Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
|
|
|
- Dulcie Tate
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GATE 08 General Aptitude (GA) Set6 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Since you have gone off the, the sand is likely to damage the car. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) course, coarse (C) coarse, course (B) course, course (D) coarse, coarse Q. A common misconception among writers is that sentence structure mirrors thought; the more the structure, the more complicated the ideas. The word that best fills the blank in the above sentence is (A) detailed (B) simple (C) clear (D) convoluted Q.3 The three roots of the equation f(x) = 0 are x = {, 0, 3}. What are the three values of x for which f(x 3) = 0? (A) 5, 3, 0 (B), 0, 3 (C) 0, 6, 8 (D), 3, 6 Q.4 For what values of k given below is (k) k 3 an integer? (A) 4, 8, 8 (B) 4, 0, 6 (C) 4, 8, 8 (D) 8, 6, 8 Q.5 Functions F(a, b) and G(a, b) are defined as follows: F(a, b) = (a b) and G(a, b) = a b, where x represents the absolute value of x. What would be the value of G(F(, 3), G(, 3))? (A) (B) 4 (C) 6 (D) 36 Q. 6 Q. 0 carry two marks each. Q.6 An password must contain three characters. The password has to contain one numeral from 0 to 9, one upper case and one lower case character from the English alphabet. How many distinct passwords are possible? (A) 6,760 (B) 3,50 (C) 40,560 (D),05,456 GA /
2 GATE 08 General Aptitude (GA) Set6 Q.7 In a certain code, AMCF is written as EQGJ and NKUF is written as ROYJ. How will DHLP be written in that code? (A) RSTN (B) TLPH (C) HLPT (D) XSVR Q.8 A class of twelve children has two more boys than girls. A group of three children are randomly picked from this class to accompany the teacher on a field trip. What is the probability that the group accompanying the teacher contains more girls than boys? (A) 0 (B) (C) (D) 5 Q.9 A designer uses marbles of four different colours for his designs. The cost of each marble is the same, irrespective of the colour. The table below shows the percentage of marbles of each colour used in the current design. The cost of each marble increased by 5%. Therefore, the designer decided to reduce equal numbers of marbles of each colour to keep the total cost unchanged. What is the percentage of blue marbles in the new design? Blue Black Red Yellow 40% 5% 0% 5% (A) (B) 40.5 (C) (D) 46.5 Q.0 P, Q, R and S crossed a lake in a boat that can hold a maximum of two persons, with only one set of oars. The following additional facts are available. (i) The boat held two persons on each of the three forward trips across the lake and one person on each of the two return trips. (ii) P is unable to row when someone else is in the boat. (iii) Q is unable to row with anyone else except R. (iv) Each person rowed for at least one trip. (v) Only one person can row during a trip. Who rowed twice? (A) P (B) Q (C) R (D) S END OF THE QUESTION PAPER GA /
3 GATE 08 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. A singlephase 00 kva, 000 V / 00 V, 50 Hz transformer has a voltage drop of 5% across its series impedance at full load. Of this, 3% is due to resistance. The percentage regulation of the transformer at full load with 0.8 lagging power factor is (A) 4.8 (B) 6.8 (C) 8.8 (D) 0.8 Q. In a salient pole synchronous motor, the developed reluctance torque attains the maximum value when the load angle in electrical degrees is (A) 0 (B) 45 (C) 60 (D) 90 Q.3 A single phase fully controlled rectifier is supplying a load with an antiparallel diode as shown in the figure. All switches and diodes are ideal. Which one of the following is true for instantaneous load voltage and current? i o L O A D v o (A) vo0 & io 0 (B) vo0 & io 0 (C) v 0 & i 0 (D) v 0 & i 0 o o o o Q.4 Four power semiconductor devices are shown in the figure along with their relevant terminals. The device(s) that can carry dc current continuously in the direction shown when gated appropriately is (are) A MT A D G K I G I MT G I K G I S Thyristor Triac GTO MOSFET (A) Triac only (B) Triac and MOSFET (C) Triac and GTO (D) Thyristor and Triac EE /5
4 GATE 08 Q.5 Two wattmeter method is used for measurement of power in a balanced threephase load supplied from a balanced threephase system. If one of the wattmeters reads half of the other (both positive), then the power factor of the load is (A) 0.53 (B) 0.63 (C) (D) Q.6 Consider a lossy transmission line with and as the sending and receiving end voltages, respectively. Z and are the series impedance and reactance of the line, respectively. The steadystate stability limit for the transmission line will be X V V (A) greater than (C) equal to VV X VV X (B) less than (D) equal to VV X VV Z Q.7 The graph of a network has 8 nodes and 5 independent loops. The number of branches of the graph is (A) (B) (C) 3 (D) 4 Q.8 In the figure, the voltages are v (t) = 00cos (ωt), v (t) = 00cos (ωt π/8) and v 3 (t) = 00cos (ωt π/36). The circuit is in sinusoidal steady state, and R << ωl. P, P and P 3 are the average power outputs. Which one of the following statements is true? R L L R v (t) P P P 3 v (t) v 3 (t) (A) P = P = P 3 = 0 (B) P < 0, P > 0, P 3 > 0 (C) P < 0, P > 0, P 3 < 0 (D) P > 0, P < 0, P 3 > 0 EE /5
