P1.15 DECADAL WIND TRENDS AT THE SAVANNAH RIVER SITE
|
|
|
- Miranda Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. INTRODUCTION P1.15 DECADAL WIND TRENDS AT THE SAVANNAH RIVER SITE Allen H. Weber, Robert L. Buckley, and Matthew J. Parker Savannah River National Laboratory, Aiken, South Carolina One possible consequence of global warming is an observed decrease in mean wind speeds over the U.S. within a band between about degrees north latitude (Zack, et al. 2005). Recent studies (Pittman, et al. (2004), Galletta, (2005), and Weber, et al. (2005)) at various locations in the eastern U.S. indicate that, indeed, mean surface wind speeds have decreased by 5 to 10% over the last couple of decades. The Savannah River National Laboratory (SRNL) operates meteorological towers at different locations at the Department of Energy s (DOE) Savannah River Site (SRS), which covers 800 km 2 in southwestern South Carolina. In this paper, we examine the trends in wind speed and vertical and horizontal turbulence intensity over the past 14 years associated with measurements at SRS eight spatially separated, 61-m towers, and discuss the results. Figure 2. Locations of 61-meter Area Towers at the SRS. 2. METHOD Figure 1: U.S. Southeast Coast with the locations of the SRS and five NWS stations used by Weber, et al. (2005) for a strong winds study. Corresponding author address: A. Weber, 820 Jackson Ave., North Augusta, SC traviata@comcast.net Figure 1 shows the U.S. Southeast Coast with the location of the SRS and five NWS stations used by Weber, et al. (2005) for a strong winds study. The SRS is ~160 km (100 mi) inland. Three of the NWS stations used in the strong wind study (Wilmington [ILM], Charleston [CHS], and Savannah [SAV]) are within ~16 km (10 mi) of the coast while the remaining two (Columbia [CAE] and Augusta [AGS]) are ~200 km (124 mi) inland. Figure 2 shows the locations of eight 61-m Area Towers (designated A, C, D, F, H, K, L, and P) within the SRS. Temperature, speed, and the standard deviations of wind direction σ A and elevation σ E were extracted from archives of the 61-m Area Towers for the time period 1991 to Data values collected at 15-minute intervals with questionable quality assurance flags were thrown out during the data selection process. In addition, checks were made to eliminate any wind speed, direction, σ A and σ E value less than zero. Finally, temperature values outside the range " 15! T < 45 ºC were also excluded during the data selection process. 1
2 Hourly averages were determined from scalar averages of 15-minute archived data of wind, temperature, σ A and σ E. In the case of σ A this is not strictly valid, since one must account for the changes in the mean wind direction from one 15- minute period to the next. However, we decided to ignore the contributions from wind direction changes in this paper and save a more exact analysis for a later presentation. 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION a. NWS Stations Weber, et al. (2005) showed a decreasing trend for the NWS stations mean wind speed for the period (NCDC, 2005) of about 5% per decade (0.5% per year). The individual NWS stations (AGS, CAE, CHS, ILM, AND SAV) annually averaged wind speeds are shown in Figure 3 with an overall trend line determined by linear least squares regression. Since the coastal stations (CHS, ILM, and SAV), seem to strongly influence the period , it was decided to group the wind data for the stations into coastal (CHS, ILM, and SAV) and inland (AGS and CAE) groups. These results are shown in Figures 4 and 5 along with the trend lines for each group. The slope of the linear regression trend line shows that the interior stations wind speed indeed is not decreasing at the same rate as the coastal stations, but the rate is still a fairly consistent downward trend of m/s per year. While seemingly quite small, in terms of the overall mean speed of around 3.5 m/sec, this is a decrease of about 0.23% per year; and when only the past 14 years for inland stations are considered the decrease is m/s per year or 0.885% per year, a significantly larger amount. Given the relatively small magnitude of an average wind speed on the order of 3.5 m/s (in this case), a decreasing trend would be expected to be rather slight since the annual mean wind speed would not be expected to approach zero. Figure 3: Time series of annual averages of all five stations (CHS, ILM, AGS, CAE, and CAE) and slope of trend line for pooled wind speeds. Figure 4: Time series of annual averages and slope of trend line of the coastal stations (CHS, ILM, SAV) pooled wind speeds. b. SRS Area Towers The SRS Area towers 15-minute-averaged measurements were broken up by daytime and nighttime, based on time of year and latitude of SRS. Results for annual means are presented for both daytime and nighttime for 4 variables: wind speed (m/s), σ A (degrees), σ E (degrees), and temperature (ºC). Figures 6 to 9 show the time series of the annual means and linear least squares regression lines for the 14-yr period. Figure 5: Time series of annual averages and slope of trend line of the inland stations (AGS and CAE) pooled wind speeds. 2
3 Figures 6 to 9 show decreasing speeds for both daytime and nighttime, fairly constant σ A, increasing σ E, and increasing temperature for the period Trends and means for the 14- year period are summarized in Table 1. Figure 9: Time series of annual averages and nighttime temperature from the Area Towers. Figure 6: Time series of annual averages and nighttime wind speed from the Area Towers. Figure 7: Time series of annual averages and slope of trend line of SRS 61-m σ A from the Area Towers. Figure 8: Time series of annual averages and nighttime σ E from the Area Towers. Trends in Table 1 show a statistically significant decline in wind speed, and increases in both turbulence intensities, with the exception of σ A during the night. The temperature is also seen to increase. The increase in σ E is greater than the increase in σ A. As one would expect, mean values for the turbulent quantities are higher during the daytime than during nocturnal periods. Note also that higher wind speeds occur at night, as one should expect of values taken from the 61-m level above ground at this location. In addition, means