Dew Point and Cloud Formation
|
|
|
- Jack Wiggins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Date: ES: Dew Point and Cloud Formation Part A: Run some water over your hands. After shaking off the excess, wave them back and forth until they are dry. 1. Describe the change in temperature you feel as you wave your hands back and forth. 2. a) What type of phase change is happening that causes the change in temperature that you felt? b) Does this type of phase change require energy or does it release energy? (use ESRT pg 1) 3. If you attached a damp cloth to the bulb of a thermometer and waved it back and forth, what would you expect to happen to the temperature reading on the thermometer? Why? Part B: How to use a sling psychrometer to find relative humidity and dew point Background: Dry bulb Thermometer Wet bulb Thermometer - Water evaporates from sock = cools bulb - The more evaporation, the lower the temperature The Dry Bulb ALWAYS has a higher temperature than the Wet Bulb. Only time it is equal is if the air is totally saturated and evaporation can t occur
2 Report Sheet 1 Dry-Bulb Temperature: C Wet-Bulb Temperature: C Dry-Bulb - Wet- Bulb: C Dewpoint Temperature (ESRT 12): C Relative Humidity (ESRT 12): % Report Sheet 2 1. Convert the dry-bulb temperature and dewpoint temperature you found in Report Sheet 1 to F. Record th information and the Relative Humidity on Report Sheet Retrieve the current conditions for your area from weather bug on the smartboard and record this information on Report Sheet 2. Your Measurements Temperature F Dewpoint F Relative Humidity % Current Observations from NWS Temperature F Dewpoint F Relative Humidity % Part C: Practice: Fill in all missing columns using the information provided and your ESRT. Location Air Wet Bulb Temp Temp A 19 o C 19 o C B 4 o C -1 o C Dry Bulb & Wet Bulb Difference C 21 o C 4 o C D 18 o C 5 o C Dew Point E 9 o C 2 o C Relative Humidity
3 1. When air temperature (the dry bulb temperature) is closer to the dewpoint, what happens to relative humidity? Use the chart you just completed and the charts of ESRT page 12 to help answer your question. Give example data points to support your answer. 2. Think about a rainforest and a desert that are both 90 o F. Which one do you think would have a higher relative humidity? Explain your answer. 3. Prediction: How do you think it would feel to be somewhere that has a relative humidity at 100%? What do you think might be happening? 4. For which location is precipitation most likely? Why? Part D: Look at the diagram below and answer the questions that follow. 1. Write down at least three observations. 2. What are some questions you have about the diagram and what it means? 3.Explain what the diagram is showing about relative humidity, temperature, dewpoint, and weather. Discuss with your partner and use your textbook to help you.
4 Part D: Use the following cartoon to respond to the questions that follow about the relationships between air temperature, relative humidity, and dew point temperature. 1. What is doing the talking in the first and second frames? 2. What happened to the difference between the dew point temperature and air temperature as the frames progress? 3. What happens to the relative humidity as the frames progress? 4. What happens when the dew point and air became the same temperature? 5. What is missing from this cartoon in order for condensation to really occur? (HINT: think small!)
5 Part F: Follow the procedure below to help visualize and relate condensation to relative humidity and dew point. Procedure: 1. Use a thermometer to measure the air temperature of the classroom. 2. Using the chart below to find the capacity of the air to hold water vapor at that temperature. 3. Fill the metal can halfway with water. Add some ice to the water and slowly stir with the thermometer.
6 4. As soon as condensation appears on the outside of the can, quickly record that temperature as your dew point temperature. 5. Use the chart below to find the capacity of air to hold vapor at the dew point temperature. This is your specific humidity. 6. Find the relative humidity by using the following formula: Relative Humidity = Specific Humidity Capacity Capacity of Air to hold water vapor Temp. C Capacity g/kg Temp. C Capacity g/kg Questions: 1. Explain how the dew formed on the outside of the can. 2. Why is it important to quickly record the temperature at which dew first appears on the outside of the can? 3. What would happen to relative humidity if the air temperature was warmer at the start?
7 4. What is the relative humidity when air temperature and dew point temperature are equal?
