Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs
|
|
|
- Melissa McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs Ulrike Lohmann ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science Reading, Acknowledgements: Sylvaine Ferrachat, Corinna Hoose, Erich Roeckner, Philip Stier Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
2 Motivation First studies of the indirect aerosol effect (IAE) Estimates of the indirect aerosol effect from combined GCM+satellite studies Climate effects of dust as an ice nucleus Indirect aerosol effect with ECHAM5 Conclusions Extra Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
3 Aerosol radiative effects Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
4 Model set-up in cloud-albedo effect studies Use monthly mean sulfate aerosol distributions Empirically relate the sulfate aerosol mass to the cloud droplet number concentration (N d ) Obtain the effective cloud droplet radius (r e ) from: ( ) 3ρa LWC 1/3 r e = k (1) 4πN d ρ w with LWC=liquid water content, k 1.1 Call the radiation code twice each time-step: Once with r e (N d ) obtained from present-day sulfate Once with r e (N d ) obtained from pre-industrial sulfate The meteorology is not affected, i.e. these estimates are pure forcing estimates Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
5 Sulfate aerosol input fields [Jones et al., Nature, 1994] Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
6 Empirical relationship between sulfate aerosols and the cloud droplet number concentration (CDNC) [Boucher and Lohmann, Tellus, 1995] Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
7 Indirect aerosol effect [Jones et al., Nature, 1994] Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
8 Indirect aerosol effect [Boucher and Lohmann, Tellus, 1995] Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
9 Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
10 Aerosol sources Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
11 Aerosol activation N d = 375(1 exp[ N a ]) (Jones et al., 1994) ( ) N a w 1.27 N d = 0.1 (Lin & Leaitch, 1997) w N a where w = w TKE, and TKE = turbulent kinetic energy (Lohmann, JAS, 2002) Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
12 Autoconversion rates ( cloud lifetime effect) AUT = αlwc 4.7 N 3.3 d (Beheng, 1994) AUT = βlwc 2.5 N 1.8 d (Khairoutdinov & Kogan, 2000) Figure: Cloud droplet number conc.= 40, 200, 1000 cm 3 Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
13 Cloud albedo versus cloud lifetime effect Figure: Lohmann and Feichter, ACP, 2005 Sulfate Black carbon (BC) and sulfate Organic aerosols (OC) and sulfate BC, OC and sulfate Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
14 Summary of aerosol forcing estimates Figure: Anderson et al., Science, 2003 Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
15 Combination of satellite data and GCM results [Lohmann and Lesins, Science, 2002] Indirect aerosol effect [W m 2 ] Original Constrained Ocean Land Global Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
16 Combination of satellite data and GCM results [Quaas, Boucher, Lohmann, ACP, 2006] Compute cloud droplet number concentration (N d ) from MODIS retrievals of cloud optical depth (τ c ) and cloud droplet effective radius (r e ) for those pixels, where the retrieval is most reliable (4 µm r e 30 µm and 4 τ c 70) LMDZ: N d = exp(a 0 + a 1 ln m aer ) where m aer = mass of all potential CCN ( ) b1 N ECHAM4: N d = 0.1 a w w+b 0 N a where w = w + b 2 TKE; N a = aerosol number concentration; TKE = turbulent kinetic energy a 0, a 1, b 0 b 2 are adjusted in order to match the MODIS fine mode aerosol optical depth - cloud droplet number relationship Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
17 Combination of satellite data and GCM results [Quaas, Boucher, Lohmann, ACP, 2006] Indirect aerosol effect [W m 2 ] Original Constrained LMDZ ECHAM Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
18 Glaciation indirect aerosol effect Figure: Lohmann, GRL, 2002 Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
19 Heterogeneous freezing Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
20 Sensitivity Simulations [Lohmann and Diehl, JAS, 2006] 10 year simulations with ECHAM4 in T30 horizontal resolution with 19 vertical levels after 3 months spin-up Double moment cloud microphysics scheme Dust and soot act as contact and immersion nuclei Simulation MON KAO CTL Description Assuming dust to be composed of montmorillonite (better freezing nuclei) Assuming dust to be composed of kaolinite (worse freezing nuclei) Reference simulation, in which both contact and immersion freezing are independent of the chemical composition of the ice nuclei Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
21 Number concentration of different aerosols Figure: Annual zonal mean latitude-height cross-sections Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
22 Annual zonal mean indirect aerosol effect Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
23 Model set-up in ECHAM5 studies ECHAM5 global climate model (Roeckner et al., 2003) Multi-year simulations in T42 resolution (2.8 x 2.8 ) after a 3-month spin-up 2-moment aerosol scheme ECHAM5-HAM (Stier et al., 2005) 4 pairs of simulations: ECHAM4: Reference simulation with ECHAM4 ECHAM5-ICNC: Reference simulation with ECHAM5 (2-moment cloud microphysics scheme, Tompkins cloud cover, N d,min = 1 cm 3 ) ECHAM5-RH: Using the ECHAM4 cloud cover scheme (Sundqvist et al., 1989) ECHAM5-RH-N40: Using N d,min = 40 cm 3 together with the Sundqvist cloud cover scheme Each simulation pair is run with present-day and pre-industrial (1750) aerosol emissions Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
24 Climate model validation Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
25 Liquid (LWC), ice (IWC) and total water content (TWC) in mixed-phase clouds [Observations from Korolev et al., QJ, 2003] Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
26 Vertical distribution of black carbon and total aerosol mass in Texas [Obs. from Schwarz et al., JGR, 2006] Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
27 Cloud properties vs. AOD [Obs. from MODIS following Myhre et al., ACPD, 2006] Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
28 Preliminary annual zonal mean changes present Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
