1/2/2016 WEATHER DEFINITION
|
|
|
- Della Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WEATHER DEFINITION Weather state or condition of the variables of the atmosphere at a given time Weather variables temperature, air pressure, wind, moisture, cloud cover, precipitation, storms Weather occurs in the troposphere (lower layer of the atmosphere) Heat energy (insolation) is what drives weather WEATHER Most weather occurs in troposphere. Due to our tilt, variations in insolation cause heat energy to be unevenly distributed The movement of heat energy results in changes in the atmosphere that are the cause of WEATHER In NY State, most of our weather comes from the West/Southwest. Weather Movement From West/SW Towards Northeast TEMPERATURE REVIEW Reminder: use page 13 on ref. table to convert temperatures Three Scales: Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin Isotherms lines that connect equal lines of temperature ISOTHERMS 1
2 HEATING THE ATMOSPHERE More insolation = higher temperatures Conduction moves heat Earth s surface to the atmosphere Absorption of insolation by gases and aerosols Absorption of infrared radiation given off by Earth s surface Condensation and (sublimation) gives off stored heat when clouds form Coriolis Effect due to rotation and winds friction between air and Earth s surface ANOTHER IMPORTANT HEAT TRANSFER Convection due to differences in density Convection Currents air moving in circular patterns EXPANSION AND COMPRESSION When a gas expands, its temperature decreases (molecules further apart) When a gas compresses, its temperature increases (molecules collide) Warm air rises- expands and then cools Cool air sinks- compresses and then warms PRESSURE WEIGHT OF AIR DIFFERENCES IN AIR PRESSURE ARE CAUSED PRIMARILY BY UNEQUAL HEATING OF EARTH S SURFACE Measured by a barometer Increase density, increase pressure Increase temperature, decrease pressure and density Increase altitude, decrease pressure Increase water vapor content, decrease pressure Isobars = lines of equal pressure (MEMORIZE THESE!!!) Increase temperature decrease pressure Mercury Barometer PRESSURE Temp. 2
3 Pressure and Density Decrease with ALTITUDE ISOBARS ARE ISOLINES OF EQUAL PRESSURE Where is the pressure gradient the steepest on this map? EFFECTS OF WEATHER VARIABLES ON PRESSURE Higher air temperature = lower density air = lower air pressure ( T = D = P ) More water vapor in the air = lower pressure (H 2 O weighs less than air nitrogen and oxygen) Higher altitude = lower pressure (remember air rises, expands, and then cools) 3
4 ATMOSPHERIC MOISTURE Exists in solid, liquid, and gas in atmosphere Water enters the atmosphere by: Evaporation liquid changes into gas Transpiration plants release water vapor Evapotranspiration evaporation + transpiration together Remember, it s the Sun that provides the energy for these to occur FACTORS AFFECTING EVAPORATION: amount of energy available (more energy = faster evaporation) surface area of the water (spread out/more s.a. = faster evaporation) degree of saturation (more saturated = slower evaporation) wind speed (greater wind speed = greater evaporation) HUMIDITY RELATIVE HUMIDITY Absolute Humidity - water vapor in each unit volume of air (or moisture capacity) - hotter air can hold more water vapor than cold air Relative humidity ratio of the amount of water vapor in the air to maximum amount it can hold The one you see in forecasts RELATIVE HUMIDITY If you had 20oz of water, which bottle would be full? The full, 20oz bottle would be at 100% relative humidity. If the same 20oz filled the 1 gal. (128oz) bottle, it would only fill about 16% of it. That would be 16% relative humidity. Or 5% of the 3 gallon. (128oz) RELATIVE HUMIDITY GIVEN IN % Does not tell you the amount of water vapor in the air DOES TELL YOU HOW CLOSE IT IS TO BEING SATURATED SATURATION filled to capacity with water vapor the RH is 100% Relative Humidity DECREASES as Temperature INCREASES 4
