the delay. (A) on (B) about (C) with (D) towards Q.3 The missing number in the given sequence 343, 1331,, 4913 is (A) 3375 (B) 2744 (C) 2197 (D) 4096 Q.4 It takes two hours for a person X to mow the lawn. Y can mow the same lawn in four hours. How long (in minutes) will it take X and Y, if they work together to mow the lawn? (A) 60 (B) 80 (C) 90 (D) 120 Q.5 Newspapers are a constant source of delight and recreation for me. The trouble is that I read many of them. (A) even, quite (C) only, quite (B) even, too (D) only, too Q. 6 Q. 10 carry two marks each. Q.6 How many integers are there between 100 and 1000 all of whose digits are even? (A) 60 (B) 80 (C) 100 (D) 90 Q.7 The ratio of the number of boys and girls who participated in an examination is 4:3. The total percentage of candidates who passed the examination is 80 and the percentage of girls who passed is 90. The percentage of boys who passed is. (A) (B) (C) (D) GA 1/2
2 GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q.8 An award-winning study by a group of researchers suggests that men are as prone to buying on impulse as women but women feel more guilty about shopping. Which one of the following statements can be inferred from the given text? (A) Some men and women indulge in buying on impulse (B) All men and women indulge in buying on impulse (C) Few men and women indulge in buying on impulse (D) Many men and women indulge in buying on impulse Q.9 Given two sets X = {1, 2, 3} and Y = {2, 3, 4}, we construct a set Z of all possible fractions where the numerators belong to set X and the denominators belong to set Y. The product of elements having minimum and maximum values in the set Z is. (A) 1/12 (B) 1/8 (C) 1/6 (D) 3/8 Q.10 Consider five people Mita, Ganga, Rekha, Lakshmi and Sana. Ganga is taller than both Rekha and Lakshmi. Lakshmi is taller than Sana. Mita is taller than Ganga. Which of the following conclusions are true? 1. Lakshmi is taller than Rekha 2. Rekha is shorter than Mita 3. Rekha is taller than Sana 4. Sana is shorter than Ganga (A) 1 and 3 (B) 3 only (C) 2 and 4 (D) 1 only END OF THE QUESTION PAPER GA 2/2
3 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry ONE mark each. Q.1 The inverse Laplace transform of H(s) = (A) 3te t + e t (C) 2te t + e t s+3 s 2 +2s+1 for t 0 is (B) 3e t (D) 4te t + e t Q.2 M is a 2 2 matrix with eigenvalues 4 and 9. The eigenvalues of M 2 are (A) 4 and 9 (B) 2 and 3 (C) -2 and -3 (D) 16 and 81 Q.3 The partial differential equation 2 u t 2 c2 ( 2 u + 2 u x 2 y2) = 0; where c 0 is known as (A) heat equation (C) Poisson s equation (B) wave equation (D) Laplace equation Q.4 Which one of the following functions is analytic in the region z 1? (A) z2 1 z (B) z2 1 z+2 (C) z2 1 z 0.5 (D) z2 1 z+j0.5 Q.5 The mean-square of a zero-mean random process is kt, where k is Boltzmann s constant, T is the absolute temperature, and C is a capacitance. The standard deviation of the random process is (A) kt C (B) kt C (C) C kt C (D) kt C Q.6 A system transfer function is H(s) = a 1s 2 + b 1 s+c 1 a 2 s 2 + b 2 s+c 2. If a 1 = b 1 = 0, and all other coefficients are positive, the transfer function represents a (A) low pass filter (B) high pass filter (C) band pass filter (D) notch filter Q.7 The symbols, a and T, represent positive quantities, and u(t) is the unit step function. Which one of the following impulse responses is NOT the output of a causal linear time-invariant system? (A) e +at u(t) (C) 1 + e at u(t) (B) e a(t+t) u(t) (D) e a(t T) u(t) Q.8 A 5 kva, 50 V/100 V, single-phase transformer has a secondary terminal voltage of 95 V when loaded. The regulation of the transformer is (A) 4.5% (B) 9% (C) 5% (D) 1% EE 1/13
4 Q.9 A six-pulse thyristor bridge rectifier is connected to a balanced three-phase, 50 Hz AC source. Assuming that the DC output current of the rectifier is constant, the lowest harmonic component in the AC input current is (A) 100 Hz (B) 150 Hz (C) 250 Hz (D) 300 Hz Q.10 The parameter of an equivalent circuit of a three-phase induction motor affected by reducing the rms value of the supply voltage at the rated frequency is (A) rotor resistance (B) rotor leakage reactance (C) magnetizing reactance (D) stator resistance Q.11 A three-phase synchronous motor draws 200 A from the line at unity power factor at rated load. Considering the same line voltage and load, the line current at a power factor of 0.5 leading is (A) 100 A (B) 200 A (C) 300 A (D) 400 A Q.12 In the circuit shown below, the switch is closed at t = 0. The value of θ in degrees which will give the maximum value of DC offset of the current at the time of switching is R=3.77 Ω L=10 mh t = 0 AC v(t)=150 sin (377t + θ) (A) 60 (B) 45 (C) 90 (D) 30 Q.13 The output response of a system is denoted as y(t), and its Laplace transform is given by Y(s) = The steady state value of y(t) is (A) (B) s(s 2 +s+100 2). (C) Q.14 The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback system is given by (D) G(s) = πe 0.25s. s In G(s) plane, the Nyquist plot of G(s) passes through the negative real axis at the point (A) ( 0.5, j0) (B) ( 0.75, j0) (C) ( 1.25, j0) (D) ( 1.5, j0) Q.15 The characteristic equation of a linear time-invariant (LTI) system is given by (s) = s 4 + 3s 3 + 3s 2 + s + k = 0. The system is BIBO stable if (A) 0 < k < 12 9 (C) 0 < k < 8 9 (B) k > 3 (D) k > 6 EE 2/13
