Towards a global climatology of cloud microphysical properties and why MODIS does not like sunsets (nor sunrise!)
|
|
|
- Barbra Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Towards a global climatology of cloud microphysical properties and why MODIS does not like sunsets (nor sunrise!) Daniel Grosvenor & Robert Wood (U. Washington)
2 Using scattered solar radiation to infer cloud properties ττ = ββ zz dddd ββ zz NN dd rr dddddddddddddd 2 rr ee kk 1 3 rr dddddddddddddd Properties are retrieved based on what reflectance we would expect to see from plane parallel clouds Optical depth (τ), droplet size (r e ), liquid water content (LWC) or path (LWP), droplet concentrations 2
3 Why do we want a MODIS droplet concentration (Nd) climatology? MODIS provides global coverage and has a long data record :- TERRA satellite since 2000, AQUA since mid 2002 This would be a very valuable dataset, e.g. for investigating Aerosol Indirect Effects (AIEs) and their representation in GCMs The representation of AIEs in climate models is complex, involving interactions between:- Cloud microphysics. Turbulent transport. Radiation Aerosol production, transport and removal. Precipitation Therefore it provides a strong test for climate models Marked differences in N d exist between different GCMs (Quaas et al., ACP, 2009, Ming et al., JAS, 2006, Gettelman et al., J. Clim, 2008) demonstrating a clear lack of understanding of the key controls Many climate models fix lower limits for N d (Hoose et al., GRL, 2009, Quaas et al., ACP, 2009) Has been shown to affect the strength of the AIE (Quaas et al., ACP, 2009) across GCMs In one model removing this limit changed the global AIE by 80% (Hoose et al., GRL, 2009). However, the robustness of the satellite data also needs to be assessed.
4 What can solar reflection tell us about clouds? Use a wavelength where ωω 0 = 1 for any droplet size, can infer the extinction and hence ττ Use a wavelength where ωω 0 is a function of droplet size to infer absorption and hence rr ee (near to cloud top) 0.86μm 1.6μm 2.1μm 3.7μm τ & r e are useful quantities for which to calculate radiative transfer But also tell us about fundamental cloud properties such as droplet sizes & concentrations, LWP
5 Obtaining droplet concentrations from MODIS The method follows that of Boers et al. (JGR, 2006) and Bennartz & Harshvardhan (JGR, 2007) and uses Cloud Optical Thickness and effecitive radius Daytime only It depends on a few assumptions:- The LWC profile within a cloud is a constant fraction of adiabatic: c = dlwc/dz = constant (for a given cloud top temperature) The droplet concentration within a cloud is vertically constant k = (r v /r e ) 3 = constant = 0.8 Scattering efficiency Q = 2 z z Given these assumptions we can relate r e at cloud top, τ and N d for our model cloud Cloud base LWC (g m -3 ) N d (cm -3 ) = Cloud Optical Thickness (Depth) r e = Effective radius Clouds are triangle shaped!
6 Comparisons with aircraft in SE Pacific Aircraft comparisons suggest very good accuracy for low clouds (e.g. stratocumulus decks, e.g. Painemal & Zuidema, JGR, 2011 But the analysis was performed in horizontally homogeneous clouds (stratocumulus) Painemal & Zuidema, JGR, 2011 Clouds are triangle shaped! However, are sub-adiabatic Cloud top Painemal & Zuidema, JGR, 2011 N d constant with height Cloud base
7 Comparisons with aircraft in SE Pacific Aircraft comparisons suggest very good accuracy for low clouds (e.g. stratocumulus decks, e.g. Painemal & Zuidema, JGR, 2011 But the analysis was performed in horizontally homogeneous clouds (stratocumulus) However, the effective radius was systematically too high by 15-20% But what about the good match for N d given the sensitivity of N d to r e? β = 0.7 sub-adiabaticity β The good match between aircraft and satellite was due cancellation of biases in r e, c and k in the formula above
8 10 km ` 2300 km ~ 3km MODIS 1 km pixels ~100 km ~475 km High resolution visible wavelength image from Eagle and Hawk hyperspectral imager courtesy of Nick King SE Pacific (VOCALS stratocumulus cloud)
9 Zhang, JGR, 2012 from LES model 100m resolution (blue asterisks) Optical Depths 100m LES retrievals R 2.1μm & R 0.86μm are reflectances fraction of incident light reflected in a given direction (MODIS measures these) r eff mean r e from LES Look-up table (LUT) elements = 19 μm based on modeled retrieved after averaging to plane 1 km parallel = 25 μm clouds Considering 8x8 LES retrievals over 0.8x0.8 km area (~MODIS pixel size) Generally: R 2.1μm, r e R 0.86μm, τ Effect is larger with more τ variation But depends on apparent r e being uniform within pixel
10 VOCALS POLDER comparisons Have co-located MODIS L2 1x1 o boxes with POLDER measurements (cloud fraction > 80%) POLDER uses polarization to measure r e An independent technique that should not be subject to artifacts Mean for o S Different MODIS wavelengths agree near the coast (where clouds are generally more homogeneous) But are ~10-30 % too high Clouds more heterogeneous Clouds more homogeneous Further west (clouds more heterogeneous) the 3.7μm retrievals become lower
11 Look-up table (LUT) based on modeled plane parallel clouds Optical Depths r eff mean r e from 2 points = ~22 μm retrieved after averaging to 1 km = 14.5 μm Previous increase depended on apparent r e being uniform within pixel Not always the case
12 Marshak (2006) simulations (at fairly high Solar Zenith Angle of 60 o ) r e decreased as averaging scale increased r e is too high to begin with though likely due to the same 3D radiative effects (shadowing & illumination) that cause the decrease with averaging (of averaging) This type of sub-pixel averaging effect, which causes an r e decrease may be playing a role in the heterogeneous clouds seen in POLDER comparison
13 VOCALS POLDER comparisons Have co-located MODIS L2 1x1 o boxes with POLDER measurements (cloud fraction > 80%) POLDER uses polarization to measure r e An independent technique that should not be subject to artifacts Mean for o S Different MODIS wavelengths agree near the coast (where clouds are generally more homogeneous) But are ~10-30 % too high Clouds more heterogeneous Clouds more homogeneous Further west (clouds more heterogeneous) the 3.7μm retrievals become lower
14 Global mean droplet concentration from MODIS using Level-3 product For liquid clouds with >80% 1x1 o cloud fraction
15 The N d climatology using the standard Level-3 product Unexpected seasonal cycle in Nd much higher in DJF than in JJA Contrary to what would be expected based on aerosol concentrations, although there are few CCN climatologies Are the retrievals flawed? Possible causes of this result:- Seasonal cycle of cloud height / type? SZA Ice below clouds? Surface characteristics (e.g. sea ice)? High Solar Zenith Angles (SZA) in winter (Sun is low in the sky)? Dec, Jan, Feb Cloud fraction >80%, y2007 Jun, July, Aug Nd (cm -3 )
16 The MODIS Level-3 product MODIS Level-3 : a 1x1 o gridded daily product Swaths start to overlap at latitudes higher than 23 o Therefore some locations will experience more than one consecutive overpass The possible number increases with latitude Polar regions can experience several overpasses per day Therefore measurements taken at different local times of day & solar zenith angles All daily measurements are averaged together for the gridded Level-3 product Consecutive orbits start to overlap Several consecutive orbits overlap near the poles