5 GATE 08 Q.9 Match the transfer functions of the secondorder systems with the nature of the systems given below. Transfer functions 5 P: s 5s5 5 Q: s 0s5 35 R: s 8s35 Nature of system I: Overdamped II: Critically damped III: Underdamped (A) PI, QII, RIII (B) PII, QI, RIII (C) PIII, QII, RI (D) PIII, QI, RII Q.0 A positive charge of nc is placed at (0, 0, 0.) where all dimensions are in metres. Consider the plane to be a conducting ground plane. Take F/m. The component of the E field at (0, 0, 0.) is closest to z x y (A) V/m (B) V/m (C) V/m (D) V/m Q. Let f be a realvalued function of a real variable defined as f ( x) x x for 0 f ( x). Which one of the following statements is true? (A) f() x is discontinuous at x 0. (B) f() x is continuous but not differentiable at x 0. (C) f() x is differentiable but its first derivative is not continuous at x 0. (D) f() x is differentiable but its first derivative is not differentiable at x 0. x x for 0, and Q. The value of the directional derivative of the function Φ(x, y, z) = xy yz zx at the point (,, ) in the direction of the vector p = i j k is (A) (B) 0.95 (C) 0.93 (D) 0.9 Q.3 The value of the integral z dz in counter clockwise direction around a circle C of C z 4 radius with center at the point z = is (A) πi (B) πi (C) πi (D) πi EE 3/5
6 GATE 08 Q.4 In the logic circuit shown in the figure, Y is given by A B C D Y (A) Y = ABCD (B) Y = (A B)(C D) (C) Y = A B C D (D) Y = AB CD Q.5 The opamp shown in the figure is ideal. The input impedance v in i in is given by Z i in v in v o R R (A) Z R R (B) Z R R (C) Z (D) Z R R R Q.6 A continuoustime input signal x(t) is an eigenfunction of an LTI system, if the output is (A) k x(t), where k is an eigenvalue (B) k e jt x(t), where k is an eigenvalue and e jt is a complex exponential signal (C) x(t) e jt, where e jt is a complex exponential signal (D) k H(), where k is an eigenvalue and H() is a frequency response of the system Q.7 Consider a nonsingular square matrix A. If trace ( A) 4 and trace ( A ) 5, the determinant of the matrix A is (up to decimal place). Q.8 Let f be a realvalued function of a real variable defined as f ( x) x [ x], where [ x ].5 denotes the largest integer less than or equal to x. The value of f ( x )dx is (up 0.5 to decimal places). EE 4/5
7 GATE 08 Q.9 V In the twoport network shown, the h parameter where, h =, when V =0 I is (up to decimal places). in ohms I V I V Q.0 The series impedance matrix of a short threephase transmission line in phase coordinates Z s Z m Z m is [ Z m Z s Z m ]. If the positive sequence impedance is ( j 0) Ω, and the zero Z m Z m Z s sequence is (4 j 3) Ω, then the imaginary part of Z m (in Ω) is (up to decimal places). Q. The positive, negative and zero sequence impedances of a 5 MVA, threephase, 5.5 kv, stargrounded, 50 Hz generator are j0. pu, j0.05 pu and j0.0 pu respectively on the machine rating base. The machine is unloaded and working at the rated terminal voltage. If the grounding impedance of the generator is j0.0 pu, then the magnitude of fault current for a bphase to ground fault (in ka) is (up to decimal places). Q. A bus admittance matrix for an electric power system has 8000 nonzero elements. The minimum number of branches (transmission lines and transformers) in this system are (up to decimal places). Q.3 The waveform of the current drawn by a semiconverter from a sinusoidal AC voltage source is shown in the figure. If I0 = 0 A, the rms value of fundamental component of the current is A (up to decimal places). voltage and current Vm sin(ωt) 0 30 I 0 I 0 80 ωt 0 EE 5/5
8 GATE 08 Q.4 A separately excited dc motor has an armature resistance R a = 0.05 Ω. The field excitation is kept constant. At an armature voltage of 00 V, the motor produces a torque of 500 Nm at zero speed. Neglecting all mechanical losses, the noload speed of the motor (in radian/s) for an armature voltage of 50 V is (up to decimal places). Q.5 Consider a unity feedback system with forward transfer function given by Gs () ( s)( s) The steadystate error in the output of the system for a unitstep input is (up to decimal places). EE 6/5
