EE"232"Lightwave"Devices Lecture"16:"p7i7n"Photodiodes"and" Photoconductors"
|
|
|
- Hortense Gwendolyn Franklin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EE"232"Lgwav"Dvcs Lcur"16:"p77n"Pooos"an" Pooconucors" Rang:"Cuang,"Cap."15"(2 n E) Insrucor:"Mng"C."Wu Unvrsy"of"Calforna,"Brkly Elcrcal"Engnrng"an"Compur"Scncs"Dp. EE232$Lcur$16-1
2 Rvrs"bas%p""n%juncon Mos%of%%volag%rop% across%%"rgon,%% man%absorpon%rgon P""n%Pooo P N Hg%fl%sparas% poognra%lcron%an% ol Larg%bangap%marals%ar% us%for%p%an%n%f%possbl Fas%rspons Ec 1 q Ev q 2 Low%nos F q 3 No%gan%(quanum%ffcncy% <%1%) 2 4 " 1 7 1" 1 7 1" 1 7 2" 1 7 x EE232$Lcur$16-2
3 I"V$Curv kbt Dark currn: I = I ( $ 1) qv I " q Poocurrn: Ip = Pop # $ Quanum ffcncy: " = " (1 $ R)(1 $ ) V kbt Toal currn: I = I ( $ 1) + I qv p I p1 I p2 Loa$Ln$for$Basng$$PD EE232$Lcur$16-3
4 Absorpon*Coffcn Lg*nnsy*cays* xponnally*n*smconucor: I( x) = I " x Drc*bangap*smconucor* as*a*sarp*absorpon*g S*absorbs*poons*w* v*>*e g =*1.1*V,*bu** absorpon*coffcn*s*small Suffcn*for*CCD A*gr*nrgy*(~*3*V),* absorpon*coffcn*of*s* bcoms*larg*agan,*u*o* rc*bangap*ranson*o* gr*cb EE232$Lcur$16-4
5 Two$Typs$of$p**n$Pooos L Surfac-Illumna p--n # " = " (1# R)(1 # ) " : nrnal quanum ffcncy R : rflcvy : absorpon layr cknss Wavgu p--n #$ L " = " (1# R)(1 # ) " : nrnal quanum ffcncy R : rflcvy $ : confnmn facor L : lng of wavgu PD EE232$Lcur$16-5
6 Ramo s'torm T currn caus n xrnal crcu by a movng carg q movng a a volocy v ( ) n a paralll pla w a sparaon of an a volag bas of V s qv() () = A Proof: Work on on carg: W = Forc Dsplacmn V = qex = q x Work prov by powr supply: W = () V " V () V = q x q x qv() () = = EE232$Lcur$16-6
7 Rspons'of'On'Poognra' Elcron4Hol'Par qv / () = () + () () P N qv / () Tm EE232$Lcur$16-7 x Hol Trajcory Elcron Trajcory v x x v Toal carg gnra: $ $ Q = () + () qv " x qv x v v = + = On absorb poon Tm on carg c q #
8 Trans(Tm () = () + () () P N () Many(lcron2ol(pars gnra v v Tm Elcron currn ns wn las lcron gnra nar P-s racs N-lcro: = v Hol currn ns wn las ol gnra nar N-s racs P-lcro: = v Hol s usually slowr " A consrvav sma of rans m: = v EE232$Lcur$16-8
9 Toal&Rspons&Tm&of&p//n (1) RC m: A " RC = RC = R ( A : ara of p--n) (2) Trans m: " Toal rspons m: " = " + " f = 3B v RC 1 $ 2#" Absorpon layr cknss for opmum frquncy rspons: R A " = " RC + " = + v $ R A%$ % " & 2 ' (' ( ) *) v * 1 1 v f3b +, = f3 B,max 2#" 4# R A Opmum banw occurs wn R A = opmum v = R Av EE232$Lcur$16-9
10 Mor%Rgorous%Analyss%of p22n%rspons%tm 2 Small-sgnal analyss: assum npu lg s moula a frquncy, poocurrn s proporonal o 2 #" $ sn 1 % & 2 ()) ' ( j RC #" $ % & ' 2 ( T frs rm s sngl-pol rspons from RC, wl scon rm s pas lay u o rans m rspons. RC #( ( ) ) 2 2' log$ H1 f Trans Tm Toal % & #( ( ) ) 2 2' log$ H2 f " 2 " % & #( ( ) ) 2 2' log$ H3 f 2 " 2 " % & 2 f f " 2 EE232$Lcur$16-1 " f
11 Exampl: f RC 3B = 14.4 ps = 2 ps EE232$Lcur$16-11 Comparson*of*Numrc*Exampls 1 1 = = 4.6 GHz 2" + RC 2 $ # % sn 1 & ' 2 ()* ( ) = H( #) 2 1+ j# RC $ # % & ' ( 2 ) 1 Solvng H( #) =, f3b = 9.7 GHz 2 T scrpancy s smallr wn RC omnas, an largr wn rans m omnas. (Trans m rspons as a sarp rop-off). RC #( ( ) ) 2 2' log$ H1 f Trans Tm Toal % & #( ( ) ) 2 2' log$ H2 f 2 " 2 " % & #( ( ) ) 2 2' log$ H3 f 2 " 2 " % & 2 " 2 " f f f
12 Banw)Effcncy/Prouc (1) For surfac-llumna p--n (assum AR coang: R=%), n xrm of n absorbng layr an rans-m-omna rspons: $ " = " (1 $ ) %" (1 $ (1 $ )) = " 1 v f3b % 2# ( 1 v ) " v Banw-ffcncy prouc: f3b *" % +,(" ) = - 2#. 2# (2) On or an, ffcncy of wavgu p--n s $' L " = " (1 $ ) %"' L 1 RC-lm banw: f3b % 2# R& Lw ( 1 ) Banw-ffcncy prouc: f3b *" % +,(" ' L) = - 2# R& Lw. / In gnral, r s a banw-ffcncy ra-off " ' 2# R& w EE232$Lcur$16-12
13 Pooconucors Dark currn: J = σ E = ( n qµ n + p qµ ) p E + 5 x Ara = w L Equvaln2Crcu Lg llumnaon gnra lcron-ol pars, ncrasng conucvy: δn = G δn τ n Say sa: / --> δn = G τ n ΔJ = δn q ( µ n + µ ) p E EE232$Lcur$16-13 Pooconucor rqurs bo conacs o b Omc an smconucor opng yp o b sam.