17 20 th December, 2007 (single day), Terra satellite Max Solar Zenith Angle Max minus Min Solar Zenith Angle Antarctica:- SZA (degrees) Maximum Solar Zenith Angle (SZA) Can see the effect of overlapping orbits High values obtained over Europe (winter) and over Antarctica (summer) But the same latitude will experience a range of max SZA depending on orbit overlap Near Antarctica there is a difference of almost 35 o between the min and max SZA on this day
18 Estimating the Solar Zenith Angle (SZA) effect on N d Scandinavia Sea-ice areal coverage (%) Have processed swaths for this region for the period th June, (Aqua and Terra) Cloud height distributions for this period and region for low and high Solar Zenith Angle ranges Very similar suggesting little physical SZA influence CALIPSO agrees with low cloud mode, but shows that MODIS misses high clouds Fairly difficult using the MODIS record due to seasonal variations of SZA with time High latitudes receive multiple overpasses per day Therefore a range of SZA (diurnal cycle) But sea-ice is ubiquitous there Except the region north of Norway - no sea-ice in the summer
19 Results optical depth vs SZA Fairly dramatic increase in mean optical depth with SZA At both low and high viewing angles (sensza) High sensza results suggest constant behavior up to SZA~65 o Main caveat could this be a real physical change with diurnal cycle? O Dell (2008) study using microwave suggests that LWP diurnal cycle is very small in this region
20 Results effective radius vs SZA At low SZA and low sensor angle all three wavelengths agree Large spread at high SZA Reduction in r e with SZA for 2.1 and 3.7μm, but not 1.6 μm Percentage reductions less than for optical depth
21 Results droplet concentration vs SZA Can get a considerable N d increase (up to 60%) Increase is largest for the 3.7μm band Sensitivity analysis shows that the majority of this is driven by the large optical depth increase, despite the sensitivity of N d to r e Except for the more heterogeneous clouds (as quantified from cloud top temperature variability) for 3.7 μm
22 More light scattered in the forward direction Reflectance at zenith Reduction in zenith reflectance Plane parallel cloud
23 Reflectance at zenith More light scattered in the forward direction More light scattered in the zenith direction (relative to plane parallel cloud) Real cloud Plane parallel cloud
24 Varnai & Davies, JAS, 1999 using artifically generated cloud field with a mean τ of 10 SW (e.g. 0.86μm) zenith reflectance Cloud Top Height variability Variable extinction Homogeneous cloud (plane parallel) Real clouds How MODIS assumes clouds behave Low SZA High SZA Plane parallel model (used for retrievals) predicts that R 0.86μm decreases with Solar Zenith Angle (SZA) however, for real clouds it increases Since R 0.86μm means τ if MODIS measures a high R 0.86μm at high SZA it will assume that the cloud had a very high τ
25 The reprocessing of individual swaths We have re-processed individual Level-2 swaths into a Level-3 like daily 1x1 degree dataset Global Period Nov 2006 to end of 2007 Various screenings including for Solar Zenith Angle (<65) (No daily averaging until after screening)
26 The climatology using the standard Level-3 product - High values near Antarctica Sea-ice extent at end of period Nd (cm -3 ) Sea-ice data source:- Cavalieri, D., C. Parkinson, P. Gloersen, and H. J. Zwally. 1996, updated yearly. Sea Ice Concentrations from Nimbus-7 SMMR and DMSP SSM/I-SSMIS Passive Microwave Data, 1 st Dec 1 st Mar. Boulder, Colorado USA: National Snow and Ice Data Center. Digital media. DJF 2006/2007 Sea-ice extent at start of period Higher Nd in the regions where sea-ice remains all summer But high Solar Zenith Angle could also be a factor
27 All Solar Zenith Angles (SZA) SZA < 65 Nd (cm -3 ) DJF 2006/2007 SZA > 65
28 Considering single months (for SZA<65 only) Jan 2007 High Nd values remain outside of sea-ice regions Undetected sea-ice? Other retrieval problems? Phytoplankton blooms? Nd (cm -3 ) Red lines indicate sea-ice extent:- Solid: start of period Dashed: end of period Feb 2007 Nd (cm -3 )
29 Southern Ocean seasonal cycle If include high Solar Zenith Angles then get elevated values in winter Removing them leaves us with no data in winter, but seasonal cycle is consistent with the in-situ observations Indicative of algae blooms in summer causing elevated CCN concentrations? ALL Solar Zenith Angles Low Solar Zenith Angles only
30 All SZA Dec, Jan, Feb Jun, July, Aug SZA <65 Dec, Jan, Feb Jun, July, Aug Nd (cm-3)
31 Seasonal cloud variations CALIPSO/CloudSat daytime low cloud fraction Dec, Jan, Feb Jun, July, Aug Fewer low clouds in JJA relative to DJF low clouds likely more polluted Dec, Jan, Feb Nd (cm -3 )
32 DJF JJA Nd (cm-3) CALIPSO Daytime Cloud Top Height PDF Significant change in the mode of cloud top heights between summer and winter More low clouds in winter likely the reason for more polluted clouds
33 GCM model evaluation MODIS obs CAM5 1 degree CAM-CLUBB 1 degree Droplet Concentration (cm -3 ) AM3-CLUBB 0.5 degree Red circles are VOCALS aircraft obs (so a different time period, but still a similar result to MODIS) CAM-CLUBB Longitude transects along 20S (VOCALS stratocumulus region) CAM-CLUBB removes the high Nd values in the stratocumulus to cumulus transition regions AM3 values are too low both base (not shown) and CLUBB CCN are too low despite sulfate loading being too low!
34 Conclusions (1) MODIS can be used to estimate cloud droplet concentrations using observed optical depths (τ) and effective radii (r e ) The assumptions made seem to hold up at least in homogeneous clouds with little precipitation However, POLDER shows that in such clouds MODIS overestimates effective radius one factor may be sub-pixel (1 km) variability In more heterogeneous clouds MODIS r e reduces to be approximately correct, or too small (esp. for the 3.7μm wavelength) MODIS retrievals of optical depth, effective radius and droplet concentrations are likely dubious at high Solar Zenith Angles (SZAs) 3D radiative effects are likely to blame both directly (due to increased upward scatter relative to the plane parallel model) and through their effect on the sub-pixel reflectances (through averaging effects) The reduction in r e at high SZA for 3.7μm is similar to that seen in heterogeneous clouds at low SZA Could real cloud heterogeneity at low SZA be having a similar effect to radiative heterogeneity at high SZA?
35 Conclusions (2) Regions around UK showed wintertime reduction with new low SZA dataset High wintertime values near China likely the result of real cloud top height variations High N d values around Antarctica not solely due to high SZA likely sea-ice is the main cause of the increase Although some high N d regions still remain phytoplankton blooms? Removing high SZA retrievals is important, especially when looking at seasonal changes, or particular times of the year MODIS N d retrievals in the Southern Ocean are consistent with a seasonal cycle of CCN that comprises higher concentrations in summer (but only when use exclude higher SZA retrievals) Is this caused by algae-like lifeforms / phytoplankton?