and trends were determined for each variable and time of day by season (MAM, JJA, SON, DJF denote spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively). Results are shown in Table 2. The results by season indicate declines in speed at all times of the year. The mean wind speeds are highest in the spring, and lowest in the summer. The largest declines have also occurred during the spring months, as well as during the autumn nocturnal period. The trends of σ A are increasing during daytime in the winter, as well as at all times in the spring and summer; declines of σ A are experienced during the winter nocturnal period and autumn daytime period, and are relatively unchanged during the nocturnal autumn period. The biggest increasing trend of σ A is during the daytime in the summer. This would seem to indicate a relationship to increasing convective activity. The highest mean values of σ A are found during the summer, both for day and night periods, while the lowest daytime values are observed in winter, and the lowest nighttime values are observed in autumn. 3
4 The trends for σ E are increasing at all times except during the winter at night. As for the yearly trends, the seasonal trends of σ E tend to be slightly higher than for σ A with the biggest increases occurring during the day in the winter and summer months. The maximum mean of σ E during the daytime is observed in summer, while at night it is observed in the winter. On the other hand, the minimum of σ E in the day is observed in winter, and in autumn at night. Temperature trends indicate an increase in all seasons except during the winter. In particular, the rates of temperature increase in spring, summer, and autumn are seen to be larger at night. Overall, temperatures have increased the most during autumn nighttime. Day Night Total Mean Slope (per yr) Total Mean Slope (per yr) Speed (mps) E E-02 σ A (deg) E E-02 σ E (deg) E E-02 Temperature (ºC) E E-02 Table 1: Least-square linear regression line slopes and mean values by variable and time of day for the 14-years of measurements on SRS 61-m towers. Day Night Variable Season Mean Slope (per yr) Mean Slope (per yr) Speed (mps) Winter E E-03 Spring E E-02 Summer E E-02 Autumn E E-02 σ A (deg) Winter E E-02 Spring E E-03 Summer E E-02 Autumn E E-04 σ E (deg) Winter E E-02 Spring E E-02 Summer E E-02 Autumn E E-02 Temperature (ºC) Winter E E-02 Spring E E-02 Summer E E-02 Autumn E E-01 Table 2: As in Table 1, but broken up into seasonal slopes and means where Winter, Spring, Summer, and Autumn denote the months of DJF, MAM, JJA, SON, respectively. DISCUSSION/CONCLUSIONS Both the NWS data and the SRNL data show clearly that the mean annual wind speed is decreasing in this area of the Southeast. We can make a comparison between the rates of decrease of mean speed of the ~60 years of NWS data taken at ~10 m and the 14 years of SRNL data taken at 61 m. The rate of ~0.885% per year for the NWS stations is about three times the rate of ~0.3% per year for the SRNL Area towers. We do not consider this difference to be significant after taking into account the differences in data collection methods, geographical locations, and heights of measurement between the two data sets. The daytime and nighttime temperatures are increasing at a rate of ~0.04 and ~0.05 ºC respectively, per year. The standard deviations of wind direction angle σ A for daytime and nighttime from the Area towers are increasing at a rate of ~0.03 and ~0.01 degrees per year, respectively. The standard deviations of wind elevation angle σ E for daytime from the Area towers are increasing at 4
5 a rate of ~0.03 degrees per year. Nighttime values have decreased by ~0.10 degrees per year. The increases in the rate of σ A and σ E for daytime and nighttime suggest that convective activity is increasing due to an increase in the mean temperatures for daytime and generally for nighttime. The daytime rate is increasing more rapidly than the nighttime rate. REFERENCES Galletta, T. (2005): Meteorological Trends at Nine Mile Point. 10 th Meeting of the Nuclear Utility Data Users Group (NUMUG) Meeting. June 28-30, Wilmington, NC. NCDC (2005): National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina. Pittman, D. E., K. G. Wastrack, and N. A. Nielsen (2004): Significance of Updating the Meteorological Data Basis Case Studies for the Tennessee Valley Authority. Topical Meeting on Operating Nuclear Facility Safety. November 14-18, Washington, D.C. American Nuclear Society. Weber, A. H., M. J. Parker, and R. L. Buckley (2005): Strong Wind Characteristics and Changes During the Last Half-Century at Five NWS Stations Near Coastal South Carolina. 15 th Conference on Applied Climatology, June, Savannah, GA, American Meteorological Society. Zack, J. W., G. E. Van Knowe, and K. T. Waight (2005): Examination of Regional Wind Trends Due to Global Climate Change to Improve Wind Resource Assessments, 15 th Conference on Applied Climatology, June, Savannah, GA, American Meteorological Society. 5
JP2.2 VISIBILITY TRENDS FOR COASTAL REGIONS. Allen H. Weber and Robert L. Buckley Savannah River Technology Center, Aiken, South Carolina 2.
 1. INTRODUCTION JP2.2 VISIBILITY TRENDS FOR COASTAL REGIONS Allen H. Weber and Robert L. Buckley Savannah River Technology Center, Aiken, South Carolina Increased biomass burning (e.g., forest fires, controlled
1. INTRODUCTION JP2.2 VISIBILITY TRENDS FOR COASTAL REGIONS Allen H. Weber and Robert L. Buckley Savannah River Technology Center, Aiken, South Carolina Increased biomass burning (e.g., forest fires, controlled
Climate. Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) January Temperature. July Temperature. Average Precipitation (Last 30 Years)
 Climate Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) Average Annual High Temp. (F)70, (C)21 Average Annual Low Temp. (F)43, (C)6 January Temperature Average January High Temp. (F)48, (C)9 Average January Low Temp.
Climate Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) Average Annual High Temp. (F)70, (C)21 Average Annual Low Temp. (F)43, (C)6 January Temperature Average January High Temp. (F)48, (C)9 Average January Low Temp.
Flooding in Western North Carolina: Some Spatial, Hydrologic, and Seasonal Characteristics CAUTION!! Outline. Basic Flood Facts.