14 Poocarrr*Gnraon*Ra Lg Innsy # " x + / x Ara = w L Pop (1 R) x (1" " ) Pop 1 1 G = " : poocarrr gnraon ra [ ] # 3 lw cm s $ " = " (1 $ R)(1 $ ) R : rflcvy of pooconucor surfac : absorpon coffcn : absorpon lng $ : fracon of lg rmans afr absorpon lng EE232$Lcur$16-14
15 Pooconucv,Gan ( )( µ µ ) $ I = lw$ J = lw G q + E n n p % Pop 1 & $ I = lw' " ( ) n( q µ n + µ p E ) # lw * Pop 1 q 1 $ I + " q( µ E) = " P v # # = : rans m v I n % q &% & " P ) *) * n $ = ' op (' ( # n n op n n Poocurrn Pooconucv Gan EE232$Lcur$16-15
16 Analogy(o(Currn(Gan(n(Bpolar( Transsor Currn gan n bpolar ranssor: E B C I = I C B T currn gan can also b xprss as " rb = " " : rans m " rb : carrr rcombnaon lfm n bas EE232$Lcur$16-16
17 Frquncy)of)Pooconucors N = η P op 1 ω lw N τ n Small sgnal rspons: N = N + N 1 jω jωn 1 = η P 1 1 ω lw N 1 τ n Pooconucv)Rspons)(B) n / = 1, n / = 1, n / = 1 n / = 1 / = 1 ηp N 1 = 1 1 n ω ( lw) jω +1/ τ n I 1 = J 1 lw = ( N 1 qv n )lw I 1 " = ηq %" $ ' τ % n 1 P 1 # ω $ &# τ ' & jωτ n +1 = ( DC Quanum Effcncy) ( Pooconucv Gan) ( Normalz Frquncy Rspons) Frquncy)(Hz) EE232$Lcur$16-17
EE 232 Lightwave Devices. Photodiodes
 EE 3 Lgwav Dvcs Lcur 8: oocoucors a p-- ooos Rag: Cuag, Cap. 4 Isrucor: Mg C. Wu Uvrsy of Calfora, Brkly Elcrcal Egrg a Compur Sccs Dp. EE3 Lcur 8-8. Uvrsy of Calfora oocoucors ω + - x Ara w L Euval Crcu
EE 3 Lgwav Dvcs Lcur 8: oocoucors a p-- ooos Rag: Cuag, Cap. 4 Isrucor: Mg C. Wu Uvrsy of Calfora, Brkly Elcrcal Egrg a Compur Sccs Dp. EE3 Lcur 8-8. Uvrsy of Calfora oocoucors ω + - x Ara w L Euval Crcu
Lecture 1: Photoconductors and p-i-n Photodiodes
 Lcur 1: Poocoucors a p-i- Pooios Isrucor: Mig C. Wu Uivrsiy of Califoria, Brkly Elcrical Egirig a Compur Scics Dp. 1 Prof. Mig Wu Poocors Covrs lig o lcric sigals Mai yps of poocors Poocoucors P-i- pooios
Lcur 1: Poocoucors a p-i- Pooios Isrucor: Mig C. Wu Uivrsiy of Califoria, Brkly Elcrical Egirig a Compur Scics Dp. 1 Prof. Mig Wu Poocors Covrs lig o lcric sigals Mai yps of poocors Poocoucors P-i- pooios
Conventional Hot-Wire Anemometer
 Convnonal Ho-Wr Anmomr cro Ho Wr Avanag much mallr prob z mm o µm br paal roluon array o h nor hghr rquncy rpon lowr co prormanc/co abrcaon roc I µm lghly op p layr 8µm havly boron op ch op layr abrcaon
Convnonal Ho-Wr Anmomr cro Ho Wr Avanag much mallr prob z mm o µm br paal roluon array o h nor hghr rquncy rpon lowr co prormanc/co abrcaon roc I µm lghly op p layr 8µm havly boron op ch op layr abrcaon
Physics 160 Lecture 3. R. Johnson April 6, 2015
 Physics 6 Lcur 3 R. Johnson April 6, 5 RC Circui (Low-Pass Filr This is h sam RC circui w lookd a arlir h im doma, bu hr w ar rsd h frquncy rspons. So w pu a s wav sad of a sp funcion. whr R C RC Complx
Physics 6 Lcur 3 R. Johnson April 6, 5 RC Circui (Low-Pass Filr This is h sam RC circui w lookd a arlir h im doma, bu hr w ar rsd h frquncy rspons. So w pu a s wav sad of a sp funcion. whr R C RC Complx
ELECTRONIC DEVICES BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR. Piotr Dziurdzia, Ph.D C-3, room 413; tel ,
 04-05-04 AGH UNVRSY O SN AND HNOLOGY M. SANSŁAWA SASZA W KRAKOW aculy of ompur Scnc, lcroncs and lcommuncaons DPARMN O LRONS LRON DVS Por Dzurdza, Ph.D. -3, room 43; l. 67-7-0, Por.Dzurdza@ah.du.pl POLAR
04-05-04 AGH UNVRSY O SN AND HNOLOGY M. SANSŁAWA SASZA W KRAKOW aculy of ompur Scnc, lcroncs and lcommuncaons DPARMN O LRONS LRON DVS Por Dzurdza, Ph.D. -3, room 43; l. 67-7-0, Por.Dzurdza@ah.du.pl POLAR
State Observer Design
 Sa Obsrvr Dsgn A. Khak Sdgh Conrol Sysms Group Faculy of Elcrcal and Compur Engnrng K. N. Toos Unvrsy of Tchnology Fbruary 2009 1 Problm Formulaon A ky assumpon n gnvalu assgnmn and sablzng sysms usng
Sa Obsrvr Dsgn A. Khak Sdgh Conrol Sysms Group Faculy of Elcrcal and Compur Engnrng K. N. Toos Unvrsy of Tchnology Fbruary 2009 1 Problm Formulaon A ky assumpon n gnvalu assgnmn and sablzng sysms usng
Engineering Circuit Analysis 8th Edition Chapter Nine Exercise Solutions
 Engnrng rcu naly 8h Eon hapr Nn Exrc Soluon. = KΩ, = µf, an uch ha h crcu rpon oramp. a For Sourc-fr paralll crcu: For oramp or b H 9V, V / hoo = H.7.8 ra / 5..7..9 9V 9..9..9 5.75,.5 5.75.5..9 . = nh,
Engnrng rcu naly 8h Eon hapr Nn Exrc Soluon. = KΩ, = µf, an uch ha h crcu rpon oramp. a For Sourc-fr paralll crcu: For oramp or b H 9V, V / hoo = H.7.8 ra / 5..7..9 9V 9..9..9 5.75,.5 5.75.5..9 . = nh,
t=0 t>0: + vr - i dvc Continuation
 hapr Ga Dlay and rcus onnuaon s rcu Equaon >: S S Ths dffrnal quaon, oghr wh h nal condon, fully spcfs bhaor of crcu afr swch closs Our n challng: larn how o sol such quaons TUE/EE 57 nwrk analys 4/5 NdM
hapr Ga Dlay and rcus onnuaon s rcu Equaon >: S S Ths dffrnal quaon, oghr wh h nal condon, fully spcfs bhaor of crcu afr swch closs Our n challng: larn how o sol such quaons TUE/EE 57 nwrk analys 4/5 NdM
A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W
 A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W Volume 52 Fall 2000 Number 1 B E F O R E D I S A B I L I T Y C I V I L R I G HT S : C I V I L W A R P E N S I O N S A N D TH E P O L I T I C S O F D I S A B I L I T Y I N
A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W Volume 52 Fall 2000 Number 1 B E F O R E D I S A B I L I T Y C I V I L R I G HT S : C I V I L W A R P E N S I O N S A N D TH E P O L I T I C S O F D I S A B I L I T Y I N
Equation For non-self Energizing Gasket
 Jun 0 0:05: - ASMEScDiv_WNFlangDsign.sm Dsign of Wld Nck Flang as pr ASME Scion Division ar.6 Dsign ol oads STE : Dsign ondiion Dsign rssur 0. Ma Dsign Tmpraur T 80 d STE : ask Facors 'm' and Minimum Dsign
Jun 0 0:05: - ASMEScDiv_WNFlangDsign.sm Dsign of Wld Nck Flang as pr ASME Scion Division ar.6 Dsign ol oads STE : Dsign ondiion Dsign rssur 0. Ma Dsign Tmpraur T 80 d STE : ask Facors 'm' and Minimum Dsign
Chapter 9 Transient Response
 har 9 Transn sons har 9: Ouln N F n F Frs-Ordr Transns Frs-Ordr rcus Frs ordr crcus: rcus conan onl on nducor or on caacor gornd b frs-ordr dffrnal quaons. Zro-nu rsons: h crcu has no ald sourc afr a cran
har 9 Transn sons har 9: Ouln N F n F Frs-Ordr Transns Frs-Ordr rcus Frs ordr crcus: rcus conan onl on nducor or on caacor gornd b frs-ordr dffrnal quaons. Zro-nu rsons: h crcu has no ald sourc afr a cran
P a g e 3 6 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9
 P a g e 3 6 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9 p r o t e c t h um a n h e a l t h a n d p r o p e r t y fr om t h e d a n g e rs i n h e r e n t i n m i n i n g o p e r a t i o n s s u c h a s a q u a r r y. J