9 GATE 08 Q. 6 Q. 55 carry two marks each. Q.6 A transformer with toroidal core of permeability is shown in the figure. Assuming uniform flux density across the circular core crosssection of radius, and neglecting any leakage flux, the best estimate for the mean radius R is r R i I sint P r is 0 v V cost P NP R N S vs (A) P Vr N I (B) P S Ir N N V (C) Vr N P I (D) Ir N P V Q.7 A 0 Ampere moving iron ammeter has an internal resistance of 50 mω and inductance of 0. mh. A shunt coil is connected to extend its range to 00 Ampere for all operating frequencies. The time constant in milliseconds and resistance in mω of the shunt coil respectively are (A), 5.55 (B), (C).8, 0.55 (D)., Q.8 The positive, negative and zero sequence impedances of a three phase generator are Z, Z and Z 0 respectively. For a linetoline fault with fault impedance Z f, the fault current is I f = ki f, where I f is the fault current with zero fault impedance. The relation between Z f and k is (A) Zf = (Z Z )( k) k (C) Zf = (Z Z )k k (B) Zf = (Z Z )(k) k (D) Zf = (Z Z )k k EE 7/5
10 GATE 08 Q.9 Consider the two bus power system network with given loads as shown in the figure. All the values shown in the figure are in per unit. The reactive power supplied by generator G and G are QG and QG respectively. The per unit values of QG, QG, and line reactive power loss (Qloss) respectively are.0.00 j0. G 0jQ G Q loss G 5jQ G 5j5 0j0 (A) 5. 00,.68,.68 (B) 6.34, 0.00,.34 (C) 6.34,.34,.68 (D) 5.00,.34,.34 Q.30 The perunit power output of a salientpole generator which is connected to an infinite bus, is given by the expression, P =.4 sin δ 0.5 sin δ, where δ is the load angle. Newton Raphson method is used to calculate the value of δ for P = 0.8 pu. If the initial guess is 30, then its value (in degree) at the end of the first iteration is (A) 5 (B) 8.48 (C) 8.74 (D) 3.0 Q.3 A DC voltage source is connected to a series LC circuit by turning on the switch S at time t 0 as shown in the figure. Assume i(0) 0, v(0) 0. Which one of the following circular loci represents the plot of i( t) versus v( t )? S it () t 0 L=H 5V C=F vt () (A) it () vt () (B) it () (C) it () (D) it () (0, 5) (5, 0) vt () (0, 5) ( 5, 0) vt () vt () EE 8/5
11 GATE 08 Q.3 The equivalent impedance Z eq j 9 for the infinite ladder circuit shown in the figure is j 9 Z eq j 5 j 5... j j (A) j Ω (B) j Ω (C) j3 Ω (D) 3 Ω Q.33 Consider a system governed by the following equations d x ( t) x( t) x( t) dt d x( t) x( t) x( t) dt The initial conditions are such that x(0) x(0). Let x f lim x ( t) and t x f lim ( ) t x t. Which one of the following is true? (A) x x (B) f f x x (C) f f x x f f (D) x x f f Q.34 The number of roots of the polynomial, s 7 s 6 7s 5 4s 4 3s 3 73s 5s 00, in the open left half of the complex plane is (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 Q.35 If C is a circle z = 4 and f (z) = z (z 3z), then C f ( z) dz is (A) (B) 0 (C) (D) EE 9/5
12 GATE 08 Q.36 Which one of the following statements is true about the digital circuit shown in the figure D Q D Q D Q fout C C C fin (A) It can be used for dividing the input frequency by 3. (B) It can be used for dividing the input frequency by 5. (C) It can be used for dividing the input frequency by 7. (D) It cannot be reliably used as a frequency divider due to disjoint internal cycles. Q.37 Digital input signals A, B, C with A as the MSB and C as the LSB are used to realize the Boolean function F = m 0 m m 3 m 5 m 7, where m i denotes the i th minterm. In addition, F has a don t care for m. The simplified expression for F is given by (A) A C B C AC (C) C A (B) A C (D) A C BC AC Q.38 Consider the two continuoustime signals defined below: t, t t, t x( t), x( t) 0, otherwise 0, otherwise These signals are sampled with a sampling period of T = 0.5 seconds to obtain discretetime signals and x [ n ], respectively. Which one of the following statements is true? x[ n] (A) The energy of x[ n] is greater than the energy of x [ n ]. (B) The energy of x [ ] n is greater than the energy of (C) x[ n] and x [ ] n have equal energies. (D) Neither x[ n ] nor x [ ] n is a finiteenergy signal. x[ n]. Q.39 The signal energy of the continuoustime signal x ( t) = [( t ) u( t )][( t ) u( t )][( t 3) u( t 3)][( t 4) u( t 4)] is (A) /3 (B) 7/3 (C) /3 (D) 5/3 EE 0/5
13 GATE 08 Q.40 The Fourier transform of a continuoustime signal is given by X ( ),, where and denotes frequency. Then the 0 j value of ln xt () logarithm to base e) at t j xt () = is (up to decimal place). ( ln denotes the Q.4 In the circuit shown in the figure, the bipolar junction transistor (BJT) has a current gain β = 00. The baseemitter voltage drop is a constant, V BE = 0.7 V. The value of the Thevenin equivalent resistance R Th (in Ω) as shown in the figure is (up to decimal places). 5 V 0 0 k 0.7 V k a b R Th Q.4 As shown in the figure, C is the arc from the point (3,0) to the point (0,3) on the circle x y = 9. The value of the integral (y yx)dx (xy x )dy is (up to C decimal places). y (0,3) C x (3,0) Q.43 3 Let f ( x) 3x 7x 5x 6. The maximum value of f() x over the interval [0, ] is (up to decimal place). EE /5