36 DJF JJA Nd (cm-3) CALIPSO Daytime Cloud Top Height PDF MODIS Cloud Top Height PDF (from Cloud Top Temp & AMSRE SST) MODIS Mean Nd vs Cloud Top Height
37
38
39
The MODIS Cloud Data Record
 The MODIS Cloud Data Record Brent C. Maddux 1,2 Steve Platnick 3, Steven A. Ackerman 1 Paul Menzel 1, Kathy Strabala 1, Richard Frey 1, 1 Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, 2 Department
The MODIS Cloud Data Record Brent C. Maddux 1,2 Steve Platnick 3, Steven A. Ackerman 1 Paul Menzel 1, Kathy Strabala 1, Richard Frey 1, 1 Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, 2 Department
Observed Southern Ocean Cloud Properties and Shortwave Reflection
 Observed Southern Ocean Cloud Properties and Shortwave Reflection Daniel T McCoy* 1, Dennis L Hartmann 1, and Daniel P Grosvenor 2 University of Washington 1 University of Leeds 2 *dtmccoy@atmosuwedu Introduction
Observed Southern Ocean Cloud Properties and Shortwave Reflection Daniel T McCoy* 1, Dennis L Hartmann 1, and Daniel P Grosvenor 2 University of Washington 1 University of Leeds 2 *dtmccoy@atmosuwedu Introduction
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations. S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences.
 The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs
 Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs Ulrike Lohmann ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science Reading, 13.11.2006 Acknowledgements: Sylvaine Ferrachat, Corinna Hoose, Erich Roeckner,
Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs Ulrike Lohmann ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science Reading, 13.11.2006 Acknowledgements: Sylvaine Ferrachat, Corinna Hoose, Erich Roeckner,
Warm rain and climate: VOCALS, CloudSat, Models. Robert Wood University of Washington
 Warm rain and climate: VOCALS, CloudSat, Models Robert Wood University of Washington Warm rain a missing climatology Image: NASA GSFC Shipboard remote sensing shows frequent precipitation from shallow
Warm rain and climate: VOCALS, CloudSat, Models Robert Wood University of Washington Warm rain a missing climatology Image: NASA GSFC Shipboard remote sensing shows frequent precipitation from shallow
Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2214 Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds Y.-C. Chen, M. W. Christensen, G. L. Stephens, and J. H. Seinfeld
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2214 Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds Y.-C. Chen, M. W. Christensen, G. L. Stephens, and J. H. Seinfeld
Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
 1/23 Remote sensing of atmospheric aerosol, clouds and aerosol-cloud interactions. Bremen, 16-19 December 2013 Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
1/23 Remote sensing of atmospheric aerosol, clouds and aerosol-cloud interactions. Bremen, 16-19 December 2013 Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
Analysis of Antarctic Sea Ice Extent based on NIC and AMSR-E data Burcu Cicek and Penelope Wagner
 Analysis of Antarctic Sea Ice Extent based on NIC and AMSR-E data Burcu Cicek and Penelope Wagner 1. Abstract The extent of the Antarctica sea ice is not accurately defined only using low resolution microwave
Analysis of Antarctic Sea Ice Extent based on NIC and AMSR-E data Burcu Cicek and Penelope Wagner 1. Abstract The extent of the Antarctica sea ice is not accurately defined only using low resolution microwave
Robert Wood C. S. Bretherton and D. L. Hartmann University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
 P2.14 DIURNAL CYCLE OF LIQUID WATER PATH OVER THE SUBTROPICAL AND TROPICAL OCEANS Robert Wood C. S. Bretherton and D. L. Hartmann University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 1. INTRODUCTION For numerical
P2.14 DIURNAL CYCLE OF LIQUID WATER PATH OVER THE SUBTROPICAL AND TROPICAL OCEANS Robert Wood C. S. Bretherton and D. L. Hartmann University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 1. INTRODUCTION For numerical
CALIPSO measurements of clouds, aerosols, ocean surface mean square slopes, and phytoplankton backscatter
 CALIPSO measurements of clouds, aerosols, ocean surface mean square slopes, and phytoplankton backscatter Yongxiang Hu, Chris Hostetler, Kuanman Xu,, and CALIPSO team NASA Langley Research Center Alain
CALIPSO measurements of clouds, aerosols, ocean surface mean square slopes, and phytoplankton backscatter Yongxiang Hu, Chris Hostetler, Kuanman Xu,, and CALIPSO team NASA Langley Research Center Alain
Comparison of MODIS cloud microphysical properties with in-situ measurements over the Southeast Pacific
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 12, 11261 11273, 2012 doi:10.5194/acp-12-11261-2012 Author(s) 2012. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Comparison of MODIS cloud microphysical properties
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 12, 11261 11273, 2012 doi:10.5194/acp-12-11261-2012 Author(s) 2012. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Comparison of MODIS cloud microphysical properties
Passive Microwave Sea Ice Concentration Climate Data Record
 Passive Microwave Sea Ice Concentration Climate Data Record 1. Intent of This Document and POC 1a) This document is intended for users who wish to compare satellite derived observations with climate model
Passive Microwave Sea Ice Concentration Climate Data Record 1. Intent of This Document and POC 1a) This document is intended for users who wish to compare satellite derived observations with climate model
Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements
 Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements Norman G. Loeb Hampton University/NASA Langley Research Center Bruce
Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements Norman G. Loeb Hampton University/NASA Langley Research Center Bruce
Developments in CALIOP Aerosol Products. Dave Winker
 Developments in CALIOP Aerosol Products Dave Winker NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Winker - 1 Outline Level 3 aerosol product (beta-version) Version 4 Level 1 product A few CALIOP assimilation
Developments in CALIOP Aerosol Products Dave Winker NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Winker - 1 Outline Level 3 aerosol product (beta-version) Version 4 Level 1 product A few CALIOP assimilation
A Novel Cirrus Cloud Retrieval Method For GCM High Cloud Validations
 A Novel Cirrus Cloud Retrieval Method For GCM High Cloud Validations David Mitchell Anne Garnier Melody Avery Desert Research Institute Science Systems & Applications, Inc. NASA Langley Reno, Nevada Hampton,
A Novel Cirrus Cloud Retrieval Method For GCM High Cloud Validations David Mitchell Anne Garnier Melody Avery Desert Research Institute Science Systems & Applications, Inc. NASA Langley Reno, Nevada Hampton,
How is precipitation from low clouds important for climate?
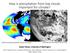 How is precipitation from low clouds important for climate? CloudSat estimated precipitation rate from low clouds Low clouds over the SE Pacific, Nov 11 th 2014 Robert Wood, University of Washington With
How is precipitation from low clouds important for climate? CloudSat estimated precipitation rate from low clouds Low clouds over the SE Pacific, Nov 11 th 2014 Robert Wood, University of Washington With
An Observational Study of the Relationship between Cloud, Aerosol and Meteorology in Marine Stratus Regions
 An Observational Study of the Relationship between Cloud, Aerosol and Meteorology in Marine Stratus Regions Norman G. Loeb NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Oct 18 th, 2006, AeroCom Meeting (Virginia
An Observational Study of the Relationship between Cloud, Aerosol and Meteorology in Marine Stratus Regions Norman G. Loeb NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Oct 18 th, 2006, AeroCom Meeting (Virginia
Long-Term Time Series of Water Vapour Total Columns from GOME, SCIAMACHY and GOME-2
 Graphics: ESA Graphics: ESA Graphics: ESA Long-Term Time Series of Water Vapour Total Columns from GOME, SCIAMACHY and GOME-2 S. Noël, S. Mieruch, H. Bovensmann, J. P. Burrows Institute of Environmental
Graphics: ESA Graphics: ESA Graphics: ESA Long-Term Time Series of Water Vapour Total Columns from GOME, SCIAMACHY and GOME-2 S. Noël, S. Mieruch, H. Bovensmann, J. P. Burrows Institute of Environmental
Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change
 Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change Jim Coakley College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Earth s Energy Budget and Global Temperature Incident Sunlight 340 Wm -2 Reflected Sunlight 100 Wm -2 Emitted Terrestrial
Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change Jim Coakley College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Earth s Energy Budget and Global Temperature Incident Sunlight 340 Wm -2 Reflected Sunlight 100 Wm -2 Emitted Terrestrial
Simulated Radiances for OMI
 Simulated Radiances for OMI document: KNMI-OMI-2000-004 version: 1.0 date: 11 February 2000 author: J.P. Veefkind approved: G.H.J. van den Oord checked: J. de Haan Index 0. Abstract 1. Introduction 2.
