STD IX GEOGRAPHY CONTENTS
|
|
|
- Oscar Ford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STD IX GEOGRAPHY CONTENTS 1. Chapter 1 - INDIA LOCATION AND SETTING 2. Chapter 2 - PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA 3. Chapter 3 - DRAINAGE 4. Chapter 4 - CLIMATE 5. Chapter 5 NATURAL VEGETATION AND WILDLIFE 6. Chapter 6 - POPULATION Project on Disaster Management Class IX/Social Science/55
2 Chapter 1 INDIA LOCATION AND SETTING 1. What is the longitudinal and latitudinal extent of India? 2. What is India s position in the world according to size? Name the countries which are larger than India? 3. Explain five important features of India highlighting its supremacy among the countries of the world. 4. Area-wise which is the smallest and which is the largest state of India? 5. What divides India into almost two equal parts latitudinally? 6. Name the southernmost point of a) The Indian Union b) Mainland India. 7. What is the length of the land boundary and that of the coastline of mainland India including Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep? 8. Why is it that inspite of having an almost equal latitudinal and longitudinal extent, the north south extent is greater than the east west extent in kilometers? 9. What is local time? 10. What is Indian Standard Time? Why do we need a standard time for India? 11. At 5 a.m. the sun has already risen in the eastern part of the country but places like Gujarat are still in darkness Explain. 12. Why has the ` E longitude been selected as the Standard Meridian of India? 13. Find out the number of Union Territories along the western and eastern coasts of India. Name them. 14. What is a subcontinent? 15. Why is the difference between the duration of day and night hardly felt at Kanyakumari but not so in Kashmir? 16. India s contacts with the world have continued through the ages. Justify the statement with suitable examples Class IX/Social Science/56
3 Chapter - 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA 1. Name the different types of physical features present in our country. 2. Why does the colour of soil vary from place to place? 3. Name the factors that have influenced the relief of India? 4. What is meant by Plate Tectonics? Explain the theory of plate tectonics? 5. What are the effects of converging and diverging crustal plates on the earth s crust? 6. Describe the formation of the Himalayas. What proof do we have about their origin? 7. How was the Arabian sea formed? 8. Differentiate between the Himadri and the Himachal ranges of the Himalayas. Give three points of difference each. 9. Describe the Shiwalik ranges of the Himalayas. Why are they prone to landslides? 10. What are Duns? Class IX/Social Science/57
4 11. The given map shows the longitudinal divisions of the Himalayas. Describe these divisions and name one major peak in each of these divisions. 12. What are the Purvanchals? Why are they so called? Mention two features of the Purvanchals. What are Patkai, Naga, Manipur, and Mizo in relation to the Purvanchals? 13. What do you understand by the term Doab? 14. According to variations in relief features the northern plains can be divided into four regions. Explain? 15. What are the two divisions of the Peninsular Plateau of India? How was the peninsular plateau formed? Describe its main features? 16. Why is the Deccan Trap so called? Where is it located? For what is this area important? 17. What are Aravalli hills? 18. Distinguish between eastern and western coastal plain? Class IX/Social Science/58
5 19. Write a short note on corals? 20. Distinguish between Lakshadweep and Andaman and Nicobar islands? 21. Explain how the diverse physical features of India complement each other? Class IX/Social Science/59
6 Chapter 3 DRAINAGE 1. Geographically, what does the term drainage mean? 2. What is a drainage basin? 3. What is a water divide? Name one such feature of India. 4. What are the different types of drainage patterns likely to be found among the Indian rivers. 5. Distinguish between dendritic and trellis patterns of drainage and give one example of each: 6. In the following diagram A) What type of drainage pattern is shown in the region marked X? B) What features would you find in the region marked Y? 7. A) What does this picture show? B) What is happening at the place marked Y? C) What will finally happen at the place marked Z? D) What will the final outcome be? Class IX/Social Science/60
7 8. Distinguish between the following and support your answer with an example of each: i) A delta and an estuary ii) A tributary and a distributary? 9. What are the basic differences between the Himalayan rivers and the rivers of Peninsular India? 10. Describe the journey of the Indus river keeping in mind its source, tributaries, direction of flow, areas it covers and special features. 11. What does the Indus Water Treaty state? How does this treaty help the states of Haryana and Punjab? 12. The Ganga is the lifeline of India. Among all the rivers flowing through the country she is the mightiest. Answer the following questions and refresh your knowledge about this river. i) Where does this river originate? ii) What are the two headwaters of the Ganga called? Where do they meet to form the Ganga? iii) Where does the Ganga descend to the plains? iv) Which river is its major tributary and where does it meet the Ganga? v) Name some of its Himalayan tributaries. vi) Name the river that joins it from the Central Highlands. vii) Exactly from where in West Bengal does it enter Bangladesh? viii) What is the name of its major distributary? Name the city situated on this distributary. ix) What is it called in Bangladesh? Which rivers form its tributaries in Bangladesh? x) What is the unique geographical feature formed by this river at its mouth? What is special about this feature? xi) What is the length of this river? xii) Name the states the river crosses while in India. 13. Why does the Brahmaputra have less water while in Tibet? 14. What are the different names by which the Brahmaputra is known and in which areas are they relevant? 15. What kind of drainage pattern does the Narmada follow and why? What are some of the spectacular features formed by this river. 16. Why is the Godavari also known as the Dakshin Ganga? Describe the basin of this river. 17. Lakes are of great value to human beings Justify the statement. 18. Observe the following picture carefully and identify the feature shown here. Which river is it commonly found in? Class IX/Social Science/61
8 19. Give three reasons why rivers are considered to be lifelines of a nation? 20. What are the 2 major causes of river pollution and give two measures to prevent it? 21. What is the Ganga Action Plan? How far has it been successful? Class IX/Social Science/62
9 Chapter 4 : CLIMATE 1. Define a) Weather b) Climate. 2. What are the atmospheric elements that govern weather and climate? 3. What is the origin of the word monsoon? What does monsoon mean? Note: Very often we notice a difference between the daytime temperature and the night temperature of a place. In the desert of Rajasthan the daytime temperature may rise upto 500C during the day and fall to 150C at night. The difference is too great. This difference between the maximum temperature and the minimum temperature in an area in one day is known as the diurnal range of temperature. In some places like Delhi the difference between summer temperatures and winter temperatures is vast. Delhi has summer temperatures like 450C and the winter temperatures fall to 50C. This difference between the summer and winter temperatures is known as seasonal range of temperature. 4. Which parts of India would have a low range of temperature between day and night? 5. Name one place in India other than Delhi that has a high seasonal range of temperature and one place that has a low seasonal range of temperature. 6. What are climate controls? Name the different controls that affect the climate of a place. 7. What role do the Himalayas play in regulating the climate of India? Note: There some facts we must always remember a) When temperature is high pressure is low. When temperature is low pressure is high. So places that are very hot have low pressure and places that are cold have high pressure. Temp α 1/Pressure b) Winds always blow from high pressure areas to low pressure areas. c) Temperature always decreases with height. 8. What are the three major factors that affect the climate of India? Class IX/Social Science/63