P a g e 3 6 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9 p r o t e c t h um a n h e a l t h a n d p r o p e r t y fr om t h e d a n g e rs i n h e r e n t i n m i n i n g o p e r a t i o n s s u c h a s a q u a r r y. J
Chapter 13 Laplace Transform Analysis
 Chapr aplac Tranorm naly Chapr : Ouln aplac ranorm aplac Tranorm -doman phaor analy: x X σ m co ω φ x X X m φ x aplac ranorm: [ o ] d o d < aplac Tranorm Thr condon Unlaral on-dd aplac ranorm: aplac ranorm
Chapr aplac Tranorm naly Chapr : Ouln aplac ranorm aplac Tranorm -doman phaor analy: x X σ m co ω φ x X X m φ x aplac ranorm: [ o ] d o d < aplac Tranorm Thr condon Unlaral on-dd aplac ranorm: aplac ranorm
10. If p and q are the lengths of the perpendiculars from the origin on the tangent and the normal to the curve
 0. If p and q ar h lnghs of h prpndiculars from h origin on h angn and h normal o h curv + Mahmaics y = a, hn 4p + q = a a (C) a (D) 5a 6. Wha is h diffrnial quaion of h family of circls having hir cnrs
0. If p and q ar h lnghs of h prpndiculars from h origin on h angn and h normal o h curv + Mahmaics y = a, hn 4p + q = a a (C) a (D) 5a 6. Wha is h diffrnial quaion of h family of circls having hir cnrs
V A. V-A ansatz for fundamental fermions
 Avan Parl Phy: I. ak nraon. A Thory Carfl analy of xprnal aa (pary volaon, nrno hly pn hang n nlar β-ay, on ay propr oghr w/ nvraly fnally l o h -A hory of (nlar wak ay: M A A ( ( ( ( v p A n nlon lpon
Avan Parl Phy: I. ak nraon. A Thory Carfl analy of xprnal aa (pary volaon, nrno hly pn hang n nlar β-ay, on ay propr oghr w/ nvraly fnally l o h -A hory of (nlar wak ay: M A A ( ( ( ( v p A n nlon lpon
P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9
 P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9 J A R T a l s o c o n c l u d e d t h a t a l t h o u g h t h e i n t e n t o f N e l s o n s r e h a b i l i t a t i o n p l a n i s t o e n h a n c e c o n n e
P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9 J A R T a l s o c o n c l u d e d t h a t a l t h o u g h t h e i n t e n t o f N e l s o n s r e h a b i l i t a t i o n p l a n i s t o e n h a n c e c o n n e
EE 529 Remote Sensing Techniques. Review
 59 Rmo Snsing Tchniqus Rviw Oulin Annna array Annna paramrs RCS Polariaion Signals CFT DFT Array Annna Shor Dipol l λ r, R[ r ω ] r H φ ηk Ilsin 4πr η µ - Prmiiviy ε - Prmabiliy
59 Rmo Snsing Tchniqus Rviw Oulin Annna array Annna paramrs RCS Polariaion Signals CFT DFT Array Annna Shor Dipol l λ r, R[ r ω ] r H φ ηk Ilsin 4πr η µ - Prmiiviy ε - Prmabiliy
Example: MOSFET Amplifier Distortion
 4/25/2011 Example MSFET Amplfer Dsoron 1/9 Example: MSFET Amplfer Dsoron Recall hs crcu from a prevous handou: ( ) = I ( ) D D d 15.0 V RD = 5K v ( ) = V v ( ) D o v( ) - K = 2 0.25 ma/v V = 2.0 V 40V.
4/25/2011 Example MSFET Amplfer Dsoron 1/9 Example: MSFET Amplfer Dsoron Recall hs crcu from a prevous handou: ( ) = I ( ) D D d 15.0 V RD = 5K v ( ) = V v ( ) D o v( ) - K = 2 0.25 ma/v V = 2.0 V 40V.
Charging of capacitor through inductor and resistor
 cur 4&: R circui harging of capacior hrough inducor and rsisor us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R, an inducor of inducanc and a y K in sris.
cur 4&: R circui harging of capacior hrough inducor and rsisor us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R, an inducor of inducanc and a y K in sris.
The Mathematics of Harmonic Oscillators
 Th Mhcs of Hronc Oscllors Spl Hronc Moon In h cs of on-nsonl spl hronc oon (SHM nvolvng sprng wh sprng consn n wh no frcon, you rv h quon of oon usng Nwon's scon lw: con wh gvs: 0 Ths s sos wrn usng h
Th Mhcs of Hronc Oscllors Spl Hronc Moon In h cs of on-nsonl spl hronc oon (SHM nvolvng sprng wh sprng consn n wh no frcon, you rv h quon of oon usng Nwon's scon lw: con wh gvs: 0 Ths s sos wrn usng h
Sinusoidal Response Notes
 ECE 30 Sinusoidal Rspons Nots For BIBO Systms AStolp /29/3 Th sinusoidal rspons of a systm is th output whn th input is a sinusoidal (which starts at tim 0) Systm Sinusoidal Rspons stp input H( s) output
ECE 30 Sinusoidal Rspons Nots For BIBO Systms AStolp /29/3 Th sinusoidal rspons of a systm is th output whn th input is a sinusoidal (which starts at tim 0) Systm Sinusoidal Rspons stp input H( s) output
Frequency Response. Response of an LTI System to Eigenfunction
 Frquncy Rsons Las m w Rvsd formal dfnons of lnary and m-nvaranc Found an gnfuncon for lnar m-nvaran sysms Found h frquncy rsons of a lnar sysm o gnfuncon nu Found h frquncy rsons for cascad, fdbac, dffrnc
Frquncy Rsons Las m w Rvsd formal dfnons of lnary and m-nvaranc Found an gnfuncon for lnar m-nvaran sysms Found h frquncy rsons of a lnar sysm o gnfuncon nu Found h frquncy rsons for cascad, fdbac, dffrnc
Chapter 4 Transients. Chapter 4 Transients
 Chapter 4 Transients Chapter 4 Transients 1. Solve first-order RC or RL circuits. 2. Understand the concepts of transient response and steady-state response. 1 3. Relate the transient response of first-order
Chapter 4 Transients Chapter 4 Transients 1. Solve first-order RC or RL circuits. 2. Understand the concepts of transient response and steady-state response. 1 3. Relate the transient response of first-order
Quantitative Model of Unilluminated Diode part II. G.R. Tynan UC San Diego MAE 119 Lecture Notes
 Quantitativ Modl of Unilluminatd Diod part II G.R. Tynan UC San Digo MAE 119 Lctur Nots Minority Carrir Dnsity at dg of quasinutral rgion incrass EXPONENTIALLY forward bias p nb n pa = p n0 xp qv a kt
Quantitativ Modl of Unilluminatd Diod part II G.R. Tynan UC San Digo MAE 119 Lctur Nots Minority Carrir Dnsity at dg of quasinutral rgion incrass EXPONENTIALLY forward bias p nb n pa = p n0 xp qv a kt
Fluctuation-Electromagnetic Interaction of Rotating Neutral Particle with the Surface: Relativistic Theory
 Fluuaon-lroagn Inraon of Roang Nural Parl w Surfa: Rlavs or A.A. Kasov an G.V. Dov as on fluuaon-lroagn or w av alula rar for of araon fronal on an ang ra of a nural parl roang nar a polarabl surfa. parl
Fluuaon-lroagn Inraon of Roang Nural Parl w Surfa: Rlavs or A.A. Kasov an G.V. Dov as on fluuaon-lroagn or w av alula rar for of araon fronal on an ang ra of a nural parl roang nar a polarabl surfa. parl
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Me n d e l s P e a s Exer c i se 1 - Par t 1
 !! Me n d e l s P e a s Exer c i se 1 - Par t 1 TR UE - BR E E D I N G O R G A N I S M S Go a l In this exercise you will use StarGenetics, a genetics experiment simulator, to understand the concept of