 Flooding in Western North Carolina: Some Spatial, Hydrologic, and Seasonal Characteristics J. Greg Dobson CAUTION!! National Environmental Modeling and Analysis Center RENCI at UNC-Asheville Engagement
Flooding in Western North Carolina: Some Spatial, Hydrologic, and Seasonal Characteristics J. Greg Dobson CAUTION!! National Environmental Modeling and Analysis Center RENCI at UNC-Asheville Engagement
Display and analysis of weather data from NCDC using ArcGIS
 Display and analysis of weather data from NCDC using ArcGIS Helen M. Cox Associate Professor Geography Department California State University, Northridge and Stephen Krug Graduate Student Geography Department
Display and analysis of weather data from NCDC using ArcGIS Helen M. Cox Associate Professor Geography Department California State University, Northridge and Stephen Krug Graduate Student Geography Department
SEASONAL AND DAILY TEMPERATURES
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 SEASONAL AND DAILY TEMPERATURES Chapter 3 Earth revolves in elliptical path around sun every 365 days. Earth rotates counterclockwise or eastward every 24 hours. Earth closest
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 SEASONAL AND DAILY TEMPERATURES Chapter 3 Earth revolves in elliptical path around sun every 365 days. Earth rotates counterclockwise or eastward every 24 hours. Earth closest
UPPLEMENT A COMPARISON OF THE EARLY TWENTY-FIRST CENTURY DROUGHT IN THE UNITED STATES TO THE 1930S AND 1950S DROUGHT EPISODES
 UPPLEMENT A COMPARISON OF THE EARLY TWENTY-FIRST CENTURY DROUGHT IN THE UNITED STATES TO THE 1930S AND 1950S DROUGHT EPISODES Richard R. Heim Jr. This document is a supplement to A Comparison of the Early
UPPLEMENT A COMPARISON OF THE EARLY TWENTY-FIRST CENTURY DROUGHT IN THE UNITED STATES TO THE 1930S AND 1950S DROUGHT EPISODES Richard R. Heim Jr. This document is a supplement to A Comparison of the Early
Meteorology. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Chapter 3 Worksheet 1 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, the daily
Chapter 3 Worksheet 1 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, the daily
Why the Earth has seasons. Why the Earth has seasons 1/20/11
 Chapter 3 Earth revolves in elliptical path around sun every 365 days. Earth rotates counterclockwise or eastward every 24 hours. Earth closest to Sun (147 million km) in January, farthest from Sun (152
Chapter 3 Earth revolves in elliptical path around sun every 365 days. Earth rotates counterclockwise or eastward every 24 hours. Earth closest to Sun (147 million km) in January, farthest from Sun (152
IMPACT OF WEATHER CHANGES ON TVA NUCLEAR PLANT CHI/Q (χ/q) Kenneth G. Wastrack Doyle E. Pittman Jennifer M. Call Tennessee Valley Authority
 IMPACT OF WEATHER CHANGES ON TVA NUCLEAR PLANT CHI/Q (χ/q) Kenneth G. Wastrack Doyle E. Pittman Jennifer M. Call Tennessee Valley Authority The TVA nuclear plants, like most others in the United States,
IMPACT OF WEATHER CHANGES ON TVA NUCLEAR PLANT CHI/Q (χ/q) Kenneth G. Wastrack Doyle E. Pittman Jennifer M. Call Tennessee Valley Authority The TVA nuclear plants, like most others in the United States,
J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD,
 J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD, 1948-2008 Richard R. Heim Jr. * NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina 1. Introduction The Intergovernmental Panel
J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD, 1948-2008 Richard R. Heim Jr. * NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina 1. Introduction The Intergovernmental Panel
Mozambique. General Climate. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
Annex I to Target Area Assessments
 Baltic Challenges and Chances for local and regional development generated by Climate Change Annex I to Target Area Assessments Climate Change Support Material (Climate Change Scenarios) SWEDEN September
Baltic Challenges and Chances for local and regional development generated by Climate Change Annex I to Target Area Assessments Climate Change Support Material (Climate Change Scenarios) SWEDEN September
AERMOD Sensitivity to AERSURFACE Moisture Conditions and Temporal Resolution. Paper No Prepared By:
 AERMOD Sensitivity to AERSURFACE Moisture Conditions and Temporal Resolution Paper No. 33252 Prepared By: Anthony J Schroeder, CCM Managing Consultant TRINITY CONSULTANTS 7330 Woodland Drive Suite 225
AERMOD Sensitivity to AERSURFACE Moisture Conditions and Temporal Resolution Paper No. 33252 Prepared By: Anthony J Schroeder, CCM Managing Consultant TRINITY CONSULTANTS 7330 Woodland Drive Suite 225
Rainfall declines over Queensland from and links to the Subtropical Ridge and the SAM
 Rainfall declines over Queensland from 1951-2007 and links to the Subtropical Ridge and the SAM D A Cottrill 1 and J Ribbe 2 1 Bureau of Meteorology, 700 Collins St, Docklands, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
Rainfall declines over Queensland from 1951-2007 and links to the Subtropical Ridge and the SAM D A Cottrill 1 and J Ribbe 2 1 Bureau of Meteorology, 700 Collins St, Docklands, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
Examining Changes to the Temporal Distribution of Seasonal-to-Annual Precipitation across the Mid-Atlantic Region,
 Examining Changes to the Temporal Distribution of Seasonal-to-Annual Precipitation across the Mid-Atlantic Region, 1982-2016 Michael Marston PhD Student, Virginia Tech Precipitation (mm) Precipitation
Examining Changes to the Temporal Distribution of Seasonal-to-Annual Precipitation across the Mid-Atlantic Region, 1982-2016 Michael Marston PhD Student, Virginia Tech Precipitation (mm) Precipitation
Intra-Annual Variations in Temperature Lapse Rate Within a Mountainous Basin in Korea A Case Study of the Punch Bowl, Yanggu
 Intra-Annual Variations in Temperature Lapse Rate Within a Mountainous Basin in Korea A Case Study of the Punch Bowl, Yanggu Choi, Gwangyong (1); Lee, Bora (2); Tenhunen, John (2); Kang, Sinkyu (3) (1)
Intra-Annual Variations in Temperature Lapse Rate Within a Mountainous Basin in Korea A Case Study of the Punch Bowl, Yanggu Choi, Gwangyong (1); Lee, Bora (2); Tenhunen, John (2); Kang, Sinkyu (3) (1)
Changes in Cloud Cover and Cloud Types Over the Ocean from Surface Observations, Ryan Eastman Stephen G. Warren Carole J.