5 WHICH IS HEAVIER? Which is heavier: dry air or wet air? Would a baseball travel further on a night where the air is saturated or dry? (ignoring wind speed) When water vapor replaces other air molecules (oxygen, nitrogen) that are heavier, the humid air actually weighs LESS! Therefore, a baseball can travel further on a night when the air is saturated. DEW POINT Dew point temperature at which air is saturated (filled with water) If air temp = dew point, relative humidity = 100% If air temp drops below dew point: water vapor condenses to liquid water If air temp = dew point, relative humidity = 100% DEW POINT TEMPERATURE The temperature that the air is saturated (filled with water vapor) Relative Humidity is 100% Air Temperature = Dew Point Temperature, CONDENSATION begins Dew Point Temperature is a measure of how much water vapor in the air Dew Point Temperature will rise as water vapor content of the air increases 5
6 MEASURING MOISTURE Sling Psychrometer instrument used to measure relative humidity and dew point Dry bulb temp ordinary thermometer (aka: air temp.) Wet bulb temp thermometer with wet wick around it DPT & RELATIVE HUMIDITY CHARTS Earth Science Reference Tables Page 12 THE DRY BULB Don t let it fool you. It is just a thermometer. It measures the air temperature. 20 C THE WET BULB A DRY DAY Has a little wet booty tied to the bottom. Gets cool when water evaporates. 12 C A lot of moisture will evaporate. The wet bulb will be a lot cooler than the dry bulb. 20 C 8 C 20-8=12; Difference between wet bulb & dry bulb is 12 C. Wet Booty 6
7 A HUMID DAY A little bit of moisture will evaporate. The wet bulb will not be much cooler than the dry bulb. 20 C 20-14= 6 Difference between wet bulb & dry bulb is 6 C. 14 C PAGE 12 OF YOUR EARTH SCIENCE REFERENCE TABLES Warning #1: Be sure to READ the correct chart: DPT or RH Warning #2: Dew Point Temperature IS NOT Difference between wet bulb and dry bulb. Warning #3: The wet bulb temp IS NOT the DPT. TO CONVERT RELATIVE HUMIDITY AND DEW POINT Dry-bulb temperature is your air temperature. 20 C You must use page 12 of ref. table 1. Subtract: dry bulb temp wet bulb 2. Locate dry bulb on left side 3. Locate answer to step 1 on top of chart 4. See where those two numbers meet ****Make sure you are using the correct chart: dew point or relative humidity**** Subtract (the difference) between the dry bulb and wet bulb Put it all together Wet bulb = 8 C 20 C 8 C 20-8=12 Relative Humidity = 11% 7
8 INGREDIENTS FOR CLOUD FORMATION 1. Evaporation and Transpiration (puts water vapor in air) 2. Air rises and cools due to expansion 3. Cools to dew point temperature 4. Condensation begins on condensation surface (aerosols dust, salt crystals) 5. Cloud forms 6. Precipitation occurs if cloud droplets get too big RISING AIR EXPANDS & COOLS 8
9 Which graph best represents the relationship between water droplet size and precipitation? 9
10 CONVECTION DUE TO UNEQUAL HEATING 1. Evaporation 2. Rising and Cooling to dew point temperature 3. Condensation begins on condensation surface (aerosols, dust) 4. Cloud forms 5. Drops get big enough precipitation begins WINDWARD / LEEWARD Humid air is forced to rise over mountains. Air rises, cools & condenses on the windward side and is warm & dry on the leeward side (rain shadow). Called the orographic effect. YOU MUST KNOW THIS! 10
11 11
Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period.