!! Me n d e l s P e a s Exer c i se 1 - Par t 1 TR UE - BR E E D I N G O R G A N I S M S Go a l In this exercise you will use StarGenetics, a genetics experiment simulator, to understand the concept of
UNIT #5 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
 Answr Ky Nam: Da: UNIT # EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Par I Qusions. Th prssion is quivaln o () () 6 6 6. Th ponnial funcion y 6 could rwrin as y () y y 6 () y y (). Th prssion a is quivaln o
Answr Ky Nam: Da: UNIT # EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Par I Qusions. Th prssion is quivaln o () () 6 6 6. Th ponnial funcion y 6 could rwrin as y () y y 6 () y y (). Th prssion a is quivaln o
EE 434 Lecture 22. Bipolar Device Models
 EE 434 Lcur 22 Bipolar Dvic Modls Quiz 14 Th collcor currn of a BJT was masurd o b 20mA and h bas currn masurd o b 0.1mA. Wha is h fficincy of injcion of lcrons coming from h mir o h collcor? 1 And h numbr
EE 434 Lcur 22 Bipolar Dvic Modls Quiz 14 Th collcor currn of a BJT was masurd o b 20mA and h bas currn masurd o b 0.1mA. Wha is h fficincy of injcion of lcrons coming from h mir o h collcor? 1 And h numbr
Quantitative Model of PV Cells The Illuminated Diode. G.R. Tynan UC San Diego MAE 119 Lecture Notes
 Quantitativ Modl of PV Clls T Illuminatd Diod G.R. Tynan UC San Digo MAE 119 ctur Nots WE FOUND WHAT WE SEEK: JJ(V) Currnt Dnsity vs Voltag Across Diod: J total qdn p qd pn J + J kt ( xp( qv / ) 1) 0 0
Quantitativ Modl of PV Clls T Illuminatd Diod G.R. Tynan UC San Digo MAE 119 ctur Nots WE FOUND WHAT WE SEEK: JJ(V) Currnt Dnsity vs Voltag Across Diod: J total qdn p qd pn J + J kt ( xp( qv / ) 1) 0 0
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PUTRAJAYA CAMPUS FINAL EXAMINATION SPECIAL SEMESTER 2013 / 2014
 OLLEGE OF ENGNEENG PUTAJAYA AMPUS FNAL EXAMNATON SPEAL SEMESTE 03 / 04 POGAMME SUBJET ODE SUBJET : Bachelor of Electrcal & Electroncs Engneerng (Honours) Bachelor of Electrcal Power Engneerng (Honours)
OLLEGE OF ENGNEENG PUTAJAYA AMPUS FNAL EXAMNATON SPEAL SEMESTE 03 / 04 POGAMME SUBJET ODE SUBJET : Bachelor of Electrcal & Electroncs Engneerng (Honours) Bachelor of Electrcal Power Engneerng (Honours)
Greenfield Wind Farm. Visual Simulation 1. Affinity Renewables Inc. Figure As viewed from Trans Canada Highway 104.
 Affinity Rnwabls Inc. Figur 6.12 Grnfil Win Farm Visual Simulation 1 As viw from Trans Canaa Highway 104 Easting: 487,437 Northing: 5,029,060 Photograph Dat: Octobr 28, 2013 Viw Angl: 163 Dgrs Imag Manufacturr:
Affinity Rnwabls Inc. Figur 6.12 Grnfil Win Farm Visual Simulation 1 As viw from Trans Canaa Highway 104 Easting: 487,437 Northing: 5,029,060 Photograph Dat: Octobr 28, 2013 Viw Angl: 163 Dgrs Imag Manufacturr:
OH BOY! Story. N a r r a t iv e a n d o bj e c t s th ea t e r Fo r a l l a g e s, fr o m th e a ge of 9
 OH BOY! O h Boy!, was or igin a lly cr eat ed in F r en ch an d was a m a jor s u cc ess on t h e Fr en ch st a ge f or young au di enc es. It h a s b een s een by ap pr ox i ma t ely 175,000 sp ect at
OH BOY! O h Boy!, was or igin a lly cr eat ed in F r en ch an d was a m a jor s u cc ess on t h e Fr en ch st a ge f or young au di enc es. It h a s b een s een by ap pr ox i ma t ely 175,000 sp ect at
ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits
 ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits Frequency Response Dr. Aydın İlker Karşılayan Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering High-Frequency Model BJT & MOS B or G r x C f C or D r
ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits Frequency Response Dr. Aydın İlker Karşılayan Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering High-Frequency Model BJT & MOS B or G r x C f C or D r
ECE 598 JS Lecture 08 Lossy Transmission Lines
 ECE 598 JS Lecture 8 Lssy Transmissin Lines Spring 22 Jse E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Cmputer Engineering University f Illinis jesa@illinis.edu Lss in Transmissin Lines RF SOURCE Signal amplitude decreases
ECE 598 JS Lecture 8 Lssy Transmissin Lines Spring 22 Jse E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Cmputer Engineering University f Illinis jesa@illinis.edu Lss in Transmissin Lines RF SOURCE Signal amplitude decreases
c. What is the average rate of change of f on the interval [, ]? Answer: d. What is a local minimum value of f? Answer: 5 e. On what interval(s) is f
![c. What is the average rate of change of f on the interval [, ]? Answer: d. What is a local minimum value of f? Answer: 5 e. On what interval(s) is f c. What is the average rate of change of f on the interval [, ]? Answer: d. What is a local minimum value of f? Answer: 5 e. On what interval(s) is f](/thumbs/87/95703678.jpg) Essential Skills Chapter f ( x + h) f ( x ). Simplifying the difference quotient Section. h f ( x + h) f ( x ) Example: For f ( x) = 4x 4 x, find and simplify completely. h Answer: 4 8x 4 h. Finding the
Essential Skills Chapter f ( x + h) f ( x ). Simplifying the difference quotient Section. h f ( x + h) f ( x ) Example: For f ( x) = 4x 4 x, find and simplify completely. h Answer: 4 8x 4 h. Finding the
Technology Corporation
 Technology Corporation ProLight PG1X-1LXS 1W Power LED Technical Datasheet Version: 2.5 Features High flux per LED Very long operating life(up to 1k hours) Various colors Good color uniformity More energy
Technology Corporation ProLight PG1X-1LXS 1W Power LED Technical Datasheet Version: 2.5 Features High flux per LED Very long operating life(up to 1k hours) Various colors Good color uniformity More energy
ANALOG ELECTRONICS I. Transistor Amplifiers DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH
 241 ANALO LTRONI I Lectures 2&3 ngle Transstor Amplfers R NORLAILI MOH NOH 3.3 Basc ngle-transstor Amplfer tages 3 dfferent confguratons : 1. ommon-emtter ommon-source Ib B R I d I c o R o gnal appled
241 ANALO LTRONI I Lectures 2&3 ngle Transstor Amplfers R NORLAILI MOH NOH 3.3 Basc ngle-transstor Amplfer tages 3 dfferent confguratons : 1. ommon-emtter ommon-source Ib B R I d I c o R o gnal appled
Why Laplace transforms?
 MAE4 Linar ircui Why Lalac ranform? Firordr R cc v v v KVL S R inananou for ach Subiu lmn rlaion v S Ordinary diffrnial quaion in rm of caacior volag Lalac ranform Solv Invr LT V u, v Ri, i A R V A _ v
MAE4 Linar ircui Why Lalac ranform? Firordr R cc v v v KVL S R inananou for ach Subiu lmn rlaion v S Ordinary diffrnial quaion in rm of caacior volag Lalac ranform Solv Invr LT V u, v Ri, i A R V A _ v
5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible. 26 Fe Cu Ni Co Pd Ag Ru 101.