29 Preliminary global annual mean changes present-day Simulation ECH5 ECH5 ECH5 ECH4 -ICNC -RH -RH-N40 Liquid water path, g m Total cloud cover, % SW radiation, W m LW radiation, W m Net radiation, W m Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
30 Conclusions The indirect cloud albedo effect on warm clouds from GCMs amounts to -0.5 to -1.9 W m 2 The indirect cloud lifetime effect varies between -0.3 and -1.4 W m 2 These estimates are larger than combined satellite+gcm estimates One possible reason for large indirect effects is the neglect of the ice phase The vertical distribution of aerosols and the dependency of cloud condensate with temperature in mixed-phase clouds are much better captured in ECHAM5-ICNC than in ECHAM4 Preliminary results show that the indirect aerosol effect in ECHAM5-ICNC is much larger than in ECHAM4 Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
31 Freezing of kaolinite vs. soot Figure: Lohmann and Diehl, JAS, 2006 Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
32 Freezing of montmorillonite vs. soot Figure: Lohmann and Diehl, JAS, 2006 Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
33 Table: Global annual mean changes ± interannual standard deviations of aerosol optical depth ( τ), liquid water path ( LWP, g m 2 ), ice water path ( IWP, g m 2 ), total cloud cover ( TCC, %), precipitation ( PR, mm d 1 ), shortwave ( F SW, W m 2 ), longwave ( F LW, W m 2 ) and net TOA radiation ( F net, W m 2 ) between pre-industrial and present-day. Simulation CTL KAO MON τ 0.04± ± ±0.001 LWP 10.5± ± ±0.39 IWP 0.20± ± ±0.03 TCC 0.07± ± ±0.16 PR ± ± ±0.008 F SW -1.63± ± ±0.14 Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
34 Global aerosol sources [Stier et al., ACP, 2005] Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
35 Vertically integrated aerosol burden [Stier, ACP, 2005] Ulrike Lohmann () Aerosol-cloud interactions Reading, / 35
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds
 Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Bacteria and fungal spores in the global climate model ECHAM5-HAM
 Bacteria and fungal spores in the global climate model ECHAM5-HAM Ana Sesartic, ETH Zurich, Switzerland Acknowledgements: Ulrike Lohmann, Trude Storelvmo, Sylvaine Ferrachat, Tanja Dallafior, Declan O'Donnell,
Bacteria and fungal spores in the global climate model ECHAM5-HAM Ana Sesartic, ETH Zurich, Switzerland Acknowledgements: Ulrike Lohmann, Trude Storelvmo, Sylvaine Ferrachat, Tanja Dallafior, Declan O'Donnell,
Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2214 Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds Y.-C. Chen, M. W. Christensen, G. L. Stephens, and J. H. Seinfeld
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2214 Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds Y.-C. Chen, M. W. Christensen, G. L. Stephens, and J. H. Seinfeld
Climate impacts of ice nucleation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd017950, 2012 Climate impacts of ice nucleation A. Gettelman, 1,2 X. Liu, 3 D. Barahona, 4,5 U. Lohmann, 2 and C. Chen 1 Received 16 April 2012;
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd017950, 2012 Climate impacts of ice nucleation A. Gettelman, 1,2 X. Liu, 3 D. Barahona, 4,5 U. Lohmann, 2 and C. Chen 1 Received 16 April 2012;
Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
 1/23 Remote sensing of atmospheric aerosol, clouds and aerosol-cloud interactions. Bremen, 16-19 December 2013 Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
1/23 Remote sensing of atmospheric aerosol, clouds and aerosol-cloud interactions. Bremen, 16-19 December 2013 Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
Aerosol Influence on Mixed-Phase Clouds in CAM-Oslo
 3214 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 65 Aerosol Influence on Mixed-Phase Clouds in CAM-Oslo TRUDE STORELVMO AND JÓN EGILL KRISTJÁNSSON Department of Geosciences, University
3214 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 65 Aerosol Influence on Mixed-Phase Clouds in CAM-Oslo TRUDE STORELVMO AND JÓN EGILL KRISTJÁNSSON Department of Geosciences, University
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory general circulation model investigation of the indirect radiative effects of anthropogenic sulfate aerosol
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006161, 2005 Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory general circulation model investigation of the indirect radiative effects of anthropogenic
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006161, 2005 Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory general circulation model investigation of the indirect radiative effects of anthropogenic
Cloud Microphysics and Climate. George A. Isaac, Ismail Gultepe and Faisal Boudala
 Cloud Microphysics and Climate George A. Isaac, Ismail Gultepe and Faisal Boudala Parameterization of effective sizes of ice crystals in climate models and the effect of small crystals: CCCMA GCM simulations
Cloud Microphysics and Climate George A. Isaac, Ismail Gultepe and Faisal Boudala Parameterization of effective sizes of ice crystals in climate models and the effect of small crystals: CCCMA GCM simulations
Simple MODIS-Simulator A light alternative for some applications
 Simple MODIS-Simulator A light alternative for some applications Johannes Quaas, MPI for Meteorology, Hamburg What should a simulator do? - emulate retrievals in GCM (not really forward operator) 1a) subgrid-scale
Simple MODIS-Simulator A light alternative for some applications Johannes Quaas, MPI for Meteorology, Hamburg What should a simulator do? - emulate retrievals in GCM (not really forward operator) 1a) subgrid-scale
Effective radiative forcing in the aerosol climate model CAM5.3- MARC-ARG
 Effective radiative forcing in the aerosol climate model CAM5.3- MARC-ARG Benjamin S. Grandey 1, Daniel Rothenberg 2, Alexander Avramov 2,3, Qinjian Jin 2, Hsiang-He Lee 1, Xiaohong Liu 4, Zheng Lu 4,
Effective radiative forcing in the aerosol climate model CAM5.3- MARC-ARG Benjamin S. Grandey 1, Daniel Rothenberg 2, Alexander Avramov 2,3, Qinjian Jin 2, Hsiang-He Lee 1, Xiaohong Liu 4, Zheng Lu 4,
Towards a global climatology of cloud microphysical properties and why MODIS does not like sunsets (nor sunrise!)