8
7. The weather instrument below can be used to determine relative humidity.
 1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period.
 Topic 8: WEATHER Workbook chapter 7 Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period. Differences in how Earth s surfaces absorb and reradiate energy from
Topic 8: WEATHER Workbook chapter 7 Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period. Differences in how Earth s surfaces absorb and reradiate energy from
Name 28-MAY-08. FA RP 1 Mr. Chase. 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of millibars?
 FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
Name Class Date. 3. In what part of the water cycle do clouds form? a. precipitation b. evaporation c. condensation d. runoff
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Water in the Air 1. What do we call the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place? a. the water cycle b. weather c. climate d. precipitation THE
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Water in the Air 1. What do we call the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place? a. the water cycle b. weather c. climate d. precipitation THE
Relative Humidity and Dew Point Lab
 Name: Relative Humidity and Dew Point Lab Weather is the present state of the atmosphere. Factors that determine the type of weather the world will have are: air pressure, wind, temperature and the air
Name: Relative Humidity and Dew Point Lab Weather is the present state of the atmosphere. Factors that determine the type of weather the world will have are: air pressure, wind, temperature and the air
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 3 Content: Weather Instruments Notes
 Introduction In order for meteorologists to accurately predict the weather, they take thousands of different weather measurements each day. Meteorologists need to use many tools in order to draw an accurate
Introduction In order for meteorologists to accurately predict the weather, they take thousands of different weather measurements each day. Meteorologists need to use many tools in order to draw an accurate
Warm-Up Draw a picture of the water cycle
 Warm-Up Draw a picture of the water cycle RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. BLACK SLIDE: Pay attention, follow directions, complete projects
Warm-Up Draw a picture of the water cycle RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. BLACK SLIDE: Pay attention, follow directions, complete projects
UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
 UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE After Unit 12 you should be able to: o Effectively use the charts Average Chemical Composition of Earth s Crust, Hydrosphere and Troposphere, Selected Properties of Earth
UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE After Unit 12 you should be able to: o Effectively use the charts Average Chemical Composition of Earth s Crust, Hydrosphere and Troposphere, Selected Properties of Earth
WONDERING ABOUT WEATHER
 NAME DATE PARTNERS WONDERING ABOUT WEATHER You are lying in the grass enjoying a few relaxing hours in the summer sun. You have your favorite cold drink and magazine close at hand. You close your eyes
NAME DATE PARTNERS WONDERING ABOUT WEATHER You are lying in the grass enjoying a few relaxing hours in the summer sun. You have your favorite cold drink and magazine close at hand. You close your eyes
latent heat/humidity
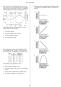 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology
 S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
WEATHER. Review Note Cards
 WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
Water in the Atmosphere
 Water in the Atmosphere Characteristics of Water solid state at 0 o C or below (appearing as ice, snow, hail and ice crystals) liquid state between 0 o C and 100 o C (appearing as rain and cloud droplets)
Water in the Atmosphere Characteristics of Water solid state at 0 o C or below (appearing as ice, snow, hail and ice crystals) liquid state between 0 o C and 100 o C (appearing as rain and cloud droplets)
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63%
 Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Water in the Air. Pages 38-45
 Water in the Air Pages 38-45 Quick Write What is the water cycle? Draw and label a diagram of the water cycle. Chapter 2, Section 1 Does this look familiar? Please open your text to page 38 and copy and
Water in the Air Pages 38-45 Quick Write What is the water cycle? Draw and label a diagram of the water cycle. Chapter 2, Section 1 Does this look familiar? Please open your text to page 38 and copy and
Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables
 Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review
 Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
Introduction to Weather Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point
 Introduction to Weather Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point No study of weather would be complete without a discussion of precipitation. Here in Seattle it seems like it can rain for days
Introduction to Weather Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point No study of weather would be complete without a discussion of precipitation. Here in Seattle it seems like it can rain for days
February 11, Weather and Water Investigation 6 Day 6
 Weather and Water Investigation 6 Day 6 What is dew point? Bell Work Response Sheet: Water In The Air Answers When we put water on our hands and waved them in the air, our skin felt cooler. That's because
Weather and Water Investigation 6 Day 6 What is dew point? Bell Work Response Sheet: Water In The Air Answers When we put water on our hands and waved them in the air, our skin felt cooler. That's because
4 Forecasting Weather
 CHAPTER 16 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather?