 Physical Chemistry II Lab CHEM 4644 spring 2017 final exam KEY 5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible h = 6.626 10-34 J s c = 3.00 10 8 m/s 1 GHz = 10 9 s -1. B= h 8π 2 I ν= 1 2 π k μ 6 P
Physical Chemistry II Lab CHEM 4644 spring 2017 final exam KEY 5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible h = 6.626 10-34 J s c = 3.00 10 8 m/s 1 GHz = 10 9 s -1. B= h 8π 2 I ν= 1 2 π k μ 6 P
C o r p o r a t e l i f e i n A n c i e n t I n d i a e x p r e s s e d i t s e l f
 C H A P T E R I G E N E S I S A N D GROWTH OF G U IL D S C o r p o r a t e l i f e i n A n c i e n t I n d i a e x p r e s s e d i t s e l f i n a v a r i e t y o f f o r m s - s o c i a l, r e l i g i
C H A P T E R I G E N E S I S A N D GROWTH OF G U IL D S C o r p o r a t e l i f e i n A n c i e n t I n d i a e x p r e s s e d i t s e l f i n a v a r i e t y o f f o r m s - s o c i a l, r e l i g i
Review Lecture 5. The source-free R-C/R-L circuit Step response of an RC/RL circuit. The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v( )
 Rviw Lcur 5 Firs-ordr circui Th sourc-fr R-C/R-L circui Sp rspons of an RC/RL circui v( ) v( ) [ v( 0) v( )] 0 Th i consan = RC Th final capacior volag v() Th iniial capacior volag v( 0 ) Volag/currn-division
Rviw Lcur 5 Firs-ordr circui Th sourc-fr R-C/R-L circui Sp rspons of an RC/RL circui v( ) v( ) [ v( 0) v( )] 0 Th i consan = RC Th final capacior volag v() Th iniial capacior volag v( 0 ) Volag/currn-division
Lecture Set 8 Induction Machines
 Lecture Set 8 Induction Machine S.D. Sudhoff Spring 2018 Reading Chapter 6, Electromechanical Motion Device, Section 6.1-6.9, 6.12 2 Sample Application Low Power: Shaded pole machine (mall fan) Permanent
Lecture Set 8 Induction Machine S.D. Sudhoff Spring 2018 Reading Chapter 6, Electromechanical Motion Device, Section 6.1-6.9, 6.12 2 Sample Application Low Power: Shaded pole machine (mall fan) Permanent
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 19. BJT Base Resistance and Small Signal Modelling
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 19 BJT Base Resistance and Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline Lecture 17 derived static (dc) injection model to predict dc currents from terminal voltages This
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 19 BJT Base Resistance and Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline Lecture 17 derived static (dc) injection model to predict dc currents from terminal voltages This
innovations shocks white noise
 Innovaons Tm-srs modls ar consrucd as lnar funcons of fundamnal forcasng rrors, also calld nnovaons or shocks Ths basc buldng blocks sasf var σ Srall uncorrlad Ths rrors ar calld wh nos In gnral, f ou
Innovaons Tm-srs modls ar consrucd as lnar funcons of fundamnal forcasng rrors, also calld nnovaons or shocks Ths basc buldng blocks sasf var σ Srall uncorrlad Ths rrors ar calld wh nos In gnral, f ou
EE 435. Lecture 16. Compensation of Feedback Amplifiers
 EE 435 Lecture 16 ompensation of Feedback Amplifiers . Review from last lecture. Basic Two-Stae Miller ompensated Op Amp DD M 3 M 4 M 5 OUT IN M 1 M IN L I T B M 7 B3 M 6 By inspection SS A o m1 o p 1
EE 435 Lecture 16 ompensation of Feedback Amplifiers . Review from last lecture. Basic Two-Stae Miller ompensated Op Amp DD M 3 M 4 M 5 OUT IN M 1 M IN L I T B M 7 B3 M 6 By inspection SS A o m1 o p 1
i sw + v sw + v o 100V Ideal switch characteristics
 deal swich characerisics. onsider he swiching circui shown in Fig. P. wih a resisive load. Assume he swich is ideal and operaing a a duy raio of 4%. (a) Skech he waveforms for i sw and v sw. (b) Deermine
deal swich characerisics. onsider he swiching circui shown in Fig. P. wih a resisive load. Assume he swich is ideal and operaing a a duy raio of 4%. (a) Skech he waveforms for i sw and v sw. (b) Deermine
Supplementary Figure 1. Experiment and simulation with finite qudit. anharmonicity. (a), Experimental data taken after a 60 ns three-tone pulse.
 Supplmnar Fgur. Eprmn and smulaon wh fn qud anharmonc. a, Eprmnal daa akn afr a 6 ns hr-on puls. b, Smulaon usng h amlonan. Supplmnar Fgur. Phagoran dnamcs n h m doman. a, Eprmnal daa. Th hr-on puls s
Supplmnar Fgur. Eprmn and smulaon wh fn qud anharmonc. a, Eprmnal daa akn afr a 6 ns hr-on puls. b, Smulaon usng h amlonan. Supplmnar Fgur. Phagoran dnamcs n h m doman. a, Eprmnal daa. Th hr-on puls s
Synchronous machines
 Synchronous gnrator (altrnator): transorms mchanical nrgy into lctric nrgy; dsignd to gnrat sinusoidal oltags and currnts; usd in most powr plants, or car altrnators, tc. Synchronous motor: transorms lctric
Synchronous gnrator (altrnator): transorms mchanical nrgy into lctric nrgy; dsignd to gnrat sinusoidal oltags and currnts; usd in most powr plants, or car altrnators, tc. Synchronous motor: transorms lctric
T h e C S E T I P r o j e c t
 T h e P r o j e c t T H E P R O J E C T T A B L E O F C O N T E N T S A r t i c l e P a g e C o m p r e h e n s i v e A s s es s m e n t o f t h e U F O / E T I P h e n o m e n o n M a y 1 9 9 1 1 E T
T h e P r o j e c t T H E P R O J E C T T A B L E O F C O N T E N T S A r t i c l e P a g e C o m p r e h e n s i v e A s s es s m e n t o f t h e U F O / E T I P h e n o m e n o n M a y 1 9 9 1 1 E T
ECE 546 Lecture 13 Scattering Parameters
 ECE 546 Lecture 3 Scattering Parameters Spring 08 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu ECE 546 Jose Schutt Aine Transfer Function Representation
ECE 546 Lecture 3 Scattering Parameters Spring 08 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu ECE 546 Jose Schutt Aine Transfer Function Representation
I. Frequency Response of Voltage Amplifiers
 I. Frequency Response of Voltage Amplifiers A. Common-Emitter Amplifier: V i SUP i OUT R S V BIAS R L v OUT V Operating Point analysis: 0, R s 0, r o --->, r oc --->, R L ---> Find V BIAS such that I C
I. Frequency Response of Voltage Amplifiers A. Common-Emitter Amplifier: V i SUP i OUT R S V BIAS R L v OUT V Operating Point analysis: 0, R s 0, r o --->, r oc --->, R L ---> Find V BIAS such that I C
4. Which of the following organs develops first?
 Biology 4. Which of h following organs dvlops firs? (A) Livr (C) Kidny (B) Har (D) Noochord 12. During mbryonic priod, animals rpa mbryonic sags of hir ancsors. This law is calld (A) Flokin s law (B) Biognic
Biology 4. Which of h following organs dvlops firs? (A) Livr (C) Kidny (B) Har (D) Noochord 12. During mbryonic priod, animals rpa mbryonic sags of hir ancsors. This law is calld (A) Flokin s law (B) Biognic
Consider a system of 2 simultaneous first order linear equations
 Soluon of sysms of frs ordr lnar quaons onsdr a sysm of smulanous frs ordr lnar quaons a b c d I has h alrna mar-vcor rprsnaon a b c d Or, n shorhand A, f A s alrady known from con W know ha h abov sysm
Soluon of sysms of frs ordr lnar quaons onsdr a sysm of smulanous frs ordr lnar quaons a b c d I has h alrna mar-vcor rprsnaon a b c d Or, n shorhand A, f A s alrady known from con W know ha h abov sysm
ECE 201 Fall 2009 Final Exam
 ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
Executive Committee and Officers ( )
 Gifted and Talented International V o l u m e 2 4, N u m b e r 2, D e c e m b e r, 2 0 0 9. G i f t e d a n d T a l e n t e d I n t e r n a t i o n a2 l 4 ( 2), D e c e m b e r, 2 0 0 9. 1 T h e W o r
Gifted and Talented International V o l u m e 2 4, N u m b e r 2, D e c e m b e r, 2 0 0 9. G i f t e d a n d T a l e n t e d I n t e r n a t i o n a2 l 4 ( 2), D e c e m b e r, 2 0 0 9. 1 T h e W o r
NAME: SOLUTIONS EEE 203 HW 1
 NAME: SOLUIONS EEE W Problm. Cosir sigal os grap is so blo. Sc folloig sigals: -, -, R, r R os rflcio opraio a os sif la opraio b. - - R - Problm. Dscrib folloig sigals i rms of lmar fcios,,r, a comp a.