10 Some interesting facts about jetstreams: Jet streams are formed by the temperature differences in the upper atmosphere, between the cold polar air and the warm tropical air. This abrupt change in temperature causes a large pressure difference, which forces the air to move. During the winter there is a greater difference in the temperature, so this is when the jet streams are at their fastest. They generally move in a west to easterly direction due to the rotation of the earth. They move north and south too, following the boundary between warmer and colder air. Jet streams flow approximately 5 to 10 miles above the surface of the earth, with speeds up to 310 miles per hour. With these kinds of speeds you see why the aeroplanes are so keen to use them. Flying along with a jetstream helps to reduce time as well as fuel consumption. However, to navigate in a jet stream is not as easy as you might think, as it is only a few hundred miles wide, just a few miles thick, and constantly moving. Entering and leaving a jet stream can be a turbulent time for any aircraft no matter how big it is, and most passengers will want to leave this roller coaster ride. An easterly jet stream at a mean height of 14 to 16 Kms is formed towards the end of June over the Indian Peninsula in the south-west monsoon season over the latitudes of 10 to 15 degrees North. It has been found that when this jet stream is strong the monsoon is very active. However it has been found that when this jet stream jet stream shifts to the north, weak monsoon conditions prevail. Another sub-tropical westerly jet stream is formed along the latitude of 27 degrees North during winter at an average height of 12 Kms. The velocity of this jet stream decreases as it migrates to north. This sub-tropical jet adds to the thunder activity in north and north-west India. We call this the Western disturbances. This brings snowfall in the mountains and light showers of rain to the northern plains and a cold wave condition prevails. 9. What are jet streams? How do they affect the climate of India? 10. What are Western Cyclonic Disturbances? What effect do they have over India in the winter season? Various questions arise about El Nino and is effects. Even scientists have not been fully convinced about its occurrence. Here are some opinions about the El Nino. El Nino is a shift in ocean temperatures and atmospheric conditions in the tropical Pacific that disrupts weather around the world. It is a poorly understood recurrent climatic phenomenon that primarily affects the Pacific coast of South America, but has dramatic impacts on weather patterns all over the world. Under normal conditions the cold Peruvian current flows along the west coast of Peru and naturally gets deflected to the west towards Indonesia, on reaching the equator. Near the Equator the water also starts to warm up. Class IX/Social Science/64
11 Normally, trade winds blowing towards the west, across the Pacific, push warm surface water away from the South American coast towards Australia and The Philippines where they accumulate into a large, deep pool just east of Indonesia, and northeast of Australia. The trade winds tend to lose strength with the onset of springtime in the northern hemisphere. By this time a large part of the ocean waters are already warm. This warm water from this large pool starts to move eastwards (towards South America) aided by surface winds and ocean currents. Over a period of four to six years the cold Peruvian current gets replaced by cover of warm water along the coast of Peru causing abnormal weather conditions which we commonly know as El Nino. Obviously evaporation is more from these waters which cause heavy rainfall to areas of South America which would otherwise have been dry. These conditions lead to extreme weather conditions. Pronounced El-Ninyo, it means the boy in Spanish and was named so by Peruvian fishermen after the Christ child since its effects are generally first felt around Christmas. The warm El Nino phase typically lasts for 8 10 months or so. Along the Peruvian coast the water is cold and nutrient-rich, supporting high levels of primary productivity, diverse marine ecosystems, and major fisheries. Warm water accumulates on the surface, which causes the nutrients produced by the upwelling of cold water to significantly come down, leading to the killing of plankton and other aquatic life such as fish and the starvation of many seabirds. A wide variety of disasters have been blamed on the El-Nino effect including a famine in Indonesia in 1983, bush fires in Australia arising from droughts, rainstorms in California, and the destruction of anchovy fishery off the coast of Peru. During 1982/83 it is said to have led to the death of some 2000 people worldwide and caused losses amounting to approximately 12 billion dollars. The impact of the 1997/98 spell of the phenomena was very damaging. Floods devastated the Americas, storms hit China, drought parched Austria, and forest fires burnt parts of South- East Asia and Brazil. Indonesia experienced the worst drought in the last 50 years and in Mexico, the town of Guadalajara saw snow for the first time since In the Indian Ocean, it affected the movement of the monsoon winds. El Nino, is one part of what's called the Southern Oscillation. The Southern Oscillation is the see-saw pattern of reversing surface air pressure between the eastern and western tropical Pacific; when the surface pressure is high in the eastern tropical Pacific it is low in the western tropical Pacific, and vice-versa. Because the ocean warming and pressure reversals are simultaneous, scientists call this phenomenon the El Nino/Southern Oscillation or ENSO for short. 11. What does burst of the monsoon mean? Class IX/Social Science/65
12 12. Q10. Describe the Cold weather season in India keeping in mind the period of occurrence, temperature and pressure conditions, direction of winds and special features associated with this season. 13. The map below shows the condition of the country during summer THE HOT WEATHER SEASON Intense low pressure trough over North India. The hottest areas during this season. 14. What is loo? Which parts of India are under its effect? What are its features? 15. What are kaalbaisakhis? Why are they so called? 16. What are mango showers? 17. What are wet and dry spells during the monsoon season? 18. Describe briefly the season of the advancing monsoons. 19. What is October Heat? 20. Describe the occurrence of tropical cyclones during the season of the retreating monsoon. Class IX/Social Science/66
13 The monsoons in India have some peculiar characteristic features: a) The time of arrival and the time of departure from the country, does not remain fixed. b) The distribution of rainfall over the country is uneven. Some areas get so much rain that they suffer floods (Assam) and at the same time other areas get so little rain that they have droughts (Rajasthan). c) The quantity of rain received every year is not the same. d) The quantity of rain received throughout the season in all the months is not the same. It is more towards the beginning and less towards the end. e) It never rains continuously throughout the season. There are wet and dry spells during the season. 21. Why do we say that the monsoons act as a unifying bond for the country? Class IX/Social Science/67
14 Chapter 5 NATURAL VEGETATION AND WILDLIFE 1. What is virgin vegetation? 2. What is the difference between endemic and exotic species? Give an example of each type to prove your point. 3. What is a biome? How are biomes identified? Give an example of a biome? 4. The southern slopes of the Himalayas and the western slopes of the Western Ghats are covered with thicker vegetation. Give reasons to support your answer? 5. Forests are an essential part of our lives. Justify this statement. 6. How do human beings influence the ecology of a region? 7. Describe the Tropical Rain Forests of India. Lay emphasis on conditions for growth, features and types of trees, areas of occurrence and animal life. 8. Why are deciduous forests so called? What is the difference between dry and moist deciduous forests? 9. Observe the given pictures and answer the following questions a) What kind of natural vegetation is shown in the two pictures? b) Name two states of India where you would find this type of vegetation. c) Name four main plant species of this region. d) What are the special features associates with the plant species found in this region? 10. As we climb higher in a mountain region there is a distinct change in the type of vegetation. What are the reasons for this change? Name the types of vegetation according to their transition. Class IX/Social Science/68
15 11. This is a picture of a typical mangrove / tidal forest. Mangroves live life on the edge. With one foot on land and one in the sea, these botanical amphibians occupy a zone of desiccating heat, choking mud, and salt levels that would kill an ordinary plant within hours. Yet the mangroves are among the most productive and biologically complex ecosystems on Earth. Birds roost in the canopy, shellfish attach themselves to the roots, and snakes and crocodiles come to hunt. Mangroves provide nursery grounds for fish; a food source for monkeys, deer, tree-climbing crabs and a nectar source for bats and honeybees. If the mangrove forests are destroyed, food chains for fish and prawns are degraded as well. Then the number of fish, prawns and crabs inhabiting the coastal area will decrease. Some sea animals cannot live without mangrove forests. For instance, crabs lay their eggs in the sea, but the newly born crabs come back to the mangrove forests. In fact all animals living in this region are dependent on the mangroves. a) Where in India are mangrove forests found? b) Which famous place in India has the largest collection of mangroves in the world? c) Which carnivore is associated with this forest? d) Name two types of mangrove trees that are found in these forests. 12. Name one animal found in the hot wet tropical rain forests of India. Name two states where they are found. Class IX/Social Science/69