CHAPTER 16 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather?
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE I. Humidity A. Defined as water vapor or moisture in the air (from evaporation and condensation). B. The atmosphere gains moisture from the evaporation of water from oceans, lakes,
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE I. Humidity A. Defined as water vapor or moisture in the air (from evaporation and condensation). B. The atmosphere gains moisture from the evaporation of water from oceans, lakes,
Introduction. Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere. How Much Heat Is Brought Upward By Water Vapor?
 Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere Introduction Over 70% of the planet is covered by water Water is unique in that it can simultaneously exist in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) at the same temperature
Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere Introduction Over 70% of the planet is covered by water Water is unique in that it can simultaneously exist in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) at the same temperature
LAB 3: Atmospheric Pressure & Moisture
 Name School LAB 3: Atmospheric Pressure & Moisture Our atmosphere is a very dynamic area especially when we see what type of interactions it has with the surrounding environment. This lab will begin discussing
Name School LAB 3: Atmospheric Pressure & Moisture Our atmosphere is a very dynamic area especially when we see what type of interactions it has with the surrounding environment. This lab will begin discussing
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
1/2/2016 WEATHER DEFINITION
 WEATHER DEFINITION Weather state or condition of the variables of the atmosphere at a given time Weather variables temperature, air pressure, wind, moisture, cloud cover, precipitation, storms Weather
WEATHER DEFINITION Weather state or condition of the variables of the atmosphere at a given time Weather variables temperature, air pressure, wind, moisture, cloud cover, precipitation, storms Weather
Key. Name: OBJECTIVES
 Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated,
Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated,
Condensation is the process by which water vapor changes from a gas to a liquid. Clouds form by this process.
 CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Atmospheric Composition הרכב האטמוספירה
 Atmospheric Composition הרכב האטמוספירה N 2 O 2 Trace Gases Water Vapor (H 2 O) Argon (Ar) Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Neon (Ne) Helium (He) Methane (CH 4 ) Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) Ozone (O 3 ) Nitrogen and oxygen
Atmospheric Composition הרכב האטמוספירה N 2 O 2 Trace Gases Water Vapor (H 2 O) Argon (Ar) Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Neon (Ne) Helium (He) Methane (CH 4 ) Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) Ozone (O 3 ) Nitrogen and oxygen
The Sun and Water Cycle
 Have you ever jumped in a puddle or played in the rain? If so, you know you can get very wet. What you may not know is that a dinosaur could have walked through that same water millions of years ago. The
Have you ever jumped in a puddle or played in the rain? If so, you know you can get very wet. What you may not know is that a dinosaur could have walked through that same water millions of years ago. The
78% : component of atmosphere! 21% : 1% : Changes depending on origin of air: - originated over - originated over Ozone = O 3 Definition:
 Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
Explain the parts of the water cycle that are directly connected to weather.
 Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. WOW (Weather on Wheels)
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Highlights Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Highlights Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
Weather. Temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness of the air. Air temperature is measured using a thermometer.
 Weather Weather Weather describes the conditions in Earth's atmosphere at a given place at a given time. Temperature, precipitation, humidity, and cloud formation are aspects of weather, and they can be
Weather Weather Weather describes the conditions in Earth's atmosphere at a given place at a given time. Temperature, precipitation, humidity, and cloud formation are aspects of weather, and they can be
Meteorology Final Exam Study Guide Part 2
 Name: Teacher Science 8. Date: Water in the Air 1. Define the following terms: Meteorology Final Exam Study Guide Part 2 Evaporation Condensation Relative Humidity Dew Point Humidity Saturation Condensation
Name: Teacher Science 8. Date: Water in the Air 1. Define the following terms: Meteorology Final Exam Study Guide Part 2 Evaporation Condensation Relative Humidity Dew Point Humidity Saturation Condensation
ATOC 1050 Summer Homework 1. Due: June 8, 2011
 ATOC 1050 Summer 2011 Homework 1 Due: June 8, 2011 Make sure your answers are legible, grammatically correct, and have units associated with them if applicable. Each question can be answered in a few sentences.