14 GATE 08 Q.44 0 Let A 0 3 and B A A 4A 5I, where I is the determinant of B is (up to decimal place). identity matrix. The Q.45 The capacitance of an airfilled parallelplate capacitor is 60 pf. When a dielectric slab whose thickness is half the distance between the plates, is placed on one of the plates covering it entirely, the capacitance becomes 86 pf. Neglecting the fringing effects, the relative permittivity of the dielectric is (up to decimal places). Q.46 The unit step response y(t) of a unity feedback system with open loop transfer function K G ( s) H( s) is shown in the figure. The value of K is (up to ( s ) ( s ) decimal places). y(t).4. y(t) Time (sec) t (sec) Q.47 A threephase load is connected to a threephase balanced supply as shown in the figure. If V an 000 V, V bn 00 0 V and V cn V (angles are considered positive in the anticlockwise direction), the value of R for zero current in the neutral wire is Ω (up to decimal places). a n R c j0 j0 b EE /5
15 GATE 08 Q.48 The voltage across the circuit in the figure, and the current through it, are given by the following expressions: v(t) = 5 0 cos(ωt 60 ) V i(t) = 5 X cos(ωt) A where ω = 00 π radian/s. If the average power delivered to the circuit is zero, then the value of X (in Ampere) is (up to decimal places). i(t) v(t) Electrical Circuit Q.49 A phase controlled single phase rectifier, supplied by an AC source, feeds power to an RLE load as shown in the figure. The rectifier output voltage has an average value given by Vo= V m π (3 cos ), where V m= 80π volts and α is the firing angle. If the power delivered to the lossless battery is 600 W, α in degree is (up to decimal places). Ω Vm sin(ωt) V O 0 mh 80 V Battery EE 3/5
16 GATE 08 Q.50 The figure shows two buck converters connected in parallel. The common input dc voltage for the converters has a value of 00 V. The converters have inductors of identical value. The load resistance is. The capacitor voltage has negligible ripple. Both converters operate in the continuous conduction mode. The switching frequency is khz, and the switch control signals are as shown. The circuit operates in the steady state. Assuming that the converters share the load equally, the average value of i S, the current of switch S (in Ampere), is (up to decimal places). i S 00 V S L C S Switch control signals S L S ms ms t t Q.5 A 3phase 900 kva, 3 kv / kv ( /Y), 50 Hz transformer has primary (high voltage side) resistance per phase of 0.3 Ω and secondary (low voltage side) resistance per phase of 0.0 Ω. Iron loss of the transformer is 0 kw. The full load % efficiency of the transformer operated at unity power factor is (up to decimal places). 3 Q.5 A 00 V DC series motor, when operating from rated voltage while driving a certain load, draws 0 A current and runs at 000 r.p.m. The total series resistance is Ω. The magnetic circuit is assumed to be linear. At the same supply voltage, the load torque is increased by 44%. The speed of the motor in r.p.m. (rounded to the nearest integer) is. Q.53 A dc to dc converter shown in the figure is charging a battery bank, B whose voltage is constant at 50 V. B is another battery bank whose voltage is constant at 50 V. The value of the inductor, L is 5 mh and the ideal switch, S is operated with a switching frequency of 5 khz with a duty ratio of 0.4. Once the circuit has attained steady state and assuming the diode D to be ideal, the power transferred from B to B (in Watt) is (up to decimal places). i L L = 5 mh D 50 V B S B 50 V EE 4/5
17 GATE 08 Q.54 The equivalent circuit of a single phase induction motor is shown in the figure, where the ' ' parameters are R R X l X l=, X M = 40 and s is the slip. At noload, the motor speed can be approximated to be the synchronous speed. The noload lagging power factor of the motor is (up to 3 decimal places). V0 jx l R X j M X j M R s j, X l, R ( s) j, X l, Q.55 The voltage v(t) across the terminals a and b as shown in the figure, is a sinusoidal voltage having a frequency ω = 00 radian/s. When the inductor current i(t) is in phase with the voltage v(t), the magnitude of the impedance Z (in Ω) seen between the terminals a and b is (up to decimal places). v(t) Z a b i(t) L 00 F 00 END OF THE QUESTION PAPER EE 5/5
GATE 2018 [Afternoon Session]
![GATE 2018 [Afternoon Session] GATE 2018 [Afternoon Session]](/thumbs/90/101431362.jpg) GATE 08 [Aternoon Session].General Aptitude. Since 004 Question Q. to Q.5 carry one mark each ( k ) For what values o k given below is an integer? k 3 (A) 4, 8, 8 (B) 4, 0, 6 (C) 4, 8, 8 (D) 8, 6, 8 Ans.
GATE 08 [Aternoon Session].General Aptitude. Since 004 Question Q. to Q.5 carry one mark each ( k ) For what values o k given below is an integer? k 3 (A) 4, 8, 8 (B) 4, 0, 6 (C) 4, 8, 8 (D) 8, 6, 8 Ans.