 Topic 8: WEATHER Workbook chapter 7 Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period. Differences in how Earth s surfaces absorb and reradiate energy from
Topic 8: WEATHER Workbook chapter 7 Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period. Differences in how Earth s surfaces absorb and reradiate energy from
Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables
 Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Weather Part I- Weather Variables
 Weather Part I- Weather Variables 3-1-19 Definitions Meteorology- is the study of the atmosphere- including weather. Weather-the daily conditions of the atmosphere. It can change from time to time and
Weather Part I- Weather Variables 3-1-19 Definitions Meteorology- is the study of the atmosphere- including weather. Weather-the daily conditions of the atmosphere. It can change from time to time and
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Atmosphere SECTION 11.1 Atmospheric Basics In your textbook, read about the composition of the atmosphere. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Most of Earth s atmosphere
Atmosphere SECTION 11.1 Atmospheric Basics In your textbook, read about the composition of the atmosphere. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Most of Earth s atmosphere
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63%
 Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review
 Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
 UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE After Unit 12 you should be able to: o Effectively use the charts Average Chemical Composition of Earth s Crust, Hydrosphere and Troposphere, Selected Properties of Earth
UNIT 12: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE After Unit 12 you should be able to: o Effectively use the charts Average Chemical Composition of Earth s Crust, Hydrosphere and Troposphere, Selected Properties of Earth
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Water in the Atmosphere
 Water in the Atmosphere Characteristics of Water solid state at 0 o C or below (appearing as ice, snow, hail and ice crystals) liquid state between 0 o C and 100 o C (appearing as rain and cloud droplets)
Water in the Atmosphere Characteristics of Water solid state at 0 o C or below (appearing as ice, snow, hail and ice crystals) liquid state between 0 o C and 100 o C (appearing as rain and cloud droplets)
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
WEATHER. Review Note Cards
 WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
Weather and Climate Review
 Weather and Climate Review STUFF YOU NEED TO KNOW and to UNDERSTAND! 1) Because water has a higher specific heat than land, water will warm and cool more slowly than the land will. Because of this: a)
Weather and Climate Review STUFF YOU NEED TO KNOW and to UNDERSTAND! 1) Because water has a higher specific heat than land, water will warm and cool more slowly than the land will. Because of this: a)
Unit 9: Climate & Meteorology. Vocabulary
 Unit 9: Climate & Meteorology Vocabulary Weather Temperature Dew Point Relative Humidity Psychrometer Air Pressure Barometer Isobars Wind Anemometer condensation Sea Breeze Land Breeze Coriolis Effect
Unit 9: Climate & Meteorology Vocabulary Weather Temperature Dew Point Relative Humidity Psychrometer Air Pressure Barometer Isobars Wind Anemometer condensation Sea Breeze Land Breeze Coriolis Effect
The Atmosphere EVPP 110 Lecture Fall 2003 Dr. Largen
 1 Physical Environment: EVPP 110 Lecture Fall 2003 Dr. Largen 2 Physical Environment: Atmosphere Composition Heat transfer Atmospheric moisture Atmospheric circulation Weather and climate 3 Physical Environment:
1 Physical Environment: EVPP 110 Lecture Fall 2003 Dr. Largen 2 Physical Environment: Atmosphere Composition Heat transfer Atmospheric moisture Atmospheric circulation Weather and climate 3 Physical Environment:
Class Notes: Weather
 Name: Date: Period: Weather The Physical Setting: Earth Science I. Cyclonic Weather Hurricane - Hurricane Statistics Largest of all the storms Approximately per year Nearly deaths per year Saffir-Simpson
Name: Date: Period: Weather The Physical Setting: Earth Science I. Cyclonic Weather Hurricane - Hurricane Statistics Largest of all the storms Approximately per year Nearly deaths per year Saffir-Simpson
A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time
 WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
SPI Analyze data to identify events associated with heat convection in the atmosphere. SPI Recognize the connection between the
 SPI 0607.8.1 - Analyze data to identify events associated with heat convection in the atmosphere. SPI 0607.8.2 - Recognize the connection between the sun s energy and the wind. o Energy from the Sun creates
SPI 0607.8.1 - Analyze data to identify events associated with heat convection in the atmosphere. SPI 0607.8.2 - Recognize the connection between the sun s energy and the wind. o Energy from the Sun creates
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1
 Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere
 Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
The troposphere is the layer closest to Earth s surface. Extends from 9-16 km above Earth s Surface It contains most of the mass of the atmosphere.
 Chapter 11 The atmosphere is the blanket of gases surrounding Earth that contains about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor The atmosphere is classified
Chapter 11 The atmosphere is the blanket of gases surrounding Earth that contains about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor The atmosphere is classified
1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents
 CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
7. The weather instrument below can be used to determine relative humidity.
 1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
above the land to be warmer, causing convection currents because of the difference in air pressure.
 Name Date Period Earth Science Unit Test Review Sheet Directions: Use my web site and/or your lab book to help to answer the following questions. 1. What type of weather does a low pressure system bring?
Name Date Period Earth Science Unit Test Review Sheet Directions: Use my web site and/or your lab book to help to answer the following questions. 1. What type of weather does a low pressure system bring?
Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts)
 Name: Section: Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 1 Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts) As air rises, it cools due to the reduction in atmospheric pressure Air mainly consists of oxygen molecules and nitrogen
Name: Section: Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 1 Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts) As air rises, it cools due to the reduction in atmospheric pressure Air mainly consists of oxygen molecules and nitrogen
Name 28-MAY-08. FA RP 1 Mr. Chase. 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of millibars?
 FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
Science Chapter 13,14,15
 Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
The Atmosphere. All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere
 The Atmosphere Structure/Layers Contains 4 major layers See E.S.R.T pg 14 o Troposphere All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere o Stratosphere Contains
The Atmosphere Structure/Layers Contains 4 major layers See E.S.R.T pg 14 o Troposphere All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere o Stratosphere Contains
78% : component of atmosphere! 21% : 1% : Changes depending on origin of air: - originated over - originated over Ozone = O 3 Definition:
 Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
The Atmosphere. 1 Global Environments: 2 Global Environments:
 1 Global Environments: 2 Global Environments: Composition Vertical structure Heat transfer Atmospheric moisture Atmospheric circulation Weather and climate 3 Global Environments: The earth s atmosphere
1 Global Environments: 2 Global Environments: Composition Vertical structure Heat transfer Atmospheric moisture Atmospheric circulation Weather and climate 3 Global Environments: The earth s atmosphere
Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology
 S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
Goal 2.5. The Atmosphere
 Goal 2.5 The Atmosphere Lesson 1 Atmospheric Basics Think About It Why would it be a bad thing if the atmosphere was mostly oxygen? Focus Question What is the structure and function of the atmosphere?
Goal 2.5 The Atmosphere Lesson 1 Atmospheric Basics Think About It Why would it be a bad thing if the atmosphere was mostly oxygen? Focus Question What is the structure and function of the atmosphere?
Weather and Climate. An Introduction
 Weather and Climate An Introduction Basic Plant Anatomy Leaves Absorbs sunlight to produce glucose for food Roots Supports the plant, absorbs water & minerals Flower Attracting pollinators to help with
Weather and Climate An Introduction Basic Plant Anatomy Leaves Absorbs sunlight to produce glucose for food Roots Supports the plant, absorbs water & minerals Flower Attracting pollinators to help with
Name Class Date. 3. In what part of the water cycle do clouds form? a. precipitation b. evaporation c. condensation d. runoff
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Water in the Air 1. What do we call the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place? a. the water cycle b. weather c. climate d. precipitation THE
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Water in the Air 1. What do we call the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place? a. the water cycle b. weather c. climate d. precipitation THE
Unit 5. Seasons and Atmosphere
 Unit 5 Seasons and Atmosphere Standard 1: Revolution Motion of a body along a path around some point in space. Earth s orbit is elliptical Earth s distance from the sun varies Perihelion Earth is closest
Unit 5 Seasons and Atmosphere Standard 1: Revolution Motion of a body along a path around some point in space. Earth s orbit is elliptical Earth s distance from the sun varies Perihelion Earth is closest
The Atmosphere. Characteristics of the Atmosphere. Section 23.1 Objectives. Chapter 23. Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science. Section 1
 The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
Weather Systems Study Guide:
 Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
The Atmosphere - Chapter Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Warm Up 1: Atmosphere LT I can describe dew point, condensation nuclei and explain the difference between relative and absolute humidity.
 Warm Up 1: Atmosphere 2-8-17 LT I can describe dew point, condensation nuclei and explain the difference between relative and absolute humidity. Q1 List as many layers of the atmosphere as you can remember.
Warm Up 1: Atmosphere 2-8-17 LT I can describe dew point, condensation nuclei and explain the difference between relative and absolute humidity. Q1 List as many layers of the atmosphere as you can remember.
Forecasts include: Temperature. Barometric (air) Pressure. Wind direction/speed Humidity
 Meteorology I Intro. to Weather 1. What is Weather? A) Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a given time and place. B) Weather changes on a regular basis. C) Meteorologists forecast weather conditions
Meteorology I Intro. to Weather 1. What is Weather? A) Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a given time and place. B) Weather changes on a regular basis. C) Meteorologists forecast weather conditions
How our atmosphere is heated.