16 13. Distinguish between the following:- i) wild life sanctuary and national park ii) extinct and endangered species 14. Mention two medicinal plants with their utility? 15. Suggest some important measures for the conservation of natural vegetation on this earth? 16. What are biosphere reserves? Which is the oldest biosphere reserve of India and where is it located? Find out what the special functions of biosphere reserves are. 17. Here are some pictures of migratory birds that visit India: Why do migratory birds visit India? Name some of these birds you would see in India. 18. To protect the flora and fauna of the country, the government has taken many steps. What are some of these steps taken by the government? Class IX/Social Science/70
17 Chapter - 6 POPULATION 1. Why is the study of population necessary? 2. Different regions have varying densities of population. Explain giving three reasons. Support your answer with examples. 3. Discuss the major components of population. 4. Define the following terms:- 5. a) Absolute increase of population b) Annual growth rate c) Sex ratio d) Age structure 6. Why is literacy a very important quality of a population? 7. How is occupational structure different in developed and developing countries? Explain with reference to India. 8. What are the various problems that affect the health situation in our country? 9. What are the significant features of the national population policy 2000? 10. Read the comparative data about age composition of population of India and Japan and answer the questions that follow:- Age in years India % of total populatiojapan % of total population and above a) Which country has a large proportion of dependent population. b) What are its implications? Class IX/Social Science/71
18 c) What are the implications of the fact that there is a greater proportion of children in India? d) What can you infer from the table about the life expectancy of the two countries? 11. What does the National Population Policy of 2000 provide within its framework? Class IX/Social Science/72
19 STD 9 PROJECT DISASTER MANAGEMENT Prepare a project on any one of the following topics a) Earthquake in Nepal, 2015 b) Chennai Floods, December 2015 Guidelines for preparing the project: 1. The project must be hand written and not more than 10 pages (includes both sides of the paper used). 2. Relevant material, pictures, newspaper clippings or any other material related to the topic may be used. 3. The project must have At the beginning i) A cover page ii) An acknowledgement iii) Table of contents / index At the end Bibliography which includes a mention of the sources from where reference material has been obtained. 4. The project must contain i) An introduction to the topic ii) Causes and consequences iii) Contingency plans and prevention iv) Rehabilitation 5. Marks will be allotted for i) Relevance of matter ii) Aesthetics and presentation iii) Timely submission. DATE OF SUBMISSION 25 TH JANUARY Marks will be deducted after the last date. Class IX/Social Science/73
20 STD IX ECONOMICS CONTENTS Chapter 1 THE STORY OF VILLAGE PALAMPUR Assignment 1 Chapter 2 PEOPLE AS RESOURCE Assignment 2 Chapter 3 POVERTY AS A CHALLENGE Assignment 3 Chapter 4 FOOD SECURITY IN INDIA Assignment 4 Class IX/Social Science/74
21 Chapter 1 THE STORY OF VILLAGE PALAMPUR 1. What are the four requirements for the production of goods and services? 2. What is the importance of land in production? 3. What is human capital? Why is human capital necessary for production of goods and services? 4. This picture shows a factory with several workers and heavy machines Which factors of production can you identify from this picture? 5. In what ways can land under cultivation be increased in a place like Palampur? 6. Name the working capitals required by the farmer who uses modern farming methods. 7. The Green Revolution has been a boon to the farmers and the country. Yet it has some negative aspects. What are some of the negative aspects of the Green Revolution? 8. Even though chemical fertilizers have given a boost to crop production, in the long run they have led to disastrous effects on land. Explain the statement with examples. 9. What kind of farmers does Palampur have? 10. Where does Palampur get its labour from? 11. What kind of labour is occupied in the cultivation of most of the land? 12. Where does the capital needed for farming come from? Class IX/Social Science/75
22 13. The given graph shows you the distribution of farmers and cultivated area. Answer the following questions i) How much is the land cultivated by small farmers? ii) From the pie diagram what is your observation? 14. Farmers sell the surplus produce in the markets. For what do they utilize the capital that they earn from their sales? 15. How does an allied activity like dairy farming help the farmers? 16. What kind of small scale manufacturing activities are common in villages? Class IX/Social Science/76
23 Class IX/Social Science/77
24 THE STORY OF VILLAGE PALAMPUR Assignment 1 Q1. Why is labour important as a factor of production? Q2. What is the difference between fixed capital and working capital. Give 2 examples of each type to support your answer. Q3. How is it possible to increase agricultural output from a fixed amount of land?. Class IX/Social Science/78
25 Q4. What is the difference between multiple cropping and modern farming methods? Q3. Why is the Green Revolution considered a boon as well as a bane in modern agriculture?.. Q4. What is land fragmentation? What effects does land fragmentation have on production? Class IX/Social Science/79
26 Q5. Why are farm labourers poor? Q6. What do large, medium and small farmers do with the capital they earn? Q7. Other than farming and small scale manufacturing what are some of the tertiary activities that villagers can undertake to supplement their income? Class IX/Social Science/80
27 Class IX/Social Science/81
28 Chapter 2 1. Why are people called resource? PEOPLE AS RESOURCE 2. Why is it said that human capital is more superior to other resources? 3. Name two countries of the world whose progress is related to the development of human resource. Why have they seen it necessary to invest in human resource? 4. What are the different sectors of economy? Name two activities each belonging to these sectors. 5. Literacy Rates in India (Census of India 2001) 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% Column1 Column2 Column3 i) What has the growth rate of literacy been from 1951 to 2001? (Approximate figures) ii) What do you get to know about the growth of male literacy from the graph? iii) In which year is the female literacy rate the least? iv) From 1951 to 2001 by how much has female literacy increased? (Approximate figures) v) Why do you think female literacy has not grown remarkably in all these years? 6. What is Sarva Siksha Abhiyan? How does this programme plan to increase literacy in the country? 7. Why do employment firms recruit healthy people? 8. What is unemployment? 9. What is seasonal unemployment? What are the specific features of seasonal unemployment? 10. What is disguised unemployment? Why does disguised unemployment happen? 11. In recent years how has the pattern of employment changed in the three sectors of economy? Class IX/Social Science/82
29 Class IX/Social Science/83
30 PEOPLE AS RESOURCE Assignment 2 Q1. When does the population of a nation become its resource?. Q2. What kind of inputs are required for the formation of human capital? What are the returns from human capital? Q3. What are economic activities? Give two examples of economic activities and two non economic activities. Q4. Differentiate between market activities and non-market activities. Class IX/Social Science/84
31 Q5. Define National Income.. Q6. What is the difference between seasonal and disguised unemployment.... Q7. What kind of unemployment is prevalent in urban areas? How is this a problem?. Class IX/Social Science/85
32 Q8. Unemployment has a detrimental impact on the overall growth of an economy. Explain why this statement is true.... Class IX/Social Science/86
33 Class IX/Social Science/87