ATOC 1050 Summer 2011 Homework 1 Due: June 8, 2011 Make sure your answers are legible, grammatically correct, and have units associated with them if applicable. Each question can be answered in a few sentences.
Where is the tropical zone? What are three biomes found in the tropical zone?
 Name CHAPTER 3 Class Date Climate 2 The Tropics SECTION BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Where is the tropical zone? What are three biomes found
Name CHAPTER 3 Class Date Climate 2 The Tropics SECTION BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Where is the tropical zone? What are three biomes found
NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel.
 NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel. REFERENCE TABLES (Videos 8.1 & 8.2 ESRT 12, 13a, 14b) 1. Use the temperature scales on page 13. (notes-air temperature conversions) a. 80 C to F
NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel. REFERENCE TABLES (Videos 8.1 & 8.2 ESRT 12, 13a, 14b) 1. Use the temperature scales on page 13. (notes-air temperature conversions) a. 80 C to F
Activity 13 Planner. Activity 13 Summary. Activity Subject and Content Objective Materials. Just Dew It! Dew point Determine the dew point of the air.
 Activity 13 Planner Students will learn how to measure the dew point of air. Activity 13 Summary Activity Subject and Content Objective Materials Just Dew It! Dew point Determine the dew point of the air.
Activity 13 Planner Students will learn how to measure the dew point of air. Activity 13 Summary Activity Subject and Content Objective Materials Just Dew It! Dew point Determine the dew point of the air.
Warm Up 1: Atmosphere LT I can describe dew point, condensation nuclei and explain the difference between relative and absolute humidity.
 Warm Up 1: Atmosphere 2-8-17 LT I can describe dew point, condensation nuclei and explain the difference between relative and absolute humidity. Q1 List as many layers of the atmosphere as you can remember.
Warm Up 1: Atmosphere 2-8-17 LT I can describe dew point, condensation nuclei and explain the difference between relative and absolute humidity. Q1 List as many layers of the atmosphere as you can remember.
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. WOW (Weather on Wheels)
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami,
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) On-Site Packet MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami,
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Multiple Choice (2 Points Each)
 ATMO 336 -- Exam 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 Points Each) 1. The atmospheric greenhouse effect keeps the average surface temperature of the Earth about 60 F warmer than if there were no atmosphere. The two
ATMO 336 -- Exam 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 Points Each) 1. The atmospheric greenhouse effect keeps the average surface temperature of the Earth about 60 F warmer than if there were no atmosphere. The two
Chapter 5: Weather. Only Section 1: What is Weather?
 Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Page 1. Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period.
 Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period. Which graph best illustrates the probable change in air pressure during the same time period?
Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period. Which graph best illustrates the probable change in air pressure during the same time period?
Name Period Date. How do surface temperatures on the earth affect the temperature of the air above it and the way air moves?