 How our atmosphere is heated. How is heat transferred around our atmosphere? 1) Radiation from the sun to the Earth. 2) Conduction passes heat from the Earth to the atmosphere. 3) Convection moves heat
How our atmosphere is heated. How is heat transferred around our atmosphere? 1) Radiation from the sun to the Earth. 2) Conduction passes heat from the Earth to the atmosphere. 3) Convection moves heat
also known as barometric pressure; weight of the air above the surface of the earth; measured by a barometer air pressure, high
 Weather Vocabulary Vocabulary Term Meaning/Definition air mass * large bodies of air that have the similar properties throughout such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure; causes most of the weather
Weather Vocabulary Vocabulary Term Meaning/Definition air mass * large bodies of air that have the similar properties throughout such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure; causes most of the weather
Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12)
 Name Class Period Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12) 1. When hot and cold air meet, the hot air rises to the top. Which process causes
Name Class Period Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12) 1. When hot and cold air meet, the hot air rises to the top. Which process causes
Mr. Lanik Practice Test Name:
 Mr. Lanik Practice Test Name: 1. New York State s Catskills are classified as which type of landscape region? mountain plateau Adirondacks Catskills lowland plain 2. In which New York State landscape region
Mr. Lanik Practice Test Name: 1. New York State s Catskills are classified as which type of landscape region? mountain plateau Adirondacks Catskills lowland plain 2. In which New York State landscape region
Page 1. Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period.
 Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period. Which graph best illustrates the probable change in air pressure during the same time period?
Name: 1) The graph below shows air temperature for an area near the Earth's surface during a 12-hour period. Which graph best illustrates the probable change in air pressure during the same time period?
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Tuesday, September 13, 16
 Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition
 Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition Air is a combination of many gases, each with its own unique characteristics. About 99 percent of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen and oxygen, with the
Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition Air is a combination of many gases, each with its own unique characteristics. About 99 percent of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen and oxygen, with the
Ch 7 Weather Practice Questions
 Practice Questions 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows two weather fronts moving across New York State. Lines X and Y represent frontal boundaries. The
Practice Questions 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows two weather fronts moving across New York State. Lines X and Y represent frontal boundaries. The
UNIT TEST PRACTICE TEST
 Page 1 of 1 Directions: Match the best answer to complete each question. Some words may be used more than once and some may not be used at all. e 1. The condition of Earth s atmosphere at a given time
Page 1 of 1 Directions: Match the best answer to complete each question. Some words may be used more than once and some may not be used at all. e 1. The condition of Earth s atmosphere at a given time
MOISTURE IN THE ATMOSPHERE MEGA PACKET
 NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A psychrometer is used to determine which weather variables? A) wind speed and wind direction B) percentage of cloud cover and cloud height C) air pressure and air temperature D) relative
NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A psychrometer is used to determine which weather variables? A) wind speed and wind direction B) percentage of cloud cover and cloud height C) air pressure and air temperature D) relative
2. What are the four most common gasses in the atmosphere and their percentages?
 Meteorology Review Directions: Answer the following open ended review questions. Utilize a diagram where appropriate and do make sure that you label and describe the drawing. Atmospheric Composition 1.
Meteorology Review Directions: Answer the following open ended review questions. Utilize a diagram where appropriate and do make sure that you label and describe the drawing. Atmospheric Composition 1.
Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17. Weather and Climate
 Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17 Weather and Climate Prediction Old way Groundhog Color of the sky Modern way satellites instruments computers Goal Weather Factors Studied by meteorologists Several factors
Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17 Weather and Climate Prediction Old way Groundhog Color of the sky Modern way satellites instruments computers Goal Weather Factors Studied by meteorologists Several factors
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17
 Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Final Weather Unit Study Guide
 Name: Atmospheric Composition and Layers Altitude Atmosphere Composition Troposphere Air Pressure Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere Ionosphere Sample Questions: Final Weather Unit Study Guide
Name: Atmospheric Composition and Layers Altitude Atmosphere Composition Troposphere Air Pressure Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere Ionosphere Sample Questions: Final Weather Unit Study Guide
1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 CHAPTER 1 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How do
CHAPTER 1 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How do
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Chapter 15 The Atmosphere and Weather
 Chapter 15 The Atmosphere and Weather Day Activity Homework 1 Notes I- II Layers of the atmosphere* 2 Notes III Air Pressure Labs* 3 Notes IV Global Winds Activity* 4 Complete Notes Concept Map Relative
Chapter 15 The Atmosphere and Weather Day Activity Homework 1 Notes I- II Layers of the atmosphere* 2 Notes III Air Pressure Labs* 3 Notes IV Global Winds Activity* 4 Complete Notes Concept Map Relative
LAB 3: Atmospheric Pressure & Moisture
 Name School LAB 3: Atmospheric Pressure & Moisture Our atmosphere is a very dynamic area especially when we see what type of interactions it has with the surrounding environment. This lab will begin discussing
Name School LAB 3: Atmospheric Pressure & Moisture Our atmosphere is a very dynamic area especially when we see what type of interactions it has with the surrounding environment. This lab will begin discussing
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERIC MOISTURE Atmospheric Moisture The Nature of Water The Hydrologic Cycle Evaporation Measures of Humidity Condensation The Buoyancy of Air Precipitation
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERIC MOISTURE Atmospheric Moisture The Nature of Water The Hydrologic Cycle Evaporation Measures of Humidity Condensation The Buoyancy of Air Precipitation
NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel.
 NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel. REFERENCE TABLES (Videos 8.1 & 8.2 ESRT 12, 13a, 14b) 1. Use the temperature scales on page 13. (notes-air temperature conversions) a. 80 C to F
NAME: Log onto YouTube and search for jocrisci channel. REFERENCE TABLES (Videos 8.1 & 8.2 ESRT 12, 13a, 14b) 1. Use the temperature scales on page 13. (notes-air temperature conversions) a. 80 C to F
EARTH SCIENCE. Prentice Hall Water in the Atmosphere Water in the Atmosphere Water in the Atmosphere.
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Water s Changes of State 1. Precipitation is any form of water that falls from a cloud. a. Examples: Snow, rain, hail, sleet 3 States of matter of water: 1.
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Water s Changes of State 1. Precipitation is any form of water that falls from a cloud. a. Examples: Snow, rain, hail, sleet 3 States of matter of water: 1.
latent heat/humidity
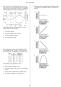 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
Weather Practice. 4. As wind velocity decreases, the distance between isobars on a weather map will A) decrease B) increase C) remain the same
 1. The chart below shows the air temperature and the dewpoint temperature near the ground at a given location for four consecutive days. All temperatures were recorded at noon. Which statement is best
1. The chart below shows the air temperature and the dewpoint temperature near the ground at a given location for four consecutive days. All temperatures were recorded at noon. Which statement is best
Atmospheric Layers. Earth s atmosphere is divided into several different atmospheric layers extending from Earth s surface outward.
 6-4.1 Compare the composition and structure of Earth s atmospheric layers (including the gases and differences in temperature and pressure within the layers). Taxonomy level: 2.6-B Understand Conceptual
6-4.1 Compare the composition and structure of Earth s atmospheric layers (including the gases and differences in temperature and pressure within the layers). Taxonomy level: 2.6-B Understand Conceptual
Weather Final Review Page 1
 Weather Final Review Name 1. Which change would cause a decrease in the amount of insolation absorbed at Earths surface? A) a decrease in cloud cover B) a decrease in atmospheric transparency C) an increase
Weather Final Review Name 1. Which change would cause a decrease in the amount of insolation absorbed at Earths surface? A) a decrease in cloud cover B) a decrease in atmospheric transparency C) an increase
The Atmosphere Made up of mainly two gases: Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Trace Gases 1%
 The Atmosphere 18.1 The Atmosphere Made up of mainly two gases: Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Trace Gases 1% Layers of the Atmosphere made made up of 5 layers: Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Ionosphere
The Atmosphere 18.1 The Atmosphere Made up of mainly two gases: Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Trace Gases 1% Layers of the Atmosphere made made up of 5 layers: Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Ionosphere
Meteorology Study Guide
 Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES. Weather. atmosphere. Weather and climate
 GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
Weather. A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket.
 Weather I. The air around us A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket. II. Weather Temperature Humidity Air pressure Wind 1. contains the air we breathe, protects us
Weather I. The air around us A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket. II. Weather Temperature Humidity Air pressure Wind 1. contains the air we breathe, protects us
Surface Processes and the Hydrosphere Unit Heating the Earth s Atmosphere Chapter 11 (pg )
 Name: Block: Surface Processes and the Hydrosphere Unit Heating the Earth s Atmosphere Chapter 11 (pg. 352 385) 11.1: Focus on the Atmosphere: Weather and Climate What is the difference between the weather
Name: Block: Surface Processes and the Hydrosphere Unit Heating the Earth s Atmosphere Chapter 11 (pg. 352 385) 11.1: Focus on the Atmosphere: Weather and Climate What is the difference between the weather
Ch22&23 Test. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch22&23 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The two most abundant compounds in the atmosphere are carbon dioxide and a. particulates.