34 Chapter 3 POVERTY AS A CHALLENGE Q1. How would you define poverty? Q2. List the factors that are indicators of poverty. Q3. According to social scientists what are the social indicators of poverty? Q4. How is poverty measured? What is taken into consideration while setting the poverty line in India? Q5. Why do different countries use different poverty lines? Give an example to support your answer? Q6. Study the table given below and answer the following questions: Poverty Ratio (%) Number of Poor ( in millions) Year Rural Urban Combined Rural Urban Combined a) Between 1973 and 2000 which sector has shown the maximum decrease in % of poverty? b) The poverty ratio declined between 1973 and 1994, yet the number of poor remained at about 320 million. Why is it so? c) The number of poor in the rural sector have decreased from 261 million to 193 million but in the urban sector the decrease is not significant. Why do you think this has happened? d) What is the total decrease in the number of poor in the rural and urban sectors? Q7. Make a list of the socially vulnerable and the economically vulnerable groups, to poverty. Explain why these groups remain poor. Q8. Name some states where the percentage of poverty is still very high. Q9. Poverty has resurfaced in some of the former socialist countries like Russia. Why has this happened? Class IX/Social Science/88
35 Q10. What does the international poverty line mean? Q11. Explain how a beneficial programme like the Green Revolution is being held responsible for the growing poverty in India. Q12. Income inequalities are known to cause increase in poverty. Explain how it has been responsible for the growing poverty rate in India. Q13. What are the two strategies by which the government has planned to combat poverty? Q14. How will economic growth help in poverty reduction? Q15. Give one feature of each of the following poverty reduction programmes: a. Prime Minister Rozgar Yojana b. Rural Employment Generation Programme c. Swarnajayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana d. Pradhan Mantri Gramodaya Yozana e. Antyodaya Anna Yozana Q16. It is expected that poverty reduction will be expected to make better progress in the next ten to fifteen years. How will this be possible? Class IX/Social Science/89
36 Class IX/Social Science/90
37 POVERTY AS A CHALLENGE Assignment 3 Q1. What is poverty?. Q2. What factors act as indicators of poverty?. Q3. What is a poverty line? How much is considered below poverty line in rural and urban areas? According to the census of 2011 at what level has the poverty line been set? Class IX/Social Science/91
38 Q4. How is a poverty line formulated?. Q5. Why do socially and economically vulnerable groups remain poor?. Q6. Explain how the following states have succeeded in reducing poverty a) Punjab and Haryana: b) Kerala: Class IX/Social Science/92
39 c) West Bengal: d) Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu:. Q7. How did poverty in India become an effect of the British Colonial administration? Q8. Explain how socio-cultural and economic factors add to the existing poverty rate in India Q9. What does NREGA stand for? What are the features of this programme? Class IX/Social Science/93
40 ... Q10. What is NFWP? What are the features of this programme?. Q11. What are the setbacks faced by the various poverty alleviation schemes? Class IX/Social Science/94
41 Class IX/Social Science/95
42 Chapter 4 FOOD SECURITY IN INDIA Q1. What does food security mean? Q2. Under what circumstances does a country face food insecurity? Q3. What is famine? What are the features of a famine? Who are worst affected most during a famine? Q4. In urban areas which group of people are worst affected by food insecurity? Q5. What was the major step taken by the government to attain self sufficiency in food, since Independence? Q6. Study the graph given below and answer the questions that follow: a) In which year did India cross the 200 million tones mark in foodgrain production? b) In which decade did India experience the highest increase in foodgrain production? c) What could be the reason for this remarkable steady increase? d) What does the year show in foodgrain production? Q7. What is buffer stock? Which government body in responsible for procuring buffer stock? Q8. What is issue price? Q9. What does PDS stand for? Why is PDS necessary? Class IX/Social Science/96
43 Q10. What are ration shops also called? What is available at these shops? Who is entitled to avail of this facility? Q11. In the wake of the high incidence of poverty levels, three important food intervention programmes were introduced. What were these programmes? Q12. What are the salient features of the National Food for Work Programme? Q13. The PDS has been revamped in recent years. According to the new system who are the beneficiaries of this system? Q14. Study the following graph and answer the questions that follow: a. Which year shows maximum foodgrain stock and how much? b. What is the minimum buffer stock norm for the Dood Corporation of India? c. Which year shows a decline in the actual stock maintained by the FCI? What was the reason for this decline? d. Why did the FCI reduce its buffer stock norm? Q15. Why did the government increase MSP? What has this resulted in? Q16. What are the effects of increased production of foodgrains, on land? Q17. What are some of the malpractices PDS dealers indulge in that have led to its decline? Q18. Here are some pictures of Grain Banks. Find out the answers to the questions given below. Class IX/Social Science/97
44 a) What are grain banks? b) Who runs these grain banks? c) Which state is implementing this concept on a regular basis? d) What are the functions of these grain banks? Class IX/Social Science/98
45 Class IX/Social Science/99
46 FOOD SECURITY IN INDIA Assignment 4 Q1. What are the three requirements that need to be fulfilled to ensure food security? Explain each of them.. Q2. How is food security affected during a calamity? Class IX/Social Science/100
47 Q3. What are the two dimensions of hunger? Explain these two dimensions.. Q4. What is buffer stock? Why is it necessary to keep buffer stock.. Q5. Why is it not advisable to maintain a large amount of buffer stock? Class IX/Social Science/101
48 Q6. What is Minimum Support Price? Why is MSP announced by the government?. Q7. What is PDS? How has PDS helped in ensuring food security?. Class IX/Social Science/102
49 Q8. What are the drawbacks related to PDS? Q9. How have co-operative societies helped in maintaining food security in India? Support your answer with examples. Class IX/Social Science/103
50 Class IX/Social Science/104
SBOA. SCHOOLAND JUNIOR COLLEGE, CHENNAI 101 ASSIGNMENT (GEOGRAPHY & ECONOMICS)
 SBOA. SCHOOLAND JUNIOR COLLEGE, CHENNAI 101 STD: IX ASSIGNMENT (GEOGRAPHY & ECONOMICS) GEOGRAPHY 1. INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION 1. Name the group of islands lying in the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal. 2. Name
SBOA. SCHOOLAND JUNIOR COLLEGE, CHENNAI 101 STD: IX ASSIGNMENT (GEOGRAPHY & ECONOMICS) GEOGRAPHY 1. INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION 1. Name the group of islands lying in the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal. 2. Name
OUR COUNTRY INDIA LOCATIONAL SETTING
 7 India is a country of vast geographical expanse. In the north, it is bound by the lofty Himalayas. The Arabian Sea in the west, the Bay of Bengal in the east and the Indian Ocean in the south, wash the
7 India is a country of vast geographical expanse. In the north, it is bound by the lofty Himalayas. The Arabian Sea in the west, the Bay of Bengal in the east and the Indian Ocean in the south, wash the
Warm Up Vocabulary Check
 Warm Up Vocabulary Check Surface current Coriolis Effect global winds upwelling Gulf Stream deep current climate El Nino convection current continental deflection 1.The apparent curving of the path of
Warm Up Vocabulary Check Surface current Coriolis Effect global winds upwelling Gulf Stream deep current climate El Nino convection current continental deflection 1.The apparent curving of the path of
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70. Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills
 Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Global Weather Trade Winds etc.notebook February 17, 2017
 Global Weather 1 north pole northern hemisphere equator southern hemisphere south pole 2 We have seasons because of the Earth's tilt The seasons are opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres winter
Global Weather 1 north pole northern hemisphere equator southern hemisphere south pole 2 We have seasons because of the Earth's tilt The seasons are opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres winter
South, Southeast, and East Asia. Physical Geography
 South, Southeast, and East Asia Physical Geography Mountains v Mountains are important in Asia because they influence: A. Population patterns B. Movement of people and goods C. Climate Mountains v The