5 Q.16 Given, V gs is the gate-source voltage, V ds is the drain source voltage, and V th is the threshold voltage of an enhancement type NMOS transistor, the conditions for transistor to be biased in saturation are (A) V gs < V th ; V ds V gs V th (B) V gs > V th ; V ds V gs V th (C) V gs > V th ; V ds V gs V th (D) V gs < V th ; V ds V gs V th Q.17 A current controlled current source (CCCS) has an input impedance of 10 Ω and output impedance of 100 kω. When this CCCS is used in a negative feedback closed loop with a loop gain of 9, the closed loop output impedance is (A) 10 Ω (B) 100 Ω (C) 100 kω (D) 1000 kω Q.18 If f = 2x 3 + 3y 2 + 4z, the value of line integral gradf dr evaluated over contour C C formed by the segments (-3, -3, 2) (2, -3, 2) (2, 6, 2) (2, 6, -1) is. Q.19 The current I flowing in the circuit shown below in amperes (round off to one decimal place) is. I 2 Ω 3 Ω 20 V 2 A + - 5I Q.20 A co-axial cylindrical capacitor shown in Figure (i) has dielectric with relative permittivity εr1 = 2. When one-fourth portion of the dielectric is replaced with another dielectric of relative permittivity εr2, as shown in Figure (ii), the capacitance is doubled. The value of εr2 is. R R ε r2 r r ε r1 = 2 Figure (i) ε r1 = 2 Figure (ii) EE 3/13
6 Q.21 The Y bus matrix of a two-bus power system having two identical parallel lines connected between them in pu is given as Y bus = [ j8 j20 j20 j8 ]. The magnitude of the series reactance of each line in pu (round off up to one decimal place) is. Q.22 Five alternators each rated 5 MVA, 13.2 kv with 25% of reactance on its own base are connected in parallel to a busbar. The short-circuit level in MVA at the busbar is. Q.23 The total impedance of the secondary winding, leads, and burden of a 5 A CT is 0.01 Ω. If the fault current is 20 times the rated primary current of the CT, the VA output of the CT is. Q The rank of the matrix, M = [ 1 0 1], is Q.25 The output voltage of a single-phase full bridge voltage source inverter is controlled by unipolar PWM with one pulse per half cycle. For the fundamental rms component of output voltage to be 75% of DC voltage, the required pulse width in degrees (round off up to one decimal place) is. EE 4/13
7 Q. 26 Q. 55 carry TWO marks each. Q.26 Consider a 2 2 matrix M = [v 1 v 2 ], where, v 1 and v 2 are the column vectors. Suppose M 1 = [ u 1 T u 2 T ], where u 1 T and u 2 T are the row vectors. Consider the following statements: Statement 1: u 1 T v 1 = 1 and u 2 T v 2 = 1 Statement 2: u 1 T v 2 = 0 and u 2 T v 1 = 0 Which of the following options is correct? (A) Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false (B) Statement 2 is true and statement 1 is false (C) Both the statements are true (D) Both the statements are false Q.27 The closed loop line integral z3 + z z + 2 z =5 dz evaluated counter-clockwise, is (A) +8jπ (B) 8jπ (C) 4jπ (D) +4jπ Q.28 A periodic function f(t), with a period of 2π, is represented as its Fourier series, f(t) = a 0 + n=1 a n cos nt + n=1 b n sin nt. If A sin t, 0 t π f(t) = { 0, π < t < 2π, the Fourier series coefficients a 1 and b 1 of f(t) are (A) a 1 = A π ; b 1 = 0 (B) a 1 = A 2 ; b 1 = 0 (C) a 1 = 0 ; b 1 = A/π (D) a 1 = 0 ; b 1 = A 2 EE 5/13
8 Q.29 The asymptotic Bode magnitude plot of a minimum phase transfer function G(s) is shown below. 60 G(jω) (db) 20 db/decade db/decade ω (log scale) 60 db/decade Consider the following two statements. Statement I: Transfer function G(s) has three poles and one zero. Statement II: At very high frequency (ω ), the phase angle G(jω) = 3π 2. Which one of the following options is correct? (A) Statement I is true and statement II is false. (B) Statement I is false and statement II is true. (C) Both the statements are true. (D) Both the statements are false. Q.30 The transfer function of a phase lead compensator is given by D(s) = 3(s+ 1 3T ). (s+ 1 T ) The frequency (in rad/sec), at which D(jω) is maximum, is (A) 3 T 2 (B) 1 3T 2 (C) 3T (D) 3T 2 Q.31 Consider a state-variable model of a system [ x 1 ] = [ 0 1 x 2 α 2β ] [x 1 x ] + [ 0 2 α ] r y = [1 0] [ x 1 x ] 2 where y is the output, and r is the input. The damping ratio ξ and the undamped natural frequency ωn (rad/sec) of the system are given by (A) ξ = β α ; ω n = α (C) ξ = α β ; ω n = β (B) ξ = α; ω n = β α (D) ξ = β; ω n = α Q.32 A moving coil instrument having a resistance of 10 Ω, gives a full-scale deflection when the current is 10 ma. What should be the value of the series resistance, so that it can be used as a voltmeter for measuring potential difference up to 100 V? (A) 9 Ω (B) 99 Ω (C) 990 Ω (D) 9990 Ω EE 6/13