 Unit 4 Handout 2 Lesson 4: Investigating Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air Purpose: Guiding Questions: - Recognize that differences in air temperature connects to the movement of air. - Investigate
Unit 4 Handout 2 Lesson 4: Investigating Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air Purpose: Guiding Questions: - Recognize that differences in air temperature connects to the movement of air. - Investigate
MOISTURE IN THE ATMOSPHERE MEGA PACKET
 NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A psychrometer is used to determine which weather variables? A) wind speed and wind direction B) percentage of cloud cover and cloud height C) air pressure and air temperature D) relative
NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A psychrometer is used to determine which weather variables? A) wind speed and wind direction B) percentage of cloud cover and cloud height C) air pressure and air temperature D) relative
METEOROLOGY 110 Lab 4 Name. Meteorological Measurements
 METEOROLOGY 110 Lab 4 Name I. Response speeds of thermometers Meteorological Measurements How do you know what the air temperature is? Most people would answer: I read a thermometer. But is the thermometer
METEOROLOGY 110 Lab 4 Name I. Response speeds of thermometers Meteorological Measurements How do you know what the air temperature is? Most people would answer: I read a thermometer. But is the thermometer
E.T. - A LOCAL WAY OF LEARNING E-56
 E.T. - A LOCAL WAY OF LEARNING E-56 Title: Author: Jane Ducey Grade Level: 4-6 Eulalie R. Rivera Elementary School- Concepts: Disciplines: 1. The Sun 1.Earth Science 6. Natural Resources Objective: With
E.T. - A LOCAL WAY OF LEARNING E-56 Title: Author: Jane Ducey Grade Level: 4-6 Eulalie R. Rivera Elementary School- Concepts: Disciplines: 1. The Sun 1.Earth Science 6. Natural Resources Objective: With
WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program
 WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH On-Site Packet Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH WEATHER ON WHEELS ELEMENTARY ON-SITE HIGHLIGHTS PACKET
WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH On-Site Packet Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH WEATHER ON WHEELS ELEMENTARY ON-SITE HIGHLIGHTS PACKET
Activity 6.5 From gas to liquid to solid
 Activity 6.5 This activity is an extension of Activity 6.4a in which ice is used to make a container cold. As in Activity 6.4a, this activity will work only with sufficient water vapor in the air. Here,
Activity 6.5 This activity is an extension of Activity 6.4a in which ice is used to make a container cold. As in Activity 6.4a, this activity will work only with sufficient water vapor in the air. Here,
4 Forecasting Weather
 CHAPTER 2 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather? How
CHAPTER 2 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather? How
COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE
 Name Air COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE 1. What are the two most abundant gases in the atmospherere? 2. Why do you think the percentage of water vapor in the air varies? 3. Would you classify carbon dioxide
Name Air COMPOSITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE 1. What are the two most abundant gases in the atmospherere? 2. Why do you think the percentage of water vapor in the air varies? 3. Would you classify carbon dioxide
Weather Packet 10. Your Name Group Members. Score. Minutes
 Weather Packet 10 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key idea 2 Performance Indicator: 2.1 Use the concepts of density and heat energy to explain observations of weather patterns, seasonal
Weather Packet 10 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key idea 2 Performance Indicator: 2.1 Use the concepts of density and heat energy to explain observations of weather patterns, seasonal
Weather Part I- Weather Variables
 Weather Part I- Weather Variables 3-1-19 Definitions Meteorology- is the study of the atmosphere- including weather. Weather-the daily conditions of the atmosphere. It can change from time to time and
Weather Part I- Weather Variables 3-1-19 Definitions Meteorology- is the study of the atmosphere- including weather. Weather-the daily conditions of the atmosphere. It can change from time to time and
Class Notes: Weather
 Name: Date: Period: Weather The Physical Setting: Earth Science I. Cyclonic Weather Hurricane - Hurricane Statistics Largest of all the storms Approximately per year Nearly deaths per year Saffir-Simpson
Name: Date: Period: Weather The Physical Setting: Earth Science I. Cyclonic Weather Hurricane - Hurricane Statistics Largest of all the storms Approximately per year Nearly deaths per year Saffir-Simpson
Three things necessary for weather are Heat, Air, Moisture (HAM) Weather takes place in the Troposphere (The lower part of the atmosphere).
 Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
Meteorology Unit Study Guide
 Name: Key Pd. Date: 1. Define meteorology Meteorology Unit Study Guide Study of the atmosphere including weather and weather patterns 2. The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises
Name: Key Pd. Date: 1. Define meteorology Meteorology Unit Study Guide Study of the atmosphere including weather and weather patterns 2. The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises
WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH Pre-Site Activities Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida
 WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH Pre-Site Activities Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida WEATHER INSTRUMENTS On Weather on Wheels, you will use a variety of
WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH Pre-Site Activities Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida WEATHER INSTRUMENTS On Weather on Wheels, you will use a variety of
Lecture Ch. 6. Condensed (Liquid) Water. Cloud in a Jar Demonstration. How does saturation occur? Saturation of Moist Air. Saturation of Moist Air
 Lecture Ch. 6 Saturation of moist air Relationship between humidity and dewpoint Clausius-Clapeyron equation Dewpoint Temperature Depression Isobaric cooling Moist adiabatic ascent of air Equivalent temperature
Lecture Ch. 6 Saturation of moist air Relationship between humidity and dewpoint Clausius-Clapeyron equation Dewpoint Temperature Depression Isobaric cooling Moist adiabatic ascent of air Equivalent temperature
Condensation is the process by which water vapor changes from a gas to a liquid. Clouds form by this process.
 CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A.
 Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A. COLUMN A 1. a unit of atmospheric pressure 2. a line joining points of equal air pressure
Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A. COLUMN A 1. a unit of atmospheric pressure 2. a line joining points of equal air pressure
Introduction to Weather: Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point
 IDS 102 Winter 2008 Introduction to Weather: Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point During fall quarter we covered the topic of pressure and it has been a while since the, so let s review a couple
IDS 102 Winter 2008 Introduction to Weather: Moisture in the Air Vapor Pressure and Dew Point During fall quarter we covered the topic of pressure and it has been a while since the, so let s review a couple
The Water Cycle. Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site:
 Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Latent Heat Evaporation & Saturation Relative Humidity Dew Point Lecture 11 Oct 2 2018
Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Latent Heat Evaporation & Saturation Relative Humidity Dew Point Lecture 11 Oct 2 2018
Chapter 4 Water Vapor
 Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
The grade 5 English science unit, Weather, meets the academic content standards set in the Korean curriculum, which state students should:
 Among the diverse meteorological elements, this area focuses on humidity, dew, fog, clouds, rain, snow, wind and atmospheric pressure. Weather influences not only our daily outdoor activities, but also
Among the diverse meteorological elements, this area focuses on humidity, dew, fog, clouds, rain, snow, wind and atmospheric pressure. Weather influences not only our daily outdoor activities, but also
Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts
 Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts Weather is a combination of local conditions at any one time. It's what's happening outside right now, right here. Weather includes: Temperature Humidity Air
Forecasting Weather: Air Masses and Fronts Weather is a combination of local conditions at any one time. It's what's happening outside right now, right here. Weather includes: Temperature Humidity Air
Weather Maps. Name:& & &&&&&Advisory:& & 1.! A&weather&map&is:& & & & 2.! Weather&fronts&are:& & & & & &
 Name: Advisory: Weather Maps 1. Aweathermapis: 2. Weatherfrontsare: a. Labelthefrontsbelow: 1. 2. 3. 4. 3. Clovercoversymbols 4. Precipitationsymbols 5. 6. 7. 8. 5. RadarEchoIntensityshows 6. Isobarsare
Name: Advisory: Weather Maps 1. Aweathermapis: 2. Weatherfrontsare: a. Labelthefrontsbelow: 1. 2. 3. 4. 3. Clovercoversymbols 4. Precipitationsymbols 5. 6. 7. 8. 5. RadarEchoIntensityshows 6. Isobarsare
Science Chapter 13,14,15
 Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
Welcome. Vaisala Industrial Measure Webinar Series - Humidity Theory, Terms & Definitions. Yumi Alanoly Vaisala Application Engineer
 Welcome Vaisala Industrial Measure Webinar Series - Humidity Theory, Terms & Definitions Yumi Alanoly Vaisala Application Engineer Agenda 1. Why do we measure humidity? 2. Dalton s Law 3. Relative humidity
Welcome Vaisala Industrial Measure Webinar Series - Humidity Theory, Terms & Definitions Yumi Alanoly Vaisala Application Engineer Agenda 1. Why do we measure humidity? 2. Dalton s Law 3. Relative humidity
Per 5 Activity Solutions: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic Picture
 er 5 Activity Solutions: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic icture 5. How Is Temperature Related to Molecular Motion? ) Temperature Your instructor will discuss molecular motion and temperature. a) Watch
er 5 Activity Solutions: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic icture 5. How Is Temperature Related to Molecular Motion? ) Temperature Your instructor will discuss molecular motion and temperature. a) Watch
Water is one of the most important natural resources. People
 60 Changing States of Water R EA D I N G Water is one of the most important natural resources. People need it for survival. Although the earth has a lot of water, it is not always in the right place or
60 Changing States of Water R EA D I N G Water is one of the most important natural resources. People need it for survival. Although the earth has a lot of water, it is not always in the right place or
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
ATM 10. Severe and Unusual Weather. Prof. Richard Grotjahn.