GATE 2018 [Afternoon Session]
![GATE 2018 [Afternoon Session] GATE 2018 [Afternoon Session]](/thumbs/78/77883687.jpg) GATE 8 [Afternoon Session].General Aptitude. Since 4 Question Ans. Q. to Q.5 carry one mark each ( k ) For what values of k given below is k 3 an integer? (A) 4, 8, 8 (B) 4,, 6 (C) 4, 8, 8 (D) 8, 6, 8
GATE 8 [Afternoon Session].General Aptitude. Since 4 Question Ans. Q. to Q.5 carry one mark each ( k ) For what values of k given below is k 3 an integer? (A) 4, 8, 8 (B) 4,, 6 (C) 4, 8, 8 (D) 8, 6, 8
EE Branch GATE Paper 2010
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
G F 1,3, G 1,3 G 4,2 F 1,3 4&G 1,3 2
 EE-GATE 08 EE-GATE 08 Section-I: General Ability. Functions F(a,b) and G(a,b) are defined as follows: F(a,b) = (a-b) and G(a,b) = a-b, where x represents the absolute value of x. What would be the value
EE-GATE 08 EE-GATE 08 Section-I: General Ability. Functions F(a,b) and G(a,b) are defined as follows: F(a,b) = (a-b) and G(a,b) = a-b, where x represents the absolute value of x. What would be the value
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
+ ( )= with initial condition
 Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
GATEFORUM- India s No.1 institute for GATE training 1
 EE-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. Given a vector field F = y xax yzay = x a z, the line integral F.dl evaluated along a segment on the x-axis from x= to x= is -.33 (B) 0.33 (D) 7 : (B) x 0.
EE-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. Given a vector field F = y xax yzay = x a z, the line integral F.dl evaluated along a segment on the x-axis from x= to x= is -.33 (B) 0.33 (D) 7 : (B) x 0.
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Given ff(zz) = gg(zz) + h(zz), where ff, gg, h are complex valued functions of a complex variable zz. Which one of the following statements is TUE? (A) If ff(zz) is
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Given ff(zz) = gg(zz) + h(zz), where ff, gg, h are complex valued functions of a complex variable zz. Which one of the following statements is TUE? (A) If ff(zz) is
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE
 Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits
 Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Lecture 11 - AC Power
 - AC Power 11/17/2015 Reading: Chapter 11 1 Outline Instantaneous power Complex power Average (real) power Reactive power Apparent power Maximum power transfer Power factor correction 2 Power in AC Circuits
- AC Power 11/17/2015 Reading: Chapter 11 1 Outline Instantaneous power Complex power Average (real) power Reactive power Apparent power Maximum power transfer Power factor correction 2 Power in AC Circuits
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
Three Phase Circuits
 Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
SE]y[-2017(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
![SE]y[-2017(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. SE]y[-2017(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.](/thumbs/94/122291001.jpg) RoU No. 300218 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SE]y[-2017(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
RoU No. 300218 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SE]y[-2017(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL
 Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator. The excitation
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator. The excitation
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
Transformer. Transformer comprises two or more windings coupled by a common magnetic circuit (M.C.).
 . Transformers Transformer Transformer comprises two or more windings coupled by a common magnetic circuit (M.C.). f the primary side is connected to an AC voltage source v (t), an AC flux (t) will be
. Transformers Transformer Transformer comprises two or more windings coupled by a common magnetic circuit (M.C.). f the primary side is connected to an AC voltage source v (t), an AC flux (t) will be
SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -1. Please read the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
 Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each GATE question papers: Electrical Engineering 00 (EE) Published by:. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe x dx, is equal to o 0 e /e. Divergence of the threedimensional
Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each GATE question papers: Electrical Engineering 00 (EE) Published by:. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe x dx, is equal to o 0 e /e. Divergence of the threedimensional
Conventional Paper-I Part A. 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy
 EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
BASIC PRINCIPLES. Power In Single-Phase AC Circuit
 BASIC PRINCIPLES Power In Single-Phase AC Circuit Let instantaneous voltage be v(t)=v m cos(ωt+θ v ) Let instantaneous current be i(t)=i m cos(ωt+θ i ) The instantaneous p(t) delivered to the load is p(t)=v(t)i(t)=v
BASIC PRINCIPLES Power In Single-Phase AC Circuit Let instantaneous voltage be v(t)=v m cos(ωt+θ v ) Let instantaneous current be i(t)=i m cos(ωt+θ i ) The instantaneous p(t) delivered to the load is p(t)=v(t)i(t)=v
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous)
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Computer Methods in Power Systems Course Code : A60222
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Computer Methods in Power Systems Course Code : A60222
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
SECTION - A. A current impulse, 5δ(t), is forced through a capacitor C. The voltage, Vc(t), across the capacitor is given by. 5 t C.
 SETION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..5) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
SETION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..5) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system.