 Changes in Cloud Cover and Cloud Types Over the Ocean from Surface Observations, 1954-2008 Ryan Eastman Stephen G. Warren Carole J. Hahn Clouds Over the Ocean The ocean is cloudy, more-so than land Cloud
Changes in Cloud Cover and Cloud Types Over the Ocean from Surface Observations, 1954-2008 Ryan Eastman Stephen G. Warren Carole J. Hahn Clouds Over the Ocean The ocean is cloudy, more-so than land Cloud
LAB J - WORLD CLIMATE ZONES
 Introduction LAB J - WORLD CLIMATE ZONES The objective of this lab is to familiarize the student with the various climates around the world and the climate controls that influence these climates. Students
Introduction LAB J - WORLD CLIMATE ZONES The objective of this lab is to familiarize the student with the various climates around the world and the climate controls that influence these climates. Students
Climatology of Surface Wind Speeds Using a Regional Climate Model
 Climatology of Surface Wind Speeds Using a Regional Climate Model THERESA K. ANDERSEN Iowa State University Mentors: Eugene S. Takle 1 and Jimmy Correia, Jr. 1 1 Iowa State University ABSTRACT Long-term
Climatology of Surface Wind Speeds Using a Regional Climate Model THERESA K. ANDERSEN Iowa State University Mentors: Eugene S. Takle 1 and Jimmy Correia, Jr. 1 1 Iowa State University ABSTRACT Long-term
1. TEMPORAL CHANGES IN HEAVY RAINFALL FREQUENCIES IN ILLINOIS
 to users of heavy rainstorm climatology in the design and operation of water control structures. A summary and conclusions pertaining to various phases of the present study are included in Section 8. Point
to users of heavy rainstorm climatology in the design and operation of water control structures. A summary and conclusions pertaining to various phases of the present study are included in Section 8. Point
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com OCTOBER 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com OCTOBER 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The
New England Climate Indicator Maps
 New England Climate Indicator Maps Maps of New England depicting region-wide change in 26 climate indicators for current conditions compared to end of the century for two different global greenhouse gas
New England Climate Indicator Maps Maps of New England depicting region-wide change in 26 climate indicators for current conditions compared to end of the century for two different global greenhouse gas
Minnesota s Changing Climate: Winter Impacts
 Minnesota s Changing Climate: Winter Impacts Dr. Mark Seeley Climatologist/Meteorologist Dept of Soil, Water, and Climate University of Minnesota 15 th Annual Road Salt Symposium Minnesota Landscape Arboretum
Minnesota s Changing Climate: Winter Impacts Dr. Mark Seeley Climatologist/Meteorologist Dept of Soil, Water, and Climate University of Minnesota 15 th Annual Road Salt Symposium Minnesota Landscape Arboretum
Regional Precipitation and ET Patterns: Impacts on Agricultural Water Management
 Regional Precipitation and ET Patterns: Impacts on Agricultural Water Management Christopher H. Hay, PhD, PE Ag. and Biosystems Engineering South Dakota State University 23 November 2010 Photo: USDA-ARS
Regional Precipitation and ET Patterns: Impacts on Agricultural Water Management Christopher H. Hay, PhD, PE Ag. and Biosystems Engineering South Dakota State University 23 November 2010 Photo: USDA-ARS
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
Changes in Observed Air Temperature in Kuwait from 2001 to 2016
 The International Journal of Engineering and Science (IJES) Volume 6 Issue 10 Pages PP 67-74 2017 ISSN (e): 2319 1813 ISSN (p): 2319 1805 Changes in Observed Air Temperature in Kuwait from 2001 to 2016
The International Journal of Engineering and Science (IJES) Volume 6 Issue 10 Pages PP 67-74 2017 ISSN (e): 2319 1813 ISSN (p): 2319 1805 Changes in Observed Air Temperature in Kuwait from 2001 to 2016
The Graniteville Train Crash: Emergency Response Support Provided by the Savannah River National Laboratory
 The Graniteville Train Crash: Emergency Response Support Provided by the Savannah River National Laboratory Matthew J. Parker, CCM, Charles H. Hunter, Robert L. Buckley and Robert P. Addis Atmospheric
The Graniteville Train Crash: Emergency Response Support Provided by the Savannah River National Laboratory Matthew J. Parker, CCM, Charles H. Hunter, Robert L. Buckley and Robert P. Addis Atmospheric
APPENDIX G-7 METEROLOGICAL DATA
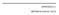 APPENDIX G-7 METEROLOGICAL DATA METEOROLOGICAL DATA FOR AIR AND NOISE SAMPLING DAYS AT MMR Monthly Normals and Extremes for Honolulu International Airport Table G7-1 MMR RAWS Station Hourly Data Tables
APPENDIX G-7 METEROLOGICAL DATA METEOROLOGICAL DATA FOR AIR AND NOISE SAMPLING DAYS AT MMR Monthly Normals and Extremes for Honolulu International Airport Table G7-1 MMR RAWS Station Hourly Data Tables
INFLUENCE OF THE AVERAGING PERIOD IN AIR TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT
 INFLUENCE OF THE AVERAGING PERIOD IN AIR TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT Hristomir Branzov 1, Valentina Pencheva 2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Sofia, Bulgaria, Hristomir.Branzov@meteo.bg
INFLUENCE OF THE AVERAGING PERIOD IN AIR TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT Hristomir Branzov 1, Valentina Pencheva 2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Sofia, Bulgaria, Hristomir.Branzov@meteo.bg
Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed
 Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed David Bosch USDA-ARS, Tifton, GA Jeff Arnold ARS Temple, TX and Peter Allen Baylor University, TX SEWRU Objectives 1. Project changes
Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed David Bosch USDA-ARS, Tifton, GA Jeff Arnold ARS Temple, TX and Peter Allen Baylor University, TX SEWRU Objectives 1. Project changes
CoCoRaHS. Carolina PAGES Hurricane Matthew in South Carolina. CoCoRaHS Observers Activity During Hurricane Matthew.