NAME: SOLUIONS EEE W Problm. Cosir sigal os grap is so blo. Sc folloig sigals: -, -, R, r R os rflcio opraio a os sif la opraio b. - - R - Problm. Dscrib folloig sigals i rms of lmar fcios,,r, a comp a.
Chapter 5 Transient Analysis
 hpr 5 rs Alyss Jsug Jg ompl rspos rs rspos y-s rspos m os rs orr co orr Dffrl Equo. rs Alyss h ffrc of lyss of crcus wh rgy sorg lms (ucors or cpcors) & m-ryg sgls wh rss crcus s h h quos rsulg from r
hpr 5 rs Alyss Jsug Jg ompl rspos rs rspos y-s rspos m os rs orr co orr Dffrl Equo. rs Alyss h ffrc of lyss of crcus wh rgy sorg lms (ucors or cpcors) & m-ryg sgls wh rss crcus s h h quos rsulg from r
Lab Day and Time: Instructions. 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start.
 Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
Name: Lab Day and Time: Instructions 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to start. 2. This exam is closed note and closed book. You are not allowed to use any outside material while taking this
Transfer function and the Laplace transformation
 Lab No PH-35 Porland Sa Univriy A. La Roa Tranfr funcion and h Laplac ranformaion. INTRODUTION. THE LAPLAE TRANSFORMATION L 3. TRANSFER FUNTIONS 4. ELETRIAL SYSTEMS Analyi of h hr baic paiv lmn R, and
Lab No PH-35 Porland Sa Univriy A. La Roa Tranfr funcion and h Laplac ranformaion. INTRODUTION. THE LAPLAE TRANSFORMATION L 3. TRANSFER FUNTIONS 4. ELETRIAL SYSTEMS Analyi of h hr baic paiv lmn R, and
REQUIREMENTS FOR EFFICIENT TRANSISTOR OPERATION I B. Icn. I cp
 RQURMNS FOR FFCN RANSSOR OPRAON r 1. AN so that the fudametal basis of trasistor atio, that of a urret otrolled by a small voltage flowig aross a large resistor to geerate a large voltage is maitaied.
RQURMNS FOR FFCN RANSSOR OPRAON r 1. AN so that the fudametal basis of trasistor atio, that of a urret otrolled by a small voltage flowig aross a large resistor to geerate a large voltage is maitaied.
CHAPTER 4 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS (BJTs)
 HAPER 4 POLAR JUNON RANSSORS (Js) haptr Outln 4.1 Dc Structur and Physcal Opraton 4.2 urrnt oltag haractrstcs 4.3 J rcuts at D 4.4 Applyng th J n Amplfr Dsgn 4.5 Small Sgnal Opraton and Modls 4.6 asc J
HAPER 4 POLAR JUNON RANSSORS (Js) haptr Outln 4.1 Dc Structur and Physcal Opraton 4.2 urrnt oltag haractrstcs 4.3 J rcuts at D 4.4 Applyng th J n Amplfr Dsgn 4.5 Small Sgnal Opraton and Modls 4.6 asc J
tcvrn Hl1 J M Hamilton P Eng Chief Geologist Kimberley Northing m Northing m I FEB 24 1QP Northing m Gold Commiuioner
 SVA M OMO TD KOOT GROP ASSSSMT RPORT KMBRY B Th fwn rpr dsrbs h rss f drn Dand Dr H K 8 4 a 8 r h D D H K 8 5 a 9 5 r h D D H K 8 5A a 67 38 r h D D H K 8 6 a 8 69 r h and D D H K 8 7 a 77 72 r h n h ana
SVA M OMO TD KOOT GROP ASSSSMT RPORT KMBRY B Th fwn rpr dsrbs h rss f drn Dand Dr H K 8 4 a 8 r h D D H K 8 5 a 9 5 r h D D H K 8 5A a 67 38 r h D D H K 8 6 a 8 69 r h and D D H K 8 7 a 77 72 r h n h ana
Ideal Diode Equation II + Intro to Solar Cells
 ECE-35: Spring 15 Ideal Diode Equation II + Intro to Solar Cells Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA lundstro@purdue.edu Pierret, Semiconductor
ECE-35: Spring 15 Ideal Diode Equation II + Intro to Solar Cells Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA lundstro@purdue.edu Pierret, Semiconductor
Guide to the Extended Step-Pyramid Periodic Table
 Guide to the Extended Step-Pyramid Periodic Table William B. Jensen Department of Chemistry University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, OH 452201-0172 The extended step-pyramid table recognizes that elements
Guide to the Extended Step-Pyramid Periodic Table William B. Jensen Department of Chemistry University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, OH 452201-0172 The extended step-pyramid table recognizes that elements
H STO RY OF TH E SA NT
 O RY OF E N G L R R VER ritten for the entennial of th e Foundin g of t lair oun t y on ay 8 82 Y EEL N E JEN K RP O N! R ENJ F ] jun E 3 1 92! Ph in t ed b y h e t l a i r R ep u b l i c a n O 4 1922
O RY OF E N G L R R VER ritten for the entennial of th e Foundin g of t lair oun t y on ay 8 82 Y EEL N E JEN K RP O N! R ENJ F ] jun E 3 1 92! Ph in t ed b y h e t l a i r R ep u b l i c a n O 4 1922
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kelleci. Spring 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Aoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kllci Spring 08 OUTLINE Th Laplac Tranform Rgion of convrgnc for Laplac ranform Invr Laplac ranform Gomric valuaion
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Aoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kllci Spring 08 OUTLINE Th Laplac Tranform Rgion of convrgnc for Laplac ranform Invr Laplac ranform Gomric valuaion
Lecture Stage Frequency Response - I (1/10/02) Page ECE Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems II P.E.