Ch22&23 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The two most abundant compounds in the atmosphere are carbon dioxide and a. particulates.
Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A.
 Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A. COLUMN A 1. a unit of atmospheric pressure 2. a line joining points of equal air pressure
Name: Date: Period: MATCHING: Select the letter of the word in Column B that best matches the phrases in Column A. COLUMN A 1. a unit of atmospheric pressure 2. a line joining points of equal air pressure
Clever Catch Weather Ball Question and Answer Sheets
 Clever Catch Weather Ball Question and Answer Sheets 1. Too much exposure to can cause skin cancer. B. Ultraviolet radiation 2. The layer of the atmosphere closest to the Earth s surface is the 3. Some
Clever Catch Weather Ball Question and Answer Sheets 1. Too much exposure to can cause skin cancer. B. Ultraviolet radiation 2. The layer of the atmosphere closest to the Earth s surface is the 3. Some
Version date 2/10/15. Disciplinary Core Ideas (Framework)
 1 What is Weather? 1 Into the Weather Students delve into the question, What is weather? They view video segments of severe weather, and generate inquiry questions stimulated by the video and discussions.
1 What is Weather? 1 Into the Weather Students delve into the question, What is weather? They view video segments of severe weather, and generate inquiry questions stimulated by the video and discussions.
Chapter 5: Weather. Only Section 1: What is Weather?
 Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE I. Humidity A. Defined as water vapor or moisture in the air (from evaporation and condensation). B. The atmosphere gains moisture from the evaporation of water from oceans, lakes,
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE I. Humidity A. Defined as water vapor or moisture in the air (from evaporation and condensation). B. The atmosphere gains moisture from the evaporation of water from oceans, lakes,
10.1 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT Name: Date: Block: (Reference: pp of BC Science 10)
 10.1 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT Name: Date: Block: (Reference: pp. 424-435 of BC Science 10) kinetic molecular theory: explains that matter is made up of tiny that are constantly. These atoms
10.1 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT Name: Date: Block: (Reference: pp. 424-435 of BC Science 10) kinetic molecular theory: explains that matter is made up of tiny that are constantly. These atoms
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project THE ATMOSPHERE. Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey
 Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project THE ATMOSPHERE Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey What we are going to cover 1. Composition of the Atmosphere 2. State Variables
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project THE ATMOSPHERE Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey What we are going to cover 1. Composition of the Atmosphere 2. State Variables
How do we understand weather?
 How do we understand weather? Fluid: a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter which includes liquids, gases, plasmas, and plastic
How do we understand weather? Fluid: a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter which includes liquids, gases, plasmas, and plastic
Three things necessary for weather are Heat, Air, Moisture (HAM) Weather takes place in the Troposphere (The lower part of the atmosphere).
 Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
* Defining Temperature * Temperature is proportional to the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. * Temperature * Internal energy
 * Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
* Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
EARTH SCIENCE. ES02 - Atmosphere
 EARTH SCIENCE ES02 - Bell Ringer List and explain how the atmosphere might affect the different spheres (hydrosphere, geosphere, & biosphere) on Earth. Bell Ringer Does pollution caused by other countries
EARTH SCIENCE ES02 - Bell Ringer List and explain how the atmosphere might affect the different spheres (hydrosphere, geosphere, & biosphere) on Earth. Bell Ringer Does pollution caused by other countries
anemometer a weather instrument that measures wind speed with wind-catching cups (SRB, IG)
 FOSS Weather on Earth Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 absorb to soak in air the mixture of gases surrounding Earth air pressure the force exerted on a surface by the mass of the air above it anemometer
FOSS Weather on Earth Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 absorb to soak in air the mixture of gases surrounding Earth air pressure the force exerted on a surface by the mass of the air above it anemometer
3. As warm, moist air moves into a region, barometric pressure readings in the region will generally 1. decrease 2. increase 3.