 Carolina CoCoRaHS SUMMER 2017 Hurricane Matthew in South Carolina H urricane Matthew was the first South Carolina hurricane landfall since Hurricane Charley and Gaston came ashore in 2004. It made landfall
Carolina CoCoRaHS SUMMER 2017 Hurricane Matthew in South Carolina H urricane Matthew was the first South Carolina hurricane landfall since Hurricane Charley and Gaston came ashore in 2004. It made landfall
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer into Harvest 2016
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer into Harvest 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University September 3, 2016 With school and football season starting a hint of fall is right on time
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer into Harvest 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University September 3, 2016 With school and football season starting a hint of fall is right on time
Supplemental Materials
 Supplemental Materials Figure S-1. Locations of the ozonesonde stations used in the TOST product for the period 2008-2012. Figure S-2. Map of the seven regions: Eastern USA, Eastern China, Atlantic, Indonesia,
Supplemental Materials Figure S-1. Locations of the ozonesonde stations used in the TOST product for the period 2008-2012. Figure S-2. Map of the seven regions: Eastern USA, Eastern China, Atlantic, Indonesia,
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW
 2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
Past and future climate development in Longyearbyen, Svalbard
 Past and future climate development in Longyearbyen, Svalbard Eirik J. Førland 1,2 and Ketil Isaksen 1 1). Norwegian Meteorological Institute 2). Norwegian Centre for Climate Services Svalbard Science
Past and future climate development in Longyearbyen, Svalbard Eirik J. Førland 1,2 and Ketil Isaksen 1 1). Norwegian Meteorological Institute 2). Norwegian Centre for Climate Services Svalbard Science
Climate Change in the Northeast: Past, Present, and Future
 Climate Change in the Northeast: Past, Present, and Future Dr. Cameron Wake Institute for the Study of Earth, Oceans, and Space (EOS) University of New Hampshire 62nd Annual Meeting of the Northeastern
Climate Change in the Northeast: Past, Present, and Future Dr. Cameron Wake Institute for the Study of Earth, Oceans, and Space (EOS) University of New Hampshire 62nd Annual Meeting of the Northeastern
Simulation of Air Quality Using RegCM Model
 Simulation of Air Quality Using RegCM Model The Regional Climate Model (RegCM) The Regional Climate Model (RegCM) is one of the RCMs that was originally developed at the National Center for Atmospheric
Simulation of Air Quality Using RegCM Model The Regional Climate Model (RegCM) The Regional Climate Model (RegCM) is one of the RCMs that was originally developed at the National Center for Atmospheric
URBAN HEAT ISLAND IN SEOUL
 URBAN HEAT ISLAND IN SEOUL Jong-Jin Baik *, Yeon-Hee Kim ** *Seoul National University; ** Meteorological Research Institute/KMA, Korea Abstract The spatial and temporal structure of the urban heat island
URBAN HEAT ISLAND IN SEOUL Jong-Jin Baik *, Yeon-Hee Kim ** *Seoul National University; ** Meteorological Research Institute/KMA, Korea Abstract The spatial and temporal structure of the urban heat island
The Climate of Bryan County
 The Climate of Bryan County Bryan County is part of the Crosstimbers throughout most of the county. The extreme eastern portions of Bryan County are part of the Cypress Swamp and Forest. Average annual
The Climate of Bryan County Bryan County is part of the Crosstimbers throughout most of the county. The extreme eastern portions of Bryan County are part of the Cypress Swamp and Forest. Average annual
WIND DATA REPORT FOR THE YAKUTAT JULY 2004 APRIL 2005
 WIND DATA REPORT FOR THE YAKUTAT JULY 2004 APRIL 2005 Prepared on July 12, 2005 For Bob Lynette 212 Jamestown Beach Lane Sequim WA 98382 By John Wade Wind Consultant LLC 2575 NE 32 nd Ave Portland OR 97212
WIND DATA REPORT FOR THE YAKUTAT JULY 2004 APRIL 2005 Prepared on July 12, 2005 For Bob Lynette 212 Jamestown Beach Lane Sequim WA 98382 By John Wade Wind Consultant LLC 2575 NE 32 nd Ave Portland OR 97212
Malawi. General Climate. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Malawi C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Malawi C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain
 ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
The Scale-dependence of Groundwater Effects on Precipitation and Temperature in the Central United States
 The Scale-dependence of Groundwater Effects on Precipitation and Temperature in the Central United States Michael Barlage, Fei Chen, Changhai Liu NCAR/RAL Gonzalo Miguez-Macho U. Santiago de Compostela
The Scale-dependence of Groundwater Effects on Precipitation and Temperature in the Central United States Michael Barlage, Fei Chen, Changhai Liu NCAR/RAL Gonzalo Miguez-Macho U. Santiago de Compostela
FRAPPÉ/DISCOVER-AQ (July/August 2014) in perspective of multi-year ozone analysis
 FRAPPÉ/DISCOVER-AQ (July/August 2014) in perspective of multi-year ozone analysis Project Report #2: Monitoring network assessment for the City of Fort Collins Prepared by: Lisa Kaser kaser@ucar.edu ph:
FRAPPÉ/DISCOVER-AQ (July/August 2014) in perspective of multi-year ozone analysis Project Report #2: Monitoring network assessment for the City of Fort Collins Prepared by: Lisa Kaser kaser@ucar.edu ph:
The Climate of Pontotoc County
 The Climate of Pontotoc County Pontotoc County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeast Oklahoma. Average
The Climate of Pontotoc County Pontotoc County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeast Oklahoma. Average
The Climate of Kiowa County
 The Climate of Kiowa County Kiowa County is part of the Central Great Plains, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from about 24 inches in northwestern
The Climate of Kiowa County Kiowa County is part of the Central Great Plains, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from about 24 inches in northwestern
Prediction of Snow Water Equivalent in the Snake River Basin
 Hobbs et al. Seasonal Forecasting 1 Jon Hobbs Steve Guimond Nate Snook Meteorology 455 Seasonal Forecasting Prediction of Snow Water Equivalent in the Snake River Basin Abstract Mountainous regions of
Hobbs et al. Seasonal Forecasting 1 Jon Hobbs Steve Guimond Nate Snook Meteorology 455 Seasonal Forecasting Prediction of Snow Water Equivalent in the Snake River Basin Abstract Mountainous regions of
North Carolina Climate December 2011
 North Carolina Climate December 2011 Online: http://www.nc-climate.ncsu.edu/office/newsletters North Carolina Climate, the monthly newsletter of the State Climate Office of NC, covers information on a
North Carolina Climate December 2011 Online: http://www.nc-climate.ncsu.edu/office/newsletters North Carolina Climate, the monthly newsletter of the State Climate Office of NC, covers information on a
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Last updated: September 2008
 North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: September 2008 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2007
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: September 2008 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2007
CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON ICE REGIME OF THE RIVERS IN MONGOLIA
 Ice in the Environment: Proceedings of the 16th IAHR International Symposium on Ice Dunedin, New Zealand, 2nd 6th December 2002 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research CLIMATE CHANGE
Ice in the Environment: Proceedings of the 16th IAHR International Symposium on Ice Dunedin, New Zealand, 2nd 6th December 2002 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research CLIMATE CHANGE
The Graniteville Train Crash: Emergency Response Support Provided by the Savannah River National Laboratory
 The Graniteville Train Crash: Emergency Response Support Provided by the Savannah River National Laboratory Matthew J. Parker, CCM, Charles H. Hunter and Robert P. Addis Atmospheric Technologies Group
The Graniteville Train Crash: Emergency Response Support Provided by the Savannah River National Laboratory Matthew J. Parker, CCM, Charles H. Hunter and Robert P. Addis Atmospheric Technologies Group
Review of medium to long term coastal risks associated with British Energy sites: Climate Change Effects - Final Report
 Review of medium to long term coastal risks associated with British Energy sites: Climate Change Effects - Final Report Prepared for British Energy Generation Ltd Authors: Reviewed by: Authorised for issue
Review of medium to long term coastal risks associated with British Energy sites: Climate Change Effects - Final Report Prepared for British Energy Generation Ltd Authors: Reviewed by: Authorised for issue
Secular Trends of Precipitation Amount, Frequency, and Intensity in the United States
 Secular Trends of Precipitation Amount, Frequency, and Intensity in the United States Thomas R. Karl and Richard W. Knight NOAA/NESDIS/National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina ABSTRACT
Secular Trends of Precipitation Amount, Frequency, and Intensity in the United States Thomas R. Karl and Richard W. Knight NOAA/NESDIS/National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina ABSTRACT
Extreme Rainfall in the Southeast U.S.
 Extreme Rainfall in the Southeast U.S. David F. Zierden Florida State Climatologist Center for Ocean Atmospheric Prediction Studies The Florida State University March 7, 2016 Causes of Extreme Rainfall
Extreme Rainfall in the Southeast U.S. David F. Zierden Florida State Climatologist Center for Ocean Atmospheric Prediction Studies The Florida State University March 7, 2016 Causes of Extreme Rainfall
An integrated assessment of the potential for change in storm activity over Europe: implications for forestry in the UK
 International Conference Wind Effects on Trees September 16-18, 3, University of Karlsruhe, Germany An integrated assessment of the potential for change in storm activity over Europe: implications for
International Conference Wind Effects on Trees September 16-18, 3, University of Karlsruhe, Germany An integrated assessment of the potential for change in storm activity over Europe: implications for
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies
 Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
The Climate of Murray County
 The Climate of Murray County Murray County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition between prairies and the mountains of southeastern Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from
The Climate of Murray County Murray County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition between prairies and the mountains of southeastern Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from
The Climate of Seminole County
 The Climate of Seminole County Seminole County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeastern Oklahoma. Average
The Climate of Seminole County Seminole County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeastern Oklahoma. Average
Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test
 Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test 1) Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature? 2) The diagram below shows the apparent path
Name Per Date Earth Science Climate & Insolation Test 1) Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature? 2) The diagram below shows the apparent path
The Climate of Grady County
 The Climate of Grady County Grady County is part of the Central Great Plains, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from about 33 inches in northern
The Climate of Grady County Grady County is part of the Central Great Plains, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Average annual precipitation ranges from about 33 inches in northern
The Climate of Marshall County
 The Climate of Marshall County Marshall County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeastern Oklahoma. Average
The Climate of Marshall County Marshall County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeastern Oklahoma. Average
Richard W. Dixon and Todd Moore Department of Geography Texas State University San Marcos May 2009
 Richard W. Dixon and Todd Moore Department of Geography Texas State University San Marcos May 2009 Study Area Texas occupies about 7% of the area of the US. Second largest state at 692,000 sq. km. Lat
Richard W. Dixon and Todd Moore Department of Geography Texas State University San Marcos May 2009 Study Area Texas occupies about 7% of the area of the US. Second largest state at 692,000 sq. km. Lat
The Pennsylvania Observer
 The Pennsylvania Observer April 2, 2009 March 2009 Pennsylvania Weather Recap Prepared by Curt Harpster For the month of March the saying, In like a lion and out like a lamb really fit the pattern quite
The Pennsylvania Observer April 2, 2009 March 2009 Pennsylvania Weather Recap Prepared by Curt Harpster For the month of March the saying, In like a lion and out like a lamb really fit the pattern quite
LOCAL CLIMATOLOGICAL DATA FOR FREEPORT ILLINOIS
 Climatological Summary: LOCAL CLIMATOLOGICAL DATA FOR FREEPORT ILLINOIS 1905-1990 Freeport (Stephenson County) has a temperate continental climate, dominated by maritime tropical air from the Gulf of Mexico
Climatological Summary: LOCAL CLIMATOLOGICAL DATA FOR FREEPORT ILLINOIS 1905-1990 Freeport (Stephenson County) has a temperate continental climate, dominated by maritime tropical air from the Gulf of Mexico
Probability distributions of monthly-to-annual mean temperature and precipitation in a changing climate
 Probability distributions of monthly-to-annual mean temperature and precipitation in a changing climate Jouni Räisänen Department of Physics, University of Helsinki Climate probability distribution of
Probability distributions of monthly-to-annual mean temperature and precipitation in a changing climate Jouni Räisänen Department of Physics, University of Helsinki Climate probability distribution of
Local Ctimatotogical Data Summary White Hall, Illinois
 SWS Miscellaneous Publication 98-5 STATE OF ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND NATURAL RESOURCES Local Ctimatotogical Data Summary White Hall, Illinois 1901-1990 by Audrey A. Bryan and Wayne Armstrong Illinois
SWS Miscellaneous Publication 98-5 STATE OF ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND NATURAL RESOURCES Local Ctimatotogical Data Summary White Hall, Illinois 1901-1990 by Audrey A. Bryan and Wayne Armstrong Illinois
Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP
 Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP Paul Earnshaw and Sean Milton Met Office, UK Crown copyright 2005 Page 1 Overview Production and use of CEOP data Results SGP Seasonal & Diurnal cycles Other extratopical
Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP Paul Earnshaw and Sean Milton Met Office, UK Crown copyright 2005 Page 1 Overview Production and use of CEOP data Results SGP Seasonal & Diurnal cycles Other extratopical
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: SEPTEMBER 19, 2016 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP,
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: SEPTEMBER 19, 2016 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sroot@weatherbank.com SEPTEMBER 2016 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The contiguous
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: SEPTEMBER 19, 2016 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sroot@weatherbank.com SEPTEMBER 2016 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The contiguous
research highlight Wind-Rain Relationships in Southwestern British Columbia Introduction Methodology Figure 2 Lower Mainland meteorological stations
 research highlight June 2007 Technical Series 07-114 Introduction Building envelope failures in southwestern British Columbia has brought to light the strong influence of wind-driven rain on building envelopes.
research highlight June 2007 Technical Series 07-114 Introduction Building envelope failures in southwestern British Columbia has brought to light the strong influence of wind-driven rain on building envelopes.
