ATOC 1050 Summer Homework 1. Due: June 8, 2011
|
|
|
- Rafe Riley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ATOC 1050 Summer 2011 Homework 1 Due: June 8, 2011 Make sure your answers are legible, grammatically correct, and have units associated with them if applicable. Each question can be answered in a few sentences. Total possible points: One May afternoon, the temperature at your house in St. Louis is 74 F, while the dew point is 65 F. You call your friend in Las Vegas, where the temperature is 88 F and the dew point is 31 F. After your phone call, you both decide to go for a swim in your swimming pools. Which one of you will feel colder when you step out of the pool you, or your friend in Las Vegas? Your answer should be a qualitative discussion regarding relative humidity and how the body responds to evaporation (10 points). Your friend in Las Vegas will feel colder than you will at your home. The reason is due to the relative humidity and how our body responds to moisture in the air. At your home in St. Louis, the temperature and dew point are much closer together than in Las Vegas, indicating the relative humidity is higher at your house than in Las Vegas. Thus, even though the temperature is higher in Las Vegas, the air is much drier, and will cause evaporation to occur more quickly from your skin than from your friend s. Because evaporation causes your skin to cool, a faster evaporation rate causes more cooling. 2. Antarctica, the coldest continent on the Earth, is also one of the largest deserts in the world, where the precipitation per year is less than 2 cm in many locations. The relative humidity, however, is generally quite high, especially during the winter, where values can regularly reach 70% or higher. Explain how the relative humidity can be so high in an area with so little moisture in the air (10 points). The relative humidity describes how much moisture is in the air relative to the total amount possible at that given temperature and pressure. It is not an absolute measure of moisture content. Colder air cannot hold as much moisture as warmer air, and as such its capacity for moisture is low. Therefore, even though there is little moisture in the air, the low temperature means that saturation can occur more easily (and as such the relative humidity is higher). Another way to state this would be that because the moisture content is low, the vapor pressure must be low. Also, because the temperature is low, the saturation vapor pressure is low. Therefore, these two values do not differ greatly, and the relative humidity must be high.
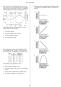
2 3. Using the Skew-T diagram given below for a Denver rawinsonde launched on 29 May 2011 at 12Z, answer the following questions (25 points). a) What is the temperature at the surface (2 points)? 10 C b) What is the dew point temperature at the surface (2 points)? 8 C c) Are there any cloud layers? If so, at what level? How do you know that there is a cloud at this level (3 points)? Yes, there is a cloud at 740 mb. We know there is a cloud there because the temperature and dew point are equal, which means the vapor pressure and saturation vapor pressures are equal. d) What is the relative humidity at the cloud layer level? How do you know what the relative humidity is? Hint you do not need to do any calculations for this question. If there is no cloud, say not applicable (5 points). The relative humidity at the cloud layer is 100%. We can see this on the diagram because our temperature and dew point temperatures are the same, but we also know this because for a cloud to occur, saturation must take place, which occurs when the temperature cools to the dew point temperature at a constant pressure. When the temperature and dew point temperatures are equal, the vapor pressure and saturation vapor pressures are equal, and the relative humidity is 100%. e) Are there any temperature inversions on this sounding? If so, at what level (2 points)? Yes, there is an inversion between 740 and 700 mb. There is also a small one just around 575 mb (you do not need to give this inversion to receive full credit). f) What is the temperature at 500 mb (2 points)? -9 C. g) What is the dew point temperature at 500 mb (2 points)? -35 C.
3 h) At what level is the tropopause? How do you know this (3 points)? The tropopause is at 150 mb. We know this because the temperature is increasing with height in the upper troposphere. i) What is the wind speed at 400 mb? What is the wind direction at 400 mb? Give your answer for wind direction in degrees (3 points). The wind speed is 50 knots. The wind direction is approximately 225. j) From what direction (in cardinal directions north, south, south-easterly, etc) is the wind at 400 mb (1 point)? The wind direction is southwesterly.