 Lecture 070 Stage Frequency esponse I (/0/0) Page 070 LECTUE 070 SINGLESTAGE FEQUENCY ESPONSE I (EADING: GHLM 488504) Objective The objective of this presentation is:.) Illustrate the frequency analysis
Lecture 070 Stage Frequency esponse I (/0/0) Page 070 LECTUE 070 SINGLESTAGE FEQUENCY ESPONSE I (EADING: GHLM 488504) Objective The objective of this presentation is:.) Illustrate the frequency analysis
ESE319 Introduction to Microelectronics. Feedback Basics
 Feedback Basics Feedback concept Feedback in emitter follower Stability One-pole feedback and root locus Frequency dependent feedback and root locus Gain and phase margins Conditions for closed loop stability
Feedback Basics Feedback concept Feedback in emitter follower Stability One-pole feedback and root locus Frequency dependent feedback and root locus Gain and phase margins Conditions for closed loop stability
Microelectronic Circuit Design Fourth Edition - Part I Solutions to Exercises
 Page Microelectronic Circuit esign Fourth Edition - Part I Solutions to Exercises CHAPTER V LSB 5.V 0 bits 5.V 04bits 5.00 mv V 5.V MSB.560V 000000 9 + 8 + 4 + 0 785 0 V O 785 5.00mV or ) 5.V 3.95 V V
Page Microelectronic Circuit esign Fourth Edition - Part I Solutions to Exercises CHAPTER V LSB 5.V 0 bits 5.V 04bits 5.00 mv V 5.V MSB.560V 000000 9 + 8 + 4 + 0 785 0 V O 785 5.00mV or ) 5.V 3.95 V V
1 of 5 14/10/ :21
 X-ray absorption s, characteristic X-ray lines... 4.2.1 Home About Table of Contents Advanced Search Copyright Feedback Privacy You are here: Chapter: 4 Atomic and nuclear physics Section: 4.2 Absorption
X-ray absorption s, characteristic X-ray lines... 4.2.1 Home About Table of Contents Advanced Search Copyright Feedback Privacy You are here: Chapter: 4 Atomic and nuclear physics Section: 4.2 Absorption
Mathematics Paper- II
 R Prerna Tower, Road No -, Conracors Area, Bisupur, Jamsedpur - 8, Tel - (65789, www.prernaclasses.com Maemaics Paper- II Jee Advance PART III - MATHEMATICS SECTION - : (One or more opions correc Type
R Prerna Tower, Road No -, Conracors Area, Bisupur, Jamsedpur - 8, Tel - (65789, www.prernaclasses.com Maemaics Paper- II Jee Advance PART III - MATHEMATICS SECTION - : (One or more opions correc Type
Pose Estimation of Multiple Cameras with Particle Filters Evaluation on Simulation
 ( ) Pose Estmaton of Multple Cameras wth Partcle Flters Evaluaton on Smulaton *R. Ueda, S. Nkolads, P. Kamol A. Hayash and T. Ara (Unv. of Tokyo) Abstract In ths paper we propose a novel algorthm for estmatng
( ) Pose Estmaton of Multple Cameras wth Partcle Flters Evaluaton on Smulaton *R. Ueda, S. Nkolads, P. Kamol A. Hayash and T. Ara (Unv. of Tokyo) Abstract In ths paper we propose a novel algorthm for estmatng
Summary: Solving a Homogeneous System of Two Linear First Order Equations in Two Unknowns
 Summary: Solvng a Homognous Sysm of Two Lnar Frs Ordr Equaons n Two Unknowns Gvn: A Frs fnd h wo gnvalus, r, and hr rspcv corrspondng gnvcors, k, of h coffcn mar A Dpndng on h gnvalus and gnvcors, h gnral
Summary: Solvng a Homognous Sysm of Two Lnar Frs Ordr Equaons n Two Unknowns Gvn: A Frs fnd h wo gnvalus, r, and hr rspcv corrspondng gnvcors, k, of h coffcn mar A Dpndng on h gnvalus and gnvcors, h gnral
Cosmic Feb 06, 2007 by Raja Reddy P
 osmic ircuis@iisc, Feb 6, 7 by aja eddy P. ou() i() alculae ou(s)/(s). plo o(). calculae ime consan and pole frequency. ou ( e τ ) ou (s) ( s) Time consan (/) Pole frequency : ω p. i() n he above circui
osmic ircuis@iisc, Feb 6, 7 by aja eddy P. ou() i() alculae ou(s)/(s). plo o(). calculae ime consan and pole frequency. ou ( e τ ) ou (s) ( s) Time consan (/) Pole frequency : ω p. i() n he above circui
Chapter 2 Problem Solutions 2.1 R v = Peak diode current i d (max) = R 1 K 0.6 I 0 I 0
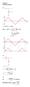 Chapter Problem Solutons. K γ.6, r f Ω For v, v.6 r + f ( 9.4) +. v 9..6 9.. v v v v v T ln and S v T ln S v v.3 8snωt (a) vs 3.33snωt 6 3.33 Peak dode current d (max) (b) P v s (max) 3.3 (c) T o π vo(
Chapter Problem Solutons. K γ.6, r f Ω For v, v.6 r + f ( 9.4) +. v 9..6 9.. v v v v v T ln and S v T ln S v v.3 8snωt (a) vs 3.33snωt 6 3.33 Peak dode current d (max) (b) P v s (max) 3.3 (c) T o π vo(
[ ]:543.4(075.8) 35.20: ,..,..,.., : /... ;. 2-. ISBN , - [ ]:543.4(075.8) 35.20:34.
![[ ]:543.4(075.8) 35.20: ,..,..,.., : /... ;. 2-. ISBN , - [ ]:543.4(075.8) 35.20:34. [ ]:543.4(075.8) 35.20: ,..,..,.., : /... ;. 2-. ISBN , - [ ]:543.4(075.8) 35.20:34.](/thumbs/74/69911105.jpg) .. - 2-2009 [661.87.+661.88]:543.4(075.8) 35.20:34.2373-60..,..,..,..,.. -60 : /... ;. 2-. : -, 2008. 134. ISBN 5-98298-299-7 -., -,,. - «,, -, -», - 550800,, 240600 «-», -. [661.87.+661.88]:543.4(075.8)
.. - 2-2009 [661.87.+661.88]:543.4(075.8) 35.20:34.2373-60..,..,..,..,.. -60 : /... ;. 2-. : -, 2008. 134. ISBN 5-98298-299-7 -., -,,. - «,, -, -», - 550800,, 240600 «-», -. [661.87.+661.88]:543.4(075.8)
Solar Cell Physics: recombination and generation
 NCN Summer School: July 2011 Solar Cell Physics: recombination and generation Prof. Mark Lundstrom lundstro@purdue.edu Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University West Lafayette, Indiana USA
NCN Summer School: July 2011 Solar Cell Physics: recombination and generation Prof. Mark Lundstrom lundstro@purdue.edu Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University West Lafayette, Indiana USA
Electronic Circuits. BJT Amplifiers. Manar Mohaisen Office: F208 Department of EECE
 Elctronic Circuits BJT mplifirs Manar Mohaisn Offic: F208 Email: manar.subhi@kut.ac.kr Dpartmnt of EECE viw of th Prcdnt Lctur Explain th DC Oprating Point Explain th Voltag-dividr Bias Othr Bias Mthods
Elctronic Circuits BJT mplifirs Manar Mohaisn Offic: F208 Email: manar.subhi@kut.ac.kr Dpartmnt of EECE viw of th Prcdnt Lctur Explain th DC Oprating Point Explain th Voltag-dividr Bias Othr Bias Mthods
Control System Engineering (EE301T) Assignment: 2
 Conrol Sysm Enginring (EE0T) Assignmn: PART-A (Tim Domain Analysis: Transin Rspons Analysis). Oain h rspons of a uniy fdack sysm whos opn-loop ransfr funcion is (s) s ( s 4) for a uni sp inpu and also
Conrol Sysm Enginring (EE0T) Assignmn: PART-A (Tim Domain Analysis: Transin Rspons Analysis). Oain h rspons of a uniy fdack sysm whos opn-loop ransfr funcion is (s) s ( s 4) for a uni sp inpu and also
ECE 497 JS Lecture -03 Transmission Lines
 ECE 497 JS Lecture -03 Transmission Lines Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 MAXWELL S EQUATIONS B E = t Faraday s Law of Induction
ECE 497 JS Lecture -03 Transmission Lines Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 MAXWELL S EQUATIONS B E = t Faraday s Law of Induction
The Fourier Transform
 /9/ Th ourr Transform Jan Baptst Josph ourr 768-83 Effcnt Data Rprsntaton Data can b rprsntd n many ways. Advantag usng an approprat rprsntaton. Eampls: osy ponts along a ln Color spac rd/grn/blu v.s.
/9/ Th ourr Transform Jan Baptst Josph ourr 768-83 Effcnt Data Rprsntaton Data can b rprsntd n many ways. Advantag usng an approprat rprsntaton. Eampls: osy ponts along a ln Color spac rd/grn/blu v.s.