Simulated Radiances for OMI document: KNMI-OMI-2000-004 version: 1.0 date: 11 February 2000 author: J.P. Veefkind approved: G.H.J. van den Oord checked: J. de Haan Index 0. Abstract 1. Introduction 2.
Standalone simulations: CAM3, CAM4 and CAM5
 Standalone simulations: CAM3, and CAM5 CAM5 Model Development Team Cécile Hannay, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman, Sungsu Park, Joe Tribbia, Peter Lauritzen, Andrew Conley, Hugh Morrison, Phil Rasch, Steve
Standalone simulations: CAM3, and CAM5 CAM5 Model Development Team Cécile Hannay, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman, Sungsu Park, Joe Tribbia, Peter Lauritzen, Andrew Conley, Hugh Morrison, Phil Rasch, Steve
A Time Series of Photo-synthetically Available Radiation at the Ocean Surface from SeaWiFS and MODIS Data
 A Time Series of Photo-synthetically Available Radiation at the Ocean Surface from SeaWiFS and MODIS Data Robert Frouin* a, John McPherson a, Kyozo Ueyoshi a, Bryan A. Franz b a Scripps Institution of
A Time Series of Photo-synthetically Available Radiation at the Ocean Surface from SeaWiFS and MODIS Data Robert Frouin* a, John McPherson a, Kyozo Ueyoshi a, Bryan A. Franz b a Scripps Institution of
VIIRS Radiometric Calibration for Reflective Solar Bands: Antarctic Dome C Site and Simultaneous Nadir Overpass Observations
 VIIRS Radiometric Calibration for Reflective Solar Bands: Antarctic Dome C Site and Simultaneous Nadir Overpass Observations Slawomir Blonski, * Changyong Cao, Sirish Uprety, ** and Xi Shao * NOAA NESDIS
VIIRS Radiometric Calibration for Reflective Solar Bands: Antarctic Dome C Site and Simultaneous Nadir Overpass Observations Slawomir Blonski, * Changyong Cao, Sirish Uprety, ** and Xi Shao * NOAA NESDIS
An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics
 An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics M. D. Shupe Science and Technology Corporation National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Environmental Technology Laboratory Boulder, Colorado T. Uttal
An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics M. D. Shupe Science and Technology Corporation National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Environmental Technology Laboratory Boulder, Colorado T. Uttal
Atmospheric Boundary Layer over Land, Ocean, and Ice. Xubin Zeng, Michael Brunke, Josh Welty, Patrick Broxton University of Arizona
 Atmospheric Boundary Layer over Land, Ocean, and Ice Xubin Zeng, Michael Brunke, Josh Welty, Patrick Broxton University of Arizona xubin@email.arizona.edu 24 October 2017 Future of ABL Observations Workshop
Atmospheric Boundary Layer over Land, Ocean, and Ice Xubin Zeng, Michael Brunke, Josh Welty, Patrick Broxton University of Arizona xubin@email.arizona.edu 24 October 2017 Future of ABL Observations Workshop
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: The CERES-MODIS retrieved cloud microphysical properties agree well with ARM retrievals under both snow-free and snow
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: The CERES-MODIS retrieved cloud microphysical properties agree well with ARM retrievals under both snow-free and snow
Interpretation of Polar-orbiting Satellite Observations. Atmospheric Instrumentation
 Interpretation of Polar-orbiting Satellite Observations Outline Polar-Orbiting Observations: Review of Polar-Orbiting Satellite Systems Overview of Currently Active Satellites / Sensors Overview of Sensor
Interpretation of Polar-orbiting Satellite Observations Outline Polar-Orbiting Observations: Review of Polar-Orbiting Satellite Systems Overview of Currently Active Satellites / Sensors Overview of Sensor
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114, D05210, doi: /2008jd010589, 2009
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jd010589, 2009 Estimate of the impact of absorbing aerosol over cloud on the MODIS retrievals of cloud optical thickness and effective radius
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jd010589, 2009 Estimate of the impact of absorbing aerosol over cloud on the MODIS retrievals of cloud optical thickness and effective radius
Influence of clouds on radiative fluxes in the Arctic. J. English, J. Kay, A. Gettelman CESM Workshop / PCWG Meeting June 20, 2012
 Influence of clouds on radiative fluxes in the Arctic J. English, J. Kay, A. Gettelman CESM Workshop / PCWG Meeting June 20, 2012 The complexity of arctic clouds Arctic Mixed-Phase Clouds Morrison et al.,
Influence of clouds on radiative fluxes in the Arctic J. English, J. Kay, A. Gettelman CESM Workshop / PCWG Meeting June 20, 2012 The complexity of arctic clouds Arctic Mixed-Phase Clouds Morrison et al.,
A new perspective on aerosol direct radiative effects in South Atlantic and Southern Africa
 A new perspective on aerosol direct radiative effects in South Atlantic and Southern Africa Ian Chang and Sundar A. Christopher Department of Atmospheric Science University of Alabama in Huntsville, U.S.A.
A new perspective on aerosol direct radiative effects in South Atlantic and Southern Africa Ian Chang and Sundar A. Christopher Department of Atmospheric Science University of Alabama in Huntsville, U.S.A.
Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements
 Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements Ching-Yuang Huang 1,2, Wen-Hsin Teng 1, Shu-Peng Ho 3, Ying-Hwa Kuo 3, and Xin-Jia Zhou 3 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements Ching-Yuang Huang 1,2, Wen-Hsin Teng 1, Shu-Peng Ho 3, Ying-Hwa Kuo 3, and Xin-Jia Zhou 3 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
Measurements are infrequent in this region due to difficulty in making both ship- and air-based measurements Natural pristine region far removed from
 PLANNED OBSERVATIONAL CAMPAIGNS OVER THE SOUTHERN OCEANS FOR DETERMINING THE ROLES OF CLOUDS, AEROSOLS AND RADIATION IN THE CLIMATE SYSTEM: SOCRATES, MARCUS & MICRE G. McFarquhar, U. Illinois C. Bretherton,
PLANNED OBSERVATIONAL CAMPAIGNS OVER THE SOUTHERN OCEANS FOR DETERMINING THE ROLES OF CLOUDS, AEROSOLS AND RADIATION IN THE CLIMATE SYSTEM: SOCRATES, MARCUS & MICRE G. McFarquhar, U. Illinois C. Bretherton,
Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch
 Improvements in CAM5 : Moist Turbulence, Shallow Convection, and Cloud Macrophysics AMWG Meeting Feb. 10. 2010 Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch CGD.NCAR University of Washington, Seattle,
Improvements in CAM5 : Moist Turbulence, Shallow Convection, and Cloud Macrophysics AMWG Meeting Feb. 10. 2010 Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch CGD.NCAR University of Washington, Seattle,
Characterization of the Present-Day Arctic Atmosphere in CCSM4
 Characterization of the Present-Day Arctic Atmosphere in CCSM4 Gijs de Boer 1, Bill Chapman 2, Jennifer Kay 3, Brian Medeiros 3, Matthew Shupe 4, Steve Vavrus, and John Walsh 6 (1) (2) (3) (4) ESRL ()
Characterization of the Present-Day Arctic Atmosphere in CCSM4 Gijs de Boer 1, Bill Chapman 2, Jennifer Kay 3, Brian Medeiros 3, Matthew Shupe 4, Steve Vavrus, and John Walsh 6 (1) (2) (3) (4) ESRL ()
Exploration of California High Resolution Snowpack Modeling with Realistic Surface-Atmospheric Radiation Physics
 Exploration of California High Resolution Snowpack Modeling with Realistic Surface-Atmospheric Radiation Physics Chaincy Kuo, Alan Rhoades, Daniel Feldman Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory AMS 15th
Exploration of California High Resolution Snowpack Modeling with Realistic Surface-Atmospheric Radiation Physics Chaincy Kuo, Alan Rhoades, Daniel Feldman Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory AMS 15th
On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties. Science Systems and Applications, Inc., Hampton, Virginia 2
 JP1.10 On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties Fu-Lung Chang 1 *, Patrick Minnis 2, Sunny Sun-Mack 1, Louis Nguyen 1, Yan Chen 2 1 Science Systems and Applications, Inc.,
JP1.10 On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties Fu-Lung Chang 1 *, Patrick Minnis 2, Sunny Sun-Mack 1, Louis Nguyen 1, Yan Chen 2 1 Science Systems and Applications, Inc.,
+SOI Neutral SOI -SOI. Melt+ Melt- Melt+ Melt- Melt+ Melt- +SAM 1 (0.76) 6 (3.02) 1 (1.13) 5 (4.92) 1 (2.27) 0 (1.89) 14
 Supplementary Table 1. Contingency table tallying the respective counts of positive and negative surface melt index anomalies in the Ross sector as a function of the signs of the Southern Annular Mode
Supplementary Table 1. Contingency table tallying the respective counts of positive and negative surface melt index anomalies in the Ross sector as a function of the signs of the Southern Annular Mode
Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions
 Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions William K. M. Lau NASA/GSFC Co-authors: K. M. Kim, M. Chin, P. Colarco, A. DaSilva Atmospheric loading of Saharan dust Annual emission
Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions William K. M. Lau NASA/GSFC Co-authors: K. M. Kim, M. Chin, P. Colarco, A. DaSilva Atmospheric loading of Saharan dust Annual emission
Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
 Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Sea of Okhotsk, MODIS image Feb. 6, 2007, NASA Earth Observatory Arctic Aerosol Remote Sensing Overview
Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Sea of Okhotsk, MODIS image Feb. 6, 2007, NASA Earth Observatory Arctic Aerosol Remote Sensing Overview
A synthesis of published VOCALS studies on marine boundary layer and cloud structure along 20S
 A synthesis of published VOCALS studies on marine boundary layer and cloud structure along 20S Chris Bretherton Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington VOCALS RF05, 72W 20S Work summarized
A synthesis of published VOCALS studies on marine boundary layer and cloud structure along 20S Chris Bretherton Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington VOCALS RF05, 72W 20S Work summarized
Combined observational and modeling based study of the aerosol indirect effect
 Author(s) 2006. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Combined observational and modeling based study of the aerosol indirect effect T. Storelvmo 1,
Author(s) 2006. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Combined observational and modeling based study of the aerosol indirect effect T. Storelvmo 1,
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
New capabilities with high resolution cloud micro-structure facilitated by MTG 2.3 um channel
 Slide 19 November 2016, V1.0 New capabilities with high resolution cloud micro-structure facilitated by MTG 2.3 um channel Author: Daniel Rosenfeld The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJ) daniel.rosenfeld@huji.ac.il
Slide 19 November 2016, V1.0 New capabilities with high resolution cloud micro-structure facilitated by MTG 2.3 um channel Author: Daniel Rosenfeld The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJ) daniel.rosenfeld@huji.ac.il
Aerosol Retrieved from MODIS: Algorithm, Products, Validation and the Future
 Aerosol Retrieved from MODIS: Algorithm, Products, Validation and the Future Presented by: Rob Levy Re-presenting NASA-GSFC s MODIS aerosol team: Y. Kaufman, L. Remer, A. Chu,, C. Ichoku,, R. Kleidman,,
Aerosol Retrieved from MODIS: Algorithm, Products, Validation and the Future Presented by: Rob Levy Re-presenting NASA-GSFC s MODIS aerosol team: Y. Kaufman, L. Remer, A. Chu,, C. Ichoku,, R. Kleidman,,
The effects of dust emission on the trans- Pacific transport of Asian dust in the CESM
 The effects of dust emission on the trans- Pacific transport of Asian dust in the CESM Mingxuan Wu, Xiaohong Liu, Zhien Wang, Kang Yang, Chenglai Wu University of Wyoming Kai Zhang, Hailong Wang Pacific
The effects of dust emission on the trans- Pacific transport of Asian dust in the CESM Mingxuan Wu, Xiaohong Liu, Zhien Wang, Kang Yang, Chenglai Wu University of Wyoming Kai Zhang, Hailong Wang Pacific
Ultra clean layers and low albedo ( grey ) clouds in CSET
 CSET RF11, near Hawaii Ultra clean layers and low albedo ( grey ) clouds in CSET Robert Wood, University of Washington Paquita Zuidema, Chris Bretherton, Kuan Ting (Andy) O, Hans Mohrmann, Isabel McCoy,
CSET RF11, near Hawaii Ultra clean layers and low albedo ( grey ) clouds in CSET Robert Wood, University of Washington Paquita Zuidema, Chris Bretherton, Kuan Ting (Andy) O, Hans Mohrmann, Isabel McCoy,
Assessing the Radiative Impact of Clouds of Low Optical Depth
 Assessing the Radiative Impact of Clouds of Low Optical Depth W. O'Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California Santa Barbara, California C. Gautier
Assessing the Radiative Impact of Clouds of Low Optical Depth W. O'Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California Santa Barbara, California C. Gautier
Aerosol-Cloud-Climate Interaction: A Case Study from the Indian Ocean. Sagnik Dey
 Aerosol-Cloud-Climate Interaction: A Case Study from the Indian Ocean Sagnik Dey Centre for Atmospheric Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Delhi sagnik@cas.iitd.ac.in Content Background and Motivation
Aerosol-Cloud-Climate Interaction: A Case Study from the Indian Ocean Sagnik Dey Centre for Atmospheric Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Delhi sagnik@cas.iitd.ac.in Content Background and Motivation
A AVHRR NDVI dataset for Svalbard. Stian Solbø, Inge Lauknes, Cecilie Sneberg Grøtteland, Stine Skrunes, Hannah Vickers, Kjell Arild Høgda
 A 1986-2014 AVHRR NDVI dataset for Svalbard Stian Solbø, Inge Lauknes, Cecilie Sneberg Grøtteland, Stine Skrunes, Hannah Vickers, Kjell Arild Høgda AVHRR series of satellites/instruments Satellite name
A 1986-2014 AVHRR NDVI dataset for Svalbard Stian Solbø, Inge Lauknes, Cecilie Sneberg Grøtteland, Stine Skrunes, Hannah Vickers, Kjell Arild Høgda AVHRR series of satellites/instruments Satellite name
MODIS-simulator for process-oriented climate model evaluation