 ATM 10 Severe and Unusual Weather Prof. Richard Grotjahn http://atm.ucdavis.edu/~grotjahn/course/atm10/index.html Moisture Mixing ratio Vapor pressure Relative humidity Lecture topics: Saturation vapor
ATM 10 Severe and Unusual Weather Prof. Richard Grotjahn http://atm.ucdavis.edu/~grotjahn/course/atm10/index.html Moisture Mixing ratio Vapor pressure Relative humidity Lecture topics: Saturation vapor
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH. WOW (Weather on Wheels)
 MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) Teacher Instructions / Answer Keys MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH ELEMENTARY PROGRAM Adventures Aboard WOW (Weather on Wheels) Teacher Instructions / Answer Keys MAST Academy Maritime and Science Technology High School Miami-Dade County Public Schools
Section 2 of 6 Applied Psychrometrics
 Section 2 of 6 Applied Psychrometrics Psychrometric chart - your energy map Key psychrometric variables for humidity Predicting building condensation Hot weather Cold weather Predicting moisture sorption
Section 2 of 6 Applied Psychrometrics Psychrometric chart - your energy map Key psychrometric variables for humidity Predicting building condensation Hot weather Cold weather Predicting moisture sorption
5) The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 C is called: Page Ref: 69
 Homework #2 Due 9/19/14 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, what would the daily mean temperature be? (Page Ref: 66) 2) How is the annual mean
Homework #2 Due 9/19/14 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, what would the daily mean temperature be? (Page Ref: 66) 2) How is the annual mean
Observing Weather: Making the Invisible Visible. Dr. Michael J. Passow
 Observing Weather: Making the Invisible Visible Dr. Michael J. Passow What Is Weather? Weather refers to the conditions of the atmosphere at a certain place and time. Weather differs from Climate, which
Observing Weather: Making the Invisible Visible Dr. Michael J. Passow What Is Weather? Weather refers to the conditions of the atmosphere at a certain place and time. Weather differs from Climate, which
Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide
 Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1
 Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
How our atmosphere is heated.
 How our atmosphere is heated. How is heat transferred around our atmosphere? 1) Radiation from the sun to the Earth. 2) Conduction passes heat from the Earth to the atmosphere. 3) Convection moves heat
How our atmosphere is heated. How is heat transferred around our atmosphere? 1) Radiation from the sun to the Earth. 2) Conduction passes heat from the Earth to the atmosphere. 3) Convection moves heat
UNIT VI: METEOROLOGY
 UNIT VI: METEOROLOGY 1. Understand that the Sun is the Earth s main energy source. a. Radiation from the is the chief source of energy for the atmosphere. b. When energy from the Sun reaches Earth s, the
UNIT VI: METEOROLOGY 1. Understand that the Sun is the Earth s main energy source. a. Radiation from the is the chief source of energy for the atmosphere. b. When energy from the Sun reaches Earth s, the
EARTH SCIENCE. Prentice Hall Water in the Atmosphere Water in the Atmosphere Water in the Atmosphere.
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Water s Changes of State 1. Precipitation is any form of water that falls from a cloud. a. Examples: Snow, rain, hail, sleet 3 States of matter of water: 1.
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Water s Changes of State 1. Precipitation is any form of water that falls from a cloud. a. Examples: Snow, rain, hail, sleet 3 States of matter of water: 1.
Condensation, Evaporation, Weather, and the Water Cycle
 Last name: First name: Date: Period: COM INC COM* Condensation, Evaporation, Weather, and the Water Cycle Evaporation and boiling are both types of vaporization, in which a liquid changes into a gas. The
Last name: First name: Date: Period: COM INC COM* Condensation, Evaporation, Weather, and the Water Cycle Evaporation and boiling are both types of vaporization, in which a liquid changes into a gas. The
5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER EARTH SCIENCE
 EARTH SCIENCE 5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER Text: The water vapor content of the air is called humidity. The amount of water vapor air can hold depends on its temperature. Warm air can hold far more moisture
EARTH SCIENCE 5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER Text: The water vapor content of the air is called humidity. The amount of water vapor air can hold depends on its temperature. Warm air can hold far more moisture
The Atmosphere. All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere
 The Atmosphere Structure/Layers Contains 4 major layers See E.S.R.T pg 14 o Troposphere All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere o Stratosphere Contains
The Atmosphere Structure/Layers Contains 4 major layers See E.S.R.T pg 14 o Troposphere All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere o Stratosphere Contains
Background: What is Weather?