South, Southeast, and East Asia Physical Geography Mountains v Mountains are important in Asia because they influence: A. Population patterns B. Movement of people and goods C. Climate Mountains v The
Weather & Ocean Currents
 Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT
 UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
Summative Assessment I
 Class: IV Time: 3 Hrs. Summative Assessment I Social Science Marks: 88 Handwriting: 2 Total: 90 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Use crayons for colouring. General Instruction I. Multiple choice questions:
Class: IV Time: 3 Hrs. Summative Assessment I Social Science Marks: 88 Handwriting: 2 Total: 90 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Use crayons for colouring. General Instruction I. Multiple choice questions:
Issue Overview: El Nino and La Nina
 Issue Overview: El Nino and La Nina By Bloomberg, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.28.16 Word Count 748 TOP: A Category 5 typhoon in the Pacific Ocean. BOTTOM: Graphics courtesy of the U.S. National Oceanic
Issue Overview: El Nino and La Nina By Bloomberg, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.28.16 Word Count 748 TOP: A Category 5 typhoon in the Pacific Ocean. BOTTOM: Graphics courtesy of the U.S. National Oceanic
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Exercise Page 51 Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong? (a)
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Exercise Page 51 Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong? (a)
World Geography Chapter 3
 World Geography Chapter 3 Section 1 A. Introduction a. Weather b. Climate c. Both weather and climate are influenced by i. direct sunlight. ii. iii. iv. the features of the earth s surface. B. The Greenhouse
World Geography Chapter 3 Section 1 A. Introduction a. Weather b. Climate c. Both weather and climate are influenced by i. direct sunlight. ii. iii. iv. the features of the earth s surface. B. The Greenhouse
SPLIT UP OF SYLLABUS ( )
 April M Unit/Chapter 1.India - our country. 2. The Northern Mountains. Concepts/Sub topic *Neighboring countries and States of India. *Physical divisions of India. Learning Outcomes Mapping Skill: Identify
April M Unit/Chapter 1.India - our country. 2. The Northern Mountains. Concepts/Sub topic *Neighboring countries and States of India. *Physical divisions of India. Learning Outcomes Mapping Skill: Identify
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES WORKSHEET NO. 06 Summary:- Tectonic Plate Theory:- This theory is based
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES WORKSHEET NO. 06 Summary:- Tectonic Plate Theory:- This theory is based
What a Hurricane Needs to Develop
 Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
Module 3, Investigation 1: Briefing 2 The ENSO game: Predicting and managing for El Niño and La Niña
 Part 5. The ENSO game How can prediction help avoid ENSO s tragic human consequences? Scientists from around the world are involved in forecasting, with computer models and sophisticated measurements,
Part 5. The ENSO game How can prediction help avoid ENSO s tragic human consequences? Scientists from around the world are involved in forecasting, with computer models and sophisticated measurements,
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Hydro-meteorological Aspect. 3.3 Rain Gauge Stations
 3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
(version 3) I. HumAN -Environment Interaction
 (version 3) I. HumAN -Environment Interaction A. Landforms 1. Earth s topography is made up of many different types of landforms. 2. While the planet is covered primarily with water, the four major types
(version 3) I. HumAN -Environment Interaction A. Landforms 1. Earth s topography is made up of many different types of landforms. 2. While the planet is covered primarily with water, the four major types
Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert
 Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert 1 Mount Everest is part of the mountain chain known as the Himalaya. Adventurers from all over the world come to try to climb it. Mount Everest is the highest mountain
Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert 1 Mount Everest is part of the mountain chain known as the Himalaya. Adventurers from all over the world come to try to climb it. Mount Everest is the highest mountain
Name. El Nino. by Cindy Grigg
 Name El Nino by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1. What do you already know about El Nino?
Name El Nino by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1. What do you already know about El Nino?
Chapter 1 Section 2. Land, Water, and Climate
 Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) SECTION - I
 BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Maximum Marks: 40 Time: 2 hrs. 15 mins. PART - A Marks:
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Maximum Marks: 40 Time: 2 hrs. 15 mins. PART - A Marks:
2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA
 2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bound by sea on three sides is referred to as (a) Coast (c) Peninsula (b) Island
2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bound by sea on three sides is referred to as (a) Coast (c) Peninsula (b) Island
Board Question Paper : March 2015
 Board Question Paper : March 2015 BOARD QUESTION PAPER : MARCH 2015 Time: 2 Hours Total Marks: 40 Note: i. All questions are compulsory. ii. Figure to the right indicate full marks. iii. Solve Q. No.3
Board Question Paper : March 2015 BOARD QUESTION PAPER : MARCH 2015 Time: 2 Hours Total Marks: 40 Note: i. All questions are compulsory. ii. Figure to the right indicate full marks. iii. Solve Q. No.3
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10
 Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Winds and Global Circulation
 Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Name Date Class. growth rings of trees, fossilized pollen, and ocean. in the northern hemisphere.
 Lesson Outline LESSON 2 A. Long-Term Cycles 1. A(n) climate cycle takes much longer than a lifetime to complete. a. To learn about long-term climate cycles, scientists study natural records, such as growth
Lesson Outline LESSON 2 A. Long-Term Cycles 1. A(n) climate cycle takes much longer than a lifetime to complete. a. To learn about long-term climate cycles, scientists study natural records, such as growth
Climate and the Atmosphere
 Climate and Biomes Climate Objectives: Understand how weather is affected by: 1. Variations in the amount of incoming solar radiation 2. The earth s annual path around the sun 3. The earth s daily rotation
Climate and Biomes Climate Objectives: Understand how weather is affected by: 1. Variations in the amount of incoming solar radiation 2. The earth s annual path around the sun 3. The earth s daily rotation
Name: Date: Hour: Comparing the Effects of El Nino & La Nina on the Midwest (E4.2c)
 Purpose: Comparing the Effects of El Nino & La Nina on the Midwest (E4.2c) To compare the effects of El Nino and La Nina on the Midwest United States. Background Knowledge: The El Nino-Southern Oscillation
Purpose: Comparing the Effects of El Nino & La Nina on the Midwest (E4.2c) To compare the effects of El Nino and La Nina on the Midwest United States. Background Knowledge: The El Nino-Southern Oscillation
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review
 Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
Chapter 32. Australia & New Zealand
 Chapter 32 Australia & New Zealand Lesson 1: Physical Geography of Australia & New Zealand Landforms Australia lies between the Pacific and Indian Oceans in the Southern Hemisphere. Although an island,
Chapter 32 Australia & New Zealand Lesson 1: Physical Geography of Australia & New Zealand Landforms Australia lies between the Pacific and Indian Oceans in the Southern Hemisphere. Although an island,
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Chapter 32. Australia & New Zealand
 Chapter 32 Australia & New Zealand Lesson 1: Physical Geography of Australia & New Zealand Landforms Australia lies between the Pacific and Indian Oceans in the Southern Hemisphere. Although an island,
Chapter 32 Australia & New Zealand Lesson 1: Physical Geography of Australia & New Zealand Landforms Australia lies between the Pacific and Indian Oceans in the Southern Hemisphere. Although an island,
5th social studies geography (5thsocstud_geography)
 Name: Date: 1. Many of the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains were nomadic people. Why did they move from place to place? A. They were finding new areas to mine. B. They were looking for fertile
Name: Date: 1. Many of the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains were nomadic people. Why did they move from place to place? A. They were finding new areas to mine. B. They were looking for fertile
3) What is the difference between latitude and longitude and what is their affect on local and world weather and climate?