 MODIS-simulator for process-oriented climate model evaluation Johannes Quaas, Max Planck Institute for Meteorology johannes.quaas@zmaw.de Deliverable D1.2: Final version of MODIS simulator The MODIS-simulator
MODIS-simulator for process-oriented climate model evaluation Johannes Quaas, Max Planck Institute for Meteorology johannes.quaas@zmaw.de Deliverable D1.2: Final version of MODIS simulator The MODIS-simulator
Retrieval of precipitation from Meteosat-SEVIRI geostationary satellite observations
 Retrieval of precipitation from Meteosat-SEVIRI geostationary satellite observations Jan Fokke Meirink, Hidde Leijnse (KNMI) Rob Roebeling (EUMETSAT) Overview Introduction Algorithm description Validation
Retrieval of precipitation from Meteosat-SEVIRI geostationary satellite observations Jan Fokke Meirink, Hidde Leijnse (KNMI) Rob Roebeling (EUMETSAT) Overview Introduction Algorithm description Validation
On the Limitations of Satellite Passive Measurements for Climate Process Studies
 On the Limitations of Satellite Passive Measurements for Climate Process Studies Steve Cooper 1, Jay Mace 1, Tristan L Ecuyer 2, Matthew Lebsock 3 1 University of Utah, Atmospheric Sciences 2 University
On the Limitations of Satellite Passive Measurements for Climate Process Studies Steve Cooper 1, Jay Mace 1, Tristan L Ecuyer 2, Matthew Lebsock 3 1 University of Utah, Atmospheric Sciences 2 University
The Spectral Radiative Effects of Inhomogeneous Clouds and Aerosols
 The Spectral Radiative Effects of Inhomogeneous Clouds and Aerosols S. Schmidt, B. Kindel, & P. Pilewskie Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics University of Colorado SORCE Science Meeting, 13-16
The Spectral Radiative Effects of Inhomogeneous Clouds and Aerosols S. Schmidt, B. Kindel, & P. Pilewskie Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics University of Colorado SORCE Science Meeting, 13-16
Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types:
 Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types: Relationships with Sea Ice and Surface Temperature Ryan Eastman Stephen Warren University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Changes in Arctic
Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types: Relationships with Sea Ice and Surface Temperature Ryan Eastman Stephen Warren University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Changes in Arctic
Sea ice concentration off Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica
 Rapportserie nr. 117 Olga Pavlova and Jan-Gunnar Winther Sea ice concentration off Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica The Norwegian Polar Institute is Norway s main institution for research, monitoring and
Rapportserie nr. 117 Olga Pavlova and Jan-Gunnar Winther Sea ice concentration off Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica The Norwegian Polar Institute is Norway s main institution for research, monitoring and
Diurnal Variations in Upper Ocean Temperature from Argo: Implications for the Ocean Mixed Layer
 Diurnal Variations in Upper Ocean Temperature from Argo: Implications for the Ocean Mixed Layer Sarah Gille Scripps Institution of Oceanography UCSD, La Jolla, CA sgille@ucsd.edu Assessing Diurnal Variability
Diurnal Variations in Upper Ocean Temperature from Argo: Implications for the Ocean Mixed Layer Sarah Gille Scripps Institution of Oceanography UCSD, La Jolla, CA sgille@ucsd.edu Assessing Diurnal Variability
Multiyear Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer observations of summertime stratocumulus collocated with aerosols in the northeastern Atlantic
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006890, 2006 Multiyear Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer observations of summertime stratocumulus collocated
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006890, 2006 Multiyear Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer observations of summertime stratocumulus collocated
Review of Q. Min et al., 2012 (M12)
 Review of Q. Min et al., 2012 (M12) This paper (M12) compares in-situ derived values of effective radius, droplet concentrations and liquid water path (from aircraft profiles) with Terra satellite derived
Review of Q. Min et al., 2012 (M12) This paper (M12) compares in-situ derived values of effective radius, droplet concentrations and liquid water path (from aircraft profiles) with Terra satellite derived
VOCALS Cloud-Drizzle-Aerosol Theme
 VOCALS Cloud-Drizzle-Aerosol Theme Understanding and modeling aerosol indirect effects Is drizzle important to Sc synoptic variability and climatology? IPCC, 2007 AEROSOL-CLOUD-PRECIPITATION HYPOTHESES
VOCALS Cloud-Drizzle-Aerosol Theme Understanding and modeling aerosol indirect effects Is drizzle important to Sc synoptic variability and climatology? IPCC, 2007 AEROSOL-CLOUD-PRECIPITATION HYPOTHESES
The Importance of Three-Dimensional Solar Radiative Transfer in Small Cumulus Cloud Fields Derived
 The Importance of Three-Dimensional Solar Radiative Transfer in Small Cumulus Cloud Fields Derived from the Nauru MMCR and MWR K. Franklin Evans, Sally A. McFarlane University of Colorado Boulder, CO Warren
The Importance of Three-Dimensional Solar Radiative Transfer in Small Cumulus Cloud Fields Derived from the Nauru MMCR and MWR K. Franklin Evans, Sally A. McFarlane University of Colorado Boulder, CO Warren
Dust in the Atmosphere of Mars 2017 (LPI Contrib. No. 1966)
 Dust in the Atmosphere of Mars 2017 (LPI Contrib. No. 1966) MARS CLIMATE SOUNDER (MCS) OBSERVATIONS OF MARTIAN DUST A DECADE-LONG RECORD. D. M. Kass1, D. J. McCleese1, A. Kleinböhl1, J. T. Schofield1 and
Dust in the Atmosphere of Mars 2017 (LPI Contrib. No. 1966) MARS CLIMATE SOUNDER (MCS) OBSERVATIONS OF MARTIAN DUST A DECADE-LONG RECORD. D. M. Kass1, D. J. McCleese1, A. Kleinböhl1, J. T. Schofield1 and
Toward Statistical Extension of CloudSat Curtain Observations to a Regional Swath
 CIRA Toward Statistical Extension of CloudSat Curtain Observations to a Regional Swath Steven D. Miller 1,2, John Forsythe 1,2, Rich Bankert 3, Manajit Sengupta 4, Phil Partain 1,2, Cristian Mitrescu,
CIRA Toward Statistical Extension of CloudSat Curtain Observations to a Regional Swath Steven D. Miller 1,2, John Forsythe 1,2, Rich Bankert 3, Manajit Sengupta 4, Phil Partain 1,2, Cristian Mitrescu,
In Situ Comparisons with the Cloud Radar Retrievals of Stratus Cloud Effective Radius
 In Situ Comparisons with the Cloud Radar Retrievals of Stratus Cloud Effective Radius A. S. Frisch and G. Feingold Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere National Oceanic and Atmospheric
In Situ Comparisons with the Cloud Radar Retrievals of Stratus Cloud Effective Radius A. S. Frisch and G. Feingold Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Condensing Massive Satellite Datasets For Rapid Interactive Analysis
 Condensing Massive Satellite Datasets For Rapid Interactive Analysis Glenn Grant University of Colorado, Boulder With: David Gallaher 1,2, Qin Lv 1, G. Campbell 2, Cathy Fowler 2, Qi Liu 1, Chao Chen 1,
Condensing Massive Satellite Datasets For Rapid Interactive Analysis Glenn Grant University of Colorado, Boulder With: David Gallaher 1,2, Qin Lv 1, G. Campbell 2, Cathy Fowler 2, Qi Liu 1, Chao Chen 1,
An Overview of the Radiation Budget in the Lower Atmosphere
 An Overview of the Radiation Budget in the Lower Atmosphere atmospheric extinction irradiance at surface P. Pilewskie 300 University of Colorado Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics Department
An Overview of the Radiation Budget in the Lower Atmosphere atmospheric extinction irradiance at surface P. Pilewskie 300 University of Colorado Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics Department
Cloud properties & bulk microphysical properties of semi-transparent cirrus from AIRS & IASI
 Cloud properties & bulk microphysical properties of semi-transparent cirrus from AIRS & Claudia Stubenrauch A. Feofilov, R. Armante, A. Guignard* ABC(t) ARA team Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique /
Cloud properties & bulk microphysical properties of semi-transparent cirrus from AIRS & Claudia Stubenrauch A. Feofilov, R. Armante, A. Guignard* ABC(t) ARA team Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique /
Model-based estimation of sampling-caused uncertainty in aerosol remote sensing for climate research applications
 QuarterlyJournalof theroyalmeteorologicalsociety Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 140: 2353 2363, October 2014 A DOI:102/qj.2305 Model-based estimation of sampling-caused uncertainty in aerosol remote sensing for
QuarterlyJournalof theroyalmeteorologicalsociety Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 140: 2353 2363, October 2014 A DOI:102/qj.2305 Model-based estimation of sampling-caused uncertainty in aerosol remote sensing for
Constraining Model Predictions of Arctic Sea Ice With Observations. Chris Ander 27 April 2010 Atmos 6030