 Weather Maps Background: What is Weather? Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere. The interaction of three important factors result in weather systems: air temperature, air pressure, and the
Weather Maps Background: What is Weather? Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere. The interaction of three important factors result in weather systems: air temperature, air pressure, and the
Final Examination. Part A Answer ONLY TWELVE QUESTIONS in Part A. (Each question is 3 points)
 ATS 210 Spring Term 2001 NAME: Final Examination This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. Calculators may be used. All answers should be written on the examination paper. Use the final sheet for any
ATS 210 Spring Term 2001 NAME: Final Examination This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. Calculators may be used. All answers should be written on the examination paper. Use the final sheet for any
Using Sprinklers to Reduce Freeze Injury to Blueberries
 Using Sprinklers to Reduce Freeze Injury to Blueberries Mark Longstroth Extension Small Fruit Educator Paw Paw, Michigan Cold Front Coming Types of Frost Radiation Clear skies Calm Winds Advective Cold
Using Sprinklers to Reduce Freeze Injury to Blueberries Mark Longstroth Extension Small Fruit Educator Paw Paw, Michigan Cold Front Coming Types of Frost Radiation Clear skies Calm Winds Advective Cold
Earth/Space Systems and Cycles (SOL 4.6)
 Earth/Space Systems and Cycles (SOL 4.6) Temperature is the measure of the amount of heat energy in the atmosphere. Air pressure is due to the weight of the air and is determined by several factors including
Earth/Space Systems and Cycles (SOL 4.6) Temperature is the measure of the amount of heat energy in the atmosphere. Air pressure is due to the weight of the air and is determined by several factors including
3.3 Phase Changes 88 A NATURAL APPROACH TO CHEMISTRY. Section 3.3 Phase Changes
 Section 3.3 Phase Changes 3.3 Phase Changes Solid, liquid and gas During a phase change, a substance rearranges the order of its particles (atoms or molecules). Examples of phase change include melting
Section 3.3 Phase Changes 3.3 Phase Changes Solid, liquid and gas During a phase change, a substance rearranges the order of its particles (atoms or molecules). Examples of phase change include melting
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERIC MOISTURE Atmospheric Moisture The Nature of Water The Hydrologic Cycle Evaporation Measures of Humidity Condensation The Buoyancy of Air Precipitation
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERIC MOISTURE Atmospheric Moisture The Nature of Water The Hydrologic Cycle Evaporation Measures of Humidity Condensation The Buoyancy of Air Precipitation
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction
 Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction Key Concepts Adding energy (heating) atoms and molecules increases their motion, resulting in an increase in temperature. Removing energy (cooling)
Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction Key Concepts Adding energy (heating) atoms and molecules increases their motion, resulting in an increase in temperature. Removing energy (cooling)
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Describing Cause and Effect
 Introduction RI.3.3 Describe the relationship between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to... cause/effect.
Introduction RI.3.3 Describe the relationship between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to... cause/effect.
Station 1: Adiabatic Decompression Materials: Can of compressed air Infrared thermometer Graph paper
 Station 1: Adiabatic Decompression Can of compressed air Infrared thermometer Graph paper 1. Using the digital thermometer, take the initial temperature of the can and record it on the table on the activity
Station 1: Adiabatic Decompression Can of compressed air Infrared thermometer Graph paper 1. Using the digital thermometer, take the initial temperature of the can and record it on the table on the activity
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Atmosphere SECTION 11.1 Atmospheric Basics In your textbook, read about the composition of the atmosphere. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Most of Earth s atmosphere
Atmosphere SECTION 11.1 Atmospheric Basics In your textbook, read about the composition of the atmosphere. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Most of Earth s atmosphere