4 4. Using the surface station plots below, answer the following questions (20 points). At station MCK (McCook, Nebraska): a) What is the temperature (2 points)? 55 F b) What is the dew point temperature (2 points)? 53 F c) What is the pressure (2 points)? mb d) What is the wind speed and direction (4 points)? Northeasterly wind at 10 knots. e) What is the cloud cover (2 points)? Overcast (or 8 octets) f) What, if any, is the significant weather occurring at this time (2 points)? Light rain. g) In Kansas City, Missouri (station MCI), what is the significant weather occurring (2 points)? Thunderstorm h) What is the cloud cover at Rapid City, South Dakota (station RAP)? Give some reasons why the cloud is what is being reported (4 points). Obscured. Might be due to fog, smoke, or maybe the station simply cannot report it. 5. Discuss the collection of observations versus using NWP models to understand the weather. What are some limitations of both? What are some benefits? What do you think is a better method for understanding the weather? (For this last part, there is not necessarily a right answer here credit will be given in your justification) (15 points). Observations collected by instruments at the surface and in the upper atmosphere provide us with direct measurements of the atmospheric state. NWP models need to infer the atmospheric state by initializing a set of values from observations or previous forecasts, and then calculating how the atmosphere changes with time. Some limitations of observations are that they are limited in how often they are taken. For example, rawinsondes are only launched twice per day. All data is limited to sampling only the
5 location where the observations are being collected observing the weather over the horizon is not possible. Problems with the instruments can also lead to incorrect data. Also, if the observations are human made, they can be subjective. Some limitations to models are that your forecasts will be incorrect if your initial conditions are wrong, if you do not have a high enough resolution to observe the weather in that region, or if you make improper assumptions within the equations that are driving the model. The benefits to observations are that they provide us with direct measurements of the weather without having to infer the atmospheric state from inexact equations. Also the collection of measurements are input into NWP models to improve their forecasts, so they are necessary. The benefits to NWP models are that they can fill in gaps where data is lacking, and their development has led to a greater ability to forecast the weather in both short and long time ranges.
Name: ATOC Homework #1 Due Tuesday February 8, 2010 BEGINNING OF CLASS!
 ATOC 1050-001 Homework #1 Due Tuesday February 8, 2010 BEGINNING OF CLASS! Instructions: Make sure that you answer all of the questions and complete all of the tables for maximum credit. Use appropriate
ATOC 1050-001 Homework #1 Due Tuesday February 8, 2010 BEGINNING OF CLASS! Instructions: Make sure that you answer all of the questions and complete all of the tables for maximum credit. Use appropriate
Multiple Choice (2 Points Each)
 ATMO 336 -- Exam 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 Points Each) 1. The atmospheric greenhouse effect keeps the average surface temperature of the Earth about 60 F warmer than if there were no atmosphere. The two
ATMO 336 -- Exam 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 Points Each) 1. The atmospheric greenhouse effect keeps the average surface temperature of the Earth about 60 F warmer than if there were no atmosphere. The two
Name 28-MAY-08. FA RP 1 Mr. Chase. 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of millibars?
 FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
STATION If relative humidity is 60% and saturation vapor pressure is 35 mb, what is the actual vapor pressure?
 STATION 1 Vapor pressure is a measure of relative humidity and saturation vapor pressure. Using this information and the information given in the problem, answer the following question. 1. If relative
STATION 1 Vapor pressure is a measure of relative humidity and saturation vapor pressure. Using this information and the information given in the problem, answer the following question. 1. If relative
Weather and the Atmosphere. RAP Short Course
 Weather and the Atmosphere RAP Short Course Syllabus 1) Vertical structure and composition of the atmosphere, basic weather variables 2) Warming Earth and its atmosphere the diurnal and seasonal cycles
Weather and the Atmosphere RAP Short Course Syllabus 1) Vertical structure and composition of the atmosphere, basic weather variables 2) Warming Earth and its atmosphere the diurnal and seasonal cycles
Name Class Date. 3. In what part of the water cycle do clouds form? a. precipitation b. evaporation c. condensation d. runoff
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Water in the Air 1. What do we call the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place? a. the water cycle b. weather c. climate d. precipitation THE
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Water in the Air 1. What do we call the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place? a. the water cycle b. weather c. climate d. precipitation THE
Dew Point and Cloud Formation
 Name: Date: ES: 1 2 3 4 Dew Point and Cloud Formation Part A: Run some water over your hands. After shaking off the excess, wave them back and forth until they are dry. 1. Describe the change in temperature
Name: Date: ES: 1 2 3 4 Dew Point and Cloud Formation Part A: Run some water over your hands. After shaking off the excess, wave them back and forth until they are dry. 1. Describe the change in temperature