 Towards a global climatology of cloud microphysical properties and why MODIS does not like sunsets (nor sunrise!) Daniel Grosvenor & Robert Wood (U. Washington) Using scattered solar radiation to infer
Towards a global climatology of cloud microphysical properties and why MODIS does not like sunsets (nor sunrise!) Daniel Grosvenor & Robert Wood (U. Washington) Using scattered solar radiation to infer
How good are our models?
 direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
Aerosols AP sizes AP types Sources Sinks Amount and lifetime Aerosol radiative effects. Aerosols. Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21
 Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
Consistent estimates from satellites and models for the first aerosol indirect forcing
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051870, 2012 Consistent estimates from satellites and models for the first aerosol indirect forcing Joyce E. Penner, 1 Cheng Zhou, 1 and Li Xu
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051870, 2012 Consistent estimates from satellites and models for the first aerosol indirect forcing Joyce E. Penner, 1 Cheng Zhou, 1 and Li Xu
Impacts of aerosols in the CORDEX-Europe domain using the regional aerosol-climate model REMO-HAM
 Impacts of aerosols in the CORDEX-Europe domain using the regional aerosol-climate model REMO-HAM Armelle Reca C. Remedio (1), Claas Teichmann (1,2), Joni-Pekka Pietikäinen (3), Natalia Sudarchikova (1),
Impacts of aerosols in the CORDEX-Europe domain using the regional aerosol-climate model REMO-HAM Armelle Reca C. Remedio (1), Claas Teichmann (1,2), Joni-Pekka Pietikäinen (3), Natalia Sudarchikova (1),
On-line Aerosols in the Oslo Version of CAM3: Some shortcomings. Seland,
 On-line Aerosols in the Oslo Version of CAM3: Some shortcomings Trond Iversen,, Alf Kirkevåg, Øyvind Seland, Jon Egill Kristjansson, Trude Storelvmo,, Jens Debernard Norwegian Meteorological Institute
On-line Aerosols in the Oslo Version of CAM3: Some shortcomings Trond Iversen,, Alf Kirkevåg, Øyvind Seland, Jon Egill Kristjansson, Trude Storelvmo,, Jens Debernard Norwegian Meteorological Institute
Aerosol Radiative Forcing DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS The AeroCom Prescribed Experiment: Towards the Quantification of Host Model Errors
 Aerosol Radiative Forcing DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS The AeroCom Prescribed Experiment: Towards the Quantification of Host Model Errors AeroCom Meeting, Reykjavik, Island 10/10/2008 Philip Stier Atmospheric,
Aerosol Radiative Forcing DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS The AeroCom Prescribed Experiment: Towards the Quantification of Host Model Errors AeroCom Meeting, Reykjavik, Island 10/10/2008 Philip Stier Atmospheric,
Satellite-derived warm rain fraction as constraint on the cloud lifetime effect
 Satellite-derived warm rain fraction as constraint on the cloud lifetime effect Johannes Mülmenstädt,1 Amund Søvde,2 Gunnar Myhre,2 Shipeng Zhang,3 Minghuai Wang,3 Toshi Takemura,4 Kenta Suzuki,5 Philip
Satellite-derived warm rain fraction as constraint on the cloud lifetime effect Johannes Mülmenstädt,1 Amund Søvde,2 Gunnar Myhre,2 Shipeng Zhang,3 Minghuai Wang,3 Toshi Takemura,4 Kenta Suzuki,5 Philip
Interannual variability of top-ofatmosphere. CERES instruments
 Interannual variability of top-ofatmosphere albedo observed by CERES instruments Seiji Kato NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA SORCE Science team meeting, Sedona, Arizona, Sep. 13-16, 2011 TOA irradiance
Interannual variability of top-ofatmosphere albedo observed by CERES instruments Seiji Kato NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA SORCE Science team meeting, Sedona, Arizona, Sep. 13-16, 2011 TOA irradiance
A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols
 A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols A. Jones, D.L. Roberts & A. Slingo Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Meteorological Office, London
A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols A. Jones, D.L. Roberts & A. Slingo Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Meteorological Office, London
Combined observational and modeling based study of the aerosol indirect effect
 Author(s) 2006. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Combined observational and modeling based study of the aerosol indirect effect T. Storelvmo 1,
Author(s) 2006. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Combined observational and modeling based study of the aerosol indirect effect T. Storelvmo 1,
SPCAM5: Multi-scale Modeling of Aerosols, Clouds and Precipitation
 SPCAM5: Multi-scale Modeling of Aerosols, Clouds and Precipitation Minghuai Wang Steven Ghan, Mikhail Ovchinnikov, Richard Easter, Xiaohong Liu, Kai Zhang, Yun Qian, Hailong Wang, Phil Rasch, Evgueni Kassianov,
SPCAM5: Multi-scale Modeling of Aerosols, Clouds and Precipitation Minghuai Wang Steven Ghan, Mikhail Ovchinnikov, Richard Easter, Xiaohong Liu, Kai Zhang, Yun Qian, Hailong Wang, Phil Rasch, Evgueni Kassianov,
Effects of stratospheric sulfate aerosol geo-engineering on cirrus clouds
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053797, 2012 Effects of stratospheric sulfate aerosol geo-engineering on cirrus clouds Miriam Kuebbeler, 1 Ulrike Lohmann, 1 and Johann Feichter
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053797, 2012 Effects of stratospheric sulfate aerosol geo-engineering on cirrus clouds Miriam Kuebbeler, 1 Ulrike Lohmann, 1 and Johann Feichter
Aerosol Monitoring and Modeling
 Aerosol Monitoring and Modeling Olivier Boucher Presentation to ECMWF seminar on Global Earth-System Monitoring 5-9 September 2005 Page 1 Aerosols are integral part of the Earth s system. CCN f(wind,convection)
Aerosol Monitoring and Modeling Olivier Boucher Presentation to ECMWF seminar on Global Earth-System Monitoring 5-9 September 2005 Page 1 Aerosols are integral part of the Earth s system. CCN f(wind,convection)
Diagnosing Model Systematic Error for Clouds and Precipitation
 Diagnosing Model Systematic Error for Clouds and Precipitation Richard Forbes (ECMWF) With Thanks to Maike Ahlgrimm, Peter Bechtold, Martin Köhler and ECMWF colleagues, and Graeme Stephens (CSU), Julien
Diagnosing Model Systematic Error for Clouds and Precipitation Richard Forbes (ECMWF) With Thanks to Maike Ahlgrimm, Peter Bechtold, Martin Köhler and ECMWF colleagues, and Graeme Stephens (CSU), Julien
Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models. Richard Forbes
 Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models Richard Forbes (ECMWF) with thanks to Peter Bechtold and Martin Köhler RMetS National Meeting on Clouds and Precipitation, 16 Nov
Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models Richard Forbes (ECMWF) with thanks to Peter Bechtold and Martin Köhler RMetS National Meeting on Clouds and Precipitation, 16 Nov
Radiative forcing of fine ash and volcanic sulphate aerosol. sulphate aerosol after a very large Northern hemisphere mid-latitude eruption
 Radiative forcing of fine ash and volcanic sulphate aerosol after a very large Northern hemisphere mid-latitude eruption Ulrike Niemeier (1), Claudia Timmreck (1), Sebastian Rast (1), Marco Giorgetta (1),
Radiative forcing of fine ash and volcanic sulphate aerosol after a very large Northern hemisphere mid-latitude eruption Ulrike Niemeier (1), Claudia Timmreck (1), Sebastian Rast (1), Marco Giorgetta (1),
Predicting cloud droplet number concentration in Community Atmosphere Model (CAM)-Oslo
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006300, 2006 Predicting cloud droplet number concentration in Community Atmosphere Model (CAM)-Oslo Trude Storelvmo, 1 Jon Egill Kristjánsson,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006300, 2006 Predicting cloud droplet number concentration in Community Atmosphere Model (CAM)-Oslo Trude Storelvmo, 1 Jon Egill Kristjánsson,
Physical Processes & Issues
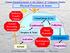 Physical Processes & Issues Radiative Transfer Climate VIS IR Cloud Drops & Ice Aerosol Processing Air quality Condensation Droplets & Xtals Cloud Dynamics Collection Aerosol Activation Hydrological Cycle
Physical Processes & Issues Radiative Transfer Climate VIS IR Cloud Drops & Ice Aerosol Processing Air quality Condensation Droplets & Xtals Cloud Dynamics Collection Aerosol Activation Hydrological Cycle
C-SOLAS Pacific Cruise Summer 2002
 Ulrike Lohmann Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science, ETH Zurich, Switzerland Thanks to: Silvia Kloster, MPI Hamburg, Germany Richard Leaitch, Meteorological Service of Canada Maurice Levasseur,Univ.
Ulrike Lohmann Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science, ETH Zurich, Switzerland Thanks to: Silvia Kloster, MPI Hamburg, Germany Richard Leaitch, Meteorological Service of Canada Maurice Levasseur,Univ.
Observed Southern Ocean Cloud Properties and Shortwave Reflection
 Observed Southern Ocean Cloud Properties and Shortwave Reflection Daniel T McCoy* 1, Dennis L Hartmann 1, and Daniel P Grosvenor 2 University of Washington 1 University of Leeds 2 *dtmccoy@atmosuwedu Introduction
Observed Southern Ocean Cloud Properties and Shortwave Reflection Daniel T McCoy* 1, Dennis L Hartmann 1, and Daniel P Grosvenor 2 University of Washington 1 University of Leeds 2 *dtmccoy@atmosuwedu Introduction
climate change Contents CO 2 (ppm)
 climate change CO 2 (ppm) 2007 Joachim Curtius Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Universität Mainz Contents 1. Summary 2. Background 3. Climate change: observations 4. CO 2 5. OtherGreenhouse Gases (GHGs):
climate change CO 2 (ppm) 2007 Joachim Curtius Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Universität Mainz Contents 1. Summary 2. Background 3. Climate change: observations 4. CO 2 5. OtherGreenhouse Gases (GHGs):
Dependence of Radiative Forcing on Mineralogy in the Community Atmosphere Model
 Dependence of Radiative Forcing on Mineralogy in the Community Atmosphere Model Rachel Scanza 1, Natalie Mahowald 1, Jasper Kok 2, Steven Ghan 3, Charles Zender 4, Xiaohong Liu 5, Yan Zhang 6 February
Dependence of Radiative Forcing on Mineralogy in the Community Atmosphere Model Rachel Scanza 1, Natalie Mahowald 1, Jasper Kok 2, Steven Ghan 3, Charles Zender 4, Xiaohong Liu 5, Yan Zhang 6 February
Exam 2: Cloud Physics April 16, 2008 Physical Meteorology Questions 1-10 are worth 5 points each. Questions are worth 10 points each.
 Exam : Cloud Physics April, 8 Physical Meteorology 344 Name Questions - are worth 5 points each. Questions -5 are worth points each.. Rank the concentrations of the following from lowest () to highest
Exam : Cloud Physics April, 8 Physical Meteorology 344 Name Questions - are worth 5 points each. Questions -5 are worth points each.. Rank the concentrations of the following from lowest () to highest
Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model
 Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model W. O Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California
Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model W. O Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California
REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT
 REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2010 2012 MEMBER STATE: Switzerland Principal Investigator 1 : Affiliation: Prof. Ulrike Lohmann Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science, ETH Zurich Address: Universitaetstrasse
REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2010 2012 MEMBER STATE: Switzerland Principal Investigator 1 : Affiliation: Prof. Ulrike Lohmann Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science, ETH Zurich Address: Universitaetstrasse
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes. Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology
 Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
MODIS-simulator for process-oriented climate model evaluation
 MODIS-simulator for process-oriented climate model evaluation Johannes Quaas, Max Planck Institute for Meteorology johannes.quaas@zmaw.de Deliverable D1.2: Final version of MODIS simulator The MODIS-simulator
MODIS-simulator for process-oriented climate model evaluation Johannes Quaas, Max Planck Institute for Meteorology johannes.quaas@zmaw.de Deliverable D1.2: Final version of MODIS simulator The MODIS-simulator
An Overview of the Radiation Budget in the Lower Atmosphere
 An Overview of the Radiation Budget in the Lower Atmosphere atmospheric extinction irradiance at surface P. Pilewskie 300 University of Colorado Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics Department
An Overview of the Radiation Budget in the Lower Atmosphere atmospheric extinction irradiance at surface P. Pilewskie 300 University of Colorado Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics Department
The effects of dust emission on the trans- Pacific transport of Asian dust in the CESM
 The effects of dust emission on the trans- Pacific transport of Asian dust in the CESM Mingxuan Wu, Xiaohong Liu, Zhien Wang, Kang Yang, Chenglai Wu University of Wyoming Kai Zhang, Hailong Wang Pacific
The effects of dust emission on the trans- Pacific transport of Asian dust in the CESM Mingxuan Wu, Xiaohong Liu, Zhien Wang, Kang Yang, Chenglai Wu University of Wyoming Kai Zhang, Hailong Wang Pacific
Global anthropogenic aerosol effects on convective clouds in ECHAM5-HAM
 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Global anthropogenic aerosol effects on convective clouds in ECHAM5-HAM U.
Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Global anthropogenic aerosol effects on convective clouds in ECHAM5-HAM U.
An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics
 An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics M. D. Shupe Science and Technology Corporation National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Environmental Technology Laboratory Boulder, Colorado T. Uttal
An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics M. D. Shupe Science and Technology Corporation National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Environmental Technology Laboratory Boulder, Colorado T. Uttal
Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements
 Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements Norman G. Loeb Hampton University/NASA Langley Research Center Bruce
Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements Norman G. Loeb Hampton University/NASA Langley Research Center Bruce
Observational constraints on mixed-phase clouds imply higher climate sensitivity
 Observational constraints on mixed-phase clouds imply higher climate sensitivity TRUDE STORELVMO AND I. TAN (YALE UNIVERSITY) COLLABORATORS: M. KOMURCU (U. OF NEW HAMPSHIRE), M. ZELINKA (PNNL) TAKE-HOME
Observational constraints on mixed-phase clouds imply higher climate sensitivity TRUDE STORELVMO AND I. TAN (YALE UNIVERSITY) COLLABORATORS: M. KOMURCU (U. OF NEW HAMPSHIRE), M. ZELINKA (PNNL) TAKE-HOME
Precipitation Processes METR σ is the surface tension, ρ l is the water density, R v is the Gas constant for water vapor, T is the air
 Precipitation Processes METR 2011 Introduction In order to grow things on earth, they need water. The way that the earth naturally irrigates is through snowfall and rainfall. Therefore, it is important
Precipitation Processes METR 2011 Introduction In order to grow things on earth, they need water. The way that the earth naturally irrigates is through snowfall and rainfall. Therefore, it is important
Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change
 Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change Jim Coakley College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Earth s Energy Budget and Global Temperature Incident Sunlight 340 Wm -2 Reflected Sunlight 100 Wm -2 Emitted Terrestrial
Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change Jim Coakley College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Earth s Energy Budget and Global Temperature Incident Sunlight 340 Wm -2 Reflected Sunlight 100 Wm -2 Emitted Terrestrial
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5
 Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Effects of Galactic Cosmic Rays on the Atmosphere and Climate. Jón Egill Kristjánsson, Univ. Oslo
 Effects of Galactic Cosmic Rays on the Atmosphere and Climate Jón Egill Kristjánsson, Univ. Oslo Overview of talk Hypotheses for Coupling between Galactic Cosmic Rays and Climate Observational studies
Effects of Galactic Cosmic Rays on the Atmosphere and Climate Jón Egill Kristjánsson, Univ. Oslo Overview of talk Hypotheses for Coupling between Galactic Cosmic Rays and Climate Observational studies
Microphysical Properties of Single and Mixed-Phase Arctic Clouds Derived From Ground-Based AERI Observations
 Microphysical Properties of Single and Mixed-Phase Arctic Clouds Derived From Ground-Based AERI Observations Dave Turner University of Wisconsin-Madison Pacific Northwest National Laboratory 8 May 2003
Microphysical Properties of Single and Mixed-Phase Arctic Clouds Derived From Ground-Based AERI Observations Dave Turner University of Wisconsin-Madison Pacific Northwest National Laboratory 8 May 2003
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle
 Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Model Systems at MPI-M. Marco Giorgetta
 Model Systems at MPI-M Marco Giorgetta Content What is a model in climate research as used here for IPCC? What is a model? Components of the climate system Climate models What is inside? Climate models
Model Systems at MPI-M Marco Giorgetta Content What is a model in climate research as used here for IPCC? What is a model? Components of the climate system Climate models What is inside? Climate models
Model intercomparison of indirect aerosol effects
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 6, 3391 345, 26 www.atmos-chem-phys.net/6/3391/26/ Author(s) 26. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Model intercomparison of indirect
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 6, 3391 345, 26 www.atmos-chem-phys.net/6/3391/26/ Author(s) 26. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Model intercomparison of indirect
Warm rain and climate: VOCALS, CloudSat, Models. Robert Wood University of Washington
 Warm rain and climate: VOCALS, CloudSat, Models Robert Wood University of Washington Warm rain a missing climatology Image: NASA GSFC Shipboard remote sensing shows frequent precipitation from shallow
Warm rain and climate: VOCALS, CloudSat, Models Robert Wood University of Washington Warm rain a missing climatology Image: NASA GSFC Shipboard remote sensing shows frequent precipitation from shallow
Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002
 Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002 Soon-Ung Park, Jae-In Jeong* Center for Atmospheric and Environmental Modeling *School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Seoul National
Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002 Soon-Ung Park, Jae-In Jeong* Center for Atmospheric and Environmental Modeling *School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Seoul National
Global climate response to anthropogenic aerosol indirect effects: Present day and year 2100
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2008jd011619, 2010 Global climate response to anthropogenic aerosol indirect effects: Present day and year 2100 Wei Ting
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2008jd011619, 2010 Global climate response to anthropogenic aerosol indirect effects: Present day and year 2100 Wei Ting
A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling. requirements of energy and water cycle. Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki
 A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling study for defining satellite measurement requirements of energy and water cycle Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki Motivation 1. Uncertainty of climate sensitivity
A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling study for defining satellite measurement requirements of energy and water cycle Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki Motivation 1. Uncertainty of climate sensitivity
Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions
 Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions William K. M. Lau NASA/GSFC Co-authors: K. M. Kim, M. Chin, P. Colarco, A. DaSilva Atmospheric loading of Saharan dust Annual emission
Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions William K. M. Lau NASA/GSFC Co-authors: K. M. Kim, M. Chin, P. Colarco, A. DaSilva Atmospheric loading of Saharan dust Annual emission
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 6: 10-14-13 Feedbacks Climate forcings change global temperatures directly
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 6: 10-14-13 Feedbacks Climate forcings change global temperatures directly
What is PRECIS? The Physical Parameters Boundary Conditions Why the Mediterranean Basin? The Sulfur Cycle & Aerosols Aerosols Impacts Data Analysis
 What is PRECIS? The Physical Parameters Boundary Conditions Why the Mediterranean Basin? The Sulfur Cycle & Aerosols Aerosols Impacts Data Analysis Sulfur Cycle Validation Future Scenarios Conclusions
What is PRECIS? The Physical Parameters Boundary Conditions Why the Mediterranean Basin? The Sulfur Cycle & Aerosols Aerosols Impacts Data Analysis Sulfur Cycle Validation Future Scenarios Conclusions
Global indirect aerosol effects: a review
 SRef-ID: 1680-7324/acp/2005-5-715 European Geosciences Union Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Global indirect aerosol effects: a review U. Lohmann 1 and J. Feichter 2 1 ETH Institute of Atmospheric and
SRef-ID: 1680-7324/acp/2005-5-715 European Geosciences Union Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Global indirect aerosol effects: a review U. Lohmann 1 and J. Feichter 2 1 ETH Institute of Atmospheric and
J. Schneider & Chr. Voigt - Physics and Chemistry of Aerosols and Ice Clouds
 Chapter 8 Contrails and contrail cirrus 8.1 Introduction - Terminology 8.2 Contrail formation conditions 8.3 Heterogeneous nucleation on volatile aerosol and soot 8.4 Indirect effect of soot on cirrus
Chapter 8 Contrails and contrail cirrus 8.1 Introduction - Terminology 8.2 Contrail formation conditions 8.3 Heterogeneous nucleation on volatile aerosol and soot 8.4 Indirect effect of soot on cirrus
Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB)
 Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB) Shani Tiwari Graduate School of Environmental Studies Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan Email: pshanitiwari@gmail.com
Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB) Shani Tiwari Graduate School of Environmental Studies Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan Email: pshanitiwari@gmail.com
Standalone simulations: CAM3, CAM4 and CAM5
 Standalone simulations: CAM3, and CAM5 CAM5 Model Development Team Cécile Hannay, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman, Sungsu Park, Joe Tribbia, Peter Lauritzen, Andrew Conley, Hugh Morrison, Phil Rasch, Steve
Standalone simulations: CAM3, and CAM5 CAM5 Model Development Team Cécile Hannay, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman, Sungsu Park, Joe Tribbia, Peter Lauritzen, Andrew Conley, Hugh Morrison, Phil Rasch, Steve
Changes in Earth s Albedo Measured by satellite
 Changes in Earth s Albedo Measured by satellite Bruce A. Wielicki, Takmeng Wong, Norman Loeb, Patrick Minnis, Kory Priestley, Robert Kandel Presented by Yunsoo Choi Earth s albedo Earth s albedo The climate
Changes in Earth s Albedo Measured by satellite Bruce A. Wielicki, Takmeng Wong, Norman Loeb, Patrick Minnis, Kory Priestley, Robert Kandel Presented by Yunsoo Choi Earth s albedo Earth s albedo The climate
National Center for Atmospheric Research,* Boulder, Colorado S. J. GHAN. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, Washington
 3660 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 A New Two-Moment Bulk Stratiform Cloud Microphysics Scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model, Version 3 (CAM3). Part II: Single-Column and Global Results
3660 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 A New Two-Moment Bulk Stratiform Cloud Microphysics Scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model, Version 3 (CAM3). Part II: Single-Column and Global Results
Global modeling of mixed phase clouds: The albedo and lifetime effects of aerosols
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2010jd014724, 2011 Global modeling of mixed phase clouds: The albedo and lifetime effects of aerosols T. Storelvmo, 1 C. Hoose, 2 and P. Eriksson
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2010jd014724, 2011 Global modeling of mixed phase clouds: The albedo and lifetime effects of aerosols T. Storelvmo, 1 C. Hoose, 2 and P. Eriksson
Evaluation of cloud thermodynamic phase parametrizations in the LMDZ GCM by using POLDER satellite data
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L06126, doi:10.1029/2003gl019095, 2004 Evaluation of cloud thermodynamic phase parametrizations in the LMDZ GCM by using POLDER satellite data M. Doutriaux-Boucher
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L06126, doi:10.1029/2003gl019095, 2004 Evaluation of cloud thermodynamic phase parametrizations in the LMDZ GCM by using POLDER satellite data M. Doutriaux-Boucher
Variability in Global Top-of-Atmosphere Shortwave Radiation Between 2000 And 2005
 Variability in Global Top-of-Atmosphere Shortwave Radiation Between 2000 And 2005 Norman G. Loeb NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Collaborators: B.A. Wielicki, F.G. Rose, D.R. Doelling February
Variability in Global Top-of-Atmosphere Shortwave Radiation Between 2000 And 2005 Norman G. Loeb NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Collaborators: B.A. Wielicki, F.G. Rose, D.R. Doelling February