 1-The steady-state error of a feedback control system with an acceleration input becomes finite in a a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system. 2-A good control system has
1-The steady-state error of a feedback control system with an acceleration input becomes finite in a a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system. 2-A good control system has
ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines. Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015
 ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015 1 Content (Materials are from Chapters 16-17) Synchronous Generators Synchronous Motors 2 Synchronous Generators
ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015 1 Content (Materials are from Chapters 16-17) Synchronous Generators Synchronous Motors 2 Synchronous Generators
EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION
 EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is single line diagram? A Single line diagram is diagrammatic representation of power system in which the components are represented by
EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is single line diagram? A Single line diagram is diagrammatic representation of power system in which the components are represented by
REACTANCE. By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013
 REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
11. AC Circuit Power Analysis
 . AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
. AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
ECE 421/521 Electric Energy Systems Power Systems Analysis I 2 Basic Principles. Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2013
 ECE 41/51 Electric Energy Systems Power Systems Analysis I Basic Principles Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 013 1 Outline Power in a 1-phase AC circuit Complex power Balanced 3-phase circuit Single Phase AC System
ECE 41/51 Electric Energy Systems Power Systems Analysis I Basic Principles Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 013 1 Outline Power in a 1-phase AC circuit Complex power Balanced 3-phase circuit Single Phase AC System
EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State. Y. Baghzouz
 EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State Y. Baghzouz Transmission Line Model Distributed Parameter Model: Terminal Voltage/Current Relations: Characteristic impedance: Propagation constant: π
EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State Y. Baghzouz Transmission Line Model Distributed Parameter Model: Terminal Voltage/Current Relations: Characteristic impedance: Propagation constant: π
Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies
 Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies Induced emf - Faraday s Experiment When a magnet moves toward a loop of wire, the ammeter shows the presence of a current When
Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies Induced emf - Faraday s Experiment When a magnet moves toward a loop of wire, the ammeter shows the presence of a current When
LO 1: Three Phase Circuits
 Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
An Introduction to Electrical Machines. P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy
 An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
ELG4125: Power Transmission Lines Steady State Operation
 ELG4125: Power Transmission Lines Steady State Operation Two-Port Networks and ABCD Models A transmission line can be represented by a two-port network, that is a network that can be isolated from the
ELG4125: Power Transmission Lines Steady State Operation Two-Port Networks and ABCD Models A transmission line can be represented by a two-port network, that is a network that can be isolated from the
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY. 1. Understands the physical construction and characteristics of basic components.
 SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
Introduction to Synchronous. Machines. Kevin Gaughan
 Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
CLUSTER LEVEL WORK SHOP
 CLUSTER LEVEL WORK SHOP SUBJECT PHYSICS QUESTION BANK (ALTERNATING CURRENT ) DATE: 0/08/06 What is the phase difference between the voltage across the inductance and capacitor in series AC circuit? Ans.
CLUSTER LEVEL WORK SHOP SUBJECT PHYSICS QUESTION BANK (ALTERNATING CURRENT ) DATE: 0/08/06 What is the phase difference between the voltage across the inductance and capacitor in series AC circuit? Ans.
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 79 CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase and three-phase self-excited induction generators has been presented
79 CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase and three-phase self-excited induction generators has been presented
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES. School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION. Session
 Name: Student ID: Signature: THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION Session 00 ELEC46 Power System Analysis TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours TOTAL
Name: Student ID: Signature: THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION Session 00 ELEC46 Power System Analysis TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours TOTAL
Power Factor Improvement
 Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
ELECTRIC POWER CIRCUITS BASIC CONCEPTS AND ANALYSIS
 Contents ELEC46 Power ystem Analysis Lecture ELECTRC POWER CRCUT BAC CONCEPT AND ANALY. Circuit analysis. Phasors. Power in single phase circuits 4. Three phase () circuits 5. Power in circuits 6. ingle
Contents ELEC46 Power ystem Analysis Lecture ELECTRC POWER CRCUT BAC CONCEPT AND ANALY. Circuit analysis. Phasors. Power in single phase circuits 4. Three phase () circuits 5. Power in circuits 6. ingle
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis
 Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
EE 212 PASSIVE AC CIRCUITS
 EE 212 PASSIVE AC CIRCUITS Condensed Text Prepared by: Rajesh Karki, Ph.D., P.Eng. Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of Saskatchewan About the EE 212 Condensed Text The major topics in the course
EE 212 PASSIVE AC CIRCUITS Condensed Text Prepared by: Rajesh Karki, Ph.D., P.Eng. Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of Saskatchewan About the EE 212 Condensed Text The major topics in the course
Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 9 Transmission Line Steady State Operation Welcome to lesson 9, in Power
Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 9 Transmission Line Steady State Operation Welcome to lesson 9, in Power
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Synchronous Machines
 Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
Alternating Current Circuits
 Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
Fault Calculation Methods
 ELEC9713 Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Fault Calculation Methods There are two major problems that can occur in electrical systems: these are open circuits and short circuits. Of the two, the
ELEC9713 Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Fault Calculation Methods There are two major problems that can occur in electrical systems: these are open circuits and short circuits. Of the two, the
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
Power Electronics
 Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 6 CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 5.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase SEIG has been discussed in the previous chapters. In this chapter,
6 CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 5.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase SEIG has been discussed in the previous chapters. In this chapter,
Electrical Machines-I Prof. D. Kastha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Electrical Machines-I Prof. D. Kastha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 20 Potential and Current Transformers (Refer Slide Time: 00:37) So far we
Electrical Machines-I Prof. D. Kastha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 20 Potential and Current Transformers (Refer Slide Time: 00:37) So far we
Work, Energy and Power
 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
Driven RLC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions
 Driven LC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions Problem : Using the same circuit as in problem 6, only this time leaving the function generator on and driving below resonance, which in the following pairs
Driven LC Circuits Challenge Problem Solutions Problem : Using the same circuit as in problem 6, only this time leaving the function generator on and driving below resonance, which in the following pairs
Lecture (5) Power Factor,threephase circuits, and Per Unit Calculations
 Lecture (5) Power Factor,threephase circuits, and Per Unit Calculations 5-1 Repeating the Example on Power Factor Correction (Given last Class) P? Q? S? Light Motor From source 1000 volts @ 60 Htz 10kW
Lecture (5) Power Factor,threephase circuits, and Per Unit Calculations 5-1 Repeating the Example on Power Factor Correction (Given last Class) P? Q? S? Light Motor From source 1000 volts @ 60 Htz 10kW
ECE 420. Review of Three Phase Circuits. Copyright by Chanan Singh, Panida Jirutitijaroen, and Hangtian Lei, For educational use only-not for sale.