ECE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves. Fall 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 15
 ECE 634 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 6 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 5 Attenuation Formula Waveguiding system (WG or TL): S z Waveguiding system Exyz (,, ) = E( xye, ) = E( xye, ) e γz jβz αz
ECE 634 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 6 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 5 Attenuation Formula Waveguiding system (WG or TL): S z Waveguiding system Exyz (,, ) = E( xye, ) = E( xye, ) e γz jβz αz
MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Second Edition
 MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Second Edition Richard C. Jaeger and Travis N. Blalock Answers to Selected Problems Updated 10/23/06 Chapter 1 1.3 1.52 years, 5.06 years 1.5 2.00 years, 6.65 years 1.8 113
MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Second Edition Richard C. Jaeger and Travis N. Blalock Answers to Selected Problems Updated 10/23/06 Chapter 1 1.3 1.52 years, 5.06 years 1.5 2.00 years, 6.65 years 1.8 113
Periodicity & Many-Electron Atoms
 Chap. 8 ELECTRON CONFIGURAT N & CEMICAL PERIODICITY 8.1-8.2 Periodicity & Many-Electron Atoms Understand the correlation of electron configuration and the periodic character of atomic properties such as
Chap. 8 ELECTRON CONFIGURAT N & CEMICAL PERIODICITY 8.1-8.2 Periodicity & Many-Electron Atoms Understand the correlation of electron configuration and the periodic character of atomic properties such as
Barrier Photodetectors for High Sensitivity and High Operating Temperature Infrared Sensors
 Barrier Photodetectors for High Sensitivity and High Operating Temperature Infrared Sensors Philip Klipstein General Review of Barrier Detectors 1) Higher operating temperature, T OP 2) Higher signal to
Barrier Photodetectors for High Sensitivity and High Operating Temperature Infrared Sensors Philip Klipstein General Review of Barrier Detectors 1) Higher operating temperature, T OP 2) Higher signal to
Feedback Transimpedance & Current Amplifiers
 Feedback Transimpedance & Current Amplifiers Willy Sansen KULeuven, ESATMICAS Leuven, Belgium willy.sansen@esat.kuleuven.be Willy Sansen 1005 141 Table of contents Introduction Shuntshunt FB for Transimpedance
Feedback Transimpedance & Current Amplifiers Willy Sansen KULeuven, ESATMICAS Leuven, Belgium willy.sansen@esat.kuleuven.be Willy Sansen 1005 141 Table of contents Introduction Shuntshunt FB for Transimpedance
Ch. 9 Common Emitter Amplifier
 Ch. 9 Common mttr mplfr Common mttr mplfr nput and put oltags ar 180 o -of-phas, whl th nput and put currnts ar n-phas wth th nput oltag. Output oltag ( V ) V V V C CC C C C C and V C ar -of-phas 10 μ
Ch. 9 Common mttr mplfr Common mttr mplfr nput and put oltags ar 180 o -of-phas, whl th nput and put currnts ar n-phas wth th nput oltag. Output oltag ( V ) V V V C CC C C C C and V C ar -of-phas 10 μ
Additional Math (4047) Paper 2 (100 marks) y x. 2 d. d d
 Aitional Math (07) Prpar b Mr Ang, Nov 07 Fin th valu of th constant k for which is a solution of th quation k. [7] Givn that, Givn that k, Thrfor, k Topic : Papr (00 marks) Tim : hours 0 mins Nam : Aitional
Aitional Math (07) Prpar b Mr Ang, Nov 07 Fin th valu of th constant k for which is a solution of th quation k. [7] Givn that, Givn that k, Thrfor, k Topic : Papr (00 marks) Tim : hours 0 mins Nam : Aitional
Section 4. Nonlinear Circuits
 Section 4 Nonlinear Circuits 1 ) Voltage Comparators V P < V N : V o = V ol V P > V N : V o = V oh One bit A/D converter, Practical gain : 10 3 10 6 V OH and V OL should be far apart enough Response Time:
Section 4 Nonlinear Circuits 1 ) Voltage Comparators V P < V N : V o = V ol V P > V N : V o = V oh One bit A/D converter, Practical gain : 10 3 10 6 V OH and V OL should be far apart enough Response Time:
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 3 Signals & Systems Prof. ark Fowler Note Set #28 D-T Systems: DT Filters Ideal & Practical /4 Ideal D-T Filters Just as in the CT case we can specify filters. We looked at the ideal filter for the
EECE 3 Signals & Systems Prof. ark Fowler Note Set #28 D-T Systems: DT Filters Ideal & Practical /4 Ideal D-T Filters Just as in the CT case we can specify filters. We looked at the ideal filter for the
ECE 6340 Fall Homework 2. Please do the following problems (you may do the others for practice if you wish): Probs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10, 12
 ECE 634 Fall 16 Homework Please do the following problems (you may do the others for practice if you wish: Probs. 1,, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 1 1 Consider two parallel infinite wires in free space each carrying
ECE 634 Fall 16 Homework Please do the following problems (you may do the others for practice if you wish: Probs. 1,, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 1 1 Consider two parallel infinite wires in free space each carrying
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Introduction to Power Systems
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.061 Introduction to Power Systems Problem Set 5 Solutions February 27, 2011 Problem 1: The inductance and
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.061 Introduction to Power Systems Problem Set 5 Solutions February 27, 2011 Problem 1: The inductance and
EE 247B/ME 218: Introduction to MEMS Design Lecture 27m2: Gyros, Noise & MDS CTN 5/1/14. Copyright 2014 Regents of the University of California
 MEMSBase Fork Gyrosoe Ω r z Volage Deermnng Resoluon EE C45: Inrouon o MEMS Desgn LeM 15 C. Nguyen 11/18/08 17 () Curren (+) Curren Eleroe EE C45: Inrouon o MEMS Desgn LeM 15 C. Nguyen 11/18/08 18 [Zaman,
MEMSBase Fork Gyrosoe Ω r z Volage Deermnng Resoluon EE C45: Inrouon o MEMS Desgn LeM 15 C. Nguyen 11/18/08 17 () Curren (+) Curren Eleroe EE C45: Inrouon o MEMS Desgn LeM 15 C. Nguyen 11/18/08 18 [Zaman,
On the Speed of Heat Wave. Mihály Makai
 On h Spd of Ha Wa Mihály Maai maai@ra.bm.hu Conns Formulaion of h problm: infini spd? Local hrmal qulibrium (LTE hypohsis Balanc quaion Phnomnological balanc Spd of ha wa Applicaion in plasma ranspor 1.
On h Spd of Ha Wa Mihály Maai maai@ra.bm.hu Conns Formulaion of h problm: infini spd? Local hrmal qulibrium (LTE hypohsis Balanc quaion Phnomnological balanc Spd of ha wa Applicaion in plasma ranspor 1.
Chapter 6. pn-junction diode: I-V characteristics
 Chatr 6. -jucto dod: -V charactrstcs Tocs: stady stat rsos of th jucto dod udr ald d.c. voltag. ucto udr bas qualtatv dscusso dal dod quato Dvatos from th dal dod Charg-cotrol aroach Prof. Yo-S M Elctroc
Chatr 6. -jucto dod: -V charactrstcs Tocs: stady stat rsos of th jucto dod udr ald d.c. voltag. ucto udr bas qualtatv dscusso dal dod quato Dvatos from th dal dod Charg-cotrol aroach Prof. Yo-S M Elctroc
PHY 410. Final Examination, Spring May 4, 2009 (5:45-7:45 p.m.)
 PHY ina amination, Spring 9 May, 9 5:5-7:5 p.m. PLAS WAIT UTIL YOU AR TOLD TO BGI TH XAM. Wi waiting, carfuy fi in t information rqustd bow Your am: Your Studnt umbr: DO OT TUR THIS PAG UTIL TH XAM STARTS
PHY ina amination, Spring 9 May, 9 5:5-7:5 p.m. PLAS WAIT UTIL YOU AR TOLD TO BGI TH XAM. Wi waiting, carfuy fi in t information rqustd bow Your am: Your Studnt umbr: DO OT TUR THIS PAG UTIL TH XAM STARTS
PART CHAPTER2. Atomic Bonding
 PART O N E APTER2 Atomic Bonding The scanning tunneling microscope (Section 4.7) allows the imaging of individual atoms bonded to a material surface. In this case, the microscope was also used to manipulate
PART O N E APTER2 Atomic Bonding The scanning tunneling microscope (Section 4.7) allows the imaging of individual atoms bonded to a material surface. In this case, the microscope was also used to manipulate
Unit 1 Part 2 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Introduction to the Periodic Table UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PART 2 INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE Contents 1. The Structure of the Periodic Table 2. Trends in the Periodic Table Key words: group, period, block,
UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PART 2 INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE Contents 1. The Structure of the Periodic Table 2. Trends in the Periodic Table Key words: group, period, block,
(C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 1
 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 1 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 1 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 2 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 2 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 3 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 3 (C) Pavel Sedach
(C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 1 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 1 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 2 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 2 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 3 (C) Pavel Sedach and Prep101 3 (C) Pavel Sedach