Aerosol-Cloud-Climate Interaction: A Case Study from the Indian Ocean. Sagnik Dey
 Aerosol-Cloud-Climate Interaction: A Case Study from the Indian Ocean Sagnik Dey Centre for Atmospheric Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Delhi sagnik@cas.iitd.ac.in Content Background and Motivation
Aerosol-Cloud-Climate Interaction: A Case Study from the Indian Ocean Sagnik Dey Centre for Atmospheric Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Delhi sagnik@cas.iitd.ac.in Content Background and Motivation
A Novel Cirrus Cloud Retrieval Method For GCM High Cloud Validations
 A Novel Cirrus Cloud Retrieval Method For GCM High Cloud Validations David Mitchell Anne Garnier Melody Avery Desert Research Institute Science Systems & Applications, Inc. NASA Langley Reno, Nevada Hampton,
A Novel Cirrus Cloud Retrieval Method For GCM High Cloud Validations David Mitchell Anne Garnier Melody Avery Desert Research Institute Science Systems & Applications, Inc. NASA Langley Reno, Nevada Hampton,
8. Clouds and Climate
 8. Clouds and Climate 1. Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few
8. Clouds and Climate 1. Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few
Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols
 Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols Mark Flanner November 2, 2011 Santa Fe Conference on Global and Regional Climate Change 1 / 18 Arctic: Unique vulnerability to positive
Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols Mark Flanner November 2, 2011 Santa Fe Conference on Global and Regional Climate Change 1 / 18 Arctic: Unique vulnerability to positive
Evaluating parameterisations of subgridscale variability with satellite data
 Evaluating parameterisations of subgridscale variability with satellite data Johannes Quaas Institute for Meteorology University of Leipzig johannes.quaas@uni-leipzig.de www.uni-leipzig.de/~quaas Acknowledgements
Evaluating parameterisations of subgridscale variability with satellite data Johannes Quaas Institute for Meteorology University of Leipzig johannes.quaas@uni-leipzig.de www.uni-leipzig.de/~quaas Acknowledgements
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle
 Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle Irina N. Sokolik School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA,
Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle Irina N. Sokolik School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA,
CHAPTER 8. AEROSOLS 8.1 SOURCES AND SINKS OF AEROSOLS
 1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
Parameterization of the nitric acid effect on CCN activation
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 5, 879 885, 25 SRef-ID: 168-7324/acp/25-5-879 European Geosciences Union Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Parameterization of the nitric acid effect on CCN activation S. Romakkaniemi,
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 5, 879 885, 25 SRef-ID: 168-7324/acp/25-5-879 European Geosciences Union Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Parameterization of the nitric acid effect on CCN activation S. Romakkaniemi,
Analyzing signatures of aerosol-cloud interactions from satellite retrievals and the GISS GCM to constrain the aerosol indirect effect
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jd009442, 2008 Analyzing signatures of aerosol-cloud interactions from satellite retrievals and the GISS GCM to constrain the aerosol indirect
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jd009442, 2008 Analyzing signatures of aerosol-cloud interactions from satellite retrievals and the GISS GCM to constrain the aerosol indirect
Aerosol-cloud-climate interactions in the climate model CAM-Oslo
 Tellus (2008), 60A, 492 512 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved C 2008 The Authors Journal compilation C 2008 Blackwell Munksgaard TELLUS Aerosol-cloud-climate interactions in the climate model CAM-Oslo
Tellus (2008), 60A, 492 512 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved C 2008 The Authors Journal compilation C 2008 Blackwell Munksgaard TELLUS Aerosol-cloud-climate interactions in the climate model CAM-Oslo
An observational study of drizzle formation in stratocumulus clouds for general circulation model (GCM) parameterizations
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D15, 8630, doi:10.1029/2002jd002679, 2003 An observational study of drizzle formation in stratocumulus clouds for general circulation model (GCM) parameterizations
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D15, 8630, doi:10.1029/2002jd002679, 2003 An observational study of drizzle formation in stratocumulus clouds for general circulation model (GCM) parameterizations
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations. S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences.
 The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
J12.4 SIGNIFICANT IMPACT OF AEROSOLS ON MULTI-YEAR RAIN FREQUENCY AND CLOUD THICKNESS
 J12.4 SIGNIFICANT IMPACT OF AEROSOLS ON MULTI-YEAR RAIN FREQUENCY AND CLOUD THICKNESS Zhanqing Li and F. Niu* University of Maryland College park 1. INTRODUCTION Many observational studies of aerosol indirect
J12.4 SIGNIFICANT IMPACT OF AEROSOLS ON MULTI-YEAR RAIN FREQUENCY AND CLOUD THICKNESS Zhanqing Li and F. Niu* University of Maryland College park 1. INTRODUCTION Many observational studies of aerosol indirect
A STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF SYNOPTIC WEATHER CONDITIONS AND WATER VAPOUR ON AEROSOL-CLOUD RELATIONSHIPS
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 A STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF SYNOPTIC WEATHER CONDITIONS AND WATER VAPOUR ON AEROSOL-CLOUD
Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 A STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF SYNOPTIC WEATHER CONDITIONS AND WATER VAPOUR ON AEROSOL-CLOUD
Polar regions Temperate Regions Tropics High ( cirro ) 3-8 km 5-13 km 6-18 km Middle ( alto ) 2-4 km 2-7 km 2-8 km Low ( strato ) 0-2 km 0-2 km 0-2 km
 Clouds and Climate Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few cm/sec.
Clouds and Climate Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few cm/sec.