 ECE 40 Review of Three Phase Circuits Outline Phasor Complex power Power factor Balanced 3Ф circuit Read Appendix A Phasors and in steady state are sinusoidal functions with constant frequency 5 0 15 10
ECE 40 Review of Three Phase Circuits Outline Phasor Complex power Power factor Balanced 3Ф circuit Read Appendix A Phasors and in steady state are sinusoidal functions with constant frequency 5 0 15 10
ECE Branch GATE Paper The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2
 Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 206 Electrical Engineering CN Mathematics
Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 206 Electrical Engineering CN Mathematics
Review of DC Electric Circuit. DC Electric Circuits Examples (source:
 Review of DC Electric Circuit DC Electric Circuits Examples (source: http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/dcex.html) 1 Review - DC Electric Circuit Multisim Circuit Simulation DC Circuit
Review of DC Electric Circuit DC Electric Circuits Examples (source: http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/dcex.html) 1 Review - DC Electric Circuit Multisim Circuit Simulation DC Circuit
Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults
 Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults Introduction The sequence circuits and the sequence networks developed in the previous chapter will now be used for finding out fault current during unsymmetrical faults.
Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults Introduction The sequence circuits and the sequence networks developed in the previous chapter will now be used for finding out fault current during unsymmetrical faults.
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering
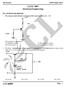 Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
TSTE25 Power Electronics. Lecture 3 Tomas Jonsson ICS/ISY
 TSTE25 Power Electronics Lecture 3 Tomas Jonsson ICS/ISY 2016-11-09 2 Outline Rectifiers Current commutation Rectifiers, cont. Three phase Inrush and short circuit current Exercises 5-5, 5-8, 3-100, 3-101,
TSTE25 Power Electronics Lecture 3 Tomas Jonsson ICS/ISY 2016-11-09 2 Outline Rectifiers Current commutation Rectifiers, cont. Three phase Inrush and short circuit current Exercises 5-5, 5-8, 3-100, 3-101,
 TELANGANA/ANDHRA PRADESH TRANSCO/GENCO/DISCUM Assistant Engineer Examination ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Previous Paper 7) AP TRANSCO - AP GENCO-AE QUESTION PAPER 1. In two wattmeter method of 3-phase power
TELANGANA/ANDHRA PRADESH TRANSCO/GENCO/DISCUM Assistant Engineer Examination ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Previous Paper 7) AP TRANSCO - AP GENCO-AE QUESTION PAPER 1. In two wattmeter method of 3-phase power
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1
 Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor. The solution of this differential equation is
 RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
3 d Calculate the product of the motor constant and the pole flux KΦ in this operating point. 2 e Calculate the torque.
 Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester. Electrical and Electronics Engineering. EE 1352 Power System Analysis
 B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
EEE3405 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES 2 - TEST
 ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
Part 4: Electromagnetism. 4.1: Induction. A. Faraday's Law. The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is
 1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 8-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 24 Electrical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 8-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 24 Electrical
Module 7. Transformer. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 7 Transformer ersion EE T, Kharagpur Lesson 5 Testing, Efficiency & Regulation ersion EE T, Kharagpur Contents 5 Testing, Efficiency & regulation 4 5. Goals of the lesson.. 4 5. Determination of
Module 7 Transformer ersion EE T, Kharagpur Lesson 5 Testing, Efficiency & Regulation ersion EE T, Kharagpur Contents 5 Testing, Efficiency & regulation 4 5. Goals of the lesson.. 4 5. Determination of
GATE-2015 ELECTRICAL ENGG 7th February 2015 Forenoon Session
 Page Section - I (General Aptitude) Q. Which one of the following combinations is incorrect? Acquiescence - Submission Wheedle - Roundabout Flippancy - Lightness Profligate - Extravagant Q. Didn t you
Page Section - I (General Aptitude) Q. Which one of the following combinations is incorrect? Acquiescence - Submission Wheedle - Roundabout Flippancy - Lightness Profligate - Extravagant Q. Didn t you
18 - ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENTS ( Answers at the end of all questions ) Page 1
 ( Answers at the end of all questions ) Page ) The self inductance of the motor of an electric fan is 0 H. In order to impart maximum power at 50 Hz, it should be connected to a capacitance of 8 µ F (
( Answers at the end of all questions ) Page ) The self inductance of the motor of an electric fan is 0 H. In order to impart maximum power at 50 Hz, it should be connected to a capacitance of 8 µ F (
Power and Energy Measurement
 Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
 Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
Electrical Engineering Fundamentals for Non-Electrical Engineers
 Electrical Engineering Fundamentals for Non-Electrical Engineers by Brad Meyer, PE Contents Introduction... 3 Definitions... 3 Power Sources... 4 Series vs. Parallel... 9 Current Behavior at a Node...