 www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands
 Name Hour Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands Essential Question: How has the physical geography of Asia influenced the development of these regions (i.e. history, population distribution, &
Name Hour Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands Essential Question: How has the physical geography of Asia influenced the development of these regions (i.e. history, population distribution, &
Website Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1
 Website http://websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1 1 Lectures 3 & 4 1. Biogeochemical Cycling 2. Solar Radiation 3. The Atmosphere 4. The Global Ocean 5. Weather and Climate
Website http://websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1 1 Lectures 3 & 4 1. Biogeochemical Cycling 2. Solar Radiation 3. The Atmosphere 4. The Global Ocean 5. Weather and Climate
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 GEOGRAPHY P1 FEBRUARY/MARCH 2015 MARKS: 225 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 12 pages and an annexure of 12 pages. *GEOGE1* Geography/P1 2 INSTRUCTIONS
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 GEOGRAPHY P1 FEBRUARY/MARCH 2015 MARKS: 225 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 12 pages and an annexure of 12 pages. *GEOGE1* Geography/P1 2 INSTRUCTIONS
Tropical Moist Rainforest
 Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India
 NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India Question 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bounded by sea on three sides in
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India Question 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bounded by sea on three sides in
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
El Niño Update. September 30, 2015 by Kaisa Stucke of Confluence Investment Management
 El Niño Update September 30, 2015 by Kaisa Stucke of Confluence Investment Management El Niño Update Meteorologists have been calling for an El Niño event since last year. Current forecasts place the likelihood
El Niño Update September 30, 2015 by Kaisa Stucke of Confluence Investment Management El Niño Update Meteorologists have been calling for an El Niño event since last year. Current forecasts place the likelihood
Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India
 Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India (Q.1) Which are the two broad classification of peninsular plateau? (Q.2) What is a Doab? (Q.3) What is an Alluvial Plain. (Q.4)
Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India (Q.1) Which are the two broad classification of peninsular plateau? (Q.2) What is a Doab? (Q.3) What is an Alluvial Plain. (Q.4)
Queensland Floods- Part A
 Queensland Floods- Part A Floods Flooding is when the water level in a creek, river, lake or the sea rises and covers land that is normally dry. The rise in water can be due to numerous causes, although
Queensland Floods- Part A Floods Flooding is when the water level in a creek, river, lake or the sea rises and covers land that is normally dry. The rise in water can be due to numerous causes, although
What a Hurricane Needs to Develop
 Massive Storms! Hurricanes What a Hurricane Needs to Develop Warm tropical water - at least 80 F High Humidity Light wind Low Pressure Area Form between 5 and 20 latitude Hurricane Ingredients Hurricane
Massive Storms! Hurricanes What a Hurricane Needs to Develop Warm tropical water - at least 80 F High Humidity Light wind Low Pressure Area Form between 5 and 20 latitude Hurricane Ingredients Hurricane
Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long
 Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long period of time Many factors influence weather & climate
Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long period of time Many factors influence weather & climate
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *5500826079* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/12 Paper 1 May/June 2016 2 hours 15 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *5500826079* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/12 Paper 1 May/June 2016 2 hours 15 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long
 Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long period of time Many factors influence weather & climate
Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long period of time Many factors influence weather & climate
Natural Disasters in Member Countries (2002 Summary)
 4.2 Member Countries and their Disaster Characteristics: Table 5: Natural Disasters in Member Countries (2002 Summary) (Country/Disaster Type/Disaster Characteristics) Data Country DisType Count of TotAff
4.2 Member Countries and their Disaster Characteristics: Table 5: Natural Disasters in Member Countries (2002 Summary) (Country/Disaster Type/Disaster Characteristics) Data Country DisType Count of TotAff
Summary and Conclusions
 241 Chapter 10 Summary and Conclusions Kerala is situated in the southern tip of India between 8 15 N and 12 50 N latitude and 74 50 E and 77 30 E longitude. It is popularly known as Gods own country.
241 Chapter 10 Summary and Conclusions Kerala is situated in the southern tip of India between 8 15 N and 12 50 N latitude and 74 50 E and 77 30 E longitude. It is popularly known as Gods own country.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2074084589* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/21 Paper 2 May/June 2016 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2074084589* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/21 Paper 2 May/June 2016 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
World geography 3200/3202 Unit 2 review
 World geography 3200/3202 Unit 2 review 1. Does this statement use the terms revolve & rotate correctly? "Saturn revolves on its axis while several moons rotate around it." 2. Does this statement use the
World geography 3200/3202 Unit 2 review 1. Does this statement use the terms revolve & rotate correctly? "Saturn revolves on its axis while several moons rotate around it." 2. Does this statement use the
Report on Disaster statistics of Nepal
 Report on Disaster statistics of Nepal Submitted by Altaf Rehman Submitted to Dr. Naveed Ahmed University of engineering and technology Peshawar Assignment 1 Section A Registration id 14PWCIV456 Page 1
Report on Disaster statistics of Nepal Submitted by Altaf Rehman Submitted to Dr. Naveed Ahmed University of engineering and technology Peshawar Assignment 1 Section A Registration id 14PWCIV456 Page 1
4th Grade Social Studies First Nine Weeks
 4th Grade Social Studies First Nine Weeks Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Name the mountains that are located in the eastern United States.
4th Grade Social Studies First Nine Weeks Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Name the mountains that are located in the eastern United States.
GEOGRAPHY. H.C.G. - Paper 2
 CLASS IX GEOGRAPHY H.C.G. - Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the answer sheet provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is
CLASS IX GEOGRAPHY H.C.G. - Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the answer sheet provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is
Upcoming Events of Interest
 Ecosystems 31 January 2007 9th class meeting Sky Islands El Nino Ecosystems 31 Jan READINGS: Sky Islands, El Nino (on website) EO Wilson book chapter Friday 02 Feb: EO Wilson book chapter (same as above)
Ecosystems 31 January 2007 9th class meeting Sky Islands El Nino Ecosystems 31 Jan READINGS: Sky Islands, El Nino (on website) EO Wilson book chapter Friday 02 Feb: EO Wilson book chapter (same as above)
SMART NOTES ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1
 ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
Name Date Class. well as the inland, found near the Tropics. 4. In the, or the regions near the Equator, you may find a lush
 WATER, CLIMATE, AND VEGETATION Vocabulary Activity DIRECTIONS: Fill in the Blanks Select a term from below to complete each of the following sentences. CHAPTER 1. The constant movement of water, a process
WATER, CLIMATE, AND VEGETATION Vocabulary Activity DIRECTIONS: Fill in the Blanks Select a term from below to complete each of the following sentences. CHAPTER 1. The constant movement of water, a process
Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China. How does China s geography affect the culture?
 Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China How does China s geography affect the culture? Con$nents of the World Label the continents. Where is China located? Where is China located? In your groups, begin filling
Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China How does China s geography affect the culture? Con$nents of the World Label the continents. Where is China located? Where is China located? In your groups, begin filling
Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes!
 Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes! A. Overview 1. Ocean in Motion -- El Nino and hurricanes We will look at the ocean-atmosphere interactions that cause El Nino and hurricanes. Using vocabulary
Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes! A. Overview 1. Ocean in Motion -- El Nino and hurricanes We will look at the ocean-atmosphere interactions that cause El Nino and hurricanes. Using vocabulary
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 1312/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography A Foundation Tier. Monday 11 June 2007 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 15 minutes
 Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 1 3 1 2 2 F Signature Paper Reference(s) 1312/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography A Foundation Tier Paper 2F Monday 11 June 2007 Afternoon Time: 1 hour
Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 1 3 1 2 2 F Signature Paper Reference(s) 1312/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography A Foundation Tier Paper 2F Monday 11 June 2007 Afternoon Time: 1 hour
How strong does wind have to be to topple a garbage can?
 How strong does wind have to be to topple a garbage can? Imagine winds powerful enough to pick up a truck and toss it the length of a football field. Winds of this extreme sometimes happen in a tornado.
How strong does wind have to be to topple a garbage can? Imagine winds powerful enough to pick up a truck and toss it the length of a football field. Winds of this extreme sometimes happen in a tornado.
Global Wind Patterns
 Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Weather Vs. Climate. Weather Vs. Climate. Chapter 14
 Weather Vs. Climate Chapter 14 Weather: Conditions of the atmosphere at a particular time and place, for short periods of time (days). Climate: Long-term averages of weather (Averaged over 30 yrs). Weather
Weather Vs. Climate Chapter 14 Weather: Conditions of the atmosphere at a particular time and place, for short periods of time (days). Climate: Long-term averages of weather (Averaged over 30 yrs). Weather
Social Studies World Geography Unit 01: Physical Geography
 Social Studies World Geography Unit 01: Physical 012 2013 1 Tectonic plate movement may be caused by all of the following EXCEPT A slab pull B ridge push C convection D magnetism 2 An earthquake is part
Social Studies World Geography Unit 01: Physical 012 2013 1 Tectonic plate movement may be caused by all of the following EXCEPT A slab pull B ridge push C convection D magnetism 2 An earthquake is part
Weather and Climate 1. Elements of the weather
 Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014
 Time:2 hrs ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014 Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will not be allowed to
Time:2 hrs ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014 Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will not be allowed to
TRIBUNE MODEL SCHOOL Syllabus for Session Subject: Social Science CLASS IV
 TRIBUNE MODEL SCHOOL Syllabus for Session 2017-18 Subject: Social Science CLASS IV Text Books 1. Candid New Trends in Social Science 4 2. Candid New Trends in Social Science (Worksheets) 4 Term I (Chapters
TRIBUNE MODEL SCHOOL Syllabus for Session 2017-18 Subject: Social Science CLASS IV Text Books 1. Candid New Trends in Social Science 4 2. Candid New Trends in Social Science (Worksheets) 4 Term I (Chapters
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 1312/4H Edexcel GCSE Geography A Higher Tier. Monday 11 June 2007 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 15 minutes
 Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 1 3 1 2 4 H Signature Paper Reference(s) 1312/4H Edexcel GCSE Geography A Higher Tier Paper 4H Monday 11 June 2007 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 15
Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 1 3 1 2 4 H Signature Paper Reference(s) 1312/4H Edexcel GCSE Geography A Higher Tier Paper 4H Monday 11 June 2007 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 15
World Geography Mid Term Review 2016
 World Geography Mid Term Review 2016 1.Latitude and Longitude Lines of latitude run and. The zero-degree line is the. Line of longitude run and. The zero degree line is called the. 2. Map Projections What
World Geography Mid Term Review 2016 1.Latitude and Longitude Lines of latitude run and. The zero-degree line is the. Line of longitude run and. The zero degree line is called the. 2. Map Projections What
Figure 1. Carbon dioxide time series in the North Pacific Ocean (
 Evidence #1: Since 1950, Earth s atmosphere and oceans have changed. The amount of carbon released to the atmosphere has risen. Dissolved carbon in the ocean has also risen. More carbon has increased ocean
Evidence #1: Since 1950, Earth s atmosphere and oceans have changed. The amount of carbon released to the atmosphere has risen. Dissolved carbon in the ocean has also risen. More carbon has increased ocean
Advanced Hydrology. (Web course)
 Advanced Hydrology (Web course) Subhankar Karmakar Assistant Professor Centre for Environmental Science and Engineering (CESE) Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Powai, Mumbai 400 076 Email: skarmakar@iitb.ac.in
Advanced Hydrology (Web course) Subhankar Karmakar Assistant Professor Centre for Environmental Science and Engineering (CESE) Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Powai, Mumbai 400 076 Email: skarmakar@iitb.ac.in
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does geography impact the distribution of population throughout South and East Asia? I CAN Explain how geography
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does geography impact the distribution of population throughout South and East Asia? I CAN Explain how geography
GEOGRAPHY Practice Answer Paper - 2
 GEOGRAPHY Practice Answer Paper - 2 Q.1) Select the correct option and rewrite the sentence : 4 1) According to Census 2011, the average population density of India is 382 persons per sq.km. 2) The rate
GEOGRAPHY Practice Answer Paper - 2 Q.1) Select the correct option and rewrite the sentence : 4 1) According to Census 2011, the average population density of India is 382 persons per sq.km. 2) The rate
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
M14/3/GEOGR/SP2/ENG/TZ0/XX/Q GEOGRAPHY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2. Monday 19 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 20 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M14/3/GEOGR/SP2/ENG/TZ0/XX/Q 22145203 GEOGRAPHY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2 Monday 19 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 20 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do
M14/3/GEOGR/SP2/ENG/TZ0/XX/Q 22145203 GEOGRAPHY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2 Monday 19 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 20 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do
Formative Test. 4 th Grading in Science VII
 Formative Test 4 th Grading in Science VII I. Latitude and Longitude 1. It is an imaginary line that divides the northern and southern hemispheres. A. Latitude B. Equator C. Longitude D. Tropic of Cancer
Formative Test 4 th Grading in Science VII I. Latitude and Longitude 1. It is an imaginary line that divides the northern and southern hemispheres. A. Latitude B. Equator C. Longitude D. Tropic of Cancer
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles.
 EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
Climate.tgt, Version: 1 1
 Name: Key Concepts Choose the letter of the best answer. (5 points each) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Date: A city located in the middle of North America experiences extreme temperature changes during
Name: Key Concepts Choose the letter of the best answer. (5 points each) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Date: A city located in the middle of North America experiences extreme temperature changes during
Unit 1 Test - Version A
 Unit 1 Test - Version A 1. Approximately, how many degrees of longitude equal one time zone change? a. 5 b. 10 c. 15 d. 20 e. 25 2. The city of Lewisville has a population of 1,000 people living in 100
Unit 1 Test - Version A 1. Approximately, how many degrees of longitude equal one time zone change? a. 5 b. 10 c. 15 d. 20 e. 25 2. The city of Lewisville has a population of 1,000 people living in 100
Geographical location and climatic condition of the
 Geographical location and climatic condition of the study sites North eastern region of India is comprised of eight states namely; Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim
Geographical location and climatic condition of the study sites North eastern region of India is comprised of eight states namely; Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim
lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry
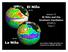 lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry SPATIAL STRUCTURE OF ENSO In 1899, the Indian monsoon failed, leading to drought
lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry SPATIAL STRUCTURE OF ENSO In 1899, the Indian monsoon failed, leading to drought
2. Can you describe how temperature and dissolved solids changes the density of water?
 Unit 4: Oceanography LT 4.1 Density: I can explain the role density plays to help form some currents. #1 Yes I can: 1. Can you explain what density is and how you calculate it? 2. Can you describe how
Unit 4: Oceanography LT 4.1 Density: I can explain the role density plays to help form some currents. #1 Yes I can: 1. Can you explain what density is and how you calculate it? 2. Can you describe how
Name period date assigned date due date returned. Natural Disasters
 Name period date assigned date due date returned Match the following natural disaster to its description. Write the capital letter of the definition in the blank in front of the natural disaster. 1. tornado
Name period date assigned date due date returned Match the following natural disaster to its description. Write the capital letter of the definition in the blank in front of the natural disaster. 1. tornado
Climate vs. Weather. Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Climate: The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
 Weather and Climate Climate vs. Weather Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Temperature, humidity, cloud cover, precipitation, winds, visibility, air pressure, air pollution, etc Climate: The
Weather and Climate Climate vs. Weather Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Temperature, humidity, cloud cover, precipitation, winds, visibility, air pressure, air pollution, etc Climate: The
Contents. Section 1: Climate Factors. Section 2: Climate Types. Section 3: Climate Effects
 Contents Section 1: Climate Factors 1. Weather or Climate?.... 2 2. Elements of Climate.... 4 3. Factors Affecting Climate.... 10 4. Comparing Climates.... 15 5. Quiz 1.... 20 Section 2: Climate Types
Contents Section 1: Climate Factors 1. Weather or Climate?.... 2 2. Elements of Climate.... 4 3. Factors Affecting Climate.... 10 4. Comparing Climates.... 15 5. Quiz 1.... 20 Section 2: Climate Types
World Geography Fall 2013 Semester Review Project
 Reporting Category RC 1: History, Government and Citizenship Standard WG.1 History. The student understands how geography and processes of spatial exchange (diffusion) influenced events in the past and
Reporting Category RC 1: History, Government and Citizenship Standard WG.1 History. The student understands how geography and processes of spatial exchange (diffusion) influenced events in the past and
Downloaded from
 I II III IV V VI Define the following terms:- a) Orbitb) Meteoroids c) Celestial bodies GEOGRAPHY ASSIGNMENTS The Earth In The Solar System d) Satellite e) Comets Give one word answers:- a) Blue planet
I II III IV V VI Define the following terms:- a) Orbitb) Meteoroids c) Celestial bodies GEOGRAPHY ASSIGNMENTS The Earth In The Solar System d) Satellite e) Comets Give one word answers:- a) Blue planet
Physical Geography: Patterns, Processes, and Interactions, Grade 11, University/College Expectations
 Geographic Foundations: Space and Systems SSV.01 explain major theories of the origin and internal structure of the earth; Page 1 SSV.02 demonstrate an understanding of the principal features of the earth
Geographic Foundations: Space and Systems SSV.01 explain major theories of the origin and internal structure of the earth; Page 1 SSV.02 demonstrate an understanding of the principal features of the earth
ENVIRONMENTAL AND DEVELOPMENT ISSUES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS
 GCSE GEOGRAPHY A Sample Assessment Materials 47 GCSE GEOGRAPHY A COMPONENT 2 ENVIRONMENTAL AND DEVELOPMENT ISSUES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS 1 hour 30 minutes Section Question Mark SPaG A B 1 2 Either
GCSE GEOGRAPHY A Sample Assessment Materials 47 GCSE GEOGRAPHY A COMPONENT 2 ENVIRONMENTAL AND DEVELOPMENT ISSUES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS 1 hour 30 minutes Section Question Mark SPaG A B 1 2 Either
Lesson- 6 WEATHER AND CLIMATE
 Lesson- 6 WEATHER AND CLIMATE New Words 1. Heat Zones:- the division of the earth according to the climate. 2. Frigid:- the zone that is the coldest 3. Temperate:- the zone that is neither too hot nor
Lesson- 6 WEATHER AND CLIMATE New Words 1. Heat Zones:- the division of the earth according to the climate. 2. Frigid:- the zone that is the coldest 3. Temperate:- the zone that is neither too hot nor
MEADOWS PRIMARY SCHOOL and NURSERY GEOGRAPHY POLICY
 MEADOWS PRIMARY SCHOOL and NURSERY GEOGRAPHY POLICY Purpose of study The teaching of Geography at Meadows is done by following the 2014 National Curriculum. The planning and teaching of the subject aims
MEADOWS PRIMARY SCHOOL and NURSERY GEOGRAPHY POLICY Purpose of study The teaching of Geography at Meadows is done by following the 2014 National Curriculum. The planning and teaching of the subject aims
4 Changes in Climate. TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why is more land exposed during glacial periods than at other times?
 Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
ENVE203 Environmental Engineering Ecology (Oct 15, 2012)
 ENVE203 Environmental Engineering Ecology (Oct 15, 2012) Elif Soyer Ecosystem and Physical Environment Atmosphere, Ocean, Weather & Climate, Internal Planetary Processes Atmospheric Circulation Different
ENVE203 Environmental Engineering Ecology (Oct 15, 2012) Elif Soyer Ecosystem and Physical Environment Atmosphere, Ocean, Weather & Climate, Internal Planetary Processes Atmospheric Circulation Different
Long Range Forecast Update for 2014 Southwest Monsoon Rainfall
 Earth System Science Organization (ESSO) Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) India Meteorological Department PRESS RELEASE New Delhi, 9 June 2014 Long Update for 2014 Southwest Monsoon Rainfall HIGHLIGHTS
Earth System Science Organization (ESSO) Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) India Meteorological Department PRESS RELEASE New Delhi, 9 June 2014 Long Update for 2014 Southwest Monsoon Rainfall HIGHLIGHTS
Word Cards. 2 map. 1 geographic representation. a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth. a visual representation of an area
 Name: Date: Hour: Word Cards 1 geographic representation a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth Example: A map is a representation of an actual location or place. 2 map a visual
Name: Date: Hour: Word Cards 1 geographic representation a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth Example: A map is a representation of an actual location or place. 2 map a visual
GLOBAL CLIMATES FOCUS
 which you will learn more about in Chapter 6. Refer to the climate map and chart on pages 28-29 as you read the rest of this chapter. FOCUS GLOBAL CLIMATES What are the major influences on climate? Where
which you will learn more about in Chapter 6. Refer to the climate map and chart on pages 28-29 as you read the rest of this chapter. FOCUS GLOBAL CLIMATES What are the major influences on climate? Where
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3640589177* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/22 Paper 2 May/June 2016 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3640589177* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/22 Paper 2 May/June 2016 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