 Constraining Model Predictions of Arctic Sea Ice With Observations Chris Ander 27 April 2010 Atmos 6030 Main Sources Boe et al., 2009: September sea-ice cover in the Arctic Ocean projected to vanish by
Constraining Model Predictions of Arctic Sea Ice With Observations Chris Ander 27 April 2010 Atmos 6030 Main Sources Boe et al., 2009: September sea-ice cover in the Arctic Ocean projected to vanish by
A. Windnagel M. Savoie NSIDC
 National Snow and Ice Data Center ADVANCING KNOWLEDGE OF EARTH'S FROZEN REGIONS Special Report #18 06 July 2016 A. Windnagel M. Savoie NSIDC W. Meier NASA GSFC i 2 Contents List of Figures... 4 List of
National Snow and Ice Data Center ADVANCING KNOWLEDGE OF EARTH'S FROZEN REGIONS Special Report #18 06 July 2016 A. Windnagel M. Savoie NSIDC W. Meier NASA GSFC i 2 Contents List of Figures... 4 List of
Interannual variability of top-ofatmosphere. CERES instruments
 Interannual variability of top-ofatmosphere albedo observed by CERES instruments Seiji Kato NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA SORCE Science team meeting, Sedona, Arizona, Sep. 13-16, 2011 TOA irradiance
Interannual variability of top-ofatmosphere albedo observed by CERES instruments Seiji Kato NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA SORCE Science team meeting, Sedona, Arizona, Sep. 13-16, 2011 TOA irradiance
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens
 Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric and
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric and
Sea Ice Metrics in CMIP5
 Sea Ice Metrics in CMIP5 Detelina Ivanova (PCMDI,LLNL) CESM, Breckenridge, 2012 Acknowledgements Program for Climate Models Diagnostics and Intercomparison Funding agency - DOE Motivation/Goals Follow
Sea Ice Metrics in CMIP5 Detelina Ivanova (PCMDI,LLNL) CESM, Breckenridge, 2012 Acknowledgements Program for Climate Models Diagnostics and Intercomparison Funding agency - DOE Motivation/Goals Follow
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L21804, doi: /2006gl027150, 2006
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L21804, doi:10.1029/2006gl027150, 2006 Influence of aerosols on the shortwave cloud radiative forcing from North Pacific oceanic clouds:
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L21804, doi:10.1029/2006gl027150, 2006 Influence of aerosols on the shortwave cloud radiative forcing from North Pacific oceanic clouds:
). It is a gas produced naturally in the stratosphere where it strongly absorbs incoming
 Page 1 of 6 What Determines How Much Ultraviolet Radiation Reaches the Earth s Surface? The amount of UV radiation reaching the Earth s surface varies widely around the globe and through time. Several
Page 1 of 6 What Determines How Much Ultraviolet Radiation Reaches the Earth s Surface? The amount of UV radiation reaching the Earth s surface varies widely around the globe and through time. Several
Simple MODIS-Simulator A light alternative for some applications
 Simple MODIS-Simulator A light alternative for some applications Johannes Quaas, MPI for Meteorology, Hamburg What should a simulator do? - emulate retrievals in GCM (not really forward operator) 1a) subgrid-scale
Simple MODIS-Simulator A light alternative for some applications Johannes Quaas, MPI for Meteorology, Hamburg What should a simulator do? - emulate retrievals in GCM (not really forward operator) 1a) subgrid-scale
Remote Sensing of Snow GEOG 454 / 654
 Remote Sensing of Snow GEOG 454 / 654 What crysopheric questions can RS help to answer? 2 o Where is snow lying? (Snow-covered area or extent) o How much is there? o How rapidly is it melting? (Area, depth,
Remote Sensing of Snow GEOG 454 / 654 What crysopheric questions can RS help to answer? 2 o Where is snow lying? (Snow-covered area or extent) o How much is there? o How rapidly is it melting? (Area, depth,
ESA Cloud-CCI Phase 1 Results Climate Research Perspective
 ESA Cloud-CCI Phase 1 Results Climate Research Perspective Claudia Stubenrauch Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique, France and Cloud-CCI Team Outline Ø Challenges to retrieve cloud properties Ø What
ESA Cloud-CCI Phase 1 Results Climate Research Perspective Claudia Stubenrauch Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique, France and Cloud-CCI Team Outline Ø Challenges to retrieve cloud properties Ø What
Studying snow cover in European Russia with the use of remote sensing methods
 40 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Studying snow cover in European Russia with the use
40 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Studying snow cover in European Russia with the use
THE SOLAR RESOURCE: PART I MINES ParisTech Center Observation, Impacts, Energy (Tel.: +33 (0) )
 MASTER REST Solar Resource Part I THE SOLAR RESOURCE: PART I MINES ParisTech Center Observation, Impacts, Energy philippe.blanc@mines-paristech.fr (Tel.: +33 (0)4 93 95 74 04) MASTER REST Solar Resource
MASTER REST Solar Resource Part I THE SOLAR RESOURCE: PART I MINES ParisTech Center Observation, Impacts, Energy philippe.blanc@mines-paristech.fr (Tel.: +33 (0)4 93 95 74 04) MASTER REST Solar Resource
ACTRIS aerosol vertical profiles: advanced data and their potential use in a aerosol observations/models combined approach
 ACTRIS aerosol vertical profiles: advanced data and their potential use in a aerosol observations/models combined approach Lucia Mona CNR-IMAA, Potenza, Italy mona@imaa.cnr.it and EARLINET Team OUTLINE
ACTRIS aerosol vertical profiles: advanced data and their potential use in a aerosol observations/models combined approach Lucia Mona CNR-IMAA, Potenza, Italy mona@imaa.cnr.it and EARLINET Team OUTLINE
The SeaFlux Turbulent Flux Dataset Version 1.0 Documentation
 The SeaFlux Turbulent Flux Dataset The SeaFlux Turbulent Flux Dataset Version 1.0 Documentation Carol Anne Clayson1 J. Brent Roberts2 Alec S. Bogdanoff1,3 1. Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods
The SeaFlux Turbulent Flux Dataset The SeaFlux Turbulent Flux Dataset Version 1.0 Documentation Carol Anne Clayson1 J. Brent Roberts2 Alec S. Bogdanoff1,3 1. Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods
Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB)
 Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB) Shani Tiwari Graduate School of Environmental Studies Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan Email: pshanitiwari@gmail.com
Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB) Shani Tiwari Graduate School of Environmental Studies Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan Email: pshanitiwari@gmail.com
Evaluation of Satellite and Reanalysis Products of Downward Surface Solar Radiation over East Asia
 International Workshop on Land Use/Cover Changes and Air Pollution in Asia August 4-7th, 2015, Bogor, Indonesia Evaluation of Satellite and Reanalysis Products of Downward Surface Solar Radiation over
International Workshop on Land Use/Cover Changes and Air Pollution in Asia August 4-7th, 2015, Bogor, Indonesia Evaluation of Satellite and Reanalysis Products of Downward Surface Solar Radiation over
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens
 Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric
Satellite and diagnostic model estimates of precipitation susceptibility in low-level, marine stratocumulus
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, 3 Satellite and diagnostic model estimates of precipitation susceptibility in low-level, marine stratocumulus Christopher. R. Terai, Robert Wood,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, 3 Satellite and diagnostic model estimates of precipitation susceptibility in low-level, marine stratocumulus Christopher. R. Terai, Robert Wood,
Algorithm for MERIS land surface BRDF/albedo retrieval and its validation using contemporaneous EO data products
 Algorithm for MERIS land surface BRDF/albedo retrieval and its validation using contemporaneous EO data products Jan-Peter Muller* (UCL) Carsten Brockmann, Marco Zühlke, Norman Fomferra (BC) Jürgen Fischer,
Algorithm for MERIS land surface BRDF/albedo retrieval and its validation using contemporaneous EO data products Jan-Peter Muller* (UCL) Carsten Brockmann, Marco Zühlke, Norman Fomferra (BC) Jürgen Fischer,
Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Engineering Commons
 University of Wyoming Wyoming Scholars Repository Atmospheric Science Faculty Publications Atmospheric Science 11-18-013 An A - train satellite based stratiform mixed - phase cloud retrieval algorithm
University of Wyoming Wyoming Scholars Repository Atmospheric Science Faculty Publications Atmospheric Science 11-18-013 An A - train satellite based stratiform mixed - phase cloud retrieval algorithm
Satellite measurements of CCN and cloud properties at the cloudy boundary layer: The Holy Grail is it achievable?