1. What influence does the Coriolis force have on pressure gradient wind direction in the Northern Hemisphere?
 1. What influence does the Coriolis force have on pressure gradient wind direction in the Northern Hemisphere? A. Pushes wind to the left B. Pushes wind to the right C. Pushes wind up D. Pushes wind backwards
1. What influence does the Coriolis force have on pressure gradient wind direction in the Northern Hemisphere? A. Pushes wind to the left B. Pushes wind to the right C. Pushes wind up D. Pushes wind backwards
7. The weather instrument below can be used to determine relative humidity.
 1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
Answers to Clicker Questions
 Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Weather Maps. Name:& & &&&&&Advisory:& & 1.! A&weather&map&is:& & & & 2.! Weather&fronts&are:& & & & & &
 Name: Advisory: Weather Maps 1. Aweathermapis: 2. Weatherfrontsare: a. Labelthefrontsbelow: 1. 2. 3. 4. 3. Clovercoversymbols 4. Precipitationsymbols 5. 6. 7. 8. 5. RadarEchoIntensityshows 6. Isobarsare
Name: Advisory: Weather Maps 1. Aweathermapis: 2. Weatherfrontsare: a. Labelthefrontsbelow: 1. 2. 3. 4. 3. Clovercoversymbols 4. Precipitationsymbols 5. 6. 7. 8. 5. RadarEchoIntensityshows 6. Isobarsare
Weather. Describing Weather
 CHAPTER 13 Weather LESSON 1 Describing Weather What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
CHAPTER 13 Weather LESSON 1 Describing Weather What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
Chapter Introduction. Weather. Patterns. Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
Deliverable 4-2: Assessment items. Activity-oriented Quiz for Weather or Not? Investigation in Exploring the Environment
 Deliverable 4-2: Assessment items Activity-oriented Quiz for Weather or Not? Investigation in Exploring the Environment In Weather or Not? you predicted the weather using satellite images and other kinds
Deliverable 4-2: Assessment items Activity-oriented Quiz for Weather or Not? Investigation in Exploring the Environment In Weather or Not? you predicted the weather using satellite images and other kinds
Pd: Date: Page # Weather Patterns -- Lesson 2 Study Guide
 Name: Pd: Date: Page # Weather Patterns -- Lesson 2 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 What are two types of pressure systems? 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 What drives weather patterns? 1
Name: Pd: Date: Page # Weather Patterns -- Lesson 2 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 What are two types of pressure systems? 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 What drives weather patterns? 1
UNIT TEST PRACTICE TEST
 Page 1 of 1 Directions: Match the best answer to complete each question. Some words may be used more than once and some may not be used at all. e 1. The condition of Earth s atmosphere at a given time
Page 1 of 1 Directions: Match the best answer to complete each question. Some words may be used more than once and some may not be used at all. e 1. The condition of Earth s atmosphere at a given time
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
How Can You Predict Weather Changes?
 How Can You Predict Weather Changes? How to Predict Weather Meteorologists make weather predictions daily. They use the same processes that you will. They collect weather data. They plot the data on maps.
How Can You Predict Weather Changes? How to Predict Weather Meteorologists make weather predictions daily. They use the same processes that you will. They collect weather data. They plot the data on maps.
ESCI 1010 Lab 6 Midlatitude Cyclones and Thunderstorms
 ESCI 1010 Lab 6 Midlatitude Cyclones and Thunderstorms Before Lab: Review pages 244-324 in your Weather and Climate textbook. Pay special attention to the sections entitled Fronts, Life Cyclone of a Midlatitude
ESCI 1010 Lab 6 Midlatitude Cyclones and Thunderstorms Before Lab: Review pages 244-324 in your Weather and Climate textbook. Pay special attention to the sections entitled Fronts, Life Cyclone of a Midlatitude
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES. Weather. atmosphere. Weather and climate
 GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
EXPLORING MOVEMENT CLIMATE FACTS WORKSHEET 1: WEATHER WATCHERS EXPERIMENT 1. You are going to measure the wind in two ways:
 WORKSHEET : WEATHER WATCHERS EXPERIMENT You are going to measure the wind in two ways: Using a weathervane to look at wind direction Using an anemometer to compare wind speed Follow the instructions to
WORKSHEET : WEATHER WATCHERS EXPERIMENT You are going to measure the wind in two ways: Using a weathervane to look at wind direction Using an anemometer to compare wind speed Follow the instructions to
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review
 Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
Chapter 5: Weather. Only Section 1: What is Weather?
 Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Introduction to Weather Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point
 Introduction to Weather Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point No study of weather would be complete without a discussion of precipitation. Here in Seattle it seems like it can rain for days
Introduction to Weather Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point No study of weather would be complete without a discussion of precipitation. Here in Seattle it seems like it can rain for days
Unit 5 Lesson 3 How is Weather Predicted? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Tracking the Weather Warm up 1 Why is it important to watch the weather forecast before traveling to another country? Tracking the Weather A meteorologist is a scientist who studies weather. Meteorologists
Tracking the Weather Warm up 1 Why is it important to watch the weather forecast before traveling to another country? Tracking the Weather A meteorologist is a scientist who studies weather. Meteorologists
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
ES1 Investigating Weather Maps/Station Models Act# 10 Name Block Date
 yay, bonus pt. because oops, no HO, book, heading this date =MP ES1 Investigating Weather Maps/Station Models Act# 10 Name Block Date Weather INTRODUCTION: Weather maps combine meteorological data from
yay, bonus pt. because oops, no HO, book, heading this date =MP ES1 Investigating Weather Maps/Station Models Act# 10 Name Block Date Weather INTRODUCTION: Weather maps combine meteorological data from
(1) a hurricane warning (2) a gale warning (3) a storm watch (4) a storm warning (5) a hurricane watch
 Instructor: Prof. Seiberling PHYSICS DEPARTMENT MET 1010 Final Exam December 15, 2003 Name (print, last rst): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Instructor: Prof. Seiberling PHYSICS DEPARTMENT MET 1010 Final Exam December 15, 2003 Name (print, last rst): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
February 11, Weather and Water Investigation 6 Day 6
 Weather and Water Investigation 6 Day 6 What is dew point? Bell Work Response Sheet: Water In The Air Answers When we put water on our hands and waved them in the air, our skin felt cooler. That's because
Weather and Water Investigation 6 Day 6 What is dew point? Bell Work Response Sheet: Water In The Air Answers When we put water on our hands and waved them in the air, our skin felt cooler. That's because
Feel free to ask me if you are confused about the meaning of any question. Good luck, and have a great spring break!
 Name: _ MEA 214 Midterm Exam, Spring 2011 Feel free to ask me if you are confused about the meaning of any question. Good luck, and have a great spring break! 1.) For each of the characteristics listed
Name: _ MEA 214 Midterm Exam, Spring 2011 Feel free to ask me if you are confused about the meaning of any question. Good luck, and have a great spring break! 1.) For each of the characteristics listed
Michael F. Stringfellow
 Michael F. Stringfellow Thermals Columns or bubbles of warm air that rise from the ground when it is heated by the sun Soaring Sustained engineless flight using natural sources of lift Boundary or mixing
Michael F. Stringfellow Thermals Columns or bubbles of warm air that rise from the ground when it is heated by the sun Soaring Sustained engineless flight using natural sources of lift Boundary or mixing
Weather. Describing Weather
 Weather Describing Weather What is weather? Weather is the atmospheric conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certain place at a certain time. Have you ever been caught in a rainstorm on what
Weather Describing Weather What is weather? Weather is the atmospheric conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certain place at a certain time. Have you ever been caught in a rainstorm on what
Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts
 Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts Weather is a combination of local conditions at any one time. It's what's happening outside right now, right here. Weather includes: Temperature Humidity Air
Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts Weather is a combination of local conditions at any one time. It's what's happening outside right now, right here. Weather includes: Temperature Humidity Air
Weather 101 Brad Jakubowski Doane College Water
 Weather 101 Fundamental Meteorology for Turf Managers Brad Jakubowski Doane College Do Baseballs Really Fly Farther at Coors Field? In theory, A well struck baseball should travel 10 percent farther at
Weather 101 Fundamental Meteorology for Turf Managers Brad Jakubowski Doane College Do Baseballs Really Fly Farther at Coors Field? In theory, A well struck baseball should travel 10 percent farther at
The Water Cycle. Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site:
 Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Latent Heat Evaporation & Saturation Relative Humidity Dew Point Lecture 11 Oct 2 2018
Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Latent Heat Evaporation & Saturation Relative Humidity Dew Point Lecture 11 Oct 2 2018
Lab 19.2 Synoptic Weather Maps
 Lab 19.2 Synoptic Weather Maps Name: Partner: Purpose The purpose of this lab is to have you read and interpret the information displayed on synoptic weather maps. You will also learn the techniques used
Lab 19.2 Synoptic Weather Maps Name: Partner: Purpose The purpose of this lab is to have you read and interpret the information displayed on synoptic weather maps. You will also learn the techniques used
What do you think of when someone says weather?