9 Q.33 The enhancement type MOSFET in the circuit below operates according to the square law. μ n C ox = 100 μa/v 2, the threshold voltage (VT) is 500 mv. Ignore channel length modulation. The output voltage Vout is V DD = 2V 5 µa V out W L = 10 µm 1 µm (A) 100 mv (B) 500 mv (C) 600 mv (D) 2 V Q.34 In the circuit below, the operational amplifier is ideal. If V1 = 10 mv and V2 = 50 mv, the output voltage (Vout) is 100 kω V 1 10 kω V 2 10 kω V out 100 kω (A) 100 mv (B) 400 mv (C) 500 mv (D) 600 mv EE 7/13
10 Q.35 The output expression for the Karnaugh map shown below is PQ RS (A) QR + S (C) QR + S (B) QR + S (D) QR + S Q.36 In the circuit shown below, X and Y are digital inputs, and Z is a digital output. The equivalent circuit is a X Y Z (A) NAND gate (B) NOR gate (C) XOR gate (D) XNOR gate Q.37 A DC-DC buck converter operates in continuous conduction mode. It has 48 V input voltage, and it feeds a resistive load of 24 Ω. The switching frequency of the converter is 250 Hz. If switch-on duration is 1 ms, the load power is (A) 6 W (B) 12 W (C) 24 W (D) 48 W Q.38 The line currents of a three-phase four wire system are square waves with amplitude of 100 A. These three currents are phase shifted by 120 with respect to each other. The rms value of neutral current is (A) 0 A (B) A (C) 100 A (D) 300 A Q.39 If A = 2xi + 3yj + 4zk and u = x 2 + y 2 + z 2, then div(ua) at (1, 1, 1) is. Q.40 The probability of a resistor being defective is There are 50 such resistors in a circuit. The probability of two or more defective resistors in the circuit (round off to two decimal places) is. EE 8/13
11 Q.41 A 0.1 µf capacitor charged to 100 V is discharged through a 1 kω resistor. The time in ms (round off to two decimal places) required for the voltage across the capacitor to drop to 1 V is. Q.42 The current I flowing in the circuit shown below in amperes is. 50 Ω 40 Ω 25 Ω 20 Ω I 20 Ω 200 V 160 V 100 V 80 V Q.43 The voltage across and the current through a load are expressed as follows v(t) = 170 sin (377t π 6 ) V i(t) = 8 cos (377t + π 6 ) A The average power in watts (round off to one decimal place) consumed by the load is. Q.44 The magnetic circuit shown below has uniform cross-sectional area and air gap of 0.2 cm. The mean path length of the core is 40 cm. Assume that leakage and fringing fluxes are negligible. When the core relative permeability is assumed to be infinite, the magnetic flux density computed in the air gap is 1 tesla. With same Ampere-turns, if the core relative permeability is assumed to be 1000 (linear), the flux density in tesla (round off to three decimal places) calculated in the air gap is. 10 cm I 10 cm 0.2 cm Q.45 A single-phase transformer of rating 25 kva, supplies a 12 kw load at power factor of 0.6 lagging. The additional load at unity power factor in kw (round off to two decimal places) that may be added before this transformer exceeds its rated kva is. EE 9/13
12 Q.46 A 220 V DC shunt motor takes 3 A at no-load. It draws 25 A when running at full-load at 1500 rpm. The armature and shunt resistances are 0.5 Ω and 220 Ω, respectively. The noload speed in rpm (round off to two decimal places) is. Q.47 A delta-connected, 3.7 kw, 400 V(line), three-phase, 4-pole, 50-Hz squirrel-cage induction motor has the following equivalent circuit parameters per phase referred to the stator: R 1 = 5.39 Ω, R 2 = 5.72 Ω, X 1 = X 2 = 8.22 Ω. Neglect shunt branch in the equivalent circuit. The starting line current in amperes (round off to two decimal places) when it is connected to a 100 V (line), 10 Hz, three-phase AC source is. Q.48 A 220 V (line), three-phase, Y-connected, synchronous motor has a synchronous impedance of ( j2.5) Ω/phase. The motor draws the rated current of 10 A at 0.8 pf leading. The rms value of line-to-line internal voltage in volts (round off to two decimal places) is. Q.49 A three-phase 50 Hz, 400 kv transmission line is 300 km long. The line inductance is 1 mh/km per phase, and the capacitance is 0.01 µf/km per phase. The line is under open circuit condition at the receiving end and energized with 400 kv at the sending end, the receiving end line voltage in kv (round off to two decimal places) will be. Q.50 A 30 kv, 50 Hz, 50 MVA generator has the positive, negative, and zero sequence reactances of 0.25 pu, 0.15 pu, and 0.05 pu, respectively. The neutral of the generator is grounded with a reactance so that the fault current for a bolted LG fault and that of a bolted three-phase fault at the generator terminal are equal. The value of grounding reactance in ohms (round off to one decimal place) is. Q.51 In the single machine infinite bus system shown below, the generator is delivering the real power of 0.8 pu at 0.8 power factor lagging to the infinite bus. The power angle of the generator in degrees (round off to one decimal place) is. G X d =0.25 pu X t =0.2 pu X L1 =0.4 pu X L2 =0.4 pu V=1 0 Q.52 In a 132 kv system, the series inductance up to the point of circuit breaker location is 50 mh. The shunt capacitance at the circuit breaker terminal is 0.05 µf. The critical value of resistance in ohms required to be connected across the circuit breaker contacts which will give no transient oscillation is. EE 10/13