 Teacher: Mr. Prizzi Castle Learning Review 1 1. Which process most directly results in cloud formation? 1. condensation 3. precipitation 2. transpiration 4. radiation 2. An air mass originating over north
Teacher: Mr. Prizzi Castle Learning Review 1 1. Which process most directly results in cloud formation? 1. condensation 3. precipitation 2. transpiration 4. radiation 2. An air mass originating over north
Weather and Climate. Weather the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
 Weather and Climate Weather the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place Climate the average year-after-year conditions of temperature, precipitation, winds and clouds in an area
Weather and Climate Weather the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place Climate the average year-after-year conditions of temperature, precipitation, winds and clouds in an area
UNIT VI: METEOROLOGY
 UNIT VI: METEOROLOGY 1. Understand that the Sun is the Earth s main energy source. a. Radiation from the is the chief source of energy for the atmosphere. b. When energy from the Sun reaches Earth s, the
UNIT VI: METEOROLOGY 1. Understand that the Sun is the Earth s main energy source. a. Radiation from the is the chief source of energy for the atmosphere. b. When energy from the Sun reaches Earth s, the
Warm-Up Draw a picture of the water cycle
 Warm-Up Draw a picture of the water cycle RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. BLACK SLIDE: Pay attention, follow directions, complete projects
Warm-Up Draw a picture of the water cycle RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. BLACK SLIDE: Pay attention, follow directions, complete projects
Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place
 Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Climate versus Weather
 Climate versus Weather What is climate? Climate is the average weather usually taken over a 30-year time period for a particular region and time period. Climate is not the same as weather, but rather,
Climate versus Weather What is climate? Climate is the average weather usually taken over a 30-year time period for a particular region and time period. Climate is not the same as weather, but rather,
Atmospheric Composition and Structure
 Atmospheric Composition and Structure Weather and Climate What is weather? The state of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Defined by: Humidity, temperature, wind speed, clouds, precipitation,
Atmospheric Composition and Structure Weather and Climate What is weather? The state of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Defined by: Humidity, temperature, wind speed, clouds, precipitation,
Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather
 Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Freezing: To become hardened into ice or into a solid body Deposition: The change in state of matter
Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Freezing: To become hardened into ice or into a solid body Deposition: The change in state of matter
Atmospheric Conditions Geography Notes JC-Learn. JC-Learn. Geography Notes Atmospheric Conditions. 1 P a g e
 JC-Learn Geography Notes Atmospheric Conditions 1 P a g e Atmospheric Conditions The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases surrounding the earth. It is usually referred to as air and it is constantly changing.
JC-Learn Geography Notes Atmospheric Conditions 1 P a g e Atmospheric Conditions The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases surrounding the earth. It is usually referred to as air and it is constantly changing.
Unit 8: Meteorology. How is Earth s weather influenced by different atmospheric variables? How can we predict weather?
 Unit 8: Meteorology How is Earth s weather influenced by different atmospheric variables? How can we predict weather? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Weather Structure of Earth s atmosphere Air Temperature
Unit 8: Meteorology How is Earth s weather influenced by different atmospheric variables? How can we predict weather? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Weather Structure of Earth s atmosphere Air Temperature
E.T. - A LOCAL WAY OF LEARNING E-56
 E.T. - A LOCAL WAY OF LEARNING E-56 Title: Author: Jane Ducey Grade Level: 4-6 Eulalie R. Rivera Elementary School- Concepts: Disciplines: 1. The Sun 1.Earth Science 6. Natural Resources Objective: With
E.T. - A LOCAL WAY OF LEARNING E-56 Title: Author: Jane Ducey Grade Level: 4-6 Eulalie R. Rivera Elementary School- Concepts: Disciplines: 1. The Sun 1.Earth Science 6. Natural Resources Objective: With
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather
 Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
General Comments about the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets
 General Comments about the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets Mercury Very little atmosphere Contents: vaporized micrometeorites, solar wind Sky is black Venus Very thick (10% density of water), dense
General Comments about the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets Mercury Very little atmosphere Contents: vaporized micrometeorites, solar wind Sky is black Venus Very thick (10% density of water), dense
Space Atmospheric Gases. the two most common gases; found throughout all the layers a form of oxygen found in the stratosphere
 Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