Ryan P. Shadbolt * Central Michigan University, Mt. Pleasant, Michigan
 14A.1 RECENT CLIMATE CHANGE IN THE HIGH ELEVATIONS OF THE SOUTHERN APPALACHIANS Ryan P. Shadbolt * Central Michigan University, Mt. Pleasant, Michigan 1. INTRODUCTION Island species are often vulnerable
14A.1 RECENT CLIMATE CHANGE IN THE HIGH ELEVATIONS OF THE SOUTHERN APPALACHIANS Ryan P. Shadbolt * Central Michigan University, Mt. Pleasant, Michigan 1. INTRODUCTION Island species are often vulnerable
Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types:
 Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types: Relationships with Sea Ice and Surface Temperature Ryan Eastman Stephen Warren University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Changes in Arctic
Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types: Relationships with Sea Ice and Surface Temperature Ryan Eastman Stephen Warren University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Changes in Arctic
WIND DATA REPORT. Vinalhaven
 WIND DATA REPORT Vinalhaven April 1, 2004 June 30, 2004 Prepared for Fox Islands Electric Cooperative By Melissa L. Ray Anthony L. Rogers April 4, 2005 Renewable Energy Research Laboratory 160 Governors
WIND DATA REPORT Vinalhaven April 1, 2004 June 30, 2004 Prepared for Fox Islands Electric Cooperative By Melissa L. Ray Anthony L. Rogers April 4, 2005 Renewable Energy Research Laboratory 160 Governors
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 1, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 1, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com FEBRUARY 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The February contiguous U.S. temperature
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 1, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com FEBRUARY 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The February contiguous U.S. temperature
5B.1 DEVELOPING A REFERENCE CROP EVAPOTRANSPIRATION CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE SOUTHEASTERN UNITED STATES USING THE FAO PENMAN-MONTEITH ESTIMATION TECHNIQUE
 DEVELOPING A REFERENCE CROP EVAPOTRANSPIRATION CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE SOUTHEASTERN UNITED STATES USING THE FAO PENMAN-MONTEITH ESTIMATION TECHNIQUE Heather A. Dinon*, Ryan P. Boyles, and Gail G. Wilkerson
DEVELOPING A REFERENCE CROP EVAPOTRANSPIRATION CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE SOUTHEASTERN UNITED STATES USING THE FAO PENMAN-MONTEITH ESTIMATION TECHNIQUE Heather A. Dinon*, Ryan P. Boyles, and Gail G. Wilkerson
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2013
 Application and verification of EMWF products 2013 Hellenic National Meteorological Service (HNMS) Flora Gofa and Theodora Tzeferi 1. Summary of major highlights In order to determine the quality of the
Application and verification of EMWF products 2013 Hellenic National Meteorological Service (HNMS) Flora Gofa and Theodora Tzeferi 1. Summary of major highlights In order to determine the quality of the
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Last updated: August 2009
 North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: August 2009 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2008 through
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: August 2009 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2008 through
1.Introduction 2.Relocation Information 3.Tourism 4.Population & Demographics 5.Education 6.Employment & Income 7.City Fees & Taxes 8.
 1.Introduction 2.Relocation Information 3.Tourism 4.Population & Demographics 5.Education 6.Employment & Income 7.City Fees & Taxes 8.Recreation & Activities 9.Climate Data 10.Economic Development History
1.Introduction 2.Relocation Information 3.Tourism 4.Population & Demographics 5.Education 6.Employment & Income 7.City Fees & Taxes 8.Recreation & Activities 9.Climate Data 10.Economic Development History
Fort Lewis, Washington (47 05'N, 'W)
 Fort Lewis, Washington (47 05'N, 122 35'W) Full Year Climatology CONVENTIONS: The spelling of place names and geographical features are those used by the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA). All
Fort Lewis, Washington (47 05'N, 122 35'W) Full Year Climatology CONVENTIONS: The spelling of place names and geographical features are those used by the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA). All
Description of the Temperature Observation and Averaging Methods Used at the Blue Hill Meteorological Observatory
 Description of the Temperature Observation and Averaging Methods Used at the Blue Hill Meteorological Observatory Michael J. Iacono Blue Hill Meteorological Observatory November 2015 The Blue Hill Meteorological
Description of the Temperature Observation and Averaging Methods Used at the Blue Hill Meteorological Observatory Michael J. Iacono Blue Hill Meteorological Observatory November 2015 The Blue Hill Meteorological
The Climate of the Carolinas: Past, Present, and Future - Results from the National Climate Assessment
 The Climate of the Carolinas: Past, Present, and Future - Results from the National Climate Assessment Chip Konrad Chris Fuhrmann Director of the The Southeast Regional Climate Center Associate Professor
The Climate of the Carolinas: Past, Present, and Future - Results from the National Climate Assessment Chip Konrad Chris Fuhrmann Director of the The Southeast Regional Climate Center Associate Professor
Spatial interpolation of sunshine duration in Slovenia
 Meteorol. Appl. 13, 375 384 (2006) Spatial interpolation of sunshine duration in Slovenia doi:10.1017/s1350482706002362 Mojca Dolinar Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, Meteorological Office,
Meteorol. Appl. 13, 375 384 (2006) Spatial interpolation of sunshine duration in Slovenia doi:10.1017/s1350482706002362 Mojca Dolinar Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, Meteorological Office,
The Hydrology and Water Resources of the Proglacial Zone of a Monsoonal Temperate Glacier
 International Conference on Architectural, Civil and Hydraulics Engineering (ICACHE 2015) The Hydrology and Water Resources of the Proglacial Zone of a Monsoonal Temperate Glacier Yuchuan Meng1, a and
International Conference on Architectural, Civil and Hydraulics Engineering (ICACHE 2015) The Hydrology and Water Resources of the Proglacial Zone of a Monsoonal Temperate Glacier Yuchuan Meng1, a and
Climatology of Paranal. Prepared by M. Sarazin, ESO
 Climatology of Paranal Prepared by M. Sarazin, ESO 1 Climatology of Paranal The Main Climate Actors The Main Parameters And their Climatology 2 Main Climate Actors Bolivian High El Nino Southern Oscillation
Climatology of Paranal Prepared by M. Sarazin, ESO 1 Climatology of Paranal The Main Climate Actors The Main Parameters And their Climatology 2 Main Climate Actors Bolivian High El Nino Southern Oscillation
Precipitation processes in the Middle East
 Precipitation processes in the Middle East J. Evans a, R. Smith a and R.Oglesby b a Dept. Geology & Geophysics, Yale University, Connecticut, USA. b Global Hydrology and Climate Center, NASA, Alabama,