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title Analyzing signatures of aerosol-cloud interactions from satellite retrievals and the GISS GCM to constrain the aerosol
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title Analyzing signatures of aerosol-cloud interactions from satellite retrievals and the GISS GCM to constrain the aerosol
Using volcanic eruptions to unlock the secrets of aerosol-cloud interactions. Jim Haywood
 Using volcanic eruptions to unlock the secrets of aerosol-cloud interactions Jim Haywood Malavelle, F., et al., Strong constraints on aerosol-cloud interactions from volcanic eruptions, Nature, June 22
Using volcanic eruptions to unlock the secrets of aerosol-cloud interactions Jim Haywood Malavelle, F., et al., Strong constraints on aerosol-cloud interactions from volcanic eruptions, Nature, June 22
Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations
 Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations Wei-Kuo Tao,1 Xiaowen Li,1,2 Alexander Khain,3 Toshihisa Matsui,1,2 Stephen Lang,4 and Joanne
Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations Wei-Kuo Tao,1 Xiaowen Li,1,2 Alexander Khain,3 Toshihisa Matsui,1,2 Stephen Lang,4 and Joanne
UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions
 UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions Nicolas Bellouin UKCA Training Workshop, Cambridge, 8 January 2015 University of Reading 2014 n.bellouin@reading.ac.uk Lecture summary Why care about aerosol-radiation
UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions Nicolas Bellouin UKCA Training Workshop, Cambridge, 8 January 2015 University of Reading 2014 n.bellouin@reading.ac.uk Lecture summary Why care about aerosol-radiation
Radiative forcing estimates of sulfate aerosol in coupled climate-chemistry models with emphasis on the role of the temporal variability
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 12, 5583 5602, 2012 doi:10.5194/acp-12-5583-2012 Author(s) 2012. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Radiative forcing estimates of sulfate aerosol in coupled
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 12, 5583 5602, 2012 doi:10.5194/acp-12-5583-2012 Author(s) 2012. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Radiative forcing estimates of sulfate aerosol in coupled
Lecture 8: Climate Modeling
 Lecture 8: Climate Modeling How to Build a Climate Model The climate is governed by many complex physical, chemical, and biological processes and their interactions. Building a climate model needs to consider
Lecture 8: Climate Modeling How to Build a Climate Model The climate is governed by many complex physical, chemical, and biological processes and their interactions. Building a climate model needs to consider
Arctic Clouds and Radiation Part 2
 Arctic Clouds and Radiation Part 2 Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 No sun Arctic Winter Energy Balance 160 W m -2
Arctic Clouds and Radiation Part 2 Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 No sun Arctic Winter Energy Balance 160 W m -2
OceanFlux Sea Spray Aerosol (OSSA): a new formulation for production fluxes and implications for climate studies
 OceanFlux Sea Spray Aerosol (OSSA): a new formulation for production fluxes and implications for climate studies G. de Leeuw 1, 2, 3, J. Ovadnevaite 4, A. Manders- Groot 3, S. Norris 5, I.M. Brooks 5,
OceanFlux Sea Spray Aerosol (OSSA): a new formulation for production fluxes and implications for climate studies G. de Leeuw 1, 2, 3, J. Ovadnevaite 4, A. Manders- Groot 3, S. Norris 5, I.M. Brooks 5,
CONSTRAIN proposal for grey zone model comparison case. Adrian Hill, Paul Field, Adrian Lock, Thomas Frederikse, Stephan de Roode, Pier Siebesma
 CONSTRAIN proposal for grey zone model comparison case Adrian Hill, Paul Field, Adrian Lock, Thomas Frederikse, Stephan de Roode, Pier Siebesma Contents Introduction CONSTRAIN Overview of UM Limited Area
CONSTRAIN proposal for grey zone model comparison case Adrian Hill, Paul Field, Adrian Lock, Thomas Frederikse, Stephan de Roode, Pier Siebesma Contents Introduction CONSTRAIN Overview of UM Limited Area
Seeking a consistent view of energy and water flows through the climate system
 Seeking a consistent view of energy and water flows through the climate system Robert Pincus University of Colorado and NOAA/Earth System Research Lab Atmospheric Energy Balance [Wm -2 ] 340.1±0.1 97-101
Seeking a consistent view of energy and water flows through the climate system Robert Pincus University of Colorado and NOAA/Earth System Research Lab Atmospheric Energy Balance [Wm -2 ] 340.1±0.1 97-101
7. Aerosols and Climate
 7. Aerosols and Climate I. Scattering 1. When radiation impinges on a medium of small particles, scattering of some of the radiation occurs in all directions. The portion scattered backward is called the
7. Aerosols and Climate I. Scattering 1. When radiation impinges on a medium of small particles, scattering of some of the radiation occurs in all directions. The portion scattered backward is called the
AEROSOL INDIRECT EFFECTS IN A COUPLED GLOBAL AEROSOL AND ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION MODEL
 AEROSOL INDIRECT EFFECTS IN A COUPLED GLOBAL AEROSOL AND ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION MODEL by Minghuai Wang A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
AEROSOL INDIRECT EFFECTS IN A COUPLED GLOBAL AEROSOL AND ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION MODEL by Minghuai Wang A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
An Observational Study of the Relationship between Cloud, Aerosol and Meteorology in Marine Stratus Regions
 An Observational Study of the Relationship between Cloud, Aerosol and Meteorology in Marine Stratus Regions Norman G. Loeb NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Oct 18 th, 2006, AeroCom Meeting (Virginia
An Observational Study of the Relationship between Cloud, Aerosol and Meteorology in Marine Stratus Regions Norman G. Loeb NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Oct 18 th, 2006, AeroCom Meeting (Virginia
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model
 Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Introduction. Effect of aerosols on precipitation: - challenging problem - no agreement between the results (quantitative and qualitative)
 Introduction Atmospheric aerosols affect the cloud mycrophysical structure & formation (observations, numerical studies) An increase of the aerosol particles: - increases CCN concentrations - decreases
Introduction Atmospheric aerosols affect the cloud mycrophysical structure & formation (observations, numerical studies) An increase of the aerosol particles: - increases CCN concentrations - decreases
The role of dust on cloud-precipitation cycle
 UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS SCHOOL OF PHYSICS, DIVISION OF ENVIRONMENT AND METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC MODELING AND WEATHER FORECASTING GROUP The role of dust on cloud-precipitation cycle Stavros Solomos, George
UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS SCHOOL OF PHYSICS, DIVISION OF ENVIRONMENT AND METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC MODELING AND WEATHER FORECASTING GROUP The role of dust on cloud-precipitation cycle Stavros Solomos, George