 Weather Our World: What is Weather? video What do you think of when someone says weather? Questions from Bill Nye video 1. What causes wind? 2. What are two things that were mentioned by Bill Nye that
Weather Our World: What is Weather? video What do you think of when someone says weather? Questions from Bill Nye video 1. What causes wind? 2. What are two things that were mentioned by Bill Nye that
Introduction to Weather: Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point
 IDS 102 Winter 2008 Introduction to Weather: Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point During fall quarter we covered the topic of pressure and it has been a while since the, so let s review a couple
IDS 102 Winter 2008 Introduction to Weather: Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point During fall quarter we covered the topic of pressure and it has been a while since the, so let s review a couple
Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know
 The Weather Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know Jon Tarleton Global Roads Marketing Manager Meteorologist Jon.tarleton@vaisala.com Page 2 / date / name / Internal use / Vaisala Weather and Our
The Weather Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know Jon Tarleton Global Roads Marketing Manager Meteorologist Jon.tarleton@vaisala.com Page 2 / date / name / Internal use / Vaisala Weather and Our
Warm Up 1: Atmosphere LT I can describe dew point, condensation nuclei and explain the difference between relative and absolute humidity.
 Warm Up 1: Atmosphere 2-8-17 LT I can describe dew point, condensation nuclei and explain the difference between relative and absolute humidity. Q1 List as many layers of the atmosphere as you can remember.
Warm Up 1: Atmosphere 2-8-17 LT I can describe dew point, condensation nuclei and explain the difference between relative and absolute humidity. Q1 List as many layers of the atmosphere as you can remember.
2. What are the four most common gasses in the atmosphere and their percentages?
 Meteorology Review Directions: Answer the following open ended review questions. Utilize a diagram where appropriate and do make sure that you label and describe the drawing. Atmospheric Composition 1.
Meteorology Review Directions: Answer the following open ended review questions. Utilize a diagram where appropriate and do make sure that you label and describe the drawing. Atmospheric Composition 1.
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 3 Content: Weather Instruments Notes
 Introduction In order for meteorologists to accurately predict the weather, they take thousands of different weather measurements each day. Meteorologists need to use many tools in order to draw an accurate
Introduction In order for meteorologists to accurately predict the weather, they take thousands of different weather measurements each day. Meteorologists need to use many tools in order to draw an accurate
Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place
 Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A.
 Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A. COLUMN A 1. a unit of atmospheric pressure 2. a line joining points of equal air pressure
Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A. COLUMN A 1. a unit of atmospheric pressure 2. a line joining points of equal air pressure
latent heat/humidity
 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
Change of Dew Point Temperature and Density of Saturated Water Vapor with High and its Impact on Cloud Cover
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 01 (January. 2016), V1 PP 06-13 www.iosrjen.org Change of Dew Point Temperature and Density of Saturated Water
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 01 (January. 2016), V1 PP 06-13 www.iosrjen.org Change of Dew Point Temperature and Density of Saturated Water
1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents
 CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
78% : component of atmosphere! 21% : 1% : Changes depending on origin of air: - originated over - originated over Ozone = O 3 Definition:
 Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period.
 Topic 8: WEATHER Workbook chapter 7 Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period. Differences in how Earth s surfaces absorb and reradiate energy from
Topic 8: WEATHER Workbook chapter 7 Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period. Differences in how Earth s surfaces absorb and reradiate energy from
5) The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 C is called: Page Ref: 69
 Homework #2 Due 9/19/14 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, what would the daily mean temperature be? (Page Ref: 66) 2) How is the annual mean
Homework #2 Due 9/19/14 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, what would the daily mean temperature be? (Page Ref: 66) 2) How is the annual mean
Name Date Hour Table. Chapter 12-AP Lesson One
 Name Date Hour Table 1. Chapter 12-AP Lesson One 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. Name Date Hour Table Directions: Answer each question to create your word bank.