 Satellite measurements of CCN and cloud properties at the cloudy boundary layer: The Holy Grail is it achievable? C 1 Daniel Rosenfeld, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem E -85 D C -89-93 E -85 D C -93-89
Satellite measurements of CCN and cloud properties at the cloudy boundary layer: The Holy Grail is it achievable? C 1 Daniel Rosenfeld, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem E -85 D C -89-93 E -85 D C -93-89
Lecture 2: Global Energy Cycle
 Lecture 2: Global Energy Cycle Planetary energy balance Greenhouse Effect Vertical energy balance Solar Flux and Flux Density Solar Luminosity (L) the constant flux of energy put out by the sun L = 3.9
Lecture 2: Global Energy Cycle Planetary energy balance Greenhouse Effect Vertical energy balance Solar Flux and Flux Density Solar Luminosity (L) the constant flux of energy put out by the sun L = 3.9
Outline of 4 Lectures
 Outline of 4 Lectures 1. Sept. 17, 2008: TC best track definition and datasets, global distribution of TCs; Review of history of meteorological satellites, introducing different orbits, scanning patterns,
Outline of 4 Lectures 1. Sept. 17, 2008: TC best track definition and datasets, global distribution of TCs; Review of history of meteorological satellites, introducing different orbits, scanning patterns,
Remote Sensing of Precipitation
 Lecture Notes Prepared by Prof. J. Francis Spring 2003 Remote Sensing of Precipitation Primary reference: Chapter 9 of KVH I. Motivation -- why do we need to measure precipitation with remote sensing instruments?
Lecture Notes Prepared by Prof. J. Francis Spring 2003 Remote Sensing of Precipitation Primary reference: Chapter 9 of KVH I. Motivation -- why do we need to measure precipitation with remote sensing instruments?
Consistent estimates from satellites and models for the first aerosol indirect forcing
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051870, 2012 Consistent estimates from satellites and models for the first aerosol indirect forcing Joyce E. Penner, 1 Cheng Zhou, 1 and Li Xu
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051870, 2012 Consistent estimates from satellites and models for the first aerosol indirect forcing Joyce E. Penner, 1 Cheng Zhou, 1 and Li Xu
CONTRAILS FROM (A)ATSR(2) DATA
 CONTRAILS FROM (A)ATSR(2) DATA Hermann Mannstein and Rüdiger Büll Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, Oberpfaffenhofen, 82230 Wessling, Germany ABSTRACT/RESUME The DLR contrail detection algorithm
CONTRAILS FROM (A)ATSR(2) DATA Hermann Mannstein and Rüdiger Büll Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, Oberpfaffenhofen, 82230 Wessling, Germany ABSTRACT/RESUME The DLR contrail detection algorithm
P2.57 PRECIPITATION STRUCTURE IN MIDLATITUDE CYCLONES
 P2.57 PRECIPITATION STRUCTURE IN MIDLATITUDE CYCLONES Paul R. Field 1, Robert Wood 2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado. 2. University of Washington, Seattle, Washington. 1.
P2.57 PRECIPITATION STRUCTURE IN MIDLATITUDE CYCLONES Paul R. Field 1, Robert Wood 2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado. 2. University of Washington, Seattle, Washington. 1.
Clouds in the Climate System: Why is this such a difficult problem, and where do we go from here?
 Clouds in the Climate System: Why is this such a difficult problem, and where do we go from here? Joel Norris Scripps Institution of Oceanography CERES Science Team Meeting April 29, 2009 Collaborators
Clouds in the Climate System: Why is this such a difficult problem, and where do we go from here? Joel Norris Scripps Institution of Oceanography CERES Science Team Meeting April 29, 2009 Collaborators
Physical Processes & Issues
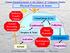 Physical Processes & Issues Radiative Transfer Climate VIS IR Cloud Drops & Ice Aerosol Processing Air quality Condensation Droplets & Xtals Cloud Dynamics Collection Aerosol Activation Hydrological Cycle
Physical Processes & Issues Radiative Transfer Climate VIS IR Cloud Drops & Ice Aerosol Processing Air quality Condensation Droplets & Xtals Cloud Dynamics Collection Aerosol Activation Hydrological Cycle
We greatly appreciate the thoughtful comments from the reviewers. According to the reviewer s comments, we revised the original manuscript.
 Response to the reviews of TC-2018-108 The potential of sea ice leads as a predictor for seasonal Arctic sea ice extent prediction by Yuanyuan Zhang, Xiao Cheng, Jiping Liu, and Fengming Hui We greatly
Response to the reviews of TC-2018-108 The potential of sea ice leads as a predictor for seasonal Arctic sea ice extent prediction by Yuanyuan Zhang, Xiao Cheng, Jiping Liu, and Fengming Hui We greatly
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting
 Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET
 TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET Activity Description: Students will use a data table to make a graph for the length of day and average high temperature in Utah. They will then answer questions based
TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET Activity Description: Students will use a data table to make a graph for the length of day and average high temperature in Utah. They will then answer questions based
On Surface fluxes and Clouds/Precipitation in the Tropical Eastern Atlantic
 On Surface fluxes and Clouds/Precipitation in the Tropical Eastern Atlantic Chris Fairall, NOAA/ESRL Paquita Zuidema, RSMAS/U Miami with contributions from Peter Minnett & Erica Key AMMA Team Meeting Leeds,
On Surface fluxes and Clouds/Precipitation in the Tropical Eastern Atlantic Chris Fairall, NOAA/ESRL Paquita Zuidema, RSMAS/U Miami with contributions from Peter Minnett & Erica Key AMMA Team Meeting Leeds,