Precipitation processes in the Middle East J. Evans a, R. Smith a and R.Oglesby b a Dept. Geology & Geophysics, Yale University, Connecticut, USA. b Global Hydrology and Climate Center, NASA, Alabama,
The Climate of Payne County
 The Climate of Payne County Payne County is part of the Central Great Plains in the west, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Payne County is also part of the Crosstimbers in the
The Climate of Payne County Payne County is part of the Central Great Plains in the west, encompassing some of the best agricultural land in Oklahoma. Payne County is also part of the Crosstimbers in the
WIND DATA REPORT. Vinalhaven
 WIND DATA REPORT Vinalhaven July 1, 2004 September 30, 2004 Prepared for Fox Islands Electric Cooperative By Melissa L. Ray Anthony L. Rogers April 4, 2005 Renewable Energy Research Laboratory 160 Governors
WIND DATA REPORT Vinalhaven July 1, 2004 September 30, 2004 Prepared for Fox Islands Electric Cooperative By Melissa L. Ray Anthony L. Rogers April 4, 2005 Renewable Energy Research Laboratory 160 Governors
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: February 15, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: February 15, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com JANUARY 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review During January, the average
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: February 15, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com JANUARY 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review During January, the average
Weather History on the Bishop Paiute Reservation
 Weather History on the Bishop Paiute Reservation -211 For additional information contact Toni Richards, Air Quality Specialist 76 873 784 toni.richards@bishoppaiute.org Updated 2//214 3:14 PM Weather History
Weather History on the Bishop Paiute Reservation -211 For additional information contact Toni Richards, Air Quality Specialist 76 873 784 toni.richards@bishoppaiute.org Updated 2//214 3:14 PM Weather History
Long-Term Trend of Summer Rainfall at Selected Stations in the Republic of Korea
 Long-Term Trend of Summer Rainfall at Selected Stations in the Republic of Korea Il-Kon Kim Professor, Department of Region Information Rafique Ahmed Professor, Geography and Earth Science Silla University
Long-Term Trend of Summer Rainfall at Selected Stations in the Republic of Korea Il-Kon Kim Professor, Department of Region Information Rafique Ahmed Professor, Geography and Earth Science Silla University
Impacts of the climate change on the precipitation regime on the island of Cyprus
 Impacts of the climate change on the precipitation regime on the island of Cyprus Michael Petrakis, Christos Giannakopoulos, Giannis Lemesios Institute for Environmental Research and Sustainable Development,
Impacts of the climate change on the precipitation regime on the island of Cyprus Michael Petrakis, Christos Giannakopoulos, Giannis Lemesios Institute for Environmental Research and Sustainable Development,
Polar Portal Season Report 2016
 Polar Portal Season Report 2016 Less ice both on land and at sea This year s report is the fourth since the Polar Portal was launched, and as an introduction, we have chosen to take a look at the trends
Polar Portal Season Report 2016 Less ice both on land and at sea This year s report is the fourth since the Polar Portal was launched, and as an introduction, we have chosen to take a look at the trends
NEW ALGORITHM TO IMPROVE THE CLOUDINESS DATA SET OVER EASTERN PART OF ROMANIA *
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 64, No. 3, P. 795 806, 2012 NEW ALGORITHM TO IMPROVE THE CLOUDINESS DATA SET OVER EASTERN PART OF ROMANIA * D.C. BOSTAN, S. STEFAN University of Bucharest, Faculty of
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 64, No. 3, P. 795 806, 2012 NEW ALGORITHM TO IMPROVE THE CLOUDINESS DATA SET OVER EASTERN PART OF ROMANIA * D.C. BOSTAN, S. STEFAN University of Bucharest, Faculty of
El Niño, Climate Change and Water Supply Variability
 El Niño, Climate Change and Water Supply Variability Talk Overview El Niño and California California Climate Variability and Change Water Management in the Face of Change California s topography affects
El Niño, Climate Change and Water Supply Variability Talk Overview El Niño and California California Climate Variability and Change Water Management in the Face of Change California s topography affects
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Fall/Winter 2016
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Fall/Winter 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University November 5, 2016 After a year where we were seemingly off by a month in terms of temperatures (March
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Fall/Winter 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University November 5, 2016 After a year where we were seemingly off by a month in terms of temperatures (March
Characteristics of long-duration precipitation events across the United States
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L22712, doi:10.1029/2007gl031808, 2007 Characteristics of long-duration precipitation events across the United States David M. Brommer, 1 Randall S. Cerveny, 2 and
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L22712, doi:10.1029/2007gl031808, 2007 Characteristics of long-duration precipitation events across the United States David M. Brommer, 1 Randall S. Cerveny, 2 and
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations. S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences.
 The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
Introduction. Observed Local Trends. Temperature Rainfall Tropical Cyclones. Projections for the Philippines. Temperature Rainfall
 PAGASA-DOST ntroduction Observed Local Trends Temperature Rainfall Tropical Cyclones Projections for the Philippines Temperature Rainfall Climate Change ssue ncreased use of fossil fuel Global Warming
PAGASA-DOST ntroduction Observed Local Trends Temperature Rainfall Tropical Cyclones Projections for the Philippines Temperature Rainfall Climate Change ssue ncreased use of fossil fuel Global Warming
Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate
 Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate Will Perrie, Lanli Guo, Zhenxia Long, Bash Toulany Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, NS Abstract
Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate Will Perrie, Lanli Guo, Zhenxia Long, Bash Toulany Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, NS Abstract
National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook
 National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook National Interagency Fire Center Predictive Services Issued: September, 2007 Wildland Fire Outlook September through December 2007 Significant fire
National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook National Interagency Fire Center Predictive Services Issued: September, 2007 Wildland Fire Outlook September through December 2007 Significant fire