Name Date Hour Table 1. Chapter 12-AP Lesson One 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. Name Date Hour Table Directions: Answer each question to create your word bank.
WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program
 WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH On-Site Packet Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH WEATHER ON WHEELS ELEMENTARY ON-SITE HIGHLIGHTS PACKET
WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH On-Site Packet Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH WEATHER ON WHEELS ELEMENTARY ON-SITE HIGHLIGHTS PACKET
5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER EARTH SCIENCE
 EARTH SCIENCE 5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER Text: The water vapor content of the air is called humidity. The amount of water vapor air can hold depends on its temperature. Warm air can hold far more moisture
EARTH SCIENCE 5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER Text: The water vapor content of the air is called humidity. The amount of water vapor air can hold depends on its temperature. Warm air can hold far more moisture
Meteorology Study Guide
 Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Meteorology Unit Study Guide
 Name: Key Pd. Date: 1. Define meteorology Meteorology Unit Study Guide Study of the atmosphere including weather and weather patterns 2. The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises
Name: Key Pd. Date: 1. Define meteorology Meteorology Unit Study Guide Study of the atmosphere including weather and weather patterns 2. The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises
Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide
 Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
WEATHER. Review Note Cards
 WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Observing Weather: Making the Invisible Visible. Dr. Michael J. Passow
 Observing Weather: Making the Invisible Visible Dr. Michael J. Passow What Is Weather? Weather refers to the conditions of the atmosphere at a certain place and time. Weather differs from Climate, which
Observing Weather: Making the Invisible Visible Dr. Michael J. Passow What Is Weather? Weather refers to the conditions of the atmosphere at a certain place and time. Weather differs from Climate, which
Weather Notes. Chapter 16, 17, & 18
 Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Weather vs. Climate. Tucson NWS homepage:
 Weather vs. Climate Tucson NWS homepage: www.nws.noaa.gov/twc/ A Weather Forecaster? Betty claims to know exactly when it s going to rain because her knee starts to hurt. Ms. Betty Martin of Newburgh,
Weather vs. Climate Tucson NWS homepage: www.nws.noaa.gov/twc/ A Weather Forecaster? Betty claims to know exactly when it s going to rain because her knee starts to hurt. Ms. Betty Martin of Newburgh,
Condensation, Evaporation, Weather, and the Water Cycle
 Last name: First name: Date: Period: COM INC COM* Condensation, Evaporation, Weather, and the Water Cycle Evaporation and boiling are both types of vaporization, in which a liquid changes into a gas. The
Last name: First name: Date: Period: COM INC COM* Condensation, Evaporation, Weather, and the Water Cycle Evaporation and boiling are both types of vaporization, in which a liquid changes into a gas. The
Water in the Atmosphere
 Water in the Atmosphere Characteristics of Water solid state at 0 o C or below (appearing as ice, snow, hail and ice crystals) liquid state between 0 o C and 100 o C (appearing as rain and cloud droplets)
Water in the Atmosphere Characteristics of Water solid state at 0 o C or below (appearing as ice, snow, hail and ice crystals) liquid state between 0 o C and 100 o C (appearing as rain and cloud droplets)
Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture
 Chapter 1: Properties of Atmosphere Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture Thickness of the Atmosphere (from Meteorology Today) 90% 70% The thickness of the atmosphere is only about 2% of Earth s thickness
Chapter 1: Properties of Atmosphere Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture Thickness of the Atmosphere (from Meteorology Today) 90% 70% The thickness of the atmosphere is only about 2% of Earth s thickness
Three things necessary for weather are Heat, Air, Moisture (HAM) Weather takes place in the Troposphere (The lower part of the atmosphere).
 Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms
 III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63%
 Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Laboratory Exercise #7 - Introduction to Atmospheric Science: The Seasons
 Laboratory Exercise #7 - Introduction to Atmospheric Science: The Seasons page - 1 Section A - Introduction: This lab consists of both computer-based and noncomputer-based questions dealing with atmospheric
Laboratory Exercise #7 - Introduction to Atmospheric Science: The Seasons page - 1 Section A - Introduction: This lab consists of both computer-based and noncomputer-based questions dealing with atmospheric
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
3 Weather and Climate
 CHAPTER 22 3 Weather and Climate SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are fronts? What are some types of severe weather? How is climate different
CHAPTER 22 3 Weather and Climate SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are fronts? What are some types of severe weather? How is climate different
Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere
 14. Day Breezes H L Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere Questions Pages 177 179 1. (3) 2. (4) 3. (4) 4. (3) 5. (2) 6. (3) 7. (2) 8. (2) 9. (3) 10. (1) 11. (4) 12. (2) Questions Pages 186 188 13. (3)
14. Day Breezes H L Chapter 7 Properties of the Atmosphere Questions Pages 177 179 1. (3) 2. (4) 3. (4) 4. (3) 5. (2) 6. (3) 7. (2) 8. (2) 9. (3) 10. (1) 11. (4) 12. (2) Questions Pages 186 188 13. (3)
5) Water vapor is water in the state. a. solid b. liquid c. *gas
 1 NAME DATE January 15, 2004_ GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water cycle ( evaporation, condensation, precipitation.). 1) The sketch above shows: a. a life cycle. b. *the
1 NAME DATE January 15, 2004_ GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water cycle ( evaporation, condensation, precipitation.). 1) The sketch above shows: a. a life cycle. b. *the
Investigation 11.3 Weather Maps
 Name: Date: Investigation 11.3 Weather Maps What can you identify weather patterns based on information read on a weather map? There have been some amazing technological advancements in the gathering and
Name: Date: Investigation 11.3 Weather Maps What can you identify weather patterns based on information read on a weather map? There have been some amazing technological advancements in the gathering and
Weather and Climate 1. Elements of the weather
 Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
Science and Literacy. Lesson Sets. Weather vs. Climate. By Elementary Ali. Created by Elementary Ali 2014
 d Science and Literacy Lesson Sets Weather vs. Climate By Elementary Ali These activities are created to incorporate reading and writing into the Science curriculum. Each lesson is designed to last about
d Science and Literacy Lesson Sets Weather vs. Climate By Elementary Ali These activities are created to incorporate reading and writing into the Science curriculum. Each lesson is designed to last about
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. WOW (Weather on Wheels)
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami,
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami,
25.1 Air Masses. Section 25.1 Objectives
 Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument.
 1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
Weather and climate. reflect. what do you think? look out!
 reflect You re going on vacation in a week and you have to start thinking about what clothes you re going to pack for your trip. You ve read the weather reports for your vacation spot, but you know that
reflect You re going on vacation in a week and you have to start thinking about what clothes you re going to pack for your trip. You ve read the weather reports for your vacation spot, but you know that
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 5 Content: Weather Maps Notes
 Introduction A variety of weather maps are produced by the National Weather Service and National Oceanographic Atmospheric Administration. These maps are used to help meteorologists accurately predict
Introduction A variety of weather maps are produced by the National Weather Service and National Oceanographic Atmospheric Administration. These maps are used to help meteorologists accurately predict
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Tracking the Climate Of Northern Colorado Nolan Doesken State Climatologist Colorado Climate Center Colorado State University
 Tracking the Climate Of Northern Colorado Nolan Doesken State Climatologist Colorado Climate Center Colorado State University Northern Colorado Business Innovations November 20, 2013 Loveland, Colorado
Tracking the Climate Of Northern Colorado Nolan Doesken State Climatologist Colorado Climate Center Colorado State University Northern Colorado Business Innovations November 20, 2013 Loveland, Colorado
COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE
 Name Air COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE 1. What are the two most abundant gases in the atmospherere? 2. Why do you think the percentage of water vapor in the air varies? 3. Would you classify carbon dioxide
Name Air COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE 1. What are the two most abundant gases in the atmospherere? 2. Why do you think the percentage of water vapor in the air varies? 3. Would you classify carbon dioxide
Contents. Section 1: Climate Factors. Section 2: Climate Types. Section 3: Climate Effects
 Contents Section 1: Climate Factors 1. Weather or Climate?.... 2 2. Elements of Climate.... 4 3. Factors Affecting Climate.... 10 4. Comparing Climates.... 15 5. Quiz 1.... 20 Section 2: Climate Types
Contents Section 1: Climate Factors 1. Weather or Climate?.... 2 2. Elements of Climate.... 4 3. Factors Affecting Climate.... 10 4. Comparing Climates.... 15 5. Quiz 1.... 20 Section 2: Climate Types
Name Period Date. How do surface temperatures on the earth affect the temperature of the air above it and the way air moves?