13 Q.53 In a DC-DC boost converter, the duty ratio is controlled to regulate the output voltage at 48 V. The input DC voltage is 24 V. The output power is 120 W. The switching frequency is 50 khz. Assume ideal components and a very large output filter capacitor. The converter operates at the boundary between continuous and discontinuous conduction modes. The value of the boost inductor (in µh) is. Q.54 A fully-controlled three-phase bridge converter is working from a 415 V, 50 Hz AC supply. It is supplying constant current of 100 A at 400 V to a DC load. Assume large inductive smoothing and neglect overlap. The rms value of the AC line current in amperes (round off to two decimal places) is. Q.55 A single-phase fully-controlled thyristor converter is used to obtain an average voltage of 180 V with 10 A constant current to feed a DC load. It is fed from single-phase AC supply of 230 V, 50 Hz. Neglect the source impedance. The power factor (round off to two decimal places) of AC mains is. EE 11/13
EE Branch GATE Paper 2010
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
+ ( )= with initial condition
 Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
ECE Branch GATE Paper The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2
 Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Given ff(zz) = gg(zz) + h(zz), where ff, gg, h are complex valued functions of a complex variable zz. Which one of the following statements is TUE? (A) If ff(zz) is
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Given ff(zz) = gg(zz) + h(zz), where ff, gg, h are complex valued functions of a complex variable zz. Which one of the following statements is TUE? (A) If ff(zz) is
ECE 585 Power System Stability
 Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL
 Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator. The excitation
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator. The excitation
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1
 Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
GATEFORUM- India s No.1 institute for GATE training 1
 EE-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. Given a vector field F = y xax yzay = x a z, the line integral F.dl evaluated along a segment on the x-axis from x= to x= is -.33 (B) 0.33 (D) 7 : (B) x 0.
EE-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. Given a vector field F = y xax yzay = x a z, the line integral F.dl evaluated along a segment on the x-axis from x= to x= is -.33 (B) 0.33 (D) 7 : (B) x 0.
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering
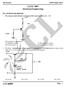 Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 08 General Aptitude (GA) Set6 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Since you have gone off the, the sand is likely to damage the car. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) course,
GATE 08 General Aptitude (GA) Set6 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Since you have gone off the, the sand is likely to damage the car. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) course,
GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + y =e (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 is 2. The Fourier series of a
GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + y =e (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 is 2. The Fourier series of a
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Electric Machines
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
Conventional Paper-I Part A. 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy
 EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester. Electrical and Electronics Engineering. EE 1352 Power System Analysis
 B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines. Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015
 ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015 1 Content (Materials are from Chapters 16-17) Synchronous Generators Synchronous Motors 2 Synchronous Generators
ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015 1 Content (Materials are from Chapters 16-17) Synchronous Generators Synchronous Motors 2 Synchronous Generators
Switched-Capacitor Circuits David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto
 Switched-Capacitor Circuits David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) University of Toronto 1 of 60 Basic Building Blocks Opamps Ideal opamps usually
Switched-Capacitor Circuits David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) University of Toronto 1 of 60 Basic Building Blocks Opamps Ideal opamps usually
EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION
 EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is single line diagram? A Single line diagram is diagrammatic representation of power system in which the components are represented by
EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is single line diagram? A Single line diagram is diagrammatic representation of power system in which the components are represented by
SECTION - A. A current impulse, 5δ(t), is forced through a capacitor C. The voltage, Vc(t), across the capacitor is given by. 5 t C.
 SETION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..5) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
SETION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..5) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis
 Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
An Introduction to Electrical Machines. P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy
 An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY. 1. Understands the physical construction and characteristics of basic components.
 SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
GATE-2015 ELECTRICAL ENGG 7th February 2015 Forenoon Session
 Page Section - I (General Aptitude) Q. Which one of the following combinations is incorrect? Acquiescence - Submission Wheedle - Roundabout Flippancy - Lightness Profligate - Extravagant Q. Didn t you
Page Section - I (General Aptitude) Q. Which one of the following combinations is incorrect? Acquiescence - Submission Wheedle - Roundabout Flippancy - Lightness Profligate - Extravagant Q. Didn t you
ONE MARK QUESTIONS. 1. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is
 ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is (a.) R L C (b.) R L C (c.) R L C (d.) R LC
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is (a.) R L C (b.) R L C (c.) R L C (d.) R LC
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005
 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE
 Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Homework Assignment 08
 Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 8-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 24 Electrical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 8-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 24 Electrical
Part 4: Electromagnetism. 4.1: Induction. A. Faraday's Law. The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is
 1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION AND TEST SETUP FOR FAULT ANALYSIS
 47 CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION AND TEST SETUP FOR FAULT ANALYSIS 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the simulation model and experimental set up used for the fault analysis. For the simulation set up, the
47 CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION AND TEST SETUP FOR FAULT ANALYSIS 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the simulation model and experimental set up used for the fault analysis. For the simulation set up, the
UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A- Two marks questions
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. Define specific magnetic
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. Define specific magnetic
Synchronous Machines
 Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 9 Transmission Line Steady State Operation Welcome to lesson 9, in Power
Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 9 Transmission Line Steady State Operation Welcome to lesson 9, in Power
ECEN 460 Exam 1 Fall 2018
 ECEN 460 Exam 1 Fall 2018 Name: KEY UIN: Section: Score: Part 1 / 40 Part 2 / 0 Part / 0 Total / 100 This exam is 75 minutes, closed-book, closed-notes. A standard calculator and one 8.5 x11 note sheet
ECEN 460 Exam 1 Fall 2018 Name: KEY UIN: Section: Score: Part 1 / 40 Part 2 / 0 Part / 0 Total / 100 This exam is 75 minutes, closed-book, closed-notes. A standard calculator and one 8.5 x11 note sheet
Power Electronics
 Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012
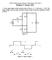 ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES. School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION. Session
 Name: Student ID: Signature: THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION Session 00 ELEC46 Power System Analysis TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours TOTAL
Name: Student ID: Signature: THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION Session 00 ELEC46 Power System Analysis TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours TOTAL
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION
 EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART: A 1. Define per unit value of an electrical quantity. Write equation for base impedance with respect to 3-phase system. 2. What is bus admittance
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART: A 1. Define per unit value of an electrical quantity. Write equation for base impedance with respect to 3-phase system. 2. What is bus admittance
SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -1. Please read the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
ECE-342 Test 3: Nov 30, :00-8:00, Closed Book. Name : Solution
 ECE-342 Test 3: Nov 30, 2010 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : Solution All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Unless otherwise stated, assume T = 300 K. 1. (25 pts) Consider the amplifier shown
ECE-342 Test 3: Nov 30, 2010 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : Solution All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Unless otherwise stated, assume T = 300 K. 1. (25 pts) Consider the amplifier shown
Power Factor Improvement
 Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
Equivalent Circuits with Multiple Damper Windings (e.g. Round rotor Machines)
 Equivalent Circuits with Multiple Damper Windings (e.g. Round rotor Machines) d axis: L fd L F - M R fd F L 1d L D - M R 1d D R fd R F e fd e F R 1d R D Subscript Notations: ( ) fd ~ field winding quantities
Equivalent Circuits with Multiple Damper Windings (e.g. Round rotor Machines) d axis: L fd L F - M R fd F L 1d L D - M R 1d D R fd R F e fd e F R 1d R D Subscript Notations: ( ) fd ~ field winding quantities
SSC-JE EE POWER SYSTEMS: GENERATION, TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University College of Engineering. Electrical Engineering Department EE 3360 Electrical Machines (II)
 Chapter # 4 Three-Phase Induction Machines 1- Introduction (General Principles) Generally, conversion of electrical power into mechanical power takes place in the rotating part of an electric motor. In
Chapter # 4 Three-Phase Induction Machines 1- Introduction (General Principles) Generally, conversion of electrical power into mechanical power takes place in the rotating part of an electric motor. In
Introduction to Synchronous. Machines. Kevin Gaughan
 Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
coil of the circuit. [8+8]
![coil of the circuit. [8+8] coil of the circuit. [8+8]](/thumbs/80/81218867.jpg) Code No: R05310202 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS (Electrical & Electronic Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: R05310202 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS (Electrical & Electronic Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
EEE3405 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES 2 - TEST
 ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, :00-8:00, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, 2012 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION 1. (25 pts) (a) Draw a circuit diagram for a differential amplifier designed under the following constraints: Use only BJTs. (You may
ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, 2012 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION 1. (25 pts) (a) Draw a circuit diagram for a differential amplifier designed under the following constraints: Use only BJTs. (You may
EXEMPLAR NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 ( ) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00
 NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 2008 (12041002) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 EXEMPLAR This question paper consists of 7 pages. EXEMPLAR -2- NC(V) TIME: 3 HOURS
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 2008 (12041002) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 EXEMPLAR This question paper consists of 7 pages. EXEMPLAR -2- NC(V) TIME: 3 HOURS
Power and Energy Measurement
 Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Fault Calculation Methods
 ELEC9713 Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Fault Calculation Methods There are two major problems that can occur in electrical systems: these are open circuits and short circuits. Of the two, the
ELEC9713 Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Fault Calculation Methods There are two major problems that can occur in electrical systems: these are open circuits and short circuits. Of the two, the
 Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each GATE question papers: Electrical Engineering 00 (EE) Published by:. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe x dx, is equal to o 0 e /e. Divergence of the threedimensional
Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each GATE question papers: Electrical Engineering 00 (EE) Published by:. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe x dx, is equal to o 0 e /e. Divergence of the threedimensional
Page 2 GATE EE
 Page GATE EE 009 www.gatehelp.com SOL. Overall gain of the system is written as G = GG G 3 We know that for a quantity that is product of two or more quantities total percentage error is some of the percentage
Page GATE EE 009 www.gatehelp.com SOL. Overall gain of the system is written as G = GG G 3 We know that for a quantity that is product of two or more quantities total percentage error is some of the percentage
3 d Calculate the product of the motor constant and the pole flux KΦ in this operating point. 2 e Calculate the torque.
 Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
Fault Analysis Power System Representation
 .1. Power System Representation Single Line Diagram: Almost all modern power systems are three phase systems with the phases of equal magnitude and equal phase difference (i.e., 10 o ). These three phase
.1. Power System Representation Single Line Diagram: Almost all modern power systems are three phase systems with the phases of equal magnitude and equal phase difference (i.e., 10 o ). These three phase
Tutorial Sheet Fig. Q1
 Tutorial Sheet - 04 1. The magnetic circuit shown in Fig. Q1 has dimensions A c = A g = 9 cm 2, g = 0.050 cm, l c = 30 cm, and N = 500 turns. Assume the value of the relative permeability,µ r = 70,000
Tutorial Sheet - 04 1. The magnetic circuit shown in Fig. Q1 has dimensions A c = A g = 9 cm 2, g = 0.050 cm, l c = 30 cm, and N = 500 turns. Assume the value of the relative permeability,µ r = 70,000
Chapter 11 AC and DC Equivalent Circuit Modeling of the Discontinuous Conduction Mode
 Chapter 11 AC and DC Equivalent Circuit Modeling of the Discontinuous Conduction Mode Introduction 11.1. DCM Averaged Switch Model 11.2. Small-Signal AC Modeling of the DCM Switch Network 11.3. High-Frequency
Chapter 11 AC and DC Equivalent Circuit Modeling of the Discontinuous Conduction Mode Introduction 11.1. DCM Averaged Switch Model 11.2. Small-Signal AC Modeling of the DCM Switch Network 11.3. High-Frequency
GATE 2011 Electrical Engineering Set C
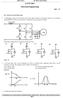 Electrical Engineering Set C Q. - Q.25 Carry One Mark each.. A three-phase current source inverter used for the speed control of an induction motor is to be realized using MOSFET switches as shown below.
Electrical Engineering Set C Q. - Q.25 Carry One Mark each.. A three-phase current source inverter used for the speed control of an induction motor is to be realized using MOSFET switches as shown below.
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous)
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Computer Methods in Power Systems Course Code : A60222
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Computer Methods in Power Systems Course Code : A60222
BASIC PRINCIPLES. Power In Single-Phase AC Circuit
 BASIC PRINCIPLES Power In Single-Phase AC Circuit Let instantaneous voltage be v(t)=v m cos(ωt+θ v ) Let instantaneous current be i(t)=i m cos(ωt+θ i ) The instantaneous p(t) delivered to the load is p(t)=v(t)i(t)=v
BASIC PRINCIPLES Power In Single-Phase AC Circuit Let instantaneous voltage be v(t)=v m cos(ωt+θ v ) Let instantaneous current be i(t)=i m cos(ωt+θ i ) The instantaneous p(t) delivered to the load is p(t)=v(t)i(t)=v
INDUCTION MOTOR MODEL AND PARAMETERS
 APPENDIX C INDUCTION MOTOR MODEL AND PARAMETERS C.1 Dynamic Model of the Induction Motor in Stationary Reference Frame A three phase induction machine can be represented by an equivalent two phase machine
APPENDIX C INDUCTION MOTOR MODEL AND PARAMETERS C.1 Dynamic Model of the Induction Motor in Stationary Reference Frame A three phase induction machine can be represented by an equivalent two phase machine
GATE 2012 Electrical Engineering Set - B
 GATE 2012 Electrical Engineering Set - B Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. 1. For the circuit shown in the figure, the voltage and current expressions are v(t) = and. The average power measured by the Wattmeter
GATE 2012 Electrical Engineering Set - B Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. 1. For the circuit shown in the figure, the voltage and current expressions are v(t) = and. The average power measured by the Wattmeter
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 206 Electrical Engineering CN Mathematics
Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 206 Electrical Engineering CN Mathematics
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
Electronics II. Final Examination
 f3fs_elct7.fm - The University of Toledo EECS:3400 Electronics I Section Student Name Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points.. 3 3. 5 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no Analog Electronics f3fs_elct7.fm
f3fs_elct7.fm - The University of Toledo EECS:3400 Electronics I Section Student Name Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points.. 3 3. 5 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no Analog Electronics f3fs_elct7.fm
NEW MEXICO STATE UNIVERSITY THE KLIPSCH SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING Ph.D. QUALIFYING EXAMINATION
 Write your four digit code here... NEW MEXICO STATE UNIVERSITY THE KLIPSCH SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING Ph.D. QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Exam Instructions: January 10, 011 9:00 AM - 1:00 PM
Write your four digit code here... NEW MEXICO STATE UNIVERSITY THE KLIPSCH SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING Ph.D. QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Exam Instructions: January 10, 011 9:00 AM - 1:00 PM
55:041 Electronic Circuits The University of Iowa Fall Final Exam
 Final Exam Name: Score Max: 135 Question 1 (1 point unless otherwise noted) a. What is the maximum theoretical efficiency for a class-b amplifier? Answer: 78% b. The abbreviation/term ESR is often encountered
Final Exam Name: Score Max: 135 Question 1 (1 point unless otherwise noted) a. What is the maximum theoretical efficiency for a class-b amplifier? Answer: 78% b. The abbreviation/term ESR is often encountered
Basic Electronics. Introductory Lecture Course for. Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011
 Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 2
Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 2
ECE-343 Test 1: Feb 10, :00-8:00pm, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-343 Test : Feb 0, 00 6:00-8:00pm, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION C Depl = C J0 + V R /V o ) m C Diff = τ F g m ω T = g m C µ + C π ω T = g m I / D C GD + C or V OV GS b = τ i τ i = R i C i ω H b Z = Z
ECE-343 Test : Feb 0, 00 6:00-8:00pm, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION C Depl = C J0 + V R /V o ) m C Diff = τ F g m ω T = g m C µ + C π ω T = g m I / D C GD + C or V OV GS b = τ i τ i = R i C i ω H b Z = Z
Electrical Machines-I Prof. D. Kastha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Electrical Machines-I Prof. D. Kastha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 20 Potential and Current Transformers (Refer Slide Time: 00:37) So far we
Electrical Machines-I Prof. D. Kastha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 20 Potential and Current Transformers (Refer Slide Time: 00:37) So far we
Fig. 1 CMOS Transistor Circuits (a) Inverter Out = NOT In, (b) NOR-gate C = NOT (A or B)
 1 Introduction to Transistor-Level Logic Circuits 1 By Prawat Nagvajara At the transistor level of logic circuits, transistors operate as switches with the logic variables controlling the open or closed
1 Introduction to Transistor-Level Logic Circuits 1 By Prawat Nagvajara At the transistor level of logic circuits, transistors operate as switches with the logic variables controlling the open or closed
Converter System Modeling via MATLAB/Simulink
 Converter System Modeling via MATLAB/Simulink A powerful environment for system modeling and simulation MATLAB: programming and scripting environment Simulink: block diagram modeling environment that runs
Converter System Modeling via MATLAB/Simulink A powerful environment for system modeling and simulation MATLAB: programming and scripting environment Simulink: block diagram modeling environment that runs
 TELANGANA/ANDHRA PRADESH TRANSCO/GENCO/DISCUM Assistant Engineer Examination ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Previous Paper 7) AP TRANSCO - AP GENCO-AE QUESTION PAPER 1. In two wattmeter method of 3-phase power
TELANGANA/ANDHRA PRADESH TRANSCO/GENCO/DISCUM Assistant Engineer Examination ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Previous Paper 7) AP TRANSCO - AP GENCO-AE QUESTION PAPER 1. In two wattmeter method of 3-phase power
AC Circuits Homework Set
 Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Homework Assignment 09
 Homework Assignment 09 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if r π = 2.5K, r o = 100K, g m = 40 ms, and C L =
Homework Assignment 09 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if r π = 2.5K, r o = 100K, g m = 40 ms, and C L =
LO 1: Three Phase Circuits
 Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
General Aptitude. Q. No. 1 5 Carry One Mark Each
 EE GATE-6-PAPER- www.gateforum.com General Aptitude Q. No. 5 arry One Mark Each. The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. (A) bare with (B) bore with () bear with (D) bare (). Identify
EE GATE-6-PAPER- www.gateforum.com General Aptitude Q. No. 5 arry One Mark Each. The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. (A) bare with (B) bore with () bear with (D) bare (). Identify
The output voltage is given by,
 71 The output voltage is given by, = (3.1) The inductor and capacitor values of the Boost converter are derived by having the same assumption as that of the Buck converter. Now the critical value of the
71 The output voltage is given by, = (3.1) The inductor and capacitor values of the Boost converter are derived by having the same assumption as that of the Buck converter. Now the critical value of the
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current. 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3.
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults
 Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults Introduction The sequence circuits and the sequence networks developed in the previous chapter will now be used for finding out fault current during unsymmetrical faults.
Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults Introduction The sequence circuits and the sequence networks developed in the previous chapter will now be used for finding out fault current during unsymmetrical faults.
CHAPTER 22 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
 CHAPTER 22 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PROBLEMS 47. REASONING AND Using Equation 22.7, we find emf 2 M I or M ( emf 2 ) t ( 0.2 V) ( 0.4 s) t I (.6 A) ( 3.4 A) 9.3 0 3 H 49. SSM REASONING AND From the results
CHAPTER 22 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PROBLEMS 47. REASONING AND Using Equation 22.7, we find emf 2 M I or M ( emf 2 ) t ( 0.2 V) ( 0.4 s) t I (.6 A) ( 3.4 A) 9.3 0 3 H 49. SSM REASONING AND From the results
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits
 Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
GATE 2018 [Afternoon Session]
![GATE 2018 [Afternoon Session] GATE 2018 [Afternoon Session]](/thumbs/90/101431362.jpg) GATE 08 [Aternoon Session].General Aptitude. Since 004 Question Q. to Q.5 carry one mark each ( k ) For what values o k given below is an integer? k 3 (A) 4, 8, 8 (B) 4, 0, 6 (C) 4, 8, 8 (D) 8, 6, 8 Ans.
GATE 08 [Aternoon Session].General Aptitude. Since 004 Question Q. to Q.5 carry one mark each ( k ) For what values o k given below is an integer? k 3 (A) 4, 8, 8 (B) 4, 0, 6 (C) 4, 8, 8 (D) 8, 6, 8 Ans.
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION
 ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 1) A Circular coil is placed near a current carrying conductor. The induced current is anti clock wise when the coil is, 1. Stationary 2. Moved away from the conductor 3. Moved
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 1) A Circular coil is placed near a current carrying conductor. The induced current is anti clock wise when the coil is, 1. Stationary 2. Moved away from the conductor 3. Moved
POWER SYSTEM STABILITY
 LESSON SUMMARY-1:- POWER SYSTEM STABILITY 1. Introduction 2. Classification of Power System Stability 3. Dynamic Equation of Synchronous Machine Power system stability involves the study of the dynamics
LESSON SUMMARY-1:- POWER SYSTEM STABILITY 1. Introduction 2. Classification of Power System Stability 3. Dynamic Equation of Synchronous Machine Power system stability involves the study of the dynamics
Conventional Paper I (a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials?
 Conventional Paper I-03.(a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials? (ii) Give one example each of a dielectric and a ferroelectric material
Conventional Paper I-03.(a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials? (ii) Give one example each of a dielectric and a ferroelectric material
POWER SEMICONDUCTOR BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES
 POWER SEMICONDUCT BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES [Time: 3 Hrs] [Max. Marks: 80] Instructions: Solve any six questions from Q.No (1 or 2), Q.No (3 or 4), Q.No (5 or 6), Q.No (7 or 8), Q.No (9 or 10), Q.No (11 or
POWER SEMICONDUCT BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES [Time: 3 Hrs] [Max. Marks: 80] Instructions: Solve any six questions from Q.No (1 or 2), Q.No (3 or 4), Q.No (5 or 6), Q.No (7 or 8), Q.No (9 or 10), Q.No (11 or
Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines
 Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems Lesson 17_et332b.pptx 1 Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how synchronous machines
Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems Lesson 17_et332b.pptx 1 Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how synchronous machines
Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]
![Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark] Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]](/thumbs/88/115570773.jpg) Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