Electrical Engineering Fundamentals for Non-Electrical Engineers by Brad Meyer, PE Contents Introduction... 3 Definitions... 3 Power Sources... 4 Series vs. Parallel... 9 Current Behavior at a Node...
IGEE 402 Power System Analysis. FINAL EXAMINATION - SAMPLE Fall 2004
 IGEE 402 Power System Analysis FINAL EXAMINATION - SAMPLE Fall 2004 Special instructions: - Duration: 80 minutes. - Material allowed: a crib sheet (double sided 8.5 x ), calculator. - Attempt 5 out of
IGEE 402 Power System Analysis FINAL EXAMINATION - SAMPLE Fall 2004 Special instructions: - Duration: 80 minutes. - Material allowed: a crib sheet (double sided 8.5 x ), calculator. - Attempt 5 out of
8 z 2, then the greatest value of z is. 2. The principal argument/amplitude of the complex number 1 2 i (C) (D) 3 (C)
 1. If z is a complex number and if 8 z 2, then the greatest value of z is z (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 4 2. The principal argument/amplitude of the complex number 1 2 i 1 3i is (A) 2 (B) 4 (C) (D) 3 4 3.
1. If z is a complex number and if 8 z 2, then the greatest value of z is z (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 4 2. The principal argument/amplitude of the complex number 1 2 i 1 3i is (A) 2 (B) 4 (C) (D) 3 4 3.
2. The following diagram illustrates that voltage represents what physical dimension?
 BioE 1310 - Exam 1 2/20/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. A particular voltage divider with 10 V across it consists of two resistors in series. One resistor is 7 KΩ and the other
BioE 1310 - Exam 1 2/20/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. A particular voltage divider with 10 V across it consists of two resistors in series. One resistor is 7 KΩ and the other
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE AND SINGLE PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 26 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE AND SINGLE PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 3.1. INTRODUCTION Recently increase in energy demand and limited energy sources in the world caused the researchers
26 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE AND SINGLE PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 3.1. INTRODUCTION Recently increase in energy demand and limited energy sources in the world caused the researchers
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION
 ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 1) A Circular coil is placed near a current carrying conductor. The induced current is anti clock wise when the coil is, 1. Stationary 2. Moved away from the conductor 3. Moved
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 1) A Circular coil is placed near a current carrying conductor. The induced current is anti clock wise when the coil is, 1. Stationary 2. Moved away from the conductor 3. Moved
SSC-JE EE POWER SYSTEMS: GENERATION, TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
ECE 585 Power System Stability
 Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits
 Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis
 Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis 1. Identify the frequency, angular frequency, peak value, rms value, and phase of a sinusoidal signal. 2. Solve steady-state
Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis 1. Identify the frequency, angular frequency, peak value, rms value, and phase of a sinusoidal signal. 2. Solve steady-state
SHORT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Year/ Semester/ Class : III/ V/ EEE Academic Year: Subject Code/ Name: EE6501/ Power System Analysis
 Srividya colllege of Engg & Tech,Virudhunagar Sri Vidya College of Engineering And Technology Virudhunagar 626 005 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering QUESTION BANK SHORT QUESTIONS AND
Srividya colllege of Engg & Tech,Virudhunagar Sri Vidya College of Engineering And Technology Virudhunagar 626 005 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering QUESTION BANK SHORT QUESTIONS AND
Tutorial Sheet Fig. Q1
 Tutorial Sheet - 04 1. The magnetic circuit shown in Fig. Q1 has dimensions A c = A g = 9 cm 2, g = 0.050 cm, l c = 30 cm, and N = 500 turns. Assume the value of the relative permeability,µ r = 70,000
Tutorial Sheet - 04 1. The magnetic circuit shown in Fig. Q1 has dimensions A c = A g = 9 cm 2, g = 0.050 cm, l c = 30 cm, and N = 500 turns. Assume the value of the relative permeability,µ r = 70,000
1 Phasors and Alternating Currents
 Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
Alternating Current. Symbol for A.C. source. A.C.
 Alternating Current Kirchoff s rules for loops and junctions may be used to analyze complicated circuits such as the one below, powered by an alternating current (A.C.) source. But the analysis can quickly
Alternating Current Kirchoff s rules for loops and junctions may be used to analyze complicated circuits such as the one below, powered by an alternating current (A.C.) source. But the analysis can quickly