 Unit 4 Handout 2 Lesson 4: Investigating Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air Purpose: Guiding Questions: - Recognize that differences in air temperature connects to the movement of air. - Investigate
Unit 4 Handout 2 Lesson 4: Investigating Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air Purpose: Guiding Questions: - Recognize that differences in air temperature connects to the movement of air. - Investigate
Final Examination. Part A Answer ONLY TWELVE QUESTIONS in Part A. (Each question is 3 points)
 ATS 210 Spring Term 2001 NAME: Final Examination This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. Calculators may be used. All answers should be written on the examination paper. Use the final sheet for any
ATS 210 Spring Term 2001 NAME: Final Examination This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. Calculators may be used. All answers should be written on the examination paper. Use the final sheet for any
UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
 UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE After Unit 12 you should be able to: o Effectively use the charts Average Chemical Composition of Earth s Crust, Hydrosphere and Troposphere, Selected Properties of Earth
UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE After Unit 12 you should be able to: o Effectively use the charts Average Chemical Composition of Earth s Crust, Hydrosphere and Troposphere, Selected Properties of Earth
WONDERING ABOUT WEATHER
 NAME DATE PARTNERS WONDERING ABOUT WEATHER You are lying in the grass enjoying a few relaxing hours in the summer sun. You have your favorite cold drink and magazine close at hand. You close your eyes
NAME DATE PARTNERS WONDERING ABOUT WEATHER You are lying in the grass enjoying a few relaxing hours in the summer sun. You have your favorite cold drink and magazine close at hand. You close your eyes
6. State two factors and explain how each influences the weather in Ohio. Respond in the space provided in your Answer Document.
 6. State two factors and explain how each influences the weather in Ohio. Respond in the space provided in your Answer Document. (4 points) Sample Response for Item 6 (Extended Response): Other Correct
6. State two factors and explain how each influences the weather in Ohio. Respond in the space provided in your Answer Document. (4 points) Sample Response for Item 6 (Extended Response): Other Correct
Meteorology Lab Activity: Interpreting Surface Observation Symbols
 Meteorology Lab Activity: Interpreting Surface Observation Symbols Introduction: Routine surface meteorological observations are represented on weather maps by a standard notation of symbols and numbers.
Meteorology Lab Activity: Interpreting Surface Observation Symbols Introduction: Routine surface meteorological observations are represented on weather maps by a standard notation of symbols and numbers.
Weather and Energy Review
 Weather and Energy Review Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents the greenhouse effect in which heat energy is trapped in Earth's atmosphere Which type
Weather and Energy Review Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents the greenhouse effect in which heat energy is trapped in Earth's atmosphere Which type
Explain the parts of the water cycle that are directly connected to weather.
 Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Introduction to Skew-T Diagrams
 Introduction to Skew-T Diagrams Have a think about a few things I m going to throw to you it will hopefully make you think a little outside the square! - LIs of -15 can give you clear skies - LIs of 0
Introduction to Skew-T Diagrams Have a think about a few things I m going to throw to you it will hopefully make you think a little outside the square! - LIs of -15 can give you clear skies - LIs of 0
Earth Science Unit 5- Weather Knowledge Packet
 Earth Science Unit 5- Weather Knowledge Packet 2B: Describe types of energy transfer We all have a pretty good idea that the Sun is where majority of the heat comes from in Earth. That heat tends to act
Earth Science Unit 5- Weather Knowledge Packet 2B: Describe types of energy transfer We all have a pretty good idea that the Sun is where majority of the heat comes from in Earth. That heat tends to act
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns. Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather
 Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
Condensation is the process by which water vapor changes from a gas to a liquid. Clouds form by this process.
 CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
How do we understand weather?
 How do we understand weather? Fluid: a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter which includes liquids, gases, plasmas, and plastic
How do we understand weather? Fluid: a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter which includes liquids, gases, plasmas, and plastic
The Atmosphere EVPP 110 Lecture Fall 2003 Dr. Largen
 1 Physical Environment: EVPP 110 Lecture Fall 2003 Dr. Largen 2 Physical Environment: Atmosphere Composition Heat transfer Atmospheric moisture Atmospheric circulation Weather and climate 3 Physical Environment:
1 Physical Environment: EVPP 110 Lecture Fall 2003 Dr. Largen 2 Physical Environment: Atmosphere Composition Heat transfer Atmospheric moisture Atmospheric circulation Weather and climate 3 Physical Environment:
